Among all diseases of the female reproductive system, a special place is occupied by the functional ovarian cyst - a tumor-like formation that occurs during ovulation, the growth of which is associated with the menstrual cycle. Usually this pathology does not pose any danger to the patient’s health, however, some complications can lead to a serious condition requiring urgent measures.
Most often, this disease is diagnosed in young women. This is due to the fact that the formation of a functional tumor is possible only during the reproductive period. Most often, the pathology occurs on one side; damage to both ovaries at the same time is very rare.
Reasons for the formation of functional cysts
At the moment, doctors cannot give an exact answer explaining the causes of a functional ovarian tumor. However, factors have been identified that increase the risk of developing pathology.
The greatest role in the formation of cysts is played by hormonal imbalance associated with increased estrogen levels. When the concentration of this hormone in the blood of a woman is high, a disruption of the menstrual cycle occurs, due to which the process of maturation of follicles in the ovaries stops, and a cavity gradually forms in their place. Over time, the cyst fills with fluid from nearby tissues, gradually increasing in size.
Hormonal imbalances can result from many reasons. For example, the risk of developing a functional ovarian cyst increases after termination of pregnancy, with uncontrolled use of hormonal contraceptives. Risk factors also include various diseases of the endocrine system - diabetes, thyroid disease and other pathologies.
In addition to reasons directly related to the reproductive system or hormonal disorders, the risk of developing a functional cyst depends on the woman’s lifestyle. Long periods of overwork, emotional stress, and physical activity can trigger tumor growth.
Often the disease is diagnosed in patients with diseases of internal organs, which are accompanied by a decrease in the body's defenses. Acute or chronic infections of the genitourinary system also play an important role. Therefore, women who frequently change sexual partners are at risk.
In rare cases, a functional cystic formation is found in young girls. Such pathologies arise due to the effect of maternal hormones on the fetus during gestation or breastfeeding. Cysts of this nature do not pose a threat to the child’s health and go away on their own after stopping breastfeeding.
https://youtu.be/XkNm8thZYvU
Causes of ovarian cysts
The appearance of a neoplasm is, in one way or another, always associated with hormonal imbalance, so gynecologists identify several common causes of ovarian cysts, which lead to hormonal imbalance:
- Delayed onset of menopause - normally, periods stop before the age of 50-52. If this period is prolonged, it is associated with the risk of cysts.
- Delayed onset of the first menstruation - normally, menstruation should begin at the age of 12-13 years.
- The onset of menstruation is too early - this includes the age of up to 11 years.
- Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs. Moreover, acute forms are less likely to contribute to the formation of cysts than chronic forms.
- Sudden weight loss or sudden weight gain.
- Significant excess body weight - excess weight, even if it is gained over a long period of time, negatively affects the functioning of the ovaries and the entire endocrine system as a whole.
- Nervous stress, psycho-emotional tension, lasting for a long time.
- Refusal of breastfeeding
- Regular heavy physical activity
- Diabetes mellitus (both type 1 and type 2)
- Diagnosis of PCOS in mother, grandmother. Doctors' observations show that the tendency to cysts may be due to a hereditary factor.
Treatment will be useless if the cause of the tumor is not eliminated. For example, if a woman who is overweight has a cyst removed, then after a certain period of time it may appear again. To normalize the functioning of the ovaries, you need to put the entire endocrine system in order.
Classification of formations
Depending on the mechanism of development, functional cysts are divided into two types:
- follicular - the reason for the occurrence of this neoplasm is due to the fact that after maturation the formed follicle remains intact. Therefore, the egg remains in it, and the follicle cavity fills with liquid over time;
- functional cyst of the corpus luteum - occurs after the rupture of the follicle, when the mature egg leaves the ovary. Normally, a corpus luteum forms in its place, which then regresses. If this does not happen, a cavity is formed, which is also filled with liquid contents.
The functional cyst of the left ovary deserves the most attention. This is due to several reasons:
- pathology of the left ovary is more common, which is associated with the characteristics of oocyte maturation;
- left-sided lesions are often accompanied by infectious complications, since nearby intestinal loops can become a source of infection.
To prevent the development of a functional ovarian cyst, it is recommended to undergo regular examination by a gynecologist, regardless of the presence of symptoms. If your menstrual cycle is irregular, you should not put off visiting a doctor, since timely detection of a neoplasm will make it possible to avoid many complications.
Types of functional cysts and reasons for their formation
Despite the fact that functional cysts are classified as tumor-like formations, they are not tumors as such and are called false. These cysts arise as a result of natural physiological processes that accompany the normal functioning of the ovaries. They rise somewhat above the surface of the latter and represent a capsule filled with a certain liquid. Depending on the source of formation, there are types of functional ovarian cysts:
- Follicular cyst.
- Luteal or corpus luteum cyst.
Symptoms of functional formations on the ovaries
Every woman should know the main signs of an ovarian tumor so that if she has the disease, she can identify it in time and consult a doctor. In most cases, this pathology is an incidental finding during examination for other diseases. This is explained by the practically asymptomatic course of this disease. In the early stages of formation, a functional cyst does not manifest itself in any way; the first symptoms appear when the tumor reaches an impressive size, when there are prerequisites for the development of complications.
Functional ovarian cysts are characterized by the presence of the following symptoms:
- pain, bursting sensations in the abdominal area on one side;
- feeling of heaviness in the groin;
- changes in the menstrual cycle - such patients usually have no menstruation, or may experience bleeding in the middle of the cycle.
The clinical picture is due to the fact that the enlarged ovary compresses the surrounding tissues, as a result of which the blood flow in them is disrupted. Therefore, the severity of symptoms is directly related to the size of the formation.
Menstrual irregularities can be associated not only with the absence of menstrual bleeding. In some cases, an increase in the volume of blood loss and the duration of “critical days” is possible. Sometimes menstruation is accompanied by pain. The opposite situation also happens - menstrual flow is scanty, spotting, without other symptoms. Therefore, you should consult a doctor if there are any changes in your cycle, even if they do not cause inconvenience.
Symptoms
The first sign of a cyst is an irregular menstrual cycle with pronounced pain in the lower abdomen. Patients may also experience the following symptoms of a functional ovarian cyst:
- Acute pain when pressing on the lower abdomen, in the groin area or during sexual intercourse.
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Pressing and bursting sensations inside the pelvis.
- Increase in body weight.
- Increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels.
- Disruptions of the menstrual cycle.
- Bloody or watery discharge.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Tension of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Violation of the act of defecation.
If the size of the formation is small, there may be no symptoms at all.
Do you use folk remedies?
Not really
Who is at risk
We can say for sure that any woman of reproductive age has a chance of developing a functional ovarian tumor. Therefore, all girls are advised to be attentive to their health and avoid exposure to provoking factors on the body.
There are several groups of women whose risk of pathology is increased. These include:
- patients with early menopause;
- all women over 40 years of age;
- patients with irregular sex life for a long period of time;
- women with periodic bleeding not associated with the menstrual cycle;
- women who have never given birth or been pregnant;
- patients with ovarian dysfunction.
Even those girls and women who do not belong to the above groups should not forget that there is always the possibility of the formation of a functional cyst. Therefore, regular examinations by a gynecologist should not be neglected by anyone.
Why do ovarian cysts appear?
The causes of ovarian cysts have not yet been fully elucidated. There are a number of factors that can provoke the development of the disease - hormonal disorders, inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, menstrual disorders (ovarian cysts are detected on average in 30% of patients with a regular menstrual cycle and in 50% of women with irregular periods), early onset of menstruation, late menopause, infertility, etc. Such factors also include poor ecology, genetic predisposition, viruses, etc.
How is a functional ovarian cyst treated?
To cure a functional ovarian cyst with the most effective method, a complete examination of the patient should be performed. Diagnostic procedures include an examination by a doctor, an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, as well as laboratory tests to determine the amount of sex hormones in the blood. To carry out a differential diagnosis with malignant neoplasms, laparoscopy with biopsy is performed.
After performing these diagnostic procedures, the doctor chooses the appropriate treatment method - conservative or surgical. The choice of treatment method is based on the size of the tumor, suspected causes, and the presence or absence of complications.
If the size of the functional cavity is small and a single formation is detected, then special treatment methods may not be used. Therapy for such women begins with lifestyle changes and regular examinations by a gynecologist to monitor the growth of the tumor. At the same time, such patients are indicated for treatment with folk remedies, for example, using herbal sedatives to reduce stress levels.
Conservative treatment
To reduce the size of the tumor, the attending physician selects a treatment regimen, the main place in which is occupied by drugs with hormones. Their action is based on blocking a woman’s follicle-stimulating hormone and stopping the process of egg maturation. As a result, a functional cyst does not increase in size, and the affected ovary can recover on its own.
Such drugs are also prescribed after the patient has been cured, as they prevent the formation of new cysts. Duphaston is considered the most effective and safe drug prescribed for this disease.
In case of complications of the neoplasm with an inflammatory process, therapy for the functional cyst of the paired gonad is selected by the doctor based on medical history. If symptoms of infectious complications appear, for example, fever, chills, it is necessary to prescribe antibacterial drugs along with immunomodulators. Bed rest is also recommended until the woman's condition improves.
Diagnostics and therapy
Most often, a cyst is discovered by chance during a routine examination by a gynecologist. Less often, a woman consults a doctor with characteristic complaints.
To clarify the diagnosis, as well as for follow-up, doctors use transvaginal ultrasound, dopography, CT, MRI, and in more serious cases, laparoscopy.
If the cyst is small and does not cause significant concern, then no specific treatment is required.
But to recover, a woman must:
- maintain the correct diet and diet;
- stop being nervous, protect yourself from stress, relax more;
- be sure to follow a sleep schedule - you need to sleep at least eight hours at night;
- walk a lot, breathe fresh air.
It is also necessary to properly treat existing acute or chronic diseases that caused the cyst to appear.
If the cyst is large and does not disappear after 2-3 cycles, then special medications may be prescribed to speed up resorption:
- hormonal (diferelin, mirolyut, buserelin);
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, diclofenac, etc.);
- analgesics.
It should be noted that traditional treatment with folk remedies includes very potent herbs that actively interact with medications. Therefore, taking them without a doctor's prescription is dangerous.
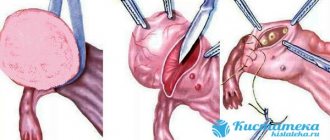
If drug therapy does not help, or if the cyst continues to grow, then the woman is offered to remove the dangerous tumor surgically. Usually, there is no need to make an incision for such an operation: the cyst is removed using laparoscopy through small punctures. There are no scars left after such an operation, and the recovery period takes only three days.
Complications
If the cyst is of significant size, complications of the disease may develop - rupture, intra-abdominal bleeding, as well as torsion of the tumor's stalk.
The following symptoms are typical for the rupture of a functional ovarian cyst:
- sudden sharp pain on the affected side, in the lower abdomen, paleness of the skin, sticky and cold sweat;
- when irritating the receptors of the abdominal organs - nausea, vomiting, tenesmus (the urge to defecate);
- dysfunction of the cardiovascular system, manifested by a sharp decrease in blood pressure and an increase in heart rate;
- decrease in hemoglobin level associated with blood loss, development of acute anemia and hemorrhagic shock.
Torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst also occurs suddenly. Usually this complication is associated with a sudden movement, but its causeless development is also possible. The ovarian pedicle is an anatomical formation that includes the fallopian tube, vessels and nerves that supply the organ. When it is compressed, blood circulation in the affected organ is disrupted, and ovarian necrosis gradually develops. Irritation of nerve fibers is also possible.
This type of complication manifests itself with the same symptoms as the rupture of a functional cyst. The main difference is the patient’s milder condition, which is associated with the absence of internal bleeding and the development of hemorrhagic shock. However, if any complication of the disease is present, emergency surgical treatment is required.
Cyst cyst discord
As already mentioned, almost every woman encounters a functional cyst, and in the vast majority of cases she does not even know about it - everything goes away by itself, without any noticeable symptoms.
But there are no rules without exceptions. This is especially clearly demonstrated by the extraordinary story that happened to 57-year-old Costa Rican resident Sonia Lopez. When she was first diagnosed with a large cyst and offered to have surgery, the woman refused. At that time, she had certain difficulties in her family, and she considered that family matters were much more important than some kind of cyst, which, perhaps, would resolve itself.
But the cyst slowly grew and after 8 years it occupied 80% of the woman’s entire abdominal cavity. This caused such severe difficulty breathing that the patient had to undergo a complex operation, during which surgeons removed a cyst of absolutely unimaginable size. The diameter of the neoplasm was more than one and a half meters, and its weight reached almost 35 kilograms. Surgeons believe that this is the largest of all known ovarian cysts.
Fortunately, the giant tumor turned out to be benign, and the patient quickly recovered after its removal.
Dear readers, if you would like to share this information with your friends on social networks, you can quickly post a link using our convenient buttons.
Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks:
This blog is read and used by 6,939 adherents of a healthy lifestyle and uses its advice and recommendations, so their health is in order, their mood is good, and their work is going well. Read it too.
I agree to the newsletter and accept the privacy policy.
You may also be interested
Troxevasin ointment is a useful addition for home...
Good day, dear readers of Alexey Shevchenko’s blog “Healthy image...
12 Read more
How to treat gumboil - what doctors suggest
Good day, dear friends of Alexey Shevchenko’s blog “Healthy Image...
12 Read more
CHRONIC HEPATITIS B AND TRADITIONAL MEDICINE
HEPATITIS B VIRUS AND WAYS OF ITS SPREAD The opinion spread by ordinary people is ...
0 Read more
Milk thistle is a universal medicine
Contents 1 Milk thistle - nature’s medicine 2 Milk thistle in ...
12 Read more
How does a cyst behave during pregnancy?
A functional ovarian cyst and pregnancy can be diagnosed in a patient almost simultaneously. Due to the fact that the symptoms of the disease are mild, in most cases it is detected during routine ultrasound diagnostics during pregnancy.
The presence of this pathology is not an indication for termination of pregnancy. For small tumors, no specific therapy is required. During the period of bearing a child, a woman's hormonal levels change, so it often happens that a functional ovarian cyst resolves on its own before delivery.
Large formations require special attention - this is associated with possible complications. A common cause of misdiagnosis during pregnancy is a complicated functional cyst of the right ovary. Its location determines that the symptoms of torsion or rupture resemble the clinical manifestations of acute appendicitis. Often inexperienced doctors confuse these pathologies. Pain with a functional ovarian cyst is similar to the unpleasant painful sensations associated with inflammation of the appendix.
Therefore, doctors should pay enough attention to such patients to prevent the development of a serious condition that threatens the life of the fetus and mother. When an ovarian cyst is detected in pregnant women, treatment is selected so that it is as gentle and effective as possible.
Education mechanism
Brief physiology of the menstrual cycle
There are three phases during the menstrual cycle:
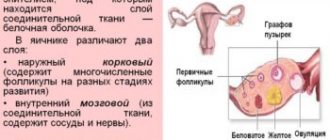
- Follicular . Starts from the first day of menstruation. At this time, under the influence of folliculotropin, the growth and maturation of one or more follicles, inside of which there are eggs, occurs.
- Ovulation . Under the influence of the release of luteinizing hormone, the dominant follicle (Graafian vesicle) ruptures, and the egg is released into the abdominal cavity, from where it then penetrates the lumen of the fallopian tubes.
- Secretory (proliferative). In place of the burst follicle, a temporary endocrine gland begins to form - the corpus luteum. Its main function is the synthesis of progesterone, a hormone responsible for preparing a woman’s body for a possible pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, then after 10-12 days the corpus luteum undergoes regression and the woman experiences rejection of the inner layer of the uterus (endometrium), which is manifested by menstrual bleeding.
Types and reasons of education
Various hormonal imbalances in the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian system are accompanied by menstrual dysfunction and often provoke the formation of functional cystic formations, which include:
| View | Reason for development |
| Follicular cyst | They usually occur in young women as a result of failure to ovulate. The dominant follicle does not rupture and continues to grow. Fluid gradually accumulates in its cavity, which leads to the formation of a cystic formation. Normally, ovulation occurs on days 11–14 of the menstrual cycle with a dominant follicle size of 17–23 mm. A follicular ovarian cyst can reach a diameter of 8–15 cm. Quite often, this form of the disease occurs under the influence of physical or psycho-emotional stress, abortion, inflammatory diseases of the genital area (nonspecific and specific), and ovarian hyperstimulation. The pathology can also be caused by uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives. |
| Corpus luteum cyst | Formed in place of the corpus luteum. The reasons for its formation have not yet been precisely established. It is assumed that disturbances in the blood supply to the corpus luteum lead to the accumulation of hemorrhagic or serous fluid in its tissue. Such neoplasms reach a diameter of 6–8 cm (normally, the size of the corpus luteum itself is 17–25 mm). According to statistics, the disease occurs in 2-5% of women of reproductive age |
Prevention of functional formations
There are no specific measures aimed at preventing the formation of a functional cyst. Therefore, prevention is aimed at reducing the risk of developing this disease. First of all, this applies to women who have previously suffered from this pathology.
Knowing the most common causes of functional ovarian cysts, several measures can be taken to prevent pathology:
- proper nutrition - you should limit the consumption of spicy and fatty foods, maintain body weight within normal limits;
- in the presence of severe obesity, it is necessary to add regular aerobic exercise to the diet;
- limiting physical activity associated with lifting weights, abdominal exercises, jumping;
- reducing stress and psycho-emotional tension, active lifestyle, adequate sleep and rest;
- be attentive to your body - in case of minor irregularities in the menstrual cycle, you should immediately consult a doctor.
If you follow the rules listed above, you can significantly reduce the risk of recurrence of the disease.
It is necessary to understand that the clinical recommendations of doctors for a functional ovarian cyst are important and must be followed. Strict adherence to them must be observed, regardless of the severity of the illness, the general condition of the body and the age of the patient.
The health of the female reproductive system requires great attention. Ignoring the signs of various pathologies can cause irreparable damage to women's health. Therefore, girls should be attentive to the appearance of certain symptoms, even in cases where they do not cause inconvenience. Knowing what a functional ovarian cyst is and how it manifests itself, you can recognize the presence of the disease in time and begin treatment at the stage when the therapy will be most effective.
What happens when a functional cyst ruptures?
If a large ovarian cyst is detected, then treatment is mandatory. Rupture of a functional cyst is fraught with severe pain, painful shock and peritonitis, which can lead to death. There are several signs by which you can determine that the formation has burst:
- high body temperature, which is not reduced by antipyretics;
- acute pain in the lower abdomen;
- weakness, vomiting, dizziness;
- heavy bleeding from the uterus;
- confusion;
- cold sweat;
- low pressure;
- tachycardia.
If you have at least one of the above symptoms, you should immediately call a doctor!
https://youtu.be/Voe8etwRFP0
Diagnostic feature
Pathology requires observational tactics. The main task of the gynecologist is to make sure that the cyst is functional. For this, a blood test is taken. When the tumor becomes malignant, the level of tumor markers increases, most often CA-125.
Additionally, a gynecological examination and histological examination are performed.
Ultrasound (with Doppler, 3-dimensional image) and sonoelastography are used to identify cysts. With their help, the good quality of education is assessed.
But it is reliable to indicate that a cyst of a functional type is possible only over time, when its size decreases or in the case of complete disappearance of the formation.
Ovarian cyst and pregnancy
The presence of the disease, as a rule, does not affect the course of pregnancy. If a cyst up to 8 centimeters is detected, even in the early stages, they try to avoid both conservative and surgical therapy in order to avoid miscarriage. At the same time, regular monitoring of the disease is important in order to take the necessary medical measures in time. If there is a pathology of large diameter, then a cesarean section is recommended to avoid cyst breakthrough or internal bleeding during the delivery of the child.
Due to hormonal changes in the body during pregnancy, a luteal cyst often goes away on its own at the end of the first or beginning of the second trimester.
Reasons for cyst formation
Despite the fact that the disease is described in detail in the medical literature and effective treatment methods have been developed, to date the exact causes that trigger the development of the tumor have not been identified. There is an opinion that the main provoking factor is a dysfunction of the endocrine glands of the female reproductive system, in particular, hyperestrogenism of the peripheral uterine tissues, which leads to a lack of ovulation during the menstrual cycle. In addition, ovarian dysfunction can also lead to the formation of a cyst, due to the following reasons:
- Miscarriage or artificial termination of pregnancy;
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- Sexual abstinence for a long period;
- Disorders of the pituitary gland, which regulates the functioning of the ovaries;
- Regular stress and emotional distress;
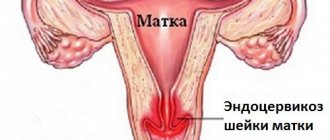
- Diseases of the reproductive system, especially endometriosis;
- Taking hormonal medications, including means of emergency abortion;
- Infections of the reproductive system;
- Inflammatory diseases of the reproductive organs;
- Hereditary predisposition.
In some situations, a cystic formation may appear in infancy or puberty; this occurs due to hormonal disorders during endocrine changes in the body. According to statistics, a functional cyst of the left ovary is much more common, and its course is less acute than a tumor on the right side.
Features of the pathology
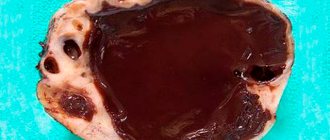
What a functional ovarian cyst is is a single-chamber benign neoplasm, usually round in shape, which can be single or paired. The tumor cavity contains fluid, including particles of an unformed egg, secretions, blood and purulent discharge. The size of the tumor can vary from a few millimeters to tens of centimeters and depends on many factors: hormonal levels, exposure to provoking factors, and the length of time the cyst remains on the ovary.
The pathology is retentional in nature and almost never becomes malignant. In some cases, the cyst can resolve on its own even without medical intervention after 2-3 full menstrual cycles. The disorder is most often diagnosed accidentally during a routine gynecological examination or during a pelvic ultrasound procedure. Ovarian cysts most often form in young women; in rare cases, the neoplasm develops in older adolescence.