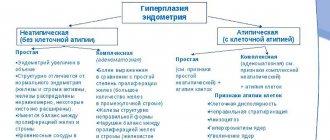
Endometrial hyperplasia is a hormone-dependent disease that involves benign growth of the endometrium in the uterus and leads to an increase in its volume, as well as thickening of the walls. Elements of the endometrium multiply rapidly. In the absence of effective and relevant treatment for this disease, benign formations can degenerate into malignant ones.
Temporary endometrial hyperplasia is typical for women during monthly cycles and is the norm. Each time the uterus prepares for pregnancy, which contributes to the natural thickening of the endometrium. If this does not happen, it is rejected by the body.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of this hormone-dependent disease include:
- non-cyclic bleeding between periods or prolongation of the menstrual cycle;
- moderate, spotting discharge. In rare cases - with clots;
- anemia due to prolonged bleeding;
- lack of ovulation, which suggests excess estrogen and the risk of infertility.
It is very rare that there are no obvious symptoms of the disease, and the only reason for concern is the failure of the long-awaited pregnancy.
A consultation with a gynecologist is required if pregnancy has not been achieved within a year. In this case, the woman is actively sexually active without using any means of protection. Symptoms of hyperplasia are quite often confused with uterine fibroids, as well as the threat of miscarriage.
Causes
Physiological hyperplasia is manifested by a slight thickening of the walls of the uterus and is directly related to the menstrual cycle.
Pathological endometrial hyperplasia has completely different causes. These include:
- hormonal imbalance, as a result of which the body produces excessive estrogen and a deficiency of progesterone;
- late onset of menopause;
- the presence of gynecological pathologies in a woman’s body, such as endometritis, fibroids, uterine or ovarian polyposis, endometriosis;
- surgical operations on the appendages, uterus due to abortion, treatment of various gynecological diseases, curettage;
- absence of childbirth;
- the presence of endocrine and metabolic diseases (dysfunction of the thyroid gland, liver, adrenal glands, diabetes mellitus, excess weight, arterial hypertension).
The highest risk of developing this disease is in adolescent girls and premenopausal women.
What is endometrial hyperplasia
The inside of the uterus is covered with a mucous membrane - this is the endometrium. Its structure is formed by 2 layers. Functional - external, which is rejected during the active phase of the menstrual cycle. Over the next month it will form again. Basal - internal, on its surface the functional layer is built up.
During reproductive age, the endometrium transforms during each menstrual cycle. At first it increases, and if fertilization does not occur during ovulation, it is rejected and comes out in the form of ichor, and sometimes clots.
When menopause begins, the endometrium gradually atrophies - this is an absolutely normal process. The layer becomes thinner, and when reproductive function fades, renewal of the mucous membrane is no longer required. Accordingly, menstruation stops. The endometrium continues to perform a protective function, so the body needs it.
Pathology is considered to be the growth of this layer, which is dangerous due to the risk of degeneration of benign structures into malignant ones. The endometrium not only increases in volume, but penetrates into the thickness of the walls of the uterus. As a result, tissues are deformed, hormonal levels are disrupted and all internal organs suffer.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease includes a standard examination, ultrasound of the pelvic organs, diagnosis and screening of endometrial hyperplasia, hormonal studies (analysis of the level of estrogen and progestron in a woman’s body), hysteroscopy to scrape out the cavity for analysis, as well as aspiration biopsy of the endometrium.
Timely diagnosis will allow you to accurately determine the disease, its location, and also develop a treatment regimen.
Proliferative processes in the body can lead to serious changes and pathological consequences, so diagnosing the disease is an important stage in its treatment. The gynecologist may also prescribe additional diagnostic tests, based on the degree of advanced disease.
Signs of the disease
Postmenopausal endometrial hyperplasia shows slightly different symptoms than in young women with the same diagnosis. This is due to differences in hormonal balance. Adenomyosis manifests itself:
- Sudden bleeding, which may be spotty or intense. It is impossible to confuse them with menstruation; at the stage described, the function of the ovaries has completely died out. However, endometrial hyperplasia in menopause without discharge also occurs;
- Pain in the abdomen, of a pulling nature;
- Increased fatigue and irritability;
- Headaches.
Some may periodically experience strong, unreasonable thirst (due to increased blood sugar) and weight gain. And sometimes endometrial hyperplasia in menopause does not show symptoms at all, being detected only during a routine examination. That is why it is important to monitor the condition of the reproductive organs even when their main functions have already been completed.
When should you worry?
A diagnosis of “adenomyosis” is made and its type determined by specialists.
For this purpose, hardware methods have been created, the main one being ultrasound. It is carried out annually and without problems. There is such an indicator as the thickness of the endometrium, in postmenopause the norm is 4-5 mm, no more. At this stage, it atrophies, because repeated changes no longer occur in the mucosa. It is also possible for some parts of the uterus to undergo fusion and fluid to appear in the cavity due to partial narrowing of the cervical canal. The norm of the endometrium during menopause also includes an assessment by a specialist of its structure. If changes are noticed in it that are not consistent with age, their nature is determined.
The thickness of the endometrium during menopause is 6-7 mm, which is a reason for closer observation. The woman will have to do an ultrasound after another 3 months and after six months.
Thick endometrium in menopause is referred to as such, starting from 8 mm. In this case, the indicator forces scraping and analysis of the resulting material. And if it is 10-15 mm, a histological examination will be necessary.
Mucus in the uterus on ultrasound during menopause should be considered in conjunction with other symptoms. If there is pain and discharge with blood, it is not just the result of natural atrophy of the organ, but a sign of inflammation, hypertrophic changes in the membrane.
The course of the disease and its types
Uterine hyperplasia, in accordance with the mechanism of development of the process, is classified into several types:
- focal, which involves the growth of endometrial polyps in a certain area;
- glandular, which suggests endometrial proliferation. It can be in both active and quiet forms;
- atypical, which is characterized by structural restructuring and proliferation of glands;
- glandular-cystic, which resembles glandular hyperplasia, more pronounced, and suggests the presence of cystic-enlarged glands.
In addition, experts divide this disease into simple and complex. The duration of treatment, as well as its features, depend primarily on the type of disease.
Types of endometrial hyperplasia in menopause
In gynecology, uterine hyperplasia is classified into several types. All of them are characterized by certain differences:
- Focal or polypoid. In the thickness of the endometrium there are many glands from which polypous growths appear on the legs. Gradually, these formations become overgrown with endometrium.
- Basal. The outer shell grows into the inner (basal) layer. This form of hyperplasia during menopause is rare, so difficulties arise with making a diagnosis, and it is important to get an appointment with a good specialist on time.
- Atypical. More often, this form is diagnosed in women of reproductive age, since the pathology actively develops against the background of a normally occurring menstrual cycle. When natural processes are slow, the risk of atypical hyperplasia is less, but it still occurs in women during menopause. The endometrium grows in all directions, and hyperplasia develops into cancer. This form of endometrial hyperplasia in menopause cannot be treated; the only way to save the patient is to remove the uterus.
- Glandular. The glands grow throughout the entire thickness of the epithelium, with pathological tissue directed towards the muscle layer. The shape and size of the epithelium change, it becomes uneven. The risk of degeneration into a cancerous tumor is low. How to treat: therapy, curettage. After curettage, antispasmodics, analgesics, and antibacterial agents are prescribed.
- Cystic. Cysts are formed due to the fact that the epithelium, growing, blocks the exit openings of the glands with cells. Cavities appear in the tissues. There are developments of cancer.
Treatment with folk remedies
Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia is carried out not only with medication and surgery, but also with folk remedies. This is the most gentle way to stop the disease. In addition, non-traditional treatment of endometrial hyperplastic processes is often used with traditional treatment to enhance the effect.
A competent combination of methods such as hormonal therapy, herbal medicine and surgical treatment is an excellent opportunity to quickly, effectively and efficiently get rid of endometrial hyperplasia. Only one dose of herbal remedies can aggravate the situation. The problem should be addressed comprehensively.
It is imperative to influence and block the excessive production of hormones, since under such conditions cancer cells rapidly divide and the consequences can be very different. Most often, in such cases, drugs are prescribed that can block this excess production of hormones, but today there is no need to take only them. There are natural remedies, namely blocking herbs, that can effectively help solve this problem.
Blocker herbs
Herbs for endometrial hyperplasia act as a blocker. These include:
- White bloodroot,
- comfrey,
- sparrow,
- bruise,
- egg capsule,
- blackroot.
In addition, it is mandatory to use herbs that are antagonists of female sex hormones, namely fireweed, jarutka, and rape. In the later stages of the disease, it would not be a bad idea to take an alcohol tincture of hemlock.
Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia with folk remedies allows you to get rid of the negative effects of toxins, and also helps restore the normal functioning of cells.
For endometrial hyperplasia, tinctures from plants such as viburnum, nettle, peony, boron uterus, hemlock, mantle, sleep grass, flaxseed, peach oil, burdock juice, beets, carrots, decoction of cucumber lashes, milk thistle meal, fruits are also effective Vitex, as well as discorrhea root.
This collection effectively copes with the task and is quite effective for prevention purposes.
Home treatment methods
In addition to herbal teas, the following folk remedies are used as a home treatment for endometrial hyperplasia:
- treatment with leeches. This therapy is repeated 2-3 times a year for 10 sessions. The essence of this technique is to thin the blood, lower blood pressure, improve metabolism, as well as immunity;
- narine. Daily consumption of fermented milk products allows you to improve the functioning of the intestines, allows you to get rid of problems such as dysbiosis, and restores human immunity;
- douching with infusion of celandine and calendula. The course of treatment for each type of herb is 12 days;
- garlic tampons, which make it easy to deal with endometrial polyps.
Juices (beetroot and carrot)
According to traditional healers, a remedy made from beet and carrot juices is an excellent way to cope with endometrial germination. You just need to mix half a glass of these juices and drink the product throughout the day. You can add a little celandine juice. The duration of such therapy reaches 1 month.
To cure endometrial hyperplasia completely, after completing the course of taking the juice, you need to continue treatment using other effective folk remedies.
Milk thistle meal
Very often, the main cause of hyperplasia is slagging in the body. Milk thistle meal allows you to get rid of toxins and other harmful substances, thereby accelerating the process of tissue regeneration. The composition is taken daily, 1 teaspoon and washed down with a sufficient amount of water.
Peach oil
This substance has a pronounced diuretic effect. Combined with antioxidant properties, peach oil helps remove waste and toxins from the body. You need to take it 2 times daily. Duration of treatment – 20 days. This time is enough to completely cleanse the body.
Vitex
Another very effective folk method for reducing the endometrium is herbal medicine with sacred vitex.
This remedy has an anti-inflammatory effect and promotes tissue healing. You can prepare a vitex tincture as follows:
- Pour 0.5 cups of plant fruits with 200 ml of alcohol and leave for 3 hours;
- Strain the tincture through cheesecloth.
It is enough to take 20 drops of the finished tincture per day, and they need to be divided into 2 times.
Hemlock
The antitumor properties of hemlock make it an indispensable folk remedy for preventing the development of malignant tumors. At the same time, do not forget about the toxic properties of the plant and follow the dosage. To prepare the tincture, take 300 grams of hemlock inflorescences and add 0.5 liters of vodka. After 1 month of infusion, the tincture is ready. The composition is taken until a noticeable improvement in the condition, 1 drop per day with a gradual increase to 15 drops.
Prevention
Prevention and treatment of endometrial hyperplasia with folk remedies includes visiting a gynecologist regularly (preferably twice a year), playing sports, fitness, daily physical activity on the body, taking hormonal contraceptives, timely and high-quality treatment of inflammatory diseases in the body, as well as other related gynecological diseases , refusal of abortion, constant monitoring of glucose levels, blood pressure, weight.
Any abnormalities in the body should be checked. Also, a mandatory preventive measure is a proper balanced diet, which allows you to keep a person’s weight within acceptable limits. Examining the uterus once a month will allow you to prevent serious disease of the woman’s genital organs.