What it is?
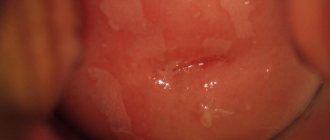
Photo of cervical leukoplakia
Cervical leukoplakia is an atypical change in the epithelium covering the cervix. Another name for the disease is cervical hyperkeratosis.
When visually examining the cervix, the doctor sees a white, dense spot or multiple spots. This explains the name of the disease, which comes from the Greek phrase “white plaque.”
The disease belongs to the group of background precancerous ones - if leukoplakia is not treated and observed, then gray and white plaques degenerate into malignant tissue.
How common is it?
Statistics vary depending on the country - the disease occurs from 1.1% to 12.5% of cases of all identified gynecological pathologies.
REFERENCE The reasons for the degeneration of plaques into a tumor and the reason for the appearance of the tumor itself are difficult to diagnose, and for this reason treatment is complicated.
ICD-10 code: other non-inflammatory diseases of the cervix (N88), the code excludes any inflammatory diseases, including polyps.
https://youtu.be/qzcAdAJe1P8
What causes pathology
Leukoplakia of the cervix is not cancer, there is no definitive data or research to support this. But the pathology is included in the category of facultative precancers - diseases that do not necessarily, but can still degenerate into malignant ones. Statistics indicate that in 30% of cases of cervical cancer, concomitant leukoplakia is found. Despite the fact that the reliable causes of cervical leukoplakia have not yet been established, there is a category of women who are most susceptible to such changes in the cervix.
- Poor hygiene. Failure to comply with basic hygiene measures, or, conversely, their excessive implementation, leads to changes in the functions of the gonads and integumentary epithelium. This is a risk factor for the development of leukoplakia. It is recommended to wash your face once or twice a day, without using intimate oils, creams, or wet wipes. Douching should not be the “norm”; it should only be performed as prescribed by a doctor.
- Sexual infections. A special role in the development of leukoplakia is played by viral lesions of the cervix and vagina. In particular, various strains of HPV (human papillomavirus), as well as CMV (cytomegalovirus) and chlamydia. This is due to the fact that these pathogens are integrated into the genome of cells, changing their metabolism and reactions, after which they acquire new properties, in particular, keratinization. Other sexually transmitted infections (STIs), if they become chronic, also play a significant role in the development of leukoplakia.
- Endocrine diseases. Pathologies such as diabetes mellitus, diseases of the thyroid gland, and adrenal glands affect not only individual organs, but also the functioning of the body as a whole. The ratio of sex hormones and the ability of cells to renew change. The risk of mutations increases, and, as a result, epithelial cells begin to slough off in an unusual way. In many situations, treatment will not be effective without a proper diet.
- Chronic immunodeficiencies. Diseases that lead to a decrease in immunity (hereditary, acquired - HIV, blood pathology) stimulate an inadequate response of body cells to external influences and internal changes. Failures lead to various diseases, including leukoplakia.
- Cervical injuries. A large number of births with cervical ruptures, frequent curettages (including during abortions), cauterization, and trauma by foreign objects lead to the fact that cells are forced to renew themselves more often than usual. This increases the likelihood of mutations and division failures.
The disease affects women of all ages, including those in their reproductive years. Therefore, timely diagnosis and subsequent competent treatment are so important.
Classification
Gynecologists distinguish the following forms of focal leukoplakia:
- Simple or flat - this is the initial stage of the disease; plaques in this form are small, smooth, light or grayish, and do not protrude above the surface of the mucosa. They are easy to miss during visual inspection.
- Verrucous, or warty, is considered the second stage of the disease, in which gray or white plaques and growths are layered on top of each other. Upon visual examination, the pathological lesions rise above the mucous membrane, the neck looks uneven, covered with tubercles.
- Erosive - cracks and damage appear on the altered tissues.
After the disease is detected, pieces of tissue must be submitted for histological examination. Histological examination makes it possible to understand whether the patient has a simple form of leukoplakia or with atypia, that is, with cells prone to transformation into cancer.
Diagnostics
To identify leukoplakia, a woman will need to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. First, you should visit a gynecologist and tell him about your complaints. The doctor will take a medical history and examine the woman in a chair. Additional tests that may be ordered:
- Studying a smear.
A smear taken from the vagina and cervix is sent for bacterial culture and PCR. This makes it possible to identify sexually transmitted diseases.
- Smear cytology.
Cytological examination provides information about what cells the epithelium consists of. The doctor takes a smear from the cervix. The procedure is performed using a special brush or Eyre spatula. In a woman with leukoplakia, stratified epithelial cells are detected in a smear from the cervix. Normally, such cells are present only in the vaginal part. The epithelium is changed, signs of hyperkeratosis are revealed (most scales do not have nuclei). It is also possible to detect signs of parakeratosis.
- Colposcopy.
If leukoplakia is suspected, the doctor examines the cervix using a special device - a colposcope. This allows you to detect changes that are invisible to the naked eye. It also becomes possible to visualize altered areas characteristic of a precancerous condition.
When pathological areas of the cervix are noticeable when examined on mirrors, the doctor makes a diagnosis of “severe clinical leukoplakia.” When abnormalities are detected only during examination using a colposcope, the doctor indicates the colposcopic form of the disease.
In the latter case, the woman will have iodine-negative zones, which can be detected during the Schiller test. To do this, the cervix is treated with iodine solution. The test is considered positive if the entire organ turns brown. A negative test is characterized by the presence of unpainted areas. Areas with leukoplakia do not respond to iodine, since there is no glycogen in the altered cells. It is this that gives the brown color when treated with Lugol's solution.
Also, using a colposcope, you can visualize puncture, which is represented by red dots. A mosaic and areas of the cervix of different thickness are visualized. Such diagnostic signs should alert you, as they indicate precancerous tissue transformation.
- Histology.
To put this method into practice, you will need to perform a biopsy of the cervix with curettage of its canal. Tissues are taken from the area that has undergone changes more than others. Histological examination allows us to assess the condition of the cells and identify atypical formations in them.
Leukoplakia is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Acanthosis.
- The presence of horny scales, which should not normally be present.
- Proliferation of multilayered epithelial cells.
- The epithelial tissues are unevenly thickened, since intermediate cells are located between them.
- Under the stratum corneum there is a granular layer.
- There are signs of hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis
- The cells are infused with lymphocytes.
- Assessment of ovarian function.
To do this, an ultrasound is performed, basal body temperature is measured, etc.
- Immunogram.
This study is prescribed only if indicated.
Reasons for the development of leukoplakia
The causes leading to the onset and progression of the disease are divided into exogenous and endogenous.
Doctors consider hormonal disorders to be endogenous - in particular, a sharp lack of progesterone, due to which anovulation is constantly observed.
Due to such pathological conditions, hyperplastic processes begin in the female genital organs.
Exogenous factors are divided into:
- chemical;
- infectious;
- traumatic.
Infectious factors are the main cause of pathology and its development. With hormonal imbalances and chronic infection, the risk of developing leukoplakia increases several times.
Signs of hyperkeratosis
Symptoms of pathology depend on the stage of development:
- with primary, poorly visible leukoplakia, there are most often no symptoms at all;
- with the warty form, the patient may experience periodic burning, itching and discomfort;
- with erosive discharge outside the cycle, small bloody or purulent discharge may appear on the underwear.
IMPORTANT If you have even mild symptoms, you should see a gynecologist as soon as possible - in addition to leukoplakia, such symptoms may indicate other unpleasant diseases of the female genital area.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis begins with a basic examination using speculum by a gynecologist. It is during the examination that the doctor most often discovers white or grayish plaques and plaque. After detecting the disease, the doctor prescribes the following tests:
- colposcopy, which allows you to identify the size, shape and extent of tissue damage;
- tests for hidden infections: human papillomavirus and herpes;
- cytological examination of a smear, in which a scraping is taken from the affected tissue;
- hormone tests showing progesterone levels;
- in cases of suspected cancer, a biopsy is performed to 100% exclude or confirm the presence of cells that have degenerated into malignant cells.
PAY ATTENTION It is necessary to find out that the detected pathological process is leukoplakia, and not thrush or specific erosion of the cervix. For this purpose, additional research is being carried out.
Symptoms of leukoplakia of the vulva, vagina and cervix
There are NO symptoms of cervical leukoplakia or specific COMPLAINTS.
Leukoplakia of the vulva, vagina and cervix forms INDISCOUSLY.
Leukoplakia of the vulva, vagina and cervix is usually detected UNEXPECTEDLY for a woman during an examination by a gynecologist.
Symptoms of vulvar leukoplakia are
- WHITE SPOTS or white scales on the skin or mucous membrane of the vulva (external genitalia), vagina, cervix;
| Photo of vulvar leukoplakia. Thinning and whitening of the skin in the clitoral area is detected | |
| Photo of vulvar leukoplakia. Same case |
- WHITE Spots or White SCALES may be localized or spread throughout the vulva, vagina, and cervix.
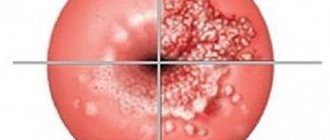
| Photo of cervical leukoplakia. Clearly demarcated white spots are identified. Cervicitis | |
| Photo of cervical leukoplakia. Extensive white areas occupy most of the cervix |
See all photos of cervical leukoplakia
Pay attention to the EXCELLENT quality of the photographs, testifying to the expert class of colposcopes of the Women's Health Resort Clinic.
You can find photographs of leukoplakia taken by our EXPERIENCED gynecologists-endocrinologists on many Russian and foreign websites and in textbooks.
How to treat cervical leukoplakia?
Before starting treatment for the pathology itself, doctors recommend preventing concomitant diseases - inflammatory and infectious processes, thrush.
Before surgery, vitamins and immunomodulators are prescribed, and it is suggested to adhere to a healthy diet for a while, without a large amount of animal fats. Doctors also recommend juice therapy - drink 2 glasses of freshly squeezed fruit and vegetable juice per day.
Once the concomitant diseases are treated, it is necessary to pay attention to the pathology itself, since if left unattended it can develop into cancer.
Leukoplakia and pregnancy
In some cases, hormonal imbalances and primary infections during pregnancy can lead to the initial form of the disease.
In this case, the doctor will prescribe additional tests to exclude the progression of the pathology, and will carefully monitor the patient throughout the entire period of gestation.
The risks for the baby include the possible development of an infectious disease, which can lead to congenital malformations and even fetal death.
To reduce the likelihood of disease progression and the development of infections, the gynecologist will prescribe regular vaginal sanitation and medications that will reduce the inflammatory process. Also during pregnancy, expectant mothers with a similar pathology are recommended:
- refuse salty and spicy foods;
- to walk alot;
- drink freshly squeezed juices, take vitamins;
- wear cotton panties, synthetics are excluded;
- carefully monitor hygiene;
- avoid hypothermia;
- try not to expose the body to additional stress.
In this case, the risk of cell malignancy will decrease, the disease will be under control and it can be treated after childbirth.
Does the disease prevent conception?
Primary and warty forms of leukoplakia in most cases do not interfere with conception. But, since during the period of hormonal changes in the body the disease can progress sharply, including creating a risk of cell malignancy, it is advisable to cure leukoplakia before planning pregnancy.
Leukoplakia of the cervix: treatment, causes, symptoms, signs, photos
Most often, the disease occurs secretly, without any complaints. Only some patients are bothered by excessive leucorrhoea, as well as bloody discharge from the vagina during sexual intercourse. There is no pain with leukoplakia.
Due to the asymptomatic course, a complete examination of the woman is of particular importance, especially if she belongs to a risk group.
When questioned, the nature of the menstrual cycle, previous diseases, including pseudo-erosion, are clarified. It turns out how the treatment of pseudo-erosion was carried out.
The lesion looks like an easily removable white film or plaques in the form of lumps, compacted, with clearly visible boundaries. These symptoms of cervical leukoplakia depend on the thickness of the stratum corneum. Beneath it are shiny pink lesions that correspond to the actual size of the damage. Leukoplakia lesions can be very small, or they can occupy a large area, even extending to the vaginal walls.
During colposcopy, leukoplakia appears as an area not stained with iodine, covered with small red dots. These points are outgrowths of connective tissue underlying the epithelium, through which capillaries pass. The pathological focus itself does not have any vessels. Red capillary filaments create a specific mosaic pattern. The Schiller test for leukoplakia is negative.
To diagnose a malignant tumor of the cervix with leukoplakia, an imprint smear is taken from the surface of the epithelium. However, this method is not always informative, because due to keratinization, the smear does not penetrate the deep layers of the epithelium, where cellular transformation occurs.
Therefore, the main diagnostic method is biopsy. For a qualitative study, it is necessary to perform a knife biopsy (using a scalpel) from the altered area of the cervix. Therefore, this procedure is carried out under colposcopy control.
Pathology can occur not only in the cervix, but also in the cervical canal. Therefore, it is necessary to perform curettage of the cervical canal mucosa simultaneously with the biopsy. The resulting material evaluates the thickness of the epithelium, the degree of its keratinization, loss of glycogen, changes in the nuclei and shape of cells and other signs.
One of the most modern diagnostic methods is microcolpohysteroscopy. It allows you to enter the cervical canal without anesthesia or dilation, examine its walls, and take a targeted biopsy.
When examining the obtained material under a microscope, the presence of cellular atypia is very important. Leukoplakia of the cervix without atypia is characterized by a normal ratio of cell sizes in the superficial and deep layers, but there are signs of excessive accumulation of keratin in them. This process is called dyskeratosis.
In leukoplakia with atypia, the upper layer is represented by dyskeratosis, and underneath it is hidden a deep layer, in which pathological changes in cells are detected. Many doctors call this condition morphological precancer.
Additionally, to clarify the causes of the disease and its treatment tactics, a bacteriological study is carried out to identify viruses and pathogenic bacteria, and the hormonal levels and condition of the genital organs are also assessed. If necessary, a study of the immune status - an immunogram - is prescribed.
In most cases, the disease is discovered accidentally during a gynecological examination. In the initial stages of development, leukoplakia does not cause any characteristic symptoms. Some women noted that they were bothered by heavy vaginal discharge, discomfort and unpleasant sensations during sexual intercourse. However, such signs are usually perceived as thrush or the consequences of hypothermia.
The presence of altered areas of the cervical mucosa is diagnosed using colposcopy during a physical examination. The reason for a visit to the doctor may be itching, white thick discharge, or discomfort during or after sexual intercourse.
- extended colposcopy;
- morphological method.
Complications
The main and most serious consequence of the disease is its probable degeneration into cervical cancer. If the pathology progresses, it enters the precancerous stage - a condition that is most likely to develop into cancer.
Therefore, patients with leukoplakia require constant medical supervision. If the lesions grow, doctors recommend removing sections of the changed tissue surgically.
Prognosis for recovery
In the case of proper treatment of leukoplakia, the disease can be completely cured in almost 100% of cases. If all concomitant diseases are treated, then relapse is excluded.
IMPORTANT There is a small probability of exacerbation of the disease and its transition to cervical dysplasia, which, in turn, often degenerates into cancer. Therefore, even small primary plaques need to be treated as quickly as possible, paying serious attention to the diagnosis and treatment of infectious and other concomitant diseases.
Are there preventive measures?
Leukoplakia of the cervix is a fairly serious pathology; with progression, it is possible to develop a malignant neoplasm and loss of reproductive function. Therefore, even the most initial form must be treated.
Measures to prevent the development of the disease are as follows:
- prevent sexually transmitted infections, treat those detected in a timely manner;
- use a barrier method of contraception;
- monitor hormonal levels - get tested on time;
- visit a gynecologist at least once a year;
- exclude artificial termination of pregnancy;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, take vitamins, and do not abuse alcohol.
After complete treatment of the initial stage of leukoplakia, the patient must undergo examination every 6 months for two years in a row - take vaginal smears, tumor markers and tests for HPV. If no relapses were detected during this time, then the woman is considered fully recovered.
Forecast
With proper treatment and following all doctor’s recommendations, leukoplakia does not pose a danger to a woman, despite the fact that it is a precancerous condition. But to prevent relapses, it is important to identify the factors provoking the disease and minimize their impact. This is not always easy to do. Many people are interested in the question of whether leukoplakia can go away on its own. Yes, indeed, small lesions can regress without treatment, provided the overall health improves.
https://youtu.be/tKWLKOHz9C4
Leukoplakia is a precancerous disease. However, timely detection and treatment will avoid such disastrous consequences. Reviews from women who have suffered this illness confirm this. In each specific case, therapy is selected individually. For some, cauterization of cervical leukoplakia is suitable, while for others, laser or liquid nitrogen is better.
What do you need to remember?
- Leukoplakia is a pathological change in the tissue of the cervix, in which white or brownish plaques appear on the mucous membrane.
- The reasons can be genetic and related to hormonal imbalances, as well as infectious and traumatic.
- There are practically no symptoms.
- Treatment consists of treating current diseases and removing the affected tissue.
- If the disease is started, there is a risk of the altered cells degenerating into malignant ones.
- The prognosis for recovery is positive with timely treatment.
The most important thing is to prevent the development and complications of the disease. To do this, leukoplakia must be detected in time, so all women should visit a gynecologist at least once a year.
Used Books
- Alov I.A., Aspich M.E., Kazantseva I.A. Determination of the mitogmic regime of tissue in the pathohistological diagnosis of precancerous processes and cancer: Guidelines, M, 1973.
- Apolikhina I.A. Optimization of diagnostic and therapeutic measures in patients with palillomavirus infection of the genitals: Author. dnss, . Candidate of Medical Sciences M., 1999.
- Bauer G. Color atlas of colposcopy: G1er. from German, -M; GEOTAR-MED, 2002.
- Vasilevskaya L.N.T Vinokur M.L., Nikitina N.I. Precancerous diseases and initial forms of cervical cancer. M. 1987.
- Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases: method, material / Ed. K.K. Borisenko, M,: SANAM, 998.
- Diseases of the cervix (clinical lectures) / Ed. V, N, Prilepskaya. M -1997
- Prilepskaya V.N., Fokina T.A. Background diseases of the cervix; pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment and obstetrics. and gynek. 1990
Treatment
To eliminate cervical leukoplakia, various treatment methods are used. But first of all, it is necessary to eliminate the inflammatory process (if present) and other provoking factors. If inflammation of the genital organs is detected or sexually transmitted infections are detected, drugs with antiviral, antibacterial, antitrichomonas or antifungal effects are prescribed (depending on the identified pathogen). If hormonal disorders are diagnosed, corrective hormonal therapy is prescribed. How to treat cervical leukoplakia is determined by many factors, and a specific treatment method is selected taking into account its disadvantages and advantages.
Diathermocoagulation
The method involves applying an electric current to the affected area, which then creates a burn. Electric waves are applied to an electrode (loop or “button”), which is in contact with the damaged part of the cervix. Since a burn surface is formed after treatment, the method is also called cauterization. Cauterization of cervical leukoplakia, although a fairly effective method (reaches 70%), is very painful. The advantages of the DTC method include only:
- cheapness;
- the presence of a DTK apparatus in almost every gynecologist’s office.
DTK has a lot of disadvantages, so it is rarely used today. Cauterization is carried out in the first phase of the cycle, after menstruation has ended. The disadvantages include:
- significant pain of the procedure;
- exacerbation of inflammatory diseases of the uterus, ovaries and tubes;
- high risk of bleeding, both during cauterization and after (premature rejection of the scab);
- long healing (up to 2 months);
- cicatricial deformation of the cervix up to atresia (fusion) of the cervical canal, therefore it is used only in women who have given birth.
Cryodestruction
Treatment of leukoplakia with cold - cryotherapy or cryodestruction - is a highly effective method. The efficiency of cryodestruction reaches 94%. The pathological area is exposed to liquid nitrogen at a very low temperature. As a result, crystals form in the cells, which lead to their destruction and subsequent necrosis. The method is contact, the duration of the procedure depends on the nature and area of the pathological focus (2 – 5 minutes). The advantages of “freezing” include:
- painlessness;
- good effect;
- bloodlessness;
- Possibility of use in nulliparous women;
- no scars.
Among the disadvantages of cryodestruction it is worth noting:
- recurrence of leukoplakia;
- the likelihood of shortening the cervix, which reduces the chances of conception.
Laser therapy
Laser therapy is considered the most effective method of treating leukoplakia today. Laser coagulation of a leukoplakia lesion is carried out in the first phase of the cycle and does not require anesthesia. The method is non-contact and involves treating the pathological focus with a CO2 laser beam. As a result, liquid evaporates from the treated (pathological) cells, which contributes to their destruction. Then a thin coagulation film is formed on the wound surface, which prevents infection from entering the wound. If the process spreads to the vagina, treatment is carried out in 2 stages. At the first stage, the cervix is treated, at the second - the vaults and walls of the vagina. The advantages of the method are:
- painlessness;
- high efficiency;
- absence of cicatricial deformation of the cervix (can be used for nulliparous women);
- bloodlessness;
- rapid healing (16 – 40 days).
Disadvantages include the high cost of the method and the availability of special equipment (available only in specialized clinics).
Read more about the indications and contraindications of laser therapy.
Radio wave method
For treatment with this method, the Surgitron device is used. The method is modern, effective and contactless. The essence of the treatment is to insert an electrode into the cervical canal, at the tip of which electrical waves are converted into radio waves. Pathological cells heat up, liquid evaporates from them and the leukoplakia lesion is destroyed. The advantages of the method include:
- painlessness;
- bloodlessness;
- absence of cicatricial deformation of the cervix;
- fast healing.
There is perhaps only one drawback. Not all antenatal clinics have the Surgitron device
Chemical coagulation
This method of treating leukoplakia consists of treating the pathological area of the cervix with the drug Solkovagin. This drug contains organic and inorganic acids that coagulate (cauterize) pathological cells. The method is painless, suitable for nulliparous women, and reaches an effectiveness of 75%. Among the disadvantages, it should be noted that the penetration depth of the drug is no more than 2.5 mm, which makes its use ineffective for atypical gross leukoplakia. And also the impossibility of treating large areas of the cervix.
Postoperative period
In the postoperative period, doctors strongly recommend maintaining sexual rest for 1.5 months. Lifting heavy objects, taking hot baths, and going to baths and saunas are also prohibited. In addition, douching and the use of sanitary tampons are prohibited. It is also necessary to observe the rules of intimate hygiene. In the first 10 days after any method of treating the cervix, heavy liquid discharge may appear, which should not frighten the woman. This is a response to treatment and indicates healing of the wound surface.
Traditional methods of treatment
In order to eliminate cervical leukoplakia, the use of any traditional methods of treatment is not allowed. Various douching, insertion of tampons with medicinal herbs, etc. will not only bring no benefit, but will also contribute to the spread of the process and the appearance of atypical cells.
Methods previously favored by doctors for treating any cervical pathology, such as inserting tampons with sea buckthorn or rosehip oil, aloe ointment, etc., are not currently used. It has been proven that the listed drugs affect tissue metabolism, which causes the proliferation of pathological cells and provokes the development of dysplasia.