Today, more and more young mothers are striving for the most pristine and natural way of feeding a newborn - breastfeeding. It’s so simple, pleasant, and most importantly – useful for the baby! But one day there may come a day when breastfeeding becomes painful. Why your breasts hurt during breastfeeding, how to deal with it and not stop breastfeeding, you can find out by reading this article.
Physiological causes of chest pain during breastfeeding
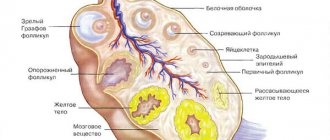
Breast pain during feeding may appear as early as the third day after birth, when milk production begins. At this time, the breasts swell and a tingling sensation may occur. You should not be afraid of this, as this is a natural process of starting breastfeeding. In the first week after birth, it is important to feed frequently or express milk as it is produced, since frequent emptying increases the number of prolactin receptors in the breast, which in turn affects the amount of milk produced in the future.
Many young mothers complain that their breasts hurt when breastfeeding . In this case, bruises, abrasions and even cracks can form on the nipples. The main reason for such conditions is the delicate skin of the nipples, but don’t worry, soon all the cracks will heal, the skin will harden, and you will forget about this problem. Possible reasons may be:
- Incorrect attachment of the baby to the breast.
The correct position is when the nipple is deep inside the baby's mouth, the chin rests on the chest, the lower lip is bent and completely covers the areola, the upper lip is unfolded and does not completely cover the areola from above, since the head is at an angle of about 140°. The nose should not be recessed into the chest, as the baby needs to breathe while sucking. - You take the breast while you suck.
You should not do this, wait until the baby has emptied the breast, different children need different amounts of time to get enough. If you see that the baby has eaten, but continues to suck “idly,” insert your little finger into the corner of the baby’s mouth between the jaws and gently turn it, so you can painlessly reach the breast. - Wash nipples with soap or treat them with disinfectants before each feeding.
Frequent use of soap or other aggressive products disrupts the water-fat balance of the skin and dries it out. For proper nipple hygiene while breastfeeding, it will be enough to take a shower once a day.
Causes of chest pain during feeding
Natural causes
During pregnancy, the breasts undergo preparation to provide adequate nutrition to the newborn baby. You can observe swelling of the mammary gland and darkening of the nipples. The following factors are distinguished:
- Fast flow of milk. Most women in labor report that this process feels similar to breast expansion or a tingling sensation;
- Pain when grasping the nipple, resulting in the formation of cracks;
- Rush of milk. Lactation is formed up to three months after birth, as a result of which we can talk about the persistence of milk leaks at this time. In a little time, the nursing mother will be able to feel the flow of milk to ensure that the baby is nourished. It is worth expressing milk, especially if you feel “bloating” in your breasts. It is best to feed the baby at this time.
If a woman regularly begins to breastfeed her baby, monitoring the correct latch of the nipple, the pain can gradually go away.
If discomfort appears at a later period of time, it is worth analyzing the possible factors for this condition.
Incorrect nipple latching during feeding
Experts consider this reason to be the main reason for lactation disorders. If the nipple girth is incorrect, the mother may feel pain. This can adversely affect the child himself, who swallows excess air.
It is worth making an effort to ensure your baby latch onto the nipple correctly. For this purpose, a woman can do the following:
- Wait for the moment when the baby opens his mouth. The reflex will work if you touch your lower lip with your nipple;
- Raise the child's head so that the mouth is placed on the nipple, which will avoid injury;
- If it is impossible to grasp the nipple, it is worth tightening the skin of the aureole so that the thumb is on top and the index finger is on the bottom. You can place the nipple in the baby’s mouth and lower the breast, which will facilitate a proper latch.
It is optimal to place the child under the arm, lying down on a suitable surface. If you adapt and learn the correct process, no pain will arise.
Circumstances arise when the baby does not clasp the chest in the correct way precisely because of physiology:
- The bridle is not long enough. The problem can be solved by contacting a dentist who specializes in treating children;
- Pathological structure of the upper palate. Whether it really exists is worth checking with a dentist.
Nipple skin injury
Lack of experience when feeding babies can lead to cracks in the nipple. This can cause painful sensations that manifest themselves due to factors:
- Incorrect grip, due to which the baby sucks only part of the nipple without a halo. This can cause mechanical injuries that cause cracks to appear;
- Regular breast washing can strip away the protective lubricant and lead to dry, thin nipple skin;
- Illiterate pumping. From time to time there is a need to express milk: to improve lactation, while the mother is leaving, during illness, or at the end of feeding. Do not squeeze your breast too much or put pressure on the nipple;
- Suddenly interrupted feeding process. Cracks may appear if the nipple is pulled out suddenly. It’s best to wait until the baby relaxes and lets go. If there is a need to interrupt, you need to insert a clean little finger into your mouth and carefully pull out the nipple.
Thrush
A crack or abrasion on the nipple can become a source of infection. You can find a whitish coating on the nipple, skin of the gums, cheeks, and tongue of the baby. He may cry and refuse food.
At this moment, the woman feels pain, including during the break between feedings. They can intensify when the infection goes deeper and the milk ducts are affected. Among the reasons are changed hormonal levels, disturbances in the functioning of the immune system and irregular hygiene (although this aspect also applies to frequent breast washing).
It is best for a woman to make an appointment with a specialist. Moreover, the doctor will be able to give recommendations regarding the use of control methods if the baby has thrush.
Lactostasis
It is called stagnation of milk in the duct of the mammary gland, which is caused by the following factors:
- Incomplete and inconsistent emptying of the breast, which can be caused by poor attachment, bottle feeding and cracked nipples;
- Holding the breast during feeding: fingers squeeze the ducts, which does not contribute to complete emptying;
- A bra that is too tight, pinching the chest, sleeping on the stomach;
- Increased milk production;
- Experiencing stressful situations, regular lack of sleep and chronic fatigue;
- Accidental bruises, injuries, chest hypothermia.
In the presence of lactostasis, a tightness is felt in the chest, and redness of the skin is observed. Increased breast temperature may be present.
Milk stagnation is not a reason to stop breastfeeding. You can put the baby to your breast for two to three days, which will help you cope with this diagnosis. At the same time, pain may be felt after the breast has emptied. If left untreated, this disease can lead to mastitis, which is not an infection.
Mastitis
It is called inflammation of the mammary gland due to stagnation of milk, cracks in the nipples, which serve as a favorable focus for the penetration of various types of infections. As a result of the diagnosis, severe pain, lumps, red skin, elevated body temperature and chills are felt.
Inflammation may be accompanied by the formation of a harmful process in the mammary glands, as a result of which pus enters the breast milk. The best option in this case is to stop breastfeeding until cured.
At the initial stage, treatment for mastitis may involve applying a cold compress to the breasts between feedings and emptying the mammary glands (feeding the baby frequently or expressing milk). Particularly difficult cases require the use of medications, and in advanced situations, it is worth contacting a surgeon.
Vasospasm
It is a sharp contraction of the blood vessels in the chest. The nipple can change color from beige to white. This process leads to blockage of blood flow, which can cause pain.
If a woman who is breastfeeding experiences pain due to spasm of blood vessels, she should make an appointment with a specialist. In addition, it is necessary to check for the presence of diseases of the immune system. Moreover, it is necessary to keep the breast warm and cover it with a cloth after feeding. Avoid strong tea and coffee. You can resort to chest massage, which will alleviate the woman’s condition.
Thrush while breastfeeding
Reduced immunity and hormonal imbalance in a woman during the postpartum period often contributes to the development of thrush on the surface of the nipples. With this disease, the chest hurts during breastfeeding, and in more advanced forms, even between breastfeeding. Swelling of the nipples, itching, burning, and white coating on the nipples occur.
If you notice similar symptoms, you should immediately contact a gynecologist who will select the appropriate treatment. In this case, it is better to feed the baby with expressed breast milk from a bottle.
Types and symptoms of mastitis
With mastitis, the chest hurts, the temperature is 38°C or higher, the symptoms progress quickly. If left untreated, one stage can change to another in just 3 days.
Types of mastitis
- Serous.
- Infiltrative.
- Purulent.
The serous variety is not characterized by high fever; the breasts become enlarged and painful.
Infiltrative mastitis is manifested by compactions, upon palpation of which unbearable pain is felt. The temperature is very high, the skin on the chest turns red, becomes hot and elastic.
In the purulent form, the breast swells greatly, becomes enlarged, turns red at the site of inflammation, and hurts unbearably even with a light touch. Migraines and weakness occur. There is noticeable pus in the milk, the lymph nodes in the armpits are enlarged. Temperatures can reach 40°C and then drop, fluctuating.
With unilateral suppuration, you can feed the baby, but only with a healthy breast, since bacteria can easily be transmitted to the newborn.
Lactostasis
One of the most common reasons why breasts hurt during breastfeeding. Lactostasis occurs in almost every woman during breastfeeding and is characterized by the following symptoms:
- In the mammary gland, you can feel a shaped lump with clear edges, painful when touched.
- The body temperature of a nursing mother rises rapidly and can reach 39 – 39.5 °C.
- Chest pain is also observed after feeding, if the lump does not go away.
There can be many reasons why milk stagnates in the milk ducts, the main ones being:
- Clothes that are too tight or the wrong bra size.
- Sleeping on your stomach.
- Incorrect breast latch by baby during feeding
- Compressing the breast with your hands when feeding, as a result of which the outflow of milk from the glands is disrupted.
- Unstable emotional state: stress, worries, overwork
- Bruises or blows to the area of the mammary glands can also lead to stagnation.
The very first and most effective way to combat lactostasis is to increase the frequency of the baby’s latching on the sore breast. It is better to apply it in such a way that the child’s chin is exactly above the lump; in this position, the most intensive resorption of the stagnant lump occurs.
If after several applications your breasts hurt during breastfeeding, then you can try to strain the lump yourself. This procedure should only be carried out with clean hands. Before expressing, it is very good to take a warm shower, while directing the flow of water to the seal to slightly relieve spasms in this area. Start with gentle stroking movements in the direction of the milk ducts (from the periphery to the nipple), and then use two fingers to press the area along the edge of the areola. You need to express milk until your breasts become soft and lumps are no longer felt.
If independent manual expression does not bring results, it is better to seek help from a lactation consultant or the emergency department of the maternity hospital. These specialists themselves will express the lumps for you, and all symptoms, including fever, will disappear in a few hours.
In any case, breast pain during feeding caused by stagnation of milk needs immediate relief by expressing the lump, otherwise you may face mastitis.
Diagnosis and treatment
A mammologist treats severe chest pain . You should contact him immediately if the symptoms are pronounced and do not go away over time, as well as if you have a high temperature. Diagnostic methods:
- chest palpation;
- blood analysis;
- analysis of milk for the presence of infections;
- Analysis of urine.
In some cases, an ultrasound of the mammary glands may be needed.
Based on the research results, the doctor identifies the cause of the disease and prescribes therapy . If an infection is found, treatment will include bacterial therapy and healing procedures. Until the young mother is completely healthy, it may be necessary to transfer the baby to artificial feeding. In case of severe pain, milk must be expressed; it is not advisable to feed the baby.
In some cases, a woman is prescribed conservative treatment. This may include applying hot compresses to the breasts, massaging the mammary glands, water procedures and diet.
What not to do?
If you have chest pain, you should not:
- Take hormonal drugs, antibiotics and other medications without a doctor's prescription. If a woman has a very high temperature, she can take an antipyretic, which is allowed during breastfeeding.
- Stop lactation on your own . Treatment of some diseases, for example, lactostasis, involves regularly putting the baby to the breast. If the baby stops sucking milk, the situation may worsen. If you suspect mastitis or another infectious disease, a young mother should urgently consult a specialist.
- Apply warm compresses before consulting a doctor . If chest pain is caused by an infection, heat can accelerate the development of harmful bacteria and cause complications.
Mastitis
It can occur against the background of prolonged lactostasis when a bacterial infection is attached. In 95% of cases, inflammation in the breast tissue is caused by Staphylococcus aureus. The gateway for this pathogen is cracked nipples or damage to the mammary gland.
With mastitis, the breast becomes red and hot to the touch, there is no tension in it due to stagnation of milk, and the inflamed area does not have clearly defined boundaries. In general, the woman feels unwell, her body temperature rises, and chills occur.
When mastitis appears, it is very important to consult a doctor as soon as possible, since as this disease progresses, suppuration of the mammary gland may occur, and this requires surgical intervention.
Also, with mastitis, breastfeeding is prohibited due to the risk of infection of the child or reinfection of the mother, as well as due to the presence of antibiotics in breast milk.
Treatment and medications
The basis for the treatment of lactostasis and mastitis is regular breastfeeding, if permitted by the doctor, as well as the procedure of complete expression using a breast pump.
With normal lactostasis, this treatment may be quite sufficient. For mastitis, additional medications are needed.
If the temperature is above 38 degrees, then the doctor will prescribe medications that lower it, containing Paracetamol or Ibuprofen.
If wounds are observed on the nipples, then it is possible to use local therapy, for example, Purelan-100, Bepanten and others.
For more serious manifestations of mastitis, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics.
Vasospasm
Some nursing mothers experience situations where their breasts hurt during breastfeeding. This condition is associated with impaired blood circulation in the vessels of the nipple, and is characterized by acute burning, pulsating, and sometimes shooting pain in the nipple, which, in turn, turns white. After the spasm subsides, the nipple returns to its natural color.
You can combat the symptoms of vasospasm by warming your breasts immediately after feeding. This can also be a warm diaper placed on the nipple; for many, carrying the child in their arms for a while is helpful, while for others the warmth of their own palm is enough.
If your blood vessels are subject to spasms, do not overcool, keep your chest warm, avoid drinking coffee and strong tea.
Breast engorgement
Breast engorgement can be called a common occurrence when mother and baby are separated in the maternity hospital, feeding on a schedule, or when milk appears a few days after birth. All this is accompanied by pronounced painful sensations: bloating, tingling of the chest. The mammary glands become larger in size, swelling leads to hardness and shine of the skin. The outflow of milk is difficult, which is also felt. The following factors often provoke such symptoms: feeding according to the schedule, improper attachment, medications used during childbirth, and also if the first feeding was delayed.
The main preventive measure for engorgement is the correct and timely application of the newborn to the breast every time the baby requests it. There is no need to limit the duration or frequency of breastfeeding.
If there is a reason why it is not advisable to put your baby to the breast, regular breast pumping should be done immediately after delivery (within 12 hours). Expressing colostrum, and then milk, should be done 6-8 times a day for 20 minutes. Milk should be expressed into sterile jars for later use when feeding the baby.
Breast care and pain prevention
It is easier to prevent a problem than to look for ways to solve it later. First you need to follow the rules of breast care:
- Use of air baths. After feeding, do not immediately hide your breasts. It must dry. It is recommended to lubricate the nipple with the remaining milk, such actions become the prevention of cracks.
- If desired, lubricate the nipples with nourishing cream after feeding.
- Use special underwear for nursing mothers exclusively from natural fabrics. Underwear should be loose and not constrict your chest.
- Do not wash the mammary glands using soap products more than once a day. Otherwise, the skin on the nipples will dry out, which will cause cracks. It is enough to simply wash your breasts several times a day with warm water.
- If possible, avoid breast pads; they lead to “rotting” of the breasts. Use only in exceptional cases.
- Lubricate the resulting inflammation with a special agent.
- In order not to injure the nipple, it is carefully removed from the baby's mouth.
Feeding is an amazing and unforgettable time for a mother, and very important for the baby. To prevent this period from being overshadowed by unpleasant incidents, it is necessary to follow the recommendations of breastfeeding specialists. If pain occurs, immediately tackle the problem without leaving everything to chance.
upbaby.ru
Recommendations for eliminating breast engorgement
If the baby is able to suck, put him to the breast. That is, it is important to attach the baby not only at his request, but also at the request of the mother herself. It will be easier for your baby to latch onto the areola if you soften it with slight pressure before feeding. To do this, you can strain the milk. If this is ineffective, you need to express yourself manually or using a breast pump and feed the baby from a bottle.
Before feeding, it is advisable to stimulate the release of oxytocin, which is the hormone responsible for pushing milk out of the glands:
- Drink a decoction of herbs or warm tea, but coffee is not recommended;
- Apply a warm compress to each breast for 15 minutes or take a warm shower;
- Self-massage or massage of the cervical-collar area;
- Massage stroking of the mammary glands (movements should be carried out with light movements from the base to the nipple);
- Stimulation of the nipple skin;
- Creating a relaxed, calm environment in the home.
You can reduce swelling after feeding by using a cold compress, which is applied to the mammary glands for 15 minutes.
Massage for milk stagnation: should the procedure be performed?
Massage complexes are an excellent means of preventing milk stagnation during lactation and inflammation. But the massage should be carried out softly and gently, without any effort.
- An obstetrician-massage therapist should show you how to properly massage your breasts. To achieve a better effect, you can use special creams and mixtures of vegetable oils. Be careful when choosing massage products so as not to provoke allergies and itching on the skin of the mammary glands.
- Make movements with your palms away from the nipples, this way you can disperse the fluid from the ducts of the mammary glands.
- Pay special attention to areas with tightness and pain.
- Massage procedures help improve lactation and also help prepare the breasts for feeding.
The duration of one procedure should be 15 minutes, and it is best performed after feeding the baby daily.
A woman who breastfeeds her baby faces many difficulties during this period. But there is no need to despair, a little experience and useful knowledge will help you not to get confused and maintain breastfeeding!