Each type of disease of the human musculoskeletal system has its own symptoms, manifestations, consequences, limitations and treatment methods. Types of arthritis are distinguished by the root cause of their manifestation. Pathologies can also be inflammatory and degenerative with deformation of cartilage tissue, infectious and non-infectious, affecting one (monoarthritis) or several (polyarthritis) joints.
Causes of arthritis and risk factors
The reasons for the development of inflammatory processes in the joints can be very diverse. Acute inflammation can be caused by injury, infection, an allergic reaction, or toxic substances entering the joint cavity from snake, spider, and poisonous insect bites. The chronic form often develops against the background of various disorders in the functioning of internal organs and systems:
- endocrine disorders;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- autoimmune, allergic and atopic conditions;
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the musculoskeletal system and birth injuries - for example, dysplasia of the head of the hip joint;
- the presence of persistent infectious foci in the body.
The occurrence of reactive arthritis is most often associated with enterobacteria, chlamydia and mycoplasma. In the case of rheumatoid arthritis, genetic predisposition is of paramount importance.
Among the statistically significant risk factors for the development of arthritis, WHO names age over 65 years, overweight, arterial hypertension, kidney disease and being female: due to sudden changes in hormonal levels during menopause, women get sick more often than men. In Russia, inflammation of the joints is observed in approximately 60% of people of retirement age against the backdrop of a trend toward increasing incidence and decreasing age of first manifestation of the disease. Diagnosis of neuroarthritic diathesis in childhood increases the likelihood of developing arthritis in adulthood.
Predisposing factors for arthritis are old age and the presence of chronic diseases
Often the cause of arthritis is constant microtrauma of joint structures during professional sports and heavy physical labor, when there is intense stress on the same muscle groups. On the other hand, a sedentary lifestyle also contributes to the development of inflammatory processes in the joints, especially when physical inactivity is combined with alcohol abuse, an unbalanced diet and a lack of vitamins in the diet.
Reasons for the development of pathology
Although the disease has been known to scientists for many years, the exact causes of arthritis are unknown. Observation of thousands of patients made it possible to find out which category of the population is most susceptible to the development of pathology.
Possible causes and factors contributing to the problem include the following:
- allergic reactions;
- neurogenic disorders;
- metabolic disorders;
- penetration of infection;
- immune failures;
- constant physical activity;
- type of professional activity associated with constant load on certain groups of joints;
- injuries received;
- presence of extra pounds;
- influence of hereditary factors;
- poor nutrition;
- frequent hypothermia.
The presence of bad habits weakens the entire body. Therefore, people who suffer from alcoholism or smoke are more likely to experience symptoms of the disease than others who strive to lead a healthy lifestyle and exercise moderately.
Important! Lack of qualified treatment can lead to the development of disability and loss of motor activity.
It is known that arthritis often develops in athletes. The etiology of arthritis in this case is associated with constant increased stress. Mostly, those who engage in weightlifting face this problem. They are the ones who are most susceptible to stress on the phalanges of the fingers and hands and more often struggle with the resulting sprains and fatigue.
Forms
Due to the variety of manifestations of arthritis, in clinical practice it is customary to distinguish different forms of the disease, which differ in the specific clinical picture and therapeutic measures. Depending on the nature of the course, acute and chronic arthritis are distinguished, and three forms of the disease are differentiated based on the number of affected joints:
- monoarthritis - inflammation of one joint;
- oligoarthritis – inflammation affects two to four joints;
- polyarthritis is inflammation of five or more joints.
Based on the prevailing etiological factor, a distinction is made between primary arthritis with an independent pathogenesis and secondary arthritis as a consequence of the underlying disease. Primary forms include infectious, traumatic and rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, Still's disease, as well as inflammation of the joints due to osteoarthritis and spondylitis.
Polyarthritis affects five or more joints
Secondary arthritis occurs against the background of a number of diseases, the most famous of which are dysentery, tuberculosis, gout, diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus, gonorrhea, borreliosis, psoriasis, purpura, hepatitis, granulomatosis, hemochromatosis, Reiter's syndrome and others. Inflammation of the joints that develops after suffering nasopharyngeal, intestinal and genitourinary infections is called reactive arthritis.
In the early stages, acute infectious arthritis responds well to treatment until complete restoration of joint function.
What kind of disease?
Arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joint, which leads to disruption of its natural mobility and deformation. Accompanied by metabolic failure in the joint capsules, thinning of intra-articular cartilage tissue, swelling and inflammation. Destruction can also be caused simultaneously by two diseases - arthrosis-arthritis. There are acute and chronic phases of deviation.
| Phases | Symptoms | Treatment |
| Spicy | One-time inflammation in the joint | Easy to treat, no further medical attention required |
| Strong pain | ||
| Increased body temperature | ||
| Chronic | Gradual development of the disease | Treatment is long-term, relapses are possible |
| Pain when moving, intermittent, acute or constant | ||
| Dislocation, subluxation | ||
| Swelling of periarticular tissues |
In the absence of therapeutic measures and in the event of disease progression, the joint becomes deformed, which leads to loss of ability to work and disability.
Stages
In the dynamics of the pathological process in arthritis, four stages are distinguished:
- The disease does not manifest itself clinically, but X-rays of the joints show the first signs of inflammation. Sometimes there is a slight stiffness of movement and periodic pain during physical activity.
- The progressive inflammatory process leads to thinning of the tissues of the articular structures and erosion of the heads of the bones. Swelling appears in the area of the affected joints; A local increase in temperature and redness of the skin are often observed, movements are accompanied by crunching.
- The gradual destruction of articular structures leads to significant deformation of the joints, limited mobility, constant pain and partial loss of joint function, which is partly compensated by muscle tension.
- Pathological changes in articular tissues become irreversible; the diseased joint is completely immobilized. When the knee joints are damaged, contractures form, and ankylosis develops in the hip joints - fusion of the heads of the articular bones due to the filling of the articular capsule with replacement bone or fibrous tissue.
Stages of rheumatoid arthritis
Classification
The following clinical forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Juvenile chronic arthritis in children - does not occur in adults, is characterized by the involvement of small joints of the extremities in the inflammatory process. Inflammation of the cervical spine and temporomandibular joint is less common. It should be noted that this form of pathology is characterized by a pronounced clinical picture with an intense course, subsequent development of deformities, contractures and shortening of the limbs;
- Chronic gouty arthritis . With this form of the disease, a person will be bothered by frequent, severe pain, sometimes lasting up to several weeks. After about 3–4 years, deformities of the affected joints, limited movement, and the formation of tophi develop. This form of the disease can affect internal organs, with corresponding diseases;
- Chronic psoriatic arthritis . Most often it is a complication of psoriasis, diagnosed in about a third of patients with this systemic disease. It is characterized by thickening of the fingers, limited mobility of the hands, and flexion contracture may be present.
- Rheumatoid arthritis . Small joints are affected, which ultimately leads to complete immobility of the lower or upper limbs.
It should also be noted that each form of the disease is characterized by its own clinical picture.
Healthy and arthritic joint
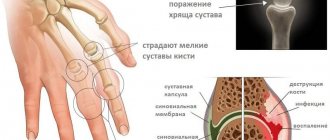
Arthritis symptoms
The symptoms of arthritis depend on the stage and form of the disease. General signs of joint inflammation are nonspecific: in the early stages of the pathological process, moderate pain and stiffness in the joints are often attributed to fatigue, hypothermia and age-related changes. When some joints become inflamed, warning signs may appear:
- swelling of the feet and increased fatigue when walking with damage to the ankle joints;
- “glove symptom” for inflammation of the hand joints;
- lameness and pain radiating to the knee, with arthritis of the hip joint;
- difficulty lifting and abducting a limb when the shoulder is affected.
In the early stages, arthritis manifests itself as moderate pain and stiffness in the joints.
Most patients consult a doctor at stage II of the disease. Constant discomfort in the joint area, the appearance of sensitive swelling caused by excess production of synovial fluid, a characteristic crunch, erythema and swelling of problem areas are clear signs of inflammation. Forced positioning of the body and limbs may indicate severe muscle spasms due to loss of joint mobility.
Specific symptoms are inherent only in some forms of the disease. Reactive arthritis is characterized by asymmetrical inflammation of the joints of the extremities accompanied by fever, headache and conjunctivitis. In some cases, signs of a urinary tract infection are added. Valgus deformities of the thumbs and toes give reason to suspect gouty arthritis, and in the case of psoriatic arthritis, the joints of the hand are severely deformed and thickened.
In rheumatoid arthritis, the joints are affected symmetrically, and dense nodules form in the flexure areas. During the period of remission, discomfort is felt mainly in the morning and practically disappears by the afternoon. Exacerbations are accompanied by fever, numbness of the extremities, pain when inhaling, inflammation of the lymph nodes and salivary glands, photophobia and pain in the eyes.
Rheumatoid foot
Symptoms
In this case, it is difficult to identify a general symptom complex, since the nature of the manifestation of the pathology will depend on its form.
The juvenile form of the pathological process is characterized by the following clinical signs:
- Insufficient development of the lower jaw, which causes the so-called “bird jaw” syndrome;
- shortening of limbs;
- motor dysfunction;
- damage to the upper extremities leads to the child having problems holding small objects in his hands;
- atrophy of the periarticular muscles;
- there may be a delay in physical development.
It is noted that this form of the disease is three times more common in girls, but the exact reasons for this predisposition have not yet been established.
The rheumatoid form manifests itself in the following clinical picture:
- three or more small joints are involved in the pathological process;
- the patient feels stiffness of movement in the morning, which disappears during the day;
- weight loss for no apparent reason;
- increased sweating, especially at night;
- periodic attacks of fever;
- S-shaped joint deformity.
If treatment for rheumatoid arthritis is not started in a timely manner, the disease can lead to complete immobility of the joints and, as a consequence, disability.
In the chronic form of gouty arthritis, the following clinical picture occurs:
- the patient may experience severe, frequent pain, the duration of which can last up to several weeks;
- the inflammatory process affects the knee, wrist, ankle joint;
- the formation of tophi - yellow-white plaques that consist of tissue accumulations of urates. The localization of such formations is joints, ears, sclera and corneas.
It should be noted that this form of pathology is fraught with the development of serious complications, which will be expressed in damage to internal organs, most often related to the genitourinary system.
In the psoriatic form of this disease, there is no pronounced pain syndrome, and the disease itself is characterized by external deformations - limited mobility of the upper or lower extremities, thickening of the fingers.
Features of arthritis in children
There are two forms of arthritis that are diagnosed exclusively in childhood - juvenile idiopathic arthritis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, or Still's disease. Both diseases are characterized by a persistent course and poor response to therapy; with Still's disease, in addition to the joints, internal organs are often affected.
Diagnosis of neuroarthritic diathesis in childhood increases the likelihood of developing arthritis in adulthood.
Children also tend to have a more acute course of infectious arthritis compared to adult patients. Soreness and severe deformation of the joints are accompanied by high fever and severe intoxication of the body - severe headache and muscle pain, confusion, nausea and vomiting.
Folk remedies for arthritis
Witch doctors and healers have a large number of folk recipes to combat arthritis. But before using them, you should consult a doctor, since they can provoke an allergic reaction or aggravate the condition of the joints. The doctor will help you choose the most effective and safe remedy.
Baths
For arthritis, medicinal baths help eliminate irritability, stress, and stimulate peripheral blood circulation. Water procedures have a gentle effect, so they are recommended even for elderly people.
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| With pine needles | Wrap 500 g of pine needles in cotton cloth. Fill them with water (7 l), put on fire, bring to a boil and heat for 30 minutes. The prepared solution is added to a warm bath. | It is recommended to take water procedures for 20 minutes every day for a month. |
| With pine or birch ash | Fill the pan 2/3 full with the selected ash. Add water until the container is full. Place on fire and heat until boiling. Leave the prepared solution in a warm place for 12 hours. For one session you will need 2 liters of it. | Water sessions should be carried out every day for 15-20 minutes. |
| Sea salt | Prepare a solution of 200 ml of water and 8 g of salt. | Add the finished product to a warm bath. One session takes 10-20 minutes. |
Water has a positive effect on a sore joint, relaxes and allows you to rest, especially after a hard day.
Compresses
After compresses, swelling decreases, material metabolism improves, and tissues are enriched with vitamins and microelements.
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| With dimexide | Before use, the pharmaceutical product must be diluted with water in a ratio of 1:4. | Gauze soaked in a solution is applied to the affected joint. Cover the top with a bag and wrap it in warm material. The compress is left for 1 hour. Dimexide relieves pain well. |
| Blue clay | Dilute the main component with water to obtain a thick consistency. | Lubricate the sore joint, wrap it in polyethylene and a warm cloth. Leave for 3-4 hours. |
| Potato | Wash, peel and chop medium-sized potatoes. | The paste should be applied to the joint, wrapped and left overnight. Sessions are carried out every evening until pain and inflammation decrease. |
After any compress, it is recommended to lubricate the treated area with a moisturizer.
Decoctions and tinctures for drinking
Traditional recipes not only reduce pain, they soften the clinical picture of arthritis.
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Lingonberry leaves | Pour dry leaves of the plant (2 tbsp) with hot water (1 tbsp). Leave for 15 minutes and strain. | The finished medicine is consumed throughout the day instead of tea. The minimum course of therapy is a month. |
| horse chestnut | Pour the flowers of the plant (20 g) with vodka (0.5 l). Leave for 14 days, then strain and use for medicinal purposes. | Horse chestnut tincture is taken 1-2 tbsp. up to 4 p.m. per day. |
| Pine nut shells | Fill a glass container (0.5 l) 2/3 full with nut shells, pre-heated in a frying pan. Next, pure medical alcohol is poured into the jar, closed and left for 3 weeks in a dark place. | Before use, the medicine is diluted with a small amount of water. On the first day of therapy, it is recommended to take 2 drops. tinctures. Then increase their number by one unit until you get 22 drops. in a day. Then continue treatment in the opposite direction, reducing the amount of medication taken by 1 drop every day. Patients with arthritis are recommended to take 3 courses per year. |
Treatment of arthritis with folk remedies should definitely be discussed with your doctor to avoid complications.
Products for external use
Homemade ointments and rubs will help with arthritis if you use effective, proven remedies and, most importantly, regularly.
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Birch bud ointment | Mix birch buds (400 g) with vegetable oil (800 g). Place the mixture in a clay container and place in the oven for 24 hours. Grind the finished product through a sieve, add a whisper of powdered camphor and leave in a cool place. | The ointment helps reduce pain due to arthritis. It is recommended to rub the affected areas every day before going to bed. |
| Herbal ointment | Mix St. John's wort, hop cones and sweet clover flowers (2 tbsp each) in equal parts. All components must first be dried and crushed. Add 5 drops to them. eucalyptus oil, petroleum jelly (50 g). Mix everything well. | The resulting ointment is applied to the affected joint every day until the pain disappears. |
| Ginger | Pour 20 g of dry powder into a jar. Add 250 ml of vodka. Mix everything well. The tincture should be stored in a dark place for at least 14 days, shaken periodically. | The resulting product is rubbed on the sore joint every day for a month. |
External use relieves pain, relieves swelling and reduces inflammation.
Diagnosis of arthritis
Although signs of joint inflammation are clearly visible even to a non-specialist, it is not possible to accurately determine the form and stage of arthritis, as well as develop the correct treatment strategy, based solely on history and physical examination.
When making a preliminary diagnosis, the doctor pays attention to the size, shape and sensitivity and mobility of the joints, the color and temperature of the skin, muscle tone; conducts functional tests. The next stage of the diagnostic search should be instrumental techniques that visualize the characteristic signs of arthritis:
- thickening and compaction of adjacent soft tissues;
- calcifications;
- tendinitis and tenosynovitis;
- periarticular osteoporosis;
- cyst-like clearing of bone tissue;
- roughness of articular surfaces;
- bone erosions;
- narrowing of the joint space;
- osteophytes, etc.
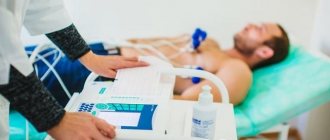
MRI guarantees maximum accuracy in diagnosing articular pathologies due to high-quality visualization of hard and soft tissues. X-ray and CT scans of the joint in direct, lateral and oblique projections make it possible to identify changes in the bone apparatus. To assess the condition of cartilage, tendons, ligaments, muscles and nerves, an ultrasound of large joints is additionally prescribed. If the knee joint is damaged, arthroscopy with collection of synovial fluid and biopsy may be required. In order to monitor the dynamics of the process in the absence of exacerbations, contrast arthrography may be appropriate.
X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans are used to diagnose arthritis.
Laboratory diagnosis of arthritis involves general, biochemical and immunological blood tests. A high erythrocyte sedimentation rate and increased fibrinogen concentration confirm the presence of an inflammatory process; an increased number of white blood cells – a bacterial infection. With eosinophilia, the likelihood of an allergic reaction is high. The detection of rheumatoid factor in the blood serum, along with exceeding the permissible level of antibodies and circulating immune complexes, clearly indicates rheumatoid arthritis. In gouty arthritis, sialic and uric acid levels increase.
In Russia, inflammation of the joints is observed in approximately 60% of people of retirement age against the backdrop of a trend toward increasing incidence and decreasing age of first manifestation of the disease.
Definition of disease. Causes of the disease
Chronic arthritis is a disease of the joints, characterized by an inflammatory process in them that lasts more than three months.
The term “arthritis” was introduced into medical practice by Hippocrates and in subsequent centuries was used to refer to any joint pathology. [1] Starting from the 16th century, the concept began to undergo changes, and separate nosological forms arose. Thus, G. de Baillou was the first to identify rheumatism among arthritis. In the 17th century, T. Sydenham described gout and rheumatoid arthritis as independent forms. The first attempt to distinguish inflammatory joint disease (arthritis) from its degenerative changes (arthrosis) was made in the 19th century by F. Muller. This division remains important to this day.
Since arthritis has a high tendency to become chronic, it often leads to complete disability. According to WHO, 3.1% of total disability in the world is due to arthritis. [1] The leading cause of arthritis disability in the United States among older adults is the increasing prevalence of risk factors (eg, obesity). Arthritis and other rheumatic conditions cover more than 100 different conditions that affect joints and surrounding connective tissue (muscles, tendons and ligaments). Some types (eg, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus) can affect multiple organ systems (eg, cardiovascular, kidney, respiratory) and often have an autoimmune component.
Over the past 10 years, researchers have made particularly significant advances in the study of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). It is believed that genetic and environmental factors play a leading role in the mechanisms of RA pathogenesis. The overall contribution of genetic factors to the development of RA has historically been studied through analysis of family pedigrees. Thus, it was concluded that men suffer from RA three times less often than women, but science does not yet know the reason for this distribution. Researchers have proposed a number of hypotheses, including the possible influence of sex hormones. In this regard, sex chromosomes have been studied in genetic studies on RA. [2]
Read also: Aching joints
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) affects men and women equally, and 10 to 30% of people with psoriasis are at risk. The disease can develop at any age, but usually affects people between 30 and 50 years of age. Although the cause is unknown, genetic factors, along with the immune system, may play a role in the development of the disease.
Up to 40% of people with PsA have a family history of skin or joint disease. Having a parent with psoriasis triples your risk of psoriasis and your likelihood of developing psoriatic arthritis.
The cause of the inflammatory reaction in the joint can be a local or general infection, allergy, autoimmune process, trauma, etc. However, the etiology of some inflammatory joint diseases, for example, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic polyarthritis, etc., is still not clear enough. The involvement of infection in their origin has not yet been proven. Also factors that contribute to the development of arthritis are hypothermia and physical overload of the joint.
Arthritis treatment
The choice of therapeutic strategy depends on the form, etiology and stage of the disease, localization of inflammation, as well as the age, health status and constitutional characteristics of the patient. To relieve the inflammatory process and pain, a complex of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants and painkillers is selected in combination with physiotherapeutic procedures. Electrophoresis and ultraphonophoresis, Hilt therapy, amplipulse therapy, magnetic therapy and SMT therapy (treatment with sinusoidal modulated currents) have a good effect.
An important component of complex treatment is taking chondroprotectors - for example, the drug Alflutop. The injection form ensures maximum bioavailability and rapid action of the drug, which helps stop the progression of cartilage destruction, relieves inflammation and stimulates the synthesis of hyaluronic acid. Due to the rapid onset of effect, there is no need for long courses of the drug. Supplementing it with the treatment of arthritis allows you to reduce the dosage and duration of NSAID use.
Physiotherapeutic methods are effective in treating arthritis
Corticosteroids in rheumatological practice are used with great caution, limited to injections into the affected joint in the absence of response to gentle treatment methods. In the case of infectious arthritis, courses of antibiotics or antiviral drugs are prescribed, and in case of rheumatoid arthritis, immunosuppressants and immunomodulators are prescribed. If purulent complications occur, arthrocentesis is performed daily.
Medicines for back and joint pain often reduce pain and inflammation, but do not help restore the structure of cartilage.
As a means of improving the structural condition and metabolism of cartilage tissue, you can use dietary supplements from the Glucosamine-Maximum , which contains two active components: glucosamine and chondroitin. These substances are natural structural elements of healthy cartilage tissue and are directly involved in metabolic processes.
Due to their natural nature, they are well absorbed and stimulate metabolism in cartilage cells, helping to restore the structure of cartilage tissue after an inflammatory process.
A therapeutic diet for arthritis involves avoiding high-calorie foods, red meat and organ meats, legumes, salt, spices and alcohol. If you have rheumatoid arthritis, you should also avoid tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants and other vegetables from the nightshade family that contain solanine. The patient's diet should contain foods rich in fiber and vitamins, as well as sources of easily digestible protein - poultry and dairy products.
To consolidate the therapeutic effect, massage, group exercise therapy and a course of balneotherapy in a specialized sanatorium are recommended. It is permissible to turn to folk remedies and unconventional methods only after consultation with your doctor.
Correction methods
Treatment of chronic arthritis is complex. It is important to remember that it is impossible to completely heal the patient, however, competent therapy will prevent further destruction. Special medications, physiotherapy and exercise therapy methods are used for treatment. In some cases, surgery is indicated.
Drug treatment includes taking:
- Antibacterial drugs.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs of non-steroidal and steroidal groups.
- Analgesics.
- Immunosuppressants (not always prescribed).
- Vitamin supplements.
Auxiliary correction methods are:
- Exercise therapy.
- Manual therapy.
- Physiotherapy.
- Use of special fixing bandages and orthopedic structures.
In severe cases of the disease, when significant tissue destruction occurs, a surgical operation is prescribed, during which the affected joint is replaced with a prosthesis.
Prevention
Preventing arthritis is not particularly difficult. It is enough to lead a moderately active lifestyle, give up bad habits, eat a balanced diet and control your weight. For infectious diseases and joint injuries, you should consult a doctor without relying on home remedies. To prevent exacerbations of chronic arthritis, it is important to follow a diet, avoid hypothermia, not lift heavy loads, and undergo sanatorium-resort treatment according to your profile at least once every two years.
There are contraindications. You need to read the instructions or consult a specialist.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Etiology
Chronic arthritis is considered such if signs of the inflammatory process persist for three or more months.
In the vast majority of cases, the development of this disease is preceded by another illness, which means that low-grade arthritis is a pathology that develops secondary.
Chronic arthritis in children and adults develops against the background of:
- tonsillitis and sinusitis;
- pyelonephritis and hypovitaminosis;
- tuberculosis and syphilis;
- gonorrhea and gout;
- psoriasis and systemic lupus erythematosus;
- sarcoidosis and Reiter's syndrome;
- polychondritis and Behcet's syndrome;
- pathological influence of pathogenic bacteria, parasites and protozoa;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- various allergic reactions;
- hepatitis C, however, the possibility of developing the underlying disease due to another type of viral liver damage is also not excluded;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- congenital hip dislocation.
In addition to the above reasons, the following predisposing factors increase the risk of developing such a disease:
- burdened heredity;
- playing sports at a professional level. In such cases, arthritis of the knee, ankle, finger joints and wrist is most often diagnosed;
- presence of excess body weight;
- poor nutrition or prolonged refusal to eat;
- abuse of bad habits;
- prolonged hypothermia of the body;
- bites of some insects - inflammation develops when biological poison enters the joint cavity;
- hormonal changes that occur during puberty or menopause;
- physical inactivity is a condition in which there is a lack of physical activity in a person’s life;
- prolonged load on the same joint.
View of a normal and diseased joint
Heat and cold treatment
Alternating cold and heat will ease the condition of the joints. You can use an electric heating pad at night and take a cold shower in the morning. Cryotherapy reduces pain and inflammation. For a compress, you can use a bag of frozen vegetables. Before applying it to the sore joint, it is recommended to wrap it in a towel.
Treatment with heat and cold is carried out alternately. It is necessary to apply ice, the skin will turn red due to the dilation of blood vessels. Remove the cold and apply heat to improve blood circulation. At the end of the session, the painful joint should be well wrapped to increase the effectiveness of therapy.
Treatments for ankle arthritis
To treat the ankle joint, baths with the addition of various natural remedies are often used.
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Herbal collection | Mix sage leaves, St. John's wort, marsh calamus, bearberry. Pour 1 tbsp. collection with hot water (1 tbsp.). Place the resulting mixture in a water bath and heat for 15 minutes. Strain and take for medicinal purposes. | It is recommended to drink the medicine 100 ml 2 times a day. per day. |
| Larkspur | The juice of the plant's rhizome is used to prepare the medicine. | It is recommended to moisten gauze or bandage with larkspur juice and place it on the joint. The compress is applied before bedtime. |
| Rowan | Pour boiling water over 1 tbsp. berries of the plant. Wrap up and leave for 4 hours. | The finished product is taken 4 rubles. per day 0.5 tbsp. |
Problem areas can be treated with eucalyptus oil. Rub it into the sore joint several times a day until the condition improves.
Establishing diagnosis
The appearance of symptoms of arthritis requires a mandatory consultation with a doctor, since it is the early stages of the disease that are most effectively treated. The diagnosis is based on an in-depth examination of the musculoskeletal system. Additionally, the following may be assigned:
- Synovial fluid analysis;
- X-ray;
- Ultrasound;
- Arthroscopy.
Special blood tests are designed to detect:
- Rheumatoid factor;
- SRB;
- Uric acid.
For infectious, rheumatic and gout-related arthritis, the underlying diseases are initially treated. Elimination of arthritis symptoms is carried out using potent drugs that are intended to:
- To improve the condition of articular cartilage (group of chondoprotectors);
- Normalization of the immune system (group of cytostatic immunostimulants);
- Normalization of bone tissue metabolism.
Drug therapy also involves the prescription of NSAIDs, glucocorticosteroids and basic therapy.
The effectiveness of therapy can be increased with the help of therapeutic exercises, physiotherapy, daily routine and diet.
Traditional treatment of the shoulder joint
Arthritis of the shoulder joint is accompanied not only by pathological inflammation, but also by painful sensations and impaired mobility. Soft tissues swell, chronic weakness and malaise appear. Folk remedies will help eliminate discomfort and unpleasant symptoms.
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Corn silk | Pour hot water (300 ml) over dry stigmas (1 tbsp), put on low heat and heat for 5 minutes. | The finished medicine is taken in ¼ tbsp. 3 r. a day before meals 15 minutes. You can add a small amount of sugar or honey for taste. |
| Black currant | Brew currant leaves (5 g) with hot water (350 ml), after crushing them. Place the resulting mixture in a water bath and heat for 10 minutes. Then cool and strain. | It is recommended to take the medicine warm, 0.5 tbsp. 3 r. in a day. |
| Lingonberry infusion | Pour dry leaves of the plant (15 g) with hot water (250 ml). Leave the mixture for 30 minutes. | The strained tincture is consumed in 2 tbsp. 4 rub. in a day. |
Treatment of arthritis with folk remedies is carried out under the supervision of a rheumatologist, since it is important to monitor the condition of the diseased joint.
Diet
For any type of inflammatory pathology of the joints, especially with rheumatoid or gouty arthritis, it is imperative to follow a certain diet. If the patient has a disturbed mineral metabolism, resulting in salt deposition, he needs to exclude salt, smoked meats, marinades, canned food, fatty meat, and alcohol from the diet. Certain foods can increase inflammation. Most often these are corn, pork, dairy products, and citrus fruits. Therefore, it is recommended to limit their consumption.
It is best to cook food with arthritis by steaming. It is not advisable to fry food and add as little salt as possible. It is useful to eat more vegetables, fruits, fish, seafood, buckwheat, and eggs. To improve the condition of cartilage tissue, it is recommended to include jellied meat, flaxseed oil, and herbs in the diet.
Traditional methods are used as an auxiliary treatment for arthritis of the joints.
Types of arthritis according to the nature of the disease
According to the nature of the course of the disease, they are distinguished:
- Acute stage.
- Chronic stage.
Acute arthritis
Acute arthritis is caused by a one-time inflammation of the joint and is usually associated with the presence of an infectious disease. This type of arthritis is easy to treat and, as a rule, does not require repeated medical attention. Common symptoms of acute arthritis are:
- presence of high temperature;
- severe pain in the joint.
Chronic arthritis
Chronic arthritis develops gradually; often the development of the chronic form can be triggered by the acute stage of the disease if sufficient attention has not been paid to its treatment. At the same time, chronic arthritis can make itself felt both by the manifestation of constant pain and by periodic exacerbations of the disease. The chronic form is said to occur when painful sensations bother the patient for 3 months or more. The main symptoms of chronic arthritis are:,
- pain that occurs when moving a joint;
- dislocations and subluxations of the joint;
- swelling of the periarticular tissues, the presence of which can be detected by palpation.
With a long course of chronic arthritis, its consequences can be a complete loss of elasticity and mobility of the joint, followed by disability, as well as unaesthetic deformation of the limbs, which does not allow one to lead the same lifestyle. Treatment of chronic arthritis can last for more than one month, and relapses cannot be ruled out.
Drug therapy
Long-term use of anti-inflammatory tablets is fraught with severe side effects on the hematopoietic and digestive systems. The safest medicinal form is ointment (gel). Their use provides a sufficient therapeutic effect with minimal risk of side effects.
- NSAIDs (Metindol, Voltaren, Etodolac, Flexen, Movalis, Arcoxia, Burana, Celecoxib, Butadione, Nise).
The medicinal effect is aimed at relieving the symptoms of arthritis (eliminating pain, relieving inflammation, eliminating fever). The appointment should be limited in time and comply with all doctor’s instructions.
- Corticosteroid drugs (Methotrexate, Inflanefran, Betazon).
Glucocorticosteroid hormones have anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, immunosuppressive effects, and also stabilize metabolism in bone tissue
- DMARDs (basic therapy).
The first-line drug is Methotrexate. Demanded due to proven effectiveness and good tolerability. A positive prognosis in 90-95% of clinical cases can be achieved with the drug "Arava" ("Liflunomide"). The most favorable prognosis is ensured if DMARDs are prescribed as early as possible.
- GIBP (Etanercept, Infliximab, Rituximab, Abatacept).
Immunosuppressants are one of the most significant achievements of genetic engineering in modern pharmacotherapy. Able to suppress inflammatory activity and inhibit joint destruction. They also increase the chances of remission. Unlike basic therapy, they provide a faster and stronger effect.
Exercise for arthritis
A set of therapeutic exercises during arthritis is designed to eliminate pain, regenerate bone tissue, increase the endurance of damaged joints and warm up atrophied muscles.
Therapeutic exercises for finger arthritis
A specialist prescribes a set of therapeutic exercises on an individual basis. Regular performance of therapeutic exercises will please you with positive results.
One of the effective exercises during arthritis is walking on your knees.
During arthritis, walk often on your knees - 500 steps daily. If you can’t complete that many steps at once, don’t despair. First, walk as much as you can, every day, adding a couple of new steps. Every day your condition will begin to improve and your health will improve.