Cystic formation in the ovary is a very common gynecological pathology that can lead to serious and dangerous complications.
Unfortunately, not all women know the symptoms of this pathology, do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, and do not think about what consequences it can lead to.
And the consequences can really be very serious - from absolute infertility to death.
The essence of pathology
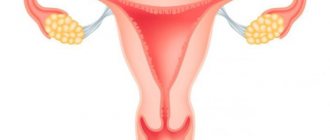
An ovarian cyst is a cavity in which there is liquid content ; it is attached to the ovary using a stalk - long or short .
The size of the neoplasm can reach 20 cm in diameter.
Cysts are divided into two groups - functional and organic.
Functional cysts develop against the background of hormonal disorders, and when hormonal balance is restored, they can resolve on their own.
Organic cysts do not respond well to drug treatment and never disappear on their own. They are usually removed surgically.
Functional cysts:
- follicular;
- Corpus luteum cyst.
Organic:
- endometrioid;
- dermoid;
- paraovarian;
- mucinous;
- serous.
NOTE!
Some types of cysts can transform into cancer, but in most cases they are benign neoplasms.
Cysts are most often diagnosed in women of childbearing age, but can sometimes occur in other age groups.
In rare cases, congenital cysts (for example, dermoid) can be diagnosed even in newborn girls.
In the absence of adequate therapy, cystic neoplasms can become complicated .
Large cysts are prone to rupture; in addition, they can twist, which leads to pinching of blood vessels. These complications are considered very dangerous and require urgent medical intervention.
https://youtu.be/SAXwaG9HQjU
What is torsion?
Pathology code according to ICD-10 No. 83.5.
Cyst torsion is a surgical complication that occurs when the pedicle is twisted, which provokes necrotic changes in the tissues.
In addition, the veins of the leg are pinched, the outflow of blood is disrupted, the size of the cyst increases, and, consequently, the risk of rupture of the tumor increases.
Torsion can be of the following types:
- Full . In this case, the neoplasm makes a full revolution around its axis, the blood supply stops, and the clinical picture is very acute.
- Partial bending of the leg . The leg moves no more than 90 degrees, the blood supply deteriorates, but does not stop. The symptoms are not pronounced. The surface of the cyst synthesizes a certain substance that promotes the attachment of the cyst to other organs. The bend stops progressing, but the cyst quickly increases in size, which threatens to rupture.
The pedicle of the cyst can be surgical or anatomical.
With an anatomical pedicle, it includes elements that are in close contact with the ovary - organ ligaments, mesentery, nerves, lymphatic and blood vessels.
The surgical leg is formed precisely at the moment of torsion. Regarding the speed of development of the pathology, torsion can be gradual and acute.
The mechanism of development of the pathology is a sharp or gradual compression of the veins (the arteries are not affected).
As a result, venous blood stagnates, and this can lead to hemorrhage or rupture of the tumor. The cyst becomes bluish or purple.
Which species are prone to twisting?
Torsion of the cyst pedicle may not occur in all types of cysts . For example, follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts very rarely lead to such a complication.
These neoplasms are not large in size and are not prone to increased mobility.
The following types of cysts are most often twisted::
- dermoid;
- ovarian;
- paraovarian;
- mucinous.
The process may involve the elements that make up the stalk of the neoplasm. In addition, it is possible that the intestines and fallopian tubes are involved in the process.
CAREFULLY!
The more elements and organs are involved in torsion, the more dangerous the complication is considered.
Symptoms and manifestations
The clinical picture of torsion is always clear.
There is a sharp pain that constantly intensifies, and in severe cases it can lead to the woman being unable to even move . Sometimes the pain can radiate to the upper abdominal cavity, and even to the upper and lower extremities.
- Vegetative disorders - increased sweating, pale skin, vomiting, increased heart rate, decreased blood pressure, increased temperature, rapid breathing.
- Problems with stool.
- Drying of the mucous membranes of the mouth, constant unquenchable thirst, which is due to the fact that a large amount of fluid is removed from the body along with sweat and urine.
- Increased gas formation.
- Vaginal bleeding, which occurs not only due to torsion, but also due to damage to organ tissue.
- Increased urination, this phenomenon is especially often observed when the cyst is torsioned in the immediate vicinity of the bladder.
- Hard belly syndrome is an involuntary tightening of the abdominal muscles.
If the leg is partially bent, the clinical picture will be less clear, however, after some time the signs of torsion will be stronger.
It is necessary to understand that after a couple of hours a woman begins to experience necrotic changes in the tissues, while the pain becomes weaker and then goes away completely.
This phenomenon is considered extremely dangerous, and if a woman is not provided with emergency medical care, she will develop peritonitis, which often causes the patient’s death.
Medical care for torsion of an ovarian cyst
Surgical treatment is the only method for detected torsion of a tumor formation. Only surgery can get rid of the problem and prevent the development of complications that threaten the woman’s life.
It is important to know
Conservative therapy for torsion of an ovarian cyst is not carried out. Self-medication is unacceptable! Folk remedies are not effective.
Urgent Care:
- When the first symptoms appear, you need to call an ambulance and prepare for hospitalization;
- Before the doctor arrives, it is necessary to provide the woman with complete rest;
- Hospitalization is carried out on a stretcher. Before arriving at the emergency room of the gynecological department, treatment is not carried out; only symptomatic therapy is possible (stabilization of blood pressure, etc.).
The sooner the operation is performed, the less likely it is to develop complications.
Surgical intervention is included in the mandatory protocol of medical care for torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst. The choice of treatment method will depend on the clinical situation. Until recently, the only option was to remove the affected ovary - adnexectomy. In this case, the surgical stalk of the cyst was cut off without preliminary untwisting, since such a tactic is fraught with the entry of blood clots into the systemic bloodstream. The operation was performed only through open access by laparotomy (with an incision in the abdominal wall). With the development of laparoscopy, it became possible to perform organ-preserving operations.
Laparoscopic intervention is the method of choice for torsion of ovarian cysts, especially in young women. During surgery, you can carefully untwist the tumor-like stalk using atraumatic forceps. Manipulations are carried out after filling the abdominal cavity and pelvis with an isotonic sodium chloride solution. The cyst floats up and can unwind on its own. If this does not happen, the doctor carefully unscrews the leg.
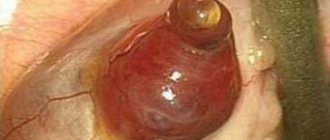
This is what torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst looks like during laparoscopic surgery.
When examining the surgical field, the twisted cyst looks like a bluish-purple formation. After the stem untwists, the cyanosis goes away and the color of the ovary is restored. The process lasts no more than 10-15 minutes. If blood flow is restored during the specified period, removal of the ovary is not indicated, and only the cyst is excised. Otherwise, the affected ovary is removed.
It is important to know
With laparoscopy, in 80% of cases it is possible to save the ovary. During abdominal surgery, adnexectomy is performed three times more often.
The only disadvantage of laparoscopy is the inability to assess the structure of the cyst without compromising its integrity. For this reason, it is recommended to perform ultrasound diagnosis of the tumor during surgery. If malignancy is suspected, they switch to laparotomy, and the scope of the operation is expanded.
Stages of removal of an ovarian cyst using laparoscopic access: untwisting, excision of the formation, suturing the ovary.
Causes
Torsion of the cyst pedicle can occur under the influence of the following factors::
- a sharp increase in intra-abdominal pressure, which is possible during heavy physical activity;
- excessive straining during bowel movements;
- failure in the hormonal system;
- sharp and prolonged cough;
- ascites – accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- sudden change in body position.
Quite often, torsion of the pedicle of a neoplasm is observed during pregnancy..
Most often, neoplasms with a long stalk are twisted.
Procedure in case of complete torsion of the leg
At the first appearance of a clinical picture describing the torsion of a cystic formation, first of all, you need to call an ambulance.
Until the specialist arrives, the patient should be completely at rest. During this period, it is necessary to exclude any movements, emotional and physical stress.
A patient with this condition can only be hospitalized on a stretcher. Until the patient is taken to a medical facility, it is not recommended to carry out any therapeutic measures. The only thing that can be done is to normalize your blood pressure.
What is the danger?
The danger of torsion in the development of even more negative consequences:
- tissue necrosis;
- breakthrough internal bleeding into the ovary;
- rupture of a cyst with leakage of contents into the abdominal cavity;
- peritonitis;
- fusion of the cyst with organs located nearby;
- development of the adhesive process.
Expert opinion
Dmitrieva Elena Yurievna
Gynecologist-endocrinologist, 40 years of experience
Torsion of the ovarian pedicle is an acute condition in which a woman must be urgently hospitalized. In this case, attacks of pain do not stop, but only intensify. With a decrease in pain, the woman believes that the danger has passed and is in no hurry to see a doctor, and this is by no means a favorable sign, but, on the contrary, indicates an even more serious complication. The cyst cavity ruptures and all its contents spill into the abdominal cavity. This phenomenon provokes peritonitis, a complication that is deadly. Every woman should clearly understand that torsion of the cyst stalk is dangerous, and if the above clinical signs are present, immediately call an ambulance.
Diagnosis of the disease
Initially, diagnosis begins with palpation of the patient's abdomen. Peritoneal tension and peritoneal signs are observed.
In addition, they are appointed:
- Blood test - ESR increases and leukocytosis increases.
- Gynecological examination in a chair - the presence of a neoplasm in the adnexal zone is determined, which, when trying to move it to the side, provokes severe pain. In some cases, the chairside examination is so painful that it is performed under anesthesia.
- Ultrasound. The contours of the cyst are blurred, the capsule is thickened, and a double contour may be observed, which indicates edema. There is effusion in the pelvis.
- Laparoscopic diagnosis. Endoscopic examination reveals a purple node, the fluid is serous or serous-hemorrhagic.
Pathology must be differentiated from:
- renal colic;
- inflammation of the appendix;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- salpingo-oophoritis.
Symptoms
When complete torsion is noted, then the woman immediately feels severe cutting pain in the area where the pathological process is localized. After this, excessive tension in the anterior abdominal wall is noted, nausea and vomiting appear, and body temperature rises. The woman will notice that her pulse has increased and her skin has become pale. Cold sweat may occur.
What pathology looks like from the inside. Source: genitalhealth.ru
It is also worth noting that women feel a condition called “acute abdomen” syndrome. Patients often confuse torsion with a tumor process. The nature of the pain can be gradually increasing, which is noted in 50% of clinical cases. It often becomes dull, intermittent or constant.
In addition, the condition is complicated by the presence of pain in the area of the tenth cervical vertebra, since the symptom is radiating in nature. Severe signs of torsion are observed during the first two days, and in only 7% of patients they persist for a week.
Treatment methods
Treatment of pathology is only surgical.
Alternative treatment measures do not provide positive results, and delay can further complicate the situation.
The main task of the surgeon is to restore blood flow and normal condition of the ovary. If tissue necrosis occurs, the appendage is completely removed.
If ovarian torsion is uncomplicated, laparoscopic intervention is performed . In this case, the neoplasm unwinds and is removed.
With the development of peritonitis, abdominal intervention is necessary - laparotomy, in this case the ovary is completely removed.
If an oncological process is suspected, an emergency examination of a tissue sample is carried out, after which complete removal of all reproductive organs is possible.
As for preventive measures to prevent possible torsion of the pedicle of a cystic neoplasm, regular examination by a gynecologist is necessary.
If a small cystic formation is diagnosed and the doctor decides to monitor the pathological process, the patient should come for a preventive examination at the frequency prescribed by the doctor.
As soon as active growth of a neoplasm is suspected, it must be treated with conservative methods or removed, since the risk of torsion in this case increases sharply.
Rehabilitation after surgical treatment
On the first day after surgery, the woman is in the intensive care unit. The doctor evaluates vital parameters: blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate, body temperature. Subsequently, the patient is transferred to the general ward. If complications develop, repeat surgery is indicated.
Pain in the lower abdomen persists after surgery for 5-7 days, but gradually subsides. In the first days, antispasmodics and analgesics can be prescribed, but later there is no need for them. In the postoperative period, antibiotics are indicated for the prevention of infectious complications for a course of 7 days.
The duration of disability depends on the type of intervention performed. After laparoscopy, sick leave is given for 7 days, after abdominal surgery - for 12. If complications develop, the recovery time increases.
After discharge from the hospital, the woman comes under the supervision of a local doctor. It is recommended to visit a gynecologist annually and undergo mandatory ultrasound monitoring. You can plan a pregnancy 3-6 months after laparoscopy and 6-12 months after abdominal surgery. You should first consult a gynecologist and make sure there are no complications.
Specific prevention of ovarian cyst torsion has not been developed. When identifying pathology, it is recommended to exercise caution and avoid sports and heavy physical activity. Observation of a detected cyst should not exceed more than 3 months. If the tumor formation does not disappear within the specified period, a planned operation is indicated. This tactic allows you to avoid torsion of a growing cyst and other complications of the disease.