Breast cancer is a malignant tumor that occurs as a result of mutation of glandular tissue cells. In the world, the incidence of breast cancer in women ranks 3rd (according to WHO) after cardiovascular diseases and lung cancer.
Stage 1 breast cancer is characterized by:
- Small tumor size (up to two centimeters);
- Lack of metastasis;
- The most effective treatment.
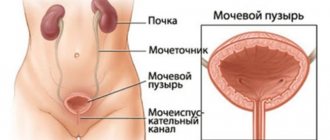
Symptoms of breast cancer
In the early stages, breast cancer is asymptomatic. Despite this, in some cases certain signs appear that indicate the presence of this oncological process. First of all, a woman should be alerted to the appearance of pain in the mammary gland and painful periods.
Symptoms of cancer are:
- Presence of compaction upon palpation;
- Changes in the shape and size of the breast;
- Changes in the appearance of the nipples and pathological discharge from them;
- Skin changes;
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
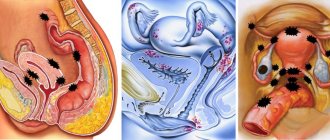
Stages of cervical cancer
The division of cervical cancer into stages is very arbitrary, but it is necessary for choosing the optimal treatment tactics and predicting the outcome of the disease.
Stage 1 – the tumor does not extend beyond the cervix.
At the same time, postoperative histological examination of removed tissues can reveal microdamage of regional lymph nodes by tumor cells (10-25% of known cases of the first stage of the disease).
Read more about the diagnosis and features of stage 1 cervical cancer: Stage 1 (first) cervical cancer - prognosis, treatment and symptoms
Stage 2 – the tumor spreads beyond the cervix (into the periuterine tissue and/or onto the body of the uterus and/or into the upper 2/3 of the vagina), but has not yet reached the walls of the pelvis and the lower third of the vagina. Micrometastases in regional lymph nodes are detected in 25-45% of cases of the second stage of the disease.
Stage 3 – the lower third of the vagina and/or pelvic wall is involved in the malignant process. Possible renal dysfunction (hydronephrosis, non-functioning kidney). Metastatic damage to regional lymph nodes - in 100% of cases.
Read more about the treatment and prognosis of stage 3 of the disease: Stage 3 (third) cervical cancer - how long do they live after treatment
Stage 4 – the tumor grows into the mucous membrane of the bladder, intestines, affects regional lymph nodes and metastasizes to distant organs (distant lymph nodes, lungs, liver, bones...)
Is it possible to cure stage 4 cervical cancer? read more: Stage 4 cervical cancer - life expectancy prognosis, symptoms
Return to contents
https://youtu.be/WFngYUdVLTY
Stage 1 breast cancer: treatment
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the prognosis is as favorable as possible (if the woman agrees to treatment for such a pathology). For stage 1 breast cancer, the cure rate is 70-98%.
When treating stage 1 breast cancer, gentle surgical treatment is often performed, namely breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy). The Yusupov Hospital is equipped with the latest medical technologies that operate according to modern international standards, thanks to which the operation is reduced to excision of the direct tumor and preservation of healthy breast tissue. If necessary, such treatment is supplemented with hormone and chemotherapy.
The prognosis of stage 1 breast cancer depends on:
- Localization of the tumor (external location is more favorable than central location);
- Dimensions of the neoplasm (should not exceed two centimeters);
- Type of cancer (negative prognosis for the inflammatory form).
Features of stage 2 cancer of any organ
Malignant neoplasms are increasingly becoming the cause of death in humans. Therefore, it is so important to identify the pathology - stage 2 cancer - in a timely manner, and carry out full-fledged comprehensive treatment.
Even at this stage of the disease, prognoses for five-year survival and a person’s return to full activity are high, about 70–90%.
This indicator most often depends on the person’s initial state of health, the presence of somatic disorders, and the mood to fight cancer.
General characteristics of stage 2 of cancer
The tumor focus in stage 2 cancer, as a rule, does not exceed 2–5 cm in diameter. In this case, the exit of atypical cells beyond the boundaries of one organ is most often not observed - the neoplasm has a local location.
The exception is certain forms of cancer with an aggressive course, which quickly metastasize to the nearest lymph nodes. Oncologists identify additional stages at stage 2 of the oncological process:
- with 2A, the tissue of the organ itself in some local area is susceptible to damage by atypical cells;
- at 2B – the tumor spreads over the entire area of the organ, penetrating it through, but does not go beyond;
- at stage 2C, single lesions of neighboring lymph structures may be observed, with their increase in size.
As a rule, the diagnosis of stage 2 cancer is the result of a preventive medical examination, since, as a rule, there are no specific symptoms.
This stage is completely reversible - five-year survival and recovery rates reach 65–90%. This indicator is significantly influenced by the speed of making an adequate diagnosis and carrying out full treatment. A person’s mood to fight a terrible disease also matters.
Early symptoms
Warning signs - this is what the early symptoms of a malignant neoplasm are called, indicate to a person that a malfunction has occurred in his body.
You should listen to and pay attention to such signals from your own body. So, most often observed:
- frequent occurrence of discomfort in any area, for example, in the epigastric region or in the sacrum, behind the sternum;
- decrease in protective forces - against the background of immunity deficiency, various viral and bacterial pathologies arise that were previously uncharacteristic for humans;
- fluctuations in temperature parameters - low-grade fever in the evening hours with a rise to 37.2–37.5 degrees;
- heavy sweats during the night, sleep disturbances;
- decreased appetite or its complete absence;
- steady weight loss without predisposing circumstances, for example, following a strict diet;
- a feeling of chronic fatigue, increasing weakness - with a balanced diet, taking vitamins and proper rest.
Having carefully analyzed your condition and identified one or more of the above signs, it is recommended to immediately consult a specialist. Advances in medicine make it possible to diagnose malignant neoplasms not only at the second, but also at the first and even preclinical stages.
Digestive system cancer
Of course, the full functioning of the digestive system is important for a person’s well-being. If a malignant focus has formed in one of the structures responsible for the absorption of nutrients, the first signs of its appearance may be:
- changes in appetite - decrease, perversion of taste preferences, aversion to any dishes;
- periodic or frequent dyspeptic disorders - nausea, vomiting, difficulty in bowel movements;
- the constant presence of a feeling of fullness in the stomach - with or without flatulence;
- change in the color of the integumentary tissues, mucous membranes - their pallor, dryness.
The above signs are not at all specific; they can be mistaken for symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases - gastritis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis. It is necessary to evaluate all the complaints presented by a person, carefully collect not only an individual, but also a family history.
However, the lack of positive dynamics during treatment requires a more thorough examination, including tests for tumor markers.
Only after a full assessment of all the information from laboratory and instrumental examinations does a specialist make a full diagnosis - stage 2 cancer.
You shouldn’t get upset and give up – the disease can still be defeated on all fronts.
Damage to the pulmonary system
The appearance of a tumor in the area of the respiratory structures can be suspected by such manifestations of deteriorating health as an unreasonable cough and shortness of breath. They appear against the background of complete health and literally exhaust a person. In this case, no symptoms of intoxication characteristic of viral or bacterial pathologies are observed.
The nature of the cough gradually changes - attacks become more frequent, become prolonged, and are periodically accompanied by sputum production. Coughing can be provoked by inhaling cold air or physical activity.
Source: //pro-rak.ru/stadii/osobennosti-2-stadii-lyubogo-vida-raka.html
Mastectomy is an effective treatment for stage 1 breast cancer
Stage 1 breast cancer rarely recurs and there is a good prognosis for treatment, however, if necessary, the oncologist may insist on total removal of the mammary gland - mastectomy.
Scientific studies show that women who refuse surgical treatment are approximately 15 times more likely to experience recurrence. And the mortality rate among women who preserved their mammary glands is 65% higher than among those who decided to have surgery. Timely treatment at the Yusupov Hospital gives the most favorable prognosis for recovery and prevents the progression of the disease.
Purely women's problems
The most vulnerable place of the main reproductive organ of women
Cervical tumors have become significantly “rejuvenated” in recent years, which experts associate with the spread of papillomavirus infection (HPV). Meanwhile, there is a high probability of detecting a neoplastic process at the stage of its inception, and in other stages this type of oncology is relatively well diagnosed. Thus, before becoming real cervical cancer, the development of the tumor goes through several stages:
Precancerous conditions of the cervix - dysplasia,
can be treated well if treated in time, but in the last degree (CIN III) it is difficult to distinguish it by cytological method from carcinoma in situ, which is one step away from dysplasia 3 and represents the zero stage of the tumor process. Histological examination, capable of detecting invasion, copes with the task remarkably well, which makes it possible not only to recognize, but also to cure the tumor.- Stage 0 – carcinoma in situ. The prognosis is favorable; with early diagnosis, this cancer can be cured in 100% of cases.
- A predominantly favorable prognosis is also observed in the first stage of cancer, because the tumor, which has grown to approximately 4-5 cm, is still within the boundaries of the epithelium of the main reproductive organ.
- At the second stage, the malignant process leaves the uterus, but as long as it does not affect neighboring organs, the prognosis remains encouraging.
- Third stage. The tumor “takes root” in nearby tissues, thereby significantly worsening the prognosis
- The last stage is the fourth. The cancer “crossed all boundaries”, grew into the organs of the excretory (bladder) and digestive (rectum) systems, its metastases reached distant organs. Surgical treatment will no longer help, there is nothing to calm the woman down, doctors can only try to alleviate the patient’s suffering.
stages of cervical cancer
The prognosis for cervical cancer, as with other tumors, depends on the stage. Factors such as the type of cancer and the degree of differentiation of neoplasia are also of considerable importance (the higher the degree, the greater the chance of survival).
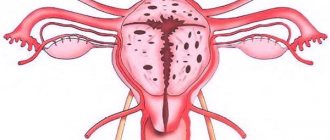
The main “killer” of gynecological oncology
Ovarian cancer, having many forms and types, is considered the most unfavorable and uncontrollable oncological process in the female genital area. The most common type is a tumor of the glandular tissue of the ovaries - adenocarcinoma, which is particularly cruel and aggressive. The insidiousness of ovarian cancer also lies in the fact that it presents particular difficulties in diagnosis. The existing symptoms are well linked to the manifestations of chronic gynecological diseases (adnexitis, uterine fibroids, etc.). However, some signs should still alert a woman:
- causeless weight loss without dieting or exercise;
- progressive enlargement of the abdomen (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity - ascites);
- indigestion.
Ovarian cancer, like other tumors, goes through 4 stages:
- The “birth” of a cancer cell, the development of the process within one ovary. The appearance of ascites is possible already at the first stage of cancer, which gives some hope for its early diagnosis and prolongation of life by 5 years in 80% of patients (of course, provided that surgical treatment is combined with other methods).
- In the second stage, both ovaries, peritoneum, fallopian tubes and uterus are affected. An enlarged abdomen (ascites) with general weight loss tells a woman about the development of a bad disease; the prognosis, of course, worsens.
- The third stage is no longer difficult to diagnose; problems can be noticed even during a routine gynecological examination. Survival rates for stage 3 cancer are low; only every tenth woman in a hundred has a chance to live five years.
- Stage 4 cancer is characterized by the spread of metastases throughout the body, but most often they can be found in the lungs and liver. There is no talk of a cure for stage 4 cancer; survival rates are reduced to zero.
The prognosis cannot be the same for everyone; one cannot speak in general about the stage of cancer and life prospects, because in each specific case other factors are taken into account: the histological features of the tumor, the age of the patient, the condition of other organs. Some people can fight longer, while others give up in the first months.
Consequences of surgical treatment of stage 1 breast cancer
At the initial stages, the consequences of surgical treatment of stage 1 breast cancer, if we are talking about breast-conserving surgery, are insignificant.
Considering that the neoplasm in the mammary gland is small in size, over time such a defect is replaced by adipose tissue. After treatment, only traces of surgery remain, which will become less noticeable over time. This type of defect can be easily corrected in cosmetology clinics, so this type of treatment should not be neglected.
Stage 1 survival
Can stage 1 breast cancer be cured? According to the US National Cancer Base, the 5-year survival rate for this stage is 100% among women who undergo treatment.
When we talk about 5-year survival rate, it does not mean that a woman will only live five years after diagnosis. This means that patients with cancer are monitored by oncologists for five years, who must make sure that recovery after cancer removal goes smoothly and that there is no need to treat relapse.
If a woman gets rid of cancer and lives without a recurrence for the first two years, the chance of the disease returning is sharply reduced. She may have to deal with other diseases and conditions, but it is unlikely that she will die from stage 1 breast cancer. The prognosis at this stage is very good.
- How to eat properly if you have breast cancer
Every year the incidence of breast cancer in women of childbearing age increases by 1... - Can breasts hurt if you have breast cancer?
Does breast cancer hurt? If I find a painful lump in my breast, is it cancer? - questions that are often asked...
- Principles of chemotherapy for breast cancer
Chemotherapy for breast cancer, as for other malignant diseases, can stop or slow down the cancer process.
Breast cancer prevention
Regular visits to the gynecologist, self-examination and mammography are the only ways to detect breast cancer in a timely manner. Oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital claim that the first pregnancy before the age of 30, breastfeeding and giving up bad habits help reduce the risk of developing cancer.
In the oncology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, in the early stages of breast cancer, they will conduct modern diagnostics, qualified treatment and provide care after the therapy. Rehabilitation programs will help return the patient to a full life. A team of professionals consisting of doctors, nurses and additional personnel will ensure a comfortable stay in the hospital in the pre- and postoperative period. To receive quality independent advice, make an appointment.
Author
Alexey Andreevich Moiseev
Head of the Oncology Department, oncologist, chemotherapist, Ph.D.
Bibliography
- ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases)
- Yusupov Hospital
- Cherenkov V. G. Clinical oncology. — 3rd ed. - M.: Medical book, 2010. - 434 p. — ISBN 978-5-91894-002-0.
- Shirokorad V.I., Makhson A.N., Yadykov O.A. The state of oncourological care in Moscow // Oncourology. - 2013. - No. 4. - P. 10-13.
- Volosyanko M.I. Traditional and natural methods of preventing and treating cancer, Aquarium, 1994
- John Niederhuber, James Armitage, James Doroshow, Michael Kastan, Joel Tepper Abeloff's Clinical Oncology - 5th Edition, eMEDICAL BOOKS, 2013