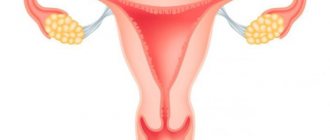
The fallopian tubes are named after the Italian physician Gabriel Fallopius, who first described their structure. These are paired hollow tubes through which fertilized eggs move into the uterine cavity. Each tube lies in a double fold of the peritoneum - the mesentery of the tube. The length of the pipe is approximately 10-12 cm. Normally, the right pipe is slightly longer than the left. Width – about 4-6 mm. The inside of the fallopian tube consists of a mucous membrane with ciliated epithelium. Thanks to the muscular activity of the tube and the oscillatory directed movements of the cilia of the epithelium, the fertilized egg is pushed towards the uterus.
What is tubal obstruction
The content of the article
Obstruction (blockage) of the fallopian tubes is one of the main causes of female infertility, in which sperm moving into the tube through the uterus cannot reach the egg to fertilize it. And if conception does occur, the large embryo does not enter the uterine cavity. In this case, a tubal (ectopic) pregnancy occurs, which is life-threatening for the woman.
For various reasons, adhesions form in pipes - dense fibers and films that glue tissues located next to each other. The resulting compaction causes obstruction of the fallopian tubes to varying degrees.
Basic methods for studying the patency of the fallopian tubes
In practice, there are several diagnostic methods for assessing obstruction of the fallopian tubes, through which the functioning of the organ is assessed throughout the entire structure of the fallopian tube and permeability is determined.
X-ray examination of the patency of the fallopian tubes is performed by injecting a contrast agent into the uterine cavity. During patency, the substance flows through the pipes and ends up in the abdominal cavity. And this is clearly determined by x-ray examination. The accuracy of such diagnostics is only 70-80%. For this reason, along with this method, other diagnostic methods are used. This procedure is usually carried out between the 5th and 9th day of the menstrual cycle in the absence of an inflammatory process. Before performing it, specialists must make sure that the patient does not have HIV, hepatitis B, C and syphilis.
Such a study is unacceptable in case of pregnancy, as well as in case of an allergic reaction to the contrast composition used. A few days before the procedure, it is necessary to exclude intimate contacts.
Along with X-ray examination, an ultrasound examination of the fallopian tubes is performed. For better visualization of the organ, a sterile saline solution is injected into the uterine cavity. In this situation, the possibility of fluid penetration into the peritoneum through the fallopian tubes is also assessed.
This method has lower accuracy compared to the previous one. Before the procedure, you should also make sure that there is no inflammatory process. A study is carried out before ovulation.
Causes: what causes fallopian tube obstruction
The pathology occurs in women of different social classes and with different lifestyles. It is mistakenly believed that its causes are only STIs and abortions. In fact, problems with the fallopian tubes are not always associated with infections and surgeries.
To understand why fallopian tube obstruction occurs, let’s consider the factors leading to the development of the disease. Having identified the problem that has become the trigger, you can understand exactly how the treatment will proceed.
Structural changes in the organ;
- Congenital underdevelopment of the fallopian tubes (often combined with uterine hypoplasia);
- Deformation of the organ (this happens after removal of adhesions);
- Damage to the mucosa (due to hydrosalpinx, inflammation, tumor).
Physiological disorders:
- Hypotonicity of the muscular layer (weak tone of the muscular layer of the appendage);
- Rigidity of the muscle layer (overstrain of the muscle layer, leading to narrowing of the lumen);
- Adynamia of fimbriae (cessation of movement of microvilli lining the inner surface of the pipe);
- Discoordination of fimbriae actions (imbalance of activity).
Functional changes:
- Infectious and inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs;
- Endometriosis (proliferation of endometrial cells beyond the inner layer of the uterine wall);
- Mechanical injury to the mucous membrane of the fallopian tube (occurs during surgery);
- Hydrosalpinx (a capsule inside the fallopian tube containing serous fluid);
- Congenital anomalies of the tube (subjective reason why there may be obstruction of the fallopian tubes);
- Disorders of embryogenesis (development of the embryo from the 1st day from conception to the 7th week of pregnancy) and postembryogenesis (birth with organs that do not correspond to the required size)
Sexually transmitted infections:
- Gonorrhea (infection caused by gonococci and leading to inflammation of the mucous surfaces);
- Syphilis (caused by a bacterium of the spirochete family, the cause of damage to the mucous membranes);
- Mycoplasmosis (the source of infection is a single-celled microorganism intermediate between a bacterium and a virus, causing infertility);
- Chlamydia (hidden infection, which causes obstruction of the fallopian tubes);
- Genital tuberculosis (causative agent ─ Koch bacterium, which affects the mucous surfaces of the tube).
What are fallopian tube diseases?
The content of the article
Female infertility in 20-30% is associated with impaired functionality or absence of the fallopian tube or both tubes. Epididymis removal is usually associated with an ectopic pregnancy, when a fertilized egg gets stuck inside the tube and begins to develop there.
Inflammatory processes threaten the occurrence of adhesions that block the lumen of the fallopian tube. Also, organ dysfunction is expressed in loss of contractility and peristalsis. Also, fimbriae, the smallest villi at the exit of the fallopian tubes, stick together after inflammation and lose their ability to capture the egg during ovulation.
Factors leading to obstruction of the appendages
To answer the question of what causes fallopian tube obstruction, the gynecologist has to carefully study the woman’s entire reproductive system. In many cases, pathology is provoked by factors associated with processes occurring in neighboring organs.
Internal factors include diseases of the uterus and ovaries:
- Uterine fibroids (a benign neoplasm in various layers of the uterus; when large, it puts pressure on neighboring organs, deforming and disrupting the blood supply);
- Endometrial polyps (benign formations inside the uterine cavity);
- Ovarian cyst (formation in the structure of the ovary with fluid inside).
Hormonal disorders:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (multiple neoplasms in the ovaries caused by hormonal disorders);
- Adrenal dysfunction (failure of the organ);
- Ovarian dysfunction.
External factors include the following conditions:
- Peritoneal factor (external compression of the fallopian tube);
- Inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity;
- Chronic sluggish appendicitis (inflammation of the appendix);
- Oophoritis (inflammation of the ovaries);
- Peritonitis (inflammation of some parts of the peritoneum);
- Enterocolitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the large and small intestines);
- Proctitis (inflammation of the rectum);
- Urethritis (inflammation of the ureter).
Inflammation in these organs also spreads to nearby pipes.
What are fallopian tubes
The uterine or fallopian tubes were named after the physician of Italian origin G. Fallopius, who first described the anatomical structure of the designated organ.
This medical term should be understood as a paired organ located almost horizontally on each side of the uterine fundus. Visually, this organ resembles cylindrical canals or tubes, one end of which opens into the abdominal cavity, the other opens into the uterine cavity.
In a healthy state, the right side of the organ is much longer than the left. The diameter of these channels is about 4–6 mm. On the inside, each of the fallopian tubes has a mucous membrane with a ciliated skin covering on the inside. The activity of the muscles and the oscillating movements of the cilia in the epithelial lining of the tubes help push the fertilized egg towards the uterus.
Surgical procedures that cause tubal obstruction
Medical manipulations, or rather their consequences, which negatively affect the functionality of the appendages:
- Curettage (removal of the fetus by curettage, an undesirable consequence - inflammation or infection)
- Diagnostic uterine curettage (removal of the endometrial layer inside the uterus);
- Failed IVF;
- Incorrectly installed intrauterine device (injures the wall of the organ, provokes infection);
- Difficult childbirth.
Surgery often leads to complications that cause problems with women's health. After surgery, the risk of the following diseases increases:
- Myomectomy (removal of fibroids from the muscular layer of the uterus);
- Tubotomy (laparoscopic surgery on the fallopian tubes);
- Cystectomy (removal of a tumor inside the ovary);
- Appendectomy (emergency surgery on the appendix);
- Treatment of ruptured ovarian cyst.
If complex operations on female organs are rare, then every second woman undergoes abortions and curettage. Even if the termination of pregnancy was completed without complications, small fragments of embryonic tissue may remain in the uterus. The decomposition of residues causes inflammation of the organ, which... It spreads to the fallopian tubes. If urgent measures are not taken, the areas of inflammation will heal and become hard and inelastic.
In some cases, hydrosalpinx is formed - a benign neoplasm with serous fluid inside, which blocks the lumen of the tube, preventing pregnancy. After removal of the hydrosalpinx, the lumen of the appendage increases, but the fimbriae can no longer function normally. Infertility occurs, which is not treated conservatively.
Drug treatment
If obstruction of the oviduct is caused by an inflammatory process, then treatment should be started immediately. Advanced stages of inflammation are accompanied by changes in the structure of the mucous membrane and then the drug method will be ineffective.
Conservative treatment is carried out using the following groups of drugs.
- Anti-inflammatory: phenylbutazole and cortisone, diclofenac, indomethacin or aspirin. The drugs are used in the form of suppositories or tablets. In addition to the anti-inflammatory effect, they have antipyretic and analgesic properties.
- Antibacterial: gentamicin or kanamycin, chloramphenicol, metronidazole or tetracycline. The drugs are effective in the fight against microorganisms (if the obstruction was caused by their activity).
- Hormonal drugs are prescribed for vascular and trophic disorders provoked by inflammatory processes.
- Sedatives in the form of vitamins, calcium and immunotherapy stimulate the immune system.
The selection of drugs, their dosage and duration of use is carried out by a surgeon or gynecologist. Throughout the course, the patient visits the attending physician, who determines the effectiveness and makes adjustments to the prescription as needed.
Conservative treatment is recommended to be combined with physiotherapy:
- Balneotherapy;
- Ultrasound therapy;
- Electrophoresis using magnesium, calcium and biogenic stimulants;
- Gynecological massages;
- Electrical stimulation of the pelvis.
If drug therapy does not have an effect, a decision is made on surgical intervention.
Surgical methods
Surgical intervention can solve problems with mechanical closure of the lumen in the fallopian tubes. Main directions in surgery:
- The laparoscopic method is most often used. The operation is performed through small openings in the abdomen, through the anus, or through the vagina. If complications or new data about the disease appear during the procedure, the course of the operation may change, and the doctor decides to use the laparotomy method.
- The laparotomy method is performed by dissecting the abdominal wall. More often used to remove tumors. In the absence of postoperative complications, the woman is discharged from the hospital on the 5th day.
- The reconstructive method involves the use of synthetic materials, thanks to which we expand the lumen in the pipes.
Modern medicine offers a fairly large selection of methods to cure tubal patency. With successful treatment, a woman can become pregnant within the first year. But the problem may arise in the future. The pathology of tubal obstruction can recur. There are also cases when the problem is solved and the egg is successfully fertilized, but its transportation to the uterine cavity does not take place. For a woman, this ends in an ectopic pregnancy and emergency surgery.
Types of tubal obstruction, pregnancy prognosis
During fertilization, both the organs of the woman’s reproductive system and the endocrine glands, central nervous system, and immunity are involved. A malfunction in at least one link in the chain leads to the development of a disease leading to tubal obstruction. Based on a number of criteria, tubal obstruction has a complex classification.
According to the degree of lumen blockage:
- Unilateral obstruction
. If there are no anatomical abnormalities in the second fallopian tube, then nothing interferes with conception, although the probability of pregnancy is reduced by 2 times. It manifests itself as irregular periods, pain in the lower abdomen, when the egg does not enter the uterus due to blockage of the lumen or due to ectopic pregnancy. - Bilateral obstruction
. 100% leads to infertility. Less common than unilateral. The causes are a consequence of inflammation, hormonal imbalance or other factors. Menstruation sometimes disappears when the fallopian tubes are obstructed on both sides.
According to the degree of lumen blockage:
- Partial obstruction
. The lumen of the epididymis is not blocked, leaving space for the passage of the egg and sperm. But the zygote will no longer be able to penetrate, and the risk of ectopic pregnancy increases. - Complete obstruction
. In this case, there is not the slightest gap left, even serous fluid does not pass through. Fertilization does not occur, the problem means complete infertility.
Due to obstruction:
- Anatomical
. The procedure for obstruction of the fallopian tubes in this case manifests itself in swelling of the mucous membrane, hydrosalpinx, tumors, adhesions, etc. The cause of anatomical changes is inflammation, which is eliminated with antibiotics, and the consequences - with surgery. - Functional
. The tissues of the fallopian tube have no functional changes, there are no adhesions or inflammations, but the organ does not work. The cause is diseases of the central nervous system caused by stress. As a result, the villi (fimbriae) cease to perform the function of capturing the egg, and the appendages lose the ability to peristalsis. - Hormonal
. When there is a hormonal imbalance, the villi stop moving and stick together, blocking the lumen. In some cases, tubal obstruction can be treated with medications and does not require surgery.
Obstruction of the fallopian tubes is not a death sentence; treatment, the price of which depends on the complexity and scale of the work, often brings positive results.
Phimosis of the infundibulum of the fallopian tube and fimbriae
Despite its small length (7-12 cm), the fallopian tube consists of several sections. The outermost section, the infundibulum, opens into the abdominal cavity. The fallopian tube does not directly contact the ovary.
Conception would be impossible if it were not for the fimbriae - the thinnest villi 1-5 cm in length, and the largest, fimbria ovarica, reaches directly to the ovary and rests on it. Without fimbriae, fertilization will simply become impossible.
Shortly before ovulation, follicle-stimulating hormone and estrogen stimulate blood circulation, causing the fimbriae to swell and move. They look like a fringe enveloping the ovary. When the follicle ruptures and leaves the egg, the fimbriae capture it and move it inside the fallopian tube. Thanks to the active blood supply, the walls of the organ begin to actively contract, moving the egg forward.
With inflammation caused by infections, the fimbriae stick together and lose mobility. The egg is freely released, but is not captured and does not end up inside the epididymis. She ends up in the abdominal cavity, where another danger awaits her.
With good lumen of the fallopian tube, the sperm passes through it and also exits into the abdominal cavity. There he has a certain chance of meeting an egg and fertilizing it. In this case, the zygote is attached near the site of fertilization: to the outer wall of the uterus, to the ovary or even to the liver, but this happens extremely rarely.
Where adhesions form, prognosis for cure, depending on location
The length of the fallopian tube is 10-12 cm, and the width depends on the specific section:
- Distal section (funnel)
. The fallopian tube in this section smoothly passes into the abdominal cavity, and the edges of the opening are bordered by microvilli (fimbriae). They are needed to gently capture the egg expelled from the ovary and direct it into the lumen of the appendage. Blockage in this department is not associated with external factors, because the funnel itself is wide. The narrowing of the lumen is caused by congenital pathologies. With proper surgical treatment, patency can be restored in more than 50% of cases. - Isthmic department (isthmus)
. A short and narrow section that passes into the uterine section. The lumen is blocked due to inflammation of the mucous surface, infection, etc. - Intramural (uterine) section
. A narrow section through which the embryo enters the uterus through an opening in the wall of the organ. Narrowing of the lumen occurs due to endometrial polyps or spasm of the smooth muscles of the uterus. The uterine section of the fallopian tube is a narrow section, so its obstruction means that the opening of the fallopian tube is blocked. If adhesions and neoplasms in other sections are subject to laparoscopic removal and further restoration of the functionality of the organ, then the intramural section is not subject to reconstruction. - Ampullary section.
This is the wide and long part of the fallopian tube where the oocyte meets the sperm and the zygote is born. The lumen narrows due to external compression (pressure from hydrosalpinx, tumor). If the cause of compression is promptly eliminated, patency is restored.
If obstruction of the fallopian tube in the ampullary section is caused by sexually transmitted infections, hypothermia and other unfavorable factors leading to inflammation of the surface of the appendage, then this threatens ectopic pregnancy.
Pathology occurs due to the formation of adhesions - a strip of connective tissue formed at the site of inflammation. Microfibers (fimbriae) lose mobility, stick together and form a bubble where serous fluid accumulates (hydrosalpinx). As a result, the fallopian tube loses its ability to peristalsis due to scarring, its lumen narrows, creating tubal obstruction.
Paired organ structure
If we talk about the structure of the fallopian tube, it includes 4 sections along its entire length. They extend to the sides, starting from the body of the uterus in an almost horizontal position and ending in an expanded part that has a fringed structure and is called the funnel.
Recalling the structure of the fallopian tube, it should be said that these funnels are located very close to the ovary, where the egg is born, which subsequently collides with the sperm.
The funnels are followed by the ampullary part of the tube, after which the fallopian tube begins to gradually narrow. This section of the isthmus is called in medicine the isthmic part.
The anatomical features of the fallopian tubes are such that they end in the part of the same name. And it is there that the pipes make the transition to the muscular organ.
Tubal obstruction: signs, symptoms, sensations
Fallopian tube obstruction does not have characteristic signs or pronounced symptoms, so it is difficult to say what sensations are typical for this disease. Often the problem is discovered only when it is not possible to get pregnant for a long time. But the root causes that caused the pathology can give quite noticeable symptoms.
Any thematic forum eloquently talks about what symptoms of fallopian tube obstruction are most common. Many women note that the main sign of obstruction of the appendages, which forced them to turn to a good gynecologist, is the absence of a long-awaited pregnancy within a year of regular sexual relations.
Most symptoms are associated with a reduction in adhesions - areas of connective tissue formed at sites of inflammation. Frequent signs of obstruction of the fallopian tubes and adhesions:
- Pain in the lower abdomen when cleaning, doing fitness, intensive walking, caused by the inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes;
- Increased temperature, fever are also symptoms of inflammation;
- Discharge mixed with pus and leucorrhoea;
- Pelvic pain syndrome - constant pain in the lower abdomen;
- Algomenorrhea (painful periods);
- Bladder problems (frequent urge, painful urination);
- Disorders in the functioning of the rectum (painful bowel movements, constipation);
- Inability to have sex due to severe pain in the genitals.
The main symptom of obstruction is ectopic pregnancy. It occurs only with pathological narrowing of the lumen of the appendages or with hydrosalpinx.
Another important symptom of tubal obstruction is irregular periods. With complete obstruction of the appendages, menstruation will be absent altogether if the disease of the reproductive organs affects the ovaries. In this case, the egg does not mature, ovulation does not occur, and the endometrium stops growing.
In Vitro Fertilization
If drug therapy does not give the desired effect, that is, pregnancy still does not occur, then the procedure of in vitro fertilization is recommended. For this manipulation, an egg is collected from women, and sperm from men, after which fertilization is carried out in the laboratory.
After 3-5 days, the embryo is placed in the patient’s uterus for subsequent gestation. This method of reproductive technology is recognized as the most effective. It is resorted to in case of complete obstruction of the tubes or in the presence of serious disorders at the cellular or chemical level in the man’s sperm.
In conclusion, it should be added that obstruction of the fallopian tubes cannot in any way be considered a serious pathology for women, but it is still fraught with the development of infertility. If the necessary actions are not taken in time to correct the indicated condition, then an ectopic pregnancy is possible, as a result of which the patient may lose one of the tubes, which significantly reduces the chances of becoming pregnant. Here you cannot rely only on traditional medicine or self-medicate, since such actions can only aggravate the situation. In order to receive adequate help, you need to contact specialists.
How to find out about obstruction of the fallopian tubes: diagnosis
In 25% of cases of infertility in women, the cause is obstruction of the fallopian tubes. How to detect obstruction of the fallopian tubes, since diagnosis is complicated by the fact that a woman, according to subjective feelings, does not know the symptoms of the disease?
You can find out about obstruction of the fallopian tubes only through an examination by a gynecologist. To ensure the accuracy of the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a series of tests, and the pelvic organs are also examined using the latest medical technology. There are methods that simultaneously establish a diagnosis and eliminate problems with the patency of the appendage.
Unfortunately, the examination can be lengthy and difficult, since a biochemical blood test and urine test can only determine the cause of the obstruction - inflammation. If it is not there, the only reliable diagnostic methods are ultrasound of the uterus and invasive methods.
Primary mandatory tests:
- Flora smear
(determines the ratio of pathogenic and lactic acid microflora). - Biocenosis smear - reveals a different number of infections, for example, femoflor gives an answer to 16 indicators;
- Enzyme immunoassay for antigens
to infectious agents (ELISA). - Serodiagnosis (determines the reaction of the patient’s serum to the protein of pathogenic microbes).
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko.
It reveals the ratio of leukocytes, red blood cells and cylinders, determining inflammation of the genitourinary tract. According to Nechiporenko’s analysis, a complete picture of the general condition of the body is visible.
Non-invasive techniques - pelvic ultrasound - are highly informative:
- Comprehensive ultrasound of the pelvic organs
. Includes (through the abdominal wall) examination method. Allows you to see complete or partial obstruction of the fallopian tubes. - Detailed ultrasound of the ovaries, appendages and fallopian tubes. Clearly demonstrates adhesions and other processes in organs.
- Detailed transvaginal ultrasound of the uterus. Determines inflammation and tumors in the organ.
- Hydrosonography
. The uterus fills with colored fluid, which is distributed along the fallopian tubes. Then, using an ultrasound machine, the doctor observes the uniform spread of the saline solution. If there are areas of obstruction, this will be reflected on the screen. The method is not as effective as laparoscopy, but is safe and does not require surgery.
Ultrasound can detect tubal obstruction quickly, safely and without pain, so it is performed first. If the examination is inconclusive, the patient is referred for further examination.
Adnexitis and salpingitis on ultrasound
Adnexitis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries) and salpingitis (inflammation of the appendages) are the most common diseases leading to infertility in women.
After suffering from inflammation of the fallopian tubes, every 4th patient develops a hormonal disorder of the ovaries, which results in decreased sexual desire or pain during sex and, as a result, problems in family life. In 40-60% of cases, adhesions and obstruction of the appendages are observed. Half of women have menstrual irregularities; periods are painful and delayed.
If adnexitis was caused by an infection, it often spreads to nearby organs, and the patient develops pyelonephritis, cystitis, and intestinal inflammation.
The main cause of inflammation of the fallopian tubes is the penetration of infections into them. Moreover, it is not necessary that a woman lead a promiscuous lifestyle and often change sexual partners. Although the main provocateur is STIs. It is enough for a woman to become hypothermic, and ordinary thrush or vaginosis will worsen, and pathogenic microorganisms will move along the ascending path into the fallopian tubes. Sometimes the infection is transmitted through the blood due to inflammation of neighboring organs (appendicitis, inflammation of the intestine).
Most often, adnexitis or salpingitis manifest themselves quite clearly. A woman experiences severe pain in the lower abdomen, not associated with her period. The attack lasts about 10 minutes, but it is very strong and impossible not to notice. If a woman’s body is young and healthy, self-healing occurs in rare cases. But basically, the disease becomes chronic, which does not manifest itself with significant symptoms, but has a destructive effect on the reproductive system.
Symptoms of salpingitis or adnexitis:
- periodic aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- slight increase in body temperature (37-37.20C);
- copious vaginal discharge in the form of mucus with an unpleasant, pungent odor;
- various menstrual cycle disorders (delay, too long or short cycle);
- libido decreases;
- painful sexual intercourse.
Adnexitis is a consequence of advanced salpingitis, and to the above symptoms is added the formation of adhesions in the ovaries and, as a consequence, the impossibility of pregnancy due to the lack of release of the egg. Self-medication and lack of normal treatment lead to a long-term inflammatory process and the development of infertility.
Diagnosis of inflammation of the fallopian tubes includes an examination by a gynecologist, analysis of microflora from the cervix and a mandatory ultrasound examination. A doctor examines a patient in a gynecological chair using medical mirrors.
Usually, with salpingitis or adnexitis, mucus with elements of pus is visible on the walls of the vagina and cervix, and the cervix itself is covered with erosion or has signs of dysplasia. During palpation, the gynecologist feels compaction of the fallopian tube, pain when touched, and also, with the development of adhesive processes, poor mobility of organs.
The most informative diagnostic method is ultrasound. Normally, the fallopian tubes are not visualized, but when they become inflamed, fluid or pus accumulates in them, and they are clearly visible on the monitor screen.
A high-precision vaginal sensor allows you to identify characteristic signs of inflammation of the appendages:
- in acute salpingitis, the fallopian tube has a curved shape in the form of a spindle;
- the ampullary section is expanded and looks like an inverted 8;
- the walls of the appendage are thickened to 5 mm;
- there is anechoic or hypoechoic content inside;
- the walls are vascularized (filled with blood).
If the patient has adnexitis, the following is added to the symptoms:
- unclear outline of the ovaries;
- spherical shape of the ovaries;
- follicles are almost not visualized;
- Fluid accumulates behind the uterus.
If an abscess has begun, then the ovaries and appendages are blurred on ultrasound, presenting contents with a complex echo structure with pronounced cysts. Hyperechoic inclusions with an acoustic shadow mean air bubbles and connective tissue partitions. The area of inflammation is intensively supplied to the tissue, which is clearly visible when the Doppler mode is turned on.
Blood tests are taken directly at the clinic, so there is no need to take tests elsewhere. It shows the level of leukocytes, which increase when the body is infected, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and a biochemical blood test will help the doctor better understand the patient’s health status. A vaginal smear reveals the causative agent of the infection that caused the inflammatory process.
Bacterial culture from the cervix is informative when selecting an antibacterial drug in the treatment of infection. It helps determine the sensitivity of microorganisms and resistance to certain pathogens.
How to determine obstruction of the fallopian tubes using fluoroscopic diagnostic methods
Effective fluoroscopic methods for diagnosing diseases of the appendages are prescribed as necessary, since they are associated with radiation. Radiography and hysterosalpingography (HSG) are usually performed.
The HSG procedure is as follows. Using a rubber tube, a contrast liquid (containing Ultravist, Triombrast iodine) heated to body temperature is injected into the woman’s uterus through the cervical canal. The fluid enters the appendages and, if there is an obstruction, is not distributed further.
Then x-rays are taken, in which, thanks to the contrast agent, the adhesions are visible - in the pictures they are visible as white stripes. If there is hydrosalpinx, the image will show a capsule with translucent contents. If the fluid is distributed in a thin stream and does not fill the lumen, this indicates partial obstruction.
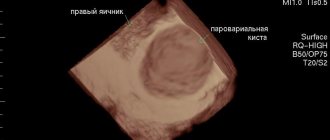
Hydrosalpinx on ultrasound
Hydrosalpinx is an obstruction of the lumen of the fallopian tube by a hollow formation in which serous fluid (sactosalpinx), pus (pyosalpinx) or blood (hematosalpinx) accumulates. Hydrosalpinx occurs at the site of adhesions, from which a capsule of connective tissue is formed, gradually filling with water. It can burst, and then the contents fall into the fallopian tube. There is a threat of developing an abscess and infection of neighboring organs.
Ultrasound diagnosis of hydrosalpinx is carried out without filling the fallopian tubes with contrast liquid. The appendages are visible only when they are swollen or filled with fluid. On the monitor you can see the expansion of the fallopian tube due to the filling of the capsule with serous substance.
Hydrosalpinx will be visualized on days 5-9 from the beginning of the cycle, but then the data will be unreliable. The procedure is not performed before the 5th day of the cycle, otherwise you may miss an ectopic pregnancy. In the 2nd half of the cycle, the endometrium grows, which also distorts the results.
How to determine fallopian tube obstruction using endoscopic methods
The endoscopic method has been used for many years to make an accurate diagnosis in gynecology. The gynecologist may prescribe one of the procedures:
- Diagnostic laparoscopy
. This is a minimally invasive diagnostic method in which an optical laparoscope with a microcamera at the end is inserted through a small hole in the abdomen. The image is displayed on the screen and enlarged 6 times. The method is contraindicated if the patient has adhesions between the pelvic organs. - Laparoscopy with chromohydroturbation.
It is carried out under anesthesia. The patient is given three punctures in the abdominal wall, through which the laparoscope is inserted. The blue-tinted saline solution shows areas of obstruction in the fallopian tubes. - Transvaginal hydrolaparoscopy (fertiloscopy)
. The endoscope is inserted through the vagina and a contrast agent is injected through a thin tube. It differs from laparoscopy with chromohydroturbation in the absence of the need for anesthesia, but the results will not be as reliable.
Perturbation hydroturbation
This method of medical correction is quite outdated, but in some institutions it is still carried out. It can also be quite painful for the patient.
The essence of the manipulation is that a woman in a gynecological chair is inserted into the uterus and air or a special liquid is supplied through the catheter. Under strong pressure, the fallopian tubes straighten, and the adhesions spontaneously break. The manipulation is carried out under the control of an ultrasonic sensor.
The disadvantage of this method of treatment is that severe stretching of the fallopian tubes may occur and displacement from their usual place.
Treatment of adhesions in the appendages and other causes of obstruction
Is adnexal obstruction treatable? Yes, it is being treated, this is evidenced by numerous reviews that former patients post on forums. Treatment is carried out comprehensively and is aimed at eliminating the cause of the pathology - STIs, hydrosalpinx, etc.
Medication method
used in the treatment of acute forms of the disease. It consists of constantly taking medications at a certain dosage. The drugs have different effects on the body: some suppress the vital activity of pathogenic microorganisms, others relieve inflammation, and others resolve adhesions. Medicines are available in the form of tablets and suppositories.
Use of anti-inflammatory drugs:
- Non-steroidal (analgesics): simultaneously relieve inflammation, relieve pain and relieve fever. They block the production of enzymes - prostaglandins, produced when an infection enters the body. They are not synthetic, so they are taken longer than steroid drugs.
- Steroids (glucocorticosteroids are hormones produced by the adrenal glands). They are divided into natural and artificial. The principle of action is to suppress the production of leukocytes produced during inflammation. Tissue erosion at the site of inflammation disappears, pain and fever go away. But steroid drugs cannot be taken for a long time; they are effective for acute inflammation and severe forms of infection.
- Antibiotics
. A drug that destroys pathogenic bacteria can cure obstruction of the fallopian tubes, or more precisely, eliminate the cause of the dysfunction of the appendages - STIs. Antibiotics are taken under the supervision of a doctor in dosage. There is a threat that with long-term use, normal microflora will be suppressed. Therefore, before prescribing antibiotic treatment, the patient undergoes a test for the sensitivity of the microbe to the active substance. Throughout treatment, the types of antibiotics are changed so that microbes do not adapt to the drug. - Hormone therapy
. Often gynecological problems, including blockage of the lumen of the appendages, are caused by hormonal disorders. Depending on how tubal obstruction is treated, the patient is prescribed natural or synthetic hormones that suppress or restore the normal functioning of the organ. - The surgical method
is used in advanced cases, as well as when medication and physiotherapeutic methods become ineffective. Before surgery, the patient undergoes diagnostics to determine the impassable area. It is usually affected by adhesions, overgrown connective tissue or scars. There are various methods of surgical intervention, each of which is effective in a particular case.
Laparoscopy has proven itself to be excellent. This is a minimally invasive method in which the peritoneum of the patient is punctured in several places, and a laparoscope, a long tube with optics and a camera at the end, is inserted through the punctures. With the help of a camera, the image is visible on the screen, and the optics magnify it 3-4 times. The doctor removes adhesions and scars, instantly cauterizing the operated area.
In some cases, laparotomy relieves obstruction of the appendages. An incision is made along the bottom of the peritoneum through which surgery is performed. After the operation, a scar remains and the woman remains in the hospital for at least 5 days.
Reconstructive surgery works in a similar way. It involves transplanting a healthy section of the donor tube to the site of the damaged one. Or this is an artificial restoration of the lumen.
Treatment
https://youtube.com/watch?v=hd6jtRyAdyo
Therapy for pathology must be appropriate and timely. Only a qualified specialist can select treatment tactics and only after conducting an examination and clarifying the cause of the blockage of the pipes. There are two approaches to treating the disease – medication and surgery.
Drug therapy
The main goal of drug treatment is to eliminate inflammation
It is very important to start treatment in a timely manner. Advanced inflammation is fraught with the development of degenerative changes in the mucosa
Often, the following medications are prescribed to treat the disease.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Indomethacin, Aspirin, Diclofenac, Cortisone, Phenylbutazone. These drugs have pronounced analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties.
- Antibacterial agents. Drugs in this group are prescribed when bacterial flora is detected. The following medications are often prescribed: Kanamycin, Gentamicin, Tetracycline, Metronidazole, Chloramphenicol. These medications have a wide spectrum of action, that is, they help destroy various types of pathogens.
- Hormonal drugs. Hormones are prescribed for vascular and trophic disorders associated with inflammation.
Along with the above medications, the use of sedatives, vitamins and calcium supplements may be prescribed.
Non-surgical treatment is almost always combined with physiotherapeutic procedures:
- balneotherapy;
- ultrasound therapy;
- electrical stimulation of the uterus and appendages;
- gynecological massage.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is often necessary. This is due to the fact that medications can only combat functional disorders, while the cause is often mechanical blockage of the lumen.
The main types of surgical therapy include: laparoscopy, laparotomy and reconstructive surgery
The most effective method of therapy is the use of laparoscopy. During the operation, a hole is made with a needle through which inert gases (carbon dioxide or nitrous oxide) are introduced. These gases are harmless and also have pronounced analgesic properties.
Thanks to the additional gas, it is possible to move the organs apart, which gives doctors excellent visibility. If problem areas are detected, an operation is performed - additional holes are made in the abdominal wall through which small surgical instruments are inserted. The surgery takes place very quickly. Short and recovery period. After approximately two to three days, the patient can return to her normal life.
As for laparotomy, this method consists of dissecting the anterior abdominal wall. It is performed in case of peritonitis or to remove tumors in the pelvic or abdominal cavity. After the operation, a scar remains. In addition, the recovery period after surgery, compared to laparoscopy, is much longer - at least a week.
Reconstructive surgery involves the use of synthetic materials to expand the tubal lumen. However, this technique is rarely used due to the lack of uniform requirements for materials and technology.
Pregnancy with fallopian tube obstruction
The ability to get pregnant with this disease depends on several factors: the tube is narrowed or blocked, one-sided or two-sided blockage.
With complete obstruction, the egg will not be able to penetrate the uterus, so the lumen is completely blocked. If a woman is diagnosed with a complete blockage of both tubes, she will not be able to get pregnant naturally. In this case, assisted reproductive technologies are used, including IVF.
In case of incomplete obstruction, only part of the lumen is closed. And since a certain part of the lumen is open, the egg can penetrate the uterus, and pregnancy can occur. Even if both tubes are partially narrowed, there is still a chance of pregnancy. Of course, the chance of conception is several times lower than with normal patency of the fallopian tubes, but it still exists, so you can get pregnant.
Additional treatments
Additional methods of treating tubal infertility are different options for physiotherapy:
- Electrophoresis
. It has an immunocorrective effect, which consists in exposing the area of the body where the drug is placed to a direct electric current. Medicines are absorbed through the skin in the form of positively and negatively charged ions. In addition, the electromagnetic field improves blood supply and resolves adhesions. - Balneotherapy
. It consists of treatment with mineral waters (nitrogen-siliceous, sodium chloride, hydrogen sulfide). The beneficial effects of medicinal water normalize hormonal levels, relieve pain and inflammation, and calm the nerves. - Ultrasound therapy
has shown high effectiveness in resolving adhesions. This is an in-office procedure in which local areas are exposed to ultrasonic waves. As a result, adhesions soften, blood circulation improves, and soft tissues become elastic. - Treatment with an electrical stimulator.
This way even old scars are eliminated. Using a special apparatus, the area of the fallopian tubes is exposed to electrical impulses with a frequency of 12 Hz. Muscle contraction occurs, as a result of which the lumen of the tube expands, scars and adhesions soften.
With minor damage to the appendages, gynecological massage will help. It is performed by a gynecologist in an examination chair, then the reproductive organs are manually massaged through the vagina. It is rarely used, but it is also quite effective and safe.
Traditional methods can also complement treatment. The boron uterus, which grows in Altai, has shown itself to be effective. It controls estrogen levels. The herb is brewed as a tea along with wintergreen, a plant in the heather family that has antiseptic and healing properties. St. John's wort, flax seeds, sweet clover, coltsfoot, and knotweed help eliminate tubal obstruction.
Using folk recipes
Traditional medicine is not officially recognized. One of these is borovaya uterus, which was previously widely used, especially in the Siberian region. It is generally accepted that this plant has anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and diuretic effects.
Alcohol and water infusions using boron uterus in the treatment of tubal infertility have survived to this day. In the first case, to prepare the product you will need 50 g of a medicinal plant and half a liter of vodka. In the case of a water infusion, you need to brew 1 teaspoon of crushed medicinal herbs in 1 glass of boiled water, and then leave it in a water bath for 15 minutes.
The alcohol infusion must be taken by dissolving 30-40 drops in a small volume of water, 3 times a day before meals. The course of treatment should continue for 6 months. In this case, one week of taking the drug should be followed by a 3-week break. During menstrual bleeding, taking boron uterus is unacceptable.
We must not forget that while taking boron uterus, an allergic reaction may develop. Therefore, before starting treatment, you should consult your doctor.
Where is tubal obstruction diagnosed and treated in St. Petersburg?
When faced with a problem, women ask the question: where and how to treat obstruction of the appendages, what to do? First of all, you need to go to a good clinic in St. Petersburg and establish the cause, and then eliminate the consequences. At the same time, you cannot self-medicate - this leads to the transition of the disease to an advanced form.
If you suspect tubal obstruction, seek qualified help at the Diana specialized clinic. Here you can inexpensively undergo examination using the latest equipment and be cured of infertility associated with this pathology.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Damage to the ampullary sections of the fallopian tubes
Home » Gynecology » Damage to the ampullary sections of the fallopian tubes
Predominant damage to the ampullary sections of the fallopian tubes has been described in all types of salpingitis of specific and nonspecific etiology, even in experiments. According to classical concepts, the predominant damage to the ampullary sections of the fallopian tubes in all types of specific and nonspecific infections is a protective mechanism that prevents the spread of infection during ascending and descending salpingitis.
Thus, with an ascending infection, damage to the ampullary parts of the fallopian tubes and their rapid closure prevent the development of pelvioperitonitis, while with a descending infection, damage to these parts of the fallopian tubes prevents the spread of infection to the remaining parts of the fallopian tubes and the uterus.
The peculiarities of blood supply to the ampullary sections of the tubes, such as venous lacunae and arteriovenous anastomoses, as well as the predominance of ciliated epithelium, unstable to damaging factors, especially infectious agents, determine the predominant damage to these sections of the fallopian tubes in all types of infection, regardless of the type of infection and the routes of its entry into the tubes. A pronounced inflammatory process in these parts of the tubes with subsequent adhesion of fimbriae in places of death of the ciliated epithelium and scarring leads to gross anatomical changes in the tubes such as saccular inflammatory pseudotumors - hydrosalpinx.
In hydrosalpinxes, the ratio of ciliated and secretory epithelium changes towards an increase in the number of secretory cells that continue to function in conditions of closed hydrosalpinxes. In this case, a vicious circle appears: the accumulation of fluid in the closed cavity of the fallopian tube leads to increased pressure and progressive atrophy of ciliated cells, an increase in the number of secretory cells and an even greater accumulation of inflammatory exudate, which again has a negative effect on the remaining ciliated cells. With the long-term existence of hydrosalpinxes, the ciliated cells die and the prognosis for cure and restoration of tube function approaches zero.
According to WHO summary data, in collaborating centers, complete occlusion of the fallopian tubes was found in 14.2% of those examined, and post-inflammatory changes in the fallopian tubes that do not lead to complete occlusion were diagnosed in 9.2% of those examined. These figures indicate that more than 20% of patients with infertility have pronounced anatomical changes in the fallopian tubes.
T. Pshenichnikova
“Damage to the ampullary sections of the fallopian tubes” and other articles from the section Infertility in Marriage
Why is it better to have tubal plastic surgery at the Swiss University Hospital?
- Our clinic welcomes leading specialists - recognized international and Russian authorities in the field of surgery, including gynecology.
- Every year, the Center performs more than 1,000 unique operations, many proprietary techniques were developed by doctors at our clinic, some of them are performed only in a few Russian medical institutions, including ours.
- Our specialists are fluent in all techniques used in the treatment of infertility. Thanks to the skill of our surgeons, more than 600 children were born, whose mothers were treated in our clinic for infertility.
- During treatment, the Center uses the most modern technologies, for example, to prevent the appearance of adhesions during surgery, all types of anti-adhesive barriers are used, including gels and self-absorbing membranes.
Indications
Tubal ligation is carried out on the basis of voluntary consent (for medical reasons or at the will of the patient), and the doctor has no right to carry out the procedure without the consent of the patient. Surgical sterilization is regulated by the Code of Fundamentals of Legislation of the Russian Federation of 1993.
The document states that for the operation to be carried out, two conditions must be taken into account:
- the woman must be at least 35 years old;
- At the time of surgery, the patient must have two or more children.
If there are medical indications for sterilization, then a woman has the right to undergo DHS, even if the conditions prescribed by law are not met. This type of contraception in incapacitated patients and women suffering from mental illness can only be performed on the basis of a court decision .
If the operation is carried out on the initiative of a woman, the indication will be the desire for protection against conception.
Surgical sterilization is also carried out for medical reasons, when pregnancy and childbirth are unacceptable due to the woman’s health.
Medical indications for sterilization include:
- cancer;
- genetic and;
- serious organs;
- hematological diseases
.
Diagnostic methods
Only a gynecologist can diagnose the disease and prescribe effective treatment.
Hysteroscopy has found the greatest application. Inflammation, cyst, tumor are determined with a high degree of accuracy. Hysteroscopy is indispensable to identify adhesions. Its consequence is obstruction, which is often followed by ectopic pregnancy. The pipe is expanded and takes on a deformed appearance. Hysteroscopy allows you to confirm or refute the preliminary diagnosis. Based on its results, a decision is made on how to treat, whether surgery is needed, and what kind. Hysteroscopy is not a surgical procedure, but has the same therapeutic effect as laparoscopic surgery. It helps to clean the fallopian tubes and remove adhesions formed in them. Like hysteroscopy, USGSS is no less informative. If there is a cyst, inflammation, or fluid inside or outside the tube, then an ultrasound will show their presence and location. When symptoms indicate infections that cause inflammation, blood, urine, and vaginal microflora are examined. They are used to judge which viruses or bacteria served as the source of infection. Depending on their type, a course of antibiotics is prescribed.
Reviews
I have two children. Both girls. During my second pregnancy, my husband and I did not know the sex of the child, and after the cesarean section the doctor said that I could no longer give birth, as there were difficulties and the sutures on the uterus began to come apart from the first operation. I didn’t think much and said that if you need to bandage it, bandage it. I can’t say that I regret it, however, when my husband found out that we were having a girl, he said that the third time it would be a boy. And I tell him - no, dear, we won’t have a son. Sometimes there is a desire to give birth again, because I am still so young, and besides, I see how my husband looks at little boys. But then I remember that I could even die if the stitch comes apart during my third pregnancy, and my babies are left without me - the desire immediately disappears.
Madina, Ufa, 28 years old
I took the plunge and did a tubal occlusion. My eldest son was born in my first marriage and is absolutely healthy, but the younger ones have problems. The geneticist said that my husband and I are incompatible. I think it's his genes. In general, I won’t give birth again - that’s for sure. In addition, after the birth of my third baby, I had a medical termination of pregnancy. I didn’t put in an IUD, I know that he doesn’t give a full guarantee either, but I don’t want to go for an abortion again. If my kids didn’t have such problems, I wouldn’t have taken such a serious step.
Anna, Kemerovo, 36 years old
On the advice of a friend, I turned to a good doctor for a tubal ligation. The operation was short, under general anesthesia. There were no problems, desire and menstrual cycle were also unchanged.
Larisa, Tver, 39 years old
After the operation everything was fine. I didn’t know then that if you tie the fallopian tubes, there are different consequences. Two years later I had an ectopic pregnancy and had my tube removed. An abscess developed and I had two more surgeries.
Anna, Lipetsk, 42 years old
Treatment of tubo-peritoneal infertility
Immediately after detection of adhesions, a woman is not referred for IVF. Treatment is indicated for her first. It must be comprehensive. There are several approaches to solving this problem. The doctor builds a specific scheme for each patient individually, after the examination.
If a partial blockage of the pipes has been diagnosed, then sometimes it is possible to do without surgical intervention. This is possible when the adhesions were caused by inflammation that occurred recently. If the tubes are completely blocked, the patient is referred for laparoscopy.
Sometimes laparoscopy is replaced by blowing or flushing the tubes. This is a very painful procedure that requires anesthesia. It will succeed only if the connective tissue has blocked one section of the pipe.
To enhance the effect of the therapy, women resort to physiotherapy, treatment with leeches, and herbs. However, unconventional treatment measures have no proven effectiveness.
A very interesting video about a new method of treating tubal patency. The method is called firtiloscopy (hydrolaparoscopy). A professor at the Reproductive Medicine Clinic talks and demonstrates this new treatment method in detail:
Tubal obstruction is quite difficult to treat. In order to undergo treatment correctly, you need a professional approach to solving this issue. After the right treatment tactics, you can get pregnant much faster. Therefore, the more experienced the doctor is, the better.
The use of folk remedies
Traditional medicine does not reject the healing properties of medicinal herbs, but, unfortunately, they do not help in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the fallopian tubes. The proposed decoctions, tinctures, and douching solutions do not have a healing effect, so you should not hope that they will help cope with a serious illness. To diagnose diseases of the fallopian tubes and their patency, methods such as hysteroscopy, ultrasound examination, and laparoscopy are used. In some cases, even they do not provide 100% confidence in the correctness of the diagnosis, so herbs can be an accompanying component, but not the main one. Moreover, hoping to get rid of problems, the woman postpones visiting the gynecologist. In the acute stage of inflammation, intrauterine pregnancy, this leads to a worsening of the condition. In such situations, the fallopian tubes are destroyed, and doctors have no choice but to remove them. The condition of the fallopian tubes determines whether a woman can conceive a child naturally. By paying attention to her health, she saves herself from many problems that are better avoided. You don’t need to experiment on yourself, but just take care. About yourself and your future baby.
Similar articles
Endometritis and endometriosis: two diagnoses – one problem
Doctors' opinion: varicocele is curable to any degree
Signs of uterine endometriosis - causes and consequences, treatment
How to identify and treat uterine endometriosis
The need for examination and treatment
Without exception, all diseases that affect the fallopian tubes require medical attention. Inflammation detected at an early stage can be treated with medication. If you feel its symptoms, you should immediately see a gynecologist. The success of quickly stopping the spread of infection depends on this. With extensive damage to the fallopian tubes, inflammation causes them irreparable damage. In this case, surgery is inevitable, and with it the chances of pregnancy are sharply reduced. Cysts and tumors can be detected during a gynecological examination. Therefore, you should not neglect systematic visits to the doctor. A timely operation to remove them helps restore the health and function of the fallopian tubes. Ectopic pregnancy and inflammation in the acute stage have similar symptoms. Timely measures can preserve the opportunity to conceive a child naturally. Reproductologists, of course, have artificial insemination in stock. Not everyone can undergo the procedure for free, nor can they get a positive result the first time. And it may require a lot of money.
You may be interested in: Insufficient sperm motility and its treatment with folk remedies
If detected in time, the disease can be treated with medication
Causes of obstruction
The causes of the pathological condition can be divided into mechanical and functional, having both acquired and congenital nature of their origin. Doctors refer to mechanical reasons as:
- Sexual infections that provoke inflammation of the internal organs of the reproductive system. Particularly dangerous for a woman is infection with chlamydia or gonorrhea, which, provoking inflammation, lead to the formation of adhesions and narrowing of the lumen in the tubes.
- Endometriosis is also a cause of pathological obstruction leading to the formation of adhesions and hardening of the lumen of the tubes.
- The oviduct can also be blocked after an abortion or gynecological surgery - in this case, obstruction occurs after the sutures become hardened, tissue inflammation or due to the development of tumors.
Doctors consider functional obstruction not so much a narrowing of the lumen in the tubes as a malfunction in the hormonal system, an imbalance in hormone levels. This is what leads to a slowdown in the movement of the cilia lining the inner walls inside the oviduct. A spasm that narrows the passage of the fallopian tubes, which occurs due to a malfunction of the central nervous system, can also provoke a functional disorder.
Relative contraindications to IVF
There are relative and absolute contraindications for women to undergo IVF. The first include pathologies:
- uterine mucosa (endometriosis, endometritis)
- liver (hepatitis)
— internal systems (endocrine, circulatory).
If the disease is curable, a woman can expect to become pregnant using IVF. Therefore, it is better not to waste time on treatment after signing up for the procedure, but to take steps towards health in advance.
What are the symptoms of diseases
The greatest discomfort is caused by infections. Under their influence, the fallopian tubes fill with pus. Fluid may also accumulate so that the fallopian tubes become blocked. The patients' complaints are related to abdominal pain, high fever, and unpleasant discharge. The cyst does not bother me until a certain point. Pain in the groin occurs with torsion. They occur during sexual intercourse or with increased physical activity. These are the main and only symptoms of the disease.
Pathology and tumor are detected during examination. They do not have any obvious symptoms, including pain caused by infection or a cyst. The presence of abnormalities is discovered when the causes of infertility are determined. All types of diseases have common symptoms. These include dysfunction of the fallopian tubes. In turn, they lead to infertility. In search of tubal dysfunction, hysteroscopy is performed and other effective diagnostic methods are used. With their help, it is possible to determine where the tumor or inflammation is localized, whether the fallopian tubes contain fluid, and which parts have suffered as a result of the spread of the negative process.
You may be interested in: How tubal laparoscopy solves women's problems
Internal female genital organs
The internal female genital organs include the ovary, fallopian tube, uterus and vagina.
A) UTERUS (uterus, metra, hyster)
The uterus is an unpaired, hollow, pear-shaped muscular organ.
Functions of the uterus:
- bearing a fetus;
- expulsion of the fetus during delivery.
The uterus is located in the pelvic cavity between the rectum and bladder.
In this position, it is fixed by ligaments: wide, round, pubic-cervical and rectal-uterine, sacro-uterine.
The length of the uterus in an adult woman is 7-8 cm, width – 4 cm, thickness – 2-3 cm.
The weight of the uterus in nulliparous women ranges from 40 to 50 g, and in women who have given birth reaches 80-90 g.
During pregnancy, the uterus rises from the pelvic cavity into the abdominal cavity and
at 9 months it reaches the costal arches and the xiphoid process of the sternum. Towards the end of pregnancy, the uterus drops somewhat.
During pregnancy, the uterus enlarges, takes on an ovoid shape, its weight increases 20 times and by the end of pregnancy reaches up to 1 kg.
After childbirth, the uterus quickly decreases in size and descends to the navel; on the 10th day it is at the level of the pubic symphysis.
Surfaces of the uterus:
- the anterior surface is vesical, facing the bladder;
- the posterior surface is intestinal, facing the rectum.
Between the posterior surface of the uterus and the rectum there is a space - the pouch of Douglas (uterorectal recess). With perforation of the uterine wall, with ectopic pregnancy, trauma, or peritonitis, blood, pus, and serous fluid can accumulate in this place, which leads to the development of inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity and in the pelvic cavity.
Uterine edges (lateral)
- right;
- left.
Parts of the uterus:
1. The fundus is the upper thickened convex part of the uterus, rising in the form of a vault above the openings of the fallopian tubes and forming angles with them - the horns of the uterus.
2. The body is the middle section of the uterus.
3. The cervix is the lower narrowed part of the uterus, it makes up 1/3 of the length of the uterus and consists of 2 parts.
Parts of the cervix:
- supravaginal part - the upper part of the cervix, makes up 2/3 of the cervix;
- vaginal part (stigma) - lower part of the cervix.
The junction of the uterine body and the cervix is narrowed and is called the isthmus of the uterus.
Position of the uterus in the pelvis
The uterus has significant mobility and, depending on the condition of neighboring organs, can occupy different positions.
Normally, the fundus of the uterus is directed forward - the uterus is tilted anteriorly.
This position of the uterus is called anterior tilt - anteversio, while the body of the uterus forms an angle with the cervix, open anteriorly - anterior bending of the uterus - anteflexio.
Uterine cavity
The uterine cavity in the frontal section has the shape of a triangle, with its apex facing downwards and passing into the narrow canal of the cervix.
At the corners of the base of the triangle, the fallopian tubes, the oviducts, open.
The apex of the triangle faces down and passes into the cervical canal - the cervical canal.
The cervical canal at the top opens into the uterine cavity through the internal opening of the uterus - this is the internal os of the uterus.
Below, the cervical canal opens into the vagina with the external opening of the uterus - the external os of the uterus, this opening of the uterus is limited by the lips: anterior and posterior (thinner).
In a nulliparous woman, the external opening of the uterus (external os of the uterus) is round, and in a woman who has given birth, it has the shape of a transverse slit.
Uterine wall
The wall of the uterus is thick and consists of 3 membranes.
The lining of the uterine wall:
1. The mucous membrane (endometrium) is the inner membrane lining the uterus from the inside, covered with a single-layer cylindrical ciliated (ciliated) epithelium.
The mucous membrane has many uterine glands.
The endometrium has 2 layers:
- basal layer - lower, lies at the base;
— functional layer – upper (surface). It is rejected during menstruation.
2. The muscular layer (myometrium) is the middle layer of the uterus, consists of 3 layers of smooth muscle - external and internal longitudinal, middle - circular (circular).
The thick muscular lining of the uterus ensures the expulsion of the fetus during delivery.
3. The serous membrane (perimetry) is the outer membrane of the uterus, formed by the peritoneum, which covers the uterus from above, in front and behind (except for the lateral edges and part of the cervix in front).
On the sides of the uterus, the anterior and posterior layers of the peritoneum join and form the broad ligament of the uterus.
Around the cervix under the peritoneum there is an accumulation of adipose connective tissue - parametrium (peri-uterine tissue)
Inflammatory processes in the uterus: endometritis, myometritis, perimetritis, parametritis.
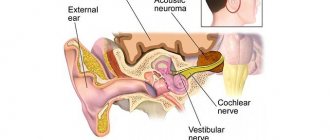
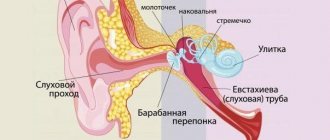
b) uterine tubes (tubae uterinae, salpinx)
Inflammation of the fallopian tubes is called salpingitis.
The fallopian tubes (fallopian tubes, oviducts) are paired cylindrical organs, 10–12 cm long and 2–4 mm in diameter.
The fallopian tubes are located in the pelvic cavity on both sides of the uterine fundus, at the upper edge of the broad ligament of the uterus.
The fallopian tubes start from the corners of the uterus, at first they are located at right angles to the uterus almost horizontally, then, having reached the wall of the pelvis, they are located in an arc around the lateral side of the ovary, forming a bend, and end at the medial surface of the ovary.
The narrow end of the fallopian tube opens into the uterine cavity, and the widened end opens into the peritoneal cavity next to the ovary. Thus, in women, the peritoneal cavity communicates with the external environment through the lumen of the fallopian tubes, the uterine cavity and the vagina.
Pathogens of sexually transmitted infections and other microorganisms in the female reproductive system spread upward - through the vagina into the uterus, then into the fallopian tubes and ovaries. This can lead to inflammatory processes in the female genital organs and infertility.
Functions of the fallopian tubes:
— carrying the egg from the ovary into the uterine cavity (that’s why they are also called oviducts);
- The fallopian tubes are the site of fertilization of the egg by sperm.
Fallopian tube openings:
— abdominal opening (d 2 mm) – connects it with the abdominal cavity;
- uterine opening (d 1 mm) - connects it with the uterine cavity.
Parts of the fallopian tube:
1. The funnel is the part of the fallopian tube facing the abdominal cavity, it has an abdominal opening surrounded by a large number of fimbriae (fimbriae), one of which, the ovarian fimbria (fimbria ovarica), is attached to the ovary (the egg moves along it into the fallopian tube).
2. The ampulla is the longest and widest part of the fallopian tube, next to the funnel, which accounts for almost half of its entire length (d 3 - 5 mm), and has a curved shape.
3. The isthmus (isthmic part - from isthmus - isthmus) is the medial narrowest part of the fallopian tube (d 1.6–1.8 mm), located medial from the ampulla, approaches the angle of the uterus between its bottom and body.
4. The uterine part (interstitial - intramural) is a part of the fallopian tube, enclosed in the thickness of the wall of the uterus and opening into its cavity through the uterine opening of the tube.
Layers of the fallopian tube wall:
1. The mucous membrane is the inner membrane lining the tube from the inside, covered with a single-layer prismatic (cylindrical) ciliated epithelium, the cilia of which flicker towards the uterus.
The mucous membrane forms numerous branching folds, more developed in the infundibulum and ampulla, where they fill their entire lumen.
Some of the cells of the mucous membrane are devoid of cilia - secretory cells, they produce nutrients for the egg and sperm.
After an abortion, endometritis (postpartum or infectious), adhesions may form on the mucous membrane of the fallopian tubes and uterus, which lead to infertility and ectopic pregnancy, because the egg cannot penetrate the uterine cavity.
2. The muscular layer is the middle layer of the fallopian tube, it thickens in the direction from the ampulla to the uterus, consists of 2 layers of smooth muscle - thick internal circular and thin external longitudinal
3. The serosa is the outer membrane of the fallopian tube, formed by the peritoneum, which covers the fallopian tubes and the uterus from above and from the sides, forming the broad ligament of the uterus.
The anterior and posterior leaves of the broad ligament of the uterus, connecting under the fallopian tube, form the mesentery of the fallopian tube - mesosalpinx.
c) VAGINA (vagina)
Inflammation of the vagina is called vaginitis.
The vagina is an extensible tube 8-10 cm long, flattened in the anterior-posterior direction, which with its upper wide end covers the cervix, and with its lower end, penetrating through the genitourinary diaphragm of the pelvis, it opens into the vestibule with the opening of the vagina.
In virgins, this opening is closed by the hymen (hymen), which separates the vestibule from the vagina. The hymen separates the external and internal female genitalia.
The hymen is a semilunar or perforated plate, which is a double fold of the mucous membrane, which is torn during the first sexual intercourse, and its remains atrophy.
In front of the vagina are the bladder and urethra, behind is the rectum, with which it grows together.
The vagina has anterior and posterior walls that are in contact with each other.
The vaginal cavity is slit-like.
The walls of the vagina, covering the vaginal part of the cervix, form around it a dome-shaped depression called the vaginal vault.
The vaginal vault is divided into an anterior, posterior and two lateral (right and left) fornix.
The posterior vault of the vagina is the deepest, and material is taken from it for examination for gynecological smears. In gynecological smears, there are 4 degrees of vaginal cleanliness.
The vaginal wall consists of three membranes:
1) The mucous membrane is the inner membrane that covers the vagina from the inside, lined with stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium, and forms numerous transverse vaginal folds. The vaginal mucosa does not have glands.
Cytological smears of the vaginal mucosa make it possible to examine the condition of the epithelium, which depends on hormonal levels and the phases of the menstrual cycle.
The cells of the surface layer of the epithelium are rich in glycogen, which, under the influence of enzymatic processes, breaks down to form lactic acid. This gives the vaginal mucus an acidic reaction, which is bactericidal against pathogenic microbes.
2) The muscular layer is the middle layer and consists of 2 layers of smooth muscle - the inner circular and outer longitudinal. At the top, the fibers of the muscular membrane of the vagina pass into the muscles of the uterus, at the bottom they are woven into the skeletal muscles of the perineum.
The striated skeletal muscles of the perineum around the vaginal opening and urethra form a voluntary urethro-vaginal sphincter.
3) The adventitia is the outer shell of the vagina, consists of loose fibrous connective tissue, is supplied with elastic and muscle fibers, contains a venous plexus and nerves.
There is also an accumulation of connective fatty tissue around the vagina - paravaginal tissue.
d) OVARY (ovarium, oophorum)
The ovary is a paired female sex gland of mixed secretion, weighing 5-8 g. The ovary has an ovoid shape, somewhat flattened in the anteroposterior direction.
Near the ovaries there are rudimentary formations - the appendages of the ovary.
Functions of the ovary:
- Exocrine (exocrine) – production of female germ cells – eggs.
- Endocrine (intrasecretory) - the production of female sex hormones - estrogens and the hormone of the corpus luteum of the ovary - progesterone.
Inflammation of the ovaries is called oophoritis.
The ovary is located vertically on the side walls of the pelvis, on both sides of the uterus, under the fallopian tubes.
They are fixed by the proper and suspensory ligaments of the ovary. The peritoneum forms the mesentery of the ovary, through which the organ is attached to the broad ligament of the uterus.
Fallopian tube: what is it?
This organ is located in the pelvis in women. It is worth noting that from birth every girl has two fallopian tubes. The length of these organs is very short. It is no more than five (in some cases seven) centimeters. The volume of this organ is also very small. The diameter of the fallopian tube is only a few millimeters.
The inner layer of the fallopian tube is represented by microscopic fingers called fimbriae. In a normal state, they contract freely.
Hysterosalpingography images
The right fallopian tube is obstructed in the ampullary section.
The left fallopian tube is freely patent.
The "R" on the image indicates the patient's right side.
The arrow indicates an obstruction in the ampullary section of the right fallopian tube.
The right and left fallopian tubes are difficult to pass due to the presence of bilateral valve sactosalpinxes.
The image clearly shows dilated and tortuous fallopian tubes.
The arrow shows the fallopian tube on the left with the presence of a valve sactosalpinx.
The "R" on the image indicates the patient's right side.
The left fallopian tube is freely patent.
The right fallopian tube is obstructed in the intramural section.
The arrow indicates the presence of an obstruction at the mouth of the right fallopian tube.
The letter "R" in the image represents the patient's right side.
The left fallopian tube is obstructed in the ampullary section.
The right fallopian tube is difficult to pass due to the presence of a valve sactosalpinx on the right.
The arrow shows the valve sactosalpinx on the right.
The "R" on the image indicates the patient's right side.
Operation
There are several basic methods for surgical removal of adhesions in the fallopian tubes. When deciding on the method of surgical intervention, the doctor proceeds from the degree of growth of adhesions and other features of the disease.
Hydrotubation
Hydrotubation is a minimally invasive technique that allows you to get rid of young and fragile adhesions in case of obstruction of the fallopian tubes. To implement this, a catheter is inserted into the uterus, through which a saline solution is supplied under a certain pressure. Thanks to the pressure of the liquid, the adhesions are broken and the lumen of the pipes is restored.
The main disadvantage of the procedure is its traumatic nature.
If sections of the pipe are damaged, new connective tissue cords will form in this place. In addition, hydrotubation will not restore the functionality of the cilia lining the tube from the inside.
Laparoscopy is a less traumatic method
Surgical intervention through laparoscopy allows you to get rid of adhesions in the fallopian tubes much faster and more effectively than drug correction.
During laparoscopy, the procedure for dissecting adhesions is performed under general anesthesia. This type of operation is the least traumatic method. During the procedure, several small punctures are made on the abdominal wall, through which instruments and a camera are inserted. Using a manipulator, the doctor cuts the adhesions. The entire operation takes place under video control. Therefore, it will be possible to start planning a pregnancy already in the middle of the next cycle.
Laparotomy
Laparotomy is rarely resorted to. This operation is indicated for women whose adhesions are located not only in the fallopian tubes, but also on the internal organs of the small pelvis. In this case, there is a risk of damage to the intestines, displacement of the uterus, ovaries, and bladder. Changing their anatomical position leads to serious consequences.
Since laparotomy is performed through an open approach, it carries more risks and complications than minimally invasive surgery. In this regard, doctors rarely resort to the procedure when it is not possible to cope with the disorder by other methods. Abdominal surgery increases the likelihood of re-formation of adhesions. Therefore, after it is carried out, a woman needs to try to conceive a child as quickly as possible. As practice shows, a year after laparotomy, the fallopian tubes again lose patency .
If the problem cannot be dealt with promptly, the woman is referred for IVF.
Price
Tubal ligation surgery is free in public hospitals under the compulsory medical insurance system. To carry it out, you must first contact your local gynecologist with medical evidence or express your will.
In private clinics, the operation is performed on a paid basis. The cost of tubal ligation there varies from 10 to 30 thousand rubles and depends on the region, the status of the institution, the professionalism of the specialists, the comfort of the wards, etc. The price includes payment for the operation, the cost of medications, examinations, stay in the ward and meals.
Diagnostic features
The mandatory task of every woman is to carry out diagnostic measures. The main problem during pregnancy is obstruction. In this regard, care must be taken to carry out examinations if violations are suspected.
Lack of patency may be due to natural or purposeful reasons. In the first case, the pathology develops due to factors beyond the control of the woman, in the second case, the patency is disrupted by special intervention to prevent conception.
If the tubes are not passable in the isthmic department, treatment will not be effective and IVF becomes the only chance for motherhood. Moreover, if the intramural section of the fallopian tube is subjected to formed adhesions, the woman is diagnosed with infertility.
Only if the mouths of the fallopian tubes are visualized, the possibility of giving birth to a child remains.
The following disorders can lead to an ectopic pregnancy:
- adhesions;
- kinks;
- narrowing.
If the mouths of the fallopian tubes are free, this means the possibility of conception with further correct development of the fetus. If the fallopian tubes are not visualized, this means that the girl is experiencing pathological processes and additional intervention is required.
Causes of reproductive disorders
One of the pathologies is the expansion of the fallopian tube. This disease is called hydrosalpinx. In most cases, the reasons why the fallopian tube is dilated are associated with the accumulation of fluid, the development of the inflammatory process and poor circulation.
Why is the fallopian tube dilated?
- simple and follicular hydrosalpinx;
- salpingitis;
- enlarged isthmus of the fallopian tube.
Simple hydrosalpinx. In this case, the increase in the size of the tube in women occurs only in one cavity. Despite the mildness of the disease, the risks of complications become maximum and treatment still becomes mandatory.
Follicular hydrosalpinx. It is assumed that the lumen is divided into several cavities, each of which is filled with liquid.
Salpingitis. The inflammatory process is complicated due to the negative impact of several types of sexually transmitted infections. The acute form of the disease leads to an increase in general temperature and pronounced pain in the intimate organs. Chronic disease leads to the fact that the size of the fallopian tubes decreases and there is a serious risk of ectopic pregnancy or diagnosing infertility.
An enlarged isthmus of the fallopian tube also indicates an inflammatory process. Initially, this part of the organ has a very narrow diameter (up to 4 millimeters) and a length of up to 20 millimeters.
Violation of dimensions indicates the need for diagnostics and initiation of a treatment course. Pathological changes can only be detected during examinations by doctors.
Doctor's comment
Are you tired of unsuccessfully trying to get pregnant? Did you know that with a diagnosis of infertility, many women today successfully become mothers? In our clinic alone, more than 600 patients who underwent treatment for infertility gave birth to babies. One of the main reasons for unsuccessful attempts to conceive or miscarriage is tubal factor. Of course, to clarify the extent of damage to the fallopian tubes, it is necessary to undergo an examination: hysterosalpingography or laparoscopy, with the help of which you can obtain information about the condition of the uterine cavity and its outer surface, the lumen of the tubes, as well as the pelvic cavity. A comprehensive examination can be performed in our clinic; for this we have the most modern equipment. Make an appointment and together we will discuss all the possibilities for the upcoming treatment, after which we will select the most optimal method based on the examination results.
Head of SwissClinic Konstantin Viktorovich Puchkov
Causes and symptoms of hydrosalpinx
Excess fluid in the uterus can develop during the formation of many diseases. Without a diagnostic examination, it is impossible to select a suitable treatment regimen.
Inflammation
The pathological condition is provoked by an inflammatory process that occurs both in the uterus itself and in nearby organs. Exudate released from the vagina is a protective reaction to inflammation. Sources of the disease are presented:
- endometritis – involving the functional mucous layer in the process;
- salpingitis - inflammation of the fallopian tubes;
- oophoritis - pathology affects the paired sex glands.
Endometriosis
It is formed during non-standard growth of the functional layer of the uterus. Common sites of endometriosis are:
- fallopian tubes, ovaries;
- abdominal wall, connective tissues.
Under the influence of hormones, problem areas secrete blood, the accumulation of which is detected on ultrasound as fluid in the uterus.
Apoplexy
The disease occurs when an ovary or cyst ruptures. The source of the pathology is rough sex, mechanical injuries, enlarged tumors or unusual enlargement of the uterus.
Fluid accumulation can occur with an ectopic pregnancy and subsequent damage to the fallopian tubes, with massive bleeding into the organ cavity.
In old age
Menopause causes abnormalities due to changes in hormonal balance. Lack of estrogen provokes narrowing and fusion of the internal pharynx; exudate does not leave the organ, gradually accumulating in it.
Nothing comes from nothing - this has been proven both by science and by personal experience. So, why does liquid begin to accumulate in pipes?
- Previous venereal diseases;
- Adnexitis - inflammation of the appendages;
- Salpingitis is inflammation of the fallopian tube tissue;
- Endometriosis, tumor processes;
- Surgical interventions - general, laparoscopic in the lower abdomen.
Liquid accumulates in the pipes as a result of untreated and untreated gynecological diseases.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
During conservative treatment, the doctor may recommend that the woman undergo physical therapy. Typically, if the fallopian tubes are obstructed, the patient is referred to the following procedures:
- Ultrasound treatment. The connecting cords are split under the influence of ultrasonic waves emitted by a special apparatus.
- Electrophoresis with enzymes. This procedure allows you to deliver them to deep tissues. Such sessions are safe for a woman’s health.
- Gynecological massage. It helps to enhance nutrition of the reproductive system organs. However, many doctors refuse such therapy, considering it ineffective and outdated.
- Balneotherapy. It comes down to taking baths: radon, hydrogen sulfide, chloride. This also includes mud treatment.
- Treatment with leeches. This method allows you to relieve inflammation, fight microbes, and resolve adhesions.
All these physiotherapeutic techniques are aimed at improving blood supply to the pelvic organs.
Physiotherapy will allow you to regulate their work and stop the inflammatory reaction that causes obstruction of the fallopian tubes.