Neurogenic bladder dysfunction is a group of symptomatic conditions of the urinary system that have a single cause. In this condition, the patient develops a urinary disorder. The violation appears due to a distortion of the algorithm of the nervous system, which is responsible for the process of emptying the bladder. The manifestation of pathology causes physical, moral and aesthetic discomfort to the patient, depriving him of the opportunity to lead a normal lifestyle. Therefore, treatment of a neurogenic bladder comes down to eliminating symptoms and improving the functioning of the excretory system.
The International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, assigns pathology code N31, which denotes neuromuscular dysfunction of the bladder. ICD 10 identifies subtypes N31.0-N31.2, as well as N31.8 and N31.9, which have individual descriptions: uninhibited, reflex bladder, neurogenic weakness, unspecified muscle dysfunction, other dysfunctions.
Causes of neurogenic bladder
Neurogenic bladder is a group of urinary disorders manifested by impaired bladder emptying in individuals with a normal anatomical structure of the bladder and urethra.
Otherwise, neurogenic bladder is also called neurogenic voiding disorder or neurogenic bladder dysfunction. Neurogenic bladder is divided into two groups:
- caused by inorganic changes in the spinal cord or lower urinary tract,
- caused by organic damage to the terminal part of the spinal cord.
Seven clinical variants of nonorganic bladder dysfunction have been identified:
- subclinical (hidden) hyperreflex bladder - observed in 14-17% of patients with functional urination disorders; the disease is manifested by involuntary urination during sleep, urinary incontinence and a combination of similar symptoms;
- normoreflex bladder - observed in 4.5-5.5% of cases, combined with increased contractile activity of the urethral sphincter, manifested by involuntary urination during sleep, urinary incontinence, or a combination thereof;
- hyperreflexive non-adapted bladder - observed in 30-36% of patients with urination disorders of neurogenic origin; manifested by frequent (with an interval of 0-2.5 hours) urination in small portions of urine, urinary incontinence, and the presence of residual urine; characterized by intermittent intravesical hypertension during the entire period of bladder filling;
- hyperreflexive adapted bladder - observed in 29-31% of patients, characterized by the same symptoms as the non-adapted one, but less pronounced; the existing detrusor hyperreflexia is not accompanied by intermittent intravesical hypertension and the state of adaptation of the bladder to the filling phase is disturbed to a lesser extent;
- the fifth, sixth and seventh clinical variants of neurogenic dysfunction of the urinary tract are characterized by hyporeflexia of the muscles that push urine out; the differences lie in the fact that the presence of a hyperreflex bladder is combined with normal function (fifth clinical option), increased contractile activity (sixth option) and insufficiency (seventh option) of the urethral sphincter).
Clinically, all of these variants of the hyporeflex bladder are characterized by rare urination (2-3 times a day) and the release of large portions of urine (up to 500 ml or more), the presence of residual urine (up to 250 ml or more), as well as various types of urinary incontinence .
Neurogenic dysfunctions of the bladder of organic origin include all forms of neurogenic disorders of urination and urinary incontinence, united by a common etiological feature - separation of the bladder by the cortical centers of the brain, which ensure the controlled nature of urination. The most important and most common types of dysfunction of the bladder are those whose occurrence is caused by organic pathological changes in the spinal and peripheral conduction innervation. There are 4 main groups of spinal cord dysfunctions:
- I - with congenital malformations of the terminal part of the spinal cord and spinal column;
- II - with traumatic injuries of the spinal cord of extramedullary fibers of the cystic plexus;
- III - with inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the spinal cord and its membranes;
- IV - with damage to the intramural nervous system of the bladder.
Causes of neurogenic bladder include :
- congenital defects of the final part of the spinal column (spina bifida, agenesis and dysgenesis of the sacrum and coccyx);
- inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the spinal cord and its membranes, peripheral nerves and nerve plexuses, intravesical nerve endings (myelitis, poliomyelitis, meningitis, encephalomyelitis, syphilis, tuberculosis of the nervous system);
- damage to elements of the intravesical nervous system in obstructive uropathy in children;
- tumors and injuries of the spinal cord and spinal column, osteochondrosis;
- brain injury, cerebrovascular accident;
- damage to the nervous system by arsenic preparations, salts of heavy metals, endogenous and exogenous intoxication of the nervous system;
- long-term use of psychopharmacological and other drugs;
- denervation of the bladder due to massive surgical interventions in the pelvic organs.
The main role in the development of neurogenic urination disorders is played not so much by the nature of the cause as by the level of distribution and degree of damage to the nerve pathways and centers that provide the function of urination.
Depending on the level of damage to the innervation of the bladder and changes in the tone of its muscles, central, spinal and peripheral (inside and outside the organs) forms of urination disorders are distinguished, as well as hypo- and atonic neurogenic bladder.
There are also reflex, hypo-, hyper- and are-reflex, sclerotic neurogenic urination disorders.
Patients with neurogenic bladder dysfunction complain of:
- feeling of heaviness in the pubic area;
- urinary disturbance
- inability to completely empty the bladder,
- paradoxical urinary retention (ischuria) when the bladder is full, involuntary urination;
- weak stream of urine even when pressing on a full bladder;
Treatment
Since each patient has a different clinical picture and the severity of bladder dysfunction, it is impossible to offer a single treatment regimen for everyone. In each case, individual treatment tactics are selected, and the approach must be comprehensive, otherwise it is difficult to achieve positive dynamics.
Medication
If there is a condition such as urine retention in the body, then it is necessary to take medications whose action is aimed at relaxing the muscles of the organ. In this case, alpha-blockers are used, among which preference is given to Tropaphen or Phentolamine, which is determined by the leading specialist.
When doctors are faced with the task of facilitating the rapid removal of biological fluid from the body, they need to create conditions of increased pressure in the organ, which will strengthen the tone of the detrusor muscles. Beta-blockers, for example, Inderal or Carbohol, do an excellent job of this task.
Inderal is used in complex drug therapy. Source: easyshipozyjb.tk
In addition, in the complex of drug therapy for patients who are faced with such a condition as the inability to independently hold urine when the bladder is full, in order to create conditions for increased sphincter tone, doctors use alpha-agonists, such as Izadrine or Ephedrine.
It is very important to seek medical help in a timely manner, since conservative treatment has a positive therapeutic effect only if the patient has only minor disorders. To consolidate the results obtained, it is recommended to undergo a course of physiotherapy.
Physiotherapy
Particularly popular among doctors and patients is a procedure called paraffin applications. Thanks to them, you can get rid of high muscle tone. As for the fairer sex, they are offered to use physical factors as part of the complex of effects on the body.
Depending on what type of pathology was diagnosed, the methodology will be determined. So, for example, in the case of the hyperreflex form, it is necessary to perform physiotherapeutic procedures that have a sympathomimetic as well as antispasmodic effect, which allows you to relax the detrusor muscles and contract the sphincter.
But in a situation with hyporeflex disorder, preference should be given to manipulations that have a stimulating effect on the detrusor. It would be good if the complex included procedures that could eliminate spasms, relieve inflammation, dilate blood vessels and improve blood circulation.
Among physiotherapy procedures, particular preference is given to electrophoresis. Source: cistitus.ru
Therefore, to eliminate spasm in the detrusor, experts advise:
- Perform electrophoresis with Atropine, Eufillin or Platyfillin (daily for 15 minutes, the course is 12 procedures);
- Carry out electrophoresis with medications that eliminate spasms;
- Be exposed to ultrasound (5 minutes for each affected area, every day for 10-12 days);
- Paraffin applications (the duration of one session is from 30 to 45 minutes, performed every day for 12-15 days).
When it is necessary to restore the functioning of muscle structures, it is recommended to carry out specific treatment in which the body is exposed to certain types of currents (manipulations should be done every day, and the course lasts ten days). You can also influence the bladder through diadynamic therapy. The duration of the session is no more than 7 minutes (maximum 10 procedures).
In addition, specialists in the field of urology have presented a whole range of physiotherapeutic effects on the body, which allows normalizing the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. For this the following is shown:
- Ultraviolet irradiation;
- Galvanization;
- Infrared laser therapy;
- Treatment with mud.
It is important to consider the duration of the procedures, as well as their number. When there is a condition of urinary incontinence, urethral or rectal stimulation of the bladder neck helps to cope with the problem. However, the procedure can only be done if the innervation system is intact.
Operational
It is immediately worth noting that surgical intervention for such problems is more of a symptomatic treatment. There are a lot of surgical options, but the main preference is given to procedures aimed at restoring the innervation of the bladder.
Such an intervention is complex and time-consuming, but due to the fact that it has been practiced for more than 20 years, it is possible to achieve the most positive results. After such treatment, the patient must perform gymnastics, take medications, and undergo physiotherapy.
If a man or woman has been diagnosed with a neurogenic bladder, treatment should not be delayed for long. The sooner a therapeutic complex begins to be developed and fully implemented, the higher the likelihood that the patient will soon fully recover and return to normal life.
How to treat a neurogenic bladder?
Treatment of a neurogenic bladder is a complex set of procedures. Treatment consists of restoring urination, maintaining sufficient bladder capacity and addressing the inflammatory process. Treatment of a neurogenic bladder of nonorganic origin should be comprehensive, aimed at correcting all identified disorders, and multi-stage. Its purpose is usually:
- maintaining normal kidney function,
- preventing (or treating) infection,
- ensuring urinary continence.
Treatment is based on periodic catheterizations under sterile conditions along with selective use of anticholinergic drugs. This helps reduce pressure in the bladder and prevents uninhibited bladder contractions.
The following areas of treatment for neurogenic bladder are distinguished:
- medicinal effects on the nervous system of the bladder with pharmacological drugs of directed mediator action + electrical stimulation;
- surgical palliative treatment;
- surgical palliative-symptomatic treatment.
Drug therapy is carried out in cases where lesions of the sympathetic or parasympathetic innervation predominate. The prescription of pharmacotherapeutic agents is combined with intraanal electrical stimulation. For its implementation, special devices “Tonus-1”, “Tonus-2”, “Bion-3” and the like are usually used. Direct electrical stimulation is carried out using a catheter-electrode, which is inserted into the bladder through the urethra. The electrode contacts the wall of the bladder through an electrolyte introduced into its cavity or directly. During neurotropic stimulation, platinum needle electrodes are inserted percutaneously into the area of the nerve roots at the level of the third segment of the spinal cord. If electrical stimulation produces a positive effect with this technique, implantation of electrodes in the cauda equina area is carried out surgically.
All methods of treating neurogenic bladder in this group of patients can be combined into 4 groups:
Influencing the effective parts of the autonomic nervous system at the segmental level or directly on the muscle that pushes urine out and the sphincter of the urethra. The goal is to restore the normal detrusor-sphincter ratio, reservoir function of the bladder and controlled urination by reducing or increasing the tone, contractile activity and reflex excitability of the muscle that pushes urine out, and to normalize the closing functions of the sphincter. They use - M-anticholinergics, M-cholinomimetics, anticholinesterase drugs and antiprostaglandin drugs, α-adrenolytics, α-adrenostimulants, calcium ion antagonists.
Influencing the efferent parts of the autonomic nervous system through the influence of pharmacological drugs against the background of preliminary activation of metabolic processes. Adrenergic agonists and antagonists of potassium ions (ephedrine hydrochloride and isoptin), as well as coenzymes and cholinomimetics (cytochrome C for injection, riboflavin mononucleotides, aceclidine) are used simultaneously.
Causing activation of detrusor-stabilizing reflexes in their effective link and restoring the normal detrusor-sphincter ratio. Various forms of electrical stimulation of the anal sphincter, perineal muscles and bladder are used.
Influencing the higher centers of autonomic regulation through the use of neurotropic antidepressants, tranquilizers, and metabolic therapy.
Treatment of neurogenic bladder of organic origin is ineffective. It is mainly aimed at prolonging the patient’s life. The cause of death of the patient may most likely be not so much dysfunction of the bladder as complications that occur in the upper urinary tract and kidneys, which leads to pyelonephritis, urosepsis and chronic kidney failure.
When conservative treatment is ineffective, it becomes necessary to choose a surgical treatment method.
In the final stage of the disease, therapy is aimed at saving the patient and prolonging his life. In such cases, a permanent catheter with a Monroe system is often installed.
For reflex bladder caused by transverse dissociation of the spinal cord above the lumbar region, tidal drainage of the bladder with Monroe has become widespread. The purpose of drainage is to develop and consolidate the reflex state of the bladder. With strict adherence to asepsis and an individual regimen, this method is safe and effective. The catheter must be changed after 3-4 days; to rest the urethra, it is necessary to periodically interrupt drainage for 2-3 days.
Pathogenetically based operations include:
- ileovesicopexy,
- ileorectovesicopexy,
- rectovesicopexy,
- reinnervation of the bladder by the rectus abdominis muscles
Intestinal plastic surgery for a neurogenic bladder is justified only in cases where the bladder is able to serve as a reservoir and provide outflow from the upper urinary tract. In practice, this is observed with an autonomous bladder due to damage to the spinal cord, with denervation of the bladder, which is observed after massive operations in the pelvic cavity.
After surgery, conservative treatment methods are used to strengthen the mechanisms of active urination, including active physiotherapy, physical therapy, and electrical stimulation of the bladder.
Contraindications to radical surgical treatment are:
- spinal cord injuries in the cervical and thoracic regions with bladder automaticity;
- severe bilateral ureterohydronephrosis, which developed as a result of vesicoureteral reflux in the presence of severe renal failure;
- massive narrowing of the urethra;
- dysfunction of the sphincters, accompanied by urinary and fecal incontinence.
The prognosis depends on the form and stage of the disease, the timeliness and correctness of the choice of a pathogenetically based method of treating neurogenic bladder dysfunction.
Diagnostics
If you have the above symptoms, you should immediately contact a urologist. If such a clinical picture is observed in a child, then you should initially contact a therapist or pediatrician.
Diagnosis of suspected neurogenic bladder begins with examination of the patient and clarification of personal and family history. Also, the doctor must familiarize himself with the medical history. After a personal examination and clarification of symptoms, instrumental and laboratory diagnostics are carried out.
The standard laboratory diagnostic program includes the following:
- blood sampling for general and biochemical studies;
- urine collection for general examination;
- donating urine for testing for infections;
- urine analysis according to Zimnitsky and Nechiporenko.
As for instrumental diagnostics, this includes the following:
- cystoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and genitourinary system;
- MRI;
- X-ray of the urinary tract;
- profilometry;
- uroflowmetry.
Features of uroflowmetry
If such diagnostic measures do not provide an accurate answer, then additional examinations are carried out in the area of the brain and spinal cord. If bladder dysfunction is observed in a child, additional consultation with a psychologist may be necessary. This method of differential diagnosis is needed in order to exclude dysfunction due to nervous shock in the child.
If, as a result of diagnosis, it is not possible to establish the exact cause of the development of such a pathological process, then a diagnosis of an idiopathic form of neurogenic bladder is made.
What diseases can it be associated with?
Bladder dysfunction is only the primary link in the pathogenesis of the disease; it gradually leads to a change in the anatomical structure of the organ, which significantly aggravates the functional disorders that already exist. Often the course of this pathology follows a “vicious circle” type. All this over time leads to profound changes in the ureter, upper urinary tract and kidneys, which are the main ones in the clinic of neurogenic bladder dysfunction and ultimately determine its consequences.
In some cases, patients with a neurogenic bladder are diagnosed with spina bifida, cleft sacral canal, etc.
The infection that occurs in such cases leads to the development of pyelonephritis, chronic renal failure, and urosepsis. Often, in its symptoms, a neurogenic bladder is similar to acute cystitis or pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, urolithiasis, which makes diagnosis difficult.
Stages and degrees
The neurogenic bladder can have different tones, depending on which the types are distinguished:
- Spastic or hyperreflexive. In this case, the tone of the bladder is increased, which is expressed by an irresistible urge to urinate with a small volume of urine in the bladder. In this case, there is no consistency between contraction of the bladder and external relaxation of the urinary sphincter.
- Lethargic or hypo-reflexive. In this case, an overfilled bladder, its receptors, weakly respond to the urge to urinate at the moment it is full, and relaxation of the muscles of the bladder walls is observed. There is low pressure in the bladder and there is no contraction.
- Mixed type. Caused by disorders: diabetes, stroke, ruptured intervertebral disc, multiple sclerosis.
The problems that arise when filling and emptying the bladder are aggravated by various types of incontinence:
- Stressful, which occurs when there is a sudden increase in intravesical pressure. It can be caused by coughing, laughing, or physical activity.
- Imperative. This is an involuntary, uncontrollable leakage caused by a strong urge to urinate.
- Mixed or combined type, which includes a stressful and imperative type.
- Temporary or transient. This type of spontaneous incontinence is associated with external factors, and the cause may be infectious diseases of the genitourinary system, medications, or heavy alcohol intoxication.
What medications are used to treat neurogenic bladder?
A wide variety of pharmaceuticals are used to treat neurogenic bladder
- M-anticholinergics - atropine sulfate, beladonna,
- M-cholinomimetics - aceclidine, carbacholine,
- anticholinesterase drugs - prozerin,
- antiprostaglandin drugs - acetylsalicylic acid, indomethacin,
- α-adrenolytics - phenoxybenzamine,
- α-adrenergic stimulants - ephedrine hydrochloride,
- calcium ion antagonists - isoptin, finoptin,
- coenzymes and cholinomimetics - cytochrome C, riboflavin mononucleotides,
- antidepressants - melipramine, amitriptyline,
- tranquilizers - seduxen,
- means of metabolic therapy - pantogam.
The dosage of medications, as well as the duration of the course, and the combination of the above drugs are determined by the attending physician, taking into account the origin of the dysfunction, the characteristics of its course and the results of individual diagnostics.
Additional recommendations for enuresis
The suffering of these patients is much more varied and deeper. This includes not only “neurological” patients after severe injuries to the spinal cord and brain, road accidents, as a result of military operations, but also a large group of our readers. With age, people experience increasing weakness and atrophy of skeletal muscles (pelvic floor and abdominal muscles), muscles of hollow organs (bladder, urinary and rectal, gastric sphincters, bronchial tree) and other parts.
That is why in their medical practice, doctors advise walking at a brisk pace for 30 minutes twice a day. In 3-5 months the disease goes away. In people who are physically developed and engaged in active work, neurogenic bladder syndrome is less common. Although there is confidence that walking at a brisk pace will benefit everyone.
In addition, doctors strongly recommend abstaining from irritating foods, excessive consumption of beer and artificial carbonated and other drinks. Much healthier and tastier are natural compotes, decoctions of rose hips, lingonberries, viburnum, sea buckthorn, cranberries, and rowan berries. It is a source of natural vitamins and medicinal substances, which has a diverse positive effect on all organs and systems.
Which doctors should you contact if you have a neurogenic bladder?
- Neurologist
- Nephrologist
- Urologist
Diagnosis of various clinical variants of the disease is always quite difficult. A preliminary idea of the degree, form of neurogenic bladder dysfunction, and concomitant changes in other organs and systems is given by a carefully collected anamnesis and examination of the patient. A correctly collected anamnesis helps not only to establish a diagnosis, but also to trace the mechanism of transition from one form of neurogenic bladder dysfunction to another, determine its cause, and clarify the pathogenesis of the disease.
When examining a patient, pay attention to:
- pale skin,
- degree of weight loss,
- child's retardation in physical development,
- in the final stage of the disease - for dry mucous membranes, swelling, and the smell of urea from the mouth.
First of all, the doctor is faced with the task of establishing:
- when the patient or his relatives notice urinary disorders,
- find out their character and dynamics,
- obtain information about a previous injury to the spine or head (birth injury, fracture, bruise, fall on the sacrum, back, etc.),
- obtain information about diseases of the nervous system or infections, the presence of spina bifida,
- obtain information about the treatment of the conditions described above, if they were noted.
When urinary incontinence occurs:
- hypertrophy of the anterior skin,
- maceration of the skin of the thighs,
- strong smell of urine
- constant dripping of urine,
- when palpating the suprapubic area, urine is released in a weak stream,
- sometimes an enlarged bladder is detected above the pubis.
A neurological examination allows you to determine the level and depth of damage to the central and peripheral innervation. After this, they resort to laboratory, x-ray, radionuclide and instrumental research methods.
Laboratory tests, excretory urography, renography, scanning and dynamic scintigraphy allow us to get an idea of the function of the kidneys, survey urography - about the state of the skeletal system, the presence of stones in the kidneys and urinary tract, the contours of the kidneys and bladder.
Cystoscopy provides information about the condition of the mucous membrane and muscles of the bladder wall, its capacity, and the amount of residual urine. The functional state of the bladder is studied according to cysto-, sphinctero- and uroflowmetry.
To determine the condition of the urethra, bladder sphincters and muscles that push urine out, and to reduce the amount of instrumental interventions, urography is combined with sphincterometry, and ascending cystography is combined with cystometry. Cystography and ultrasound examination allow the slow introduction of a radiopaque substance into the cavity of the bladder to accurately determine its real capacity. Electrocystometry performed in parallel provides important information about the state of the contractility of the muscle that pushes urine out.
To assess the denervation mechanisms of the bladder, special electrophysiological research methods have been developed, the principle of which is that the development of a neurogenic bladder largely depends not on the nature of the disease, but on its topography and relationship to the spinal centers.
What does the term "Neurogenic Bladder" mean?
This is a disruption in the interaction between the nervous system and the muscles of the bladder. Excessive activity of the bladder muscles is fraught with the occurrence of spontaneous uncontrollable and frequent urges. At the same time, decreased tone of other muscles does not allow the bladder to fully contract. First, this leads to incomplete emptying and excessive emptying - the accumulation of urine, which begins to ooze drop by drop. And then a secondary infection in the urinary system and other complications occur, accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen.
Neurogenic dysfunction is often hidden and, accordingly, in this case it is unsuccessfully treated under the guise of other common diseases such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder mucosa). Long-term and ineffective treatment ultimately leads to a search for hidden problems, for example in the nervous system. But time may already be lost, and the task of combating pathology becomes more complicated.
Treatment of other diseases starting with the letter - n
| Drug addiction treatment |
| Treatment of neurasthenia |
| Treatment of obsessive-compulsive neuroses |
| Treatment of neurocirculatory dystonia |
| Treatment of Anorexia Nervosa |
| Treatment of diabetes insipidus |
| Treatment of ulcerative colitis |
| Treatment of unstable angina |
| Treatment of nephrogenic hypertension |
| Treatment of nephropathy |
| Treatment of nephroptosis |
| Treatment of nephrotic syndrome |
| Treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma |
The information is for educational purposes only. Do not self-medicate; For all questions regarding the definition of the disease and methods of its treatment, consult your doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal.
Prevention
In some cases, injuries, congenital pathology, diseases of the musculoskeletal system, and NMP cannot be prevented. But in most cases, the occurrence of this pathology can be prevented.
To do this, it is enough to eat properly and on time, not to be overcooled, not to abuse alcohol, based on the characteristics of the body, to play sports, to perform acts of urination and defecation when the need arises.
To prevent any bladder disease, you need to drink plenty of fluids, but in small portions. People prone to inflammatory processes should avoid juices made from sour fruits. For patients with low blood pressure, coffee, beet juice, and watermelon juice are recommended.
In medicine, there are no special preventive methods to prevent the occurrence of bladder neurogenicity.
But a number of measures can be taken to prevent problems with urination:
- It is necessary to learn to control your emotions and avoid situations that aggravate the symptom. To do this, you can use sedatives and attend psychological training.
- Contact a urologist as soon as possible to relieve the problem in order to prevent its further development.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle: eat right, get plenty of rest, and do not overuse physical activity.
People prone to developing the syndrome can try Kegel exercises.
Video on the topic
About the etiology and methods of treatment of neurogenic bladder:
If a woman feels discomfort when urinating, or notices irregularities in her urination regime, she should not get carried away with alternative medicine methods and self-medication, but should immediately contact a qualified specialist. The sooner the doctor identifies the causes of the disease and prescribes treatment, the higher the likelihood of a favorable response of the body to therapy.
The bladder performs a lot of important tasks: it stores urine and facilitates its excretion. The nervous system is responsible for this process. When the process is disrupted, the area of the brain that controls the process of urination is damaged, a disease called neurogenic bladder is formed.
During the course of the disease, there is a decrease in the activity of the bladder, or, conversely, a hypertensive state, in which the activity of the organ increases. The entire pathological process leads to urinary incontinence, which brings a lot of problems to the victim.
- Etiology of the disease
- Signs and symptoms of pathology
- Diagnostics
- Effective treatments
- Folk remedies and recipes
- Possible complications
- Preventive recommendations
Physiotherapy and exercise therapy
Regardless of the type of disorder, methods that determine how to treat a neurogenic bladder are selected with the aim of restoring the functions of the organ and eliminating associated symptoms. Physiotherapy in this case allows you to solve both problems.
Treatment of bladder neurosis is carried out using the following techniques:
- Electrophoresis with anticholinergics. A 0.03% solution of “Platifillin”, a 0.1% solution of “Atropine” or a 0.2% solution of “Eufillin” are used. For successful treatment, up to 10-12 sessions of electrophoresis will be required.
- Paraffin applications. Eliminate spasm and promote relaxation of smooth muscles. Treatment with applications is carried out over 10-15 procedures.
- Ultrasound. The procedure improves blood supply to the sphincter and muscle fibers.
- Diadynamic therapy. The method is used for hyperreflex type of disorder. The procedure allows you to restore the reflex contraction of the sphincter muscles.
- SMT therapy. Restores the contractile function of the sphincter.
- Galvanization. The method is used to restore blood flow in the subcortical structures of the brain. The procedure is carried out every 2 days.
- Ultraviolet irradiation. During the procedure, the doctor influences the sacral region or buttocks.
- Peloid therapy. The technique involves application of peat mud. This approach is used to stimulate the adrenal glands.
For nervous disorders, electrosleep therapy or a galvanic collar are used. Both approaches reduce brain arousal.
If bladder dysfunction is caused by a decrease in muscle tone, a complex of exercise therapy is often prescribed to restore the latter. To strengthen the fibers of the pelvis, women are recommended to regularly perform Kegel exercises. To restore smooth muscle tone, it is necessary to periodically tense and relax the muscles that support the internal organs.
How is the disease diagnosed?
To know how to treat bladder atony, you need to diagnose the disease. To begin with, a special medical examination is performed by a urologist. You may also need to visit specialists in a narrow profile. During diagnosis, the following examinations are performed:
- ultrasound examination of the genitourinary organs;
- CT scan;
- taking urethral tests.
Diagnostics are carried out in special medical centers.
Clinical manifestations
At the initial stages of the disease, the clinical picture is represented by various disorders of the act of urination. These include:
- weakening of urges or their complete absence;
- frequent or intermittent urination;
- urinary incontinence;
- straining to urinate and urinary retention;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Urge disorders as the first link in the reflex chain are noted by all patients, but their nature may be different depending on the form of dysfunction.
- In the cortical uninhibited variant of the disease, the urge is preserved, but has an imperative nature.
- Reflex dysfunction is characterized by the absence of urge with the formation of its equivalent in the form of pressure in the lower abdomen.
- In unadapted forms of the disease, the urge is weakened; it can be caused by forced stretching of the bladder.
Another important symptom of this pathology is urinary incontinence. Primary urinary incontinence develops when the sympathetic lumbar centers are affected. This is often caused by spina bifida. Secondary incontinence is the outcome of chronic urinary retention. It is often combined with symptoms of kidney damage:
- lower back pain;
- fever;
- inability of the kidneys to perform their function fully.
All forms of areflex and mixed dysfunctions are accompanied by urinary retention. Such patients complain:
- extra effort when urinating;
- the presence of a “tumor” in the lower abdomen;
- feeling of pressure in this area.
Associated complaints may include:
- bowel dysfunction (constipation or fecal incontinence);
- change in gait;
- decreased sensitivity of the lower extremities;
- trophic changes in the lower extremities.
Possible complications
With bladder dysfunction, stones can form in the ureter, which also leads to complications when urinating. This, in turn, leads to fluid entering the cavity of the ureter and kidney, which is the reason for the development of the inflammatory process and other diseases.
A neurogenic bladder is especially dangerous for a child. At an early age, the child’s genitourinary system is formed and if treatment is not started in a timely manner, this can lead to serious problems in the functioning of the kidneys and the genitourinary system as a whole. The psychological factor should not be overlooked. Involuntary loss of urine in a child can lead to the development of the complex in adulthood.
The origin and development of NDMP
In the structural elements of the kidneys, the calyces and pelvis, urine is filtered from accumulated waste products: salts, pathogenic microorganisms, compounds formed after the breakdown of proteins. Through the ureters, urine, saturated with dissolved substances, enters the bladder, from which it must be excreted. But dysregulation of the urination process does not allow urine to be released as desired, even if he feels that his bladder is full.
The bladder performs in the human body the function of storing urine and releasing it with a volume of more than 600-650 ml. A person is able to urinate even if the volume of biological fluid does not exceed 250 ml.
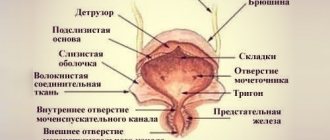
The bladder is a hollow organ consisting of three layers:
- The inner lining contains many epithelial mucous cells that come into direct contact with urine.
- The middle layer contains smooth muscle fibers. Their main accumulation is located at the bottom of the bladder, near the opening of the urethra - the sphincter. This is what the detrusor looks like, the muscular lining of the bladder responsible for excreting urine from the human body.
- Fibrous tissue fibers protect and shape the bladder.
Before the process of urination, an impulse arises in the parasympathetic nerve nodes of the bladder, which enters the brain, is converted and returned. There is a urge to urinate, contraction of the detrusor and release of the bladder.
When neurogenic bladder dysfunction of any etiology occurs, the impulse directed to the brain is not processed and does not return. The bladder is full, but there is no urge - spontaneous emptying occurs. In most cases, a person does not have time to reach the toilet.
Schematic structure of the human urinary system
Disease provocateurs
Reasons why neurogenic bladder develops in adult women and men:
- brain diseases (Parkinson's syndrome, multiple sclerosis, acute cerebrovascular accident, senile dementia of the Alzheimer's type and discirculatory neuropathy);
- diseases of the spinal cord (degenerative-dystrophic lesions of small intervertebral joints, Schmorl's hernia, osteochondrosis, damage and unfavorable outcome of surgical actions on the ureter and urethra);
- congenital anomalies of the lower spine and spinal cord;
- damage to bladder receptors;
- HIV infection.
Causes of neurogenic bladder dysfunction in children:
- birth defects in the lower back;
- hypoplasia of the vertebral artery;
- congenital underdevelopment of the sacral part of the spinal cord;
- impairment of physical and mental functions in a child due to brain damage;
- spinal hernia;
- agenesis and dysgenesis of the sacrum and coccyx;
- birth injury
- damage, bruises, fractures;
- tumors;
- acute, chronic and degenerative pathologies.
Principles of treatment of hypotension
If, based on the diagnostic results, the cause of the pathology has been identified, then treatment of detrusor hypotension should begin, the price of which will depend on the chosen method. For this purpose, medications, non-drug methods, and surgical interventions can be used. A complex treatment method using modern medical equipment is often used.
Treatment of detrusor hypotonia in Moscow depends on the symptoms, causes and stage of the disease. All principles of therapeutic therapy are explained to the patient. If the chosen methods do not have the necessary effect, then doctors may recommend another regimen of therapy or surgery. It is imperative to seek medical help if detrusor hypotension is detected, the cost of treatment of which is at an affordable level. Otherwise, the patient may face complications, which will be much more difficult to get rid of.
Predisposing factors to overactive bladder
These include:
- age;
- overweight and obesity;
- chronic nicotine intoxication;
- dysfunction of the intestines of the hypotonic type with constipation;
- persistent microbial flora;
- hormonal instability.
Drug treatment
Treatment tactics for neurogenic bladder are selected taking into account the characteristics of the disorder. The hyperactive form of the pathological condition responds better to the action of medications. With such neurogenic bladder dysfunction, medications are used that help:
- decreased muscle tone;
- improving blood circulation in the organs of the urinary system;
- getting rid of hypoxia (lack of oxygen).
To achieve these goals, the following are assigned:
- Antiolinergic drugs. This group includes Oxybutynin, Hyoscine, and Propantheline.
- Tricyclic antidepressants. Imipramine is mainly used.
- Calcium antagonists. Nifeipin is used in the fight against bladder neurosis.
- Alpha adrenergic blockers. Neurogenic bladder is treated with Phenoxybenzamine or Phentolamine.
Instead of tricyclic antidepressants, you can use Rexetine or its analogues. Unlike the former, the latter drugs are better absorbed by the digestive system and are less likely to cause side effects such as dry mouth and constipation.
Recently, for innervation of the bladder with concomitant dysfunction of the sphincter, botulinum toxin injections are often used.
The drug is injected directly into the wall of the organ or urethral canal. Instead of botulinum toxin, injections of capsaicin or resinfeatoxin are also performed. This treatment is supplemented by taking medications:
- based on succinic acid;
- L-carnitine;
- hopantenic acid;
- coffee-based forms of vitamins;
- N-nicotinoyl-gamma-aminobutyric acid.
The hypoactive form of dysfunction is more difficult to treat with medication. With such a violation, stagnant processes occur, which create favorable conditions for the addition of a secondary infection and the development of concomitant pathologies of the pelvic organs. With a hypoactive form, drug treatment alone cannot be carried out. The patient must ensure regular and complete emptying of the bladder through special exercises and other techniques.
The goal of treatment for this type of disorder is to achieve the following results:
- increased wall motility;
- restoration of organ volume and residual urine.
To achieve these results, the following are used:
- distigmine bromide;
- aceclidine;
- galantamine;
- bethanechol chloride.
If necessary, treatment is supplemented with alpha-blockers (phenoxybenzamine, diazepam, baclofen) and alpha-sympathomimetics if cases of involuntary urine loss are detected.
In order to prevent the addition of a secondary infection, which is predisposed by congestive processes in the pelvis, patients with neurogenic dysfunction of the urinary system are prescribed antibacterial drugs.
If the diagnostic results show that the pathological condition is caused by nervous disorders, treatment is supplemented with herbal-based sedatives:
- Valerian tincture;
- motherwort root and others.
In more severe cases, the use of barbiturates is indicated, replacing sleeping pills.
Complications after illness
If you do not promptly seek help in treating detrusor hypotension, unpleasant consequences may occur in the form of complications. The main types of complications include the following:
- cystitis, which leads to deformations of the urinary organ;
- stones in the urethral canals;
- development of infectious diseases;
- kidney inflammation.
Hypotension is a disease that can be cured. And early contact with medical specialists will make it possible to speed up recovery and avoid related health problems.
Ask a Question
Forecast
Treatment of neurogenic cystitis in most cases ends with complete recovery of the patient. If the cause of the disease has been correctly identified, the prognosis is favorable. In advanced conditions, complications may arise in the form of a chronic form of the disease, pathological changes in the organs of the urinary system, urolithiasis and renal failure.
With the right treatment tactics and under the supervision of the attending physician, recovery usually occurs after the first course. In some cases, it is necessary to repeat the course after some time.
Causes of the disease
Pathological processes
Hyperreflex disorders can develop against the background of pathologies or injuries of the nervous system.
For example, this is Parkinson's disease, mechanical damage to the spinal cord, multiple sclerosis, malignant neoplasms affecting the innervation centers of the bladder, polyneuropathy.
In addition to the above reasons, dysfunction occurs due to age-related changes and ischemia, which disrupts the blood supply to the organ.
Also, urinary disorders in men can be observed against the background of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
How to detect pathology in time?
The clinical picture of the disease largely depends on its type, as well as at what level the NS lesion occurred. Manifestations of the syndrome can be permanent, periodic or episodic.
With bladder hypertension, patients experience specific symptoms in the form of a frequent urge to urinate (pollakiuria), an increase in the number and volume of nighttime urination, false sensations that the act of urination is about to begin (imperative urge), urination can be caused by mechanical or thermal stimuli of the pubic and femoral area, urinary incontinence or difficulty urinating may occur.
In addition to the above symptoms, vegetative symptoms appear, namely increased sweating, increased blood pressure, tachycardia and redness of the skin.
With hypotension of the bladder, the main complaints of the patient are:
- straining when the patient wants to urinate;
- after urination, a person feels the bladder full;
- complete retention or very difficult urination.
You can understand that the sphincter tone is stronger than the detrusor tone when it takes a lot of effort to perform the act of urination. Sometimes there is complete retention of urine.
A frequent occurrence is paradoxical ischuria - a pathological process in which a person has difficulty urinating, but at the same time, urine is released involuntarily in small portions or drops. The phenomenon is caused by the accumulation of a large volume of urine in the bladder, resulting in pressure on the sphincter and the release of a small amount of fluid.
If you seek medical help in time, the prognosis will be positive. However, the patient’s recovery is influenced by many factors - concomitant diseases of the urinary organs, the presence of infections, advanced age, problems with the endocrine system, etc.
Treatment of neurogenic dysfunction
Therapy for NDMP is based on an integrated approach. If a pathology that causes urination problems is detected, non-drug, drug and (or) surgical treatment is used.
Non-drug therapy
This treatment method can be successfully combined with other methods of therapy to speed up and consolidate the result. The absence of contraindications and side effects allows the use of non-drug therapy even in very young children. The main areas of eliminating urinary incontinence include:
Overactive Bladder Syndrome
- Treatment with pulse therapy using electric current with a frequency of about 80 Hz.
- Use of sinusoidal simulated currents.
- Therapy using warm air currents.
- Regular physical therapy with Kegel exercises. It is based on training the muscle responsible for urination using the method of tension and relaxation.
- The use of molecular oxygen under high pressure in special hyperbaric chambers.
- Carrying out physical procedures using electrophoresis using solutions of chemical compounds.
- Use of ultrasound and laser.
When treating neurogenic bladder dysfunction in children, it is important to establish their daily routine - this will make it easier to control urination, as well as evaluate its quality:
- Walk outdoors regularly.
- Avoid active games before bedtime.
- Provide your baby with adequate sleep.
If the cause of urination problems is a stressful situation, then it is necessary to protect the child from it.
Drug treatment of NDMP
Neurogenic dysfunctions of the bladder are almost always accompanied by inflammatory infections, so antibiotics and antimicrobial drugs cannot be avoided. In the absence of allergies, cephalosporins of various generations, combination drugs with clavulanic acid (Amoxiclav, Augumentin), Metronidazole are used. Amoxicycline and Clarithromycin have proven themselves well in the treatment of incontinence. To consolidate the results and prevent relapses, antimicrobial drugs Nolitsin, Normobact, Norfloxacin are used.
Herbal medicines are also used:
- Canephron.
- Monurel.
- Cyston.
With the development of dysbacteriosis, the intestinal microflora is restored with a course of Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin, Acipol. To strengthen the body, immunostimulants and vitamin complexes with microelements are needed. B vitamins, vitamin K and ascorbic acid are especially important for urinary disorders. Vitamins A and E help restore vascular walls and prevent a decrease in their elasticity. The course of treatment is 1-2 months.
Neurogenic dysfunctions are often accompanied by instability of the emotional state, irritability, insomnia, and increased anxiety. To eliminate such symptoms that aggravate the problem, consultation with a neurologist and endocrinologist is required.
Light tranquilizers, antidepressants or sedatives are prescribed. For kids it is usually recommended:
- Tenoten for children.
- Calming children's fees.
- Novopassit syrup.
Depending on the type of disorder, treatment is carried out:
- Anticholinergic drugs.
- Cholinomimetics.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Additionally, prostaglandins, drugs with amino acids (Glycine), and nootropic drugs (Pantogam) are prescribed.
Surgical intervention
Surgeries are performed only if pharmacological therapy is ineffective. If the cause of neurogenic dysfunction is a pathology that can only be eliminated with the help of surgeons, then such therapy will be a priority. And only then drug treatment is carried out for incontinence as a symptom of the underlying disease.
The following types of operations are performed using endoscopic methods:
- Collagen is implanted into the lumen of the ureters.
- Resection of the bladder neck is performed.
- The volume of the bubble increases if necessary.
After treatment, children and adults must be registered at the dispensary. Once a trimester, they are required to undergo biochemical blood and urine tests to monitor the progress of recovery. This is also necessary to prevent relapses.
If a small child cannot control urination after 4-5 years, you should visit a pediatrician who will write a referral to more specialized specialists. As a rule, neurogenic dysfunctions do not cure on their own, but only progress. If a disease is detected, a hospital stay is required for diagnosis and treatment.