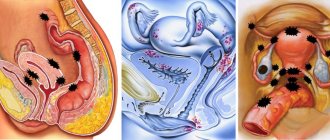
How does a cystic neoplasm occur?
During menstruation, the follicle where the egg develops increases in size and fills with fluid. In the very middle of the cycle, it is overcome by degradation, the egg is released and a yellow body is formed. And when this does not happen, the girl develops formations that resemble bubbles, leading to a cyst.
The development of the whale ovary can occur in both a virgin and a sexually active girl. As for a benign cyst, it can resolve on its own in just two months, without having any effect on the body at all.
https://youtu.be/SAXwaG9HQjU
Types of ovarian cysts
The right ovary is most often affected, but ovarian cysts differ in etiology and symptoms. Gynecologists identify the following types of formations in the body of teenage girls:
- follicular;
- corpus luteum cyst;
- mucinous.
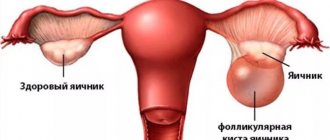
The cause of a follicular cyst is the concentration of fluid in unruptured follicles, while the egg dies, and the duration of menstruation increases, making them painful. This type can reach impressive sizes - up to 10 cm.
https://youtu.be/0fyzTNiSUIc
A corpus luteum cyst is characterized by the appearance of fluid mixed with blood in the so-called corpus luteum; most often this formation is a consequence of hypothermia and excessive physical activity. Less commonly, doctors identify a mucinous cyst, characterized by abundant mucus secretion, as well as polycystic ovaries.
Causes
The main reason for the appearance of this pathology is the puberty period with hormonal changes, which are accompanied by pain. It may also appear due to the following factors:
- individual structural features of organs;
- diseases of the reproductive system;
- hormonal imbalance;
- problems in the functioning of the thyroid gland;
- early onset of menstruation or irregular cycles;
- stressful situations;
- hereditary predisposition;
- excessive loads.
Causes of the disease
Testicles (Latin name "testicles") are the sex glands responsible for the production of sperm and male hormones. Depending on which side the benign formation arose, doctors distinguish:
- right epididymal cyst;
- bilateral cyst (this diagnosis is made if the tumor is present in both the right and left testicle);
- left-sided cyst.
Doctors do not have a consensus on the causes of the cyst. Most likely, an epididymal cyst appears due to the fact that the walls of the epididymis first expand and then narrow, resulting in the formation of a cavity inside.
Testicular cyst
The expansion of the walls can have many causes, from previous viral and bacterial infections to mechanical injuries to the scrotum. The latter especially often occurs in adolescents, as well as those adolescents who engage in strength sports and often receive groin injuries. Among preschoolers and primary schoolchildren up to the age of 10, this thickening often appears as a consequence of past illnesses, especially in children who are often ill.
Symptoms
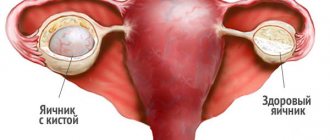
An ovarian cyst is a benign neoplasm consisting of glandular cells and fluid, the appearance of which can occur either outside the ovary itself or inside it. A cyst appears during reproductive age, from the moment a girl has her first menstruation. Since it is at this time that hormonal disruptions may occur in a teenager’s body due to its restructuring, which is the cause of the appearance of a neoplasm.
As a rule, the formation of a cyst on the ovary is not felt in any way by a teenage girl, so the process of identifying it is quite difficult. It is for this reason that doctors recommend checking the pelvic organs with ultrasound scanning from time to time. Such a study will help identify a tumor that has arisen in a teenager.
In more advanced cases, when the size of the tumor has reached a decent size, the following symptoms of an ovarian cyst may appear in a teenage girl:
- aching pain in the lower abdomen, which can occur with blood clots from the vagina outside of menstruation;
- nagging abdominal pain after exercise;
- failure of the menstrual cycle and pain during its passage;
- discomfort during urination;
- increased body temperature;
- the occurrence of frequent fatigue;
- failures in defecation.
In newborns
A cyst in children is formed in utero, and, as a rule, it resolves on its own immediately after birth. This phenomenon does not pose a danger to the baby, but sometimes provokes headaches and vision problems.
The clinical picture of the child is as follows:
- periodic pain in the lower abdomen - the child cries and presses his legs to his stomach,
- presence of a lump in the lower abdomen.
A cyst can be diagnosed during intrauterine development after 24 weeks of pregnancy. The causes of this pathology may be the following:
- heredity,
- severe pregnancy,
- late toxicosis,
- infectious diseases in the mother during pregnancy,
- mother taking hormonal drugs,
- inflammation of the genital organs during pregnancy.
In a newborn, education can be of 3 types:
- unilateral cyst, homogeneous structure, clear contours,
- the formation has several partitions,
- The contents of the cyst are dense, not liquid.
Since cysts in newborns can resolve on their own, doctors choose observational tactics for a period of a year.
If the cyst grows, surgery is prescribed. More often, only the tumor itself is removed, but in some cases doctors have to remove part of the damaged ovary or even the entire organ. However, this does not mean that the baby will be infertile in the future - she will have a chance to get pregnant, since the functionality of the second ovary is preserved.
Diagnostics
The first thing that should alert a girl or her parents is that the teenager has heavy, heavy periods, when they have to change pads approximately every hour or two. Severe painful manifestations are also observed during this period. But this is not a reliable diagnostic method; the reason for this is the girl’s age, because adolescents may not have periods immediately. Therefore, it is not always possible to track what is allocated these days. But if you were able to determine the pathology, then you should immediately contact a pediatric gynecologist for advice.
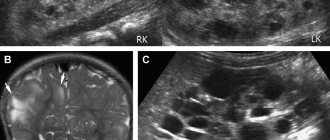
Initially, diagnosis consists of an examination by a gynecologist. The pelvic organs will be palpated to check for any lumps. If painful sensations appear during the examination, this indicates that the cyst is large. One of the most common diagnostic methods is a painless ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs in a teenager. The patient needs to attend an ultrasound procedure, and with its help it will be easy to identify a tumor. An ultrasound will also show what shape, nature and dimensions the seal is, which is very important.
Ultrasound examinations in teenage girls who are not sexually active are performed only abdominally (superficially through the abdominal wall), and only as a last resort, when viewing is difficult, the abdomen can be viewed transrectally (through the rectum). As soon as the cyst is identified, observation and treatment will be prescribed, and there are two types. Everything will depend on the severity of the disease. Treatment can be either medication or surgery. With such a phenomenon, it cannot be ignored.
Diagnosis of the disease in adolescence
In most cases, an ovarian cyst in a teenage girl is detected accidentally during an ultrasound scan of the pelvic organs. Menstruation in girls at this age may be irregular, so at the initial stage the disease goes unnoticed by parents.
Painful menstruation and heavy discharge are symptoms indicating problems. If these signs appear, you should contact a pediatric gynecologist or a specialist who provides care to women.
The most informative, accessible and safe method is ultrasound diagnostics, which allows you to determine the location of the tumor, its size and shape. When examining girls who are not sexually active, an ultrasound is performed through the abdominal wall.
Ultrasound examinations at the Yusupov Hospital are carried out in a modern diagnostic center. Patients of the Yusupov Hospital have the opportunity to undergo examination at a convenient time, without queues, by making an appointment in advance for a certain time.
Types of cysts
For teenage girls at such a young age, only the formation of cysts of a follicular and hemorrhagic nature can be characteristic.
- Follicular ovarian cyst in a 14-year-old teenage girl. With this type of cyst, menstruation is always very painful, prolonged, often irregular and heavy. Also, 20% of adolescents with such a cyst experience juvenile uterine bleeding.
- Hemorrhagic cysts. Characterized by frequent aching pain in the lower abdomen at the end of the menstrual cycle and general malaise.
The following types of ovarian cysts in a teenage girl aged 16 are also distinguished:
- Corpus luteum cyst. The appearance of water with bloody impurities in the yellow body, which is lined with luteal cells. The onset of the disease can be caused by hypothermia, the use of aspirin-containing medications and excessive physiological activity.
- Mucinous. Similar to follicular. There is a strong secretion of mucus.
- Double sided. Two ovaries are damaged, which leads to polycystic disease.
Reasons for the development of a cyst in a girl
In medicine, there are cases where an ovarian cyst was found in newborn girls, but these cases are extremely rare. An ovarian cyst in a teenage girl can be congenital or acquired. Experts believe that one of the reasons for the pathological process is hormonal changes during puberty and the onset of the first menstruation.
When consulting adult patients with this disease, specialists from the Oncology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital explain not only the principles of treatment, but also the reasons for the disorder in order to exclude them. An ovarian cyst in adolescence in girls can form as a result of various factors:
- decreased immunity;
- sudden weight loss or excess weight;
- endocrine disorders;
- abdominal injuries;
- regular stress;
- hypothermia of the reproductive system as a result of incorrect choice of clothing;
- infectious processes in the reproductive system;
- hereditary predisposition;
- bad habits;
- concomitant liver and kidney diseases.
The combination of these factors causes disruption of the ovaries, blocks the possibility of the egg leaving the follicle and promotes the accumulation of fluid. For girls whose mothers have suffered from this disease, the likelihood of developing an ovarian cyst is high, so specialists at the Oncology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital recommend that women be attentive to the reproductive health of their children and, if predisposed, undergo routine examinations.
Treatment
Often, doctors prescribe treatment only when active growth of the tumor has been detected. For example, a follicular ovarian cyst in a teenage girl can resolve on its own after several menstrual cycles. When drug treatment is still necessary, the specialist will select a medication, taking into account age, whether there are chronic diseases and other personal characteristics of the teenager’s body.
The goal of treating an ovarian cyst in a teenage girl is not only to completely get rid of the formation, but also to preserve reproductive functions and improve the functioning of the ovaries. Doctors often use hormonal treatments, but sometimes use birth control to slow the growth of the cyst. Treatment time for adolescents takes about three months. Treatment of the ovary should be strictly under the supervision of a specialist. The patient must also adhere to bed rest, take anti-inflammatory drugs and vitamins.
How to treat ovarian cysts in teenagers
Often benign formations of the follicle and corpus luteum go away on their own. Treatment of ovarian cysts in adolescents that are asymptomatic and small in size (up to 4 cm) is based on observation for 3 months.
Drug treatment
In the absence of complications, but existing menstrual cycle disorders and the size of the formation is more than 4 cm, combined oral contraceptives or gestagens are prescribed (contraindicated in the inflammatory process). Treatment with hormonal drugs is also carried out for 3 months under the supervision of a doctor (gynecologist or endocrinologist).
In complicated cases, treatment is aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process and pain. In the acute period, the following is prescribed:
- bed rest;
- ice on the ovarian area;
- anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs: aceclofenac, ibuprofen, meloxicam and others);
- intravenous injections of sodium chloride or glucose;
- biogenic stimulants (vitamins, aloe extract, intramuscular).
- It is possible to prescribe antibacterial drugs.
Surgical treatment
In the following cases, surgical treatment is performed:
- When blood accumulates in the abdominal cavity due to a cyst rupture;
- When the cyst is torsion;
- If there is no reduction or growth of the cyst after three months of drug therapy.
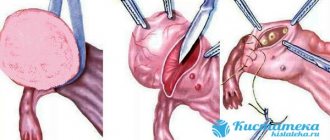
Surgery is performed by laparoscopy or laparotomy. In the first option, the operation is performed through punctures in the abdominal wall, in the second, by cutting the abdominal wall for direct access to the organ.
In cases of rupture, ovarian resection is often performed.
(removing part of it). In severe cases (with torsion with necrosis or malignant course), the ovary is removed completely (oophorectomy).
How is laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst performed?
Cyst surgery
Surgery to remove the cyst should be performed using laparoscopy and laparotomy. If the disease has complications, then the following may be prescribed:
- cystectomy (a tumor near the ovary is removed to preserve healthy tissue);
- oophorectomy (the cyst is removed together with the ovary);
- adnexectomy (appendages are completely removed; such removal is prescribed only in exceptional situations).
Surgical removal is not so common, but laparoscopy is often used, and it allows you to preserve reproductive function.
Possible complications
If this phenomenon is not treated, then it is fraught with a number of pathologies, and they can lead to death. That is why this phenomenon simply needs to be treated. You must visit a gynecologist at least twice a year. There are also such complications:
- The cyst suppurates. As a result, the structure changes and the volume of accumulated liquid increases.
- Malignancy, as a result of which the neoplasm increases in size, and this provokes pressure on nearby organs.
- The appearance of adhesions, which can lead to infertility in the future.
- Torsion of the neoplasm's legs. All this occurs together with symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and pain in the lower abdomen, which do not go away even after taking medications with an analgesic effect.
- Cyst rupture. If the accumulated fluid in the cyst is released, peritonitis may occur.
The symptoms are pronounced: sharp pain around the ovaries, elevated body temperature, profuse vomiting, fainting.
Prevention
There are no preventive measures to prevent this disease. To prevent a girl from developing an ovarian cyst, her parents simply must monitor the menstrual cycle, the girl should not be stressed, her condition should be calm, and there should also not be much physical activity. You must visit a gynecologist twice a year, no less. The mother should have conversations with the girl about sex life; the girl should know that if she experiences pain symptoms during intercourse, this is not at all good. You also need to limit the girl from solariums or bad habits. If you follow all of the above, the likelihood that a girl will develop an ovarian cyst will noticeably decrease. That is why parents should be very careful and monitor the health of their child.
Drug treatment
For ovarian cysts, gynecologists prescribe:
- Oral contraceptives (Rigevidon, Jess, Diane-35, Marvelon). This treatment is prescribed only for small tumors. Oral contraceptives reduce the size of tumors and prevent the appearance of new ones. The therapeutic effect is achieved after several menstrual cycles.
- Gestagens (steroid hormones). These include: Norkalut, Danol, Danazol, Decapeptyl, Utrozhestan, Visanne, Duphaston. These drugs block the production of hormones by the pituitary gland. The gynecologist individually prescribes the dosage and duration of taking these medications. But even after the condition improves, treatment with gestagens cannot be interrupted, but the therapeutic course should be completed.
- Antibiotics. If the cause of an ovarian cyst is a pathogenic microflora, then experts prescribe antibacterial agents - Lincomycin, Fluoroquinolone, Vancomycin.
- Local preparations (Longidaza suppositories, indomethacin and ichthyol suppositories). These can be vaginal or rectal suppositories. The course of treatment should be no more than 3 months. Local medications reduce pain, stabilize the menstrual cycle, improve hormonal levels, relieve inflammation, accelerate regeneration processes, and strengthen the immune system. It is recommended to combine local and systemic treatment, as well as undergo physiotherapy sessions.
- Vitamins. Strengthening the immune system helps launch a defense mechanism that will be aimed at fighting the tumor. For ovarian cysts, doctors often prescribe folic and ascorbic acid, vitamin E.
- Painkillers. For pain, patients are prescribed No-shpu, Indomethacin, Nurofen, Nimegesic.
Treatment of ovarian cysts without surgery is discussed in detail in our separate work.
Consequences of the cyst
In teenage girls, ovarian cysts occur as often as in women, and doctors say that this pathology does not select victims based on age. Most often, patients aged 12 to 15 years come to the gynecologist with this problem, and the cyst was localized in such patients in the right ovary.
What consequences can the appearance of an ovarian cyst in a girl in adolescence lead to?
In the absence of proper treatment, this pathology can lead to various complications, primarily to serious disruptions in the functioning of the ovaries. You should not hope that a cyst that appears in one of the ovaries will go away on its own; you need to consult a doctor in a timely manner, otherwise the tumor will gradually grow and put pressure on those internal organs that are nearby. So, as the cyst grows, it will put strong pressure on the intestines, ureters, and also on the bladder. In addition, adhesions will appear in the abdominal cavity, which will ultimately lead to infertility, but that’s not all, as pus may form inside the hand. This will lead to secondary infection and the formation of tumor necrosis.
Treatment of pathology in adolescents
Mothers are very worried if a girl is diagnosed with such an unpleasant pathology. They are often interested in the question of whether such a disease needs to be treated. In fact, doctors prescribe drug therapy or surgery only in cases of complicated disease. As a rule, follicular cysts and other functional neoplasms go away on their own after several cycles. Treatment may be required if they begin to grow or remain unchanged for more than three months. To prevent a complex course of the disease, it is recommended to regularly visit a gynecologist who will monitor the condition of the tumor.
Even if there are no complications, but there are disruptions in the cycles, a combined drug therapy regimen is prescribed. Most often it consists of contraceptive drugs and gestagens. For most patients, three months of treatment is enough to restore the cycle and eliminate cystic tumors.
Important! During the treatment period you need to be under the supervision of your doctor. This will allow us to determine how the girl’s body reacts to the drugs used.
Surgical treatment is rarely required for this pathology. It is prescribed for torsion of the cystic pedicle, tumor rupture, or ineffectiveness of drug therapy. Most often, the removal of the tumor is carried out without the need to remove the ovary. If the disease worsens, you may need to take anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs.
Please note: Ignoring the disease may lead to the need for surgical removal of the affected ovary.
In the absence of timely treatment, the likelihood of such complications increases:
- tumor growth and pressure on nearby internal organs;
- development of adhesive processes in the abdominal cavity, which may become a cause of infertility in the future;
- implantation of a cystic body into the abdominal cavity;
- suppuration of fluid inside the tumor or its walls due to the formation of a secondary infection;
- development of neoplasm necrosis;
- formation of a malignant tumor.