What are the reversal options?
Most often, cervical ectropion is limited only to the outer part of the canal, which is closest to the external cervical pharynx. However, a more pronounced inversion of the endocervix will be quite realistic.
Under normal conditions, the cervical glands produce a mucous secretion with an alkaline reaction. With ectropion, the inverted endocervical surface is exposed to an acidified vaginal environment, which provokes the formation of inflammation. With cervical eversion, in the vast majority of cases, cervicitis and endocervicitis occur, which look like a bright red inflammatory surface. Eversion is often accompanied by pseudo-erosion located along the periphery of the ectropion.
Rehabilitation after treatment
View gallery
After the operation, a number of conditions must be met:
- abstain from sexual activity until complete healing;
- you cannot lift weights;
- you cannot engage in heavy physical labor and sports;
- do not visit open reservoirs, swimming pools, saunas and baths;
- do not use tampons.
Causes of the disease
- Birth injuries
The main causative factor in the occurrence of eroded eversion is any birth cervical trauma. The most common cause is bilateral traumatic rupture of the cervix during natural childbirth, which occurs in the following situations:
- the birth of a large baby;
- incorrect presentation of the fetus during childbirth (extensor cephalic, pelvic);
- decreased extensibility of cervical tissue (rigidity);
- ineffective and incorrect use of labor-stimulating drugs;
- the use of delivery operations during childbirth (birth of a child using vacuum extraction or special obstetric forceps);
- postpartum complications (delay or disruption of the integrity of the placenta, requiring surgery to manually examine the uterine cavity).
- incorrect comparison of tissues when suturing cervical tears, especially with deep injuries (2-3 degree tears).
The muscle layers of the cervix consist of longitudinal and circular fibers. Birth trauma disrupts the processes of muscle contractility, which causes gaping of the cervical canal and the formation of eroded ectropion.
- Damage to the cervix during abortion
Forced expansion of the cervical canal, which is always performed before artificial termination of pregnancy, leads to multiple minor traumatic injuries to the cervical tissues, blood vessels and nerves. Severe eversion with subsequent erosion of the cervical surface appears against the background of:
- frequent medical abortions;
- induced abortions for long periods (12-14 weeks);
- late pregnancy termination, regardless of the reason;
- therapeutic and diagnostic examination requiring expansion of the cervical canal (hysteroresectoscopy).
In fact, any violation of the integrity of the cervical muscles can cause the formation of eroded ectropion.
- Congenital variant
Although it is quite rare, congenital inversion, found in young girls, is quite possible. The reason for this pathology is an abnormality of the muscle tissue of the cervix, leading to gaping of the external pharynx and the formation of ectropion.
Causes of ectropion, including after childbirth
Ectropion is an eversion of the mucous membrane of the cervix, which should normally be hidden deep in the cervical canal. Sometimes the concept is used to describe ectopia, in which case they speak of congenital ectropion, although this is not entirely true.
After childbirth
The reasons for the formation of such an eversion of the mucous membrane are associated with injuries to the cervix during childbirth. Deep tears and their subsequent not entirely correct healing lead to the formation of pathology.
Additionally, the following circumstances provoke the occurrence of ectropion:
- Inadequate comparison of tissues, which subsequently leads to disruption of the anatomy and mechanical eversion of the internal mucous membrane.
- Use of quickly absorbable suture material, for example, catgut, when suturing. This way, good hemostasis can be achieved, but already on the 3-4th day such threads lyse on their own, and the tissues that they held diverge. It turns out that the tear was sutured during childbirth, but then the seam literally fell apart.
- Concomitant inflammatory processes in the vagina. They slow down the healing of cervical tissue, leading to complications and suture failure.
In these cases, ectropion is always combined with cicatricial changes in the cervix: it is deformed and has an ugly shape even when examined in ordinary gynecological mirrors, which is a consequence of ruptures during childbirth.
We recommend reading about the treatment of cervical ectopia of the cervix with chronic cervicitis. From the article you will learn about the causes and symptoms of cervical ectopia with chronic cervicitis, diagnosis and treatment of the pathology. And here is more information about when it is better to cauterize erosion.
After gynecological manipulations
Rough actions during various surgical interventions can lead to the formation of ectropion of the cervix. Most often, pathology occurs after:
- diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity, hysteroscopy;
- abortions, miscarriages, frozen pregnancies;
- biopsies.
The risk of developing ectropion of the cervix increases with an increase in the number of manipulations performed, as well as with rough, careless actions of the doctor.
Symptoms of cervical inversion
With eroded ectropion, most often there are no manifestations. Some women may notice the following inflammatory symptoms:
- increase in leucorrhoea;
- contact bleeding during sexual intercourse;
- minor nagging pain in the perineum or lower abdomen.
Some women may have problems conceiving or bearing a fetus, manifested by infertility or recurrent miscarriage. However, this is more due to inflammation in the cervical canal, which occurs against the background of eversion and the formation of erosion.
Symptoms
With both erosion and ectropion, there may be no signs at all . The initial stages of changes in the epithelium are sometimes accompanied by slight deviations in well-being.
Symptoms become severe during inflammation or infection of the genital organs.
Signs of ectropion and ulcerated areas:
- heavy or scanty periods;
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle - irregularity;
- pain in the lower abdomen during and after sexual intercourse;
- blood or white discharge after sexual intercourse;
- systematic pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower back;
- pain increases with physical activity;
- clear, white discharge between periods with an unpleasant odor;
- general weakness;
- fast fatiguability.
Diagnosis of eroded ectropion
- Inspection on mirrors
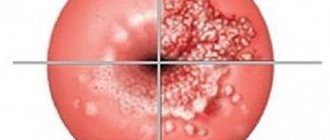
During a medical examination or during a preventive visit to a gynecologist, the doctor will pay attention to pathological changes in the cervix during a standard examination. Visual signs of eroded ectropion include:
- gaping cervical pharynx with eversion;
- pronounced redness of the mucous membrane, sharply standing out against the background of the pale pink outer cervical part;
- thickened edematous and hyperemic folds;
- the appearance of areas of defects in the integumentary epithelium;
- the presence of cloudy muco-milky discharge.
Unlike ordinary or pseudo-erosion, when examined on mirrors, the doctor will not see an eroded eversion when the anterior and posterior cervical lips come together (folded).
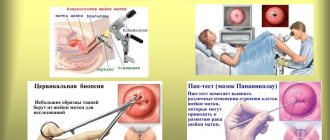
If an eroded ectropion is detected, the doctor will definitely perform an oncocytology examination (taking smears with a cytobrush or using liquid-based cytology).
- Colposcopy
To accurately detect inversion and identify associated pathological problems, a special microscopic examination is used. Colposcopy for eroded inversion allows:
- distinguish erosion and pseudo-erosion from post-traumatic cervical inversion;
- identify normal and pathological changes in the cervical epithelium during inversion;
- assess the risk of dysplasia and pre-invasive cervical cancer.
As a rule, extended video colposcopy is used, in which, in addition to microscopic examination, special solutions are used for accurate diagnosis of cervical diseases.
- Biopsy
Usually no additional examinations other than examination and colposcopy are required. However, if suspicious areas are identified on the inverted part of the cervix (areas of leukoplakia, suspected dysplasia), it is necessary to take material for histological examination from the outer and inner surfaces of the ectropion.
Inflammatory form
View gallery
Basically, ectropion and erosion are accompanied by an inflammatory process - cervicitis. This disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- itching, burning;
- discomfort when urinating;
- increased discharge;
- swelling;
- cysts may form;
- When examined, a whitish coating and redness can be detected on the cervix.
An accurate diagnosis is made after receiving the smear results. Symptoms will be more pronounced in the case of increasing inflammation. Then chills, fever, and headache may be added to the symptoms.
Treatment
All therapeutic measures for eroded ectropion involve several main goals:
- restoration of natural cervical protection, protecting the inner surface of the uterus from infection;
- improvement of fertility;
- prevention of dysplasia and cervical cancer.
- Diathermopuncture
With a slight eversion and a moderate cervical defect, diathermocoagulation can be used. Pinpoint cauterization around the ectropion helps form scar structures that narrow the cervical inversion. The closure of the anterior and posterior cervical lips eliminates ectropion.
- Cryodestruction
The use of liquid nitrogen for cryodestruction of the eroded surface of the inverted cervix creates conditions for the healing of the pathological area of the cervical canal and the formation of a normal external pharynx. In addition, cryotherapy is an excellent prevention of precancerous changes on cervical epithelial cells.
- Radiosurgery and laser vaporization
Modern high-tech methods of treating cervical problems are most optimal in the presence of an eroded surface and a high risk of pathological changes in the cellular structures of the cervix. In some cases, even simple removal of erosion ensures restoration of the cervical structures, creating conditions for getting rid of eversion.
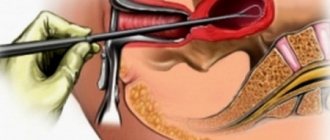
- Plastic surgery
A severe postpartum cervical-cervical defect with the formation of ectropion can become a reason for surgical reconstructive plastic surgery. Before surgery, it is necessary to conduct an examination to exclude oncological processes. All operations for the treatment of cervicitis and colpitis must be performed. Correction of anatomical disorders in the muscular layers of the cervix helps to get rid of pathological eversion.
- Conization of the cervix
At the slightest suspicion of dysplasia or pre-invasive cervical cancer, surgery will be required. Typically, the doctor performs a cone-shaped excision of the problem area within healthy tissue. Typically, conization removes most of the inverted and eroded cervix.
If an oncological process is detected that accompanies eroded cervical inversion, radical surgery will be required to remove the entire organ. Hysterectomy for cervical cancer becomes the only option to preserve the health and life of a woman.
Treatment of cervical ectropion
In the presence of this pathology, only surgical treatment is performed, which is carried out after clarification of the diagnosis and anti-inflammatory therapy. The choice of method depends on the area and depth of the lesion, as well as on the severity of scar tissue changes.
Diathermocoagulation
The method involves cauterization of the ectropion of the cervix using high-frequency alternating electric current. Treatment of ectropion with diathermocoagulation has been used for a long time throughout the world. However, it has a number of significant disadvantages:
- deep damage to healthy underlying tissues due to different (at a given current strength) depth of coagulation;
- long process of morphological tissue restoration after treatment (up to 9-12 months);
- lack of possibility of histological examination of the material (due to its destruction) and timely diagnosis of cancer at its initial stages (pre- and microinvasive cancer);
- a wide range of complications during surgery and at various times after it, developing in 36-54% of treated patients.
Due to such shortcomings, diathermocoagulation treatment is almost never used at present.
Electroexcision and conization
Electrosurgical excision consists of layer-by-layer excision of pathological tissues without damaging them, and conization is the same method, but tissue removal is carried out within a cone with its apex facing the internal pharynx.
This method allows not only radical removal of pathological tissues within healthy tissues, but also establishing a final diagnosis based on an in-depth morphological study of stepwise serial tissue sections. In addition, it is characterized by relatively rapid healing, a low percentage of complications, and the ability to preserve the physiological function of the organ.
Excision of pathological tissues using conization method, with ectropion of the cervix
At the same time, the main disadvantages of diathermocoagulation conization are:
- significant thermal damage to adjacent tissues;
- the need to remove pathological tissues with a considerable supply of healthy border tissues;
- the possibility, although quite rare, of pronounced scarring with the development of stenosis of the cervical canal (after 6-24 months) - a complication called coagulated cervix syndrome;
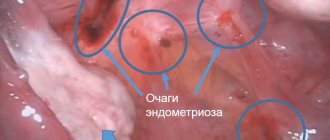
- postcoagulative endometriosis;
- relapse of the disease;
- reducing its length and some others.
Thus, electroconization is an effective treatment method that allows for histomorphological control, but is characterized by a significant number of negative consequences.
Treatment of cervical ectropion with radio waves
Radiosurgical excision and conization is an atraumatic method of coagulation and dissection through a high concentration of high-frequency radio wave energy that does not lead to destruction of soft tissue.
Thanks to coagulation of the nerve endings in the wound, the procedure is practically painless, and a decrease in the secretion of the liquid part of the blood by the wound surface and a decrease in the resorption (absorption) capacity of the latter significantly reduces the healing time.
An important advantage of the radiosurgical method is the absence of recurrence of pathology and wound healing without scar formation.
Laser destruction
Laser destruction and vaporization are carried out using carbon dioxide, neodymium, argon, ruby and other high-energy lasers. The procedure is almost painless, and healing occurs in approximately the same time as with radio wave exposure. In addition, damage to adjacent healthy tissue is minimal, and there is no risk of scarring or stenosis of the cervical canal.
Laser vaporization is more accessible, since laser conization can only be carried out using expensive foreign devices of the latest models.
When using laser destruction, complications are possible:
- increased bleeding in cases of simultaneous vaporization in the presence of extensive and/or deep (more than 3 mm) lesions;
- the formation of adhesions and adhesions between the vaginal wall and the posterior cervical surface;
- frequent (about 22%) development of secondary infection;
- frequent postcoagulative endometriosis.
The main disadvantages of the method include:
- the difficulty of treating the affected area in terms of obtaining destruction of the required depth and uniformity;
- the need for repeated procedures (in the case of a large area of the pathological area) in order to achieve complete treatment results;
- lack of opportunities to conduct control histological examination;
- dependence of treatment effects on the area and depth of the pathological focus;
- the need for expensive equipment and specially equipped premises.
"Knife" treatment
It consists of performing surgical plastic surgery using the Emmett or Sturmdorff method. Recently, many authors consider these methods to be the most promising treatment for ectropion, especially when combined with pseudo-erosion, hypertrophied or grossly deformed neck, as well as in the absence of treatment effects by other methods or when it is impossible to use them.
Complications
If nothing is done when identifying an eroded ectropion, then the following problems will be possible consequences:
- chronic inflammatory process in the inversion area, which will lead to dysplasia and significantly increase the risk of cervical cancer;
- against the background of infection and in case of violation of the cervical protective barrier, the risk of penetration of microorganisms into the upper parts of the reproductive organs increases (endometritis, salpingoophoritis, parametritis);
- cervical changes against the background of eversion and inflammation become the basis for the formation of infertility or habitual miscarriage;
- When pregnancy occurs against the background of eroded ectropion, the risk of isthmic-cervical insufficiency and untimely rupture of amniotic fluid, which are the causes of premature birth, significantly increases.
Acquired ectropion
The acquired form occurs due to exposure to certain external factors. These include:
- childbirth, especially those with complications;
- abortions;
- multiple pregnancy or large baby;
- rupture of the cervical mucosa;
- mechanical impact;
- rapid labor;
- wrong attempts.
Tears that occur for these reasons require sutures. After this procedure, a scarring process occurs, during which blood flow and oxygen enrichment of the epithelium are disrupted in the damaged area of the mucosa. All this leads to changes in the cervix, namely, eversion of the mucous membrane.
It is not difficult to identify acquired ectropion if the woman previously had a clean cervix without pathologies. In the case where the patient has not previously consulted a doctor, it will be very problematic to establish the congenital form.
Prevention
Effective measures to prevent the formation of eroded ectropion are:
- absolute rejection of induced abortion;
- mandatory theoretical and practical preparation of a pregnant woman for childbirth;
- a complete examination at the end of pregnancy for the timely detection of complications that can cause birth injuries;
- careful handling of the birth canal during childbirth, observing all the rules for protecting the perineum and cervix;
- correct layer-by-layer suturing of the neck for birth injuries and ruptures;
- use of mini-hysteroscopy for diagnostic examination of the inner surface of the uterus, which does not require forced expansion of the cervical canal.
The detection of eroded ectropion in women in the postpartum period is a reason for examination and subsequent treatment. The main goal of therapy is to restore the cervical canal and prevent precancerous changes in the area of the eroded surface. In case of infertility and recurrent miscarriage, surgical intervention may be required to help a woman experience the happiness of motherhood again.
Cost of services
| Name of service | price, rub. |
| Primary, outpatient appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist (complaints, history taking, examination, drawing up an examination plan) | 2200 |
| Repeated appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist, outpatient | 2200 |
| Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, candidate of medical sciences | 2500 |
| Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, head of department | 2700 |
| Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, candidate of medical sciences, head of department | 2900 |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with an obstetrician-gynecologist, doctor of medical sciences, professor | 4100 |
| Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, chief physician of the clinic | 3400 |
| Appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist to interpret the results of an examination conducted in another medical institution | 3400 |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with an obstetrician-gynecologist based on the results of the examination with the appointment of a treatment regimen | 4600 |
| Treatment of eroded ectropion of the cervix using radiosurgical method, category 1 of complexity (up to 3 cm) | 35 000 |
| Treatment of eroded ectropion of the cervix using radiosurgical method, category 2 of complexity (more than 3 cm) | 40 000 |
Dear patients!
You can view the full list of services and price list at the reception or ask a question by phone.
The administration tries to promptly update the price list posted on the website, but in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we advise you to clarify the cost of services on the day of contact at the reception or call center by calling 8(495)223-22-22
. The posted price list does not constitute an offer.