The article will talk about treatment methods and ways to prevent food poisoning in adults.
Perhaps, at least once in our lives, each of us has encountered food poisoning. This, at first glance, not a serious disease has a number of unpleasant symptoms: nausea, weakness and vomiting.
If food poisoning is not cured in time, you can get serious illnesses that can be treated with IVs and injections. In order not to delay such treatment methods, it is necessary to identify poisoning in the early stages. Sometimes the symptoms of poisoning are mild, difficult to recognize and can be mistaken for a mild illness.
You need to know the symptoms of such a disease in order to provide timely help to yourself and your family members. If food poisoning is accompanied by severe symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
.
What can cause food poisoning in an adult?
Food poisoning is quite common in adults. All due to the fact that people do not monitor the correctness of their diet. There are several most common causes of food poisoning, which can be divided into 3 groups:
- Food poisoning caused by pathogens. In this case, microbes, which are called toxin infections, enter the human body along with food. Such microorganisms may have a fungal or bacterial environment. Their main mission is to force people to destroy their colonies. Therefore, the main symptoms of this type of poisoning are severe vomiting and diarrhea.
- Food poisoning caused by poisons. Some plants, mushrooms and even animals contain substances that are toxic to the human body. By consuming such products without proper processing, a person’s internal organs can be damaged, even resulting in death. Such poisonings include: poisoning with mushrooms (fly agarics, toadstools and other species), plants (belladonna, belladonna, wolfberry), some species of animals and fish
- Food poisoning caused by chemicals in food. Sometimes, when we consume food, we do not know what harmful substances are contained in them. The most common poisonings are pesticides and nitrates.
Causes of food poisoning
One of the world's "high-profile" cases of food poisoning: In Germany in 2011, about 4,000 people were hospitalized as a result of mass poisoning, 53 of whom did not survive. It took several months to trace the source of the infection. As a result of numerous studies, the cause of the outbreak of food poisoning was established - it turned out to be fenugreek seeds imported from Egypt, the sprouts of which are used as a seasoning for dishes. Food poisoning is common. The peak incidence occurs in the warm season. Food poisoning in an adult is provoked (symptoms and treatment will be discussed below) by various microbes and bacteria, the toxins they secrete and their metabolic products (exo- and endotoxins), as well as non-microbial poisoning (toxic products).
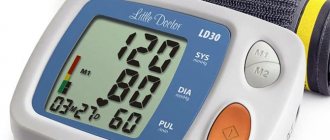
Fever in food poisoning in adults
Fever occurs due to toxicity in the body. By raising the temperature, the body wants to overcome pathogens or poisons that have entered the body. In the first stages of poisoning, the temperature will be about 37 degrees. Later, if microbes penetrate from the food tract into the blood, the temperature will rise sharply. Even a slight increase in temperature in combination with nausea requires attention.
Reasons for the development of poisoning
There are many factors that provoke intoxication of the body. The most common is the consumption of food or water filled with microbes and harmful bacteria that can negatively affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. These are mushrooms and berries collected in an environment with unfavorable conditions for their growth (near factories, highways).
Important! Poisoning is also caused by microorganisms that are dangerous to life and health, such as E. coli, staphylococcus, salmonella and various viruses found in the food consumed.
What to do if you have food poisoning in an adult?
If food poisoning occurs suddenly and there is no way to see a doctor, you need to give yourself first aid before going to the hospital.
- The first thing to do if there is no vomiting is to induce it. This is necessary so that the stomach is cleared of toxins and they do not penetrate further into the body. It is best to rinse the stomach with warm boiled water. Also. You can dissolve a crystal of potassium permanganate in it so that the solution acquires a pinkish color. 1 liter of this solution is enough. To rinse, the patient must drink the prepared liquid in small sips over a short period of time. This procedure should induce vomiting
- The rinsing procedure causes severe dehydration. Therefore, when the nausea subsides a little, the patient needs to drink mineral water or unsweetened green tea
- If the poisoning is minor, absorbent drugs can be used. For example, activated carbon
- After several hours after the treatment procedures, you need to pay attention to your well-being. If the temperature does not subside and nausea continues, you should immediately consult a doctor.
- In case of poisoning, it is not recommended to take antibiotics and other strong drugs on your own, without the advice of a doctor.
- Do not neglect treatment of poisoning. If this disease is started, the liver and nervous system may begin to be damaged, and infection of the blood and internal organs may occur.
Basics of first aid before paramedics arrive
If the first symptoms of food poisoning develop, you should immediately call emergency medical help . By phone, inform the dispatcher of the patient’s symptoms and name your exact location.
Remember that if it is not possible to call a doctor at home, you need to urgently go to the hospital yourself. Self-medicating poisoning is very dangerous. Only an experienced doctor can accurately diagnose and prescribe correct, effective treatment, so you should seek his help as quickly as possible.
Immediately after calling doctors, you need to begin providing independent assistance. It can help relieve intoxication and remove some toxins. In cases of severe poisoning, the prognosis of survival of the injured person depends on first aid.
The main components of first aid are listed below.
Gastric lavage
Gastric cleansing should be carried out as quickly as possible after the first clinical signs of food poisoning appear. This procedure helps to stop the increase in intoxication and remove the remnants of spoiled food, the toxins of which have not yet entered the bloodstream.
To cleanse the stomach yourself at home, you should drink a liter of ordinary clean water at a neutral temperature in one gulp. Then you need to provoke vomiting. This can be done the “folk” way by pressing your two fingers on the back of the tongue. In order to completely rinse the gastric cavity, you need to repeat this procedure several times.
Remember that gastric lavage is strictly prohibited if dark vomiting develops or the patient’s consciousness is impaired.
Previously, it was believed that cleansing the stomach was best done using a solution of potassium permanganate. According to recent studies, this substance is ineffective and dangerous and can cause burns to the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus.
Colon cleansing with an enema
The enema is performed using plain water.
It is done until the intestinal waters are clean. The temperature of the rinsing water should be room temperature. The use of cold or warm water for an enema is prohibited. Colon cleansing is an effective method of quickly removing toxins and pathogenic microorganisms that cause poisoning from the body.
Drink plenty of fluids
After gastric lavage, the patient should begin to drink plain or mineral water without gases. You need to drink little and often, a sip every 5 minutes . This is necessary to prevent new vomiting attacks, which at this stage of care will only worsen the person’s condition and increase dehydration.
Sorbents
For food poisoning, you can take any sorbents , for example polysorb, activated carbon, enterosgel, smecta, atoxyl.
Drugs in this group quickly cleanse the intestines of toxins and pathogenic bacteria. They also reduce the severity of diarrhea, thereby preventing the loss of fluid by the body and the development of infectious-toxic shock. Before taking any sorbents, you should check their expiration date and read the dosage calculation rules in the instructions.
What to do if gastrointestinal bleeding begins
If the patient has black or bloody vomit or dark stool (melena), he should be sent to bed and an ice pack should be placed on the stomach area .
Remember that if gastrointestinal bleeding is suspected, the patient should not be given any liquid or medications to drink. Such actions can increase damage to the vascular wall and increase the volume of blood lost.
Actions in case of loss of consciousness
If consciousness is impaired, the patient should be placed on a flat surface. He needs to raise his legs up and turn his head to the side. Before doctors arrive, you should constantly check for pulse and breathing , and if they are absent, immediately begin closed chest compressions.
How to treat food poisoning in adults?
After diagnosing food poisoning, the doctor finds out the cause of its occurrence. Only after this is a comprehensive treatment prescribed:
- Washing the stomach and intestines. In the hospital, these procedures are performed using special devices. Inducing vomiting and diarrhea is the best way to rid the body of food toxins
- Next, the water balance is established. For this purpose, special solutions are used: regidon, citraclucosol or glucosolan. Sometimes you have to use droppers
- After the main procedures, the use of absorbents is attributed, for example, white or activated carbon, polysorb
- If necessary, relieve pain with painkillers
- If rinsing was done late and intoxication occurred, antibiotics are prescribed
- I also attribute drugs that restore intestinal microflora and protect the mucous membrane
Description and manifestation of possible complications of food poisoning
Food poisoning can lead to severe complications from internal organs. The risk of their development is reduced if there is a minimum period of time between the appearance of the first symptoms and treatment.
A list of pathological conditions that can complicate food poisoning is presented below:
- Gastritis is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa, which can be caused by toxins and bacteria that come from spoiled food. With gastritis, heartburn, vomiting, pain in the stomach, and belching develop. Body temperature may rise.
- Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. This complication develops especially often with the abuse of fatty foods and alcohol. Acute pancreatitis can only be treated surgically. It is characterized by a sharp increase in temperature, the appearance of girdling pain in the abdomen and purple spots in the navel area.
- Acetone syndrome is an increase in the level of ketone bodies in the blood. This condition develops mainly in children under 10-12 years of age. A characteristic symptom is the appearance of the smell of acetone from the child’s mouth and urine. Acytonemic syndrome is accompanied by damage to the pancreas.
- Infectious-toxic shock is a critical condition that occurs against the background of severe intoxication and severe dehydration. The patient's blood pressure drops sharply, shortness of breath, tachycardia occurs, and consciousness may be impaired.
- Acute kidney failure can develop when eating poisonous mushrooms. It is characterized by the development of anuria (lack of urine) and edema throughout the body. The patient develops bad breath and the skin may turn yellow.
- Gastrointestinal bleeding most often occurs during poisoning in people who suffer from peptic ulcers or chronic gastritis. Profuse vomiting and toxins can disrupt the integrity of the vessel in the submucosal ball of the stomach or duodenum. Internal bleeding is characterized by the appearance of black vomiting and diarrhea , pale skin, tachycardia, low blood pressure, and hypothermia.
- Malfunction of the liver or gall bladder is manifested by pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, jaundice of the skin, and fever.
Folk remedies for food poisoning
Folk remedies are not the main method of treatment. However, they can have an auxiliary therapeutic effect. You can use any of the traditional medicines only after consulting a doctor.
- Eating foods rich in vitamin C will reduce the feeling of nausea. You can use lemon juice. But it is recommended to add it to foods or tea; pure juice can harm the affected gastric mucosa.
- In case of poisoning, it is recommended to use a decoction of dill with honey. It is best to use dill seeds for the decoction. But, if they are not available, dry herbs will do.
- Ginger also works well against poisoning. To use it, you need to pour a teaspoon of dry root with a glass of hot water. Then, apply a tablespoon of solution three times a day
- If you have food poisoning, it is recommended to drink plenty of fluids. Water, green tea, rosehip decoction will do.
- Chamomile is a mild and harmless antiseptic. You can prepare delicious and aromatic medicinal tea from chamomile, mint and lemon balm.
- According to folk medicine, there are special points on the human body that can improve well-being, overcome nausea and weakness
Signs of a pathological condition
In most cases, a child experiences acute food poisoning, characterized by pronounced symptoms that appear two hours after ingesting expired products. In an adult, intoxication of the body takes longer to develop. Symptoms can appear even after 10 hours, or even a day later.
The clinical picture of food poisoning consists of the following signs:
- constantly increasing headaches, dizziness;
- feeling of constant thirst, dry mouth;
- bloating and pain in the lower abdomen;
- problems with urination;
- increased body temperature, sometimes up to 39 degrees;
- lack of desire to eat;
- sudden vomiting and diarrhea;
- development of hypotension;
- muscle pain and weakness;
- increased salivation and sweating;
- general malaise, weakness;
- change of skin color to blue.
In children with food poisoning, disruptions in the functioning of the heart and kidneys are observed. This condition threatens the life of the baby, especially if she is under one year old. Therefore, at the first signs of intoxication in a baby, call emergency help. Self-medication here will not bring results or, worse, will aggravate the situation.
Pregnant women experience food poisoning in the same way as all adults. Against the background of toxicosis, the clinical picture can be expressed more clearly, which brings more discomfort to the woman in this situation. It is important to take timely measures so that thrombosis does not develop or the uterus does not begin to contract strongly.
Otherwise, such a deviation does not pose a threat to the health of the mother and baby. Self-medication with folk remedies during pregnancy is excluded. Therapy should be carried out exclusively under the supervision of a physician. It is important to adhere to a strict diet.
When a person is poisoned and has the following symptoms, you need to urgently call an ambulance:
- diarrhea and vomiting with blood;
- slow pulse, convulsions;
- raising body temperature to 40 degrees;
- swelling of the arms, legs, face;
- clouding of mind;
- hard breath;
- muscle weakness (an adult cannot hold even light objects in his hands, a child is not able to hold his head upright).
Such a clinical picture without the necessary medical care leads to a comatose state of a person.
Diet for food poisoning in adults
With food poisoning, the human digestive system is extremely weakened. By treating and washing, all beneficial bacteria and enzymes are removed from it. Therefore, it is recommended to follow a special diet in case of poisoning.
- In case of poisoning, it is recommended not to overload the digestive system with an abundance of food. It is better to eat 4 - 6 times a day in small portions
- In the first days of poisoning, you need to exclude fatty foods and even vegetable oils from your diet. During the entire treatment period, it is not recommended to consume fatty meat and fish.
- You can’t eat fast food and processed foods
- You need to reduce carbohydrates in your diet. Some fruits can cause fermentation processes in the intestines. However, you cannot completely give up carbohydrates.
- Food should be less frequent than with a normal diet. Eating soups and low-fat broths is beneficial
- It is recommended to boil and steam food
- It is better not to eat heavy foods such as nuts and legumes during poisoning.
Treatment
Prompt first aid is the key to successful treatment
The effectiveness of treatment for any ailment largely depends on how quickly first aid was provided to the victim. Therefore, let’s get acquainted with the basic recommendations on what to do if you are poisoned by food.
Gastric lavage
A manganese solution is often used to lavage the stomach.
If less than half an hour has passed since the ingestion of the poisoned product, then treatment should begin with gastric lavage. In this way, it will be possible to remove toxins that have entered inside, and they will not have time to be absorbed into the blood.
After this procedure, attacks of vomiting usually stop, so it makes sense to take medications.
Taking enterosorbents
Taking enterosorbents is important in the first hour after exposure to toxins.
The main treatment for food poisoning at home is the use of enterosorbents. Such drugs are usually completely harmless, they do not require a doctor’s prescription, and most of them can be used even in children from the first month of life.
Important: Before taking any drug yourself, be sure to read the list of contraindications, which always contains instructions for use.
Currently, there are a lot of sorbent drugs, but their main effect boils down to one thing: these drugs sorb toxic substances on their surface and remove them from the body.
Rehydration
Rehydrants are needed to prevent dehydration.
The next stage in the treatment of poisoning is the restoration of water and electrolyte balance. Vomiting and diarrhea contribute to the development of dehydration, so fluid restoration is vital.
But what should you drink if you have food poisoning?
The best way to restore fluid is to take special rehydration medications. These medications help quickly and effectively replenish not only the loss of water, but also electrolytes. Their price is low, so it is better to take care of their availability in your home medicine cabinet in advance.
Restoration of microflora
Violation of intestinal microflora leads to decreased immunity.
Another important component of the treatment of food poisoning is taking medications to restore the microflora, since any eating disorder contributes to the development of dysbiosis. Disruption of microflora always causes discomfort and delays recovery. And special preparations, prebiotics and probiotics can speed up this process. They have a natural composition and most of them are used even in children from birth.
Typically, the groups of drugs listed above are sufficient to treat most food intoxications. In combination with them, a special diet is prescribed for food poisoning, which allows you to recover much faster and return to a full life. The table below shows photos of the most popular drugs from each category.
| Therapeutic group | Trade names |
| Enterosorbents | Activated carbon Enterosgel |
| Rehydrants | Regidron Hydrovit |
| Probiotics | Acipol |
| Prebiotics | Duphalac |
You should always have at least one drug from each group of medications listed in your home medicine cabinet. This will allow you not to waste time and provide assistance to a poisoned victim much faster.
How to eat after food poisoning as an adult?
When the poisoning is cured, you need to follow a few tips to prevent the disease from recurring:
- Do not eat foods that have expired or that smell or look stale.
- Don't drink raw eggs
- When marinating or salting foods, you must follow the cooking technology
- Do not eat food purchased in stalls or on the street (for example, pies, pasties and puff pastries)
- It is necessary to wash your hands before eating and wash dishes thoroughly
- Do not forget that it is necessary to wash vegetables and fruits before eating.
- Do not eat unfamiliar mushrooms and plants
Dietary food for poisoning
For several days after intoxication with low-quality food, you need to eat liquid food. For example, mashed potatoes, milk porridges. It is better to exclude fibrous foods for now. You can eat a cracker that has been previously soaked in water or tea. Portions should be small so that the stomach and intestines do not stretch. It is prohibited to consume carbonated drinks, yeast products, corn, legumes and whole milk. In general, all foods that can cause bloating, or after which nausea may occur.
After food poisoning, you can eat salted rice porridge. It quickly removes waste and toxins from the body. Buckwheat and oatmeal have the same effect. You need to drink as much as possible. Teas and decoctions of medicinal herbs will be useful. Coffee, strong black tea and alcohol should be excluded.
Intestinal poisoning significantly spoils the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract, so there is a list of products that quickly normalize its condition:
- wheat flour crackers;
- bananas, apple puree;
- baked or boiled vegetables;
- rice, oatmeal;
- vegetable puree soup;
- steamed fish cutlets;
- green tea;
- dried fruits compote.
Important! After intoxication of the body, all sour, pickled, over-salted and spicy foods, butter, fermented milk products, as well as semi-finished products, baked goods, alcoholic drinks and soda are excluded.
How to cure food poisoning in adults: tips and reviews
- During the summer, the number of food poisonings increases. Monitor the safety of food, put food in the refrigerator on time
- Do not delay treatment of poisoning. There is no need to wait for the morning if nausea and fever appeared in the evening. Urgently rinse your stomach and drink activated charcoal
- It is necessary to figure out what product caused the poisoning. It is necessary to throw away spoiled or harmful product so that other family members do not suffer
- After providing first aid, be sure to go to the hospital. Food poisoning can easily be confused with E. coli, jaundice or other infectious diseases
- Follow your diet and drink plenty of fluids to speed up the treatment process.
With the right approach, curing food poisoning is quite simple. From now on, you need to be more careful about the food you eat.
Rare symptoms
Severe visual impairment can also be a symptom
But the clinical picture of food poisoning does not always fit into the framework of the listed signs; in some cases, for example, when confronted with neurotoxic poisons, other symptoms appear:
- visual impairment;
- diplopia (split objects);
- violation of muscle tone;
- fainting;
- increased salivation (hypersalivation);
- neurological disorders (hallucinations, delirium, coma, etc.);
- paresis or paralysis.
Toxic infections such as salmonellosis, listeriosis and botulism are considered especially dangerous in this regard. In order to suspect something is wrong in time, let’s take a closer look at the signs of each of these dangerous food infections.
Important: These diseases often cause death, so treatment for food poisoning in this case should be started as early as possible.
Signs of salmonellosis
The main source of salmonellosis infection is eggs.
Salmonellosis is an acute intestinal food infection caused by microbes of the Salmonella genus. Its symptoms usually begin within a few hours after ingesting contaminated food, but in some cases the disease may begin only after 1-2 days.
Poisoning develops quickly and can manifest itself in different ways, depending on the form of intoxication:
- Gastrointestinal - the most common, characterized by standard signs of food poisoning (nausea, vomiting, pain and bloating in the abdomen), and is also accompanied by hyperthermia and the presence of blood or mucus in the stool. In some cases, severe headaches, delirium, seizures and loss of consciousness may occur.
- Typhoid - is rare, first manifests itself as a common eating disorder with elevated temperature, after which hepatomegaly (enlarged liver) and splenomegaly (enlarged spleen) develop, cough and sore throat, and sometimes a slight pink rash appears on the body.
- Septic fever is the rarest and most dangerous variant, characterized by prolonged fever, which is complicated by the development of purulent foci in various organs and tissues.
With timely diagnosis, salmonellosis can be treated quite quickly. The difficulty is that this toxic infection is often mistaken for a mild eating disorder and medical help is sought when the disease has already reached its peak and becomes dangerous.
Signs of listeriosis
Inflammation of the lymph nodes is a characteristic symptom of listeriosis.
Listeria food poisoning differs from all others in that these microbes can affect lymphoid tissue and the nervous system. This effect gradually disrupts the functioning of many organs, and, if left untreated, can lead to disability or even death.
Listeriosis is characterized by a long incubation period; from the moment the pathogen enters the body until the first signs of the disease appear, it can take from several days to 1.5 months.
Symptoms of listeria poisoning depend on the form of the infection:
anginal-septic
– when the tonsils are primarily affected, which is accompanied by their enlargement, redness, general hyperthermia, pain when swallowing and enlarged lymph nodes. If left untreated, sepsis may develop;
nervous
– manifests itself in neurological symptoms: headaches, delirium, confusion, vomiting, hallucinations, convulsions and seizures. in the form of meningitis, meningoencephalitis or brain abscess. Provokes the development of brain abscess, meningoencephalitis and meningitis;
septic-granulomatous
– occurs mainly in children, first manifests itself in damage to the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. It develops rapidly and ultimately invades the central nervous system.
Listeriosis can only be treated with antibiotic therapy. The specific drug and its dosage are prescribed by the doctor. Therefore, at the first symptoms of such poisoning, you should immediately seek medical help, because the mortality rate from listeriosis is quite high and amounts to 30% of cases.
Signs of botulism
Typically, botulism infection occurs through fish and canned food.
Botulism is a deadly poisoning characterized by rapid damage to the nervous system by botulinum toxin. This is one of the most dangerous natural poisons; it is synthesized by bacteria of the genus Clostridium botulinum. The first symptoms of botulism begin to appear within a few hours after the toxin enters the body, but sometimes the incubation period reaches 10 days.
Symptoms appear in this order:
- visual impairment: double vision, loss of clarity;
- muscle weakness;
- decreased reflexes;
- breathing problems;
- nausea and vomiting;
- stomach ache;
- stool disorder;
- neurological disorders: dizziness, insomnia, headache.
The final symptoms boil down to the development of paralysis, which affects the muscular layers of the internal organs and often leads to death.
Foods that most often cause food poisoning
There is a list of products that, according to statistics, most often cause poisoning. The following vegetables, fruits or dishes not only often lead to illness, but under certain circumstances can also cause irreversible consequences:
- Eggs. Chicken eggs can lead to salmonellosis, a disease caused by the Salmonella bacteria entering the body. This microorganism develops in stale eggs, products with cracks in the shell, and can also remain on the surface of the egg for a long time along with traces of brood hen feces. To reduce the risk of poisoning, it is necessary to thoroughly wash the shell with soap and process the contents thermally at a temperature of at least 70 degrees.
- Raw fish and sushi. Raw fish itself is dangerous, because if purchased from unscrupulous suppliers, it can contain parasites and bacteria. However, sushi is also dangerous because it contains mayonnaise, which quickly spoils. This trendy dish should not be consumed in unverified cafes.
- Not cooked meat. The main cause of poisoning in this group is rare steak. This popular restaurant dish can actually lead to diarrhea and vomiting, and in the long run, a heartworm infection. Carpaccio, thinly sliced raw beef, is also dangerous. It is recommended to avoid eating such foods.
- Oysters. Like raw meat dishes, this product is dangerous due to the lack of heat treatment. The presence of parasites in shellfish is unlikely, but poisoning due to the ingestion of toxins after the expiration date is quite likely.
- Melon crops. Watermelons and melons that appear in June and early July are pumped with a lot of chemicals. In nature, the fruits ripen only in August, and an earlier harvest is dangerous, especially for sensitive people.
- Milk that has not been heat treated. Dairy products sold in sealed packaging in supermarkets are pasteurized. But fresh milk, which people like to drink in villages, can lead to infection with helminths or the entry of pathogenic bacteria into the gastrointestinal tract.
- Smoked meats. Properly smoked meats and cheeses do not pose a danger to the consumer, but poor-quality products can cause serious harm. Some manufacturers save on smoking and, instead of using the correct algorithm, replace some of it by soaking the meat in a special solution. As a result, the buyer simply purchases raw meat under the guise of smoked meat and can easily become poisoned by it.
- Canned food. Homemade preparations are especially dangerous, since they are often created in unsanitary conditions with non-compliance with technology. If the container and its contents have not been properly disinfected by heat treatment, dangerous anaerobic bacteria will develop in the canned food. They can cause botulism.
- Mushrooms. If you pick mushrooms yourself or buy them from retailers, you can get seriously poisoned. The danger is associated with the presence of a large number of “false” mushrooms: false mushrooms, oyster mushrooms, chanterelles. They have an external resemblance to the real thing, but contain dangerous toxins.
Characteristics
A feature of toxic poisoning and food poisoning is a short incubation period, about 2-6 hours, after which rapidly developing manifestations occur in a person.
These diseases usually occur in the form of outbreaks in a group or family among those who have consumed these products.
Even if the appearance and taste are normal, poisoning can still occur because the product may have been contaminated with dangerous microorganisms as a result of being prepared by a sick person.
Type of poisoning
An acute form of illness develops with the consumption of alcohol, drugs, and other harmful substances and products. The reasons are different, as are the provoking factors. At the same time, the pathology develops rapidly, the composition of the blood changes. Today, medicine distinguishes between sources of poisoning in the body. This means that subsequent treatment is also different.
Food
This type of poisoning is considered extremely common. Consumption of low-quality food leads to the ingestion of toxic compounds formed in food. Any product is dangerous. And it doesn’t matter how they were stored, where they were, or how well the temperature was maintained. Once the expiration date has passed, such foods should be taken with caution. Spoiled food creates an ideal environment for the proliferation of pathogenic flora.
The most dangerous are considered dishes prepared from livestock meat: beef, pork. Dairy products, fish, and mushrooms threaten health. As a rule, E. coli and its varieties actively develop in an expired product, causing salmonellosis and dysentery. It is these diseases of infectious origin that become provocateurs of organic intoxication, pathologies that pose a danger to humans.
Escherichia coli under a microscope
Alcoholic liver pathology
Often adults suffer from poisoning after excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages or the alcohol-containing product turned out to be of poor quality. What happens in the body when alcohol gets ingested? First of all, ethanol tends to accumulate and be easily absorbed into the bloodstream. As a result, the toxic substance spreads throughout the internal organs, especially the brain and liver. Not only a person’s consciousness is negatively affected, but also the functioning of vital organs becomes unstable, which leads to a disruption in the general condition of the body.
In medicine, there is a conventional division of alcohol poisoning into three stages:
- Stage 1 – easy. The person is in high spirits, and the condition manifests itself through external signs such as sweating, dilated pupils, and increased urine flow.
- Stage 2 – middle. The patient notes that objects appear double before his eyes, movement is impaired, it is difficult to navigate in space, and control over the limbs is partially lost. The man speaks unintelligibly.
- Stage 3 – severe. Here there are signs of a complex disorder in the functioning of internal organs. It is difficult for the poisoned person to breathe, pathology of the pancreas occurs, the cardiovascular system fails, arrhythmia is recorded, and complete cardiac arrest is possible. Often at the last stage, alcoholic coma occurs, causing disability or death.
The clinical picture of poisoning looks like this:
- A headache appears. When alcohol enters the body, a sharp dilation of blood vessels occurs, which can cause an unpleasant condition, increasing pressure in the head.
- Nausea, vomiting. The phenomenon occurs when the body tries to remove ethanol. Alcohol penetrates the bloodstream and enters the brain, where it begins to negatively affect the cerebellum. This department is responsible for the level position of a person in space. When the functioning of an organ is disrupted, it becomes more difficult to maintain balance, which is why drunk people demonstrate an uneven gait and cannot get up after a fall. Signals are sent from the brain to immediately remove the toxic substance from the body, resulting in nausea and vomiting.
- Feeling dizzy due to improper functioning of the cerebellum under the influence of ethanol.
- The patient is constantly thirsty. This condition appears after the first sips of alcohol-containing drinks. Under the influence of alcohol breakdown products inside, the content of antidiuretic hormone, which regulates the outflow of urine, decreases.
It is worth noting that the negative impact begins after the first glasses or glasses of alcohol. If the drink you drink is of poor quality, the body’s reaction occurs immediately. Alcohol has a similar effect on younger patients: children, teenagers.
The organ responsible for cleansing the blood of foreign compounds is the liver; it is the first to take the hit of alcohol-containing products, allowing the blood to flow through. Toxins and ethanol breakdown products settle in the organ, which leads to dysfunction. If the intake of poison is insignificant, the liver copes with the poisoning on its own and recovers internally. When large doses of alcohol regularly enter the body, the liver malfunctions and the gland needs help.
Intoxication due to cancer
The oncological process spreads inside the body, the cancerous tumor kills new cells that decay, and the decay products disperse to other organs. Also, treatment methods against cancer often become a provoking factor in intoxication. The fight kills not only the harmful and dangerous virus. The body's defense system weakens and opens the way for microbes that attack the human body every second.
Cancer tumor under a microscope
The main external signs of present intoxication, its endogenous type:
- Weakness in the body;
- Fast fatiguability;
- The skin is pale;
- Feeling of thirst and dry mouth. The mucous membrane of the eyes is damaged, a burning sensation from dryness is constantly felt;
- There is no appetite, body weight is rapidly lost;
- Increased sweating;
- The temperature is not controlled and is constantly rising;
- Pain syndrome can occur in bones and joints;
- Difficulty falling asleep or frequent interruptions in sleep;
- Often the negative impact affects the nervous system, causing disorders;
- The content of red cells in the blood decreases, which leads to anemia;
- The body's defenses are not working.
The malignant neoplasm grows rapidly. Blood vessels grow more slowly and cannot provide oxygen and nutrients to the tumor. Despite the fact that cancer cells are able to function normally in the absence of blood, they still die, causing poisoning of the body. As a rule, a similar phenomenon is observed with a large size of the cancer tumor.
Tuberculosis poisoning
This intoxication manifests itself in the first stages of infection with pathogenic microorganisms that cause tuberculosis. At the same time, there are no clearly defined foci of development of inflammatory processes. As a rule, such phenomena most often develop in childhood, when the immune system is not strong enough and cannot actively resist illnesses.
The main signs confirming the penetration of infection into the body:
- Rapid patient fatigue;
- Increased sweating;
- Visual examination confirms enlarged lymph nodes;
- During the day, body temperature varies between 37.1-38.0. Moreover, this condition lasts for a long time - from 14 days to 2-3 months.
- The child’s physical development is inhibited.
- Body weight decreases sharply.
To make a diagnosis, a test for tuberculosis is done. Changes are observed in the blood passing away from the hematopoietic organs. Therapy is carried out using chemicals aimed at combating tuberculosis infection.
Infection and the manifestation of signs of intoxication occur in children who are faced with a similar illness for the first time. The factor that provokes infection is the presence of a patient with an open form of tuberculosis. Sneezing, coughing or talking releases thousands of disease germs into the air. Most often, infection occurs through airborne droplets. Infection through household appliances as a result of manipulation of the placenta is much less common.
Being in the lungs, pathogenic microorganisms do not create foci of inflammation, but their active activity begins in the lymph nodes. As a result, the organs become inflamed, and the virus continues to travel along with the lymph through the internal systems, provoking the development of symptoms of poisoning. MBT settle in different organs, causing changes, small tubercles appear, called tuberculous granulomas. This is how the immune system tries to fight the disease.
Heavy metals
Today, the use of metals considered heavy is widespread. They can be found in industrial products and medical products. Even in everyday life there are many items containing salts of heavy metals.
If substances are used for other purposes, this leads to their accumulation in the body and negative consequences. The operation of internal systems is disrupted and goes astray from the correct mode.
Metals that can cause an exogenous type of dysfunction of internal organs:
- Zinc;
- Mercury;
- Copper;
- Lead;
- Nickel;
- Antimony.
Don't forget about arsenic - half a metal, but extremely dangerous for children and adults.
Often the first signs of poisoning appear after contact with the substance or after prolonged use of the product. A chronic type of intoxication occurs in people constantly associated with these salts. Heavy metals are also found in car exhaust smoke and in pest control products used in the garden. Substances for repelling or destroying small rodents in a house, apartment, or industrial premises. Cigarette smoke contains salts of heavy metals, so when inhaled, the poison penetrates inside and causes irreparable damage to the body.
For medical purposes, heavy metals are used to prepare ointments. Medicines help patients cope with purulent lesions on the skin. Use for other purposes or non-compliance with the instructions for use leads to severe poisoning.
Chronic intoxication with heavy metal salts leads to irreversible reactions in the body. Damage extends to internal systems. The central nervous system is the first to suffer. Therefore, it is important to start treatment on time and eliminate the toxin that causes the bad effects.
On the part of the brain, damage affects the state of memory, periodic convulsive phenomena, and mental disorders. The child's body is susceptible to poisoning, which leads to impaired mental development.
Symptoms of toxic hepatitis appear due to liver damage from toxic substances. The organ increases in size and functionality is impaired. The skin turns yellow, the pain in the right side under the ribs intensifies.
Liver pathology develops against the background of complications after the accumulation of heavy metals in the body. The kidneys are unable to cleanse the blood, urine production becomes excessive or stops.
The number of red cells in the blood sharply decreases, which leads to anemia. This is especially pronounced after hemolysis. Under the influence of toxic substances, red blood cells disintegrate.
Drug poisoning
Pharmacy medications should only be taken as prescribed by a doctor. The dosage is selected according to the instructions for use. Despite numerous warnings, people continue to take medications at their own discretion. There is also the deliberate taking of large doses of drugs for suicidal purposes.
The clinical picture of poisoning depends on what medication was ingested. Different classes of drugs have individual symptoms:
- Overdose of an analgesic drug. Aspirin makes headaches worse. Nausea and vomiting occur in the stomach. Often the negative impact extends to the intestines, resulting in frequent urge and defecation of liquid feces. Depending on the number of tablets eaten, shortness of breath may occur, the heart rate may increase, and blood pressure may drop sharply.
- Medicines prescribed for heart patients. Exceeding the permissible consumption of heart medications leads to diarrhea, vomiting, and nausea. Pain occurs in the abdomen and head. Since the action of the drugs is aimed at normalizing the heart rhythm, an increased number of tablets can lower the pulse and reduce organ contractions so much that cardiac arrest and death are recorded. For older people, drug intoxication threatens delirium and impaired brain activity.
- Sulfonamides also pose a danger if the permissible consumption volumes are exceeded, for example, the drugs Norsulfazol and Sulfadimezin. As a result, patients develop renal colic and acute pain in the abdominal area on the right. A person cannot go to the toilet due to lack of urine. As with toxic poisoning, nausea, vomiting appears in the stomach, and an allergic reaction to the medication occurs.
Toxic drug poisoning can vary in symptoms. However, a common symptom is present in all types of intoxication: the skin becomes pale, with isolated areas of redness, and irritation is observed. Toxins and poisonous substances affect the functioning of the brain, which affects the behavior and condition of the patient.
Pregnancy
When a woman becomes pregnant, she becomes responsible not only for her own health, but also for the unborn baby. For the proper development of the fetus, a sufficient amount of nutrients must enter the mother’s body. Compliance with the diet, quality of food, healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits - all this is important for the expectant mother.
When the baby is developing inside, taking most medications is prohibited. However, an unpleasant moment during pregnancy is inevitable - the occurrence of toxicosis, which is exhausting and worrying constantly. You should visit your doctor to resolve the issue. Folic acid is considered a popular and effective medicine that reduces the manifestation of an unpleasant symptom. The drug copes well with heartburn and eliminates nausea. Doctors recommend taking acid during the 9 months of expecting a child.
A natural remedy that reduces negative symptoms is tea with chamomile, rose hips and mint.
Remember, complete elimination of nausea and vomiting is impossible, however, a gradual reduction in symptoms is likely to have a positive effect on the health of the woman and the unborn child.
Diagnostics
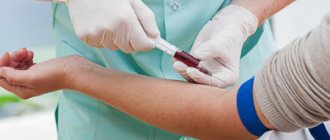
Diagnosis of intoxication is not difficult; it can be much more difficult to determine the type of toxin that caused disruption of body functions. For this purpose, they resort to laboratory tests aimed at detecting the toxin itself or its metabolic products in the biological fluids of the body.
The cause of endogenous intoxication is the formation of toxic products caused by extensive tissue damage.
A biochemical blood test is carried out, the results of which make it possible to identify changes in the functions of systems and organs associated with exposure to toxic substances.
The main syndromes that occur during intoxication
Increased body temperature is one of the main general toxic symptoms
Despite the fact that each type of poisoning has its own pathogenetic and symptomatic features, there are a number of syndromes that consistently occur with most known intoxications.
General toxic syndrome
: occurs due to the action of poison on the sympathetic-adrenal system. It is characterized by symptoms such as hyperthermia, muscle aches, flying joint pain, tachycardia, hypertension. These symptoms of intoxication are most pronounced in children during infectious and inflammatory diseases (bronchitis, pneumonia, tonsillitis).
Gastrointestinal syndrome
: occurs more often with enteral administration of poison. It is characterized by the appearance of vomiting, nausea, flatulence, abdominal pain, profuse diarrhea. May lead to dehydration and water-electrolyte imbalance.
Neurotoxic syndrome
: patients experience headaches, fatigue, decreased mental performance, tearfulness and moodiness. In severe poisoning, damage to the central nervous system can lead to loss of consciousness, coma, and disruption of the innervation of internal organs.
Headache is the first sign of central nervous system dysfunction
As a rule, children suffering from acute toxic pathology refuse food. Therefore, toxic-dystrophic syndrome, a nutritional deficiency that results in general depletion of the body, can also be classified as a characteristic of intoxication. The syndrome usually develops with prolonged intestinal infections.
Note: it is useless to force a child to eat if he refuses food. Intestinal infections impair the absorption of nutrients. Therefore, even the food that the child ate is not beneficial. In severe cases, it is recommended to use parenteral nutrition (oliclinomel).
Symptoms
Some types of this pathology have their own symptoms. So, the symptoms of alcohol intoxication are:
- loud, incoherent speech;
- active facial expressions;
- increased appetite;
- change in heart rate.
These are symptoms of the first, initial stage of intoxication. After a certain time, which is individual for each person, these signs are replaced by other indicators - increased fatigue and lethargy.
The second stage appears:
- frequent mood changes;
- irritation;
- aggression;
- speech becomes less intelligible;
- inability to maintain balance;
- bouts of vomiting;
- after sleep, a person feels exhausted, lethargic and complains of a severe headache.
The most severe degree of liver intoxication manifests itself:
- unintelligible muttering;
- strong swaying from side to side;
- inability to hold in urine and feces;
- stupor.
If you do not stop a person from drinking alcohol in time, it can lead to a coma.
Symptoms of tuberculosis intoxication:
- irritability and weakness;
- migraine;
- caries;
- decreased or complete lack of appetite;
- increased sweating at night, which causes sleep disturbance;
- pale skin color.
Such signs are observed in the acute type of pathology. In chronic tuberculosis intoxication, the following prevail:
- developmental delay;
- constant rapid heartbeat;
- memory loss;
- conjunctivitis;
- fast fatiguability;
- weight loss due to refusal of food.
Indicators of cancer intoxication:
- weakness;
- critical decrease in body weight;
- profuse sweating;
- gagging;
- severe pain and dizziness;
- apathetic state;
- sleep disturbance or complete absence;
- aversion to food.
Other symptoms of body intoxication:
- unstable psyche;
- heat;
- decreased level of performance;
- disruption of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- dermatic skin problems;
- the skin becomes less elastic;
- nails often break;
- dull hair.
These are just general symptoms of intoxication - the symptoms may be different for each individual person (depending on the characteristics of the body).
First aid
The first signs of food poisoning in adults should be a reason for immediate action:
- Urgent gastric lavage is necessary to completely empty it. For these purposes, a weak solution of potassium permanganate is used. It should be pale pink in color. To prepare it, potassium permanganate is dissolved in water and filtered through 4 layers of gauze.
- In addition, you can use a soda solution consisting of 1 teaspoon of soda per 1 liter of water.
- The solution must be at least 10 liters. It should be at an average temperature, not lower than 37⁰, this will help avoid hypothermia of the body and slow down the process of intestinal motility, which will act as a brake on the movement of toxins through the gastrointestinal tract.
- For the first dose, it is enough to drink about 2-6 glasses of the solution and try to induce vomiting by pressing on the tongue.
- This must be done until the stomach is completely cleansed, as evidenced by the flow of clean water after vomiting.
- The next necessary step is to take absorbents. This must be done at least 4 times every 20 minutes.
- It is important to ensure complete rest for the patient and wrapping up during chills.
- Complete abstinence from food is necessary for the first 24 hours after poisoning. On the second day, the patient can be fed broth, pureed soup with rice and vegetables, mucous decoctions, trying not to introduce smoked foods, pickles, spicy and too fatty foods into the diet, which negatively affect the gastric mucosa. The patient should get enough fluids. Boiled water, light sweet tea, berry juice, and jelly are suitable for this. The consumption of carbonated drinks in this case is extremely contraindicated.
Causes
Why can intoxication of the body occur? Signs of this problem may be due to the following reasons:
- External environment. This is the most common cause of intoxication in the body. In this case, you can be poisoned by chemicals, heavy metals, plant and animal poisons, decay products of living microorganisms, low-quality products, as well as medications (in case of overdose).
- Endogenous intoxication of the body can occur in the event of a violation of the integrity of the tissues of the human body. So, this can occur as a result of burns, injuries, radiation injuries.
- The body can be affected by toxins in the event of its own malfunction. Example: in case of renal failure, uremic intoxication or metabolic disorders are possible.
Alcohol intoxication
It is worth saying that most often people experience alcohol intoxication. What is it? Thus, alcohol intoxication is a special psychological state of a person, which is caused by excessive accumulation of ethanol in the body, i.e. alcohol However, it is worth saying that during alcohol intoxication not only a person’s consciousness changes, but the functioning of his organs is also disrupted. Alcohol intoxication has the following symptoms:
- Headache. When drinking alcohol, blood vessels dilate too quickly, which causes discomfort.
- Nausea, vomiting. Occurs due to ethanol entering the body. This element begins to immediately affect the cerebellum, which is responsible for balance. The body, in turn, receives the task of getting rid of a toxic substance that negatively affects the body.
- Dizziness. Occurs as a result of disruption of the cerebellum.
- Intense thirst. Occurs immediately after drinking alcohol. This happens because the body's level of antidiuretic hormone, which is responsible for the body's excretion of urine, sharply decreases.
Important: even a small dose of alcohol can cause intoxication in the body. This can happen if low quality alcohol has been taken, or if children or teenagers have tried the drink.
Popular medicines
Pharmacy counters are overflowing with various remedies for poisoning. Which drug to choose in this or that case? Let's look at the most effective ones for food poisoning:
- Entoban. Release form: capsules, syrup. Made from plants. It has an adsorbent, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effect. It also acts as an antispasmodic. It has a number of contraindications. These are individual intolerance to components, renal and liver failure, inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as children under twelve years of age, pregnancy and lactation, infectious diarrhea, intestinal obstruction.
- Polysorb. Powder for preparing a suspension. It is an enterosorbent that eliminates intestinal infections, intoxication of the body, heparasotemia, and hyperbilirubinemia. Do not take if you have a stomach ulcer, hemorrhages of the gastrointestinal tract, or intolerance to the components of the drug.
- Linux. A remedy that normalizes intestinal microflora. Do not use if you are intolerant to dairy products or medication components.
- Enterosgel. An effective drug in the form of a paste for intoxication of the body. Allowed for children. Contraindications include individual intolerance to the composition of the drug and intestinal atony.
- Regidron. It is used to remove toxins from the gastrointestinal tract, performing rehydration (replenishment of fluid) of the body. It is not recommended to use the drug for diabetes, kidney problems, intestinal obstruction, as well as loss of consciousness and hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Among the popular antitoxic agents are Cerucal and Intetrix.
Important! Before using any drug, consult a specialist. All medications have contraindications.
How do you usually begin to treat poisoning at home?
Those who trust pharmacology more, in case of food poisoning, drink sorbents Smecta, Enterosgel , and dilute Rehydron to reduce dehydration processes. But this is not much better than activated carbon and water, plain clean water.
A more complex and expensive medicine does not guarantee greater effectiveness. I gave smecta on the recommendation of the pediatrician to my child, he continued to vilify as he vilified. But after coal and a slight refusal of food, everything quickly went smoothly. Yes, children themselves refuse food in this state.
And many mothers immediately begin to panic: “My child is starving, I need to do something urgently, how will he, poor child, fight toxins if he misses a full three-course meal!” And they feed the dodging child with all sorts of tricks and jokes, thereby prolonging his torment.
Treatment at home
The victim, regardless of the intensity of the manifestations of poisoning, will need the help of an infectious disease specialist. The medicinal correction prescribed by him will allow him to avoid an increase in intoxication and the development of chronic pathologies of the digestive canal. Dysentery and botulism can only be cured in the infectious diseases department of a hospital.
Treatment at home is effective for victims with mild poisoning. Medicines and diet are prescribed by a local internist or family doctor. Attempting to solve the problem yourself is strictly prohibited. The intake of all medications must be agreed with the doctor. Among the basic requirements for home treatment are the following:
- Complete rest, bed rest.
- Ventilation of premises.
- Dieting. Smoking, alcohol, carbonated water, and coffee are prohibited. You should not eat spicy, fatty foods, smoked foods, or baked goods. Fractional meals and small portions are recommended.
Take antibiotics prescribed by your doctor strictly according to the regimen. For pain, antispasmodics are used to cope with flatulence and intestinal colic. Enzyme preparations (Mezim, Creon) provide better functionality of the pancreas and regulation of the breakdown of nutrients.
To restore the number of beneficial bacteria in the intestines, take probiotics:
- Bifidumbacterin.
- Linux.
In case of severe condition, hospitalization is carried out in the intensive care unit or infectious diseases department.
Main clinical signs
Symptoms of food poisoning depend on a number of conditions: the type of microorganism and toxin, the amount of poison ingested, the general health of the body, etc.
But at the same time, a number of standard signs of poisoning can be identified, which are observed in 95% of cases:
- nausea is usually the body’s first signal that a toxin has entered it;
- vomiting – follows nausea, is aimed at removing a toxic substance through the mouth in order to prevent its absorption into the blood and further spread throughout the body;
- painful abdominal cramps - localized in the stomach area, below the navel or in the upper abdomen;
- diarrhea - appears due to irritation of the gastrointestinal mucosa under the influence of toxins;
- low-grade body temperature – inhibits the activity and reproduction of bacteria and viruses, triggers immune defense mechanisms;
- general weakness;
- lack of appetite.
All these processes have a cleansing function and are aimed at quickly ridding the body of toxins and poisons. There is no need to hinder them, but you also cannot do nothing. Therefore, everyone should know what to do when food poisoning occurs. This is discussed in more detail in the video in this article.
First aid and treatment
As in all other cases, assistance to a patient with poisoning is divided into first, first medical and medical.
It's important to act quickly
First aid
Any instructions for assistance first of all require stopping the effect of the damaging factor. In case of gas poisoning, the victim is taken out into fresh air; if the poison is consumed through the mouth, the stomach is washed out in a “restaurant” way.
Note: the “restaurant” method of removing poison is not used in cases of poisoning with cauterizing poisons, as well as in cases where the patient is unconscious.
After rinsing, the patient must be laid on his side, ensure a flow of fresh air and wait for the emergency medical team. Other actions are not recommended unless absolutely necessary, when the cost of inaction is human life.
First aid
Gastric lavage through a tube is the basis of first aid for the victim
First medical aid usually consists of repeated gastric lavage through a tube, ensuring adequate breathing and hemodynamics, stabilizing the condition, and starting detoxification therapy.
Gastric lavage is performed for all patients who have consumed poison by mouth. The exception is food infections with a mild course and mild symptoms. Unconscious patients are intubated and placed on mechanical ventilation before the procedure.
Adequate breathing is ensured by sanitation of the oral cavity using an electric suction device or a gauze swab. In case of central impairment of pulmonary ventilation, mechanical ventilation is necessary.
Blood pressure is stabilized by infusion of colloidal solutions (reopolyglucin, volulite), administration of vasopressors or antihypertensive drugs if the pressure is elevated.
Detoxification begins with the introduction of enterosorbents into the stomach (with the exception of chemical burns, gas injuries, parenteral poisoning) and infusion therapy. The patient is injected with 400 ml of Trisol solution. Further treatment is carried out in a hospital setting.
Health care
Specialized medical care depends on what, when and how seriously the patient was poisoned.
The main list of therapeutic measures for each of the poisonings described above is as follows:
- Alcohol: forced diuresis, unithiol.
- Medicines: antidotes, forced diuresis, stool stimulation, hemodialysis, enterosorbents, hepatoprotectors.
- Gases: ventilation, nootropics, antidotes.
- Cauterizing poisons: hemostatic agents, forced diuresis with preserved renal function, hemodialysis for anuria, glucose-novocaine mixture, anesthesia, and, if necessary, hardware hemostasis.
- Food poisoning: enterosorbents, intestinal bacteria, antidiarrheals. In case of severe gastroenteritis, drink plenty of fluids, antiemetics and antipyretics, chloramphenicol, infusion.
- Water intoxication - limiting the amount of liquid consumed in food, diuretics, inhalation of alcohol vapor during pulmonary edema. In severe cases - hemodialysis.
In most cases, hospitalization is required
General information
The term “intoxication of the body” is widely used in the medical literature, which specialists in various branches of practical medicine have to deal with (toxicologists, infectious disease specialists, surgeons, intensive care doctors, emergency ambulance doctors, etc.).
Currently, the concept of “intoxication syndrome” is widely used by doctors as one of the most important criteria determining the severity of the condition and the prognosis of the disease. This term includes both clinical and clinical laboratory manifestations of a pathological condition that develops under the influence of various toxic substances of endogenous/exogenous origin on the body. Despite the apparent obviousness of the intoxication pathological process, its strict definition today has not been fully formulated, which is due to objective reasons, including a wide variety of toxic factors and, accordingly, a wide polymorphism of intoxication manifestations; multifaceted interaction in the body between toxin production and detoxification processes; the dominance of nonspecific manifestations of intoxication processes due to the universality of metabolic disorders during the development of various intoxication syndromes. Modern science considers intoxication syndrome as a dynamic process in which the processes of toxins entering from the outside or their formation within the body (autointoxication) dominate the capabilities of detoxification systems and its ability to eliminate them (removal).
There are two large groups of intoxications of different origins.
Exogenous intoxication . With exogenous intoxication, various toxins enter the body from the outside. Exogenous intoxications are encountered primarily by toxicologists and, to a lesser extent, infectious disease doctors when treating diseases caused by pathogens that produce exotoxins (botulism, diphtheria, tetanus). As a rule, exogenous intoxications are characterized by clear clinical symptoms, and the optimal means of detoxification include the administration of toxoids or specific antidotes . Most often occurs when toxic substances of natural or chemical origin are consumed/ingested into the body from the external environment with food, air or water (food poisoning, alcohol, nitrates, nitrites, heavy metals, chemicals, drugs, toxic substances, etc.) .
Endogenous intoxication . In cases of endogenous intoxication, toxic products are produced directly in the body. Endogenous intoxication syndrome includes various pathological conditions of varying etiology and severity caused by excessive accumulation of endotoxic substances in biological fluids/tissues of the body that have direct, indirect or mixed toxic effects. Various components can act as endotoxic substances (ETS), among which there are several groups of substances:
- products of normal physiological metabolism in high concentrations (urea, ketone bodies, lactate, bilirubin, pyruvate, lactic acid, etc.);
- substances formed in excess due to metabolic disorders (aldehydes, alcohols, ketones, ammonia, mercaptan, indole, skatole, carboxylic acids, etc.);
- products of cellular decay from foci of tissue destruction (tumor necrosis factor) or from the gastrointestinal tract when membrane function is impaired (lysosomal enzymes, lipases, phenols, cationic proteins, etc.);
- various kinds of biologically active substances (biogenic amines, kinins, serotonin), acute phase proteins, inflammatory mediators (interferons, interleukins), etc.;
- microbial/bacterial exo- and endotoxins toxins (lipopolysaccharide);
- proteolytic, lysosomal activated enzymes, fibrinolysis enzymes and blood coagulation systems;
- highly active compounds formed as a result of lipid peroxidation;
- foreign immune products of cell breakdown, immune complexes and antigens.
Endogenous intoxication syndrome is considered by many scientists as a reflection of the consequences of disruption (overstrain) of adaptation mechanisms (immunity, macro/microcirculation, gas exchange, rheology, etc.), that is, as a breakdown of compensation mechanisms, manifested by an imbalance of reactions at the biomolecular level, which leads to changes in metabolism and the development of homeostasis .
At the same time, a number of substances under conditions of unbalanced self-regulation can potentially acquire the properties and qualities of endotoxins, without being such under conditions of physiologically normal functioning of the body. This approach is extremely relevant, since the clinical symptoms of metabolic disorders in the early stages of their development are not clearly manifested; accordingly, syndromes of impaired metabolism lag behind the pathological processes developing at the cellular and biochemical level.
The pathological process in endogenous intoxication syndrome has a phase (stage-by-stage) nature of development, according to which several phases are distinguished:
- compensatory;
- phase of incomplete compensation or accumulation of toxic products;
- phase of temporary decompensation of organs/detoxification systems;
- phase of irreversible decompensation of organs/systems (membrane failure);
- terminal phase (complete disintegration of all detoxification systems and the body as a whole).
Symptoms of food poisoning in adults
For each person, the manifestation of symptoms of poisoning is different.
This can be influenced by many factors:
- the type of bacteria that caused the poisoning;
- amount of product consumed;
- general health of the patient.
There are common symptoms of food poisoning:
- there is a temperature fluctuation from 37 to 39 ⁰;
- worried about lack of appetite and general weakness;
- there are loose stools and cramping painful manifestations in the abdominal area;
- the stomach is swollen;
- nausea, often accompanied by vomiting, bothers you;
- blood pressure decreases;
- bothered by headaches;
- diarrhea appears with a rather unpleasant odor and food residues;
- there is chills and cold sweat throughout the body.
Cases of poisoning with neurotoxic poisons are considered one of the most dangerous.
This is often fraught with:
- visual impairment;
- double vision;
- violation of muscle tone;
- copious secretion of saliva;
- increased heartbeat;
- the appearance of hallucinations;
- loss of consciousness;
- coma;
- paralysis;
- dehydration of the body;
- weight loss.
Usually, after 30 minutes after eating poor quality food, symptoms of poisoning are observed. Sometimes this happens after 4-5 hours or a day later. If treatment is started on time, many serious complications can be avoided.
What is the easiest way to get poisoned?
The most dangerous products in terms of the development of toxic food poisoning are:
- dairy products,
- eggs, especially raw ones,
- meat dishes,
- fish dishes, especially with raw fish,
- confectionery with protein cream,
- home-made canned food and pickles in violation of preservation technology,
- perishable products that require cold storage,
- products with violation of the integrity of packaging and shelf life,
- food service products in violation of sanitary rules during their preparation.
Drug intoxication
A person may also have drug intoxication. Symptoms in this case will depend on the medication with which the person was poisoned.
- The drug "Aspirin". Sharp headaches, nausea, vomiting, loose stools. In some cases, there may be shortness of breath, increased heart rate, and decreased blood pressure. Sometimes your blood pressure may drop.
- "Heart" drugs. If the patient has drug intoxication of the body, signs may be as follows: diarrhea, vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain. A headache may occur. Also, often in such people the pulse slows down, the heart rhythm is disturbed, and in some cases cardiac arrest is possible. Elderly people may experience delirium and disruption of brain activity.
- Poisoning with sulfonamides (for example, the drug Norsulfazole or Sulfadimezin). May be accompanied by renal colic, acute pain, and lack of urination. There may also be vomiting, nausea, and various allergic reactions.
If a person has intoxication of the body with drugs, the symptoms can be very different. So, for example, in one case there may be increased salivation, and in another case there may be dry mouth. However, it is worth saying that with such poisoning, a person’s appearance often changes (redness on the skin, pallor, irritation), and a reaction from the nervous system or brain function is also possible.
Liver toxicity
Liver intoxication occurs most often due to the consumption of alcoholic beverages. The substances included in these drinks are, in fact, poisons for the body. And the function of the liver is precisely to neutralize poisons. Therefore, it takes the first blow when alcohol enters the body.
Liver intoxication comes in two forms: acute and chronic. Acute intoxication is liver poisoning with alcohol, multiplied by liver poisoning with medications that are used to normalize the victim’s condition. Liver intoxication can be of three degrees: mild, moderate and severe. In case of any degree of liver poisoning, the victim should immediately rinse the stomach, give him at least thirty grams of bitter salt for relief, as well as a packet of special drugs to rid the intestines of toxins (lactulose).
Toxic agents and types of intoxication
Drug poisoning is one of the most common types of endotoxicosis.
All intoxications can be divided into two large groups:
- Endotoxicosis is caused by poisons that form inside the body. Most often, the doctor encounters intoxications caused by tissue breakdown during necrotic and destructive processes. A striking example is pancreatic necrosis, prolonged compression or crush syndrome (CRASH syndrome). Symptoms of general intoxication that occur during infectious diseases can also be classified as endotoxicosis.
- Exotoxicosis - caused by poisons that enter the body from the external environment through the gastrointestinal tract, blood, lungs, skin, etc.
In clinical practice, the most common are:
- Symptoms of alcohol intoxication;
- medications (psychotropic drugs, salicylates, antibiotics);
- drugs (heroin, methadone, “club” drugs);
- cauterizing solutions (MOLE, vinegar essence);
- natural poisons (puppeteer, mushroom toxins);
- Symptoms of food intoxication.
Alcohol is poison for the body
When using narrow dosage medications, symptoms of intoxication in a child may occur even when the correct dose of the medication is prescribed. This is due to the individual characteristics of the child’s body.
In addition to the above, all toxic effects are divided into acute and chronic. Acute-type processes occur when a large amount of xenobiotic enters the body simultaneously. Chronic poisoning is the result of frequent intake of small doses of poison over a long period of time (mercurialism).
According to the clinical course of intoxication, they are divided into:
- Lungs;
- Medium-heavy;
- Heavy.
Food poisoning and viral infections (flu) usually occur in a mild form. In this case, the patient is not hospitalized, the disease does not lead to disruption of vital functions.
Moderate poisoning is characterized by moderate disruptions in vital systems. The clinical picture of the disease is clearly expressed, but not to the maximum. The patient is conscious.
Severe intoxication poses a danger to the patient's life. The patient's breathing and cardiac activity are impaired, convulsions, coma, and infectious-toxic shock develop.
Tuberculosis intoxication
Tuberculosis intoxication is distinguished as a syndrome characteristic of all forms of tuberculosis, and as an independent form of this disease in children and adolescents (tuberculosis intoxication in children and adolescents). Tuberculosis intoxication in children and adolescents is a form of active primary tuberculosis, in which local specific lesions are not detected using X-ray and other research methods. This form of tuberculosis is detected in children and adolescents with a range of tuberculin reactions and hyperergic reactions to tuberculin.
Symptoms manifest themselves in the form of increased fatigue, irritability, headache, decreased appetite, poor weight gain or deficiency, and intermittent low-grade fever. Enlarged peripheral lymph nodes of elastic or dense consistency; sometimes the phenomenon of periadenitis. Many children have bronchitis, tachycardia, and in young children - dyspeptic disorders, abdominal pain, and sometimes enlargement of the liver and spleen.