Metabolism or metabolism is a set of various interconnected chemical reactions that occur in the body and are the fundamental mechanism of its work. Metabolic disorders can be a consequence of dysfunction in the thyroid gland, pituitary gland, adrenal glands, gonads, fasting and poor nutrition. These disorders lead to many functional changes and are harmful to health.
Symptoms of metabolic disorders
Metabolic disorders are indicated by:
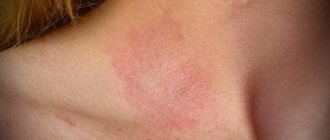
- change in complexion;
- deterioration of hair and nails;
- sudden change in weight;
- labored breathing;
- problems with thermoregulation;
- insomnia;
- tooth decay;
- skin rashes, swelling;
- pain in joints and muscles.
Shcheglova Raisa Alexandrovna
doctor therapist
Metabolic disorders mean a huge number of diseases and syndromes that can be caused by internal or external factors. Among internal causes, endocrine diseases predominate. Metabolism is always disrupted by a deficiency or excess of certain hormones. It is also caused by congenital deficiency of enzyme systems. Temporary metabolic disorders are possible against the background of micronutrient deficiency, dehydration, overhydration of the body, serious illness, overheating, hypothermia and other unfavorable factors.
Some people, noticing symptoms of metabolic disorders, begin to self-medicate. SM-Clinic doctors warn that this can cause irreparable harm to the body.
Protein metabolism
Proteins are one of the most complex structural elements of the human body. They are necessary for normal breathing, digestion, neutralization of toxic substances, normal functioning of the immune system and many other functions, for example:
- Participation in chemical reactions as catalysts. Currently, more than 3 thousand enzymes are known, which by their nature are protein compounds.
- Transport function. With the help of the hemoglobin protein, every cell in our body receives oxygen, lipoproteins help “package” and transport fat, etc.
- Protecting the body from infection. The immune system would not be able to effectively cope with the tasks assigned to it if there were no antibodies, which are also protein compounds.
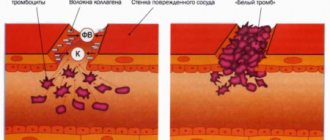
- Stop bleeding. Fibrin, a fibrinogen that is essential for blood clot formation and subsequent thrombus formation, is also a protein.
- Contraction of muscles, providing the ability to carry out movements. This is possible due to the presence of contractile proteins – actin and myosin – in each muscle cell.
- Frame and structure. Proteins are part of the framework of cell walls; hair, nails, and protein molecules are made up of proteins; they are included in the composition of tendons, ligaments, and provide the elasticity and strength of the skin.
- Ensuring the functioning of the body as a whole. Numerous hormones that regulate various processes and the functioning of individual organs are also proteins.
- Anti-edematous function. Albumin proteins protect the body from the appearance of so-called hunger edema.
- Energy supply. As you know, the breakdown of 1 g of protein provides energy of 4 kilocalories.
Symptoms of protein metabolism disorders
One of the manifestations of protein metabolism disorders in the body is a decrease in bone mineral density, or osteoporosis.
Excess protein in the body can manifest itself as the following symptoms:
- bowel disorders (constipation, diarrhea),
- loss of appetite, lack of it,
- hyperproteinemia (increased amount of proteins in the blood plasma),
- development of kidney diseases and renal failure (they have to excrete an increased amount of protein breakdown products),
- development of osteoporosis (to utilize excess protein, calcium is needed, which the body takes from bones),
- salt deposition (for example, the occurrence of gout due to impaired nucleic acid metabolism).
Most often, excess protein is associated with increased consumption, when the diet mainly consists of protein foods. Symptoms of protein deficiency are:
- swelling,
- general and muscle weakness,
- decreased immunity, manifested in the fact that a person more often suffers from various bacterial and viral infections,
- drowsiness,
- weight loss to the point of exhaustion and dystrophy,
- increased levels of ketone bodies (acetone in urine),
- in children: decreased intelligence, delayed growth and development, possible death.
Most often, protein deficiency occurs in the following diseases: kwashiorkor, nutritional dystrophy, as well as an unbalanced diet.
What tests need to be taken to check protein metabolism?
In order to get an idea of protein metabolism, the following types of tests are usually prescribed:
- Proteinogram (total protein, amount of albumin, globulin, their ratio).
- Kidneys: determination of the level of creatinine, uric acid, residual nitrogen.
- Liver: urea level, thymol test.
Diagnostics
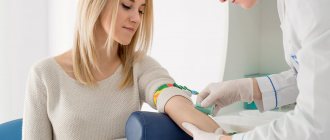
A person who suspects they have a metabolic disorder will first be referred to a GP. The specialist will conduct a general examination, collect the patient’s complaints, take an anamnesis and prescribe the necessary tests and procedures.
Among them may be:
- blood and urine test for sugar;
- biochemical blood test (to determine the protein ratio, creatinine level, etc.);
- blood sampling to determine cholesterol levels;
- glucose tolerance test.
After the test results are obtained, the patient will be referred to a specialized specialist (gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, nutritionist, etc.) for further treatment.
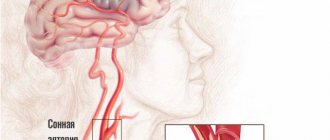
Disturbances of water-salt metabolism
Complex systems in the body work to maintain a constant internal environment. Balance is achieved through the balance of incoming and outgoing water and mineral salts.
Lack of fluid in the body can lead to:
- to a drop in blood pressure;
- decrease in circulating blood volume;
- decrease in the volume of intercellular fluid.
Excess water is also extremely dangerous for humans. In severe cases, such an imbalance can cause brain swelling and death of the patient.
Water metabolism is largely determined by the work of the hypothalamic-pituitary system. These central endocrine glands synthesize and release into the blood a special hormone - antidiuretin. If the hormone is low, diabetes insipidus is diagnosed. Patients with this pathology experience extreme thirst, frequent urination, dry skin, and low blood pressure.
Excessive and inadequate secretion of antidiuretin leads to an equally serious disease - Parhon's syndrome. In this condition, excess fluid accumulates in the body and plasma sodium levels drop. As a result, general weakness, vomiting, convulsions, and coma develop.
The level of electrolytes in the blood is influenced by different endocrine glands. The parathyroid glands and adrenal glands (glomerular layer) are largely responsible for mineral metabolism.
The parathyroid glands produce a special hormone (parathyroid hormone). An excess of this biologically active compound provokes hyperparathyroidism. It is characterized by an increase in calcium levels and a decrease in phosphorus levels in the blood.
This metabolic failure manifests itself:
- decreased bone mineral density;
- the appearance of stones in the kidneys, gall bladder;
- development of pancreatitis and gastric ulcer;
- psychopathy (up to the development of psychosis);
- myopathy.
Treatment of metabolic disorders
Treatment of metabolic disorders is quite lengthy and labor-intensive. If the cause is a genetic disorder, then constant therapy under the supervision of a doctor will be required. Acquired diseases can be cured completely if they are detected in the early stages.
Much attention is paid to diet during treatment. Depending on the type of disorder, the patient is prescribed a special diet, and a complex of vitamins and minerals is also indicated.
If necessary, the patient will be consulted by a nutritionist and psychotherapist.
It is very important to follow not only a diet, but also a sleep regimen, since healthy sleep has a beneficial effect on the psyche and normalizes processes in the body.
In certain cases, a properly selected physical activity program is indicated.
Metabolic disorders usually indicate more serious problems in the body. Therefore, if you notice symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. You can make an appointment for a consultation at SM-Clinic by calling the phone number listed on the website.
How to speed up your body's metabolism at home
Slow metabolism often begins due to low physical activity, excess weight or genetic predisposition. Metabolic inhibition becomes more pronounced with age. It occurs twice as often in women as in men. You can reverse this process by changing your daily routine: you need to include feasible workouts, do wellness treatments (massage, bath), and follow a rest schedule. At the same time, you need to change your diet. In some cases, on the recommendation of specialists, you may need to take medications.
Tablets
Taking medications to start the weight loss process should be done under the supervision of a nutritionist. A specialist can prescribe tablets to speed up metabolism with different effects:
- "Reduxin" - increases the feeling of satiety;
- "Oxandrolone", "Methylandrostenediol" - anabolic steroids, reduce fat deposits and stimulate muscle growth, which consume more energy, thereby speeding up metabolism;
- “Glucophage” – enhances lipid metabolism;
- “Xenical”, “Orsoten” - block the absorption of fats;
- "Metaboline", "Formavit" - regulate carbohydrate-fat metabolism.
Using products that improve metabolism
The first points that answer the question of how to restore a disturbed metabolism are the consumption of a sufficient amount of water (to maintain water-salt balance) and a competent diet. To properly start this process in the morning, you need to have breakfast. What speeds up metabolism? Your diet should include foods rich in protein (legumes, eggs, fish, lean meat) and healthy omega-3 fats. During the day, you need to eat 5 servings (the size of a handful) of fresh vegetables and fruits, which will provide the body with the fiber, vitamins and minerals necessary for proper digestion.
Special products that speed up this process will help normalize metabolism. These include cocoa beans (not chocolate!), seasonings and spices: curry, red pepper, cinnamon, ginger. To correct metabolic processes, experts advise drinking several mugs of green tea throughout the day. If you wish, you can drink a couple of cups of high-quality brewed coffee without sugar. Semi-fermented oolong tea is good for speeding up metabolism.
- Accelerating metabolism for weight loss - food and drugs to improve metabolism
- How to lose 10 kg very quickly
- Restoring your period after losing weight
Treatment of metabolic disorders with folk remedies
Herbs will help regulate abnormal metabolic processes. How to restore metabolism using traditional medicine? For example, you can drink decoctions from the following plants, the preparations of which are always on sale at the pharmacy:
- stinging nettle, woodlice, burdock - these drugs will help control appetite;
- ginseng – has a tonic effect and speeds up metabolism.
If you have no contraindications, try using the following recipes to speed up your metabolism:
- 2 tsp. walnut leaves, dried and crushed, pour a glass of boiling water, then let it brew for 2 hours. Use 0.5 tbsp. after meal.
- Grind 200 g of garlic, pour 250 ml of vodka into a glass container. Leave the mixture for 10 days in a dark cabinet, then strain off the liquid. Take according to the following scheme: dissolve 2 drops of the drug in 50 ml of milk. Every day increase the dose by 2-3 drops, bringing the concentration to 25 drops at a time. Drink the infusion before meals three times a day.
Using a metabolism recovery diet
It is necessary to understand that in order to normalize metabolism, you need not just to get rid of excess weight, but to harmonize the functioning of the digestive and endocrine systems. In this case, nutritionists recommend to their patients the diet according to Pevzner, table No. 8. A diet for metabolic disorders in the body does not imply a reduction in portion size, but a restructuring of the diet mainly to protein and plant foods. The first requirements for changing your diet in order to restore metabolism is to exclude from the diet:
- fat;
- roast;
- spicy;
- smoked;
- alcohol.
How to restore impaired metabolism by adjusting your diet? In order to establish the metabolic process, you need to eat in small portions throughout the day. When preparing food, it is recommended to season it with spices - they force the body to actively burn calories, increasing the metabolic rate by about 10%. It is useful to eat whole grain bread, more greens and citrus fruits. A variety of dairy products can help build muscle mass.
- Tests before losing weight: how to take them correctly
- How to lose weight after 45 years for women and men - diets with menus for every day and recipes
- How to lose weight during menopause
Vitamins
Minerals and vitamin preparations to improve metabolism can also do a good job. For example, iodine activates the thyroid gland, thereby speeding up metabolism. When taking chromium, the processes of processing nutrients are accelerated, and this mineral also maintains normal blood sugar levels. Calcium combined with vitamin D will help improve the proportion of fat tissue and muscle in the body. The B group of vitamins helps speed up metabolic processes at the cellular level. You should start taking vitamin complexes after consulting a doctor.
With the help of biostimulants that improve tissue metabolism
As prescribed by a specialist, in cases where the metabolism is seriously disturbed, treatment with biostimulants can be carried out. Taking these drugs, which are also called adaptogens, activates the body's defenses and improves metabolic processes in tissues. The specialist will recommend what drugs can be prepared and determine the duration of treatment. Biostimulants - metabolism accelerators include the following herbs:
- ginseng;
- Eleutherococcus senticosus;
- the lure is high;
- Aralia Manchurian;
- Schisandra chinensis;
- Rhodiola rosea;
- Leuzea safflower.
Our clinics in St. Petersburg
metro station "Dunayskaya" Dunaysky Prospekt, building 47
metro station "Ladozhskaya" Udarnikov Avenue, building 19
m. "Leninsky Prospekt" st. Marshala Zakharova, house 20
m. "Prospekt Prosveshcheniya" Vyborg highway, building 17
Slowing down the flow of amino acids into organs and tissues.
Amino acids absorbed from the intestine enter directly into the blood and partially into the lymphatic system, representing a supply of various nitrogenous substances, which then participate in all types of metabolism. Normally, amino acids absorbed into the blood from the intestines circulate in the blood for 5–10 minutes and are very quickly absorbed by the liver and partly by other organs (kidneys, heart, muscles). An increase in the time of this circulation indicates a violation of the ability of tissues and organs (primarily the liver) to absorb amino acids.
Since a number of amino acids are the starting material for the formation of biogenic amines, their retention in the blood creates conditions for the accumulation of corresponding proteinogenic amines in the tissues and blood and the manifestation of their pathogenic effect on various organs and systems. An increased level of tyrosine in the blood promotes the accumulation of tyramine, which is involved in the pathogenesis of malignant hypertension. A prolonged increase in histidine content leads to an increase in the concentration of histamine, which contributes to impaired blood circulation and capillary permeability. In addition, an increase in the content of amino acids in the blood is manifested by an increase in their excretion in the urine and the formation of a special form of metabolic disorders - aminoaciduria. The latter can be general, associated with an increase in the concentration of several amino acids in the blood, or selective - with an increase in the content of any one amino acid in the blood.
About the experiment
In order to find out what type of metabolism a person has, it is not necessary to visit the Institute of Endocrinology. In this case, you can use a proven method. To do this, you need to get up in the morning (preferably on Sunday) and do all the hygiene procedures. Having gone to the kitchen, you need to heat up and quickly eat 300 g of porridge. Next you need to wait a couple of minutes.
- With accelerated metabolism, perspiration will appear.
- If it gets warm, your metabolism is normal.
- If a person does not feel or feel anything at all, he has an economical type of metabolism.
Vitamin exchange
Vitamins are essential substances that are not incorporated into the tissues of the body, but ensure the occurrence of energy and metabolic processes in it.
Their absolute deficiency (vitaminosis) is rare and is manifested by diseases such as scurvy, rickets, beriberi and others. Their manifestations are nonspecific:
- dizziness;
- irritability;
- decreased memory and concentration;
- headache;
- fatigue and others.
To treat hypovitaminosis, only adequate nutrition is often sufficient.
The main causes of hypovitaminosis
- reducing intake of vitamins from food;
- lack of culture of taking synthetic vitamins;
- disruption of the intestinal microflora due to treatment with antibiotics and poor nutrition;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including liver failure;
- increased need for vitamins during pregnancy, breastfeeding, hyperthyroidism, stress.
Manifestations of vitamin A deficiency:
- dry skin, mucous membranes of the eyes, mouth, respiratory tract;
- frequent respiratory and skin infections;
- “night blindness” and others.
Treatment consists of eating foods rich in this vitamin: liver, dairy products, cod and halibut liver. Provitamin A is found in carrots, red peppers, tomatoes, rose hips, and sea buckthorn. Usually, adding these foods to your food is enough to compensate for vitamin A deficiency.
The main causes of hypovitaminosis D:
- rare exposure to the sun;
- pancreatitis and cholelithiasis;
- chronic renal failure.
A manifestation of vitamin D deficiency is osteomalacia - softening of the bones. Vitamin D is found in butter, egg yolk, liver and fish oil, as well as in vegetable oils.
Vitamin E deficiency leads primarily to reproductive dysfunction, as well as to degeneration of internal organs. It occurs rarely, mainly when refusing to eat vegetable oils. Vitamin E is also found in lettuce, cabbage and grains, meat, butter and eggs.
Vitamin K deficiency is rare because it is synthesized by intestinal microflora. It can be caused by intestinal surgery, overtreatment with antibiotics, and other intestinal diseases.
It manifests itself in bleeding and hemorrhages, the rapid formation of hematomas and bruises. Cabbage, lettuce, spinach, rowan, pumpkin, and pork liver are rich in this vitamin.
Symptoms of vitamin C deficiency:
- fragility of blood vessels;
- weakness and apathy;
- susceptibility to infections;
- gum diseases.
Ascorbic acid is found in plant products: pepper, cabbage, rowan, black currant, potatoes, citrus fruits. In women, the need for vitamin C increases during pregnancy and lactation.
The main sign of vitamin B1 deficiency is damage to the nervous system: neuritis, paralysis, and heart failure. Mental disorders also appear. It occurs in hyperthyroidism, overdose of diuretics, and diseases of the digestive system. The vitamin is found in wholemeal bread, soybeans, beans, peas, potatoes, and animal liver.
Vitamin B2 deficiency is manifested primarily by inflammation of the red border of the lips with the formation of cracks in the corners of the mouth. The skin is affected in the form of dermatitis. These phenomena occur mainly with insufficient intake of the vitamin from food, as well as with severe diseases of the digestive system. The vitamin is found in wholemeal bread, meat, eggs, and milk.
With a lack of nicotinic acid, weakness, apathy, fatigue, dizziness, insomnia, and frequent infections appear. Then damage to the skin and oral cavity occurs. This condition occurs when there is a decrease in vitamin intake from food, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, carcinoid syndrome, and alcoholism. There are also congenital metabolic disorders of this substance. The main source of vitamin PP: rice, meat, bread, potatoes, liver, carrots.
Vitamin B6 deficiency appears during stress, fever, and hyperthyroidism. It is accompanied by inflammation of the lips, tongue, peeling of the skin, and anemia. Vitamin B6 is found in bread, legumes, meat and potatoes, liver, and cereal seeds. The need for this vitamin increases during pregnancy.
A deficiency of vitamin B12 develops with strict vegetarianism, as well as with certain stomach diseases, and leads to the development of severe anemia, damage to the digestive organs and nervous system. It is found in meat, liver, fish, milk, and eggs.
Folic acid deficiency can occur when taking sulfonamides, barbiturates, and alcohol. In addition to the fact that this causes symptoms similar to vitamin B12 deficiency, the division of young cells, primarily blood and epithelium, is simultaneously disrupted. Folic acid deficiency is very dangerous during pregnancy; it can lead to delayed fetal development and other pathological conditions. Folic acid is found in green plants, tomatoes, meat, kidneys, and liver.
So, a lack of vitamins in the body can manifest itself as damage to almost any organ. Diagnosis of hypovitaminosis is difficult. This condition can be prevented with the help of good nutrition (meat, bread, vegetables, dairy products are especially useful) and treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Laboratory diagnosis of metabolic syndrome
Today, the term “metabolic syndrome” refers to a complex metabolic disorder. Actually, “metabolic syndrome” is a condition of the body in which there are already a number of specific abnormalities in biochemical and hormonal blood tests, which, in the absence of lifestyle changes and treatment, can lead to the development of diseases such as type 2 diabetes, diseases of the cardiovascular system, including atherosclerosis. This makes it necessary not only to identify, but also to promptly correct such conditions. Early diagnosis in combination with the recommendations of an endocrinologist will eliminate or reduce the severity of the main manifestations of this syndrome.
Metabolic syndrome is characterized by a decrease in the susceptibility of body cells and tissues to the hormone insulin ( insulin resistance ). In this case, there is often a compensatory increase in this indicator in the blood to maintain blood sugar levels within target values. However, the body's reserve capabilities are individual and not unlimited, and ultimately this can lead to additional disturbances in the body's functioning. As a result, various disorders arise - metabolic, hormonal, cardiovascular, etc.
The pathological process develops slowly, often without pronounced symptoms. Frequent “companions” of excess body weight - high blood pressure, fatigue and shortness of breath - may indicate problems in the body. Visually, this endocrine disorder can be “hinted” by a steadily expanding waistline: in patients with metabolic syndrome, excess fat accumulates mostly in the abdominal organs (which entails further disorders of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism).
You can suspect such deviations in yourself by measuring your waist and hips. With metabolic syndrome, women have a waist circumference of more than 80 cm, and men have a waist circumference of more than 94 cm. This indicates the deposition of fatty tissue around the internal organs, which impairs their functioning.
Most often, metabolic syndrome is diagnosed in men over thirty, but in recent decades the number of recorded cases of pubertal insulin resistance has been growing - that is, similar health problems arise in adolescents. Most likely, this is due to poor nutrition.
For representatives of the fairer sex, the risk of developing this syndrome increases significantly after 50 years.
In Russia, the prevalence of this syndrome reaches 20-35%, and in women it occurs 2.5 times more often, and the number of patients increases with age.
Only an endocrinologist can timely identify pathology and differentiate it from other ailments with similar symptoms (for example, from hypothyroidism Laboratory diagnosis of this syndrome includes assessment of the state of carbohydrate metabolism, lipid spectrum indicators, sometimes this is supplemented by a number of hormonal studies.
Important: blood samples are taken on an empty stomach. Before the test, the patient must measure his blood pressure and waist circumference. These indicators will be required by the laboratory during the test.
List of prescribed tests
Excess weight (from 18 years):
- Glycated Hemoglobin;
- Glucose;
- C-reactive protein (C-Reactive Protein) - highly sensitive method - CRP;
- Triglycerides;
- High-density lipoprotein cholesterol;
- Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol;
- Cholesterol total;
- Hormonal studies;
- C-peptide (C-peptide);
- Insulin;
- Cortisol;
- Leptin;
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone;
- Insulin resistance.
Metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents - primary diagnosis (10-17 years):
- Glucose;
- Triglycerides;
- High-density lipoprotein cholesterol;
- Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol;
- Cholesterol total.
Metabolic syndrome - primary diagnosis (from 18 years of age):
- Glucose;
- Triglycerides;
- High-density lipoprotein cholesterol;
- Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol;
- Cholesterol total.
Causes
More than 30 different substances are involved in metabolism, with the synthesis, breakdown and absorption of which a variety of problems can arise. They lead to disturbances in metabolic processes. Scientists are still studying the factors that provoke such failures, but they are not yet ready to answer why this happens. They give only approximate reasons:
- age;
- genetic mutations;
- slagging, intoxication of the body;
- alcohol and smoking abuse;
- disturbances in the functioning of the adrenal glands and pituitary gland;
- heredity;
- poor nutrition;
- birth injuries and intrauterine hypoxia;
- refusal of healthy lifestyle;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- passive lifestyle;
- stress, depression, prolonged nervous tension, severe emotional stress;
- postpartum disorders, when a woman’s hormonal levels cannot recover after pregnancy and childbirth.
This is probably not a complete list of reasons, but scientific research is still underway in this direction. Perhaps very soon we will find out exactly why a failure occurs in this or that case. After all, if the provoking factor is not eliminated, the disease will remain untreated.
The main causes of disturbances in processes associated with carbohydrate metabolism can be:
- Impaired phosphorylation of glucose in the intestinal wall (usually this occurs if the intestinal wall is inflamed, in case of poisoning with phloridzin and monoiodoacetag).
- Violation of neurohormonal regulation.
- Impaired carbohydrate function of the liver.
- Violation of neurohormonal regulation of carbohydrate metabolism.
- hereditary (inability to produce certain enzymes);
- disruptions in carbohydrate liver function;
- pathologies of neurohormonal regulation;
- tumors;
- circulatory disorder;
- toxic lesions;
- exhausting physical activity, unhealthy diet, stress.
Treatment of carbohydrate metabolism disorders is carried out under mandatory medical supervision and is accompanied by constant monitoring of blood glucose levels. The therapy program includes:
- sugar-lowering agents (aspart, lispro, short-acting insulin, nateglinide);
- acarbose (α-glucosidase inhibitor) and biguanides;
- treatment of the underlying disease if the disorders developed as a complication (including hormonal therapy and surgical procedures);
- reduced calorie diet;
- moderate controlled physical activity, massage;
- psychotherapy;
- herbal remedies (burnet, viburnum, oregano, nettle, dried grass, celery, string, buckthorn).
Energy and basal metabolism
The energy contained in food is released outside when digested. Half of it is converted into heat, and the other half is stored in the form of adenosine triphosphoric acid (ATP). The following reasons can disrupt the processes of ATP formation:
- hyperthyroidism (excess thyroid hormones);
- infectious diseases;
- exposure to cold;
- Excessive intake of vitamin C.
Under the influence of these factors, the body stores less energy than it needs.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W4CeBd8s-so
Basal metabolism is the amount of energy that is sufficient to maintain the body's life at rest. For men it is 1600 kcal per day, for women it is 10% less. The following conditions increase basal metabolism:
- stress, anxiety;
- neuroses;
- fever;
- diabetes;
- increased production of thyroid-stimulating, somatotropic hormones, thyroid and sex hormones, catecholamines (adrenaline and norepinephrine);
- allergy;
- physical activity and others.
As a result of disruption of energy metabolism and increased basal metabolism, the body spends more energy than it receives and begins to use its reserves: first muscle tissue, then carbohydrate reserves in the liver and muscles, and then its own proteins. The result is a decrease in body weight, disruption of the functioning of all internal organs, and disorders of the nervous system.
The following conditions reduce basal metabolism, that is, reduce energy consumption:
- starvation;
- anemia;
- decreased hormone production;
- damage to the nervous system, for example, senile dementia;
- dream.
When the basal metabolism decreases, the body receives little energy, since the processes of food absorption are suppressed or there is not enough energy at all. As a result, he is also forced to use his resources and become depleted. The treatment of such types of disorders is completely determined by the cause that caused them.
Consequences
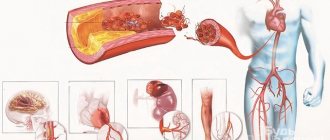
In the absence of comprehensive and timely treatment, metabolic disorders can provoke the development of the following diseases:
- nutritional dystrophy;
- amyloidosis;
- anemia;
- atherosclerosis;
- Gierke's disease;
- hepatosis;
- hyperglycemia;
- hypoglycemia;
- kwashiokor;
- nervous exhaustion;
- obesity;
- gout;
- sexual dysfunction;
- rickets;
- diabetes;
- tetany.
Some of them cannot be treated, so it is recommended to restore metabolism as quickly as possible to avoid such irreversible consequences.