The sigmoid colon is an important part of the large intestine that absorbs water from food consumed. This department received its name because of its unusual shape. The sigmoid colon is represented as a sigma - a letter of the Greek alphabet. Diseases lead to disruption of the digestive system and the performance of nearby organs.
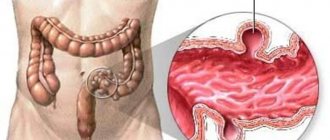
A polyp in the sigmoid colon is a common disease, representing a growth on the inner wall. The tumor tissue is glandular epithelium, which is covered by a mucous layer. There are 2 types: spherical with a stem, flat with a wide base. Polyps can be single or multiple. The average size of the formation is 1-2 cm.
Based on statistical data, polyposis more often affects men after 40 years of age. A fifth of the population suffers from growths in the sigmoid colon. The large intestine, its left part, including the sigmoid region, suffers more often. Finding growths on the right side of the intestine is less likely. Polyps in the small intestine are rare.
A polyp is a benign growth. The danger is that some species transform into a malignant growth. The villous subtype of the adenomatous type of polyps has a tendency to malignancy.
Classification of types of sigmoid colon polyp
Benign tumors are divided by number and type. When diagnosing, there can be up to several of them. Polyps reach sizes of 5 cm. Then they are classified according to the type of disease. This depends on the location of the tumor.
Therefore, the following types of intestinal neoplasms are distinguished:
- adenomatous glandular polyp;
- hyperplastic tumor;
- diffuse neoplasms.
Adenomatous tumor in the sigmoid colon is a benign tumor. However, due to provoking factors, the polyp turns into a malignant growth. This type of tumor reaches 5 cm in diameter. In addition, adenomatous polyp is divided into subtypes. Therefore, tubular and villous are distinguished. However, the disease can involve both subtypes.
Adenomatous polyposis in the sigmoid colon does not manifest itself in a specific clinical picture. Signs begin to appear when the tumor grows in size. In addition, patients experience problems during bowel movements. Digestive function begins to deteriorate, and the growth becomes malignant.
Hyperplastic polyp of the sigmoid colon occurs frequently in most patients. The growths remain in a benign state for a long time. This is a feature of hyperplastic polyposis. After diagnosing this type of disease, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the body.
Your doctor will conduct preventive examinations to monitor the size of the tumors. To get rid of this type of polyps, you will need to follow the doctor’s recommendations and undergo a simple operation to remove the tumor.
Schematic photo of polyp removal
Diffuse growths occur due to a family predisposition. This often manifests itself during the formation of organs during the embryonic period. The appearance of the first symptoms of the disease in adolescence leads to the only treatment – removal of the tumors.
The diffuse form can be complicated by an abdominal cyst or cancer.
Why are they dangerous?
Progressive polyposis of the sigmoid colon can cause serious complications, the most dangerous of which are:
- Severe bleeding due to mechanical damage, which is most typical for villous growths. Frequent blood loss can cause anemia.
- Acute intestinal obstruction when the intestinal lumen is blocked.
- Enterocolitis in acute form as a result of inflammatory processes.
- Transformation of a benign formation into a malignant tumor (malignancy).
A certain danger is also present during surgical treatment. If the procedure was performed incorrectly, perforation of the intestinal wall may occur at the site of removal of the lesion. This can cause peritonitis.
Accompanying signs of the disease
Any type of polyposis does not appear in the initial stages. Therefore, the diagnosis is made by chance when an examination is carried out due to another disease. Symptoms of a polyp in the sigmoid colon appear after the tumor grows over 30 mm or the formations are multiple.
The first manifestation is recorded with the appearance of sharp pain located in the lower abdomen. The symptom occurs with sudden movements or bending forward. In addition, blood inclusions are located in the stool. Otherwise, there is mucus covering the feces. Along with this, false urges to empty the bowel and constipation occur. Additionally, diarrhea occurs. The growths can fall out of the rectum due to their large size. The patient should pay close attention to gas, belching and heartburn along with the first signs.
In the final stages, the disease manifests itself in a lethargic state of the patient. The patient complains of increased fatigue and headache with a slight increase in temperature.
Prognosis and clinical observation
Based on the fact that even neoplasms of the large intestine are prone to recurrence, during the first 2 years after surgery, constant follow-up with periodic examinations (every 3 months) and colonoscopy (once a year) is recommended. According to statistics, relapse of the disease in the first few years is observed in 15% of patients, and half of them experience the appearance of polyps in other parts of the intestine. Identification of a new polyp is an indication for urgent re-operation, since in this case the risk of malignancy of the process with the development of sigmoid colon cancer increases.
When initially removing an already malignant area, more careful monitoring is required: an examination once a month and a colonoscopy once every six months. After 2 years, if there are no symptoms of relapse of the disease, an examination is required once every six months and a colonoscopy once every 2 years. Such patients are subject to lifelong dispensary registration.
There is currently no specific prevention of polyps. To reduce the risk of their occurrence, a balanced diet, an active lifestyle, and timely detection and treatment of diseases of the digestive tract are recommended.
How is the diagnosis made?
Diagnosis of polyposis is carried out by a proctologist or gastroenterologist. To establish the size and condition of the growths, the following studies are carried out:
- sigmoidoscopy - an endoscopic method, with the introduction of a device into the rectum for examining the intestine;
- irrigoscopy - x-ray method using a contrast agent;
- colonoscopy - used to establish a diagnosis followed by removal of one tumor.
When an irrigoscopy or colonoscopy is performed, the doctor is able to examine polyps in the sigmoid colon. In addition, a biopsy is performed. This is required to determine the nature of the growth. Sometimes doctors more accurately determine the condition of the polyp using sigmoidoscopy.
Diagnosis
Polypoid formation of the sigmoid colon is rarely diagnosed in the first stages. Growths that do not manifest symptoms are never detected. Colonic polyposis is diagnosed randomly. Diagnosis consists of a physical examination of the patient and diagnostics using instruments.
The first thing to start with the examination is a conversation with the patient. The patient talks about symptoms, previous illnesses, and nutrition. The doctor will also ask about any history of intestinal diseases in your immediate family. After the conversation, the doctor palpates the lower rectum for growths.
Diagnostics using special tools:
- Colonoscopy. A colonoscope examination helps detect tumors in the sigmoid and examine the colon. A thin and flexible metal tube allows you to examine the entire colon - right up to the cecum. The colonoscope is inserted through the anus. To improve visibility, the intestine is straightened using air flow. If a growth is detected, a biopsy is taken. Small benign growths are removed immediately.
- Sigmoidoscopy. Inspection with a sigmoidoscope is possible in the rectum and part of the sigmoid colon. The device has a camera and biopsy forceps.
- Sigmoidoscopy. The sigmoidoscope is gentle compared to the colonoscope. The examination allows you to make an accurate diagnosis. The limitations of the sigmoidoscope are that it cannot detect polyps with a diameter of 1 cm.
- Irrigoscopy. The point of the study is to introduce barium sulfate into the human colon. A contrast agent allows you to take x-rays that allow you to see tumors.
Prescription of therapeutic measures
Sigmoid colon polyp is treated surgically. However, there are several basic operations for removing growths. For some, the doctor performs additional diagnostics.
Surgical treatment methods
The polyp can be attached with a thin stalk or a wide base. To treat, you will need to hold a special instrument with a loop at the end to the growth. This involves removing the tumor using polypectomy. In this case, a loop is wrapped around the polyp, and the formation is tightened. After this, a current of increased frequency is passed through the instrument. Because of this effect, the stalk and the polyp itself are separated, and the wound is cauterized.
Photo of a polyp in the intestines
If several formations are detected, the intervention is carried out in a couple of stages. Between operations there is a break of 14 days.
Depending on the characteristics of the polyposis, the doctor can choose one of the following treatment methods:
- transanal removal - surgery to remove the tumor is carried out by introducing a rectal speculum into the rectum, and then special clamps are used for the formations, and the polyp is cut off (large growths are removed with a scalpel);
- endoscopic removal - the operation is performed using a proctoscope and is effective against any type and size of tumor;
- resection - the operation is performed not only with the removal of the polyp, but also with the excision of nearby affected tissue;
- radical surgery - removal of a section of the sigmoid colon and lymph nodes.
Methods of treating polyposis with folk remedies
In addition to traditional treatment, in the initial stages, patients are able to cure polyps located in the sigmoid colon at home. For this disease, enemas with celandine juice are used. Otherwise, treatment with folk remedies involves the use of infusions of golden mustache. For treatment against these tumors at home, it is recommended to consult with your doctor.
Medical nutrition in the postoperative period
After one of the surgical treatment methods, the patient is prescribed a certain diet. The goal of adjusting your diet is to prevent constipation. In addition, during recovery you should not eat foods that irritate the walls of the intestinal mucosa.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis must be made by a proctologist. At the initial visit, the doctor interviews and examines the patient. Analyzing the patient's complaints about general weakness, pain in the left iliac region, weight loss, streaks of scarlet blood in the stool, one can suspect the involvement of the lower intestines. Upon visual examination, such a patient may be pale (anemic) and emaciated. Palpation reveals pain in the left iliac region. If the polyp is large in size, then upon palpation you can feel the formation in this location.
During laboratory tests, stool analysis is of greatest importance. When examining stool, streaks of scarlet blood are found in them. Color matters a lot. For example, if the upper gastrointestinal tract is damaged, the blood will be dark. If the bleeding is not intense, then an occult blood test will be needed.
Of the instrumental methods, the most relevant is irrigoscopy. This manipulation allows you to assess the patency and condition of the walls of the colon. For irrigoscopy, it is necessary to perform a retrograde (through the rectum) injection of a contrast solution, followed by visualization using an X-ray machine. This technique allows you to fix a polyp larger than 10 mm. To detect tumors less than 10 m2, you can use colonoscopy.
Principle of colonoscopy
Endoscopic research methods are performed with special optical instruments inserted into the lumen of hollow organs. Colonoscopy allows you to evaluate the condition of the gastrointestinal tract from the rectum to the ileocecal angle. This manipulation is prescribed if there is a suspicion of the presence of polypous formations in the upper parts of the digestive tract.
Why and how do complications appear?
If polyps in the sigmoid colon are not treated and the symptoms of the disease are ignored, then patients will develop further polyposis. This leads to unpleasant consequences for the patient’s entire body. In this case, degeneration into a malignant formation occurs. The presence of polyps in the sigmoid colon causes frequent bleeding and anemia. Due to the constant growth of growths, the lumen decreases, and all food enters through the resulting hole.
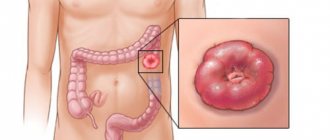
Photo of sigmoid colon polyp
The development of the disease into enterocolitis is dangerous because inflammation of the intestinal wall occurs. In addition, Crohn's disease or diverticulosis develop. After removal of the growth by polypectomy, a complication arises. The patient has perforation of the wall of the large intestine. After surgery to remove a polyp, the attending doctor takes measures to prevent the inflammatory process.
Definition
A polyp of the sigmoid colon is a tumor that has a benign etiology and affects the mucous tissue of the descending sigmoid colon. The sigmoid colon is located on the left side of the abdominal cavity and looks like the letter S. In this organ, the final formation of feces and the final process of absorption of nutrients and moisture occur. If a polyp has formed in this organ, the patient experiences symptoms that are initially similar to symptoms of indigestion, but as the tumor grows, the patient develops pain, which requires consulting a doctor.
Types of pathologies
In neoplastic neoplasms, a distinction is made between non-epithelial and epithelial forms:
- Nonepithelial varieties: accumulation of tissue under the mucosa. Non-epithelial types include, for example, lipomas, fibromas, hemangiomas or lymphoid tumors,
- Epithelial types are usually adenomas. They are the most common (80% of all tumor cases). About 30% of adults over the age of 50 suffer from this disease. About 3% of adenomas have malignant tissue.
Adenomas are divided into:
- Villous,
- Tubular (tubular),
- Tubular-villous.
More than half of the cases occur several times (usually tubular adenomas). Villous adenomas have the greatest risk of degeneration into malignant neoplasms.
Severe transverse polyposis of various parts of the intestine
Attention! If a patient has 50-100 polyps, this condition is called “polyposis” in medical practice.