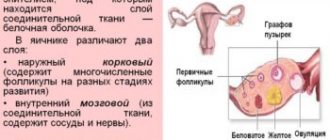
The ovarian reserve is a reserve of viable follicles in the ovaries, which can subsequently develop, causing the ovulation of the egg and making further pregnancy possible for the woman.
ovulation
Basically, the ovarian reserve indicator is established in women who, for one reason or another, cannot become pregnant, and have been diagnosed with infertility. If, after the test, a woman’s indicator is reduced, we can say that specialized treatment and further attempts to become pregnant are unlikely to bring any results. The chances of pregnancy for a woman who has been diagnosed with problems after the study become less and less every year, therefore it is advisable to apply for the IVF .
The level of ovarian reserve is also determined before the procedure of artificial ovarian ; the result of the analysis allows you to select the most effective treatment regimen.
In some cases, the analysis is prescribed to patients who are experiencing irregular menstruation, or who are planning surgical treatment of diseases of the uterus or appendages in the near future.
It is customary to define what ovarian reserve is in several terms:
- Doctors consider the reserve to be the number of follicles in a woman’s body that are able to respond to stimulation.
- The number of oocytes that are in a woman’s body depending on the age at which the test is taken).
Stages of follicle development
It is customary to distinguish several stages of normal development of follicles in the female body:
- Stage zero type. In the body of a female child, follicles of this type appear in the early stages of pregnancy after the child is conceived. By the time it is time to give birth, the number of follicles in total exceeds two million.
- Primary. Follicles of the zero stage gradually begin to develop; about 10 zero follicles turn into primary follicles by the time a girl reaches puberty. The stage is also characterized by a sharp decrease in the number of cells from 2 million to 300 thousand due to the natural process of cell death occurring in the body.
- Secondary. Estrogens begin to be released into the follicular cavity, at this stage the follicle begins to actively increase in size.
- Tertiary . In the follicle on the ovarian mound, the egg . At this stage, the cell is considered by doctors to be fully mature.
Where do eggs come from?
The laying of the genital organs in the embryo occurs at an early stage of development. But by the 10th week, the female fetus has formed ovaries. By week 12, primordial follicles form in them. They consist of oocytes - primary germ cells. They divide intensively during the fetal period of development.
Their number begins to decrease with puberty. During ovulation, most often one mature egg is released, ready for fertilization. If this does not happen, it is washed out along with menstrual blood. Gradually, with age, the follicular reserve of the ovaries decreases.
Oocyte loss occurs evenly throughout life. But the ovarian reserve for a 37-38 year old woman is already significantly lost, and the rate of its decline at this age is accelerating. Although there are more than 10 years left until menopause.
The quality and quantity of eggs in the follicular reserve is extremely important. The reason for the decrease in ovarian reserve is a natural physiological process. The optimal childbearing age is 20-30 years, that is, after 30 years, the likelihood of getting pregnant is reduced by 2 times. Pathological conditions, inflammatory reproductive diseases, unhealthy lifestyle, adverse effects on the ovaries and other processes cause a decrease in reserve.
Genetic predisposition implies some kind of disorder in the female line. For example, various menstrual disorders, infertility, early menopause, or problems with gestation and pregnancy that were observed in the mother, grandmother or sisters.
A decrease in the initial reserve is caused by severe pregnancy:
- gestosis conditions;
- intrauterine fetal hypoxia;
- infection.
Intoxication of the body is a factor in reducing ovarian reserve. This is explained by the fact that regular contact with toxic substances is the result of the appearance of chronic intoxication. Industrial waste, agricultural chemical solutions, occupational hazards and household toxic components are causes of egg damage.
Premature ovarian failure syndrome, a condition that is manifested by amenorrhea for more than 4 months, under the age of 40, high levels of pituitary gonadotropins, especially FGS (follicle-stimulating hormone) and a decrease in estrogen in the blood. This syndrome adversely affects the ovarian tissue, resulting in its depletion.
Radiation rays negatively affect the function of a woman’s reproductive system. There are factors that contribute to damage to ovarian function:
- age of the woman receiving therapy;
- dose of radiation (4 Gray rarely causes changes in the functioning of a woman’s ovaries, and a dose of 5 to 10.5 Gray over the age of 40 contributes to the appearance of persistent menopause);
- localization of irradiation.
Chemotherapy, in some cases, causes irreversible menopause. Influencing factors:
- patient's age;
- drug dose;
- the selected drug (antimetabolite cytarabine, melphalan, cyclophosphamide, vinblastine and others).
If inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system (acute endometritis, adnexitis, oophoritis, salpingoophoritis, endometriosis, adenomyosis) are not treated in a timely manner, the inflammation becomes chronic, leading to changes in blood supply, immunological disorders and ultimately cell death.
Surgical interventions on the pelvic organs have a strong impact on the reduction of ovarian reserve. Women very often have a history of undergoing surgery for infertility, as well as other female reproductive diseases. An operation such as ovarian resection significantly reduces the reserve.
What are the reasons for decreased ovarian reserve?
Assessment of ovarian reserve , which showed deviations from the standard after the analysis in the direction of decrease, may be associated with a number of factors:
- The number of follicles decreases for natural reasons as a result of the aging of the body. The decline is triggered by regular ovulations;
- Once all the eggs in a woman’s have been used up, the period of menopause begins. With each year of a woman’s life, the quality of oocytes decreases, the likelihood of developing chromosomal and genetic pathologies in eggs increases;
- The number of eggs can fluctuate in women depending on the genetic and hereditary characteristics of the body. As a result, some women continue menstruation and the ability to become pregnant until they are 50 years old, while other patients experience menopause after 30 years;
- The patient underwent surgery to treat a particular disease. Surgeries on the organs of the female reproductive system can affect the level of follicles in the body;
- Most medications have a negative impact on female sexual health. In addition to medications, dangerous environmental conditions in the area of residence and consumption of unhealthy foods also have a negative impact;
- Long-term smoking. It has been proven that the longer and more a woman , the faster she experiences menopause;
- Some diseases, such as diabetes, can also provoke a decrease in ovarian reserve.
Hormonal tests
If the follicular reserve is reduced, then a natural question arises as to how to find out how many eggs a woman has left. For this purpose, modern medicine has many different laboratory tests. Next, we will analyze in detail each hormonal analysis for the supply of eggs that doctors can offer.
FSH in the follicular phase. This study is the best way to determine the depletion of the ovarian reserve. During the period when a woman has already reached menopause, the levels of this hormone are more than 30 mIU/l. If the supply of germ cells is sufficient, then after the study the indicators will be set from 3 to 8 mIU/l.
In some cases, approximately 5-6 years before the onset of menopause, when performing an FSH test, if a woman has a regular menstrual cycle, there may be a slight increase in normal values, which indicates that the woman’s egg supply is reduced. If the patient is over 35 years old and was tested for FSH in the first phase of the cycle, if the reading is more than 10 mIU/L, it can be said that insufficient stimulation was performed.
If the fluctuations in the indicators are significant, this will indicate that the follicular reserve is decreasing. As for the reaction to insufficient stimulation of the ovaries, it is worth considering an insufficient amount of luteinizing hormone on the third day of the cycle.
Estradiol. The presented egg test determines the norms of this hormone with good and poor ovarian reserve. If the patient has a reading of 250 pg/ml or more, then doctors diagnose a decrease in ovarian reserve, even if the FSH readings are within normal limits. If a woman aged 38-42 years has been identified with a decrease in ovarian reserve, treatment, provided that it is determined to be less than 80 pg/ml on the third day of the cycle, will be successful.
Inhibin B. The level of this hormone should be determined on the third day of the cycle. Thanks to it, you can predict how effective the drug stimulation of ovarian ovulation will be. If there is a small amount of inhibin B, then the FSH level will increase earlier than expected, and accordingly, the body will respond poorly to stimulation.
Anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH). Another fairly effective test for the number of eggs. If a low level of this hormone is detected in the body, we can say that there are very few germ cells left in the ovaries, and accordingly, there will be a poor response to drug stimulation of ovulation.
Before performing in vitro fertilization, specialists must perform an AMH test, and normal values should range from 1.2 to 5 ng/ml. If the results show 0.8 ng/ml or less, it means that the woman has very few eggs left, and the likelihood of pregnancy will be extremely low, but the possibility of fertilization and conception is not excluded.
Methods for determining ovarian reserve
There are several methods for determining ovarian reserve.
Ultrasonography
The body examination should be carried out from 1 to 4 days after the start of menstruation. The technique allows you to determine the number of small follicles that are located in each ovary . In normal condition, the average number of follicles ranges from 11 to 25 pieces. The data obtained as a result of the study helps predict when a woman will begin menopause and up to what age she will be able to successfully conceive a child.
FGS level
The level of FGS in a woman’s is determined 2 or 3 days after the start of the menstrual cycle . FGS is a female sex hormone that is produced by the pituitary gland and directly affects the process of growth and maturation of follicles until ovulation.
Indicators may indicate:
- At the onset of menopause – FGS is above 30 IU/l;
- A normal ovarian reserve is considered to be between 3-8 IU/l.
If a woman over 35 years of age has an indicator of ovarian reserve determined using this method that is within the normal range, additional examinations are prescribed.
Inhibin level
The analysis is taken 2 or 3 days after the start of the menstrual cycle . A decrease in the level of inhibin in the blood indicates a decrease in the number of viable follicles, as a result, doctors can conclude that the ongoing hormonal therapy will not bring the desired result.
Reserve assessment
Ovarian reserve, an analysis of their balance, should be performed on women who have reached 35 years of age. If you do not give birth to a child before this time, problems with pregnancy will subsequently arise, since not only the number of germ cells decreases, but their quality also suffers. Also, during fertilization, the likelihood that the embryo will attach to the wall of the uterus is low.
Assessment of ovarian reserve is indicated for the fairer sex in the following situations:
- Previous chemotherapy treatment;
- The presence of infertility, the nature of which has not been established;
- In the future, assisted reproductive technologies will be implemented;
- If a decision is made about the need to treat menorrhagia during premenopause.
The ovarian reserve, if it decreases, will be the likely reason that in vitro fertilization will not result in pregnancy. The fact is that the main task when performing IVF is to obtain the maximum number of germ cells suitable for fertilization, starting from 9-13, then 7-11 and finally 5-9. If the supply of eggs is low, then you may not get enough of them during puncture.