Gram-variable coccobacilli are one of the bacterial species. It combines in large quantities two forms of microorganisms that are considered pathogenic. We are talking about cocci and bacilli. Most often, such microflora is represented by Haemophilus influenzae. Such a detection often indicates a hemophilic infection. This category also includes Gardenerella vaginalis, which becomes the causative agent of gardenerellosis, as well as the causative agent of chlamydia.
If coccobacillary flora is present in the smear, then we are talking about the presence of a disease in a woman that is spread sexually. In addition, such microflora may be a consequence of vaginal dysbiosis. In a woman’s body, such disruptions are practically normal if microorganisms living in the vagina multiply in large numbers, especially gram-variable coccobacilli, which are considered pathogenic.
What to do in such a situation? To get started, we recommend reading this article. This article describes in detail methods of controlling parasites. We also recommend that you consult a specialist. Read the article >>>
If the analysis showed a sexually transmitted disease, then the reason is clear. However, if an abundant coccobacillary component is found in bacterial vaginosis, then it is much more difficult to find out what the problem is.
Very often, sexually transmitted diseases are intertwined with vaginosis. If the norm of bacteria in a woman’s vagina is disturbed, then we are talking about a change in pH, therefore, the environment changes to alkaline or acidic. Both of these conditions indicate that the norm has been violated, which causes a change in protective functions. In this case, infections, including sexually transmitted infections, will penetrate into the woman’s body much more easily.
There are also the opposite cases, when pathogens of a sexually transmitted disease are found in the smear and a course of antibiotics is prescribed to combat them. As a result, the natural microflora is destroyed. Such treatment often causes the growth of large numbers of coccobacilli.
It is worth noting that in men the identification of such bacteria is difficult. The fact is that in most cases there are simply no manifestations of such a violation. As a result, a man can spread a sexually transmitted infection, especially when sexual intercourse is carried out without contraception.
Symptoms in men and women
Vaginal dysbiosis is accompanied by severe symptoms. Therefore, a smear is usually taken from women when characteristic signs occur. Typically, exacerbations occur when immunity decreases, so it is easier to detect infection in the female body.
Symptoms include:
- Discharge with an unpleasant odor.
- Burning sensation.
- Intense itching.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Frequent urination.
It is with such symptoms that a smear test for coccobacilli is performed in women. The procedure may be repeated over several days to monitor the progress of the infection or determine the effectiveness of therapy.
Due to its latent course, there are no symptoms of coccobacilli in men. The occurrence of intense symptoms means the development of an inflammatory process occurring in the urethra, rarely reaching the bladder.
Symptoms of an infectious process include:
- Pain when urinating.
- Burning, itching.
- Discharge from the urethra.
- Redness of tissues.
In severe cases, inflammation is accompanied by general symptoms. Patients develop a fever, weakness, nausea, and loss of appetite.
Gram-variable coccobacilli in a smear: normal
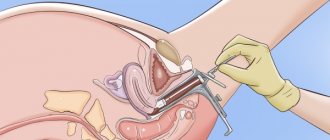
A smear is a small scraping from the surface of the mucous membrane. This analysis is effective and after it is carried out, a complete “picture” of the possible disease is revealed. It is important to know that coccobacilli are not observed in a healthy person.
When diagnosing a smear, four factors :
- Flat epithelium . If the condition of the epithelium is normal, then the conclusion should be o. This indicates that the number of cells is within the normal range, that is, 5 - 10. If the number of cells is more than 10, this indicates an inflammatory process. In case of a lack of epithelium in the body, there is a lack of female hormones;
- Leukocytesresponsible for the destruction of bacteria. If a smear is taken from the vagina, then the permissible norm of leukocytes is 10, if from the cervix, then 30. If the number of leukocytes is exceeded, inflammatory processes are observed;
- Lactobacilli or gram are positive rods that perform a protective role, which is to suppress pathogenic microbes. An unpleasant odor similar to rotten fish indicates a malfunction of lactobacilli;
- Slime . It should be remembered that if the amount of mucus is small, then this is quite normal.
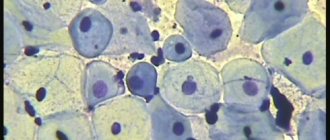
Cocci and bacilli
In microbiology, each bacterium has its own name. Cocci are spherical bacteria, bacilli are rod-shaped. And there is an intermediate form that resembles three-dimensional rods under a microscope; they are called coccobacilli.
These bacteria are detected not only in the results of a gynecological smear, but also in an analysis of the pharynx (throat), for example. Some bacilli or cocci (streptococci, staphylococci, etc.) are opportunistic and can harm the body only under special circumstances when immunity declines. Other pathogenic ones need to be gotten rid of, as they always pose a danger.
There are many types of bacteria, but in a vaginal smear with coccobacillary flora, Gardnerella vaginalis (Gardnerella vaginalis) and Chlamydia trachomatis (chlamydia) are found most often than others. It is about them that we will discuss in our material.
The first is traditionally considered to be the causative agent of bacterial vaginosis (also called dysbacteriosis or vaginal dysbiosis, gardnerellosis), and the second is a sexually transmitted disease - chlamydia. Dysbiosis is not a sexually transmitted disease.
If you find a note in your smear that your flora is coccobacillary, this does not necessarily mean that you should be treated. Normally, the flora should be rod-shaped, represented by lactomorphotypes in large numbers. But the presence of coccobacilli is possible, especially gram-positive (gr +), which rarely give negative symptoms and are not potentially hazardous to health.
Treatment is required if:
- there are symptoms of the disease, for example: homogeneous creamy discharge with the smell of rotten fish, burning, itching (these are symptoms of gardnerellosis) + key cells were identified in the smear;
- if chlamydia is detected as a result of microflora culture or PCR, especially in pregnant women and those planning pregnancy.
Back to contents
Diagnosis rules
The doctor can make a diagnosis based on the following indicators in the tests (cytology and general flora smear, Gram-stained).
- Large amount of epithelium.
- Key cells with coccobacilli associated with them (Gardnerella vaginalis, Mobiluncus spp., etc.) were found. Key cells are epithelial cells with gardnerella adhering to them.
- Complete absence or single lactobacilli.
- A large number of the following types of microorganisms: G. vaginalis, Bacteroides spp, Fusobacterium spp, Mobiluncus spp.
- Absence or low concentration of polynuclear neutrophils (a type of white blood cell).
I would like to say separately about the last point. Bacterial vaginosis is generally not characterized by leukocytosis in a smear on flora from the vagina, urethra or cervix. An increase in the number of leukocytes does not occur due to the huge number of vaginal gardnerella, they can thus reduce the local immunity of a woman.
Meanwhile, a gynecologist, even during an examination in a chair, may suspect this disease in a woman. Its most obvious symptom is a fishy smell. This smell is produced by gardnerella. Add to this complaints of itching and unusual discharge, key cells in the smear, and we get typical bacterial vaginosis.
You should not rely solely on the results of a vaginal smear. Especially if there are no symptoms of the disease. Coccobacillary flora in moderate or scant quantities in the visual field (in the field of view of the clinician 0-1, 2, 3) can be detected before the onset of menstruation. This is fine. The squamous epithelium is usually normal.
Mixed flora is also diagnosed in the last days of menstrual bleeding. It is better to visit a gynecologist from 10 to 20 days of the cycle.
Is bacterial vaginosis sexually transmitted?
No, this is not a sexually transmitted disease (not an STD). However, during intimate contacts without barrier protection (condom), partners exchange microflora, which can sometimes provoke inflammatory processes in a woman. But opportunistic cocci, that is, transient (from the word transit - temporary) microflora in a partner, is not a reason for treating her partner.
Chlamydia is a hidden sexually transmitted infection
As you probably already guessed, this is a sexually transmitted disease. It occurs practically asymptomatically in women, but causes enormous problems in the future.
Why is chlamydia dangerous and its manifestations in women?
In women with chlamydia, infertility also occurs due to the inability of the fertilized egg to implant into the uterine wall. Conception occurs, but the fertilized egg cannot penetrate into the mother’s tissue for its development. And if it does succeed in implantation, then developmental disturbances and early miscarriage occur.
Even more dangerous is chlamydia, which worsens in the first weeks after the onset of delayed menstruation during pregnancy. Neural tube defects can occur in children. After the 20th week of pregnancy, the disease threatens intrauterine infection of the fetus, premature birth and acute postpartum endometritis of the mother.
Unobvious symptoms of the disease may appear 2-4 weeks after infection, less often after 1 week. Chlamydia is transmitted absolutely through sexual contact, as well as during natural childbirth. Theoretically, it is possible to become infected with chlamydia through household means (for example, when using the toilet), since they can remain viable for 2 days. But there is no evidence yet of this type of disease transmission.
The woman herself is unlikely to pay attention to the signs of chlamydia. This is a scanty mucous discharge with a purulent admixture. The cervix and the entire cervical canal also become inflamed. This can already be seen during an examination by a doctor when using a gynecological speculum. There is no pain or itching.
Diagnosis of chlamydia: reliable tests
There are several ways to determine chlamydia, but most often doctors prescribe a PCR smear from the cervix or ELISA - a blood test from a vein. In this case, the smear only shows whether there is chlamydia or not. And the second shows the presence of antibodies in the blood. Based on the result of the first, it is impossible to say how long the woman has been sick, whether a significant amount of antibodies was found in the blood or a small one. But based on the result of the second, it is possible.
However, gynecologists prefer the PCR smear. This is a very accurate analysis. Usually, doctors do not prescribe a separate smear for chlamydia, but for hidden infections (that is, asymptomatic ones). These also include mycoplasmosis and ureaplasmosis.
Another way to find out about the disease is to take a chlamydia culture. In this way, the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics can be immediately determined if they are detected.
A regular smear on the flora (there is a very good and detailed article about it here) in this case is not informative. However, it is this that usually gives rise to additional examination for hidden infections. It’s not for nothing that we are telling you about chlamydia as part of an article about the coccobacillary flora of the vagina.
When should you be treated and with what medications?
This disease is treated with antibiotics. First choice drugs on the tablet.
Drug name
Recommendations for admission.
1 tablet 500 mg for 3 days or 1 g orally once (regimen for pregnant women).
100 mg 2 times a day for 7 days.
Tablets of 500 mg 4 times a day for 7 days or tablets of 250 mg for 14 days.
1 tablet 500 mg per day for 7 days.
Tablets 300 mg 2 times a day for 7 days.
In Europe, Josamycin is prescribed at a dose of 500-1000 mg for a week. And European doctors generally do not recommend prescribing Erythromycin for chlamydial infection. Also, domestic doctors sometimes prescribe Clarithromycin.
, and pregnant women are treated with
Vilprafen
,
Erythromycin
or
Amoxicillin
(500 mg tablets 4 times a day for one week).
And these are not all possible treatment regimens for chlamydia. We invite you to familiarize yourself with modern Russian recommendations for choosing an antimicrobial drug for non-pregnant women. When clicked, the tables enlarge and open in a new browser tab.
This is a table with recommendations for treatment of pregnant women.
If the disease is not chronic and there are no complications, one antibiotic is usually sufficient. Moreover, the sexual partner should also take the medicine, even if his test is currently negative.
When can we talk about healing?
Some doctors advise taking a blood test (ELISA) 1.5-2 months after finishing taking the antibacterial drug; the antibody titer should decrease by 4-8 times. But only domestic doctors practice this approach. Abroad it is considered incorrect. There, 4 weeks after the end of treatment, a smear is taken using the PCR method; if cured, it is negative, or after 3 weeks, a culture test for chlamydia is taken (there should be no growth of chlamydia).
And remember, immunity to chlamydia is not developed, and after you stop taking the medications, you can easily catch it again. Be careful.
If unprotected sexual intercourse has taken place, or the condom has broken, and you are afraid that you might have become infected with something, use the Miramistin antiseptic. It effectively kills most cocci and other types of pathogens. But not 100%, of course.
Terms you may see in smear results
Gram-variable coccobacilli morphologically similar to g vaginalis are just Gardnerella, cocci, which, if key cells are present, indicate bacterial vaginosis.
Polymorphic coccobacillary flora - the smear contains a large number of coccobacilli, this is unlikely to be a normal variant, it needs to be treated.
Undifferentiated coccobacilli - read simply as "coccobacilli".
Haemophilus influenzae is a microorganism that causes inflammation of the vagina and cervix.
Leptothrix is an opportunistic bacterium that is often found simultaneously with other pathogens of bacterial vaginosis and chlamydia. A detailed article about it is here.
If you like to understand your smears, then you will probably be interested in this very informative video from a medical practitioner.
https://youtu.be/yvhHgZsw1u8
How to properly prepare for a smear test
Coccobacillary flora in a smear is detected using microscopic or bacteriological examination. To get a reliable result, you must adhere to certain rules:
- exclude sexual contact two days before taking a smear test;
- It is not recommended to take a smear immediately before the start of menstruation, or immediately after its end;
- You can’t take a bath the day before;
- exclude douching;
- stop using vaginal tablets and suppositories;
- During hygienic procedures, you cannot use hygiene products; you can only wash yourself with clean warm water;
- 3 hours before taking a smear, you should avoid visiting the toilet.
If all recommendations are followed, the smear result will be reliable and will allow the doctor to accurately establish a diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribe effective treatment. The coccobacillary flora may not be detected if the preparation for the analysis is improper, which will lead to further progression of the disease.
Decoding the smear
Most often, when obtaining results, you can come across several conclusions, the terms of which are not always clear:
- gram-variable flora - indicates the presence of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria in the smear (determined by staining);
- polymorphic flora - indicates the presence of bacteria and viruses contained in large quantities in the smear;
- moderate or significant coccobacillary flora indicates the presence of an infection, which can be determined using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or bacterial culture.
Knowing the correct definition of medical terms, you don’t have to worry while waiting for your next trip to the doctor.
Coccobacillary flora - what is it?
Coccobacilli - a mixed form of microbes, a symbiosis of cocci and bacilli - are gram-positive and gram-negative. Most often, such representatives of this pathogenic microflora are found as chlamydia, gardnerella and hemophilus influenzae. Parasites are transmitted sexually; a large number of them indicates the presence of a sexually transmitted disease.
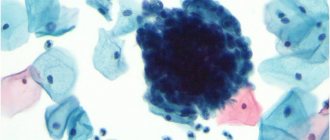
What do coccobacilli look like? Cocci look like rods, bacilli look like balls. Since coccobacilli combine the properties of cocci and bacilli, their shape is similar to an elongated ball.
Coccobacilli (mixed form of microbes) under magnification
Coccobacilli may be present in small quantities in the vaginal microflora; their active growth begins when the balance of bacteria is disturbed. Sometimes, during the treatment of sexually transmitted infections with antibiotics, the balance of the vaginal microflora is disturbed, which leads to the active growth of coccobacilli.
To get rid of the parasites, you just need to drink on an empty stomach.
Additional tests
If a woman’s smear reveals abundant coccobacillary flora, it is necessary to additionally examine urine and blood. A comprehensive examination allows you to accurately determine the type and number of cocci and bacilli that inhabit a woman’s vagina.
If dysbiosis is suspected, it is also necessary to undergo medical imaging and, if necessary, undergo additional tests. To eliminate pathogenic flora in this case, oral antibiotics are most often prescribed, which can kill pathogenic flora.
After this, it is important to normalize the balance of microflora and take probiotics that restore the beneficial microflora of the vagina and intestines.
Prevention
In order to avoid the occurrence of coccobacilli in the vagina, it is necessary:
- refuse to frequently change sexual partners;
- monitor your health;
- exercise;
- spend more time in the fresh air;
- do not drink alcohol;
- keep the genitals clean;
- wash yourself after each act of urination or defecation;
- wear underwear made from natural, breathable materials.
Every woman should be regularly examined by a gynecologist so that if a disease is detected, it can be treated promptly, without waiting for adverse consequences for the health of the reproductive organs.
https://youtu.be/f-QPVj6Ev38
Coccobacilli are a special type of bacteria that belongs to the pathogenic flora in the smear. Their presence in a smear from the genital tract is not normal and may indicate the development of bacterial vaginosis and sexually transmitted diseases in a woman.
What does coccal, bacillary and coccobacillary flora mean in a smear in women, including during pregnancy, what are the causes of abundant and poor microflora, how to treat this condition?
Treatment of vaginal dysbiosis
The main thing here is an antimicrobial, antibacterial drug. Usually prescribed drugs containing metronidazole
.
For example, vaginal tablets "Trichopol"
.
If a woman is also diagnosed with candida (thrush), then together with an antifungal component, so that candidiasis can be immediately cured. For example, candles "NEO-PENOTRAN"
or
"Klion D"
.
Example of a treatment plan:
- Klion D for the night No. 10;
- Diflucan 150 mg No. 3 every 3 days.
During pregnancy and after childbirth during lactation, Hexicon
,
"Terzhinan"
or
"Polyzhinaks"
.
Drugs for bacterial vaginosis are used topically, that is, vaginally. There is no point in taking metronidazole orally.
Danger level during pregnancy
The detection of gram-variable coccobacilli in a smear in pregnant women is not uncommon, which is due to hormonal imbalance and decreased immunity.
Treatment is required, otherwise there is a high risk of transmission of infection to the child (during passage through the birth canal), development of hypoxia in the fetus, serious inflammation of the uterus in a woman, including metroendometritis.
Therapy includes gentle antimicrobial drugs in the form of medications for external use: Klacid gel and Metronidazole in the form of suppositories.
The drug is available in the form of tablets, solution, gel and suppositories
After suppressing harmful bacteria, it is necessary to use products containing lacto- and bifidobacteria (suppositories and medicinal tampons).
Additionally, pregnant women are prescribed vitamin complexes (Elevit, Complivit mama) and eubiotics (Linex, Bifiform) for general strengthening of the body and prevention of dysbiosis.
We looked at what coccal, bacillary and coccobacillary flora are in a smear in women, what the treatment for such a condition is.
The detection of coccobacillary flora indicates serious problems in the female reproductive system.
The presence of infectious diseases or dysbiosis of the genital organs is a reason for immediate examination and treatment.
If you consult a gynecologist in a timely manner, you can successfully get rid of pathogenic flora within a month without negative consequences.
Tactics of therapeutic correction
If coccobacilli are detected in a smear, the doctor must prescribe a certain range of additional blood and urine tests. This is important for detecting other sexually transmitted infections. After making a specific diagnosis, the specialist prescribes comprehensive treatment.
In case of vaginal dysbiosis, the following measures are prescribed:
- diet including fermented milk products;
- probiotics in different forms, both for internal use and for local use - in the form of suppositories;
- vitamin therapy.
If a sexually transmitted disease is established, the doctor prescribes antimicrobial treatment, including sulfonamides and antibiotic medications. At the same time, it is also rational to use dosage forms both for local use and for oral administration. Antibiotic therapy requires the simultaneous administration of probiotic agents to prevent the progression of dysbiosis. If coccobacilli are detected in a smear during pregnancy, treatment should be strictly controlled by a specialist: many drugs are contraindicated in this situation.
Self-medication in any situation is unacceptable. Only a qualified doctor, after a comprehensive diagnosis, can prescribe the correct course of therapeutic correction of the condition.
https://youtu.be/geZIhT5vflc
Ignoring pathology: what are the consequences?
Any disease requires qualified treatment. Otherwise, ignoring the disease can lead to various complications.
For example, women who refuse treatment for coccobacilli risk pyelonephritis or cystitis. This is due to the close location of the vagina to the urethra. This way, bacteria can quickly travel to the kidneys or bladder.
In men, gram-variable coccobacilli can cause urethritis, which contributes to discomfort when urinating.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Interesting to know:
Causes of coccobacilli
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! A remedy for getting rid of parasites that works immediately. Read more >>>
Since infection with coccal microflora occurs through sexual contact, the main reason for its appearance in the body is unprotected sex.
Why do coccobacilli appear:
- promiscuity in sexual relations - in women, such a lifestyle often causes an imbalance in the microflora, and the active growth of pathogenic bacteria begins;
- improper douching procedure - beneficial flora is washed out;
- constant use of panty liners;
- underwear made of synthetic materials;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- diabetes;
- intrauterine device is a common cause of imbalance in the vaginal microflora;
- changes in hormonal levels - the growth of coccobacilli is observed during pregnancy, during menopause;
- taking oral contraceptives, long-term therapy with antibacterial drugs.
Coccobacilli begin to actively multiply during pregnancy
Coccobacillary flora appears with weakened immunity, vaginal dysbiosis, which develops against the background of diseases of the digestive system.
Sometimes sperm blocks the growth of beneficial lactobacilli, as a result of which the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria is activated.
Bibliography
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Brucellosis. Parasites. Link
- Corbel MJ Parasitic diseases // World Health Organization. Link
- Young EJ Best matches for intestinal parasites // Clinical Infectious Diseases. — 1995. Vol. 21. - P. 283-290. Link
- Yushchuk N.D., Vengerov Yu.A. Infectious diseases: textbook. — 2nd edition. - M.: Medicine, 2003. - 544 p.
- Prevalence of parasitic diseases among the population, 2009 / Kokolova L. M., Reshetnikov A. D., Platonov T. A., Verkhovtseva L. A.
- Helminths of domestic carnivores of the Voronezh region, 2011 / Nikulin P. I., Romashov B. V.
An article for patients with a doctor-diagnosed disease. Does not replace a doctor's appointment and cannot be used for self-diagnosis.
The best stories from our readers
Topic: Parasites are to blame for all troubles!
From: Lyudmila S. ( [email protected] )
To: Administration Noparasites.ru
Not long ago my health condition worsened. I began to feel constant fatigue, headaches, laziness and some kind of endless apathy appeared. Problems also appeared with the gastrointestinal tract: bloating, diarrhea, pain and bad breath.
I thought it was because of the hard work and hoped that it would go away on its own. But every day I felt worse. The doctors couldn’t really say anything either. Everything seems to be normal, but I feel like my body is not healthy.
I decided to go to a private clinic. Here I was advised, in addition to general tests, to get tested for parasites. So in one of the tests they found parasites in me. According to doctors, these were worms, which 90% of people have and almost everyone is infected, to a greater or lesser extent.
I was prescribed a course of antiparasitic medications. But it didn’t give me any results. A week later, a friend sent me a link to an article where some parasitologist shared real tips on fighting parasites. This article literally saved my life. I followed all the advice that was there and after a couple of days I felt much better!
Digestion improved, headaches went away and the vital energy that I so lacked appeared. To be sure, I took the tests again and no parasites were found!
Anyone who wants to cleanse their body of parasites, no matter what types of these creatures live in you, read this article, I’m 100% sure it will help you! Go to article>>>
Still have questions? Ask them in our Anonymous group on VK
How to get rid of parasites in a week. The answer is here!
A reliable and effective remedy for combating worms. Removes all parasites in 21 days.
Go to website
Reviews
Read online
Symptoms that 100% indicate parasites! Take the Test.
How to rid your body of life-threatening parasites before it’s too late!
Read more
Website
To get a consultation
The doctor tells how to quickly get rid of parasites for adults and children!
A parasitologist explains what effective methods exist to combat helminths.
More details
Read completely
Comments
Search for cures for parasites
Other tests
We recommend reading
Parasites of ciliates: description of representatives, danger to humans
03/29/202003/29/2020ecoliv94
Do lice jump on people's clean hair? Do they know how to fly?
08.03.202008.03.2020ecoliv94
Types of amoebas in humans: description, class, type and order, appearance and structure
03/07/202007.03.2020ecoliv94
Trichomonas Hominis in humans: description of the parasite, mating cycle, routes of infection
03/07/202007.03.2020ecoliv94