General information about cervical sarcoma
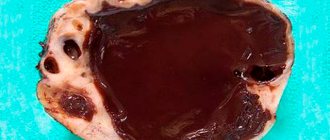
Uterine sarcoma is a malignant tumor of the body of the uterus or cervix, arising from the undifferentiated connecting elements of the myometrium or its stroma. The disease does not manifest itself symptomatically for a long time, which is why this type of oncology is called “silent tumor”. Acyclic bleeding, acute abdominal pain, discharge with a putrid odor often appear as the pathology progresses, that is, after the disease passes to stage 3.
Diagnosis of the disease includes bimanual examination, ultrasound, diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity. Samples obtained during curettage must undergo cytological and histological examination. In the early stages, if the tumor does not grow into adjacent tissues, it is removed during an extended panhysterectomy. Combination with chemotherapy or radiation treatment helps to exclude the development of sarcoma from secondary lesions.
Attention! Sarcoma of the uterine body is diagnosed more often than of the cervix.
Sarcoma makes up no more than 5% of cases of total oncology, but its danger should not be underestimated. Women with uterine fibroids are at risk of developing pathology. The lesion is diagnosed in women of different ages, but the most unfavorable period is considered to be postmenopause and premenopause. It is worth noting that the tumor is also detected in children. In this case, its development is associated with disembryogenesis.
Symptoms
Unfortunately, uterine sarcoma may show virtually no symptoms for quite a long time; it is not without reason that in the early stages it is called a “silent tumor”. Also, often the signs of sarcoma can be mistaken for symptoms of other diseases - adnexitis, polyposis, uterine fibroids, pathologies of the menopause. As a result, the woman turns to a specialist untimely, the diagnosis is made late, as a result of which the prognosis significantly worsens, even if the patient began treatment immediately.
The following signs may indicate uterine sarcoma:
- aching pain that occurs periodically, a feeling of discomfort and heaviness in the lower abdomen, manifested as a result of physical activity, bowel movements, and intimacy. In the future, they are present on an ongoing basis;
- irregular bleeding, changes in the nature of menstruation;
- possible change in abdominal volume;
- the presence of leucorrhoea - unpleasant-smelling, purulent, abundant with a watery structure, or, on the contrary, scanty;
- an increase in anemia even in the absence of bleeding;
- fever, intoxication of the body.
At the fourth stage, uterine sarcoma is manifested by symptoms from the affected organs, severe pain, and cachexia.
Classification of cervical sarcoma
There are several types of sarcoma depending on its location and nature of the course:
- Carcinosarcoma. The tumor forms in the endometrial tissue and is diagnosed in women over 60 years of age during menopause.
- Endometrial stromal sarcoma. Often found during premenopause.
- Leymyosarcoma. The most unfavorable in terms of treatment and prognosis, characterized by rapid progress, quickly metastasizes. It is detected in women aged 30-40 years.
- Mixed type. Combines the histological features of several types of sarcomas.
In the modern classification, there are 4 stages of tumor development.
Stage 1 – the neoplasm is limited to the muscular or mucous layer of the body or cervix:
- 1a – affects the myometrium or endometrium;
- 1b – affects the myometrium and endometrium.
Stage 2 – sarcoma is limited to the body of the uterus or cervix, does not extend beyond:
- 2a – localized in the body of the reproductive organ, distal or proximal infiltration can be traced without transfer to the walls of the pelvis;
- 2b – the tumor spreads to the cervix.
Stage 3 – sarcoma is located outside the uterus, but is located in the pelvic area:
- 3a – there is unilateral or bilateral infiltration of the parametrium extending to the walls of the pelvis;
- 3b – typical tumor metastasis to regional lymph nodes, organs of the reproductive system, germination into large veins;
- 3c – germination of the serous layer of the uterus, conglomerates form with neighboring structures without damaging them.
Stage 4 – sarcoma grows into neighboring organs and can extend beyond the pelvis:
- 4a – the neoplasm grows into the rectum and bladder.
- 4b – metastasis to distant organs is observed.
In gynecological oncology practice, the following types of sarcomas are distinguished:
- Sarcoma of the cervix. Presented in the form of a polyp covered with ulcerative lesions. The development of the disease is preceded by radical changes in the structure of the cervical tissues. The provoking factor is erosion, polyposis, fibroma. The tumor has a progressive course and metastasizes early.
- Sarcoma of the uterine body. It grows rapidly and quickly reaches significant sizes. Quickly spreads to the ovaries and rectum. Metastases affect the liver, mammary glands and spinal cord.
- Stromal sarcoma. A distinctive feature is unpredictable growth; it is quite difficult to identify the moment of tumor progress. In some cases it can be aggressive, but sometimes it is sluggish.
Varieties
Depending on the clinical form of the malignant neoplasm, its structural content, the degree of spread, as well as the nature of the course of the disease, the following varieties are distinguished. Each of them has its own specifics and symptoms.
Malignant tumors of epithelial tissue
- papillary cancer - characterized by a high mortality rate. Such tumors are structurally different from other types of anomalies in that they have an internal capsular compartment containing fluid mass and papillae. The papillaries contain layers covered with epithelial tissue. Difficult to diagnose as a separate type of pathology;
- glandular cancer (adenocarcinoma) is one of the most common forms of the disease. Diagnosed in more than 45% of identified cases. Education grows rapidly, reaching a huge size, and rapidly grows into neighboring departments and systems of life;
- solid cancer – it is preceded by adenocarcinoma, which, through the process of cellular mutation, develops into solid cancer. It has a mixed structure. DNA molecules have a blurred pattern and a twisted lattice. It is rarely diagnosed in its pure form.
Connective tissue tumors
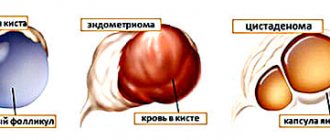
This type of tumor in medical terminology is interpreted as ovarian sarcoma. It is characterized by the absence of clear localization zones , since pathology develops in connective tissues, which are present in several fragments of the organ.
It is often detected in very young patients. Cancer cells divide rapidly and are classified as highly malignant.
Tumors from the tissue covering the follicle and the granular layer of the follicle
- Granulosa cell carcinoma belongs to a heterogeneous type of tumor. Often the cells are of benign origin and only after a certain time they mutate into cancer. The disease can last for many years, practically without making itself felt;
- malignant thecoblastoma – actively produces hormones, which is why it is often detected in young girls. The main symptom is premature sexual development. It has a good prognosis for full recovery, since it is mainly diagnosed at the initial stages of the onset of the anomaly;
- Dysgerminoma (seminoma) is one of the most aggressive forms of tumor formations. Belongs to the germinal type. In terms of structural content, it is a nodular connection, dense to the touch. It can be either single or multiple.
Ovarian connective tissue tumors
Pathologies arising from the connective tissue of the organ account for no more than 3% of all diagnosed cases. Occurs only in childhood and adolescence.
Almost always turns into cancer from a benign formation. It has a complex macroscopic structure. Includes almost all forms of the disease, ranging from squamous cell. Depending on the degree of carcinogenicity, it can either progress rapidly or remain latent for years.
Benign salivary gland adenoma: clinical picture and treatment. This article provides an example of a nutritional menu for pancreatic cancer.
Lung carcinoma creeps up unnoticed. Find out here https://stoprak.info/vidy/legkix-i-plevry/lung/karcinoma-klinicheskaya-kartina-terapiya-vyzhivaemost.html hidden signs.
Metastatic malignant tumors
- Krukenberg cancer – refers to metastatic manifestations of ovarian cancer against the background of aggressive atypical spread of cells throughout the patient’s body. It is considered a secondary oncology. Almost incurable. Almost always recurs;
- metastatic adenocarcinoma - stems from a pathology that originates in neighboring sections and develops in the ovaries as a secondary manifestation of oncology. Cancer cells often enter the organ through the blood. They are distinguished by an extremely severe form of the flow.
Causes of cervical sarcoma formation
The exact causes of cancer development have not yet been identified. Doctors were able to identify factors. Predisposing to the development of sarcoma of the cervix and uterine body, these include:
- benign neoplasms localized in the female reproductive organs in the absence of treatment;
- viral diseases (herpes and papillomavirus) localized to the genitals;
- injuries to the uterine cavity and its cervix as a result of abortion or violation of diagnostic curettage technology;
- presence of harmful addictions in a woman (alcohol, smoking, drugs);
- working with toxic chemical compounds;
- imbalance of hormones in the body.
The most important factor is the presence of tumors in the organs of the woman’s reproductive system. It is he who provokes the formation of sarcoma in 60% of cases. Gynecologists say that it is impossible to underestimate the danger of cysts, fibroids or polyps; later they can cause the development of aggressive cancer.
The list of provoking factors also includes:
- long-term and uncontrolled use of hormonal contraceptives;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- no history of childbirth;
- injuries during labor;
- oncological lesions of the mammary glands;
- late menopause;
- undergone radiation therapy.
Since sarcoma has a fulminant course, women at risk need to undergo regular gynecological examinations, including pelvic ultrasound and colposcopy.
Classification
There are several forms of tumor - round cell, spindle cell, small cell and polymorphic cell.
They differ in their cellular structure, and the most aggressive are those with a soft tissue structure. They are prone to rapid growth, as a result of which signs of the disease develop faster than with other forms of adnexal cancer. A separate type of ovarian sarcoma is also determined - undifferentiated. It has a different structure from other types of formations and is rarely highly aggressive.
Malignant mixed Müllerian ovarian tumors (MCMT) are a type of tumor with a combined structure. They contain cells that form the basis of adenocarnicomas, stromal and mesenchymal tumors of the ovary. Due to their high degree of malignancy, the disease is detected already at stage 3, when in patients the pelvic organs and nearby lymph nodes are affected by metastasis.
Most often, the disease is diagnosed after 45 years of age, less often in young women and adolescents. Infants are also susceptible to the development of oncology - this is possible with embryonal ovarian sarcoma in newborn girls. This tumor forms in the womb.
Clinical manifestations of cervical sarcomas
In the initial stages, sarcoma progresses silently. A malignant neoplasm does not make itself known for a long time, and sometimes doctors can detect a tumor only in the last stages. In some cases, sarcoma can masquerade as a benign fibroma. Only histological examination helps to identify the disease.
Symptoms appear quite sharply, but at stages 3-4. The disease progresses very rapidly, so it is not always possible to start treatment on time.
The list of characteristic signs that allow one to suspect the development of a tumor includes:
- purulent, bloody, thin or watery vaginal discharge that has a strong and sometimes putrid odor;
- periodic bleeding not associated with menstrual bleeding;
- cycle failure;
- change in volumes of discharge;
- yellow discharge after menstruation is characteristic;
- a noticeable decrease in performance and attention, weakness and apathy;
- refusal of food;
- shift in leukocyte blood count;
- manifestation of symptoms of anemia;
- rapid weight loss, progressive exhaustion;
- a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, which manifests itself after bowel movements;
- rapid tumor growth, abdominal enlargement;
- a feeling of chills, quickly replaced by fever.
Attention! The described clinical picture is typical for all cancer lesions.
In the last stages of development, rapid metastasis is observed. Lesions can be traced not only to nearby organs, but also to distant ones. If germination is observed in the bladder, problems with urination appear, and blood may appear in the urine. When the rectum is damaged, defecation is characteristically impaired, and blood may appear in the stool. When the spine is affected by metastases, disturbances in the functioning of the entire musculoskeletal system appear, and a predisposition to fractures is observed.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the disease as accurately as possible, the following methods are used:
- CA-125 analysis is a test to determine cancer in a specific department. At the initial stage, the indicator can be practically unchanged, which makes it difficult to identify the disease, but as the disease develops, it determines it unmistakably;
- Ultrasound - determines the exact size of the tumor, as well as the area of its localization. In addition, it is possible to monitor reproductive disorders;
- CT scan – gives a complete clinical picture of the pathology, the degree of organ damage and allows you to diagnose even the smallest anomaly;
- cytology is a detailed fragmentary study of the affected area at the cellular level. If a tumor is present, it determines its nature of origin.
Diagnosis of cervical sarcoma
When conducting diagnostics, it is necessary to differentiate sarcoma from benign tumors. The development of a malignant tumor can be suspected if the tumor grows aggressively in the body. A woman’s condition is often aggravated by heavy bleeding not associated with menstruation, symptoms of anemia appear, and ESR in the blood increases.
When examining the genitals in a mirror, blue discoloration of the mucous membranes may be detected. In some cases, swelling can be observed, signaling the imminent exit of the node from the uterine cavity into the cervix. Using a gynecological examination, the size and location of the tumor are determined. All patients with suspected sarcoma are recommended to undergo a full examination of the body, in particular an MRI.
Diagnostic methods
To identify sarcoma of the appendages, a thorough and extensive diagnosis of the body is required. The doctor prescribes the following examinations:
- Ultrasound of the pelvis - determining the size, type and location of ovarian sarcoma, the condition of the woman’s genital organs, examining nearby lymph nodes and organs for the presence of metastases;
- colonoscopy - assessment of the condition of the intestine, the degree of its damage;
- blood test for tumor markers - detects the presence of cancer cells in the body;
- MRI of the pelvis – a detailed study of the condition of all pelvic organs, the structure of the malignant formation;
- biopsy – necessary to accurately determine the type of tumor and its degree of malignancy;
- fluorography of the lungs to detect metastases;
- Mammography - a study aimed at detecting traces of a tumor in the mammary glands.
Additionally, general and biochemical blood and urine tests are performed. This allows you to determine the state of the body.
Treatment of cervical sarcoma
To treat sarcoma, different treatment methods are used, most often they are combined to obtain more lasting results. The main difficulty is that it is impossible to completely remove sarcoma and forget about the disease. Education causes significant damage to health and is still classified as incurable. Therapy is often palliative in nature, aimed at prolonging life and slightly improving its quality, because the prognosis for 5-year survival when the process is detected at stage 1 is about 40%. This means that less than a third of women will live 5 years after sarcoma is diagnosed and treated. The mortality rate is high.
The influence tactics used include:
- surgical intervention;
- chemotherapy;
- hormonal treatment.
The most effective method of exposure is determined by the attending physician, depending on the stage of the process.
Surgery for cervical sarcoma
Surgery is the most radical and common method that allows you to accurately determine the stage of the tumor and cut it out. Most often used at an early stage. In advanced cases, surgery is pointless; you should not expect the body to recover. During the operation, the uterus and ovaries are completely removed, sometimes with the capture of lymph nodes if they are affected. To consolidate the result, chemotherapy is performed.
Chemotherapy and radiation treatment for cervical sarcoma
Chemotherapy is an important step in the treatment of uterine sarcoma. It is used after surgical removal of a tumor to prevent its re-development. When performing surgery in the later stages, chemotherapy drugs are used before the intervention. This therapy helps reduce the likelihood of relapse and helps eliminate distant foci of pathology. For treatment, cytostatics, progestin and antiestrogenic drugs are used.
Radiation treatment may be given before or after hysterectomy. In some cases, it is alternated with courses of chemotherapy. The method is applicable when the tumor is located within the uterus. Remote irradiation is provided.
Treatment
In the treatment of sarcoma, doctors usually use several methods at once. Their interaction is necessary to increase the effectiveness of therapy. The best result is usually achieved with a combination of chemotherapy and surgery.
Operation
Surgery is the main method of treatment. It is not used if the tumor has reached the fourth stage, since there is a high risk to the patient’s life. In other cases, surgery significantly improves survival prognosis.
The operation involves not only removing the tumor, but also the ovary itself. The optimal situation is when all genitals are cut out. This is done to prevent relapse.
For surgical intervention, doctors choose the laparotomy method. The duration of the operation does not exceed 1.5 hours, the course of action may change during the process. By dissecting the anterior abdominal wall, the following elements are removed:
- The neoplasm itself
- Affected tissues
- Organs,
- Lymph nodes,
- All internal genital organs, if necessary.
Chemotherapy
A biopsy is performed before chemotherapy. The results of this analysis allow us to understand what the structure of the tumor is.
Attention! Chemotherapy may not be prescribed due to a high degree of insensitivity to certain types of drugs.
Combinations of drugs:
- Cisplatin, Doxorubicin,
- Carboplatin, Taxol,
- Cisplatin, Ifosfamide,
- Cisplatin, Doxorubicin, Cyclophosphamide,
- Paclitaxel, Cisplatin.
A positive effect is recorded as a result of using platinum products. They manage to kill most cancer cells. Chemotherapy itself lasts 1.5-3 years. During this period, 6 to 8 courses of IV drips are carried out at a certain interval.
Survival prognosis for cervical sarcoma
It is quite difficult to answer the question of how long people live with uterine sarcoma; much depends on the stage of detection of the formation, the characteristics of the patient’s body and the therapy used. In general, sarcoma has the least favorable prognosis among all genital malignancies. Even if it is detected at the first stage, only 40% of women will be able to cross the 5-year survival line.
At the same time, in the absence of therapy, the pathology progresses rapidly. The patient's quality of life is rapidly declining. The patient dies within 1-2 years after diagnosis. Living with uterine sarcoma is impossible; as the degree of spread of metastases increases, the woman’s condition will worsen and problems will appear in the functioning of other internal organs.
Sarcoma of the uterus and its cervix is quite rare in gynecological oncological practice, but has the most aggressive course and has a less favorable prognosis. The tumor is asymptomatic at an early stage of development, rapidly progresses, and becomes incurable. The survival prognosis at stages 3-4 is minimal, and it is at this stage that the tumor is most often discovered.
There are no specific means to prevent the development of the problem. A woman can protect herself by regularly visiting a gynecologist, but this does not provide 100% protection against sarcoma, because it is not visible to the naked eye and is often disguised as a benign neoplasm.
Features of treatment
If pathology is detected late, treatment is carried out with chemotherapy, which also includes painkillers.
The approach to treating a patient with ovarian adenocarcinoma depends on the stage of the process and the type of atypical cells. A combination of surgery and chemotherapy is most often used. If cancer was detected in the initial phase, the affected ovary is removed without subsequent chemotherapy. In case of widespread lesions or contraindications, only drugs are used for surgical manipulation. Cytostatics, corticosteroids and other drugs that slow down the progression of tumor cells or kill them are more often used. The patient is prescribed analgesic, antiemetic and restorative therapy.
Physiotherapeutic treatment in the form of magnetic therapy, mud therapy and electrophoresis is recommended.
Drugs
| Therapeutic group | Action | Examples |
| Platinum drugs | Suppressing cancer cells | "Cisplatin" |
| "Lipoplatin" | ||
| "Carboplatin" | ||
| Ethyleneamines and chlorethyleneamines | React with cells, disrupting metabolic processes, causing the latter to die | "Cyclophosphamide" |
| "Sarcolysin" | ||
| "Lofenal" | ||
| "Thiophosphamide" | ||
| Antimetabolites | Cancer DNA synthesis blockers | "Mercaptopurine" |
| "Tegafer" | ||
| "Methotrexate" | ||
| "Fluorouracil" | ||
| Antibiotics | Cytostatic effects to disrupt the process of reproduction of cancer genes | "Bruneomycin" |
| "Adriamycin" | ||
| "Actinomycin" | ||
| Alkaloids | Have a toxic effect on cancer cells, inhibiting development due to changes in pH | "Vincristine" |
| "Kolkhamin" | ||
| "Vinblastine" | ||
| Steroids | To stabilize hormonal levels | Estrogens, progestins, corticosteroids, androgens |
Personal experience “I'll go bald again”: How I live with ovarian cancer
During my illness, I managed to receive two degrees: art history and design, the second - at the “Details” studio school, one of the five strongest in the world. This has long been my dream, and at first I put it off - for the first time after the diagnosis, I planned something for a maximum of a month in advance. But I still went and studied, defended myself as one of the best, and now we are aiming for publication in AD. When I think about my life, I realize that I would not give up everything that happened to me. No matter how scary and difficult it is, I assess everything positively. The depth and quality of life, the rethinking, the people I got to know - everything became better. This is a test when you don’t know how much time you have, but you always have to hope for the best.
Ovarian cancer is now considered an incurable chronic disease; Most likely, it will come back, and I will have to fight again, but that doesn’t scare me. Sometimes I remember how I wanted new impressions and new knowledge, and I say “be careful what you wish for” - after the diagnosis, there were more than enough impressions. And I also joke that I once wanted to have “chemistry” - although I thought about a perm, but ended up with chemotherapy. Sometimes it is very difficult; Because of the removal of my ovaries, I entered surgical menopause, and with it depression. I started taking hormone replacement therapy and developed toxic hepatitis. After that, I switched to a local hormonal drug. There is always something you can do, even when it seems like there is nothing left.
Many acquaintances and friends want to participate, to help in some way - they advised me bioenergetics, white magicians, repairing biofields, endless lotions, diets, buckwheat with water and rubbing salt into the hair. But I am for evidence-based medicine. Treatment protocols exist and include optimal surgery and gold standard chemotherapy. Probably, if a person is treated according to the standard, then let him, if he wants, go on diets and repair his biofield, as long as he does not replace normal treatment with this. Many people waste precious time, and those who advise such “methods” are simply criminals. People who spoke with Steve Jobs' doctor told me that he should have come for the operation rather than go to Tibet. The same thing happened with Abdulov - he went to Tyva to see some shaman, and returned with a tumor that could not be operated on.
Unfortunately, there is very little good information available about cancer treatment, which makes people even more afraid. Some people turn a blind eye to their diagnosis, pretend it doesn’t exist, and don’t begin treatment. If you have been diagnosed with cancer, don’t panic and don’t give up, start treating your disease like any other. If it seems to you that dangerous diseases occur only in others, but will not affect you, still think about regular medical screenings. It is very important to educate people, to give access to information - even now many people tell me that I should write a book, but I don’t know how to choose the time for this. Within a week after receiving the diagnosis, I found everything there is in the world on this topic, including some of the latest dissertations. I am interested in life, a lot awaits me ahead, I have many plans - by the way, they call me to teach at the “Details” school, from which I graduated. I will continue to live fully, love, learn new things. Everything will be cool.