Cholecystitis is a disease of the gallbladder, accompanied by its inflammatory process. Tests for cholecystitis are taken after a general examination by a doctor and are needed to make an accurate diagnosis (chronic, acute or initial cholecystitis). The most effective way to determine the disease is a biochemical study of bile using a special probe.
Cholecystitis is a disease of the gallbladder, accompanied by its inflammatory process.
Diagnostics
Due to the fact that chronic cholecystitis has symptoms similar to a huge number of liver diseases and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the process of studying the disease has its own characteristic features.
You should know that at the first manifestations, you must immediately go to see a doctor, and then conduct a comprehensive examination to study the functioning of the gallbladder.
The diagnostic procedure is as follows:
- An initial examination is performed by a doctor, after which you will need to undergo a number of prescribed laboratory tests;
- Collection of material for further study in the laboratory (general blood test, AST - determination of protein metabolism enzymes in the body, biochemical study of the gallbladder).
- To create a more complete picture, the attending physician may send the patient for an ultrasound or computed tomography scan.
- You will also have to go through the rather unpleasant procedure of inserting a probe for duodenal intubation and collecting bile samples;
- In some cases, a radiological examination is performed, during which the patient is given a special radionuclide agent. Next, the components of the drug enter the gallbladder through the circulatory system. Then a spectral analysis of the walls of the organ and bile is performed.
- The last method by which cholecystitis can be confirmed is x-ray structural analysis.
What does cholecystitis look like?
Cholecystitis is a common inflammation of the gallbladder and its ducts. It can be caused by stress and poor nutrition. Other causes are also taken into account: worms, bacteria or gallstones.
The disease presents many inconveniences to the body. It can occur either in an acute form, when there is a sharp pain in the right side, severe attacks of nausea and vomiting, or in a chronic form, causing weight loss, deterioration in health and periodic pain in the right hypochondrium, accompanied by nausea and sometimes vomiting.
Without appropriate laboratory tests, it is difficult to identify the cause of cholecystitis. In addition, there are a number of diseases that have similar symptoms:
- pancreatitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- gastritis and stomach ulcers;
- myocardial infarction;
- appendicitis;
- helminthic infestation.
Therefore, from the moment of the first visit to the doctor and examination of the patient, various tests are prescribed to make an accurate diagnosis.
Blood analysis
Laboratory study of blood composition can play an important role in establishing the correct diagnosis and choosing the right tactics to combat the disease. A timely blood test can help detect the initial stages of progression of some dangerous complications that develop against the background of chronic cholecystitis.
Your doctor may order the following blood tests:
Blood tests are important in diagnosing cholecystitis
- General blood analysis.
- Biochemical study of blood composition.
- Blood clotting study.
- A test that determines the amount of sugar.
- To obtain information about your blood group and its Rh factor.
- For the presence of infectious diseases in the patient under study.
If you have the first signs of cholecystitis, doctors recommend undergoing a series of studies:
- liver test (alt and ast, bilirubin, thymol test);
- studying urine and feces for the presence of amylases in their composition;
- test for GGT (gamma-glutamyl transpeptidiase - an enzyme contained in the cells of the liver and bile ducts). The most effective way to determine the existence of bile stagnation.
- alkaline phosphatase (in case of inflammation of the gallbladder, it is increased by a quarter of normal);
- protein fractions.
Highly informative results for the inflammatory process developing in the gallbladder are a general clinical blood test and a study of the biochemistry of the blood composition.
If the attending physician suspects cholecystitis, the first test on the list is always a general blood test. It is prescribed for the diagnosis of most diseases. The main objective of this study is to identify infectious contamination in the body. This is evidenced by elevated white blood cells.
With all this, a patient with cholecystitis, even in acute form, may not get the desired result, since hemoglobin and red blood cells will be in the normal range. People suffering from chronic cholecystitis have deviations from the norm in the number of eosonophils in the blood, usually by 1-2%. In a situation where the number of eozonophils is reduced or completely absent, this indicates a severe course of the disease.
If the doctor has even the slightest doubt about inflammation of the gallbladder, then he sends the patient for a biochemical blood test.
Laboratory methods
Laboratory diagnosis is of utmost importance and includes biochemical and general blood tests, stool and urine tests, as well as liver tests.
General clinical blood test
Laboratory blood testing helps to obtain information about the cellular composition of the blood and identify pathological abnormalities. In addition, a general blood test allows you to determine the inflammatory focus and diagnose acute cholecystitis.
For a general clinical blood test, biomaterial is taken from a finger. The analysis must be carried out on an empty stomach. Normally, the content of blood components should be:
- Leukocytes – 4.5-11.0;
- Platelets – 150-400;
- Hemoglobin – 11.7-17.44
- ESR – up to 30;
- Red blood cells – 3.8-5.8.
Biochemical study of blood composition
A biochemical blood test for cholecystitis will help to find out what caused the disruption of the healthy functioning of the organ. The main indicator will be bilirubin. If the content of this element in the blood is higher than the standard value, this indicates its poor utilization by the gallbladder. Also, the detection of cholestasis in the blood allows us to talk about disturbances in the functioning of the organ.
In a situation where there is an increase in the level of bilirubin in bile, only one conclusion can be drawn - the bile does not reach the intestines. And this will require paying attention not only to the gallbladder, but also to the liver.
In addition to bilirubin, determining the level of alkaline phosphatase in cholecystitis is of high value. Deviations from the norm towards an increase in this indicator indicate the existence of pronounced bile stagnation. In the chronic form of the disease, the level may be slightly higher than normal (up to 200 units/l). During the acute course of the disease, the coefficient in most cases is greatly overestimated.
Bile analysis
This type of laboratory study helps to find deviations in the balance of bile constituents and acids.
When studying the duodenum, different portions of bile samples are taken. The material for analysis is produced by fractional probing and consists of 5 phases.
Probing phases:
Bile tests are performed using probing
- First phase. Material is collected from the duodenum. Bile from portion “A” is collected within half an hour immediately after insertion of the probe before the introduction of a special solution;
- The second phase is the contraction phase of the sphincter of Oddi. It begins immediately after the infusion of a special solution that stimulates contraction of the gallbladder;
- Third phase. Bile is collected from the extrahepatic bile ducts. The duration of this stage does not exceed three minutes from the opening of the sphincter of Oddi until the appearance of bile from the bladder;
- Fourth phase. Bile portion “B” from the bladder is produced within 30 minutes;
- Fifth phase. Bile from the liver of portion “C”. The duration of this stage similarly does not exceed half an hour.
When deciphering the indicators of this study, you need to focus on the indicator of portion “A”. A deviation from the norm to a lesser extent indicates an early stage of cholecystitis or hepatitis.
A reduced bile content in portion “B” indicates the presence of cholecystitis. The white tint of bile from this sample is also observed during chronic cholecystitis.
An increased or decreased level of bile acids in the 5th phase sample (portion “C”) informs about the initial stage of development of calculous cholecystitis.
Bile exchange
Bile consists of bilirubin, cholesterol, bile acids, and phospholipids. Bilirubin is mainly formed in the spleen due to the breakdown of hemoglobin. Next, binding to blood proteins, it enters the liver, undergoes transformation and is secreted into the gallbladder. Cholesterol enters the body with food, and bile acids, in turn, are synthesized from cholesterol. Bile plays a very important role in the human body, because. The bile acids it contains promote the breakdown and absorption of fats in the intestines.
When eating food, bile formation increases. Depending on the needs of digestion, the sphincter of Oddi relaxes - bile and pancreatic juice enter the lumen of the duodenum. In the small intestine, bilirubin is converted into urobilinogen. Part of the urobilinogen is absorbed back into the blood and goes back to the liver, while part is excreted through the kidneys in the form of urobilin in the urine. The main amount is excreted along with feces in the form of stercobilinogen, which is oxidized in air into stercobilin. It is stercobilin that colors stool brown or yellow.
Analysis of urine and feces
To diagnose cholecystitis, urine and feces are analyzed
An imbalance in the bilirubin content in the body can be detected by studying the feces and urine of the person being tested. These additional tests help determine the quality of the gallbladder. During healthy organ functioning, the amount of bilirubin released is regulated by the liver.
If a low level of content is determined in the collected material, then the patient’s skin should have a yellowish tint, since bilirubin begins to enter the epidermis in large quantities. Upon receipt of such results and the presence of obvious symptoms of cholecystitis, the doctor makes a final diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
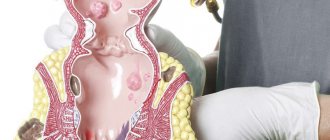
Anatomical structure of the hepatobiliary system
The gallbladder is located on the lower surface of the right lobe of the liver, is a sac-shaped organ and has a pear-shaped shape. Bile is secreted in the liver. The hepatic ducts carry bile through the cystic duct, the duct of the gallbladder, directly into the bladder itself. When the common hepatic and cystic ducts merge, the common bile duct is formed - the common bile duct. Through it, bile enters the duodenum through the large duodenal papilla. In addition to the common bile duct, the pancreatic duct opens into the lumen of the major duodenal papilla. The flow of bile occurs in portions. This mechanism is regulated by the contraction and relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi. When its function is normal, reverse reflux of bile is excluded. Up to 700 ml of bile enters the intestines per day.
Thus, the gallbladder performs a reservoir (receptacle for bile), evacuation, secretory (secretes mucus), concentration (increases the concentration of bile up to 20 times) function. The gallbladder of an adult can hold up to 80 ml of bile.
Ultrasound and computed tomography
Ultrasound of the gallbladder helps in diagnosing cholecystitis
Ultrasound is a non-invasive examination of the human body using ultrasonic waves. This method of diagnosing cholecystitis allows you to study the abdominal cavity as a whole or each organ separately. Thanks to ultrasound, the diagnostician can determine the thickness of the walls of the gallbladder, as well as existing physical pathologies of the internal organ.
Among other things, ultrasound can detect signs of unbalanced accumulation of bile in the organ, as well as its density. The denser the bile structure, the worse the situation with the patency of the bile canals, and, consequently, the organ itself.
Ultrasound diagnostics and computed tomography have made it possible to diagnose canal blockage and future study of their heterogeneous structure. Only with the help of these procedures does the determination of cholelithiasis become realistic.
Instrumental methods
Diagnosis of cholecystitis cannot be done without instrumental research methods. These include:
- Ultrasound diagnostics is considered the main study that helps to identify thickening and compaction of the gallbladder walls, determine the uneven composition of bile secretion, the presence of stones and adhesions in the organ;
- X-ray examination helps to identify the presence of stones in the bladder and ducts;
- An ECG is usually prescribed to all patients, regardless of the type of pathology, to check the activity of the cardiovascular system;
- FEGDS is carried out to exclude pathological processes in the upper gastrointestinal tract; this study allows you to evaluate the duodenal nipple for lesions, etc.;
- Radioisotope diagnostic techniques are used for cholecystitis quite rarely, when specialists need to check for abnormalities in gall bladder motility;
- Endosonography is an ultrasound study in which a special sensor is inserted into the lumen of the esophagus, then into the stomach and intestines. As a result, the monitor displays a high-quality image of the mucous surfaces of the organs being examined. If necessary, this study is combined with a biopsy. Endosonography allows you to detect pathologies of the bile ducts, pancreas, esophagus and stomach;
- CT is inferior to ultrasound in terms of information content and is prescribed to assess the condition of the liver structures, bile and pancreas. Tomography can also reveal cholecystitis, accompanied by changes in the parenchyma.
The list of necessary instrumental studies in each specific case is determined by a gastroenterologist.
Video about types of diagnosis of cholecystitis:
Examination of the gallbladder with a special probe
Even before the procedure begins, the patient is given a choleretic agent. After a certain period of time, a special probe is inserted into the patient’s intestines. Thanks to this miracle of technology, material is collected for further laboratory research.
By studying the biochemical composition of bile, gallbladder diseases are diagnosed. The essence of the analysis is that after eating food, there are two different biles in the intestines. The first is delivered directly from the liver, and the second is its concentrate and is supplied from the gallbladder.
In a situation where there is inflammation of the gallbladder, bile stagnation occurs. This process is characterized by an increased content of bilirubin, which cannot be dissolved by water or other elements that make up the bile.
Bacteriological culture
To determine the presence or absence of pathogenic microflora that can cause inflammation of the gallbladder, bacteriological culture of the duodenal contents is performed.
The following microorganisms are detected by laboratory methods:
- Giardia cysts.
- Helminth eggs.
Technique
Bile is inoculated onto the cultural nutrient medium. Optimal conditions are created for the growth of microorganisms. Next, a qualitative analysis is carried out - identifying the types of bacteria. And quantitative analysis - calculating the degree of contamination. After identifying the type of parasites, narrow-spectrum drugs are prescribed.