Green stool in an adult can be caused by various factors. Feces may change color if there is a disease of the gastrointestinal tract at an early stage. And as practice shows, greenish stool can be observed when the diet changes. Let's take a closer look at when you should worry and what you need to pay attention to if your stool turns green.
What affects the color of stool
The normal color of stool can be dark or light brown depending on the diet (presence of vegetables, chemical dyes in food). The stool turns brown due to the breakdown of bile.
There are several main reasons that contribute to the change in the color of feces to green with different shades:
- Food;
- medications;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
If you have green stools, it is necessary to analyze the diet in the last 2-3 days, since this is the time it takes for food masses to pass through the small and large intestines from the esophagus to the rectum.
Foods that can turn your stool green usually consist of significant amounts of chlorophyll, a greenish substance found in the leaves and stems of plants. Changes in the color of stool are possible after eating the following foods:
- broccoli;
- Brussels sprouts;
- celery;
- spinach;
- sorrel;
- chard;
- green smoothies;
- sprouted wheat with sprouts;
- green algae;
- juices from vegetables and fruits;
- red fish;
- red meat and products made from it;
- Red beans.
Also, a green tint of feces is observed after eating food with chemical dyes in the composition: carbonated drinks, caramels, filled candies, colored ice cream, etc.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine has proven itself well. These include:
- Oak bark. Pour in a pinch of crushed bark and 0.3 liters of water. The mixture is boiled over low heat for 10 minutes. The decoction is effective during the treatment of chronic diarrhea.
- It is possible to get rid of green diarrhea using walnut kernel tincture. Its inner part is crushed. Pour the mixture with 2 cups of boiling water and cook over low heat for about 15 minutes. The cooled tincture is filtered through cheesecloth. Take 100 g once a day.
- Wormwood. To prepare the decoction, you need to mix 1 tbsp with boiling water. l. wormwood leaves and boil for 5 minutes. The product is best consumed warm, without sugar.
- A decoction of St. John's wort is beneficial for green diarrhea in adults. It is taken 100 g three times a day before meals.
- Blueberry. It is a universal berry containing substances that can eliminate severe diarrhea. With constant consumption of blueberry jelly, the patient’s general well-being improves.
When green diarrhea is diagnosed, it is necessary to prevent dehydration, in particular in a situation where a child has diarrhea.
Prevention of dehydration consists of increasing the volume of fluid consumed and using special rehydrating solutions.
They help replenish the loss of water and electrolytes in the body. To prescribe treatment for green diarrhea in an adult, its root cause must be identified.
When intense diarrhea is observed, it is not recommended to take any medications yourself until the doctor arrives, since this can complicate diagnosis.
Causes of green stool in adults
Medicines and dietary supplements (dietary supplements) can have a significant impact on the color of stool, in which changes in color occur without diarrhea and abdominal pain and other symptoms accompanying diseases of the digestive system.
The following groups of medications can affect changes in the color of stool:
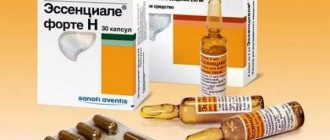
- preparations with iron for the treatment and prevention of anemia (Totema, Ferrotab, Sorbifer, Tardiferon, etc.);
- multivitamins with iron;
- herbal remedies for constipation (Laminarid, Mucofalk, Senade, Rektaktiv);
- preparations containing iodine (Iodomarin, Antistrumin, Micro-Iodine, Iodbalas);
- Dietary supplements with chlorophyll (NSP Liquid chlorophyll);
- Dietary supplements with iron (Fersinol-3, Medefer, Spaton).
Light green stool
The cause of light green stool may be insufficient digestion of food in the gastrointestinal tract, when there is a deficiency of digestive enzymes, as well as an increased rate of movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract.
If liquid green stool is observed for a long time, this indicates diseases such as:
- celiac disease;
- maldigestion;
- chronic entrocolitis;
- disaccharidase deficiency;
- fermentative dyspepsia;
- liver diseases (cirrhosis, hepatosis).
Dark green
Dark green stool is a serious symptom in combination with abdominal pain, vomiting, decreased blood pressure, and indicates internal bleeding of the upper gastrointestinal tract in the following diseases:
- stomach ulcer or erosion;
- duodenal ulcer;
- chronic gastritis;
- hypertrophic polydemat gastritis;
- varicose veins of the esophagus or stomach;
- angiodysplasia of gastric vessels;
- rupture of an aortic aneurysm into the lumen of the duodenum;
- pancreatic tumors;
- damage to the bile ducts.
Green stool with mucus
The presence of mucus in feces is an additional symptom of pathological processes in the organs of the digestive system. The main reasons for the appearance of excrement with mucus are the following gastrointestinal diseases:
- dysentery;
- rotavirus (intestinal flu);
- helminthiasis;
- ulcerative colitis;
- irritable bowel syndrome.
These diseases often cause not only changes in color, but also in the consistency of excrement: diarrhea and undigested food residues in the feces are observed.
Smell
The unpleasant smell of feces indicates a violation of the digestion of nutrients at different stages of the breakdown of proteins, fats and carbohydrates:
- a decrease and even absence of odor indicates accelerated movement of contents through the small and large intestines;
- a sour smell appears with fermentative dyspepsia;
- the smell of rot is noted with ulcerative colitis;
- an unpleasant fetid odor reminiscent of rancid oil indicates a violation of the secretion of pancreatic enzymes and a deficiency of bile acids in the intestines.
In addition to the color and smell of stool, you should also pay attention to the consistency of the stool, since the density of the stool can also be used to assess the functioning of the digestive system:
- formed stool indicates normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, but is also observed with insufficient digestion in the stomach;
- mushy feces in combination with a green color confirm chronic enteritis, colitis, increased evacuation of colon contents;
- ointment-like feces are observed with insufficiency of bile in the large intestine, with insufficient secretion of digestive enzymes;
- diarrhea is observed with colitis and enteritis.
If, along with a green tint of intestinal secretions, bloating, fever, sharp or dull pain in the abdomen, diarrhea or vomiting are noted, this indicates poisoning and serious pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diet
To eliminate disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract, you must follow a strict diet. It involves the consumption of astringent food products that help “strengthen the stomach”, as well as the removal from the menu of dishes that irritate the mucous membrane.
Dietary nutrition is aimed at normalizing the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins, as well as restoring the inflamed mucous membranes of damaged parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
When a patient has diarrhea, it is necessary to limit the intake of any product that causes the formation of gases, fermentation, or increases gastric motility.
The list of prohibited products includes:
- fatty foods, which make it difficult to process food masses;
- fermented milk products, since they increase fermentation in the gastrointestinal tract;
- semi-finished products that contain flavorings and dyes;
- fruit juices, which contribute to the deterioration of the patient’s well-being during diarrhea;
- consumption of salty foods and marinades affects irritation of the intestinal walls;
- During the period of diarrhea treatment, the intake of spicy foods should be avoided;
- mushrooms increase the load on the digestive system weakened by the disease;
- the menu of a person who has green diarrhea should not include legume dishes;
- It is forbidden to eat cabbage, radish and onions;
- highly carbonated drinks make it difficult to treat the patient;
- When green diarrhea is diagnosed, it is forbidden to drink alcohol.
The following products are used to help the patient recover during digestive disorders:
- crackers and biscuits that benefit patients at any age;
- dried black bread helps reduce the frequency of bowel movements;
- jelly with blueberries eliminates complications of severe diarrhea;
- strong tea can speed up recovery when greenish diarrhea appears;
- Bird cherry decoction has the same properties;
- It is permissible to eat baked apples and bananas.
If the patient’s general condition has improved, then lean meats can be included in the menu. It is optimal to pass it through a meat grinder. This makes it easier to digest food products.
Diseases that lead to green stool
The most common causes of green stool are poisoning, dysbiosis and fermentative dyspepsia.
Poisoning is an acute digestive disorder, which is manifested by fever, diarrhea with green feces, vomiting and nausea. The causes of poisoning may be:
- low-quality products, which lead to the proliferation of pathogenic microflora;
- poisonous mushrooms;
- intoxication of the body with toxic substances found in alcohol, medications, plants, etc.
In case of poisoning, the stomach should be emptied of contents by lavage, general intoxication of the body should be eliminated with the help of medications and water balance should be restored.
Fermentative dyspepsia is a digestive disorder caused by a large amount of carbohydrates with coarse fiber in the diet, as well as a decrease in the amount of gastric juice.
The appearance of dyspepsia is also accompanied by poor chewing of food, eating at a fast pace, and drinking carbonated drinks. Symptoms of the disease appear as follows:
- bloating;
- feeling of transfusion and rumbling in the stomach;
- constipation and diarrhea;
- light green stool.
To eliminate discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract, it is necessary to adhere to a protein diet for 7-10 days with the exception of vegetables and fruits, since foods with a large amount of fiber (white cabbage, apples, etc.) provoke increased gas formation.
Dysbacteriosis is a violation of the digestion of food in the intestines due to a lack of lactobacilli and an excess of putrefactive bacteria.
The development of dysbiosis is accompanied by abdominal disorders, bloating, and abdominal pain. In addition to the change in the color of the feces to yellow and green, you can see many undigested pieces of food in the stool.
To eliminate symptoms, pre- and probiotics are used to replenish beneficial lactobacilli, and you should also follow a special diet to maintain normal microflora.
Drug therapy
When the cause of green diarrhea is an infection, treatment requires serious medication.
The doctor must prescribe the following medications:
- Antibiotics. The most commonly used drugs include Amoxicillin, Metronidazole, and Tetracycline. However, knowing about the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, the doctor is able to prescribe other medications. The course of treatment usually lasts a week, and even if you feel better on the 2nd day after therapy, you should drink them to the end. You should not purchase antibiotics yourself or carry out self-treatment.
- Probiotics to preserve intestinal microflora. The most popular medication is Linex, although it has a large number of analogues, for example, Normoflorin, Acipol. These drugs are prescribed when the cause of green diarrhea is dysbacteriosis. They have a calming effect on the mucous membrane, reducing inflammation.
- Sorbents. They are drugs that help eliminate poisoning and cleanse the body. These include Enterosgel, Smecta or Polysorb.
The main advantage of these medications is that they stop diarrhea, reduce the formation of gases in the gastrointestinal tract, remove toxic substances and stabilize the patient’s well-being.
What to do
If a green tint to the stool is observed for a long time (from 2 weeks), then it is necessary to identify the exact cause of the pathological processes in the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. For this purpose, laboratory tests should be taken, namely:
- general stool analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- clinical blood test;
- stool culture for dysbacteriosis.
To detect the causes of changes in the color of excrement, a stool analysis is required to determine the following indicators:
- reaction (pH) – alkaline and sharply alkaline (pH more than 8.0) for colitis, acidic (pH less than 5.5) for impaired absorption of fatty acids in the small intestine due to pancreatitis, liver diseases, pancreatic insufficiency;
- the presence of mucus in the stool, which indicates inflammation, infectious intestinal diseases and poisoning;
- blood impurities in stool;
- food residues in the stool indicate reduced stomach acidity;
- reaction to bilirubin.
Bacterial culture of stool when green feces appears is used to detect dysentery and intestinal flu pathogens.
To identify pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, the following is used:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- gastroscopy;
- intestinal colonoscopy;
- X-ray examination.
If diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are detected, it is necessary to carry out appropriate drug treatment and adhere to a therapeutic diet:
- for stomach and duodenal ulcers, gastritis - diet 1 table;
- for fermentative dyspepsia and dysbacteriosis - table 4a;
- for enteritis and colitis - diet table 4.
Useful video
A change in the color or content of feces in all cases indicates the presence of malfunctions in the gastrointestinal tract or other systems within the body.
Green diarrhea is a symptom of a large number of diseases, therefore, in order to determine the root cause of its occurrence, it is necessary to consult a doctor in a timely manner and determine what caused its formation.
Green diarrhea in an adult may indicate some dangerous pathological process. Even if there is a slight change in the shade of stool, you should pay close attention to this.
Feces of an uncharacteristic color will be a signal of disorders within the body. To find out why the disease manifested itself, you need to consult a specialist.
During pregnancy
Light green stools during pregnancy can be a dangerous sign of gastrointestinal disease, since the enlargement of the fetus puts pressure on the gastrointestinal tract, which in some cases leads to the following digestive disorders:
- abnormal transit of feces through the large intestine, which is manifested by frequent stools, regular diarrhea with green or yellow excrement;
- colitis - inflammation of the intestines, the symptoms of which are abdominal pain, green stools with mucus, and in severe forms, blood in the feces;
- dysbacteriosis;
- allergy to lactose and gluten.
Also, the reason for the appearance of green excrement is sometimes the use of vitamins and dietary supplements for pregnant women with iron in their composition. Some of the iron is not absorbed and is excreted from the body, causing the stool to turn green.
First aid at home
If the color of stool changes, you should reconsider your diet, excluding sweets and foods rich in chlorophyll and containing dyes from the menu.
If you have diarrhea, you must take Smecta or Regidron. This will normalize water and electrolyte balance and avoid dehydration.
Atoxyl is an excellent sorbent that is used to remove toxins, especially during vomiting. But the drug should be taken after gastric lavage.
In cases of severe dysbiosis, it is useful to take probiotics. If improvements are not observed within several days or the condition is accompanied by a rise in temperature, bloody stools, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, you should consult a doctor.
After conducting a series of tests, the specialist will make a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment. These can be anti-inflammatory, antibacterial drugs, antispasmodics, vitamin complexes. In case of internal bleeding, urgent hospitalization followed by surgical intervention is indicated.
Lack of digestive enzymes
Colorless or yellow-white feces are observed when the process of bile entering the intestines is disrupted. Moreover, the more serious the problem, the lighter the stool. Obstructions can be all the way from the gallbladder to the duodenum. Impaired bile expulsion occurs in the following cases:
- dyskinesia of the gallbladder (too strong or, conversely, weak contraction),
- constipation (creates tension in the intestinal wall, making it difficult to secrete bile),
- cholecystitis,
- condition after removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy),
- stones in the gallbladder or its ducts,
- compression of the bile duct by the enlarged head of the pancreas (tumor, edema, inflammation) lying next door.
A characteristic combination of these disorders is light yellow stool and dark urine. This means that bilirubin, instead of entering the intestines, is absorbed into the blood and excreted in the urine.
After removal of the gallbladder, the control of bile flow is impaired, so some portions of stool may be lighter than others. With cholecystitis, as well as cholelithiasis, in addition to the discharge of yellow-white feces, sharp pain is observed under the ribs on the right side after alcohol or fatty foods.
When consuming a large amount of fats or their breakdown is impaired (decreased activity of the pancreas), we observe loose yellow feces with the presence of a gray coating. This type of fatty, oily stool is called steatorrhea. Undigested fat in the intestines envelops the food bolus and prevents enzymes from breaking down proteins and carbohydrates.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of liquid green feces, you must follow simple rules:
- undergo an examination of the body at least once a year in order to promptly detect the presence of hidden pathologies;
- eat right: exclude fast food, alcohol and an abundance of fatty, fried foods;
- take medications only as prescribed by a doctor;
- exercise moderate physical activity;
- Maintain hygiene: wash your hands thoroughly before eating and after visiting public places.
The health of every person is in his hands. The percentage of hereditary severe pathologies is extremely small, and if you maintain the condition of your intestines in a normal manner, then it will work like clockwork, and the problem of diarrhea and green feces is unlikely to arise.
Source: stomach-info.ru
Unhealthy gut?
Among the intestinal causes that lead to changes in the color of stool in an adult, Crohn's disease stands out. This is an autoimmune disease in which ulcers form in the intestinal mucosa. Crohn's disease is characterized by yellow-gray mushy stool, often foul-smelling with white flecks. If you see balls or lumps in white stool, and the stool is formed, then the reasons for such inclusions may also be:
- inflammation of the colon (mucus with white inclusions),
- antibiotics,
- candidiasis (veins of fungal colonies resemble a whitish coating),
- dead pinworms.
Pasty stool in adults is observed with intestinal infections of viral origin. The most common causative agent of this infection is rotavirus. You can “catch” it by consuming dairy products or by contact with a sick person. Rotavirus also causes acute respiratory infections, so you can get sick by getting infected by sneezing.
Necessary examinations and treatment
The condition in which the stool turns green cannot be ignored. We need to find the cause of this phenomenon. If something green was eaten the day before, and the general condition was not disturbed, then there is no reason to worry. However, if objective symptoms of intoxication or inflammation appear (nausea, diarrhea, headache, abdominal cramps, temperature), medical attention is needed, sometimes emergency.
Dangerous conditions that require immediate action include salmonellosis. The infection quickly provokes dehydration and can cause toxic shock and death. If you have symptoms of salmonellosis (vomiting, diarrhea, pain in the lower abdomen, fever, foul-smelling stools of all shades of green), you need to call an ambulance. Before the arrival of doctors, it is necessary to give the patient sorbents orally and provide plenty of fluids. Do not hesitate in case of intestinal bleeding. This condition threatens human life. You need to promptly call an ambulance, explaining to the dispatcher the reason for the call. The patient should not be given anything until the doctors arrive. You need to lay it horizontally with a cushion under your head and cold on your stomach, this will reduce the bleeding.
Necessary research
If the pathology does not require emergency care, then you need to contact a specialist to determine its cause. The clinic will conduct a full clinical and laboratory examination, which includes:
- UAC and OAM.
- Blood chemistry.
- Bacterial culture of feces or vomit on nutrient media.
- Ultrasound, CG or MRI of the abdominal organs.
- ECG.
- Colonoscopy.
- FGDS.
- Determination of blood electrolytes.
The examination is prescribed by the doctor on an individual basis, so the list can be supplemented or shortened depending on the suspected pathology. In parallel with the examination, treatment is usually prescribed. If the patient is hospitalized in a hospital, then examination and treatment are carried out under the supervision and careful supervision of a doctor.
Treatment
Therapy for green stool depends on the cause of the pathology, its severity and the general condition of the patient. Salmonellosis, food poisoning, and acute intestinal infections require hospitalization in the infectious diseases department of a hospital. Bleeding - to surgery. Treatment is comprehensive and consists of:
- A diet with the exclusion of alcohol, which is prescribed by a doctor on an individual basis (fasting is one of the options).
- Antibiotic therapy with preliminary culture of feces or vomit on nutrient media to identify the pathogen and determine its sensitivity to antibacterial therapy. Before receiving the results, two antibiotics from different pharmacological groups are prescribed at once to ensure the widest possible spectrum of action on pathogenic microbes.
- Choleretic agents, which are designed to eliminate congestion in the biliary system of the liver (chophytol, allohol).
- Detoxifiers that remove toxins and waste from the body (Polysorb), antidiarrheal drugs (Smecta).
- Probiotics, prebiotics, symbiotics that restore normal intestinal microflora (atsipol).
- Droppers with saline solutions, glucose, plasma, stopping dehydration, restoring blood loss.
- Symptomatic remedies.
In severe cases, direct blood transfusion, plasmapheresis, hemodialysis and surgery are possible. Self-medication is unacceptable and can lead to the most dire consequences, including death.
Changes in the color of stool do not only occur in children. Green stool in adults is often a cause for concern; the reason for the change in color of stool depends on many factors.
Healthy stool has a well-shaped appearance and medium consistency. Normal feces are brown, brownish-yellowish, or light brown in color. Feces do not emit the smell of rot, decomposition or fermentation.
What disorders can cause yellowish or orange stool?
If you have practically ruled out the influence of food on the coloring of stool, then you need to become familiar with diseases that may be accompanied by a change in the color of stool in an adult. And this will allow you to quickly respond to the development of the disease and receive qualified help in the early stages of the disease.
In this case, the light yellow color of stool appears due to the fact that these organs do not produce the enzymes necessary for digestion. This prevents the body from absorbing nutrients from foods. This can occur when liver cells are destroyed and stones form in the gall bladder. With this clinical picture, yellowing of the stool occurs, and the person begins to experience pain in the areas where the organs are located.
The pancreas takes an active part in the digestion process, so any disorders and diseases lead to bad consequences for the whole body. Light yellow stool can be an indicator that a person has pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, or gland cancer. This phenomenon may also accompany blockage of the ducts.
Celiac disease
When asking why stool is light yellow in color, it is worth remembering that the foods we eat often contain gluten. Its high concentration is observed in barley, rye and wheat grains. Excessive content of this substance in the body leads to a decrease in the immune function of the body and the enveloping of the stomach walls with gluten, and this does not allow nutrients to be absorbed. In this case, a number of other symptoms are observed:
- Nausea.
- Bowel problems (constipation or diarrhea).
- Fatigue.
- Unreasonable headache.
- Skin rash.
- Excessive formation of gases.
- Reduced bone density.
If this problem is identified quickly, then complex therapy will not be needed - simply a dietary diet will be selected. But a complex form of the disease will require thorough long-term treatment.
Gilbert's syndrome
This disease is genetic and its essence lies in the body’s excessive production of too much bilirubin, which causes the orange color of stool. There is no specific therapy for this disease, however, specialists can constantly monitor the functioning of the digestive system and prevent the development of associated disorders. In this case, the child has orange stools almost from infancy.
This disease is characterized by the colonization of the gastrointestinal tract by parasites. They penetrate with food and drink. In this case, there may be yellow stools or orange-colored stool, and in addition to this there is another group of disorders:
- Vomit.
- Nausea.
- Diarrhea with a strong unpleasant odor.
- Skin rashes.
- Severe headaches.
- Sudden weight loss with a normal diet.
Giardiasis is detected by examining stool in the laboratory. Treatment of the disease is often carried out by taking antibiotics for several weeks. It is extremely rare that the disease becomes chronic.