How to understand that an ovarian cyst has burst
Symptoms that an ovarian cyst has burst appear instantly. The intensity of the sensation depends on the type of rupture, the amount of hemorrhage and related factors. In some cases, there is no bleeding, but the contents of the burst sac, entering the abdominal area, can provoke many complications.
Painful sensations
The pain manifests itself acutely, on the left or right side of the lower abdomen, in the first seconds after apoplexy of the cyst. This often forces a woman to take a bent position, instinctively trying to reduce discomfort. Acute pain is short-lived - after a few minutes it becomes less intense, but loses its clear localization.
The rupture of the formation provokes the penetration of its contents into the abdominal cavity, which subsequently leads to pain throughout the abdomen. The patient is not able to clearly indicate the source of pain. Subsequently, it can spread to the buttocks, lower abdomen, and sides of the torso.
Sometimes pain appears a day or several hours before the onset of pathology. In this case, they are aching, pulling in nature, their intensity can increase over time. This is explained by the progressive thinning of the walls of the formation.
If you detect aching pain on the right or left side of the lower abdomen, you should immediately consult a doctor - if you follow his recommendations and timely medical intervention, cyst rupture can be avoided.
Changing the nature of discharge
With apoplexy, the amount of vaginal discharge increases.
However, they do not cause any discomfort; normally there should be no odor. They often contain streaks of blood, and the discharge itself can turn brownish or reddish. This indicates a violation of the integrity of the cyst tissue or possible bleeding.
The discharge contains the contents of the burst formation, so its consistency may be heterogeneous and contain foreign impurities. When a corpus luteum cyst or follicular ovarian cyst ruptures, there are no symptoms of this kind.
Intoxication of the body
This condition is caused by the contents of the formation and blood entering the peritoneum. In severe cases of intoxication, body temperature rises to 40 degrees, fever and chills are present. Most often, the signs of a ruptured ovarian cyst are less obvious - the patient feels weakness, general unsatisfactory condition, nausea, and vomiting. The mucous membranes of the mouth dry out, which causes constant thirst. The body temperature reaches 37-38 degrees.
Change in blood pressure
With apoplexy of a cyst of the right or left ovary with hemorrhage, blood pressure decreases and the pulse quickens. The skin becomes pale, rarely bluish. This is caused by a sharp drop in hemoglobin and severe pain in the affected area. With a significant drop in pressure, there is a risk of the woman losing consciousness and hallucinations.
Digestive disorders
Disruption of the digestive organs occurs due to bloating, which, in the absence of excess weight, is noticeable upon visual examination. Upon palpation, the doctor notes tension in the peritoneum. Due to excessive bloating, patients sometimes suffer from diarrhea and gas formation in the intestines.
A significant deterioration in the woman’s condition in the form of loss of consciousness, high body temperature, excessively low blood pressure and other similar symptoms requires immediate hospitalization.
What does a cyst look like on ultrasound?
During the examination, the doctor can see cystic neoplasms of different etiologies, which are divided into two types:
- functional;
- pathological
Functional education
| Follicular cyst | One of the most common pathologies. During ovulation, the follicle releases a mature egg containing fluid, resulting in the formation of a tumor. It is distinguished by an oval or round shape, has an expressive contour and thin walls. Grows no more than 10 cm - requires urgent medical intervention. For small sizes (no more than 3 cm), only observation of the neoplasm is necessary. |
| Corpus luteum cyst | If the corpus luteum remains in the ovarian tissues after menstruation, a tumor forms in it. This tumor tends to resolve on its own, sometimes requiring surgical intervention. Quite often it is mistaken for an ectopic pregnancy. It grows up to 5 cm and has thick walls. |
| Hemorrhagic cyst | It is a complicated functional neoplasm. The inside is filled with blood. As the blood vessels grow, they stretch and burst. A common pathology among women after 35 years. |
Non-functional
| Endometrioid cyst | It is a striped neoplasm on the ovary, contains inside the blood that was not released during menstruation, the membrane consists of endometrial tissue. For therapy, they resort exclusively to surgical methods, after which the woman needs to undergo a long course of hormonal treatment. The neoplasm is distinguished by dense walls of 2-8 mm, which may contain small round cavities. |
| Dermoid cyst | It is an oval formation formed from embryonic cells. To avoid malignancy into a malignant tumor, surgical therapy is resorted to. Can grow up to 20 cm. |
| Ovarian cystadenoma | It is divided into 2 types - papillary and simple serous cystadenoma. In the first case, there are small bulges on the walls on the inside. This is their only difference. Single-chamber neoplasm requires surgical treatment. |
Risk group
The risk group includes women who have health problems or other factors that contribute to dysfunction of the genital organs:
- hormonal imbalance;
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- diseases of the pelvic organs;
- abortion and other similar gynecological manipulations.
In these cases, there is a high risk of formations on the ovaries. Typically, functional cysts are found that develop against the background of changes in hormone levels.
Ovarian cyst and pregnancy
It is not uncommon for a woman to be diagnosed with an ovarian cyst on an ultrasound scan during pregnancy. For many expectant mothers, such a situation in the first trimester becomes a reason for panic. However, in fact, a corpus luteum cyst in the early stages is not a dangerous pathology. Towards the end of the 12-13th week, when the placenta is actively involved in its work and takes over the functions of synthesizing progesterone, the cyst regresses on its own.
Is it possible to get pregnant with an ovarian cyst?
Changes in ovarian tissue that occur against the background of cystic transformations can cause problems with conception. Immediately after an ovarian cyst is detected on an ultrasound, many people wonder what to do in this case and how to become a mother. Thus, an ovarian cyst that has been present for a long time, which is difficult to treat, provokes the development of secondary infertility. However, in most cases, a follicular ovarian cyst does not cause such situations. Pregnancy does not occur as a result of developing hormonal imbalances that provoke cysts.
How to get pregnant with an ovarian cyst?
Women who have problems conceiving try to independently find the answer to the question of how to get pregnant with an ovarian cyst. However, in practice, the correction methods they use are not always able to lead to the expected effect. In order not to harm your health, you must strictly follow your doctor's recommendations. Among the main areas of therapy:
- correction of hormonal levels;
- normalization of body weight;
- increasing immunity;
- normalization of nutrition and proper diet.
Causes of pathology
Apoplexy can occur in the presence of any type of cyst on the ovary.
Most often, rupture occurs in the second phase of the cycle - it is caused by a disruption in the course of ovulation. The growth of the dominant follicle containing the egg can put pressure on the existing formation. This is also likely when the corpus luteum appears, which is necessary for the production of the hormone progesterone, which promotes the movement of the egg through the fallopian tube.
High predisposition to the appearance of apoplexy in the second half of the menstrual cycle
explained by the peculiarity of blood supply to organs. During this period, local blood supply increases, causing excessive vascular congestion. As a result, the permeability of the walls of the latter increases, which can contribute to apoplexy.
Internal reasons contributing to the rupture of an ovarian cyst:
- hormonal imbalances;
- frequent stress, increased anxiety, mental illness;
- inflammation of the genitals and adjacent organs;
- irregular menstruation;
- twisting of the cyst stalk;
- abortions;
- taking oral contraceptives;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- drug stimulation of ovulation;
- vascular diseases;
- stagnant processes in the pelvis;
- adhesions in the genitals.
The most commonly diagnosed cyst rupture is on the right ovary - this occurs due to more intense local blood circulation and high activity of this organ.
External factors:
- high intra-abdominal pressure – is a consequence of active sports, weight lifting, constipation and diarrhea;
- local circulatory disorders after injuries to the peritoneum and pelvis;
- active sexual intercourse;
- inaccurate performance of gynecological procedures.
Overexertion is especially dangerous on the days of ovulation - at this time, due to increased local blood supply, rupture of not only the formation, but also the ovary itself is possible.
Rupture of ovarian cyst symptoms
Cyst rupture is usually accompanied by a clinical picture of the so-called “acute abdomen.”
Before the onset of the main symptoms of ovarian cyst rupture, nagging pain in the lower back, a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen, and discomfort in the pelvic organs are possible.
Symptoms:
- Increased body temperature (from 38 degrees and above), which antipyretic medications cannot cope with
- Sharp pain in the lower abdomen that increases (doctors compare it to a dagger strike). The pain may radiate to other parts of the abdomen - the upper region, for example
- General weakness, semi-fainting (fainting is also possible)
- Bleeding from the uterus
- Unusual vaginal discharge (especially bloody)
- Nausea, vomiting
- Intestinal disorders
- Blue or pale skin
- Low blood pressure, blood pressure surges
- Rapid heartbeat that increases in intensity
The last two symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst are considered especially alarming, as they may indicate internal bleeding, which is life-threatening.
However, this does not mean that you can give up on the other symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst listed in the list. All of them should be a reason for immediate hospitalization of the patient and urgent surgery.
You should be aware that symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst may differ in nature and intensity, depending on the type of cyst, the general health of the woman and the day of the menstrual cycle when the rupture occurred.
Symptoms of a ruptured corpus luteum ovarian cyst:
- Sharp, piercing pain in the lower abdomen, from which the patient literally folds in half
- Weakness
- Cold sweat
- Signs of intoxication
- Body temperature may remain normal
Symptoms of ruptured follicular (functional) ovarian cyst:
- Dagger pain syndrome in the lower abdomen
- Signs of intoxication
- Body temperature may not rise
- Weakness, dizziness, pale skin, rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure (with hemorrhage in the peritoneum)
- Bloody vaginal discharge
Symptoms of a ruptured endometrioid ovarian cyst:
- Pain in the lower abdomen comes in attacks
- Nausea, vomiting
- Loss of consciousness
- Bloating
- Constipation
- Body temperature may remain normal
Severity of pathology
There are three degrees of severity of cyst rupture:
- Easy. The volume of blood loss is less than 150 ml.
- Average. Up to half a liter of lost blood.
- Heavy. Large blood losses - over 500 ml.
Types of disease according to symptoms:
- Painful apoplexy. Severe pain in the damaged area in the absence of blood loss.
- Anemic (hemorrhagic). Profuse hemorrhage with mild pain.
- Mixed. A combination of the two previous types.
For painful forms of the pathology, conservative treatment is usually sufficient. To prevent negative consequences from apoplexy of a mixed or hemorrhagic form of a cyst of the left or right ovary, it is necessary to perform a surgical operation, the method of which depends on the abundance of hemorrhage.
Why does an ovarian cyst burst?
Rupture of an ovarian cyst occurs when its walls burst. Each patient should look within herself for the reasons for the rupture of an ovarian cyst. This unpleasant occurrence occurs when you overexert yourself during exercise. You can look for the prerequisites in too violent an intimate act or in the presence of injuries to the genital organs.
Education does not burst prematurely. To do this, he needs to mature sufficiently. During this time, the tumor will increase in size. Therefore, many women do not suspect that they already have a cyst until it bursts.
Symptoms of ovarian cystoma rupture appear quite clearly. When the walls of the formation burst, the patient feels a sharp pain, which gradually intensifies.
Please note: Symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst manifest differently in each patient. If these are painful sensations, then they arise in the internal organs. The most common phenomenon is discomfort in the lower abdomen or lumbar region.
Many people complain of headaches and fever. The main mistake of such patients is that they attribute these alarming signals to a common cold or migraine.
Look for signs of a ruptured ovarian cyst, which are usually very clear. As soon as the formation bursts, nagging pain begins in the lower abdomen, which gradually develops into sharp pain. At the same time, you may begin to feel sick, but vomiting will not ease the unpleasant symptoms. Painful sensations are especially acute during intimacy.
Ovarian cysts in women cause pain when their internal contents enter the peritoneal area. In addition to the fact that this process causes pain, it also provokes the occurrence of peritonitis. Body temperature rises to thirty-nine degrees. The patient may lose orientation in space, suffer from dizziness and often lose consciousness. If the internal hemorrhage is very severe, blood pressure drops rapidly. This appears as a blue tint on the skin in the area of the abdomen and navel. The skin acquires this color because blood accumulates under it in the form of a hematoma. We recommend you learn: About ovarian rupture and Complications after abdominal surgery for ovarian cysts
Can a woman's ovarian cyst burst?
An ovarian cyst can rupture at any time. The likelihood of pathology in certain conditions:
- pregnancy – the risk of apoplexy remains, it can occur when there is excessive pressure from the growing fetus on the uterus or due to disrupted hormone levels, therefore, if the size of the formation is more than 8 cm, surgery is required;
- period of menstruation - at this time the cyst tends to decrease or completely disappear, so the likelihood of its rupture is minimal in the absence of physical activity and sexual intercourse;
- sexual contact - with intimate intimacy, the risk of apoplexy increases significantly due to intense mechanical stress and a rush of blood to the genitals;
- trauma to the abdomen and pelvis – when the ovary and nearby organs are injured, the likelihood of pathology occurring is high, especially if the formation is large;
- lifting weights and excessive sports activities - contribute to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, which, if this condition persists for a long time, leads to the cyst bursting;
- hormonal imbalance – provokes disruption of the menstrual cycle and lack of ovulation, which is fraught with the rapid growth of a large number of formations that can burst under external influences;
- bleeding disorder - this pathology poses a danger if it ruptures in the form of heavy blood loss.
Most often, several factors simultaneously lead to apoplexy of an ovarian cyst, so if one of them is present, you should be careful during physical activity and regularly visit a gynecologist to monitor your health.
What are the symptoms of an ovarian cyst in women when it ruptures?
Signs of an ovarian cyst during rupture are characterized by intense pain that blocks the woman’s independent movement. Calling an ambulance is necessary if a woman has the following symptoms:
- sharp, paralyzing pain in the lower abdomen;
- nausea, vomiting;
- bleeding, both internal with swelling of the abdomen, and external;
- a sharp decrease in pressure;
- dizziness, in some cases loss of consciousness;
- increase in body temperature, which is not affected by antipyretic medications;
- blue lips, pale skin.
Types of ovarian cysts prone to rupture
Functional types of cysts:
- Follicular. Goes away on its own within 2-3 months and is asymptomatic. Occurs due to menstrual irregularities. Rupture of an ovarian follicular cyst is accompanied by symptoms such as vomiting and sharp pain in the lower abdomen.
- Yellow body. It resolves on its own and develops in the absence of regression of the corpus luteum itself. With her apoplexy, the patient's blood pressure sharply decreases, and the skin becomes pale.
Nonfunctional formations are the most dangerous; their rupture is accompanied by a clear manifestation of symptoms. As a result, many negative consequences are possible. Their main types:
- Endometriotic. Formed during the course of endometriosis, it consists of a brown liquid that includes blood impurities.
- Mucinous. It is highly likely to develop into cancer. Consists of many compartments filled with mucus. Elastic, capable of reaching large sizes.
- Dermoid. Formed even before birth, it is a consequence of developmental disorders of the fetus in the womb. Consists of fat, body tissue, hair, nails.
- Carcinoma. Malignant formation is considered the most dangerous type.
Against the background of a long course of endometriosis, an endometriotic ovarian cyst can spontaneously rupture, which is accompanied by severe pain symptoms and a sharp deterioration of the condition.
Surgery is required to treat nonfunctional cysts.
Types of ovarian cysts and their characteristic features
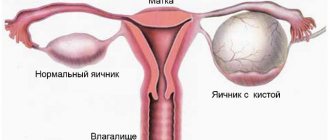
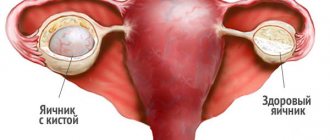
Why does inflammation of an ovarian cyst occur, how does it appear and how do the types differ? First you need to understand what a neoplasm is, which often appears in women of childbearing age. A cyst is a cavity shaped like a sac filled with fluid that appears on the surface or inside the ovary. The dimensions, structure, reasons for which it appeared, and detection method may be different.
Functional
The most common type is functional, and can appear on both the left and right ovary. It is formed due to a hormonal disorder, if the overripe follicle could not rupture in time before the onset of the next menstruation. The main signs of a functional ovarian cyst are that it disappears on its own in one or more menstrual cycles and does not require surgical intervention, although the size sometimes reaches several centimeters in diameter.
Follicular
A woman's egg matures in a small sac attached to the wall of the ovary called a follicle. If there is a hormonal imbalance in the body or in the presence of inflammatory processes in the pelvis, ovulation may not occur. In this case, the follicle does not burst, but becomes increasingly filled with liquid, forming a voluminous capsule. Over a period of time, the reverse process occurs, the cavity with fluid decreases in size, and signs of cystosis are not visible.
Corpus luteum cyst
A similar process can occur in the corpus luteum, which is formed on the basis of a ruptured follicle. The expansion of the walls of the cavity where the egg has matured is provoked by the presence of endocrine diseases and the malfunction of the ovaries during inflammation. With insufficient production of the necessary hormone progesterone, a compaction appears with liquid contents inside. Discomfort will be felt when the formation grows to a large size (8-10 cm in diameter). The corpus luteum cyst resolves on its own.
Mucinous
A very dangerous form is mucinous. The structure has a multi-chambered tuberous surface. According to the characteristics of an ovarian cyst, it is distinguished by the presence of internal partitions; the chambers are filled with mucous secretion. Very often, the mucinous type is diagnosed in women before menopause. Severe nagging pain appears, the cystic formation quickly reaches enormous sizes, sometimes the diameter reaches 30-35 cm. Urgent surgical care is able to stop the process, which can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Dermoid
The reasons why the dermoid appearance occurs are not fully understood. This often happens in the presence of abdominal injuries. Due to the large accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, the capsule reaches a size of about 12-18 cm in diameter. Often, during ultrasound diagnostics, torsion of the pedicle of the dermoid cyst, which contains nerves and blood vessels, is detected. This causes sudden sharp pain. It is possible to get rid of the tumor only by performing surgery, with further rehabilitation treatment.
Endometrioid
The endometrioid ovarian cyst received its name for the similarity in its tissue composition with the mucous membrane inside the uterus. Small dense capsules that appear on the surface of the ovary are filled with a dark, thick liquid consisting of the remains of blood released during menstruation and lymph. Depending on the stage of development of the formation, treatment is surgical or hormonal therapy is prescribed.
Articles on the topic
- Pain due to ovarian cysts in women: what to do
- Ovarian apoplexy - causes, diagnosis, forms and clinical recommendations
- Causes, signs and how to treat endometrioid ovarian cyst
Hemorrhagic
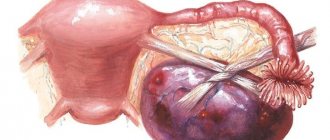
Gynecologists classify the hemorrhagic type as functional. It differs from others in that blood vessels rupture inside the corpus luteum or follicle. Signs of a hemorrhagic cyst are hemorrhage with severe pain in the lower abdomen. It is impossible to do without surgical intervention. The removed ovary or part of it, together with the unwanted formation, undergoes histological examination to exclude the diagnosis of a cancerous tumor.
Possible complications and consequences of pathology
The occurrence of consequences if the ovarian cyst bursts is not necessary. With timely medical intervention, the following conditions can be avoided:
- severe pain shock;
- severe anemia;
- oophorectomy;
- infertility;
- development of oncological processes;
- adhesions in the pelvis;
- purulent peritonitis - extensive inflammation in the abdominal area.
In the most severe cases, death is possible.
Differential diagnosis of ovarian cyst
The clinical picture of cystic formations has identical symptoms, so ultrasound plays a leading role in differential diagnosis. By detecting a fluid formation in the ovary, one can already suspect the presence of a cyst. However, to determine the type of formation, an appropriate diagnosis of an ovarian cyst is carried out. In this case, pay attention to the following parameters:
- Follicular cyst
- formed from mature follicles, combined with a pathology such as uterine fibroids. It has one chamber, inside of which the light contents can be traced. Visualized as an echogenic structure. - Corpus luteum cyst
is similar in structure to the corpus luteum, but is larger in size. It has a folded inner surface and a clear liquid inside. In most cases, it undergoes reverse development. - Endometriotic
- often bilateral formation, the internal contents are dark in color. On ultrasound, the cyst is not clearly visible. - Parovarian cyst
- small in size, ovoid in shape, smooth surface.
Diagnostic measures
If a pathology is suspected, the patient should undergo several types of examinations:
- medical examination - examination of the condition of the genital organs and the nature of vaginal discharge, palpation of the abdominal cavity;
- Ultrasound – examination of the pelvic organs, identifying the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- puncture of the peritoneum through the vagina - determining the nature of the secreted fluid;
- diagnostic laparoscopy - examination of organs during non-cavitary surgical intervention, if necessary, leading to treatment;
- urine and blood tests - examination of the general condition of the body;
- determination of hormonal levels.
Symptoms - in detail
When the cyst bursts, the sensations and first signs will depend on several factors:
- the size of the cyst, that is, how much fluid immediately came out into the abdominal cavity;
- which vessels are damaged by rupture; if they are large enough, then signs of internal bleeding will increase rapidly;
- what nerves are affected by the rupture? If a large nerve is damaged, then there can be very severe pain.
When a small cyst ruptures, the sensations may be quite weak:
- pain and tingling in the lower abdomen, as during menstruation;
- mild nausea and weakness;
- pale skin;
- dizziness.
A slight bleeding opens into the abdominal cavity from a burst ovarian cyst, and gradually the abdomen fills with blood, some of which may leak out if you do not pay attention to your condition in time. Gradually, the gushing blood begins to put pressure on the organs, the pain intensifies, the woman gives up everything and... It’s good if she calls an ambulance.
But our seasoned representatives of the fairer sex can simply go to an appointment with a gynecologist and wait in line. And only then go to the intensive care unit for urgent surgery for life-saving reasons straight from the antenatal clinic. This is not the worst case scenario.
Signs of a cyst rupture may also depend on its type.
Symptoms of different types of ovarian cyst rupture
| Ovarian cyst shape | Symptoms |
| Follicular | Aching pain on one side radiates to the rectum, a headache may appear, and the temperature may rise slightly. |
| Corpus luteum | Increasing pain in the lower abdomen, decreases with rest, very strong during sexual intercourse, nausea, vomiting without relief. |
| Endometrioid | Unbearable pain, dizziness to the point of fainting, temperature up to 38 and above, severe decrease in blood pressure, bluish lines on the abdomen in the lower half and around the navel |
Signs of a ruptured ovarian cyst can be either very strong or mild, similar to appendicitis, intestinal colic, or an attack of acute cystitis; only a gynecologist or a hospital emergency department doctor can accurately determine.
If there are no clear indications for urgent abdominal surgery, then an ultrasound scan is performed with a vaginal probe; to clarify the diagnosis, they can puncture the abdominal fluid with a very thin needle through the vagina and its posterior wall. If a ruptured ovarian cyst is confirmed, surgery is performed to stop the bleeding and remove the blood that has spilled into the abdominal cavity.
Treatment
When functional cysts rupture, treatment without surgery is used - conservative therapy. In this case, the patient is prescribed bed rest, during which time she should abstain from sexual intercourse. In parallel, it is necessary to take medications:
- antispasmodics – relieve pain;
- hemostatic drugs;
- vitamin complexes - normalize hemoglobin levels and the general condition of the woman.
If there is bleeding from a ruptured functional type ovarian cyst, surgical intervention is required.
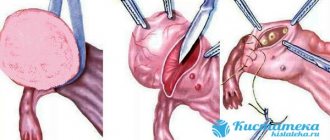
Surgery is necessary for apoplexy of any type of non-functional ovarian formation. Two main types of intervention:
- Laparoscopy. It is performed under general anesthesia by inserting a laparoscope through small incisions. The image of the organs is displayed on the screen from a special camera; all manipulations are carried out in 30-40 minutes. During this time, the remnants of the cyst and blood are removed, damaged vessels are sutured, and bleeding stops. A week after the intervention, the patient is discharged from the hospital.
- Laparotomy. Abdominal surgery is performed when laparoscopy is insufficiently effective. It is distinguished by the possibility of a complete overview of organs. The duration of rehabilitation is up to two weeks.
In most cases, when this pathology occurs, the laparoscopy method is used. The second type of operation is performed in the most severe conditions of the patient or in case of emergency - this is a measure to prevent hemorrhagic shock, acute peritonitis and other consequences.
Treatment of ruptured ovarian cyst
To prescribe therapy, it is necessary to establish the presence of a rupture, determine the predominant symptom, and the severity of hemodynamic disturbances. The main criterion that determines the patient’s management tactics is the amount of blood loss. The more massive the bleeding a woman has, the more pronounced the symptoms of the disease. To confirm the severity of the condition, special studies are carried out.
Conservative methods
If an ovarian cyst ruptures, treatment without surgery is carried out exclusively with a confirmed painful form of apoplexy. In most cases, the main symptom of the disorder is pain; bleeding in this case is minor. The wound is small and quickly closes with a blood clot.
Conservative therapy is reduced to taking antispasmodics, painkillers and hemostatic agents. During the treatment period, the patient adheres to strict bed rest. If there are positive dynamics, treatment is continued until the symptoms disappear. If signs of deterioration appear, the patient is prepared for surgery.
Surgical methods
In most cases, if there is a rupture of the ovarian tissue tumor, surgery is performed. The scope of surgical care is mainly determined immediately at the time of the procedure. If the damage is minor, tissue can be sutured and the tumor capsule can be peeled off. If it is not possible to stop the bleeding and the organ becomes saturated with blood, it is necessary to remove the affected ovary. A ruptured right ovarian cyst is usually repaired laparoscopically.
Important! If signs of rupture appear, you should not self-medicate. Even conservative therapy is carried out in a hospital setting under the close supervision of a doctor.
Contraindications to surgery
Abdominal surgical interventions are contraindicated in the following cases:
- hypertension;
- infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract;
- diabetes;
- history of myocardial infarction;
- oncological processes in other organs;
- heart failure.
Contraindications to laparoscopy are all of the above cases, as well as high degree obesity, purulent lesions of the skin of the abdomen, adhesions in the abdominal cavity, heavy bleeding, and large size of the formation.
Ultrasound picture of ovarian pathology
Ultrasound examination can identify the following types of pathological formations of the appendages:
- Functional cysts: luteal and follicular, as well as their variety - hemorrhagic;
- Organic cysts: paraovarian, dermoid, serous;
- Ovarian endometriosis;
- Polycystic ovary syndrome;
- True gonadal tumors: benign and malignant.
According to the classification, polycystic ovary syndrome does not relate to gonadal cysts and tumors, but is usually considered together with this pathology in terms of differential diagnosis.
In the description of the ultrasound, the doctor always indicates:
- Size of formation (diameter);
- Localization of the identified pathology;
- The presence of concomitant changes in other pelvic organs.
Let's take a closer look at the ultrasound picture for each pathology.
Ultrasound helps to indirectly determine the type of cyst; the final diagnosis is made by histological examination.
Follicular cyst
On ultrasound it looks like a hypoechoic single-chamber oval or round formation with thin walls. The contour is clear and smooth, inclusions are not detected. The contents of the cavity are anechoic. The size of the formation is usually no more than 12 cm. Normal ovarian tissue can be seen behind.
With Doppler ultrasound, blood flow inside and around the cavity is not determined. The photo below shows a follicular cyst:
In rare cases, a follicular ovarian cyst is detected in the fetus. This formation persists throughout intrauterine development and usually regresses spontaneously in the first months after the birth of the child. The photo shows this pathology:
Corpus luteum cyst
Defined as a hypoechoic round or oval formation with a thick wall. The contour of the cavity is clear and even, no inclusions are detected. Sizes – from 3 to 8 cm.
With Doppler ultrasound, a distinctive sign of a luteal cyst is observed - the appearance of a “ring of fire” around the cavity (parietal blood flow). This is clearly demonstrated in the photo below:
Recovery after surgery
After surgery, the patient is prescribed antibiotics,
anti-inflammatory, painkillers, immunomodulators and vitamin complexes. It is necessary to follow a diet - take only liquid soups and cereals, jelly, fruit drinks, steamed fruits and vegetables. In the future, these restrictions are gradually lifted.
To speed up the healing of sutures, it is recommended to wear a special postoperative bandage.
Full recovery of the body occurs 3-4 weeks after the intervention. During this period, any physical activity, sexual intercourse, or heavy lifting should be avoided. In the first week, it is recommended to remain in bed.
Preventive measures
In order to avoid pathology, you should regularly visit a gynecologist. This will prevent the development of many sexual diseases.
Other rules of prevention:
- carrying out a full examination when planning pregnancy, and, if necessary, treatment of detected diseases;
- timely treatment of any inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system;
- taking precautions when detecting an ovarian cyst;
- immediate removal of the formation as prescribed by a doctor.
When treating formations on the ovaries, it is necessary to strictly follow all the recommendations of the gynecologist - this will speed up the healing process and prevent the occurrence of complications.
Ovarian cyst apoplexy is a pathology, the consequences of which are minimized with timely medical intervention. To prevent its occurrence, physical activity and other factors that contribute to rupture of the formation should be avoided. Properly selected treatment can preserve a woman’s reproductive function.
Causes of ovarian cyst rupture
Rupture of a left ovarian cyst can be caused by the following factors:
- hormonal imbalance, manifested in disruption of ovulation processes;
- accession, exacerbation of chronic inflammatory process of the appendages;
- physical overexertion, lifting heavy weights;
- rough sexual intercourse;
- injuries, falls, blows to the lower half of the abdominal cavity;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- pathology of the blood coagulation system.
In some cases, the tumor bursts without any special triggers: at rest, during sleep.
Attention! Patients with adnexal growths need to avoid the main causes leading to rupture of the formations.