A pretty young woman, looking around, tries to hide. But a white goat chases her on the street. The woman, in despair, gets on the bus, but even there she is waylaid by sharp goat horns and yellow, attentive eyes. Thus begins a popular television advertisement for a drug for thrush. In the video, with great delicacy and allegory, the role of a fungal infection was “performed” by a goat.
In fact, this is exactly what happens. Women, perhaps in the midst of “full health,” may experience symptoms of thrush. The real name for this condition is vaginal candidiasis. What is this condition, how to diagnose and treat it, and how can you avoid unpleasant and painful symptoms?
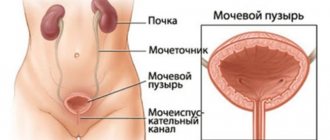
Thrush: what is it?
Why is the disease called that?
Thrush is a “folk term”. In fact, vaginal or urogenital candidiasis is a complex of clinical signs that occur in the organs of the genitourinary system, which is caused by fungi from the genus Candida. Most often it is C. albicans, less often - C. tropicalis, C. krusei. It is the first species that has the most pronounced properties for colonization and colonization of mucous membranes.
Typically, healthy mucous membranes contain single elements of the fungus in the form of blastospores. But, in the event of a decrease in immune defense, blastospores begin to germinate and form filaments of pseudomycelium. It is the rapid development of threads that indicates the beginning of candidal colonization of the mucous membranes. Mushrooms need animal starch - glycogen. And, like all yeasts, candida are also “sugar lovers,” so they begin to destroy mucosal epithelial cells, which contain a lot of glycogen.
These fungi are conditionally pathogenic microflora. They are constant companions of humans, just like the intestinal microflora. What does it mean? This means that there is a rather complex relationship between these fungi and humans (the host). In a healthy body, they behave quietly, being content with “crumbs”, for example, particles of dead epithelium. But, as soon as the body’s immune defense decreases, fungal mycelium grows, which begins to cause harm to already living tissues.
If you look at ICD-10, which currently codes all diseases, then there is no diagnosis of urogenital candidiasis. Candidiasis has been “removed” from the number of sexually transmitted infections, and, moreover, since 1999, statistics on this disease have been abolished in our country. This happened for the same reason: candida lives in both sick and healthy people, but does not cause the disease in everyone. But, nevertheless, in the structure of diseases of the genitourinary system in women, candidiasis sometimes accounts for up to 50%. And it is of particular importance because against its background various pathogenic microorganisms “feel good.”
Causes of thrush
Why didn't we use the word "disease"? Yes, because thrush is not a disease in the full sense of the word. Yes, there are unpleasant symptoms and discomfort. These are, of course, signs of illness. But, on the other hand, every disease, and especially with the participation of an infectious agent (virus, protozoa, fungus, bacteria), must have a cause.
In the case of candidiasis, this cause is the altered reactivity of the female body itself, a decrease in immune status. A large number of factors can lead to this. The most common reasons for the appearance of symptoms of thrush include the following:
- Long-term and frequent use of antibiotics, or their occasional use. They destroy the normal vaginal flora, changing the acid-base state to the alkaline side;
- Taking hormonal drugs. Most often these are corticosteroids, powerful immune suppressors. They are usually prescribed for systemic rheumatological diseases, multiple sclerosis (pulse therapy), bronchial asthma and other serious diseases;
- Pregnancy is also a powerful factor that reduces a woman's immune defense;
- The presence of intestinal dysbiosis (as a result of taking antibiotics, and as a result of chronic diseases of the digestive system). For example, enzymatic deficiency in chronic pancreatitis contributes to the development of protein, putrefactive and fermentative dyspepsia;
- Diabetes;
- Infections causing severe immunosuppression (HIV);
- Chronic liver failure and cirrhosis (the liver does not produce protein for the synthesis of antibodies).
There are also more prosaic factors that can be avoided, for example, prolonged wearing of synthetic underwear, frequent use of medicinal douches, which deprive the vagina of protective secretions, or frequent stay in damp and warm rooms.
Of course, this list of causes of thrush in women is not exhaustive. The doctor’s task is to find this root cause, since knowing the source will prevent relapses.
What else causes thrush in girls?
In addition to the above factors, the causes of thrush in a girl may be as follows:
- Pregnancy. This period is characterized by a reactive “physiological” immunodeficiency and, in addition, the composition and basic balance of vaginal secretion changes to a more acidic direction, which is favorable for the proliferation of fungi.
- Poor nutrition, namely the predominance of easily digestible carbohydrates in food.
- Failure to comply with the rules of intimate hygiene: infrequent washing and irregular changes of linen.
- Excessive self-care can also cause thrush. Many girls almost daily use douching to clean the vagina, which simply blows up normal microflora from it. Using soaps and sanitary pads with fragrances is exactly what causes thrush in girls.
- Frequent wearing of tight and synthetic underwear, resulting in a “greenhouse” effect – a favorable environment for fungi.
- Lack of microelements and vitamins in the body leads to a decrease in the body's defenses.
- Prolonged hypothermia of the body.
To summarize, we can conclude that the causes of urogenital candidiasis are varied and require a scrupulous approach to diagnosis and treatment. At the same time, a woman’s health means a long life and a healthy generation.
https://youtu.be/Psjss-LCfbI
What are the first symptoms of acute thrush?
How to recognize at an early stage?
Digression - classic thrush in women most often occurs as vulvovaginitis. Urethritis and cystitis, as well as cervicitis, are somewhat less common. If the vagina is involved in the process (candidal vaginitis develops), then the cervix (its vaginal part) is usually also affected.
The first signs of thrush in women, in the presence of classic vulvovaginitis, are characterized by the appearance of itching and discomfort in the vagina and mucous membranes. In this case, there is practically no discharge, or it is extremely scanty, and does not have an unpleasant odor. Upon examination (and self-examination), a peculiar cheesy coating is visible on the mucous membrane and in the vaginal folds. This plaque can be in the form of films, and if they are removed, there may be bright red erosions, or just a red surface.
This coating of cheesy lumps and films is the budding, growing mycelium of the fungus, desquamated epithelium, and the films are fibrin that has fallen out in the form of threads. If you rub the curdled coating between your fingers, you can smell a light, mushroom smell. This convincingly proves that it is fungi that are part of the plaque.
In acute candidiasis, severe hyperemia of the vaginal mucosa also develops. The folds of the vagina become swollen and thickened, but at the same time they are dry. These are the classic symptoms and signs of thrush: with other common diseases (chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis), the first thing that catches a woman’s eye is the discharge, which is accompanied by other symptoms.
The course of chronic candidal inflammation
If the process becomes chronic, the swelling of the vaginal mucosa gradually disappears. Congestive plethora occurs, and scanty discharge appears, reminiscent of cream. This is where the term “thrush” comes from, which implies that the population is predominantly familiar with chronic forms of candidiasis.
The big problem with the chronic course of thrush is that there is a high risk of secondary bacterial infection. This is evidenced by the following manifestations:
- discharge becomes abundant and more liquid;
- their unpleasant smell attracts attention;
- cheesy lumps that were previously kept inside now come out among the liquefied secretions;
- pain appears and discomfort increases.
In relation to vulvitis, candidal lesions can be very unique. So, there may be congestive congestion of the labia majora, which is combined with swelling and dryness of the labia minora. The vestibule of the vagina contains a typical cheesy coating in its folds. If immunity is reduced, then thrush spreads beyond the genitals, and superficial candidiasis of the skin of the perineum and inguinal folds develops.
In case of chronic vulvitis, coarsening of the skin pattern and thickening of the labia majora may occur, with the appearance of scratching, cracks and even erosions. This picture can occur with high blood sugar levels, with cholestasis. These conditions are accompanied by severe itching and burning.
Manifestations of urethritis, cystitis and inflammation of the cervix almost always accompany vulvovaginitis.
Of course, with a pronounced decrease in immunity, intestinal candidiasis, systemic forms of the disease with damage to internal organs, and even candidal sepsis occur.
About diagnosing candidiasis
In the classic textbooks of dermatovenereology, published in the last century, it was believed that only the unconditional receipt of fungal mycelium in scrapings, its microscopy and culture can make a diagnosis of candidiasis. Currently the situation has changed. In addition to these methods, which remain in the arsenal of doctors, PCR, a method in which the species-specific DNA of a fungus is determined, has gained great importance.
For PCR, a scraping is taken from the epithelium in the plaque area, urine, and a scraping from the ampullary part of the rectum. Additionally, serological tests are used, which detect specific immunoglobulins from the blood. But the diagnostic value of serological tests is high only if it is necessary to exclude suspicion of systemic candidiasis and sepsis. If the result is negative, you need to look for another reason.
In the event that the patient has a long-term, chronic candidiasis, it turns out that the main “old-fashioned” and reliable method of direct microscopy of the fungal mycelium has become unreliable - if you do not take the acute stage, then only in 30% of all cases it was possible to detect the mycelium, and in other cases, blastospores were found, which do not prove anything.
How to prepare for research?
Since “Candida” is translated as “hidden”, it is very important for a woman to follow some rules in order to maximize the chances of identifying candidiasis. To do this you need:
- Conduct research during ovulation;
- It is advisable that at least 5 days pass after the last sexual intercourse;
- 2(!) months before the study, you need to stop taking not only antifungal tablets, but also antibiotics;
- 3 weeks before the study, the administration of antifungal vaginal suppositories should be stopped;
- The day before and on the day of the study, you should not douche;
- You should stop urinating 3 to 4 hours before the test.
Materials are taken from several places: the urethra, rectum and posterior lateral vaginal fornix. At the same time, they are sent for microscopy and culture. Such “harsh” conditions maximize the chances of making a correct diagnosis.
It should be added that such measures should be taken if it is not possible to carry out PCR.
Treatment at home
Treatment of thrush should be comprehensive.
First, you must definitely consult a doctor who will conduct an examination and make an accurate diagnosis. Self-medication of thrush is contraindicated because the symptoms of thrush are similar to other infectious diseases of the reproductive system. For example, itching and burning, and other symptoms of vaginal inflammation (colpitis) can be caused not only by fungi, but also by the onset of gonorrhea, ureaplasmosis, genital herpes and many other infections.
Treatment for thrush, which is prescribed by a doctor, consists of taking medications, using vaginal creams and suppositories. All kinds of procedures that a woman can carry out at home using various recipes that are available in folk medicine will help to enhance the effectiveness of drugs.
Doing douching
Excellent results in the treatment of thrush can be achieved by douching with herbal infusions.
- Yarrow, sage, rosemary and oak bark herbs are taken in equal quantities (20g). The resulting mixture is poured with three liters of water and boiled for 20-30 minutes. Then cool and strain. Douche 2-3 times a day for two weeks.
- Douching with St. John's wort, calendula, and eucalyptus globulus is effective.
- Rinse the vagina with a warm solution, using a bulb, which perfectly irrigates the vaginal walls.
- During thrush, the tissues of the mucous membrane are affected, ulcers appear, causing pain. To restore the mucous membranes of the genitals, it is necessary to treat with an infusion of herbs: calendula, chlorophyllipt, rosanolone, birch buds.
Warm baths with chamomile
There is an old proven method for treating thrush - taking a bath with chamomile infusion. You can buy chamomile at any pharmacy, and taking such baths will not cause harm. To make the infusion, take one pack of chamomile and pour two liters of boiling water.
For the best result, it is recommended to leave it in a thermos for about 6 hours, but you can leave it in any other vessel that is well wrapped in a towel. The duration of a bath with chamomile should be no more than an hour, the water should not be hot. At the beginning of treatment for thrush, it is recommended to use chamomile treatments 2 times a week, and then once a week until complete recovery.
Herbal decoction inside
You should chop the fresh root of the yellow capsule (3-5 mm). Take 3 tbsp. per one liter of water. Boil thoroughly for 10 minutes and let sit for up to an hour and a half. Take 1 tbsp. up to 3-5 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
This decoction can also be used for douching in the morning and evening. The course of treatment is a week. And it is carried out from the first day after the end of menstruation. This treatment should be continued for up to three months in courses. And it is advisable that the partner also takes this tea and rinses his reproductive organ.
Water lilies can be replaced by calendula, poplar buds, birch leaves, blackberries, chicory and galangal roots, calamus, oak bark, chamomile, shepherd's purse. The dose and treatment method are the same as with the capsule.
Treatment regimen for thrush, medications and suppositories
What to do first?
Acute candidiasis, the cause of which is known (taking antibiotics, hormones), is much easier to treat than chronic candidiasis. If the immune system is strong, and only at the local level it has “shaken”, then tablets for thrush, or even better - local intravaginal forms, can cope with this fungal infection.
Currently, there are many drugs that are recommended for use for 1 to 7 days in the form of vaginal suppositories: “Canesten” (clotrimazole), “Klion-D” (miconazole), “Ginofort” (imidazole), “Diflucan”, "Mikosist" (fluconazole).
Often popular medical websites describe all these drugs “lumped together.” Meanwhile, a patient who is not going to go to a specialist, but tries to self-medicate, will not take into account an important thing: different localizations of candidiasis require the prescription of different local antimycotic agents.
So, if predominantly candidal urethritis is detected, then fluconazole should be used; if proctitis is diagnosed, then ketoconazole is better.
Chronic and recurrent forms
How to treat thrush in women who cannot cope with it, or in the presence of chronic diseases (diabetes, anemia)? This is a serious problem, and the combined use of topical and tablet medications alone will not help. An integrated approach is needed here. The basic principles of treatment of chronic, recurrent urogenital candidiasis in women are:
- Clearly identifying and eliminating the risk factor (for example, reducing the dose of hormones, reducing blood sugar levels as much as possible);
- Correct selection of antifungal drugs, taking into account not only activity, but also taking into account accumulation and long-term presence in tissues;
- Desensitizing and antiallergic protection (all yeasts are strong antigens and allergens);
- Prescription of antioxidants and vitamins. The most needed are PP, C, vitamins B1 and B2;
- Enzyme therapy to ease digestion. If intestinal dysbiosis is detected, and even more so, its candidiasis, this may indicate the presence of systemic intestinal candidiasis. In this case, the use of the antifungal antibiotic natamycin is indicated;
- The use of hepatoprotectors during the course of antifungal therapy;
- According to indications, after studying immunity, it is possible to use immunomodulators;
- Expanded local therapy, using not only fungicidal drugs, but also physiotherapeutic treatments, alcoholic agents and dyes. Douching with sterile weakly acidic solutions is used (to wash away fungal secretions). Microenemas, cervical irrigation, and intracervical administration of antifungal drugs are used.
In this case, it is advisable to conduct a full examination of regular sexual partners and treat them.
Is it curable?
We examined in detail the symptoms and treatment of thrush in women, and as it became clear, thrush is not always easy, and it is not always possible to get rid of it. Quite often, during the treatment and examination of women, many errors are revealed. Risk factors are not addressed, women are under-examined (for example, rectal smears are not taken). Sometimes the wrong medications are prescribed, or in short courses. Sexual partners who can reinfect a woman during treatment are overlooked. The carriage of fungi in the intestines is not taken into account.
All these mistakes, as well as the woman’s poor adherence to treatment, not only contribute to the formation of chronic candidiasis, but also contribute to the addition of a bacterial infection. If the doctor carefully explains to the patient the importance of seemingly the most insignificant facts, then a complete cure can be achieved.
Tags:
women's health candidiasis
Lifestyle Tips
For home treatment of thrush to be effective, you need to pay special attention to lifestyle and a number of precautions:
- Strictly observe the rules of intimate hygiene.
- Change pads during your period at least three times a day.
- Avoid wearing underwear made from synthetic materials.
- Do not use soap for washing. Preference should be given to special intimate hygiene products that do not wash away beneficial microflora.
- Review your diet, include a sufficient amount of vegetables and fruits and minimize salty, fried and sweet foods.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
You can cope with thrush at home, but only if you follow these recommendations and use medications.
Thrush responds well to treatment, and with timely consultation with a doctor, all its clinical manifestations are quickly eliminated. The main thing is to strictly adhere to the gynecologist’s recommendations even at home and not resort to self-medication. Only in this case the prognosis will be favorable.