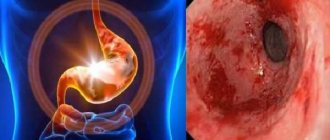
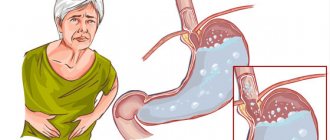
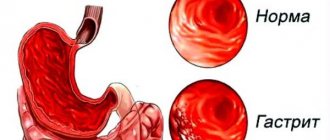
Chronic gastritis is a disease caused by inflammatory changes in the gastric mucosa and impaired production of hydrochloric acid. Along with unpleasant and painful sensations, gastric and intestinal disorders caused by food intake or nervous stress, patients often experience irritability, increased fatigue, general weakness, and decreased blood pressure. According to the results of numerous mass surveys, chronic gastritis affects more than 50% of the adult population of developed countries; in the structure of diseases of the digestive system it makes up 35%.
The main forms of gastritis at present are chronic gastritis A (accounting for 15-18% of cases of the disease) and chronic gastritis B, caused by a special microbe - Helicobacter pylori (70% of all chronic gastritis). Other forms of gastritis are much less common.
Exacerbation of gastritis during pregnancy
World statistics are such that almost half of the adult population of the globe have some degree of development of inflammation of the gastric mucosa - gastritis. The exception was not young women who are in the active period of their lives and can give birth to children. The pace of life in modern society is such that the weaker sex, on an equal basis with men, and maybe more than them, works, studies and realizes their capabilities in a variety of areas of business, culture, sports, and science.
Such a tense rhythm involves a lot of factors unfavorable for digestion:
- irregular food intake;
- fast food products;
- eating patterns throughout the day at large intervals;
- stress;
- carbonated or strong drinks;
- foods processed by frying;
- unconscious eating - while running, in front of the computer, etc.
Most working, active women do not consider pregnancy, especially in the early stages, a reason to change their life schedule, so exacerbation of chronic gastritis during pregnancy is a logical development of events.
Prevention
Even before conceiving a child, a woman must take care of her health. To avoid the appearance or exacerbation of gastritis, prevention is necessary. First of all, it is necessary to exclude factors that cause inflammation of the gastric mucosa:
- bad habits (excessive drinking and smoking);
- taking certain medications;
- nervous exhaustion and shock, emotional stress;
- unhealthy diet (abuse of spicy and fatty foods, low quality and unnatural products, lack of routine, overeating);
- irregular daily routine, chronic lack of sleep, night work;
- some diseases of internal organs (gallbladder, pancreas, liver);
- food infections and allergies;
- metabolic disorders.
Causes of gastritis during pregnancy
If such diseases have already occurred before this period, then chronic gastritis risks worsening at any stage of gestation of the unborn baby.
The causes of symptoms are as follows:
- irregular meals;
- the predominance in the diet of foods that irritate the gastric mucosa;
- toxicosis phenomena;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- stress.
Eating at long intervals leads to a long stay of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, which gradually leads to erosion of the mucous membrane. This is the process of forming areas that can subsequently ulcerate. They are not capable of normal motor activity, the process of digesting and moving food further.
The same applies to a diet dominated by fried foods, salty, fatty, spicy or carbohydrate foods. Constant load on the enzymatic apparatus leads to depletion of its reserves, stagnation of food masses in the stomach, its distension and inflammation.
Toxicosis does not contribute to the health of the stomach at all, especially during a chronic process. Certain dyspeptic phenomena: nausea, vomiting, aversion to food, lead to constant tension in the muscular system of the organ. Attacks of vomiting cause the sphincters to contract in an unnatural way. Stomach acid irritates the esophagus, which additionally causes heartburn and painful belching.
Even periodic, irregular vomiting adversely affects the course of chronic gastritis in pregnant women. A woman begins to be afraid to eat, thereby exposing her digestive organs to additional stress. The stomach muscles are spasmed, contract poorly and do not move food through the digestive tract.
During pregnancy, the nervous system becomes more unstable. Emotionally dependent women indicate tearfulness and mood swings in the first months of pregnancy. This situation also negatively affects the digestive process and the condition of the gastric mucosa.
What does burping mean?
During the period of bearing a baby, some ladies notice that their belching becomes more frequent. This symptom indicates a disease that is accompanied by an increase in the level of gastric juice, as well as a failure of intestinal motility. Incompletely digested food will provoke the release of gases from the stomach. Melissa tea usually helps to combat this problem; if it is not available, mint is used. But if after some time the problem does not go away, and the condition worsens, it would be right to consult a doctor, he will be able to prescribe individual treatment.
Methods for diagnosing gastritis in pregnant women
First of all, this is a thorough collection of anamnesis of the patient’s life and illness. After which it is necessary to examine the patient and establish the localization of pain, if any. At this stage certain difficulties arise:
- palpation of the abdomen in the area of the intestines and stomach is difficult; how much depends on the stage of pregnancy;
- Many people mistake belching, vomiting, and nausea for symptoms of toxicosis;
- it is difficult to determine the degree of bloating and flatulence for the same reasons.
Pregnancy is not a contraindication for fibrogastroduodenoscopy. The patient can tolerate this manipulation quite calmly with due attention from medical personnel.
X-ray or ultrasound examination is carried out strictly according to indications, especially x-rays. It is unsafe for the health of the unborn baby, so radiography is not indicated for pregnant women at any stage. As for ultrasound examination, it is not very informative for gastritis, and is also undesirable, since it increases the radiation load on the body of the pregnant woman and the fetus.
Features of gastritis in pregnant women
Clinical manifestations of acute or chronic gastritis in pregnant women are no different from those in any other patients. Features may be individual for each person. The difference between exacerbation of gastritis during pregnancy is the treatment that a doctor can prescribe.
In the early stages, aggravated gastritis may be mistaken for toxicosis and not given any significance. But over time, as histological changes worsen, the symptoms become more detailed, and a connection is traced with food intake or lack thereof, certain foods or drinks. Exacerbation of gastritis in a pregnant woman can be provoked by foods that begin to dominate the diet, as taste preferences have changed. Everyone knows about the desire to eat something salty or sour in the early stages of pregnancy.
How to determine acidity
Before starting treatment, even with traditional methods, it is important to find out what your stomach acidity is. During pregnancy, this is necessary, since the wrong medication will increase painful symptoms and cause harm.
So:
- The pain is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness - low acidity.
- Burning sensation – increased secretion.
- A dull, aching sensation in the stomach area is a normal secretory function.
- Intense, sharp and sharp pain - possibly an ulcer.
But if you cannot determine your acidity, it is worth conducting a diagnosis. Typically, your doctor will order an endoscopic procedure to examine your stomach juices. This study is acceptable during pregnancy. A correct diagnosis will help determine treatment.
Symptoms that occur with gastritis
Clinical manifestations, symptoms of a disease are subjective sensations or complaints that are indicated by the patient when visiting a doctor or during a conversation at the diagnostic stage. Using them, you can preliminarily determine the direction of not only the examination, but future treatment.
Gastritis can be with reduced or increased levels of hydrochloric acid production. These features determine the clinical manifestations: the severity of pain, the presence of belching, nausea, vomiting, bloating, flatulence, stool upset.
How to distinguish gastritis from other gastrointestinal diseases
To carry out differential diagnosis, it is necessary to collect all examination data: anamnesis, examination, instrumental research methods. Based on the totality of the results, it is possible to distinguish gastritis from, for example, cholecystitis or pancreatitis. In these diseases, the localization of the pain syndrome is different, there are characteristic features of clinical symptoms, blood tests show signs of inflammation, as well as disorders of the enzymatic systems of the liver or pancreas.
During FGDS, it is established that inflammation of the gastric mucosa has a characteristic appearance and localization for gastritis. If there is a digestive disorder in adjacent sections, then there are symptoms of irritation of the mucous membranes of these sections.
Treatment of gastritis during pregnancy
Without determining the level of acidity, it is impossible to treat aggravated gastritis, especially in a pregnant woman. The correct approach means establishing the type of gastritis: increased or decreased production of hydrochloric acid.
Treatment of gastritis with high acidity
First of all, eliminating the cause of the disease. This is a correction of the diet with the removal of spicy, salty, sour, pickled, and fatty foods. Preference is given to lean varieties of meat, boiled, steamed or stewed. Dairy products are allowed only in the form of cottage cheese casseroles, steamed cheesecakes, and lazy dumplings made from low-fat varieties of cottage cheese. Fermented milk products are completely excluded. Butter is allowed in dishes; sandwiches are not recommended.
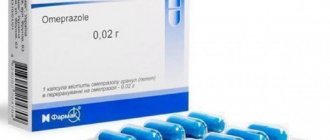
Antacids, acid-lowering drugs, and proton pump inhibitors are indicated. You cannot take these medications on your own. Only a doctor will prescribe the correct combinations of medications, doses, course duration and frequency of administration.
Treatment of gastritis with low acidity
Also, therapeutic nutrition comes to the fore: it is necessary to give preference to products that have a stimulating effect on gastric motility to prevent food stagnation. You can take mineral waters that increase the motor activity of the stomach.
Drugs are necessary for the production of gastric juice, stimulating the contractile activity of the gastric muscles, enzyme agents to improve the digestion of food mass, as well as drugs containing microorganisms to normalize the biocenosis.
Diet
Regardless of the cause of diarrhea, you need to reconsider your nutritional principles. Food portions should be small, it is better to eat often, every 2-3 hours. All fried, smoked and spicy foods should be completely removed from the menu. And you also cannot drink kefir, fermented baked milk, milk, or eat products made from it, or sweets. From the very beginning of the disorder, any vegetables and fruits are also prohibited.
In the first 12–24 hours, you should refuse food, but be sure to take plenty of fluids - still water, teas. On the second day, you can add fruit juice or compote, light broth with vegetables or chicken. Then you can start introducing food: watery porridge without salt and sugar. Porridges made from whole grains of brown rice, oats and millet are healthy. Dietary or diabetic breads and crackers are allowed.
From the third day you can diversify your diet with boiled, steamed, stewed vegetables, a couple of spoons of grated fresh apples. But you need to remember that some fruits have a laxative effect. This:
- cabbage;
- cucumbers;
- beet;
- pumpkin;
- plums;
- pears;
- bananas.
You can add lean boiled meat or a steamed cutlet to the vegetables; soup with light broth is also allowed. Herbal teas - chamomile or mint - will help soothe irritated intestines.
The diet must be followed for at least 7 days, then, if the condition improves, gradually introduce familiar foods. But “aggressive” foods - fried, fatty, spicy and salty - should be limited as much as possible. It is better to refrain from unusual combinations of products.
Most often, adjusting your diet or stopping taking any medications helps get rid of diarrhea in a matter of days. If diarrhea is caused by microbes or nervous tension, then you need to be treated under the supervision of a doctor. It is he who will explain what pregnant women can drink for diarrhea and how exactly to take medications.
Medicines
Depending on the acid level, antacids are prescribed, for example, “ Phosphalugel ”, “ Altan ” or motor stimulants, for example, “ Motilium ”. Enzyme preparations are indicated for hypoacid gastritis, these are usually “ Mezim ”, “ Pancreatin ”. Biological products to normalize the biocenosis in the intestines are taken to get rid of flatulence, diarrhea or constipation. “ Lactofiltrum ”, “ Biogaia ”, “ Baktisubtil ” have proven themselves well.
Vitamins
To compensate for the lack of vitamins from food, pregnant women take vitamin complexes. This must be taken into account when prescribing treatment for gastritis.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
This type of therapy is indicated only in the remission stage. As for pregnant women, this type of treatment is contraindicated for them.
Traditional treatment and homeopathy
Recipes from herbalists and traditional medicine can be used for gastritis in pregnant women. It is necessary to consult with your doctor; self-medication is contraindicated. You can brew flax seeds, mint, lemon balm, coltsfoot, valerian root, passionflower. Such training will help cope with stress, reduce muscle tension, and reduce the symptoms of toxicosis.
Surgical treatment
It is unlikely that surgical intervention is indicated for pregnant women during exacerbation of gastritis. Only if the inflammation of the stomach is complicated by a peptic ulcer with gastric bleeding.
Proper nutrition
An appropriate diet is the key to speedy subsidence of symptoms and relief of the patient’s condition. In addition, a diet with a predominance of proteins in an easily digestible form, a decrease in simple carbohydrates, an increase in the proportion of boiled and steamed vegetables, and baked fish is extremely beneficial for a pregnant woman and her gastrointestinal tract.
Vegetables in this diet are allowed with low fiber content, which do not complicate the digestion of food. For culinary processing, boiling, stewing or steaming is recommended