Obstructive jaundice – what are the diagnostic and treatment options?
Obstructive jaundice is dangerous for the body, causing severe intoxication and dysfunction of all organs. In oncology, it is more often diagnosed during the treatment of metastatic cancer abroad, and such patients are often given up as not promising for treatment.
This formulation of the question is typical for medical institutions, the level of which leaves much to be desired, where there are no new technologies for examining and eliminating this complication.
However, in modern clinics and centers, both foreign and domestic, methods are used that allow:
- pinpoint the causes;
- jaundice level;
- take measures to restore normal bile circulation.
Next, we will look at the clinical nature of the development of this condition, and also find out how long obstructive jaundice lasts.
Phototherapy
Drug support for treating adults at home will be effective in conjunction with phototherapy sessions for jaundice. During such sessions, under the influence of ultraviolet rays, the pigment is destroyed and the patient feels better.
Phototherapy uses ultraviolet lamps to treat adults. Bright sun rays can also have a positive effect.
The procedure is used to treat jaundice in newborns. However, phototherapy is also deservedly popular in the treatment of jaundice in adults.
The lamp for the treatment of jaundice in adults has an optimal radiation spectrum; as a result of its exposure, bilirubin acquires a water-soluble form and becomes non-toxic.
What is obstructive jaundice and why is it dangerous?
For many, the term jaundice is associated only with infectious viral hepatitis. Yes, jaundice is one of its manifestations, and it is associated with the destruction of liver cells of hepatocytes under the influence of the virus. As a result, bile produced and contained in these cells is absorbed into the blood and spread throughout the body, causing a jaundiced coloration of the skin, mucous membranes, and internal organs.
Obstructive jaundice has a different origin. It is associated with a block in the path of bile outflow from the liver, that is, with compression of the bile ducts.
For obstructive jaundice:
- overflow of the bile ducts occurs,
- bile pressure in the intrahepatic bile ducts increases;
- the bile ducts expand and become thinner;
- The pigment bilirubin and bile acids are absorbed into the blood from them;
- the concentration of toxic substances increases, and they have a toxic effect on all organs and tissues, disrupting metabolic processes in them;
- the immune system and hematopoiesis are suppressed;
- blood clotting is impaired;
- the kidneys, heart muscle, and liver itself suffer;
- The function of hepatocytes decreases and their death gradually develops.
On the other hand, when the common bile duct (common bile duct) is blocked, bile does not enter the duodenum, and as a result, fats and fat-soluble vitamins (A, E, K) are not digested. All this leads to energy starvation of the body and vitamin deficiency, exacerbating already impaired functions.
Symptoms from other organs
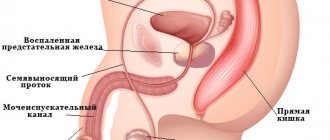
The gland is intimately adjacent to the liver, stomach and duodenum; with the growth of a cancerous node, they are involved in the process, which is manifested by symptoms of their inflammation and compression. This is pain and dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract in the form of belching and anorexia. Loose stools and constipation are likely, all against the background of flatulence. Compression of the outlet of the stomach leads to nausea and vomiting of the food eaten; the formation of the tail part can partially block the lumen of the small intestine.
Compression of the bile ducts is accompanied by inflammation, hence the fever. A temperature reaction can be caused by gland tissue disintegrating due to enzymes in the cells.
A characteristic symptom of the disease is a sharp weight loss due to digestive disorders and lack of enzyme synthesis. Anemia develops.
When and why does obstructive jaundice occur in cancer patients?
Blocking of the bile ducts - common bile duct, right and left hepatic, as well as intrahepatic ducts in cancer patients occurs due to compression of them by the tumor in the following cases:
- for cancer of the head of the pancreas;
- for cancer of the common bile duct (common bile duct);
- for duodenal cancer;
- for gallbladder cancer;
- for cancer of the papilla of Vater (the place where the common bile duct enters the duodenum);
- with primary liver cancer, when the tumor is located near large ducts;
- with liver metastases from cancer of other organs;
- for lymphomas.
Most often, obstructive jaundice is diagnosed during cancer treatment abroad and it is believed that this is associated specifically with metastases to the liver, and here’s why. The fact is that the main function of the liver is to cleanse the entire body of toxins, and venous blood flows to it through the portal vein, collecting from all organs and parts of the body. It contains metabolic products, various unnecessary and toxic compounds. From the portal vein, along its branches, this blood passes through the liver cells, which purify it, and in a purified form it goes through the hepatic veins into the inferior vena cava, then into the superior and to the heart.
If there is a malignant tumor in any organ or part of the body, its cells can be washed out and enter the tissue fluid, from there into the lymph and blood, and then into the liver. Settling there, they multiply and form a metastatic node - a secondary cancerous tumor. This happens in advanced cases of cancer, when it grows and becomes more friable. Metastases in the liver always indicate stage 4 cancer.
They can come from literally any organ when:
- lung cancer;
- breast cancer;
- stomach cancer;
- bowel cancer;
- uterine cancer;
- prostate cancer;
- ovarian cancer;
- breast sarcomas.
Obstructive jaundice in the treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphomas abroad is associated with damage and enlargement of the lymph nodes at the porta hepatis, which compress the bile ducts.
Undoubted causes of pancreatic cancer
The causes of pancreatic cancer will help reveal ways to prevent a disease in which the incidence rate is slightly higher than the mortality rate. This is a male tumor; women are affected three times less often and at a much older age. Diagnostics in Europe is better, and therefore the incidence is higher.
To date, no single root cause of the disease has been identified, but certain pathological conditions significantly increase the risk of malignant pathology of the pancreas.
Smoking tobacco doubles the risk of malignant tumors of the gland; for every fourth smoker, tobacco becomes the main cause of the disease. The likelihood of pancreatic cancer is directly dependent on the duration of the bad habit and the volume of daily cigarette portions.
The second proven cause of morbidity is type 2 diabetes, which is not congenital, but acquired. A diabetic's risk of developing a malignant tumor increases by 60%, and after the age of 50, every hundred diabetics are diagnosed with pancreatic cancer.
The third reason is chronic pancreatitis of any etiology; it increases the likelihood of tumor pathology by 20 times. Inflammation leads to intraepithelial neoplasia, which for most patients is a direct path to cancer. With neoplasia, cells divide too quickly, losing the ability to recover when damaged, and the slender architecture of glandular tissue is lost. The same proliferative processes in an aggravated form also occur in malignant neoplasms.
How does obstructive jaundice manifest?
Obstructive jaundice in cancer develops gradually, with increasing symptoms. Sometimes it is the first sign of cancer if the tumor in the organ is small and does not manifest itself in any way, but is very malignant, aggressive, and metastasizes early (such as melanoma or sarcoma).
The first signs are:
- yellowness of the sclera of the eyes, which can be noticed when looking up;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- urine becomes dark in color, reminiscent of beer;
- The skin and mucous membranes of the mouth also acquire a jaundiced tint;
- feces become faintly colored until it is completely lost and acquire a white-gray color;
- the abdomen increases in volume due to an enlarged liver and ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdomen);
- areas of dilated saphenous veins appear on the skin of the abdomen, as well as on the face, neck, and chest.
The patient’s subjective sensations are quite painful:
- itching of the skin appears all over the body, which sometimes becomes unbearable;
- general condition worsens;
- headache appears;
- dizziness;
- severe general weakness;
- tinnitus;
- chills appear with an increase in body temperature to high numbers;
- nausea;
- vomit.
In terms of skin color, obstructive jaundice differs from parenchymal jaundice associated with viral hepatitis. With hepatitis, jaundice has a bright orange tint, with obstructive jaundice it has a greenish-gray tint.
Complications of jaundice
Obstructive jaundice is a very dangerous condition. If left untreated, it leads to the death of the patient.
As the process develops, damage to hepatocytes inevitably occurs, the detoxification functions of the liver are disrupted, and a large amount of toxic substances are formed in the body, which affect all organs and systems. Endotoxemia syndrome develops.
In parallel with this, renal function is impaired due to the development of microvascular thrombosis and spasm of blood vessels. The function of nephrons is impaired, renal failure increases, and the level of urea and creatinine in the blood increases. Hepatic-renal syndrome develops, against the background of which many severe pathological reactions develop:
- Toxic substances penetrate the blood-brain barrier, leading to the development of encephalopathy, which is accompanied by confusion, stupor and, ultimately, leads to coma and death of the patient. The effect of toxic substances on nerve fibers leads to disruption of the heart, which is accompanied by a decrease in heart rate (bradycardia).
- The synthesis of blood coagulation factors is disrupted, which leads to the development of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, a life-threatening condition in which many intravascular blood clots first appear, and then, when the blood clotting factors are depleted, bleeding develops against this background, which is very difficult to stop.
- Under the influence of bile acids, surfactant is destroyed - the main substance of lung tissue, which ensures the enrichment of blood with oxygen. Because of this, hypoxia increases and acute respiratory failure develops.
What examination is carried out for obstructive jaundice in cancer patients?
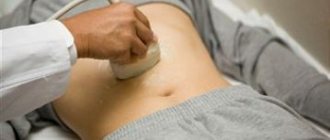
When examining a cancer patient with obstructive jaundice, liver ultrasound and Doppler sonography are performed, which make it possible to determine the presence and location of the tumor, the condition of the bile ducts - their narrowing, expansion, deformation. Additionally, MRI and PET are prescribed to accurately determine the spread of the tumor in the abdominal cavity; cholangiography is mandatory - an X-ray examination of the bile ducts with contrast. Such studies are carried out in all clinics in Israel and other countries with developed healthcare systems.
It can be done in two ways:
- endoscopic retrograde - through a probe inserted into the duodenum, contrast is injected into the lumen of the common bile duct and photographs are taken.
- percutaneous puncture , in which a liver puncture is made in the intercostal space on the right under ultrasound control, a large bile duct is penetrated and contrast is injected, then pictures are taken.
Such a study allows you to accurately determine the level of compression of the duct, which is very important for choosing a treatment method.
In addition to these studies, the patient undergoes:
- scanning of all organs;
- full laboratory examination;
- determination of the amount and fractions of bilirubin;
- research on tumor markers;
- molecular genetic tests.
Diagnostics
It should be noted that such a disease primarily occurs
in adults whose age has already reached 40 years or more. If the problem is a tumor, then the diagnosis can be made quite easily and quickly by an experienced oncologist, because in this case it is easy to detect with a banal palpation of organs. At the initial stage, diagnosis is not so simple, since symptoms can indicate a wide range of diseases. Laboratory studies in the initial stages are not able to give an accurate answer, and therefore doctors use instrumental methods, including the following:
- ultrasound diagnostics;
- radioisotope liver scan;
- x-ray of the duodenum;
- ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography);
- laparoscopy.
How is obstructive jaundice treated for cancer abroad?
Treatment of obstructive jaundice is carried out in parallel with complex treatment of the underlying disease (cancer, sarcoma, lymphoma). This treatment does not eliminate the tumor, but only eliminates the blockage of the bile ducts, creates conditions for the outflow of bile into the intestines, thereby saving the patient from death, increasing life expectancy with obstructive jaundice. In some cases, droppers are prescribed for obstructive jaundice.
Of course, it is possible to eliminate the block of bile and restore the patency of the bile ducts only through surgical intervention. In modern clinics, so-called drainage operations on the bile ducts are used, which are performed after cholangiography and determining the level of blockage of the duct.
The following drainage methods are used:
- external drainage - a probe is installed that removes bile outside. At the same time, its stagnation and obstructive jaundice are eliminated. The disadvantage of this method is the lack of flow of bile into the intestines and associated digestive disorders - indigestion of fats and fat-soluble vitamins. However, the advantages are that the probe can be used to introduce chemotherapy drugs into the liver, for selective radiotherapy of cancer (injection of a solution with radioisotopes).
- internal drainage - restores the passage of bile into the intestines, eliminating jaundice and normalizing digestion. Such operations are called biliodigestive anastomoses, when the common bile duct is cut off from the place of its compression and sutured into a loop of the small intestine. However, these operations on the abdominal cavity are more complicated, and not every patient can perform them, taking into account the general state of health.
- combined (external-internal) drainage - bile partially enters the intestines and is partially excreted. The drainage method is selected individually, depending on the location of the bile blockage, the nature and location of the tumor, anatomical features and the general condition of the patient. Most often, these operations are performed using minimally invasive methods - endoscopic, laparoscopic, so as not to cause additional trauma to the patient.
stenting is becoming very popular - dilating the duct with a special probe and introducing a tubular metal or plastic frame (stent) into its lumen, which does not allow the duct to narrow.
Such operations are performed when the duct is surrounded by a tumor, and there is no way to remove it; they expand its lumen from the inside, using a stent.
In modern clinics, stenting is performed using endoscopic video systems (Olympus, etc.) and a tomographic digital stenoscope (General Electric). The procedure is precise, low-traumatic and takes little time.
New types of intraductal stents are also being developed. The fact is that the service life of a conventional stent is 2-3 years; it gradually becomes clogged with a putty-like mass formed from bile and ceases to perform its function.
Today it is possible to use self-expanding nitinol wire stents, which respond to changes in the lumen of the duct and the degree of its compression, and the period of their installation is not limited.
Nutrition
Comprehensive treatment of jaundice at home in adults prescribed by a gastroenterologist includes, first of all, diet.
The diet should be high-calorie, balanced, consisting of dishes that will not harm the liver. Food should only be eaten fresh and warm. The patient's diet must contain sufficient amounts of protein, vitamin D (found in meat and animal products) and iron.
You need to eat at home often in small portions, at least 5 times a day. A diet is prescribed for the treatment of jaundice in adults, which consists of three stages.
The first stage (about two days) involves the consumption of glucose solution, fruits, sweet compotes and tea. Due to the intake of glucose, processes in the liver cells are normalized. Solid food is not recommended during this period; liquids help remove toxins from the body.
The second stage (about a week) involves the inclusion of vegetable broths and cereals, as well as a small amount of solid food, in the diet.
The third stage (until recovery) allows you to eat dietary foods allowed for liver diseases.
What can be done during the treatment of jaundice in adults:
- dry bread, crackers, biscuits;
- vegetable and cereal soups, stewed vegetables and cereals;
- lean meat, poultry and fish only boiled or baked, steamed cutlets;
- low-fat milk, kefir and cottage cheese, casseroles and puddings made from them, hard cheeses;
- sweet compotes, jelly, marmalade, jam, caramel.
When treating jaundice at home in adults, the consumption of fresh berries - raspberries and strawberries, herbs - dill and parsley is encouraged.
What is not allowed during the treatment of jaundice in adults:
- canned food, smoked food, pickles and marinades, fried foods;
- fatty meat, poultry and fish, broths made from them;
- spices, chocolate, herbs, coffee, alcohol (under especially strict prohibition);
- legumes, radishes and radishes, mushrooms;
- fresh bread, cream cakes, pastries.
What are the results and prognosis of surgical treatment of obstructive jaundice in oncology?
Many patients are interested in the question: how long do people with obstructive jaundice live? Drainage operations for obstructive jaundice and stenting of the biliary tract are very effective; they actually save the patient’s life, or rather, eliminate the threat of death from developing obstructive jaundice. Of course, this prolongs his life by years, even in cases of inoperable cancer, and improves his quality of life. And in combination with modern methods of chemotherapy, radiotherapy and treatment with biological drugs, the patient has a great chance of overcoming a fatal disease.
According to statistics provided by different clinics, drainage operations and stenting for oncological obstructive jaundice within 2-3 weeks allow:
- eliminate liver failure;
- normalize digestion;
- prepare the patient for a course of chemotherapy and radiotherapy, which are highly undesirable during jaundice.
Medication support
When answering the question of how to treat jaundice at home in adults, we must not forget about medications in addition to diet.
- Etiotropic (eliminating the cause) therapy - a medicine for jaundice in viral hepatitis (lamivudine) and (antiviral drugs based on sofosbuvir, daclatasvir; ribavirin, interferon), for an inflammatory process in the gallbladder - antibacterial drugs.
- Improving digestion - taking enzyme preparations (Creon, Pancreatin, etc.).
- Vitamins A, K and D.
- Boosting immunity.
- Increasing the concentration of active acids, reducing cholesterol synthesis in the liver - hepatoprotectors (ursodeoxycholic acid - UDCA).
- Relieving skin itching (antihistamines).
- Strengthening the metabolic function of the liver (Essentiale, Heptral, etc.).
- Antispasmodics in case of obstructive jaundice (No-spa, Dibazol, etc.).
Treatment for the disease in adults includes IVs and medication injections. These manipulations belong to classical drug therapy.
Forecast and preventive measures
The outcome of the disease that caused obstructive jaundice depends on the time of treatment and the patient’s compliance with the doctor’s recommendations. In most cases, it is not possible to completely restore health due to the fact that salt metabolism is disrupted and chronic diseases are present. However, many people manage to significantly improve their condition.
If the patient consults a doctor on time, the prognosis for obstructive jaundice is favorable.
The prognosis for life with breast cancer against the background of cancer is not so favorable. This is due to the fact that it is quite difficult to completely remove the tumor. The patient will have to undergo surgery (and possibly more than one), which can lead to additional complications.
Thus, obstructive jaundice is a reason to urgently consult a doctor. Self-medication is strongly discouraged, as the patient can only worsen his condition and waste valuable time. It is important to visit a doctor who will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and identify the cause of jaundice. If the treatment rules are followed, the patient has a chance of a full recovery.
Basic information, statistics
Many patients do not know what obstructive jaundice is. This pathology is a complication of many diseases of the pancreas and biliary tract (bile ducts, sphincters that regulate the outflow of liver secretions). When the disease occurs, the skin and mucous membranes become yellow, urine darkens, feces, on the contrary, become light, itching and abdominal pain appear. These symptoms occur because bilirubin in the blood increases. The higher the level of bile pigment, the more severe the patient's condition.
In obstructive jaundice due to cancer, the ducts are blocked by the tumor
Important. If the bile ducts are blocked, the concentration of bilirubin increases by 30–40 µmol/hour each time.
The question of whether subhepatic jaundice is contagious is quite relevant. According to doctors, the pathology cannot be transmitted from person to person, since it does not arise due to a virus, but due to a violation of the excretion of bile. You can only become infected with viral jaundice, which occurs against the background of hepatitis A or B. Based on this, obstructive jaundice is not transmitted through blood, saliva, etc.
Reference. The mechanism of transmission of viral hepatitis A is fecal-oral. It is realized through water, household and food transmission routes. Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood or other body fluids.
Acholic jaundice is dangerous, since the following complications may occur during the pathology: functional failure of the liver, kidneys, purulent inflammation of the bile ducts. In the absence of proper therapy, the following consequences may develop: biliary sepsis (purulent inflammation), biliary cirrhosis. A complication such as cholangiogenic liver abscess (infection of the bile ducts) is also possible.
Reference. In adults, in 29% of cases, obstructive jaundice (IJ) occurs against the background of cholelithiasis, in 67% - due to malignant tumors. Often in infants, pathology is provoked by congenital malformations of the bile ducts. Breast cancer is diagnosed more often in women than in men.
Diet
During treatment of obstructive jaundice, the patient must follow nutritional rules. This is necessary to reduce the load on the digestive tract. And after surgery, a diet is needed to quickly restore the body.
With obstructive jaundice, you must follow a diet
The patient should drink at least 1.5 liters of fluid to reduce the negative effects of toxins on the kidneys and cleanse the blood of bilirubin. To meet energy needs, you can drink drinks that contain carbohydrates, for example, sweet weak tea, compote, glucose solution. This is necessary to normalize metabolic processes and relieve the liver.
When the patient's condition improves slightly after surgery, the diet can be expanded. To do this, the diet is replenished with vegetable soups, cereals with milk, and juices. It is important to monitor the temperature of food. The best option is dishes at room temperature. It is prohibited to consume products that have expired.
A little later, the menu is supplemented with meat and fish (low-fat varieties), which are recommended to be boiled or steamed. Meat or fish dishes can be served with porridge.
Important. To ensure that food is better absorbed and does not overload the gastrointestinal tract, products are carefully processed and crushed before cooking.
Dishes are allowed to be supplemented with a minimum amount of vegetable or butter.
When the patient’s condition has stabilized, he can supplement the diet with fermented milk products with a low fat content, day-old or oven-dried bread.
Conservative treatment
Treatment of obstructive jaundice should be carried out after identifying the first symptoms. The primary task of doctors is to eliminate stagnation of liver secretions. The following drugs are used for this purpose:
- Hepatoprotectors: B vitamins, Essentiale, Silymarin, Gepabene, Ursodeoxycholic acid. These drugs protect the liver from the influence of toxins and restore its structure.
- To stimulate metabolism, use Pentoxyl and Methyluracil.
- Amino acids reduce intoxication in hyperbilirubinemia: Glutamic acid, Methionine.
- Hormonal drugs (Prednisolone). To prevent the appearance of defects in the gastrointestinal mucosa and exacerbation of ulcers, Rebaprazole is used.
- To improve hepatic blood circulation, use Rosorbilact, Reopoliglyukin, Neorondex.
- Antibacterial drugs help cope with secondary infection: Ampicillin, Imipenem.
Various drugs are used to treat jaundice
Vikasol helps prevent bleeding. If necessary, plasmapheresis (blood purification) is performed, and enterosorbents are also used to cleanse the body of toxins.