Hemangiomas in children may resolve on their own or require immediate medical intervention. This article will tell you how the type and treatment of hemangiomas in children are determined.
One of the ailments of a child’s infancy is hemangioma, a tumor-like defect of blood vessels that looks like a dirty spot on the skin.
Externally, a hemangioma resembles a dirty spot on the skin
Such “spots” can have different colors: from pale pink to purple, but most often hemangiomas are reddish-bluish in color.
IMPORTANT: Hemangiomas may not appear on the child’s body immediately, but only after 1 – 2 months from birth. Hemangiomas occur slightly more often in female infants than in male infants.
The most common color of hemangiomas is reddish-blue.
Hemangioma in children. Causes
The exact causes of the formation and growth of hemangiomas are not known to this day, but most likely they are:
- colds and viral diseases of a woman in early pregnancy (up to 12 - 14 weeks)
- unfavorable environmental living conditions for the expectant mother
- multiple pregnancy
- severe prematurity
- mother’s age is over 32 – 35 years (the older the pregnant woman, the higher the risk of developing hemangiomas in the fetus)
- fetoplacental insufficiency
IMPORTANT: There is an opinion that the possibility of hemangiomas in infants is influenced by the method of birth. According to statistics, hemangiomas are observed somewhat more often in children born by cesarean section than in babies born naturally.
Viral diseases contracted by a woman during pregnancy can cause hemangioma in the child.
Causes and risk factors
The exact reasons for the formation of hemangiomas have not been established. Based on the fact that they appear in the first months of a child’s life, most researchers agree that their occurrence is associated with disturbances in the formation of blood vessels in the embryonic period. In turn, various factors that have a negative impact on a pregnant woman can lead to a disorder of vasculogenesis:
- viral diseases (flu, measles, ARVI);
- taking certain medications;
- living in environmentally unfavorable conditions;
- smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages.
A certain role in the pathological mechanism of the formation of hemangiomas in children appears to be played by hormonal characteristics. This assumption is confirmed by the fact that vascular tumors occur several times more often in girls, that is, there is a clear gender dependence of their development.
Hemangioma in children photo
Hemangiomas in children can be small and light-colored. They, as a rule, rarely cause inconvenience and almost never grow.
Small, light-colored hemangiomas disappear quickly without medical intervention
However, there are also hemangiomas, the appearance and location of which causes a lot of problems and suffering in the child.
Some hemangiomas look terrible and cause a lot of suffering and anxiety to the baby
Surgery
Today, not a single modern clinic removes hemangiomas with a scalpel. There are many ways to perform the procedure quickly and efficiently. Surgical treatment is a last resort when other methods cannot solve the problem.
One of the most modern approaches is laser removal of hemangioma in children. This laser removes pathological tissue carefully and layer by layer. The accuracy of the surgeon's actions is very high. In this case, healthy tissues are not injured.
Removal of hemangioma with a laser in children is carried out without contact. This is a completely sterile procedure. Moreover, the technique is absolutely bloodless. The doctor visually controls his actions. At the same time, the cosmetic effect after laser therapy will be high. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. This is possible if the hemangioma is small.
With a significant tumor size, treatment will be much more difficult and lengthy. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. If the area of the formation is large, you will need to take a donor flap from a part of the body that will be under clothing. This is especially important when performing surgery on the face or eyelid. Such intervention is carried out only in exceptional cases. During the process, the child receives a blood transfusion.
Hemangioma on the head of a child
Hemangioma on the head of a child is a very common occurrence. This benign tumor can appear anywhere in the skull. Hemangiomas located on the head are dangerous due to their close proximity to the brain, eyes, ears and respiratory organs.
IMPORTANT: The first signs of hemangioma formation on the head may be swelling of the skin and a slight change in its color.
Growing hemangiomas of the head require medical supervision. If the tumor, growing, begins to compress vital organs, the doctor must decide to remove it.
Hemangiomas of the head, prone to proliferation, require constant medical supervision
Forms of the disease
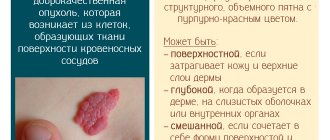
Depending on the characteristics of the morphological structure, hemangiomas in children are divided into the following forms:
- Capillary (simple). It comes from the blood capillaries of the skin, has clear boundaries, a purplish-bluish or red color, a flat, tuberous-flattened or tuberous-nodular surface. When pressed, the hemangioma turns pale, then its original color is restored. In 95% of cases, this form of hemangiomas is observed in children.
- Cavernous (cavernous). It is located in the subcutaneous tissue in the form of a nodular, tuberous formation, which has a soft-elastic consistency and is formed by separate blood-filled cavities (cavities). The vascular formation is covered with bluish or normal skin. When pressed, it decreases, which is associated with the outflow of blood from the cavities. When crying, coughing or straining, due to the flow of blood into the cavities, on the contrary, it increases - the so-called erectile symptom. It is most pronounced in the case of cavernous hemangioma located on the child’s head.
- Combined. Combines the features of cavernous and capillary hemangiomas.
- Mixed. It has a complex histological structure: it contains not only blood vessels, but also lymphoid, nervous and connective tissue. Such tumors include hemlymphangiomas, angioneuromas, and angiofibromas. Appearance, consistency, color depend on the tissues that make up the vascular formation.
Hemangiomas are observed in approximately 10% of children in the first year of life. They develop twice as often in girls.
Hemangiomas in children can have different sizes and locations, be single or multiple.
What does a hemangioma look like in children?
Depending on the speed of development of the pathological process, hemangiomas are distinguished with no growth, with slow or rapid growth.
Hemangioma on the lip of a child
In addition to its unaesthetic appearance, a hemangioma located on the lips can cause discomfort for a child when eating and chewing food. Babies born with lip hemangioma often refuse to breastfeed because they are unable to latch onto the nipple properly.
IMPORTANT: If the hemangioma has a tendency to grow, it may eventually extend beyond the lips and “spread” to the chin, cheeks or nasolabial folds.
Two methods can be used to remove hemangiomas from a child’s lips:
- scarless laser surgery (for capillary hemangiomas)
- burning with liquid nitrogen (for cavernous and mixed forms of hemangiomas)
If the hemangioma on the lip increases, then over time it will spread to neighboring areas of the skin
Prevention of hemangioma
Prevention of hemangiomas in newborns should begin long before their birth. The expectant mother should carefully monitor her health and promptly treat any viral and infectious diseases. Mom also needs to eat right in order to strengthen her immunity.
If a hemangioma is detected in a newborn baby, the woman should immediately seek advice from her pediatrician. Preventive work with such children is carried out constantly. Until the age of 5, children should be examined by a doctor every year.
Hemangiomas are one of the most common tumors among newborns; they account for up to 90% of all early-life tumors. Despite the fact that they belong to tumor formations, have a tendency to grow rapidly, do not look aesthetically pleasing and are unpleasant, they also have positive aspects - they are well treated, removed and have the properties of reverse regression if treatment is started in time.
Hemangioma on the face of a child
Hemangioma on the face of a child sometimes poses a danger to the normal functioning of the organs of vision, smell and hearing.
In addition, this is a serious cosmetic defect, which over time can make the child feel “not like everyone else.” Regardless of what type, color and shape a hemangioma on the face has, it will certainly attract sympathetic glances from others.
IMPORTANT: In cases of minor external manifestations of the defect, doctors recommend that parents do not rush into surgery, but rather observe the condition of the affected area of skin for some time. Often hemangiomas on the face resolve on their own, without any medical intervention.
Hemangioma on a child’s face is a serious cosmetic defect
Signs, symptoms and manifestations
In the first three weeks after birth, the baby may notice a slight redness on the body, which over time increases in area of distribution. Soon, an increase in the localized surface above the skin is noticeable. In the first three months, the tumor quickly grows in diameter. If you press on it during this period, it will acquire a pale tint, after which it will return to color.
When the newborn cries, cackles, or makes active movements of the limbs, the hemangioma becomes more saturated in color and increases in diameter. This happens due to the fact that a large amount of blood flows to the site of the lesion. If you feel the affected area, it will be hot compared to nearby tissues.
In 80% of cases, the appearance of such spots is not dangerous for the baby. Within 3 to 5 years, such neoplasms tend to resolve on their own. But if the tumor grows after 5 years of age, then the parents need to visit a doctor to study the tumor and rule out its development into a malignant form.
Infantile hemangiomas, located in the nose, ears, or oral mucosa, can sometimes cause problems with breathing, vision, or hearing. In this case, parents need to take serious measures to treat the tumors.
If the tumor is localized in the area of the external genitalia or in areas of the skin that are often injured (for example, rubbed by clothing), its surface often ulcerates.
Hemangioma on the back of a child
Hemangiomas on the back appear in 19 children out of 100. Most of them are congenital. They form on the baby's body when he is still in the mother's womb and can be located on the lower back, spine, ribs or shoulder blades.
Hemangiomas on the back in most cases are not dangerous to the health and life of children. Capillary formations can grow, or, on the contrary, they can shrink and turn pale. Cavernous and mixed hemangiomas do not change their appearance and size and often grow into the subcutaneous layers.
IMPORTANT: Hemangiomas on the back do not degenerate into malignant tumors, so you can postpone their surgical removal. By the age of 5–7 years, back hemangiomas disappear without a trace in many children.
Hemangioma on the back does not pose a threat to the child’s health
Phases of development
Hemangioma in a child on the head, face, and parts of the body is most often located in “safe” places. It is located at a distance from vital organs and mucous membranes. However, there are exceptions. In some cases, surgery is absolutely necessary.
In other cases, the neoplasm needs to be monitored. It has several stages of development. First, the hemangioma appears. This can happen in the womb or in the first few weeks after birth. Next comes the phase of its active growth. It lasts until the child turns one year old. After this, its growth slows down and stops. Then it stops growing completely.
After this, a phase of reverse development begins. The hemangioma begins to gradually decrease. The phase of involution and complete disappearance of the neoplasm occurs when the child reaches the age of 5-7 years. In some cases, this process lasts up to 10 years. In this case, not even traces of the hemangioma remain on the skin.
According to statistics, 50% of such formations pass when the child reaches the age of five. Of the remaining mass of children with hemangioma, 70% will say goodbye by the age of 7. Another 28-29% of them will forget about the tumor by 9-10 years of age. Only in 1-2% of children such formations degenerate into other forms of pathologies and do not go away on their own. Recurrence of hemangioma is absolutely excluded. It passes without consequences.
Hemangioma in children under one year of age
When hemangiomas are discovered in children under one year of age, parents often panic. In fact, everything is not as scary as it might seem right away.
If the size, shape and location of the hemangioma do not cause suspicion among doctors, parents just need to observe it and note any changes.
IMPORTANT: 2% of children are born with hemangiomas, and in 10% of babies they form during the first year of life. Of all cases, 95% are simple (capillary) hemangiomas.
Hemangiomas in children under one year of age require constant monitoring
Progress of treatment of neoplasms
Classic surgeries to eliminate tumors are now considered the most effective treatment methods. Indications for this option are:
- Localization of tubercles on the mucous membranes of the mouth, face, head, inside the eye.
- The occurrence of complications, progressive tumor growth at any location of the growth.
The presence of these factors indicates the need for rapid removal of the tumor. However, such a procedure is prohibited for infants and children with unwell health.
Removal of growths is possible using a number of other methods. Among the most effective, in addition to traditional surgery, are:
- laser removal of growth;
- cryotherapy (cannot be used on the face and neck);
- electrical influence;
- X-ray radiography;
- chemical destruction.
After removing a simple hemangioma in children under one year of age, a specialist may prescribe special therapy. It includes taking antibiotics and daily treatment of the wound with an antiseptic. It is prohibited to independently select funds for these tasks, because different clinical cases require an individual approach.
Hemangiomas on the lip in infants can also be removed with the help of medications. Doctors prescribe hormonal therapy, supplemented with Propranolol. Thanks to hormonal drugs, the tubercles resolve faster. However, many experts note numerous disadvantages of drug treatment.
The use of hormonal drugs is characterized by low effectiveness, when such drugs can cause a huge number of side effects. For this reason, doctors often recommend limiting the use of Propranolol, which reduces the pressure in the blood vessels of the growth. This effect on the swelling deprives it of nutrients, causing cell death and subsequent recovery.
Qualified doctors recommend using anti-glaucoma drops for treatment. The solution must be dripped onto the affected area 3 times a day for several months. The first results will be noticeable after 2-3 weeks of regular use of the medicine.
ethnoscience
Traditional healers also offer their own methods for the disease in question. Moms received positive feedback from:
- dandelion infusion;
- celandine decoction;
- juice of unripe walnuts;
- use of kombucha.
However, doctors do not recommend using folk remedies on their own, especially when it comes to treating young children. Any actions of this nature can lead to irreversible unpleasant consequences, so be sure to consult a qualified doctor first.
Hemangioma in newborns
Hemangiomas in newborns are a common occurrence. The main reason for the appearance of hemangiomas on the body of the fetus in the womb is a disruption of the normal formation of the vascular system (3 – 6 weeks of pregnancy).
Typically, the size of hemangiomas in newborns does not exceed 2 cm, but there are exceptions when the skin lesions are extensive and numerous. In most cases, they all resolve on their own during the first years of the child’s life.
IMPORTANT: Treatment of hemangiomas in newborns primarily involves monitoring the child by a pediatrician, dermatologist and surgeon.
Typically, the size of hemangiomas in newborns does not exceed 0.5 cm
Causes
In medical science, such a disease as hemangioma in newborns has been known for a long time, but the causes of this anomaly have not yet been established. Experts do not confirm the hereditary nature of its origin.
There is an opinion that the appearance of hemangioma can be provoked at a time when the baby is still in the mother’s stomach.
It is believed that if a woman during pregnancy (especially at 3–7 weeks) suffered from a cold or was exposed to some other adverse effect (taking medications, smoking, poor environment, etc.), then disruptions may occur in the formation of the vascular system of the embryo , which then lead to the appearance of similar marks.
Also, the risk of hemangioma in newborns increases in the following situations:
- late pregnancy (mother over 38 years old);
- multiple pregnancy;
- the birth of a premature or low birth weight baby;
- cases of eclampsia in a pregnant woman;
- Rhesus – conflict between the fetus and mother;
- the presence of hormonal disorders in a pregnant woman or newborns.
All these theories exist only in the form of assumptions and are not binding. Therefore, even if you are included in the described risk group, this does not mean at all that the newborn will develop a hemangioma.
Skin hemangioma in children
There are 2 types of skin hemangioma in children:
- congenital - if the child was born with a hemangioma
- children's - if the defect appeared some time after birth
Congenital hemangiomas usually do not change in size and resolve on their own before the age of ten. Children's hemangiomas can either increase or decrease until they disappear without a trace.
IMPORTANT: The diagnosis of “hemangioma” cannot be made independently. If you notice an unusual reddish spot on your child's skin, contact a dermatologist to determine the nature of the defect.
The presence of hemangiomas on a child’s skin in most cases does not in any way affect his physical and mental development.
Often, skin hemangioma remains simply a cosmetic defect
What is hemangioma?
Hemangioma is a benign vascular tumor. It looks like a bright red (possibly bluish tint) spot.
Such a mark is either present on the baby’s body from the moment of his birth, or is formed during the first month of the baby’s life. On average, this disease occurs in one in ten newborns. According to statistics, girls are more susceptible to it than boys (3:1).
Click and get a nutrition GUIDE for a nursing mother to protect your baby from allergies, colic and abdominal pain.
To distinguish a hemangioma from a mole or birthmark, you can perform the following test. If you press lightly with your finger, the red spot will noticeably fade, and as soon as you remove your finger, it will return to its original color. This is exactly how a hemangioma behaves.
Most often, hemangioma in newborns is located on the head (on the scalp, face, eyelid). It can also be on the baby's neck, arms, legs or back. A pattern has been established: if more than three spots are noticeable on the skin of a newborn, it means that they are also on the internal organs (most often the liver is affected), muscles or bones.
As the child grows, you will notice that the hemangioma also increases in size. Don't be afraid, this is how it should be. This usually lasts until the newborn is 6 to 12 months old.
After this age, growth stops, and then the reverse process begins - the spot begins to gradually decrease and completely disappears when the child reaches 5–9 years of age. In rare cases, you will have to wait until adolescence begins.
Know! It is important to note that the degeneration of a hemangioma into a cancerous tumor is extremely rare.
In most cases, this disease does not require treatment.
Parents should especially be reassured by the fact that hemangioma never reoccurs. Having gotten rid of it once, you don’t have to worry about relapses.
However, you definitely need to know that in some cases, hemangioma can pose a danger to the development of the body of newborns and even cause serious harm to health:
- This tumor can destroy nearby tissues and thereby disrupt their normal functioning. If localized near the eyes, ear or larynx, this neoplasm during the growth period can lead to deterioration of vision or hearing, and cause difficulty breathing;
- There is a risk of hemangioma rupture, which can result in heavy bleeding. Of particular danger is injury to internal tumors located in the liver, spleen or brain;
- Hemangiomas, which are located in places of rubbing (at the waist, in the groin area, on the neck), are constantly exposed to mechanical stress. In this case, ulcers may appear on their surface, and there is a risk of infection.
This leads to the following conclusion: having discovered a hemangioma on the body of a newborn, parents and the doctor are obliged to constantly monitor the development of the tumor, until its complete disappearance, and, if necessary, carry out treatment.
Subcutaneous hemangioma in a child
Subcutaneous hemangioma has clear boundaries on the surface of the skin and is distinguished by a red or blue color. A bright spot on the skin will turn pale if you press a little on it with your finger.
This happens due to the rapid outflow of blood. Subcutaneous hemangioma feels slightly warmer than healthy skin areas.
IMPORTANT: Subcutaneous hemangioma is dangerous due to the possibility of complications in the form of bleeding, phlebitis and thrombophlebitis if it is damaged.
Subcutaneous hemangioma
Treatment tactics
Modern medicine has different methods of treating hemangioma, ranging from traditional surgery to the latest advanced methods (laser removal, use of beta blockers, cryodestruction). The treatment method is selected depending on several factors:
- localization of hemangioma (on the skin or on internal organs);
- degree of tumor growth (fast growing or slow);
- the extent of the location (how much space the neoplasm occupies).
If the hemangioma grows rapidly, its removal is indicated, but in case of slow growth, monitoring the baby or drug treatment is recommended.
Surgery
Such an intervention is considered a radical method of treatment, which is resorted to only in extreme cases, for example, when the tumor has grown greatly or is located internally on organs (which threatens the health and life of the child). Surgical treatment is a quick and effective way to remove hemangiomas in children, but at the same time it has its drawbacks:
- profuse bleeding that is difficult to stop during tumor removal;
- scar remaining after surgery;
- the possibility of relapses (surgical removal of a hemangioma is not a 100% guarantee that it will not subsequently appear again).
The operation is performed under general anesthesia in a hospital setting. Excision of a vascular tumor can be complete (if it grows deep into the tissue) or partial (if the hemangioma is of impressive size and cannot be removed in 1 session).
Cryodestruction
This is a method of removing a tumor by freezing it with liquid nitrogen. Advantages of cryodestruction over other treatment methods:
- passes painlessly;
- lasts only a few minutes;
- hemangioma removal is carried out without general anesthesia;
- no scars after treatment.
The disadvantage of cryodestruction is its lack of accuracy, i.e. the doctor cannot control how deeply the affected tissues are frozen, which creates a risk of damage to healthy areas of the skin or mucous membranes. If the tumor is too large, a course of procedures may be required.
Hemangiomas larger than 4 mm are not subject to cold treatment, since it is ineffective.
Sclerosing therapy
Sclerosing therapy involves the injection of special drugs into the hemangioma - a solution of 70% alcohol, quinine, salicylate, table salt, etc. In this case, an inflammatory process of an aseptic nature occurs and the development of new connective tissue begins, which replaces the tumor tissue. As a result, the hemangioma stops growing.
The disadvantages of this method include the following features:
- a long course of injections is required, because one procedure is not enough;
- pain during treatment;
- with the introduction of a large amount of sclerosing substances (and this is inevitable in the case of a large hemangioma), skin ulceration and scar formation are possible.
Sclerosing therapy is indicated in the presence of a combined neoplasm.
Electrocoagulation
This is an effect on a vascular tumor using direct electric current. The method is considered one of the most effective and fastest for eliminating tumors. But it is applicable only for the removal of capillary (simple) hemangioma located on the surface of the skin.
The progress of the operation is as follows:
- the skin is treated with an antiseptic and local anesthesia is given;
- within 1-5 minutes the formation is cauterized with electric current;
- then a wound is formed, covered with a crust, which cannot be touched with hands, torn off, or combed; After healing it will disappear on its own.
The advantages of electrocoagulation include elimination of the tumor in 1 session, minimal risk of infection of the affected area and rapid healing.
Removal of hemangiomas with laser
This is the most gentle and painless method in childhood. After the procedure there are no scars or scars left on the skin. It is safe at any age, starting from 1 month of age. The required result is usually achieved in 1 session. Relapses are extremely rare.
During rehabilitation, the wound must be regularly treated with antiseptics and lubricated with healing ointments. Picking the crusts is contraindicated.
Use of beta blockers
This therapy is used to treat large hemangiomas localized on the face, body and internal organs. It is carried out under the strict supervision of a pediatric surgeon, pediatrician and cardiologist. The doctor calculates the dose of the drug depending on the age and body weight of the child. Usually several courses of therapy are required. Drugs in this group act on blood vessels (including in the area of hemangioma), reducing their blood supply and softening the affected tissue. Beta blockers include: Propranolol, Sotahexal, Trandate.
Drug treatment
To slow down the growth of hemangioma, it is recommended to use certain groups of medications. The effectiveness of drug therapy is extremely low, but drugs are sometimes prescribed before surgical removal of the tumor. These include:
- Synthetic glucocorticosteroids are hormonal drugs that lead to compression of the capillaries in the tumor and cessation of blood flow, which causes its destruction. For these purposes, Prednisolone (tablets), Medopred (solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration), Akriderm (ointment) are used.
- Cytostatics are antitumor agents that block cell division processes and lead to the destruction of hemangioma. These include: Vindesine (dry substance in a bottle), Vinblastine (solution for intravenous administration), Docetaxel Sandoz (solution for infusion).
The dosage and course of use of certain drugs are prescribed by the doctor; self-medication is unacceptable.
Treatment with folk remedies
Folk remedies are effective in the presence of a tumor at an early stage of development. The following recipes are indicated as therapy:
- Compress with kombucha - apply a piece of the plant to the neoplasm and secure with a gauze bandage. After 3-4 hours the compress must be changed. It is recommended to repeat the procedure 3 times a day. Course of therapy: 20 days.
- Celandine decoction - 1 tbsp. l. dry herbs, pour a glass of boiling water and let it brew for an hour. Next, moisten a cotton swab in the prepared broth and apply to the tumor for 20-30 minutes. Repeat the procedure 3-4 times a day. Course of treatment: 2 weeks.
In case of allergic reactions on the skin (rash, itching, redness), therapy should be stopped and consult a doctor.
Vascular hemangioma in children
Vascular hemangioma consists of blood vessels, lymph nodes and other tissues. Externally, it appears on the child’s skin as red or blue spots ranging in size from 0.5 to 10 cm. Most often it is localized in the head area.
The color and consistency of the formations are determined by the tissues that make up the tumor. In the area of skin with a vascular hemangioma, the blood supply is impaired, but this should not frighten the child’s parents, since such defects are prone to self-healing.
Vascular hemangioma
Diagnostics
If a hemangioma is suspected, the child is referred for consultation to a dermatologist and surgeon. Depending on the location of the vascular formation, it may be necessary to consult other specialists, for example, a gynecologist, dentist, urologist, otolaryngologist, ophthalmologist.
During the examination, the hemangioma is palpated, its consistency and area are determined. To assess blood clotting ability and identify Kasabach-Merritt syndrome (blood clotting disorder, decreased platelet count, and rapid growth of hemangioma), a complete blood count with platelet count and a coagulogram are performed.
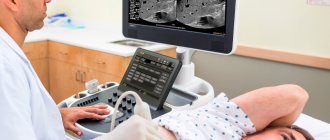
The structure, anatomical and topographical features and depth of germination of a vascular tumor can be assessed by ultrasound scanning with measurement of blood flow velocity both in the tumor itself and in peripheral vessels.
The diagnosis of hemangioma is made by a dermatologist and surgeon
Angiography is performed to study the relationship between the hemangioma and the blood vessels. In some cases, it may be necessary to take x-rays of certain anatomical areas (pelvis, chest, skull).
About 10% of neoplasms are destructive. When such a tumor grows, it compresses soft tissues, nerves, and blood vessels, which can lead to dysfunction of organs, for example, decreased vision when the tumor is localized near the eye.
Magnetic resonance imaging is used in diagnostically difficult cases, allowing one to identify the structural features of all types of vascular tumors, except those located superficially.
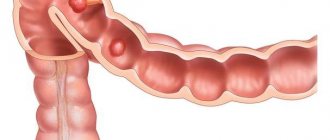
Liver hemangioma in children
Liver hemangioma in a child may not be noticed by parents. If its size does not exceed 5 cm, then no symptoms of its presence can be detected. Most likely, over time it will resolve and will never remind of itself again.
If the size of the liver hemangioma increases over time to 10 cm or more, the child will complain of aching pain in the right hypochondrium, a feeling of constriction in the stomach and intestines.
IMPORTANT: From a benign tumor, a liver hemangioma, which is a tangle of blood vessels, can transform into a malignant one. Rupture of a liver hemangioma is also dangerous - because of this, the child may experience internal bleeding.
If a liver hemangioma is detected in a child, parents should exclude spicy, fatty, smoked, salty and fried foods from his diet. Instead, you can offer strawberries, carrots, beets, fish, liver or dairy products.
Strawberry is a product recommended for liver hemangiomas
Symptoms
Hemangioma in newborns is usually detected in the first days, less often than a week, of life. Typically, neoplasms are localized on the scalp, face (nose, cheeks, eyelids), mucous membranes of the mouth, genitals, upper torso, upper and lower extremities. Less commonly, hemangiomas form in internal organs and bones.
Hemangioma in newborns is a flat or raised bumpy-nodular or cavernous neoplasm, ranging in color from pale pink to burgundy with a cyanotic tint, ranging in size from 1 mm to 10 cm in diameter, and sometimes more. Superficial hemangiomas are characterized by temperature asymmetry: the vascular tumor feels warmer to the touch than the surrounding tissue.
Capillary hemangiomas
Capillary hemangioma in newborns protrudes slightly above the surface of the skin and usually does not spread to the deeper layers of the skin. The size usually does not exceed 1 cm in diameter.
This is what capillary hemangioma looks like
Capillary hemangioma of the eye forms as a limited growth of bright red color. The tumor rises above the surface of the skin, increases in size when the child cries or screams, and turns pale when pressed. Capillary hemangioma of the eye usually occurs on the upper eyelid and can spread to the orbit. In case of regression of the tumor, a spot of hypopigmentation or a scar remains in its place.
Cavernous hemangiomas
Cavernous hemangioma in newborns has a soft structure. Most often it is localized on the skin, but can also form in organs with an abundant blood supply (brain, lungs, liver, spleen, kidneys, adrenal glands). As a rule, with internal localization, cavernous hemangioma is asymptomatic, being discovered either by chance during an examination for another reason or with the development of bleeding, which is usually caused by trauma. Bleeding from an internal hemangioma can be life-threatening.
Cavernous hemangioma in a newborn
Cavernous hemangioma of the eye has the appearance of a clearly demarcated pink spot that does not fade when pressed. As the pathological process progresses, the neoplasm acquires a purple or dark red color. This form of hemangioma is usually not prone to spontaneous regression. The skin under the tumor may become rough, loose, nodular, inflamed, or bleed.
Combined hemangiomas
Combined hemangiomas have features of both capillary and cavernous, cutaneous and subcutaneous parts. Clinical manifestations depend on the predominance of the capillary or cavernous component.
In approximately 7% of cases, hemangiomas in newborns progress during the first year of life, and then undergo reverse development, which, however, can be long-term - sometimes until puberty.
Mixed hemangiomas
The mixed form of hemangioma is characterized by a complex structure and includes elements of vascular and other (lymphoid, connective, nervous) tissues. The appearance and consistency of such neoplasms depend on the components they contain.
Spontaneous regression of hemangioma begins with the appearance of pale colored areas in the center of the tumor, which gradually spread to the periphery of the tumor. The tumor regresses over several years.
Cavernous hemangioma in children
Cavernous hemangioma is a formation consisting of two or more vascular cavities filled with blood. It grows from the subcutaneous fat layer. If a cavernous hemangioma begins to grow, the overlying skin will turn bluish-purple.
Only a doctor can diagnose this type of hemangioma, based on the results of ultrasound and laboratory tests.
IMPORTANT: If a child has been diagnosed with cavernous hemangioma, its treatment must be started immediately.
Cavernous hemangioma
Conservative treatment
Hemangioma in children can be treated with conservative methods. One popular approach is cryotherapy. In this case, carbon dioxide snow is used. This method is applicable for hemangiomas with a diameter of up to 2.5 cm.
Carbon dioxide snow is applied to the tumor site. In this case, healthy tissue of about 0.5 cm is captured. After this, the appearance of a depressed surface can be observed. It swells and turns into a bubble. Then a crust appears. It disappears after 2 weeks.
Another option is to use injections. They have a sclerosing effect on hemangioma vessels. After such treatment, connective tissue appears in its place. Alcohol and quinine solution are used as the active ingredients.
Using injections, an infiltration cushion is created. It forms first around the tumor. Then such formation is concentrated in its center. The procedure is repeated once a week. At this time, the swelling should disappear. If the tumor is on the eyelid or in the mouth, surgical methods will be quite difficult to perform. Therefore, this approach is used. The injections have proven their effectiveness.
If the hemangioma is small, the doctor may recommend electrocoagulation. The size of the tumor should not exceed 5 mm. It is affected by electric current. As a result, the tissues of the formation coagulate. Then a crust appears. It goes away on its own over time.
Radiation therapy is used to treat subcutaneous tumors. This is one of the few methods that allows you to remove such tumors from internal organs. Radiotherapy has a bad effect on the patient's entire body. Therefore, it is prescribed no earlier than the 6th month of the child’s life.
Treatment of hemangiomas in children
According to statistics, in 10% of children, hemangiomas resolve by the age of one, in 50% by the age of five, and in 70% by the age of 7. However, if the hemangioma increases in size or threatens the child’s health, it is necessary to treat it.
Hemangiomas can be treated using one of the following methods:
- with the help of medications
- cryotherapy
- cauterization
- injections of sclerosing agents
- laser therapy
- using folk remedies
IMPORTANT: In each individual case, treatment is selected individually depending on the type, size and severity of the defect.
Treatment of hemangioma should be prescribed by a doctor
Features of childhood tumors
Such mounds are characterized by progressive growth. Localization of this hemangioma on the eyelid of a newborn or on the nose can lead to disorders of the respiratory or visual system. Also, the swellings in question are characterized by bleeding, the formation of ulcers, infection and other problems that can lead to all sorts of complications.
For approximately 65-70% of clinical cases, regression of the disease is relevant. The tumor usually resolves completely within a few years. Most of these tumors disappear by age 7. Early regression leaves no traces behind. The complete disappearance of the tumor by primary school age can be noticeable by a small scar.
Laser removal of hemangioma in children
Modern removal of hemangiomas in children involves a painless laser treatment of the affected area of skin.
The laser “reduces” the tumor to a minimum size, while simultaneously eliminating traces of it. Wounds after this procedure heal very quickly, without complications.
IMPORTANT: Laser removal of hemangiomas is the safest way to solve the problem. The result of the removal procedure depends only on the qualifications of the surgeon who performed it.
The disadvantage of this method is the inability to remove the hemangioma in one go. On average, for the defect to completely disappear, it will take 3–5 procedures with an interval of 2–3 weeks.
Removal of hemangioma with laser
If you notice a suspicious spot on your child’s body that is described as a hemangioma, do not despair. Take your child to an experienced doctor who, upon examination, will accurately determine the origin of the skin defect and, if necessary, prescribe adequate treatment.
Are propranolol and timolol effective for hemangioma?
Treatment with drugs containing propranolol and timolol is a fairly new method of combating infantile hemangiomas.
Propranolol is especially effective for cavernous and internal hemangiomas. Drugs containing propranolol (most often Anaprilin) have been used to remove such tumors since 2008.
- Propranolol is taken orally for 6 to 12 months.
- By constricting blood vessels, it is able to stop tumor growth and trigger regression mechanisms, but you cannot take such drugs on your own.
- The individual dose is calculated only by the attending physician, taking into account the opinion of the cardiologist, since the main effect of propranolol is on cardiac activity.
- On the contrary, insufficient drug intake will not have the expected therapeutic effect on tumor development.
Effect after treatment of hemangioma with propranolol
Timolol is included in eye drops and gel against glaucoma. The therapeutic effect in the fight against cutaneous hemangiomas was discovered by chance in 2010.
- A drug containing timolol is rubbed into the tumor every 8 hours for 2 - 3 months with intervals of 1 - 2 months to avoid the body becoming addicted.
- The paleness of the neoplasm is noticeable after 2-3 weeks of use.
Classification
The tumor in children can be internal (localized on organs), subcutaneous, or skin hemangioma. Most often, hemangioma in young children appears on the skin of the eyelid, on the forehead, on the face in the mouth area. Hemangioma on the eyelid is considered the most common location. The spot can also form on the neck, on the back, on the limbs (on the leg or arm). On the baby’s leg, the pathology is widespread in the hip area; on the arm, the tumor is more often localized on the hands. The spot can be small or extensive, single or multiple.
By structure, there are vascular (cavernous) hemangioma, which consists exclusively of vessels, capillary, consisting of capillaries, combined and mixed. Externally, these types of neoplasms differ from each other, therefore an experienced doctor can almost always determine what type a particular neoplasm belongs to without resorting to additional research.
Cavernous
Cavernous hemangioma in newborns has cavities, which is where it gets its name. Vessels containing venous or arterial blood pass through these cavities. This tumor is soft and is located mainly on the surface of the skin. If the tumor affects internal organs, then only those with good blood circulation - the spleen, liver, lungs, kidneys and adrenal glands. Throughout life, the child and his parents may not even know about the pathology if the tumor is located inside the body.
Capillary
Capillary hemangioma is a tumor of a simple form and is formed from small vessels - capillaries, passing through the skin layers. This is not a very large formation; more often it does not reach one centimeter in size. Such hemangiomas do not tend to bleed and rarely cause complications. This type of neoplasm is the most common and occurs in ninety-five percent of cases. If the spot is located on the scalp, then it can sometimes be noticed only after several years and then by accident.
Combined
In children, combined hemangioma combines capillaries, which can be seen from the outside, and the vascular part of the tumor - cavernous, located in the deeper layers. Such neoplasms often appear on the head of babies. A combined hemangioma on the surface of the skin may look like a raised mole, but under the skin it grows strongly, forming a large vascular tangle. Inexperienced people often mistake such a hemangioma for a capillary one; sometimes even a doctor cannot accurately determine the structure of the tumor without additional examination.
Mixed
If a baby develops a mixed type of tumor, then in addition to blood vessels, it contains other tissues - connective, fatty, nervous, lymphoid. Such neoplasms are rare. This form can be found in only one child out of ten who have hemangiomas.
We recommend reading Pituitary tumor - causes, types, treatment
Frequent localization
Most often (in about 80% of cases), hemangiomas are located on the head and face of the newborn, for example, on the forehead, on the back of the head or on the lip. About 1% of hemangiomas are found on the eyelids. Approximately 5% of formations are detected on the child’s body, for example, on the back, leg, neck, arm. Up to 1% of such vascular formations are localized in the liver and other internal organs.
In most cases, hemangioma in newborns appears on the skin of the back of the head, forehead, face or head. In 5% of patients, pathology is detected on the eyelids. Upon visual examination, in 10–15% of infants, a hemangioma in the form of a red spot is found on the arms, legs, neck or back. Formations on the surface of organs are observed in only 2% of patients.
Treatment
Hemangiomas need to be treated in cases where the tumor interferes with normal life activities or spoils the aesthetic appearance of the face. Treatment and removal of hemangioma is individual.
Before treating a tumor, careful and regular monitoring of the development of the tumor (increases, disappears, changes color, etc.) should be established.
Modern medicine has non-traumatic and effective treatment methods. Still, removal through surgery can cause stress to a child under one year of age. Therefore, doctors recommend taking radical measures in extreme cases and only after confirming active tumor growth.
Treatment is recommended in the following cases:
- The formation is located on the eyelid and can damage vision or cause lazy eye syndrome;
- The tumor is located in the respiratory tract and can cause suffocation;
- A tumor on the lip poses a risk of injury during feeding;
- A tumor in the area of the ear can interfere with normal perception of sound;
- Hemangioma on the forehead should be removed due to the possibility of injury from headgear;
- Formations on the body in places of constant friction with clothing are removed urgently (on the leg, wrist, neck, etc.).
Cavernous hemangioma on the head or face is dangerous and must be treated. If the growth of the spot could cause harm to the child, removal of the cavernous hemangioma is mandatory.
In cases where the cavernous tumor is located on the back, abdomen and other places not subject to mechanical stress, treatment can be medicinal. In such cases, you should not resort to mechanical intervention; it is better to limit yourself to regular observation.
Operation
In a child, any surgical intervention can leave a more pronounced defect on the skin than the tumor itself. In 70% of cases, the disease disappears without a trace without requiring removal. If there are no critical indications for removing the stain, then surgical intervention should be replaced with a more gentle treatment.
Sclerosis
For the sclerotherapy procedure, 70% alcohol or other drugs prescribed by the attending physician are used. Sclerotherapy is used for deep vascular tumors of small size and difficult to localize. Treatment with sclerotherapy is indicated for areas in the facial area (lip, nose, etc.).
Cryodestruction
Cryodestruction involves cauterization of the affected area of skin. Removal with liquid nitrogen is applied to formations of small sizes. Cauterization can be performed on newborns; the procedure is painless and does not cause bleeding. Cryodestruction leaves a bubble at the site of the tumor, which requires proper care. With proper treatment, the wound heals quickly without leaving a mark.
Diagnosis of hemangiomas in a baby
The main thing that every adult should do, when they discover a tiny unknown spot on their body, is to seek help from a surgeon. It is this doctor who examines this phenomenon in newborns, but for an accurate diagnosis you will need to undergo laboratory tests and an ultrasound examination.
Benign tumors located on internal organs are quite poorly diagnosed. They are often identified during examination of completely different pathologies. Parents may not realize that their child has such a problem.
In addition, angiography is used . This method is an X-ray study of the condition of blood vessels by introducing a contrast agent into the body. Thus, the doctor is able to not only recognize the type of tumor, but also even examine the area where it is located.
Stages of the disease
The clinical picture of hemangiomas is divided into the stage of active tumor growth, the stage of cessation of growth and, in some cases, the stage of reverse development.
There are three stages of development of hemangioma in a child:
- The vigorous growth stage during which the hemangioma increases in size.
- Stage of growth arrest, when the tumor does not change.
- The stage of involution, during which the benign formation decreases.
It is important for parents to know the stages of development of cerebral hemangioma in newborns. There are three main stages of the disease in children:
- Stage of accelerated development. At the first stage, tumors quickly increase in size by 2–3 times.
- Developmental arrest stage. When the first phase of the disease ends, the growth of the tumor completely stops and its size does not change.
- Involution stage. At this stage, vascular hemangioma in newborns gradually decreases.
Why is it dangerous?
As the tumor grows, more and more capillaries and vessels are added to the tangle. In large hemangiomas, blood clots can form. This phenomenon leads to a decrease in the number of platelets in the bloodstream, which impairs blood clotting. Hemangiomas located near important organs, such as the ear, eye, nose, and respiratory tract, can lead to disruption of the functionality of these organs. Large tumors, growing, impair the baby’s vision and hearing, and disrupt his respiratory function.
When a cavernous hemangioma is injured, severe bleeding occurs that is difficult to stop. This is especially dangerous when the tumor is localized on internal organs. Their damage often leads to death due to bleeding into the liver, spleen, and brain. As you can see, hemangioma is not a completely safe neoplasm.
Despite the fact that most often the growth of a hemangioma ends by the age of one year, and by the age of seven it resolves, complications can arise at any time. That is why, if you find a spot of any size on your baby, you need to consult a doctor.
Peculiarities
In general, hemangioma is a benign tumor of blood vessels. Abnormalities in the embryo while in the womb appear immediately after birth in the form of a reddish spot. The structure of the tumor consists of normal and atypical cells and has a thickened shape with uneven edges.
- There are several types of hemangiomas according to their shape and color: flat, cavernous, stellate and strawberry.
- With normal development, the tumor should gradually grow with the child and not change its color.
- To distinguish a hemangioma from a pigment spot, you need to press on it with your finger. The vascular formation will certainly turn pale and disappear completely.
- A simple tumor has a painless development process. Its size and color may change slightly only in stressful situations for the baby, when he cries and screams. The temperature of the hemangioma is higher than that of the surrounding tissues.
- The location of the formations can be on the skin and internal organs. Most often, hemangioma in newborns is located on the child’s head, his face, especially on the nose and forehead. You can less often notice it on the back and leg. Hemangioma is most dangerous when located near the upper eyelid, on the lip, ears and oral mucosa, since the location leads to disruption of important vital functions.
- Under favorable conditions, hemangioma goes through several stages of development in newborns: appearance (either from the moment of birth, or formation in the first month of life), active growth (ends by the first year), growth arrest, loss of size, complete regression and disappearance.
- More than ⅔ of cases of hemangioma have a positive outcome, and the tumors disappear without intervention by seven to ten years, which means it is not always worth treating them.
When does growth most often end and involution begin?
In almost all newborns, hemangioma on the back of the head and other parts of the body appears in the first day after birth and actively grows within six months. Then the development of pathology slows down and stops. Growth stops completely when the baby is 10–12 months old. By the age of six, the neoplasm should resolve.
In most babies, hemangiomas form in the first days or weeks of life. The most active tumor growth is observed before 6 months of age.
Danger of pathology
Hemangioma, as numerous studies show, for the most part do not pose a threat to life and health. However, some of its species are characterized by destructive development. Some complex forms, growing into the deep layers of the skin, can affect vital organs and disrupt their functioning.
Experts note that a growing tumor can cause a deterioration in the child’s well-being. Moreover, mixed hemangiomas can negatively affect the functioning of nearby organs. In some cases, internal bleeding is diagnosed.
In large hemangiomas (especially the cavernous type), the formation of blood clots is often observed. This condition negatively affects the quality characteristics of the blood. This is especially true for platelet levels, which negatively affects coagulation.
In medical practice, there are cases of damage to cavernous hemangioma as a result of blunt trauma. The condition is accompanied by profuse bleeding, which is difficult to stop. If it is not possible to receive medical care in a timely manner, death cannot be ruled out. Of particular danger is cavernous hemangioma formed in the brain.
Problems or complications
Most childhood hemangiomas will go through phases of growth and regression without causing any problems. However, about 25% of cases have complications. Your doctor will help determine whether your child's hemangioma is likely to cause complications based on size, location, and growth rate.
Possible complications of childhood hemangiomas include:
Organ dysfunction
As the hemangioma grows, it can impair organ function.
The most common case is when the hemangioma affects the eyelids or periorbital tissues. Hemangiomas can lead to amblyopia through three mechanisms: physical obstruction of the visual axis, astigmatism from direct pressure on the anterior segment of the eyelid lesion (more often than the upper eyelid), and unilateral myopia. Strabismus may be secondary to amblyopia or paralysis of the extraocular muscles infiltrated by the orbital hemangioma.
If a hemangioma around the eyes grows quickly, it can block a child's vision, which can lead to permanent vision loss.
If your child has a hemangioma in the periorbital area, monitor him closely and consult with your pediatrician. Other affected areas that may need urgent treatment are the genital area and around the mouth.
Airway obstruction is a rare complication of hemangioma. Injuries to the upper lip very rarely obstruct the two nasal passages.
Hemangiomas located on the lower back and spine may be associated with vertebral defects.
Hemangiomas affecting the genital area can cause abnormalities in the pelvis and urinary system.
Several cutaneous hemangiomas are often associated with hemangiomas of internal organs, including the liver, lungs, and intestines. Rarely, even the brain may be affected. Extensive hepatic hemangiomas may be associated with heart failure and hypothyroidism.
Ulcer formation
The skin over the lesion may be broken. Explication occurs in 10-15% of hemangiomas in children. The cause of ulceration is unclear, but may be the result of blood flow to the skin over the lesion or the action of certain cytokines.
Explication usually occurs with rapidly growing hemangiomas. Hemangiomas that are located around the mouth, nose, ears, or anogenital area have a higher risk of ulceration.
The ulceration(s) can be very painful for the child, which can lead to irritability, poor feeding and sleep problems. Ulcers may result in scarring after curing, which may take several months. Secondary infection is possible, but cellulitis, abscess, and bacteremia are rare.
Ulcers heal slowly, so your doctor may recommend treatment to speed up the process and prevent infection and scarring. Treatment for ulcers may include topical or oral antibiotics, dressings, laser surgery, becaplermin gel (recombinant platelet-derived human growth factor), and topical compression therapy (especially useful for lesions in the extremities).
Bleeding
The skin above the lesion protects the hemangioma from bleeding. If the hemangioma is damaged, it may bleed or develop a crust. The blood vessels that make up the hemangioma are abnormal.
When hemangiomas bleed, they usually bleed quickly, but only for a short time. Bleeding can be stopped by applying light, direct pressure to the wound for 15 minutes. If bleeding occurs again or does not stop with this method, contact your child's doctor.
Traditional therapy
If neoplasms are found on the spine or liver, you can try using some traditional medicine. If the spine is affected, an infusion of St. John's wort, celandine and alcohol is prepared. Apply to the tumor for three hours. It is recommended to repeat for 10 days. Kombucha is used for skin lesions. A piece of his body is directly applied to the affected area. The compress is changed once a day. This procedure should be repeated for three weeks.
For internal vascular tumors, oat infusion gives a good effect. First, 1 cup of grain is soaked in 1 liter of water. After 10-12 hours, boil for about half an hour and leave again for the same time. Then the broth should be filtered and taken orally, 100 ml before meals. This drink should be stored in a cool, dark place.
Reviews from parents
Parents whose children have been diagnosed with hemangioma often insist on surgery or other treatment for the tumor. However, over time, if the doctor does not recommend such interventions, they agree with the statement that the hemangioma should not be treated. If it is in a safe place, it is better to let it pass on its own. Many procedures, although they are as safe as possible, cannot guarantee that after such effects there will be no scars. Therefore, parents say that if the doctor does not recommend surgery, you just need to monitor the tumor.
Having considered the features of the occurrence and treatment of hemangioma in children, parents will be able to make the right decision on subsequent actions.
Complications and prognosis
Hemangioma without treatment threatens to block blood vessels and cause blood clotting problems. When an injury occurs in the area where the pathology is located, bleeding develops, which is very difficult to stop. The expanding tumor puts pressure on surrounding tissues and nerves. Located near the eyes and ears, it can cause vision and hearing loss. With timely treatment, these complications can be avoided. The prognosis for hemangioma is good, as in most cases it goes away by the age of seven. After treatment, relapses almost never occur.
How is it treated?
In recent years, modern medicine has changed the approach to the treatment of childhood hemangioma. If the tumor had not previously grown and did not threaten the child’s health, observational therapy was applied to it. However, an analysis of recent studies has shown that early diagnosis of the disease and timely initiation of treatment can avoid a number of serious complications.
How to treat? Removal of hemangiosal tumors in children is carried out by:
- Cryodestruction . Freezing with liquid nitrogen tumors located at a shallow distance and small in size (no more than two centimeters in diameter). As a result, the formation is rejected and dies. This procedure is not performed for facial tumors or large tumors because the risk of wide scarring is very high. The advantage of this method is the targeted destruction of tumor tissue, painless nature, minimal risk of damage to healthy tissue, and rapid rehabilitation. The cryotherapy process takes a little time, and to achieve maximum effect it is necessary to repeat this session two or three more times with a break of 5 days. After the procedure, the site of the hemangioma must be smeared with brilliant green until a crust forms in the form of a sore. The healing period is up to 1 month;
- Laser irradiation. The most effective, gentle and relatively cheap method of removing hemangiosal formations in children (in Moscow, the average cost is from 1.5 to 2 thousand rubles). It is used to treat deep-lying hemangiomas (more than two centimeters). This method is effective because: it destroys tumor tissue, prevents the possibility of bleeding and scarring;
- Sclerosis . Used to remove large hemangiomas located both on the skin surface and on internal organs. The method involves cauterizing the tumor with some elements and further destroying it. The procedure is repeated with a break of a week or ten days. The hemangioma completely disappears within two years after treatment;
- Electrocoagulation method . Destruction of the tumor through the application of high-frequency current, as a result of which the formation is charred and rejected. The advantage of using electrocoagulation is that it minimizes the chance of bleeding.
- Methods of close-focus radiotherapy . Exposure to X-rays leads to the destruction of formation capillaries. This method is mainly used as an additional method - on the eve of surgery in order to reduce the size of the tumor. However, X-rays are not advisable for the child, since this may lead to the development of malignant neoplasia;
- Surgical elimination of a tumor is an operation to completely remove it and send it for histological analysis.
General information
This formation appears as a result of pathologies occurring in the blood vessels during the embryonic development stage.
In appearance, hemangioma in children is a flat, convex, homogeneous or multiple red spot (the color can also be crimson or purple) on the skin or subcutaneous surface. Most often observed in newborns immediately after birth (congenital pathology). In this case, there are cases when the formation appears at a later age, for example, during adolescence, when the hormonal background undergoes changes (acquired hemanginoma). According to medical statistics, hemangiomas are recorded in 1–2 percent of newborn infants and in 10 percent of children in the first years of life.
At the same time, hemangioma is one of the most common benign formations that form in children on the skin and mucous membranes - it accounts for approximately 50 percent of all tumor-like processes in soft tissues. At the same time, girls are susceptible to this disease 2 or 3 times more often than boys.
The predominant places where hemanginoma appears are the face (on the lip, nose and mouth, forehead, eyes), back and scalp. In infants, vascular tumors are localized in the area of the lower extremities (on the arm or leg, mainly on the foot and heel), perineum and genitals. Despite the fact that hemangioma in children is benign, it is prone to rapid growth and even bleeding. Due to its growth in width and depth into nearby tissues, hemangioma can lead to problems with vision, hearing and respiratory organs.
Treatment methods
Dr. Komarovsky writes in his books and talks about this in his programs that it is imperative to treat hemangioma in newborns. However, as he states, surgical or any other method of therapy must be resorted to in cases where the hemangioma begins to grow or does not go away on its own by the age of seven.
First, an experienced doctor chooses observational tactics, since neoplasms often regress on their own, starting to lighten in the middle. If the spot does not shrink or, worse, begins to grow, or is located on the face or near the genitals, it is removed surgically using freezing, cauterization, or other procedures. Small lesions can be treated with conservative methods.
We recommend reading Moderately differentiated adenocarcinomas, their types and treatment
Medication
Small hemangioma can be treated with hormonal therapy, for example, Prednisolone or Propranolol. The baby is given injections and also given hormone tablets. During therapy, the spot becomes light and disappears in eighty percent of cases.
Surgical method
This method is used if conservative therapy has not yielded results, or if the hemangioma is rapidly increasing in size. Depending on the size of the tumor, the anesthesiologist administers general or local anesthesia, after which the surgeon excises the vascular tangle with a scalpel, simultaneously cauterizing the capillaries.
Sclerosis
The method is used only for cavernous hemangiomas. An agent is injected into the middle of the tumor, which seals the vessels from the inside, leading to their death. This method is quite painful and time-consuming. Large tumors may take two to four weeks to heal.
Cryodestruction
Cold treatment is carried out for small tumors that are not localized on the face. The tumor is susceptible to exposure to liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide. Under cold conditions, frostbite occurs on the skin and blood vessels; after a while, a crust appears at the site of the hemangioma, under which healthy skin forms. In some cases, cryotherapy leaves a small scar.
Radiation therapy
Radiation treatment is justified for large flat tumors and cavernous hemangiomas of subcutaneous localization. In addition, irradiation is used in the treatment of tumors located in the eye. Radiation therapy is not used until six months; after this age, the baby is irradiated in several sessions with breaks from a couple of weeks to six months.
Electrocoagulation
The method of cauterization of hemangioma is used to treat children after three years of age, however, after such therapy, scars on the skin are possible. The procedure is performed on areas of the body that are under clothing.
Laser therapy
This is the best method for treating tumors on the face, since after excision of the tumor with a laser, no traces remain on the skin. Since laser therapy is completely painless, it is used even for newborns. But this method has two disadvantages - the high cost of the procedure and the need for repeated treatment for large or deep hemangiomas.
Treatment with traditional methods
Some people are against modern medicine and try to cure any disease with traditional medicine. Unfortunately, treatment of hemangioma with folk remedies is not justified. Using celandine for lotions can burn the baby’s delicate skin and lead to a secondary infection.
Self-medication is dangerous, especially when it comes to newborn children.