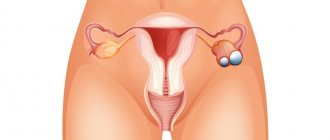
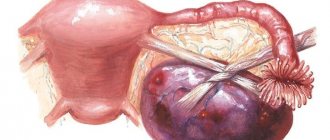
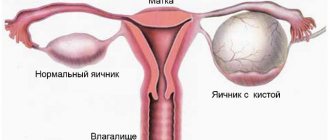
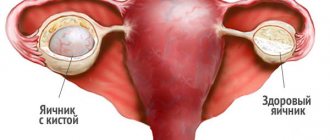
What is a cyst?
The formation of the disease on the female reproductive glands is directly related to their main reproductive function - the process of maturation of the egg. A female cell matures according to a clear schedule, which has a certain order. If the chain of formation is disrupted, pedunculated capsules with liquid of various compositions may appear on the walls of the ovaries.
An increase in fluid in the capsule base leads to the growth of the tumor. During this period, a woman may feel some discomfort and notice signs of the disease. Ovarian cyst ICD 10 is divided into several varieties. It all depends on the reasons for its occurrence and the chemical composition of the liquid. This disease can be recognized by some manifestations:
- failure of the menstrual cycle from 5 to 30 days;
- pain during menstrual periods, heaviness in the ovarian area, nausea;
- a change in the volume of discharge that is not typical for normal menstruation.
Benign ovarian neoplasm (D27)
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! An effective remedy for CYSTS without surgery and hormones, recommended by Irina Yakovleva! Read more.
Representatives of this group include cysts:
Endometriotic cysts
Such neoplasms are the result of the development of endometriosis. When endometriotic lesions merge, cysts are formed, which often contain menstrual blood.
Quite often, the formation of an endometrioid ovarian cyst is preceded by medical manipulations on the internal genital organs, including abortions and diagnostic curettages. But in some cases it occurs against the background of complete health, and a thorough examination reveals endocrine pathologies or banal exhaustion of the nervous system due to frequent stress.
An increase in tumor size often leads to the destruction of follicles, the appearance of follicular cysts and adhesions between the pelvic organs and the walls of the fallopian tubes. If this process is not stopped in time, the woman risks facing the problem of infertility.
Paraovarian cysts
Cavities located in the tissues of the appendage, that is, between the ovary and the fallopian tube, are called paraovarian cysts. They are found quite often (15–20% of all benign ovarian tumors), and mainly in women 20–40 years old, since it is during this period that the maximum development of the appendages is observed.
The only reason for the formation of such neoplasms is the occurrence of disturbances during embryonic development. They grow due to the accumulation of liquid secretion, which is facilitated by overheating of the body, observed, for example, when taking excessively hot baths, visiting saunas, baths, etc.
Follicular
Follicular ovarian cyst ICD 10 in the table of varieties has No. 83.0. Most often, it affects women of childbearing age whose reproductive system has malfunctioned. The onset of menopause prevents the appearance of a follicular cyst, as it is formed from an unruptured follicle. A neoplasm of this type is a capsule with an ovarian membrane filled with colorless mucus with estrogens.
Important. In size it can reach up to 10 centimeters.
Reasons for education:
- infections;
- occurs in women who have not yet reached menopause;
- inflammatory processes;
- surgical interventions;
- endocrine system disorders;
- long-term stress and depression.
Treatment of ovarian cysts according to ICD
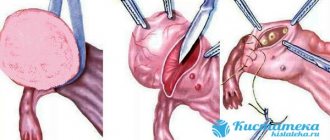
If a patient has a torsion of an ovarian cyst according to ICD 10, and she does not go to the clinic on time, removal of the tumor will most likely be accompanied by cutting off the affected organs and appendages. It often happens that after a rupture in a woman’s fallopian tubes, a large number of abnormal nodules and flagella are formed, due to which the follicle cannot advance to the uterus and fertilize. Such atypical formations cannot be removed surgically, so they often cause infertility.
An ovarian cyst code according to ICD 10 on the reproductive organs is removed if its walls have a pathogenic effect on neighboring organs. If the abnormal body is small in size and does not cause discomfort to a person, its growth is controlled by courses of medication and regular ultrasound examinations.
It is worth saying that there is a certain type of ICD 10 ovarian cysts, unspecified (follicular cysts). In 98% of cases, this type of benign formation does not show symptoms of its presence and resolves on its own during menstruation and the ovulation cycle. However, abnormal formations of the pathogenic type can grow up to 15-20 cm in diameter and significantly worsen the patient’s well-being. Large foreign bodies are cut off surgically. In this case, not only the capsule is removed, but also the connective tissues, threads and systems formed by it to prevent relapse of the disease and eliminate dangerous complications and consequences.
Depending on the type of capsule, the tissues that form the tumor, the reasons for its appearance and growth characteristics, all foreign bodies on the reproductive organs of women are traditionally divided into several groups. We list them below.
Corpus luteum cyst
An ovarian cyst receives No. 83.1 in the presence of a corpus luteum. The process of fertilization is possible after the reproductive cell matures in the woman’s body and the hormone progesterone is produced in sufficient quantities in the gland. In the absence of pregnancy, the corpus luteum resolves, but there are many reasons for the formation of disease on the organ. This type of tumor is filled with serous fluid. It is formed to a greater extent in the second period of the menstrual cycle. The formation of the corpus luteum is in most cases single-chambered and reaches a size of up to 8 centimeters.
Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of follicular ovarian cyst
The course of a follicular ovarian cyst can be asymptomatic, and a woman accidentally finds out about its presence only during an ultrasound examination. Manifestations largely depend on the general condition of the woman’s body, concomitant diseases of the pelvic organs of various etiologies and the size of the tumor.
The most common symptoms are:
- Aching, cramping pain in the lower abdomen;
- Excessive blood loss during menstruation;
- Bloody discharge in the middle of the cycle and after sexual intercourse;
- Severe premenstrual pain during physical activity.
For some reason, it is believed that a cyst on the right ovary develops more often than a cyst on the left. Perhaps this theoretical opinion was formed due to the fact that the right ovary is located in a place of increased blood supply - the junction of the main aorta and the renal artery. In modern gynecology, this theory has not been confirmed. But given the fact that the neoplasm on this side resembles the symptoms of inflammation of the appendix, more attention is paid to the right ovary.
If the cyst does not resolve on its own within 2-3 menstrual cycles, then it is subject to conservative, and in some cases, surgical treatment. The doctor determines further tactics based on diagnostic observations and the general condition of the patient’s body.
At the oncology center of the Yusupov Hospital, all conditions have been created to successfully solve this problem. An individual approach to each patient ensures the most positive effect from the therapy.
Other types of cysts from the general classification
There are situations when the neoplasm did not appear as a result of a malfunction of the gonads. In such cases, it is not possible to identify the cause of the occurrence, because the symptoms and cycle period contradict each other and it is impossible to determine the exact subtype. Such diseases are classified under No. 83.2. This group includes the following subtypes of neoplasms:
- Endometrioid - tissue from the uterine mucosa enters the ovary;
- Dermoid - the capsule is filled with skin fibers, elements of hair and tooth enamel;
- Paraovarian - the ovarian appendages participate in the formation;
- Mucinous - the cyst is filled with mucus, grows quickly and has the ability to degenerate.
The ovaries are a paired organ with the same structure of both parts. Typically, all diseases and the occurrence of possible complications are characteristic of both ovaries. However, their location can affect the formation of cysts of one or another subtype.
The right ovary is more supplied with blood, and high blood pressure encourages capsule growth, which leads to more frequent rupture and complications. On the right side, endometrioid and hemorrhagic cysts most often form. The right ovary produces more symptoms and suffers more often from complications.
Paraovarian ovarian cyst: treatment without surgery
A paraovarian ovarian cyst is the only type of formation that does not become malignant, but still significantly worsens a woman’s quality of life. Therefore, the interest of patients with this diagnosis in how an ovarian mass can be cured without surgery is natural.
In the early stages of cyst development, when there is no need for surgical treatment, you can try treatment with folk remedies. For this use:
- Aloe, yarrow, St. John's wort, wormwood (all herbs 50 g each), ethyl alcohol (0.5 l) and honey (0.5 kg). Plants are poured with 3 liters of boiling water and poured into a thermos overnight. Then the remaining ingredients are added to the broth. Take 1 tbsp orally. l three times a day before meals
- Olive or sunflower oil (200 ml), 30 g beeswax and boiled egg yolk. The olive oil is heated, wax and crumbled yolk are added. Bring to a boil and leave to cool. The procedure is repeated 2 times. The resulting ointment is applied to a tampon, which is kept in the vagina for a long time for 5 - 8 hours.
The use of traditional methods must be agreed upon with the attending physician after examination and diagnosis.
Treatment of paraovarian ovarian cysts is carried out in the best oncology center in Moscow, as well as in the network of partner clinics of the Yusupov Hospital. The staff includes experienced doctors and nurses who ensure a comfortable stay in the hospital. You can make an appointment with a specialist by phone.
Hemorrhagic cyst of the corpus luteum
ICD-10 alphabetical indexes
External Causes of Injury - The terms in this section are not medical diagnoses, but rather a description of the circumstances under which the event occurred (Class XX. External Causes of Morbidity and Mortality. Heading Codes V01-Y98).
Medicines and chemicals - table of medicines and chemicals that have caused poisoning or other adverse reactions.
In Russia, the International Classification of Diseases
10th revision (
ICD-10
) was adopted as a single normative document for recording morbidity, reasons for the population’s visits to medical institutions of all departments, and causes of death.
ICD-10
introduced into healthcare practice throughout the Russian Federation in 1999 by order of the Russian Ministry of Health dated May 27, 1997 No. 170
The release of the new revision (ICD-11) is planned by WHO in 2022.
Abbreviations and symbols in the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision
NOS
- without other instructions.
NEC
— not classified in other categories.
What are the complications associated with ovarian cysts?
Intense and regular loads lead to rupture of the tumor membrane and the release of fluid into the body cavity. Cysts themselves do not cause discomfort to a woman, but damage to them can lead to sudden attacks of pain, weakness and complications. A rupture of the membrane of an ICD 10 ovarian cyst requires immediate medical intervention.
https://youtu.be/XkNm8thZYvU
Cyst formation in the throat: symptoms and therapy
Previous article
Sinus cyst of the right kidney: diagnosis and treatment
Next article
Echogenicity
The term “echogenicity” refers to the degree of tissue density . An increase in echogenicity indicates the presence of some kind of formation in the organ. In relation to the ovaries, these can be tumors - malignant or benign.
Ovarian cysts are defined as anechoic formations, that is, they appear black on an ultrasound monitor. In other words, an ovarian cyst does not reflect ultrasound waves . The more fluid inside, the less echogenicity there will be. Thus, an anechoic ovarian formation is a cyst.
Ovarian cyst is the most common pathology of the female reproductive system. Many types of cysts are not dangerous and do not have severe symptoms. Some significantly impair quality of life and must be removed surgically. The risk of a cyst degenerating into cancer does not exceed 1%.
A gynecologist will tell us in a video clip whether ovarian cysts are really dangerous:
https://youtu.be/TnZivENt83c
Cystic change of the ovary
Cystic change in the ovary is a gynecological disease that occurs as a result of dysfunction of the female body due to hormonal factors.
Cysts can be different in their characteristic features and are determined by which ovarian structures produced hormones in each individual case.
The largest part of the total number of cases in which cystic changes in the ovary are noted are represented by functional cysts or, as they are also called, false cysts. They are characterized by spontaneous appearance, not provoked by any obvious visible causes, and have a tendency to the same spontaneous disappearance. Their occurrence is not associated with the appearance and spread of cellular atypia, which is characteristic of cancer. The formation of functional cysts is caused by dysfunction of the ovaries; they are not large in size, in some cases they can provoke clearly localized unilateral pain and lead to disturbances in the monthly cycle.
One type of false cyst is a follicular cyst. With it, after two weeks of the cycle, the egg is not released from the follicle, but estrogen production continues. This causes delayed menstruation and lack of ovulation.
It happens that the corpus luteum does not resolve after ovulation has occurred, and it continues to produce estrogen and progesterone. This phenomenon provokes the appearance of a corpus luteum cyst. All the signs inherent in pregnancy begin to appear, but test results indicate that the woman is not pregnant.
For this cystic change, surgery is not required.
Cysts of an organic nature are not related to hormonal imbalances in the body; spontaneous remission does not occur in their presence. If the cyst is large, it can put pressure on nearby organs - the rectum, intestines, bladder. The existence of a small cyst may be asymptomatic.
Dermoid organic cysts are formations containing fluid with the presence of sebum. Pseudomucinous cysts are filled with a yellowish fluid, a thick viscous liquid with a consistency reminiscent of gelatin. Serous cysts have light yellow serous contents.
It is recommended to remove all organic cysts due to the possibility of their degeneration into cancer.
ilive.com.ua
Rupture of ovarian cyst symptoms consequences | Cystablog
Functional cysts burst more often because their capsule is thinner than that of organic neoplasms. Rupture in the right ovary occurs more often due to increased blood supply and high pressure in the supply artery that arises from the aorta. Whereas on the left the artery arises from the renal artery.
Causes of ovarian cyst rupture
Can an ovarian cyst burst? Yes. This will be facilitated by:
- Active sex life.
- Impaired blood clotting system.
- Physical activity.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Abdominal damage.
- Inflammation of the reproductive organs.
- Congestion in the pelvis.
Each situation is individual and depends on the type, size of the lesion, as well as the condition of its walls. Sometimes apoplexy of an ovarian cyst occurs in absolute peace. The mechanism is based on an increase in intra-abdominal pressure and overstretching of the capsule by its contents.
Symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst
Symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst
If an ovarian cyst ruptures with the release of its contents into the abdominal cavity, the clinical picture is pronounced. The main symptom is acute pain in the abdomen on the side of the rupture. In addition, other manifestations may occur:
- Abdominal muscle tension.
- Pain in the lower back or inner thigh.
- Increase in temperature (does not respond to antipyretic drugs).
- Reduced blood pressure.
- Flatulence, nausea and vomiting.
- Spotting vaginal discharge outside the menstrual cycle.
- Malaise, weakness, pale skin.
- Reduced blood pressure.
- Uterine bleeding outside the menstrual cycle.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Decreased hemoglobin levels.
The clinical picture also depends on the degree of blood loss (the greater the amount of blood loss, the worse the condition).
What pain occurs when an ovarian cyst ruptures?
The intensity and nature of pain depends on:
- A type of pathological formation.
- Physical activity of the patient.
- Individual characteristics of women in the perception of pain. Physiologists say that everyone has a different pain threshold.
It should be noted! It is strictly forbidden to take painkillers before being examined by a doctor. Taking analgesics will blur the clinical picture and cause a false diagnosis.
The nature of the pain is sudden, with high intensity. Therefore, the woman takes a forced position that will ease the sensations. Signs of the condition: nagging pain in the lower back, discomfort, heaviness. If an ovarian cyst bursts, the pain covers the entire abdomen. Sometimes leads to loss of consciousness.
Pathogenesis
The endometrioid ovarian cyst has a special development mechanism, which is very often bilateral. Most often, the tumor appears in women aged 20-50 years. Cystic formation is accompanied by diseases such as uterine fibroids or endometrial hyperplasia. The size can reach 15 cm. When conducting a histological analysis, you can find out that the main sign of ovarian disease is the absence of glands in the walls of the tumor.
[13], [14], [15], [16], [17], [18], [19]