Medications to eliminate pathology
To figure out how to cure vulvitis, you need to identify the harmful irritant. If the disease is caused by pathogenic microorganisms, then a long recovery period will be required. In this case, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive treatment of vulvitis with the mandatory use of broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs:
- cephalosporins - destroy the cell walls of microorganisms;
- penicillins - block bacterial defenses;
- tetracyclines – inhibit protein synthesis;
- fluoroquinolones – disrupt microbial DNA.
Attention! Self-medication with these drugs can provoke dysbacteriosis, the appearance of Candida type fungi, the disease becoming chronic, and a decrease in the overall level of immunity.
One of the conditions for the effectiveness of therapeutic treatment is limiting sexual contact.
Vulvovaginal candidiasis
Vulvovaginal candidiasis is based on an infectious process caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. It occurs more often in young women, much less often in girls and menopausal women.
During pregnancy, vulvovaginal candidiasis is detected in almost half of women.
Yeast-like fungi Candida are present in small quantities in the opportunistic microflora of the vagina and do not cause negative changes. Candidal inflammation develops only if the amount of fungal microflora in the vagina begins to increase.
The causes and mechanism of vulvovaginal candidiasis have not been sufficiently studied; it is known that disruption of the vaginal microbiocenosis with a subsequent change in its pH is important in the development of infection.
Sometimes Candida fungi in quantities exceeding the “norm” may be present in the vagina in the complete absence of clinical signs of the disease. This condition is called carriage. Carriage does not exclude the development of the disease.
With vulvovaginal candidiasis, the inflammatory process is localized in the superficial layers of the epithelial layer. The inability of fungi to penetrate into deeper and more favorable areas of the mucous membrane leads to the fact that the infection can be present in the vagina for many years. If the protective properties of the vaginal environment are not lost, it will try to remove the pathogen from the body, preventing it from causing the disease, which leads to carriage. Loss or reduction of the protective mechanisms of the vaginal microflora leads to the development of the disease.
Vulvovaginal candidiasis has three clinical forms: carriage, acute vulvovaginitis and recurrent (chronic) vulvovaginitis.
Asymptomatic candidiasis is possible only with a slight increase in the fungal population in the vaginal environment. It occurs in every fifth pregnant woman.
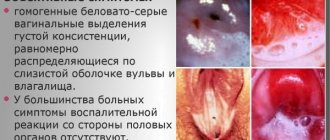
A peculiarity of candidal inflammation is the nature of the discharge: it is white (sometimes with a yellowish tint), thick in consistency and resembles cottage cheese in appearance. The remaining clinical manifestations are similar to those of vulvovaginitis of other origins and do not differ in specificity.
Acute vulvovaginal candidiasis has a pronounced clinical picture. Upon examination, hyperemia of the mucous membranes and abundant or moderate curdled discharge are revealed. Laboratory testing reveals a high titer of fungal flora. The acute phase of the disease lasts no more than two months.
Chronic candidiasis differs in the duration of its course (more than two months). When examined, signs of atrophy and infiltrates (thickening) can be seen on the mucous membranes of the vulva and vagina.
The clinical picture of vulvovaginal candidiasis depends on many factors: the composition of the vaginal microflora, concomitant gynecological diseases, and the state of the immune system. If the patient has intestinal dysbiosis, vulvovaginal candidiasis is considered as part of a generalized process.
Vulvovaginal candidiasis can be triggered by non-gynecological diseases. It can be a consequence of allergies, diabetes, intestinal infections, and so on. This complicates the treatment process.
Diagnosis of vulvovaginal candidiasis is not difficult. The presence of characteristic cheesy discharge and microscopy of smears of vaginal contents make it possible to make a diagnosis in the vast majority of cases.
Use of soft drugs
At the initial stage of treatment of vulvitis, in order to eliminate the pathological process, a hypoallergenic diet and topical medications are sufficient. The advantage of such drugs is their direct effect on the source of inflammation. The following ointments for vulvitis for women have proven themselves to be effective:
- Erythromycin ointment - belongs to the group of macrolide antibiotics that have a bactericidal effect;
- Levomekol is a combined, regenerative, antimicrobial agent;
- Chlorhexidine is a pharmacological antiseptic;
- Citeal is an antiprotozoal, antibacterial, antifungal drug;
- Clindacin – contains a bacteriostatic substance.
A tampon with ointment applied to it is inserted deep into the vagina. Suppositories are also widely used for treatment of vulvitis. For example:
- Terzhinan - treatment of vulvitis of mixed etiology in women;
- Betadine – effective against fungi, spores, bacteria;
- Pimafucin is an antifungal polyene antibiotic, effective for candidal vulvitis;
- Vagilak - replaces pathogenic bacteria with beneficial species, which normalizes the microflora of the female reproductive system.
Reference! Suppositories are not recommended for virgins. To avoid damage to the hymen, suppositories are prescribed after the onset of sexual activity.
Diagnosis of vulvitis
Diagnosis is carried out by a gynecologist as follows:
- Inspection;
- Collection of complaints, medical history;
- Colposcopy (if necessary);
- Lab tests.
To determine which microorganisms provoked the pathological process, bacterioscopy of smears is performed, as well as cultural inoculation with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics. It is also important to identify concomitant diseases that may cause inflammation or affect the body's defense mechanisms.
Pathology of the genital organs in girls
It is not difficult to suspect the development of vulvitis in a child. The girl becomes restless and often tries to touch her genitals. In this case, personal hygiene procedures are carried out more carefully. They use baths with infusions of medicinal herbs. The external genital area and vagina are washed with solutions: potassium permanganate, furatsilin, rivanol, dioxidine, lysozyme. Sessions of dosed ultraviolet irradiation of the vulva are performed.
If the above methods do not bring results, ointments with antibiotics, estrogens, and nitrofurans are prescribed. Treatment of vulvitis in girls, as well as in adult women, should be comprehensive, including:
- antiseptic treatment of the genital tract;
- restoration of the microflora of the vaginal mucosa;
- general strengthening therapy of the body's defenses;
- improving immune status.
In case of allergic etiology of vulvitis, antihistamines are used to relieve itching. To normalize the psycho-emotional state, sedatives are prescribed. If vulvitis has developed as a result of helminthic infestation, the therapeutic complex is replenished with anthelmintic drugs.
Causes and symptoms
In gynecology, there are several forms of vulvitis and vulvovaginitis:
- infectious (caused by fungi and bacteria);
- allergic;
- atrophic (against the background of hormonal changes during menopause).
The type of vulvitis will determine treatment tactics and the choice of medications. Vulvitis during pregnancy deserves special attention. The use of medications during this period is limited due to the high risk of negative consequences for the fetus.
Symptoms:
- hyperemia (redness) and swelling of the skin of the external genitalia in the area of the labia minora and majora, clitoris;
- itching, burning and pain in the vulva;
- pathological discharge;
- plaque on the labia.
In the acute stage, the symptoms will be most pronounced, in the subacute stage they will be smoothed out. In a chronic course, there may be a complete absence of symptoms. If the first signs of vulvitis occur, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Restoring health with herbal medicine
In the table you can see the most popular recipes for treating vulvitis with herbs.
| Medicinal plants | Method of preparation and method of application |
| Chamomile | 1 tsp. flowers, leave for 4 hours in a glass of water brought to a boil, take 100 ml in the morning, on an empty stomach. |
| Calendula | 1 tbsp. l. steam in a water bath with 300 ml of water for 15 minutes. Cool, take 50 ml 3 times a day before meals. |
| Viburnum flowers | 1 tbsp. l. Steam the flowers for 10 minutes. Strain, use 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day. |
| nettle leaves | Pour boiling water over 50 grams of leaves and leave for 1 hour. Use the infusion for baths. |
| St. John's wort | 2 tbsp. l. herbs pour 600 ml of water, bring to a boil. After cooling, strain. Apply when washing. |
| Celandine | 1 tbsp. l. pour 250 ml of boiled water. Leave for 1 hour, take 50 ml in the morning, 20 minutes before meals. |
| Calendula, tansy, chamomile, plantain, celandine | 1 tsp. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over each herb. Leave in the thermos for 5 hours. Use for douching. |
| Alcohol solution of chlorophyllipt | Dilute 10 ml of solution in 0.5 liter of boiled, cooled water. Use for douching. |
Symptoms of the disease
With the development of vulvovaginitis, the patient has complaints:
- burning and itching in the genital area;
- the appearance of vaginal discharge (yellow, green, yellow-green, brown, cheesy).
The nature of the discharge may be different. If the disease is caused by bacteria, then the vaginal secretion is thick, heterogeneous, and purulent. With vulvovaginitis caused by Trichomonas, the discharge is purulent, foamy, with an unpleasant fetid odor. A fungal infection is characterized by a curd-like discharge.
During an examination of the genital organs, the doctor pays attention to the following signs:
- Swelling and redness of the mucous membrane. Such a change can affect the labia, the area of the vestibule of the vagina, and the vaginal walls.
- The appearance of erosions. This symptom is characteristic of herpetic and diphtheria vulvovaginitis.
- Formation of bubbles filled with clear liquid. This symptom is characteristic of herpes.
- Synechia (fusion) between the labia minora. Often found in young girls. The cause is chronic vulvovaginitis.
Acute vulvovaginitis can also manifest as general symptoms, especially for girls of preschool age. In this case, the child may become capricious, whiny and get tired quickly. If the patient is sexually active, then symptoms arise in the form of decreased sexual desire, anorgasmia and pain during sexual intercourse.
Therapy at home
You should not discount old, time-tested methods of fighting vulvitis using folk remedies. They remain a popular adjunct to at-home drug treatment:
- Honey , melted in a water bath, is soaked in a small roller and inserted into the vagina. Such tampons have an antibacterial, therapeutic and healing effect.
- Sea buckthorn oil is used to lubricate the vagina and external genitalia. The plant product has high biological value, the ability to restore and regenerate tissue.
- Streptocide . After hygiene procedures, wipe the intimate area dry and sprinkle with powder. Cleanses the external genital organs from staphylococci.
- Baking soda . 0.5 tsp. A glass of water once a day will reduce itching and burning in the genital area. Douching with this component has a healing effect and eliminates unpleasant odor.
- Flaxseed oil . Contains a complex of vitamins, minerals and amino acids. A tampon soaked in the product is placed into the vagina. Can be taken before meals, 1 tbsp. l. or add to food.
There are many ways to influence pathological changes in the body, but how to treat vulvitis in women, the dosage of medications should be determined by a specialist. Therefore, even with minor functional disorders of the body, you should visit a gynecologist.
Share the article on social media. networks:
Treatment
Photo: gynodek.com
Most often, vulvitis is accompanied by vaginitis - inflammation of the vagina. The disease can be caused by various bacteria (pyogenic, E. coli), yeast-like fungi and helminths.
Treatment is based on eliminating the causes of the disease. In a complicated period, it is necessary to observe bed rest and abstain from sexual activity.
Treatment of the disease is prescribed individually for each patient. It is necessary to regularly wash the genitals 3 times. per day with tinctures of medicinal plants, a solution of potassium permanganate, 2% boric acid, mramistine, dioxidine, chlorhexidine.
Antibacterial agents are also prescribed, which are applied to the organs (Makmiror cream, Vagitsin), suppositories are inserted into the vagina (Polygynax, Terzhinan, Ginalgin).
Treatment is carried out until the disease disappears completely. In combination with these drugs, vitamin A is also used, which provides protection to the epithelium, vitamins C, E to increase the body's immunity. Sea buckthorn oil, rosehip oil, and solcoseryl are also used, which ensure restoration of the body during complications.
If itching occurs, anesthetic ointment is used, taken orally (tavegil, suprastin, diphenhydramine). If atrophic vulvitis and vaginitis occur, which can occur during the postmenopausal period, hormones (estrogens) are taken for local and, in some cases, regular use. When specific vulvitis occurs, the doctor prescribes special treatment.
The main causes that lead to the formation of vulvitis should be eliminated.
With the correct diagnosis of the disease and timely treatment, vulvaginitis is curable and can go away without a trace. If the doctor has diagnosed acute vulvitis, then you should use dry sterile pads, regular douching with chamomile decoction, tampons with synthomycin, and suppositories. If there is itching, girls use ointments and powders. Applying cold helps relieve pain. Baths with potassium permanganate, silver nitrate, protargol, and douching with a solution of lactic acid are also prescribed.
Today, there are various new clinical treatment methods: magnetophoresis, laser phoresis, ultraphonophoresis.
Without appropriate treatment, vulvitis can become chronic, and in this case its nature can be complicated. Acute vulvitis, which was suffered in infancy, can cause fusion of the labia in a girl. One of the common factors in the formation of acute vulvitis are: staphylococcus, enterococcus, Escherichia coli, diphtheria coli, gonococcus.
Treatment of vulvitis
If a diagnosis of acute vulvitis is made, treatment is prescribed taking into account the nature of the disease. If the cause of the disease is allergic reactions of the body, desensitizing drugs are prescribed. In this case, you need to follow a diet. Vulvitis in women caused by infections such as chlamydia, gonococci, trichomonas, fungal flora and other diseases requires special therapy.
The cause of vulvitis characterizes the course of the disease. Inflammation in primary vulvitis can be caused by obesity, diaper rash on the genitals, cystitis, helminth infection, and glandular diseases. If vulvitis is diagnosed, treatment is prescribed by the doctor after examining the patient.
Treatment of vulvitis during pregnancy
Treatment of vulvitis during pregnancy should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor and after a smear examination. A pregnant woman is recommended to take medications in combination with healing methods that are aimed at increasing immunity. Untreated vulvitis can cause the baby to become infected with cocci during childbirth. The complex course of the disease requires treatment with antibacterial and antifungal drugs.
Prevention of vulvitis is carried out using a decoction of medicinal plants; it is also necessary to maintain daily genital hygiene using special means.
Treatment of vulvitis with ointments is most effective in combination with drug treatment. Treatment with ointment can also be carried out if there is candidal and atrophic vulvitis, using drugs such as: vocadine, betadine, miramistin, citealom, instillagel.