Depending on age and physical activity, a healthy adult's heart rate may change over the years. The resting heart rate is minimal, since the body in this state does not need additional energy.
A normal heart rate for an adult between the ages of 18 and 50 should be between 60 and 100 beats per minute.
Normal human heart rate by age (table)
The normal heart rate for adults is 70-90 beats per minute. This is a general indicator that should be clarified. The average values are presented in the table:
| Age (years) | Minimum | Average | Maximum allowed |
| 12-18 | 65 | 70 | 95 |
| 18-30 | 55 | 72 | 90 |
| 31-40 | 57 | 75 | 89 |
| 41-50 | 61 | 72 | 87 |
| 51-60 and older | 70 | 80 | 91 |
The individual characteristics of the organism are taken into account, as well as the factors described above in the material. There is no single norm for everyone; we are talking about a representative sample based on gender and age characteristics (usually from 5 to 25 thousand people participate in the study).
The normal pulse rate of a person by age without load is determined by the number from 65 to 100 beats per minute. In children, the level may be higher (up to 170 bpm), due to the underdevelopment of the heart.
Deviation of heart rate indicators from the norm
- Voltage. When determining the pulse, do not use force. The pulsation is easily felt if you simply place your fingers on the vessel. If at the same time there is a feeling of resistance, we can talk about pathological changes in the arteries.
- Synchronicity. When measuring the pulse on both hands at once, the beats should occur simultaneously.
- Regularity. The pulsation in the arteries should be constant. If there are intervals between fluctuations, sharp jumps and slowdowns, then this may be a sign of a malfunction of the cardiovascular system, arrhythmias.
It should also be noted that a single measurement is not enough to assess the patient’s condition. Indicators must be monitored over time to eliminate single deviations from standard values. If abnormal phenomena persist for a long time, this is a reason to contact a medical institution for a thorough examination.
| Age | Pulse rate, beats/min |
| Newborn (0-1 month) | 130-160 |
| Child up to one year (1-12 months) | 110-150 |
| 1-2 years | 100-140 |
| 3-7 years | 80-120 |
| 8-11 years | 70-100 |
| 12-15 years | 55-95 |
| 15-60 years | 60-85 |
| 60-80 years | 70-90 |
Now it’s easy to determine what the normal heart rate of an adult should be by year, because this table is quite simple. Doctors use the same standards when conducting a medical examination.
A slow, accelerated or arrhythmic pulse is considered pathological. Rhythm disturbances are clearly visualized on the ECG.
ECG with bradycardia, arrhythmia, tachycardia differs from the norm in the frequency of QRS waves
You can talk about a slow heartbeat when the heart rate is below 50 beats/min. Bradycardia can be physiological or pathological.
Treatment of bradycardia caused by disruption of the conduction system of the heart involves installing a pacemaker.
The pacemaker is fixed under the skin on the chest, and the electrodes are installed directly in the heart and deliver electrical impulses to the myocardium
If a slow heart rate is associated with beta-blockers or peripheral vasodilators, the cardiologist will reconsider treatment with these drugs.
For moderate bradycardia, conservative treatment with the following pharmaceuticals is possible:
- Izadrin (Euspiran, Novodrin, Isoprenaline), Orciprenaline sulfate from the group of synthetic catecholamines that stimulate β-receptors. These drugs increase the excitability and contractility of the myocardium. Does not affect blood pressure levels. The risk of atrioventricular block (impaired conduction of electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles) or fibrillation is minimal. Prescribed both by injection and orally according to an individually selected regimen;
- Ipratropium. Used for sinus bradycardia (reduced heart rate with normal rhythm). Causes a prolonged increase in heart rate. Does not affect the nervous system. Prescribed 1 tablet 3 times a day;
- Ephedrine. Causes vasoconstriction, increases blood pressure, causing the heart to beat faster. Prescribed by injection and orally. The duration of the course of treatment is no more than a month with a gradual reduction in dosage.
DETAILS: Afobazol - instructions for use, indications, doses, reviews
The listed drugs have side effects, so they are used as prescribed by a doctor.
When a bradycardial attack occurs, the pulse drops to 35 beats/min or lower. The patient experiences severe dizziness, nausea, shortness of breath and other symptoms. This indicates the development of heart failure, leading to loss of consciousness and even death.
To provide first aid, you need to perform the following manipulations:
- Lay the patient on a hard surface, place bolsters under the head and legs so that the lower limbs are higher than the level of the head.
- Unfasten the buttons on your clothes, loosen your tie, belt, and provide access to fresh air.
- Brew strong hot tea, you can add 15-20 drops of belladonna or ginseng tincture.
- For severe chest pain, place one Nitroglycerin or Isadrinum tablet under the patient’s tongue.
- If after 5–15 minutes there is no improvement, call an ambulance.
If, as a result of an attack of bradycardia, fainting occurs and the patient does not come to his senses, you need to call an emergency medical team as quickly as possible
With frequent attacks of tachycardia, you need to adjust your diet - give up coffee, strong tea, energy drinks and alcohol. It is advisable to reduce your intake of sugar and salt, since foods high in them thicken the blood. As a result, the heart is forced to pump faster to pump blood.
Treatment of physiological tachycardia is carried out with the help of sedatives of natural origin (Persena, tincture of valerian, motherwort, peony, hawthorn, etc.).
Sedatives of natural origin are sold without a prescription because they have virtually no contraindications
If you don’t have medications on hand, you can lower your heart rate using the following manipulations:
- close your eyes and press your fingers on your eyeballs for 20–30 seconds (Aschner test);
- take a deep breath and then try to exhale with your mouth and nose closed (Valsalva maneuver);
- wash your face with cold water, and then do a unilateral neck massage in the area of the carotid artery (you cannot do both sides at the same time!);
- provoke a cough or gag reflex.
Self-massage of the neck with tachycardia should be performed with moderate pressing movements in the direction from top to bottom
For pathological tachycardia, the doctor prescribes the following medications:
- β-blockers (Egilok, Atenolol, Concor);
- sodium channel blockers (Allapinin, Ritmonorm);
- potassium channel blockers (Cordarone);
- combined sedatives (Corvalol, Barboval, Valocordin), which include phenobarbital. This substance has a depressant effect on the nervous system, causing sedative and hypnotic effects. Under its influence, the smooth muscles of the heart and blood vessels relax, due to which the number of heart contractions decreases;
- peripheral vasodilators (Captopril, Enalapril). They dilate small vessels, evenly distributing the volume of circulating blood throughout the body. Due to this, blood pressure on the walls of the arteries and the load on the heart are reduced.
You can determine whether a person is healthy from the first seconds, because in a healthy person the pulse rate (the intervals between heartbeats) should be the same and uniform. An abnormal frequency is already a symptom of problems in the body, for example, heart pathologies.
You should measure your pulse correctly; you need to find areas on the body in which vascular vibrations are felt very well. It is also necessary to know the values of the measured pulsation, which differs depending on the age, gender of the person and his type of activity (sports person or person with chronic diseases).
The pulse should be measured on the radial artery, which can be easily felt on the wrist. Measurement time – 30 seconds. If rhythm cannot be established in the first 30 seconds, then the pulse should be measured for a minute. If you cannot measure your pulse on your wrist, you can also feel it in your temples.
| Woman's age | Minimum (normal) number of beats | Average (normal) number of beats | Maximum (normal) number of strokes | Blood pressure (normal) |
| 50 | 60 | 75 | 80 | 110-130 |
| 50, 55, 60 | 65 | 75 | 85 | 140-80 |
| 60, 70, 80 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 140-160 |
Correct measurement
- Person's age
- Human body position
- Food
- Body temperature
- Exercise stress
- Stress
- Human hormonal background
- Environment
A man's pulse, or rather its frequency, is greatly influenced by the man's age. It is also necessary to take into account the physical state of health of a man (child, boy, guy) and his physical fitness, meal times (how long ago he ate) and what he was doing before measuring his pulse (sleeping, walking, running).
| Man's age | Minimum (normal) number of beats | Average (normal) number of hits | Maximum (normal) number of strokes | Blood pressure (normal) |
| Up to 50 years old | 60 | 70 | 80 | 120-140 |
| From 50 to 60 years | 65 | 75 | 85 | 140-80 |
| From 60 to 80 years | 70 | 80 | 90 | 145-165 |
Pulse - heartbeat
| Child's age | Minimum (normal) number of beats | Average (normal) number of beats | Maximum (normal) number of strokes | Blood pressure (normal) |
| Up to 1 month | 110 | 130 | 165 | 60-80/85 |
| Up to 12 months | 100 | 130 | 160 | 80-110 |
| From 12 months to 2 years | 90 | 130 | 150 | 90-110 |
| From 2 to 3 years | 90 | 100 | 130 | 90-110 |
| From 3 to 4 years | 90 | 100 | 130 | 90-110 |
| From 4 to 5 years | 85 | 105 | 125 | 110-120 |
| Woman's age | Minimum normal number of strokes | Normal number of strokes (average) | Maximum normal number of strokes |
| From 20 to 30 years | 60 | 65 | 70 |
| From 30 to 40 years | 70 | 73 | 75 |
| From 40 to 50 years | 70 | 75 | 80 |
| From 50 to 60 years | 80 | 83 | 85 |
| From 60 to 70 years | 83 | 85 | 87 |
| More than 70 years | 83 | 85 | 88 |
Pulse rates
What is the heart rate in sleeping patients?
During rest, a person is in a state of homeostasis, that is, the body self-regulates most actively during hours of unconsciousness.
Specific substances are produced, and corticosteroids involved in accelerating cardiac activity are synthesized in smaller volumes (peak secretion occurs at 7-8 am).
A change in this state of affairs is possible when circadian rhythms are disrupted as a result of stress, lifestyle and pathologies of the hypothalamus.
The normal heart rate for a sleeping person is 50-70 beats per minute. Any more is already a violation. The reasons need to be sought.
Types of heart rate disorders
A decrease or increase in the number of strokes at any age indicates disorders in the cardiovascular system. Therefore, with such a symptom, it is necessary to take care of your health, otherwise with age the pathology will develop and the problems will become more serious.
It is important to know two pathological types of pulse:
- Tachycardia - acceleration of heart rate.
- Bradycardia is a slow heart rate.
Tachycardia
There are physiological causes of tachycardia:
- strong pain;
- stress;
- physical overload;
- cold;
- medications.
The pathological causes of tachycardia are as follows:
- cardiac ischemia;
- increased blood pressure;
- diseases of the autonomic nervous system;
- neoplasms;
- diseases of the heart muscle;
- hormonal imbalances;
- bacterial and viral pathologies;
- blood loss.
A man’s normal pulse changes not only from strength work, but also naturally (due to emotional excitement, overeating, cold). In this case, the heartbeat returns to normal when the influencing factors disappear. In the presence of vegetative-vascular dystonia, not only tachycardia, but also rhythm disturbances can be observed, however, in the absence of stress, the heart pulse in men returns to normal in 20–40 minutes.
Bradycardia
There are natural causes of bradycardia, namely, when the vagus nerve is irritated, a reflex slowdown of the heartbeat occurs.
Pathological causes of bradycardia are:
- stomach ulcer;
- myocarditis;
- hypothyroidism;
- myocardial infarction;
- use of cardiac glycosides, β-blockers;
- disruption of the innervation of the heart.
Interesting! There is a diagnosis of “idiopathic bradycardia”, which is written in situations where it is not possible to find the etiological factor for the decrease in heart rate.
Healthy heart and heart with bradycardia
What happens to the indicator after eating?
Eating is associated with an increased load not only on the gastrointestinal tract, but also on the cardiovascular system in general. To digest food you need a lot of liquid. Organs work more actively. More blood is needed. The heart begins to pound.
For a healthy person, the reference value is 80-100 beats per minute. Patients observe an increase in heart rate of 120-150 and even more. This is not normal and indicates pathologies of the cardiovascular system, hormonal disorders, or kidney disease.
Consultation with a cardiologist and, if necessary, other specialized specialists is required.
The ratio of heart rate at rest and during exercise
If you need to compare your indicators with what heart rate is considered normal in men, then you need to analyze not only the heart rate during rest or training, but also the ratio of these parameters to each other. To do this, a Ruffier test is performed at any age.
First, the resting heart rate in a sitting position is determined, this data is used in variable A. Do 30 deep squats in half a minute. Then the heart rate is measured in a standing position immediately after performing the exercise, this indicator is recorded in B. After a minute, the pulse is measured again and the value in variable C is used.
The formula for the Ruffier index for any age is as follows: [ (A+B+C) - 200] /10
A man needs to evaluate the result like this:
- Ruffier index less than 0 is an excellent indicator;
- from 1 to 5 - good;
- from 6 to 10 - satisfactory;
- from 11 to 15 - unsatisfactory;
- more than 15 is an extremely bad indicator.
During physical activity
Here everything depends on the degree of training of the body. If a person sits still most of the time, even a minimal load will lead to pronounced tachycardia: this is a compensatory mechanism, the organ does not know how to eject blood effectively, it takes it at speed, otherwise tissue hypoxia, ischemia and death will occur.
At a certain moment (when the pulse exceeds 180 beats), a sharp drop in blood pressure occurs. Therefore, it makes no sense, when coming to training, to immediately take on heavy weights or torment yourself on treadmills. This can result in cardiogenic shock and death.
Athletes who tend to overwork are more tolerant of stress, but again it all depends on the person.
What can change your heart rate?
Physiological causes or diseases of various organs, including the heart, can slow down, speed up the heartbeat or cause its irregularity.
A slow heartbeat (bradycardia) is normal and does not harm the human body in the following cases:
- increased environmental humidity, moderate body cooling;
- good physical fitness;
- sleep state;
- taking certain medications, such as sedatives or beta blockers.
Diseases accompanied by slow heartbeat:
- IHD and other heart diseases, primarily sick sinus syndrome;
- overdose of antiarrhythmic drugs, in particular cardiac glycosides;
- poisoning with lead compounds, FOS, nicotine;
- gastric ulcer, traumatic brain injury, stroke, brain tumor, increased intracranial pressure;
- hypothyroidism (reduced hormonal activity of the thyroid gland).
A physiological (natural) increase in heart rate is possible in the following situations:
- physical activity and stress;
- fever;
- increased ambient temperature;
- staying on top;
- pregnancy;
- drinking caffeine-containing drinks.
The main causes of pathological rapid heartbeat (tachycardia):
- diseases of the nervous system (neuroses, autonomic disorders);
- hyperthyroidism;
- anemia;
- heart failure;
- chronic lung diseases;
- heart diseases - ischemic heart disease, myocarditis, some valve defects.
Factors influencing changes in heart rate not related to diseases
Natural reasons for a decrease or increase in heart rate are as follows:
- Body type. Patients who are dense, obese, or have a large amount of fat or muscle are more likely to experience tachycardia compared to the population average.
This is due to an increase in tissue mass and the need to provide these structures with blood and, accordingly, nutrients to maintain normal life functions. But this is not an axiom. Variants are possible.
- Floor. Representatives of the female half of humanity have a tendency to increase heart rate due to hormonal characteristics.
Estrogen and progesterone are quite aggressive substances that have a stimulating effect on the third reflex zone of the heart, which is responsible for adequate regulation of the beat rate. This is especially noticeable during pregnancy.
In addition, the organ of the fairer sex is smaller than that of men. Hence the need for more frequent work.
- Gestation. Bearing a fetus is associated with generalized restructuring of all systems to please the growing body of the child. The interests of the mother's body fade into the background, at best, and even further.
Hemodynamics are disrupted, the heart itself does not receive enough nutrition, trophism decreases, hence the acceleration of the heart rate by 20-30 beats. min. more than the normal heart rate for age. Now you have to provide for two people at once; it’s not easy for one body to do this.
- Professional activity. Persons whose work involves high physical activity suffer from chronic bradycardia. Although this is said quite loudly. For such patients, a decrease in heart rate is a physiological phenomenon.
The organ contracts more intensely. By throwing out more blood, it means there is no need to work as hard (in terms of speed). 40-50 beats per minute is quite common. Moreover, against the background of severe hypotension.
However, there is one “but”. People of this type are more susceptible to developing emergency conditions as soon as they stop working.
- Hormonal changes. Puberty, menopause and the menstrual cycle. Apart from the already mentioned pregnancy, with which everything is clear. Puberty (adolescence 12-19 years) is associated with frequent changes in heart rate and blood pressure. In the morning the organ can beat at a speed of 60 beats per minute, and in the evening the pulse rate increases to 100 and this is not the limit.
Hormones are to blame, as well as the mental makeup of the individual. Climax. Endocrine disorders have an effect, but of a different kind. Replacement therapy will help.
Finally, cyclical monthly changes. They occur in several phases. At each stage, a group of hormones prevails, therefore, throughout the entire period, jumps in the pulse rate within a wide range are possible.
- Climatic conditions. Residents of hot regions of the planet are more susceptible to the development of physiological bradycardia. For them, this is a normal phenomenon that does not require medical attention.
Doctors turn to these factors first. Usually, the theory of the natural etiology of the process can be refuted by taking an anamnesis.
How to measure your pulse correctly?
At its core, the pulse represents slight vibrations of the vascular walls, which are driven by the work of the heart (i.e., rhythmic contractions of the myocardial muscles).
Ideally, the intervals between pulsations are equal, and the average values at rest do not reach the upper limits. When the heart rate (HR) is disturbed, this gives reason to think about problems in the body and the presence of a serious disease.
Finger method
Vibrations of the heart muscle are usually measured by palpation using arterial beats. Basically, they use the radial one, which is located on the inside of the wrist. It is at this point that the vessel can be better palpated, since it is located as close as possible to the surface of the skin.
- If no rhythm disturbances are detected, the pulse is measured for half a minute, and the result is multiplied by 2.
- If fluctuations or irregularity are observed, the beats are counted for one minute.
- To obtain the most accurate indicator, the pulse is measured on both hands at the same time.
In some cases, heartbeats are counted in places where other arteries are located. For example, on the chest, neck, thigh, upper arm. In young children, the pulse is measured mainly on the temporal part, since it is not always possible to feel the beats on the hand.
Hardware methods
- In addition to the finger method, you can also use special devices, for example, a heart rate monitor (chest, wrist) or an automatic blood pressure monitor. Although the latter device is more suitable for determining blood pressure.
- If a person is suspected of any disturbances in the functioning of the heart, the pulse is measured using special methods and medical equipment (ECG or 24-hour (Holter) monitoring).
- In particularly difficult cases, a treadmill test is used. A person's heart rate is measured using an electrocardiograph during physical activity. This method helps to see hidden problems at the earliest stages of the disease, as well as make a forecast about the state of the cardiovascular system in the future.
But even the most advanced methods will not give an accurate result if the pulse is measured incorrectly.
So, you cannot take measurements after the following actions:
- sudden change in body position (stand up, lie down);
- physical activity, as well as after sexual intercourse;
- emotional tension, stress;
- psychological experiences, including fear or anxiety;
- taking medications, alcohol;
- visiting a sauna, bathhouse, taking a bath;
- hypothermia.
Pathological causes
The heart rate can vary in one direction or the other due to pathological changes in the body. We are talking about six main diseases.
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a deficiency of thyroid hormones and the reverse process is hyperthyroidism with an excess of substances in the bloodstream. Hemodynamic disturbances affect the third reflex zone of the heart.
In the first situation, tachycardia occurs, in the second - a decrease in heart rate per minute. Prolonged course of both conditions is associated with an increased risk of fatal or disabling complications.
Diabetes
Generally destroys organs and systems, right down to the visual analyzer. With endocrine pathology, the heart wears out faster; without proper treatment, natural death occurs 10-15 years ahead of schedule.
Diabetes of the first type is especially dangerous, since it is not treated, but only corrected with medication, and not always to a sufficient extent.
Hypercortisolism or Addison's disease (reverse phenomenon)
Impaired synthesis of cortisol and other corticosteroids (to a lesser extent). Maintenance hormonal therapy and surgery to eliminate the root cause are required (in the vast majority of cases, the main factor is a tumor in the adrenal glands or pituitary gland).
Congestive heart failure
Causes cardiac ischemia and accelerates the rhythm, sometimes to significant levels. The course without therapy entails a heart attack, sooner or later (usually within 3-5 years from the onset of the first symptoms, by which time the disease is far from at the initial stage of development).
The first signs of heart failure are described in this article.
Acute myocardial ischemia
Leads to death in 35-50% of cases. An extensive type of heart attack is fatal in 95% of clinical situations. Arrhythmia is the hallmark of the process, along with accompanying manifestations.
Lesions of cranial nerves and centers regulating vascular tone
Usually as a result of osteochondrosis or vertebrobasilar insufficiency. The neurogenic component of the heart rate control process is disrupted.
A special case is a tumor of the brain stem. Mortality is 100%, and in the same number of recorded cases there is inoperability due to the delicate situation.
The list is incomplete, but other causes are so rare that they are not of significant significance in the diagnostic process.
When is your heart rate high?
In the absence of pathological changes affecting the heart rate, the pulse may increase under the influence of physical activity, be it intense work or sports. The following factors can also increase it:
- stress, emotional impact;
- overwork;
- hot weather, stuffy indoors;
- severe pain.
With a functional increase in pulse there is no shortness of breath, dizziness, headaches or chest pains, the eyes do not darken, the heartbeat remains within the maximum normal range and returns to its normal value within 5-7 minutes after cessation of exposure.
Pathological tachycardia is spoken of if there is any disease, for example:
- pathologies of the heart and blood vessels (for example, rapid pulse in hypertensive patients, people with coronary artery disease);
- arrhythmia;
- nervous pathologies;
- heart defects;
- presence of tumors;
- infectious diseases, fever;
- hormonal disorders;
- anemia;
- heavy menstruation (menorrhagia).
A slight increase in the number of pulse waves is observed in pregnant women. In children, functional tachycardia is normal, observed during active games, sports and other activities and allows the heart to adapt to changing conditions.
An increase in heart rate, and therefore a high pulse, is observed in adolescents with vegetative-vascular dystonia. During this period, it is important to pay close attention to any changes - chest pain, the slightest shortness of breath, dizziness and other symptoms are a reason to show the child to the doctor, especially if there are diagnosed heart diseases.
Indicators for which you need to see a doctor
Specialists are required in all controversial cases. As soon as the heart begins to beat abnormally, relative to normal, or arrhythmically, a consultation is necessary.
The following symptoms are noteworthy:
- Intense chest pain for no apparent reason. A person can become a heart patient in an instant. But the factors preceding this were always on the surface, you just need to see them.
- Dizziness. Vertigo accompanies a sharp drop or rise in blood pressure.
- Cephalgia. Headache of a stabbing nature. The unpleasant sensation is localized in the temples, crown, and back of the head, and does not go away after using anti-inflammatory and even analgesics. This is due to the well-innervated blood vessels of the brain.
- Shortness of breath, suffocation at rest.
- Nausea and vomiting. Usually they go as a complex.
- Frequent yawning. Indicates a lack of oxygen in the blood.
- With long-term changes in the nature of cardiac activity - problems with potency, libido and menstrual cycle disorders in women.
In case of gross changes, you need to call an ambulance to resolve the issue of moving the patient to the hospital.
Measurement Rules
The simplest and most convenient way is to measure the pulse on the radial artery - it is located almost immediately under the skin along the inner edge of the wrist, under the thumb, so there are no problems with how to find it. You need to feel the pulsation with three fingers and count the number of beats per minute. But there are other areas where arterial pulsation is obvious:
- whiskey;
- carotid artery in the neck;
- popliteal or ulnar fossa;
- groin or inner thigh (junction of the lower limb and pelvis);
These zones are used in emergency cases when the radial artery is damaged or affected by atherosclerosis (stiff).
List of necessary examinations
Management of patients with arrhythmias is the prerogative of a cardiologist. At the discretion of the doctor, it is possible to involve third-party doctors: an endocrinologist, nephrologist and neurologist. Particularly difficult cases are resolved at a consultation.
An approximate diagnostic scheme looks like this:
- Questioning the patient, assessing health complaints. Essentially, identifying symptoms.
- Collection of anamnestic data. What did you get sick with, how, for how long and why. What treatment did you receive? And other questions of a similar nature. Specialists are also interested in the family history of pathologies.
- Electrocardiography. Study of cardiac activity using a special technique. It is impossible to read the result without appropriate qualifications. Even doctors don't always cope.
- Echocardiography. Ultrasound diagnostics.
- Blood tests for hormones, biochemical indicators, formed cells, etc.
- Nephrological and neurological status.
- Assessment of specific reactions during palpation and physical examination.
Only the comprehensive nature of diagnostics makes it possible to quickly identify pathology.
What deviations from the norm are considered dangerous?
When determining heart rate indicators, it is important to take into account not only heart rate, but also the rhythm of heart contractions. The heart should beat without pauses or interruptions, but single rare additional beats are not a cause for concern.
You should consult a doctor in the following cases:
- irregular heart rhythm;
- heart rate deceleration is less than 50/min or acceleration is more than 100/min;
- attacks of rapid heartbeat with heart rate more than 140/min.
These signs may accompany the following dangerous conditions:
- atrial fibrillation;
- paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia;
- frequent ventricular extrasystole and paroxysms of ventricular tachycardia;
- sick sinus syndrome;
- sinoatrial or atrioventricular block II – III degree.
Why is my heart rate higher?
A rapid pulse can cause attacks of anxiety and worry about life
Pulse rate is a purely individual indicator; it will depend on the state of health, emotional state, and the conditions under which the measurement takes place. As tables with normal indicators by age demonstrate, a woman’s pulse of 85 will never be the same as that of a 25-year-old girl. In some cases, the pulse may differ from the norm due to individual characteristics, without the presence of any pathology.
Factors for a temporary increase in heart rate
The pulse may increase for a short time under the influence of the following factors:
- medications whose side effects include increased heart rate;
- physical exercise;
- emotionally active moments, they can be both negative and positive;
- drinks that contain caffeine - coffee, tonic drinks and others;
- hypothermia of the body;
- overheating of the body - exposure to the open sun, bath or sauna, stuffy room;
- overeating, including abuse of foods that are too fatty and sweet;
- alcohol consumption.
Women also have their own, female-specific causes of heart palpitations:
- excessive menstrual bleeding;
- menopause;
- pregnancy, especially in the presence of severe toxicosis.
It is worth knowing that these “female reasons” should not provoke a heart rate of more than 115 beats per minute. If this happens, the woman should be examined by a gynecologist-endocrinologist and cardiologist. You may need to perform some tests - a blood clinic and a test for female and thyroid hormones.
Modern methods for those who need to take measurements frequently
The reasons for the temporary increase in heart rate act in such a way that the indicator increases than the value that is considered normal in women. The heart rate in such situations quickly returns to normal.
Important: in any situation, the pulse is normal, which should be no more than 220 beats in 60 seconds; exceeding the indicator requires close attention to yourself and seeking help if the pulse does not return to normal within the required amount of time.
Causes of pathological increase in heart rate
It happens that the normal pulse in women at rest increases due to the presence of pathological changes in the body.
Diseases and disorders that cause increased heart rate:
- Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland produces too much of its own hormone. This pathology occurs in women 5.5 times more often than in men.
- Neurotic conditions, prolonged stress.
- Atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease.
- Heart defects, both congenital and acquired.
- Acute diseases - viral, bacterial infection, respiratory diseases, any inflammatory processes in the body that provoke an increase in body temperature.
- A state of anemia when the level of hemoglobin, an oxygen carrier protein, is reduced in a person’s blood.
- Blood loss - this condition is especially dangerous when there is internal bleeding, which is often difficult to quickly diagnose.
With age, by the age of 65, women may experience not only fluctuations in pulse, but also instability in blood pressure. It, just like the pulse, needs to be monitored in order to track the occurrence of pathological changes.
There are additional symptoms of rapid heartbeat, or tachycardia. Knowing them will help identify problems with the pulse if the person himself does not feel its increase.
Signs of tachycardia:
- shortness of breath - a feeling of lack of air;
- a feeling of anxiety, a feeling that something terrible is about to happen, often people at this moment are afraid of death;
- dizziness;
- soreness in the heart area.
What pulse is considered normal, and what does it equal?
What heart rate is considered normal worries many people. For a complete understanding, a simple formula is given: it is necessary to subtract years of life from 180. This way we will get a value indicating how many times the pulse should beat per minute when the heart rhythm beats, subject to the conditions of absolute rest and absence of illnesses.
To verify the information obtained as a result, it is necessary to count the frequency of the heartbeat over the course of a couple of days in an identical period of time and in one position of the body.
The process is that they are also amenable to changes taking into account the position of the body.
In particular, when lying down, it approaches a record high (the heart begins to beat 10–15 beats per minute more). Additionally, minor disturbances are observed after ingestion of food or hot drinks.
To calculate the authenticity of changes in cardiac vibrations per minute, it is worth placing your index finger as well as your central finger on the radial aorta. Actually, in this place the aortic pulsation can be palpated as clearly as possible.
There is another approach to detecting the radial aorta, which involves placing your thumb slightly above the first crease on the wrist. This aorta is located above the second finger.
What to do if heart rate abnormalities are detected
First of all, you need to visit the clinic and get a cardiogram. And then you need to go to a cardiologist with a cardiogram. The doctor will prescribe further examination or refer you to another specialist. It is especially important to visit a doctor for men in their fifties and sixties.
Timely seeking help will help avoid serious consequences that develop with pulse deviations:
- myocardial infarction;
- severe forms of stroke;
- development of severe hypotension.
Often deviations from normal pulse limits are associated with additional diseases. An example is a pathology such as osteochondrosis. When it worsens, not only heart rhythm disturbances often occur, but also pain in the heart area.
Heart rhythm disturbances are also observed in cases of serious kidney dysfunction, hypertensive pathology, coronary artery disease and other pathologies. Therefore, visiting a doctor with these deviations cannot be avoided.
Cause of increased heart rate
When the pulse increases, the following symptoms may appear: confusion, lightheadedness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, increased sweating, tremor. In this case, the help of a doctor is required. There may be several reasons for this condition:
- cardiovascular diseases;
- oncology;
- poisoning;
- hormonal disorders;
- failure of the central nervous system.
Such symptoms should not appear even after training. Within 20 minutes, the heart rate should recover after physical activity. The norm is considered to be its leveling within 40 minutes.
Impact of different conditions on heart rate
Various factors influence fluctuations in heart rate:
- age threshold;
- training;
- growth indicators;
- Times of Day;
- selected foods, drinks;
- air temperature indicator;
- emotional condition.
Changes in heart rate occur under the influence of external and internal factors. The number of heart beats per minute can be affected by a person’s age, gender, physical and psycho-emotional stress, air temperature, body temperature and much more.
Reasons for rejection
Increased heart rate
The female body undergoes several stages of restructuring. First in adolescence, then at the beginning of each menstrual cycle, pregnancy, menopause. All these factors influence the normal pulse in women and girls. But, in addition to these natural physiological processes in the female body, a pathological increase in heart rate can be caused by the manifestation of such diseases:
- thyroid diseases accompanied by high production of hormones;
- neuroses;
- congenital or acquired heart defect;
- the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the body;
- ischemic disease.
Decreased heart rate
In athletic girls, the indicator deviates from normal downward.
A low heart rate is also a pathological phenomenon. Such deviations are often observed in women who play sports. In addition, it may indicate a disruption in the conduction system of the heart. Therefore, if the normal heartbeat in women is disturbed to a greater or lesser extent, then it is necessary to consult a doctor in order to promptly identify and begin treatment of heart pathologies.
Heart rate at night
Daily time (morning, evening) is an important criterion that affects changes in heart rate. During the full sleep phase, metabolic processes will slow down significantly.
Internal organs reduce their activity, and accordingly, the usual heart rate per minute drops. The normal heart rate for all ages in women during night rest is considered to be 40–45 heartbeats. The lowest pulsation number at complete rest is observed during dawn, and the norm can be represented by 30–35 contractions in 60 seconds. This feature of the female body is explained by the fact that the vagus nerve is activated, which inhibits the contractile function of the heart at night.
Change in heart rate during exercise
When you exercise, your heart rate increases and your body requires additional energy. To obtain it, it is necessary to deliver oxygen to all tissues. This is achieved by increasing blood circulation, heart rate and blood pressure.
The heart rate usually increases during physical activity. But sometimes there are situations in which the heart rate becomes less frequent and bradycardia appears. The symptom occurs in athletes or people with a malfunction of the cardiovascular system.
An uneven pulse after exercise indicates sinus arrhythmia. The heartbeat is within normal limits or increased. This is not a pathology and usually does not require the abolition of physical activity.
What can affect heart rate values?
With normal heart rate values of 60-90 beats in women and men in the absence of physical activity, due to certain circumstances it may increase for a short time or, conversely, decrease. Its failure can be affected by age, sports, food consumption, changes in body weight, temperature and other factors, stressful conditions, and the release of hormones into the circulatory system.
The rate of pulse beats that appear in 60 seconds each time depends on the number of contractions in the same period of time. At rest, men's heart rate is several beats lower (5-8) than women's.
This is absolutely normal, even though each person's heart rate is different. The physiological characteristics of the female and male bodies are clearly different, and because of this, the pulse is also different.
In general, the pulse shows only the state of the cardiovascular system, but since the processes occurring in the body are interconnected, we can talk about determining the entire functional state by heart rate.
Functional state refers to how well the body is prepared to withstand physical activity. To do this, use 3 main methods:
- Ruffier's test (lying position and subsequent squats).
- Martinet test (squats after sitting).
- Orthostatic test (lying and standing position).
The point is to measure the difference in heart rate in different states and whether this indicator corresponds to the norm.
Author of the article: Practicing physician V. O. Chubeiko. Higher medical education (Omsk State Medical University with honors, academic degree: “Candidate of Medical Sciences”).
Where can you feel your pulse?
The pulse can be felt in several places on the human body and therefore can be measured:
- On the wrist - the radial artery pulsates
- Ulnar Artery - Look for the ulnar artery, which is located in the crook of the elbow.
- In the armpit
- On the temples
- Temporal artery above the eyebrows
- The neck is the location of the carotid artery
- Corner of the mouth (edge of the jaw) – there you can feel the facial pulse.
- Groin – here you can feel the femoral pulse
- Below the knee (where the leg bends is the popliteal artery).
- Foot or arch
Where to take your pulse?
How to measure the pulse on the hand on the wrist yourself and determine the pulse on the carotid artery?
Measuring your pulse is very simple:
- You will need to have a watch that will measure the time and number of heartbeats over a certain period of time.
- Calm down and sit down, find a quiet and peaceful room.
- Place the index and middle finger of your right hand at the site of the artery pulsation (wrist, neck or other part of the body).
- Record the time (from 30 to 60 seconds) and count the number of beats during this period of time.
- Check the data with the table
It is necessary to measure your pulse in a calm emotional and physical state. The procedure for measuring heart rate should be postponed for 40-50 minutes after drinking tea, coffee, a large portion of hot food, after taking a bath, smoking, intense work or a stressful situation. Heart rate is measured on the body, with a minimum amount of muscle and fat tissue, namely:
- on the wrist on the radial artery;
- carotid artery in the neck;
- in the elbow bend, where the brachial artery is located;
- on the femoral artery in the groin;
- in the popliteal cavity.
To measure your pulse on your arm, you need to sit with your elbows on the back of a chair or lie down. At the same time, the hand is freed from everything that interferes with blood circulation: compression by clothing, bracelets and watches.
DETAILS: Blood pressure tablets that increase heart rate
The hand for counting the pulse should be placed at heart level. Next, use the index and middle fingers to press the radial artery on the wrist to better feel the pulsation.
It is necessary to count the number of pulsations of the artery in 1 minute, or in 10 seconds, and the result is multiplied by 6. If a high pulse is observed, then the most informative result is tracking the heart rate for a minute, and the measurement is carried out 2 times on symmetrical areas of the body (on both wrists, elbow bends, etc.).
Neck measurement
Pulse measurement in the neck is done while sitting or lying down. In this case, you should fold your index and middle fingers and place them in the submandibular fossa on the neck, trying to feel the pulsation of the carotid artery. Next, the pulsation is calculated for 10, 15, 30 seconds or a minute.
It should also be remembered that the pulse is not measured using the thumb, since the thumb has its own pronounced capillary pulsation, which affects the heart rate calculation.
What does it depend on
The number of heartbeats, rhythm and other indicators are not stable and depend on the individual characteristics of the cardiovascular and nervous systems of each person, as well as on lifestyle, physical fitness, etc. The main factors influencing heart rate are as follows:
- muscle load causes an increase in heart rate;
- fitness (the more the body is adapted to prolonged exercise, the more the heart rate decreases, for example, for professional runners, the norm is up to 40 beats per minute);
- emotional state (stress, anxiety, joy increase performance);
- heart disease, thyroid disease;
- medications (cardiac medications, such as beta blockers, can cause a decrease in heart rate);
- age (elderly people have a higher pulse rate than young people);
- temperature (heat and high humidity lead to increased heart rate).
What heart rate is considered normal?
Heart rate is affected not only by diseases, but also by temporary external influences. As a rule, a temporary increase in heart rate can be restored after a short rest and elimination of provoking factors. What should be the normal heart rate for a person in various conditions?
At rest
The value that is considered the normal heart rate for an adult is actually the resting heart rate.
That is, when talking about the norm of a healthy heartbeat, we always mean the value measured at rest. For an adult, this norm is 60-80 beats per minute, but under certain conditions the norm can be 50 beats (in trained people) and 90 (in women and young people).
During physical activity
To calculate what a person’s normal heart rate is during moderate physical activity, experts offer the following mathematical operations:
- The maximum heart rate is calculated as the difference between the number 220 and the number of complete years of a person. (For example, for 20-year-olds this value will be: 220-20=200).
- Minimum heart rate value (50% of maximum): 200:100x50 = 100 beats.
- Normal heart rate under moderate loads (70% of maximum): 200:100x70 = 140 beats per minute.
Physical activity can have different intensities - moderate and high, depending on which the heart rate of the person receiving these activities will be different.
Let us remember that for moderate physical activity the heart rate ranges from 50 to 70% of the maximum value, calculated as the difference between the number 220 and the total number of years of a person.
When running
During high physical activity, an example of which is running (as well as speed swimming, aerobics, etc.), the heart rate is calculated according to a similar scheme. To find out what a person’s heart rate is considered normal while running, use the following formulas:
- Find out the difference between the number 220 and a person’s age, that is, maximum heart rate: 220-30 = 190 (for 30-year-olds).
- Determine 70% of the maximum: 190:100x70 = 133.
- Determine 85% of the maximum: 190:100x85 = 162 beats.
The normal heart rate when running ranges from 70 to 85% of the maximum value, which is the difference between 220 and the person’s age.
For burning fat
The formula for calculating maximum heart rate is also useful when calculating the heart rate rate for burning fat.
Most fitness trainers use for calculations the method of the Finnish physiologist and military doctor M. Karvonen, who developed a method for determining heart rate limits for physical training. According to this method, the target zone or FBL (fat burning zone) is a heart rate ranging from 50 to 80% of your maximum heart rate.
When calculating the maximum heart rate, the norm by age is not taken into account, but age itself is taken into account. For example, let’s take the age of 40 years and calculate the heart rate rate for life-saving lifestyle:
- 220 – 40 = 180.
- 180x0.5 = 90 (50% of the maximum).
- 180x0.8 = 144 (80% of the maximum).
- The heart rate ranges from 90 to 144 beats per minute.
Why is there such a discrepancy in numbers? The fact is that the normal heart rate for training should be selected individually, taking into account fitness, well-being and other characteristics of the body. Therefore, before starting training (and during it), a medical examination is necessary.
After meal
Gastrocardiac syndrome - a noticeable increase in heart rate after eating - can be observed in various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular, and endocrine systems. A pathological condition is indicated by a heartbeat that is significantly higher than normal. Is there really a norm for heart rate to increase while eating?
Strictly speaking, a slight increase in heart rate during or 10-15 minutes after a meal is a physiological condition. Food entering the stomach puts pressure on the diaphragm, which forces a person to breathe deeper and more often - hence the increase in heart rate. Exceeding the normal heart rate occurs especially often when overeating.
But even if little food is eaten, and the heart still starts beating faster, this is not always a sign of pathology. Simply, digesting food requires an increase in metabolism, and for this a slight increase in heart rate is required.
The heart rate after eating is approximately equal to the normal value during moderate physical activity.
We have already learned how to calculate it, all that remains is to compare your own pulse after eating with the norm calculated using the formula.
Why do you need to measure your pulse?
Measuring your pulse is a fairly accurate way to assess the condition of your blood vessels and heart. Both excessive deceleration and strong acceleration of the heart rate lead to insufficient blood ejection into the aorta and the appearance of oxygen deficiency. This condition is manifested by shortness of breath, weakness, sweating, dizziness, and a feeling of chilly limbs.
Therefore, before visiting a doctor, it is recommended to regularly measure your pulse for several days and record it, indicating the time and degree of activity:
- in a dream;
- at rest;
- while walking;
- when climbing stairs and so on.
This will help the specialist understand how pronounced the abnormalities in the functioning of the heart are, because some pathologies in the body can manifest themselves, for example, only during sleep, and others when climbing a flight of stairs.
By giving your body a load, you can determine your level of physical fitness and calculate your heart rate to increase endurance:
- when running and swimming;
- cycling;
- exercises in the gym and so on.
Women's heart rate is on average higher than men's. This is due to the peculiarities of the nervous and hormonal regulation of the heart.
The number of pulse waves can be easily determined at home using the following methods:
- put two fingers on the wrist, feel the pulsation, count the number of beats in 20 seconds and multiply by three;
- measure pressure using a semi-automatic or automatic tonometer, which will also determine the pulse value.
How to properly place your fingers on your wrist when measuring your pulse?
With age, heart rate values gradually decrease. An excessively rapid heartbeat in older people can be one of the signs of various diseases - from anemia to heart failure.
Diet therapy
Diet therapy is used as a comprehensive treatment and allows you to saturate the body with substances that have a positive effect on the functioning of the heart. Proper nutrition for bradycardia and tachycardia not only improves the functioning of the cardiovascular system, but also helps to activate metabolism and get rid of excess weight, which negatively affects the functioning of the heart.
The basic principles of the diet for heart rate disorders are:
- eating small portions of food;
- cooking food using stewing and boiling methods;
- maintain daily calorie intake, taking into account the necessary proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
Must-have products:
- greens, vegetables, fruits;
- whole wheat bread;
- various cereals;
- foods high in calcium and potassium (dairy and fermented milk products, bananas, avocados, spinach);
- fish, lean poultry and rabbit meat, beef;
- greenery;
- fresh juices;
- legumes
What you need to give up:
- alcohol;
- carbonated drinks;
- fried, fatty, too salty foods;
- fast food;
- confectionery and bakery products.
A normal heartbeat per minute is an indicator of the absence of problems with the cardiovascular system. However, heart disease is not always the cause of heart rhythm disturbances. In women, the occurrence of arrhythmia is often associated with an emotional state, thyroid disease or hormonal imbalance.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
How is it measured?
To check the indicator, you can use the cervical artery.
One of the simplest and most accessible ways to determine the pulse rate in men and women is to count the number of beats on the inside of the wrist joint, where the vascular network is located closest to the surface of the skin. If the heart rate is normal, then measuring the indicator does not need to be carried out for the entire minute. 15 seconds are enough for this. The result obtained is multiplied by 4. In addition, using the same principle, diagnostics can be carried out on the arteries of the neck, shoulder, hip or subclavian region. If a woman is suspected of having serious heart problems, the pulse rate is recorded using an electrocardiograph.
Exercises for the heart
Exercise for heart disease is also extremely important. The main thing is movement. So for starters, take walks before bed lasting 30-40 minutes. Before walking, try not to overeat and maintain a steady walking pace. Also, for diseases of the cardiovascular system, outdoor games, cycling, swimming and skiing are very useful. Beware of heavy lifting - it can only cause harm. The main tasks of exercise therapy for heart diseases:
- Prevention of possible complications;
- Improving the condition of the cardiovascular system;
- Restoration of motor skills, adaptation to normal household stress after surgery;
- Creating a good mood and positive emotions.
Pulse zone
The number of heart contractions per minute is called the pulse. Experts determine pulse zones from a state of rest to the maximum load of the body. When playing sports, zone information is useful. With a heart rate in one zone, a person loses weight, in another he increases endurance or may have a heart attack. The boundaries of the zones are determined by special laboratory tests that athletes undergo, but approximate indicators can also be calculated at home.
The maximum permissible heart rate is calculated using the formula Pmax = 220 – age. Depending on the larger indicator, the remaining zones are calculated as follows:
- In the range of 50-60% of the highest value. Easy running. Allows you to train your heart and blood vessels. Breathing is calm, the person can speak and sing.
- 60-70% of fat deposits are burned. Easy running. A person can talk to a running partner.
- 70-80% of the body develops endurance. It turns out to talk in fragments. Breathing is rapid.
- 80-90% strength and speed endurance. For an unprepared body, this zone can become critical. The pulse of a normal person, physical activity at the limit. Heavy breathing, difficulty speaking, redness of the face.
- 90-100% speed endurance for those who play sports constantly. The limit to which a trained person’s body can cope with stress.
Natural factors for falling or rising heart rate in women
One of the frequently asked questions to a cardiologist is “what is the normal heart rate for women?” Of course, this indicator depends on many factors, including:
- age;
- presence or absence of physical activity;
- weight and height;
- general health;
- concomitant pathologies, especially disorders of the heart and blood vessels.
The normal pulse rate per minute for women of all ages varies between 60–90. Do not forget that this is a generally accepted framework, and depending on individual physiological characteristics, the resting pulse (normal) in women may be slightly different.
At rest
As mentioned earlier, the normal heart rate for women in young and middle age is about 60–90 beats per minute at rest. This is a fairly wide range in which the heart rate can fluctuate. At a young age, resting rates can reach 70–85 beats, while in older people they can be lower (65 beats). This decrease is explained by the following factors:
- changes in the functioning of the heart muscle and nervous system;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- changes in the hormonal system.
All of the above directly affects your heart rate.
When walking
As mentioned earlier, physical activity, even the most insignificant, has a great influence on the frequency of strokes. This raises the question: “What should be the normal heart rate of an adult (woman) while walking?”
While walking, the work of the muscles of the lower and upper extremities increases, which in turn requires energy expenditure. Increased blood circulation, acceleration of metabolism and enrichment of tissues with oxygen - all this leads to an increase in heart rate.
The normal pulse rate per minute in young and middle-aged women with intense and active walking can reach 100–120 beats per 60 seconds. Exceeding these established limits indicates that fast walking is difficult for the body. In this case you should:
- balance physical activity;
- pay more attention to your health;
- try to pay more attention to a proper and healthy lifestyle.
When doing yoga
There are several types of yoga: some are aimed at relaxation and harmonization, while others are characterized by increased physical activity, developing flexibility and endurance of the body.
Like any sport, yoga is characterized by an increase in the activity of the heart muscle, and at the same time the heart rate increases. The norm for women of any age under such loads can reach 110–120 beats per 60 seconds.
With regular and correct performance of certain asanas, you can achieve the following effect:
- normalize blood pressure in the arteries;
- restore metabolism;
- increase immunity;
- enrich tissues and cells with oxygen;
- reduce blood cholesterol levels;
- relieve tension and achieve peace.
A pulse of 60 beats per minute is normal in women, and this is the result that can be achieved with the help of therapeutic exercises and the right lifestyle.
Time of day is another criterion that affects how much the pulse per minute should be in women. During sleep, the activity of all organs decreases, the heart rate decreases, metabolism slows down, and at the same time the stroke rate drops.
So, what is considered normal heart rate for women of all ages at night? On average, this figure can reach 40–45 blows.
The opinion that the standard for assessing heart rate changes over the years is erroneous. The same values are considered normal. Doctors give one answer to the question “what is the normal pulse of a person at 50 years old.”
The norm is a heart rate of 60–90, which is shown in the table of norms for different ages. Schematically, three age categories can be distinguished, but if you estimate what the pulse of a person should be at 30 years old, the numbers are the same.
Up to 35 years old
It is assumed that people in this age group (see table by age) are healthy, do not have acquired diseases, and the consequences of bad habits and unhealthy lifestyles have not yet fully manifested themselves. At rest, the rate of cardiac activity varies from 72 to 75 beats. /min., which is displayed in the table of the normal heart rate of an adult depending on age.
With physical overload, a jump to 120 or even 200 beats per minute is possible. When assessing what a person’s heart rate should be at the age of 30, they take into account the presence of objective reasons for the jump. If there are none, immediate medical intervention is required. This is a sufficient reason to diagnose pathological changes in the body.
From the age table below, you can see what the normal heart rate is for a person at 40 years old. If the heart rate is in this range, it can be said that his cardiovascular system is working normally.
In an elderly person
The pulse rate established by doctors (in the age table for an adult) in old age should not exceed 90 pulses. This refers to people aged 60 to 80 years. The average value is considered to be 70 beats. The fatigue of the body and the consequences of the loads endured throughout life affect.
Indicators of normal blood pressure with age and by gender have minor differences. In young women, it is slightly lower due to less weight in youth. And after sixty years, the blood pressure of men and women becomes equal, due to the possible risks of vascular pathologies.
Table 2 - blood pressure norms for adult women and men by age
| Age | Normal blood pressure in men | Normal blood pressure in women |
| 20 | 123/76 | 116/72 |
| 30 | 126/79 | 120/75 |
| 40 | 129/81 | 127/80 |
| 50 | 135/83 | 135/84 |
| 60-65 | 135/85 | 135/85 |
| older | 135/89 | 135/89 |
A decrease in pulse blood pressure may be a consequence of a drop in heart rate caused by a heart attack, tamponade, paroxysmal tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, or surges in peripheral vascular resistance to the blood flow ejected by the heart.
High pulsation indicates atherosclerotic problems.
The indicator is determined by years of life; in childhood, a normal heartbeat is characterized by 60-170 beats per minute, since the organ is small and requires more activity to pump blood throughout the body.
Up to 30 years old
At this time, the indicators are very variable and range from 60-160 beats per minute, depending on age. The younger the patient, the more significant the heart rate. The normal pulse rate for women aged 30 is from 55-90 beats per minute. Perhaps a little more, but not significantly, especially at rest.
From 35 to 45
The indicator does not change significantly. Deviations of 10-15 units are possible due to hormonal imbalances and gestation periods.
After 60
The heart rate level in the elderly falls and grows unstably and chaotically, which is explained by the end of menopause and the onset of menopause.
| Age (years) | Normal indicator | Possible limit for trained people |
| 15-18 | 61-85 | 150 |
| 18-31 | 62-90 | 170 |
| 32-51 | 68-90 | 200 |
| 52-62 | 70-95 | 180 |
| Over 60 | 71-95 | 160 |
The normal heart rate for women aged 40 is 70-80 beats per minute. This is the turning point when the heart rate steadily rises and the maximum possible level drops.
This feature of the body (which is also inherent in men) allows one to assess the degree of functional activity of the heart using stress tests.
With a significant increase in the frequency of contractions, we are talking about a pathological process.
The normal pulse rate depends on the woman’s age, current physical activity, endocrine status, place of residence, time of day and some other factors. It is worth considering them in more detail.
When walking
Weak physical activity can change the pulse rate in the minimum range: from 10 to 15 beats per minute for the average person. A trained body will not notice such a slight strain of force, therefore it is possible to maintain the same numbers.
If your heart begins to ache from an ordinary walk, this does not bode well. We are most likely talking about pathologies of the muscular organ, blood vessels, pulmonary structures, and kidneys.
A comprehensive examination with stress tests is necessary. But they are carried out with caution and under the supervision of a group of doctors to quickly provide assistance in case of an emergency (there is a possibility of cardiac arrest in sick women).
The level of preparedness of the body and the intensity of the stimulus play a big role. The more the patient tenses, the more her pulse and blood pressure increase.
In a normal position, if the body is sufficiently trained, the heart rate increases gradually until it reaches the necessary optimum, which is required for adequate nutrition of tissues and organs, including the brain and muscles.
At a certain point, the growth of the indicator stops; a healthy person does not feel this.
For an untrained woman, the opposite is true. The pulse rate jumps, grows chaotically, without taking into account the need for nutrition of the body. A spontaneous drop in blood pressure and the development of cardiogenic shock are possible.
It is almost impossible to get out of this condition; the mortality rate is close to 100%. Therefore, classes should be intensified gradually, preferably under the supervision of a competent instructor. From small to large.
A sharp transition “to a new level” is fraught with the development of dangerous complications for health and life. There's definitely no need to take risks.
After meals
Eating, especially abundant food, is often associated with an excessive risk of developing arrhythmia such as tachycardia (acceleration of cardiac activity). This is not a normal phenomenon; a comprehensive assessment of the quality of health is necessary.
The patient is in optimal condition and does not suffer from heart rhythm problems even after intensive eating. Probable factors: failure, ischemic disease, pathologies of the renal structures and brain.
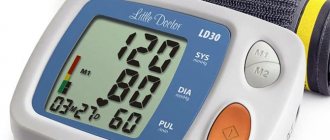
What is pulse and blood pressure
Blood pressure is the pressure with which blood fluid circulates through the large arteries of the human body.
The components of the quantity are:
- systematic (upper) - shows the pressure during the period of maximum compression of the heart;
- diastolic (lower) - indicates the pressure during complete relaxation of the heart muscle.
It is measured in millimeters of mercury. The ideal indicator for an adult is 120/80. Deviations from the norm to a greater extent indicate the danger of a hypertensive crisis, heart attack and stroke. Requires medication adjustment.
Pulse - jerky, periodic contractions of the heart muscle, at the moment of filling the vessels and veins with blood fluid.
Capillary, arterial and venous pulsation are divided:
- arterial - shows the constriction of the arteries at the time of filling with blood;
- venous - pulsation of the jugular veins located close to the heart muscle;
- capillary - establishes the coincidence of cardiac pulsation with a change in the shade of the nail bed, pressed lower lip, and skin tissue of the forehead. It is not typical in a healthy body, since it manifests itself only at the time of dysfunction of the precapillary sphincters, as a result of a large difference between the components of blood pressure. Normally, capillary blood flow is constant.
The pulse of a healthy person at rest is 61-92 beats/min. A significant deviation in any direction indicates dysfunction in the cardiovascular system and requires thorough research and medical adjustment.
This is the speed at which the heart pumps blood into the vessels, a marker of the cardiovascular system, indirectly related to blood pressure, but does not affect its indicators. Pulse and blood pressure have their own mechanism of formation and action.
Heart rhythm in women is correlated with age, physiological characteristics, and concomitant diseases, but normally such fluctuations do not exceed 10-15 units.