Indications for drug treatment
The incidence of benign tumors increases in young patients. Myoma is found even in girls after menarche. Over the past 40 years of observation in women under 30 years of age, the incidence has increased from 2% to 12%. On average, fibroids are discovered at 33-35 years of age, when many women are planning a pregnancy. Therefore, not everyone agrees to radical surgery.
Drug treatment of leiomyoma is prescribed in the following cases:
- desire to preserve reproductive function;
- asymptomatic course of the disease;
- uterine size no more than 12 weeks of pregnancy;
- the node is located interstitially or subserousally on a broad base.
For severe extragenital diseases that increase the risk of an unfavorable outcome of surgery or anesthesia, drug therapy is also limited. These conditions include:
- poorly controlled hypertension;
- severe heart defects;
- cerebrovascular accidents;
- pathology of the blood coagulation system;
- acute vascular diseases;
- feverish conditions;
- acute infections.
Conservative therapy can be a stage of complex treatment. Hormonal drugs can cause a reduction in the size of the nodes. This feature is used in preparation for myomectomy to reduce trauma to the uterus.
Medicines are not used for the medical treatment of large uterine fibroids. This is due to the peculiarities of the morphological structure of large nodes. In the initial stage of the disease, the tumor consists of muscle fibers and a small amount of layers of connective tissue. Gradually, their ratio levels out, and in large nodes fibrous tissue begins to predominate. Medications lead to a reduction in the size of nodes due to myocytes and have little effect on connective tissue elements. Therefore, the use of hormonal drugs is not justified and increases the risk of side effects.
Preference is given to surgical treatment in the following conditions:
- heavy bleeding, heavy menstruation, which leads to anemia;
- chronic pelvic pain;
- the node is located submucosally on the pedicle, inter-ligamentous, cervical;
- uterine size greater than 12 weeks of pregnancy;
- an enlarged uterus disrupts the function of neighboring organs;
- rapid growth of fibroids;
- the tumor was discovered during postmenopause.
Women with infertility are also recommended breast-conserving surgery or other treatments that will help get rid of fibroids and restore reproductive function.
Drugs for the treatment of fibroids
It must be remembered that medications will not eliminate the causes of the disease. They fight the consequences of hormonal disorders, help reduce the severity of unpleasant symptoms, and improve the quality of life. But 2-3 months after the end of treatment, the size of the tumor approaches its original size.
Drug treatment is prescribed for a period of no more than 6 months. This is due to the large number of side effects of the drugs. The main direction of therapy is suppression of estrogen synthesis. Suppression of the ovaries causes artificial menopause, which ends in a decrease in bone mineralization.
Treatment results are assessed every 3 months. If there is no regression of the nodes, the tactics are revised in favor of surgery or minimally invasive methods of therapy. Before prescribing medications, the doctor must evaluate not only the possible effectiveness, but also the safety. In some cases, breast-conserving surgery, uterine artery embolization or FUS ablation is less harmful to the general condition and is economically beneficial.
For the drug treatment of small uterine fibroids, hormonal and non-hormonal agents are used. The latter have less effect on the size of the node, but help eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of the disease.
Recommendations and reviews
Fibroids are a benign tumor, but they cannot be ignored. It is important to protect yourself so that you do not have to face ethical problems and remove the deformed uterus along with the fetus. Reviews from grateful patients who come to the clinic for minimally invasive methods and complex therapy note that in most cases there were no surgical operations.
For successful treatment, doctors recommend trying to disturb the uterus with the tumor process as little as possible, not overheating, and not lifting heavy objects. Self-medication should be treated with great caution. Treatment with traditional methods is justified only with a second course, which is approved by the attending physician who monitors the development of the process.
https://youtu.be/9FISnUr-gic
Non-hormonal agents
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) help reduce pelvic pain and the intensity of menstrual bleeding. For fibroids use:
- acetylsalicylic acid;
- Diclofenac;
- Ibuprofen;
- Ketorolac;
- Naproxen;
- Indomethacin;
- Piroxicam;
- Nimesulide;
- Meloxicam.
Studies have shown that women with fibroids have increased prostaglandin synthesis. These biologically active substances increase contractions of the uterus during menstruation, which leads to severe pain. NSAIDs reduce the synthesis of prostaglandins. The effects are manifested in the form of reduced pain, reduced loss of menstrual blood.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
A 2013 Cochrane review found that any non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug can be used to reduce symptoms. The effect of their use is comparable to other drugs:
- sodium ethamsylate;
- progestogens;
- oral contraceptives.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs belong to different chemical substances and have differences in metabolism and mechanism of action. But studies have shown that they do not differ in effectiveness.
NSAIDs are effective for aseptic necrosis of nodes. They are prescribed to women to reduce pain after FUS ablation or UAE.
Pregnant women with leiomyoma may experience pain and slight bleeding in the 2nd and 3rd trimester. They are prescribed Ibuprofen as a more effective and safe drug. Treatment is carried out in short courses.
Hormonal changes during pregnancy can lead to activation of the growth of nodes or their inhibition. Degeneration occurs with severe pain. Indomethacin helps to cope with it.
Tranexamic acid is superior to NSAIDs in its ability to reduce bleeding. It belongs to antifibrinolytics. The mechanism of action is manifested in the suppression of blood plasminogen activation. This substance triggers a cascade of reactions aimed at dissolving the blood clot in the lumen of the damaged vessel. Tranexam prevents the activation of fibrinolysis and has a systemic hemostatic effect.
The mechanism of action of Tranexam is similar to aminocaproic acid. But its efficiency is 20 times higher. The volume of blood loss during treatment is reduced by 40%. Tranexamic acid is prescribed in courses during menstruation. The FDA recommends taking no more than 4.0 g per day, the maximum course of therapy is 5 days.
If the recommended doses are followed, there are no side effects. In rare cases, headache, nausea and nasal congestion may occur.
Medicines that affect hormonal levels
Reproductive age can occur with changes in hormonal levels, which are manifested by relative or absolute hyperestrogenism. Therefore, the prescription of drugs that affect the hormonal system is pathogenetically justified.
Progestogens
Steroid hormones from the progestogen group are used in different dosage forms. Their effect is associated with the presence of receptors in the uterus and hypothalamus. The central action blocks the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis. In response to the effect, the synthesis of estrogen decreases, the symptoms of fibroids disappear, and small nodes regress. With continuous dosing of progestogens, changes occur in the endometrium, which gradually lead to its atrophy and a decrease in menstrual bleeding. Progestogens suppress prostaglandin synthesis, so women note a decrease in pain.
The Mirena hormonal system has been developed for intrauterine use. This is a spiral whose contraceptive effect is supplemented with levonorgestrel. It is set for 5 years. Every day, 20 mcg of levonorgestrel is released from the spiral. According to research, the effectiveness of Mirena for fibroids is 74-97%. It reduces blood loss, helps restore hemoglobin concentration and cure anemia.
Mirena spiral
Mirena only acts in the uterine cavity. It reduces endometrial proliferation, but does not affect the function of the ovaries and pituitary gland. Studies in 2010 showed that under the influence of levonorgestrel, the growth of myomatous nodes is inhibited and apoptosis is triggered. Periodic monitoring of patients showed that small leiomyomas regress. Timely administration of Mirena leads to a reduction in the number of hysterectomies in 89% of women.
For a long time, gynecology used oral progesterone preparations, for example, Duphaston, for the drug treatment of uterine fibroids. The following effects were noted during therapy:
- reduction of pain syndrome;
- reduction of blood loss;
- inhibition of node growth.
Duphaston was prescribed in several modes:
- cyclically – from 14 to 26 days of the cycle;
- 21-day regime – from 5 to 26 days.
Long-term use of progestogens is considered more effective. But later studies showed that there is no such dependence.
Observations of pregnant women with fibroids and targeted clinical studies have revealed that under the influence of progestogens, the tumor can be activated and accelerate its growth. An increased number of progesterone receptors was found in her tissues. Therefore, taking this drug does not improve the woman’s condition, but accelerates the appearance of severe symptoms of the disease.
Low-dose oral contraceptives
In women of reproductive age, after drug therapy and tumor regression, it is necessary to switch to maintenance treatment. To stabilize the condition, low-dose combined oral contraceptives are used:
- Midiana;
- Yarina;
- Tri-mercy;
- Lindinet-30;
- Janine;
- Femoden;
- Regulon;
- Marvelon;
- Rigevidon;
- Belara;
- Diana-35;
- Chloe.
The mechanism of action is based on the daily intake of a fixed dosage of estrogens and progestogens into the body, which does not change throughout the cycle in monophasic contraceptives. At the same time, the ovaries go into sleep mode: the follicle does not mature, there is no release of estrogen and no increase in progesterone in the luteal phase. While taking oral contraceptives, the thickness of the endometrium decreases, and the amount of menstrual discharge decreases in volume and duration.
Low-dose combined oral contraceptives
Low concentrations of estrogen suppress the activity of myomatous tumor cells. After regression of the nodes is achieved, the constant use of COCs will not allow them to begin new growth.
Maintenance therapy is necessary for women who have not reached the time of natural menopause. After 50-55 years, oral contraceptives may not be used.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists
These are artificially synthesized protein compounds that are similar in structure to human gonadotropin-releasing hormone. But unlike the endogenous substance, they bind to receptors for a long time. This leads to inhibition of the hypothalamic-pituitary function and ovarian function, and reduces the synthesis of estrogen. For the drug treatment of fibroids, the following substances are used:
- leuprolide acetate – drugs Lucrin Depot, Luprid Depot;
- triptorelin – drugs Triptorelin-long, Diferelin, Decapeptyl;
- goserelin - Zoladex drug.
Clinical randomized studies have shown that the use of drugs in this group can reduce the size of fibroids by 50%. Lucrin Depot and its analogues not only lead to regression of leiomyoma, but also reduce the volume of the uterus, suppress bleeding, and improve overall well-being.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists are often prescribed during preoperative preparation. Therapy for 3 months before surgery significantly improves the prognosis. During this period, the normal concentration of hemoglobin has time to restore. Therefore, in the postoperative period, blood loss is tolerated more easily.
Drug treatment before surgery leads to a significant reduction in the size of the internal genital organs. The standard hysterectomy technique involves surgery through the anterior abdominal wall due to the large size of the tumor. But some research centers have been able to reduce the number of interventions by laparotomy and perform hysterectomy through the vagina. This operation causes less trauma to the woman, reduces the risk of postoperative complications and speeds up rehabilitation.
The duration of drug treatment with GH agonists is limited to 6 months. This is associated with severe adverse reactions. A decrease in ovarian function causes artificial menopause with all its characteristic symptoms:
- hot flashes;
- mood swings;
- vaginitis;
- disruption of the heart;
- vaginal dryness;
- decreased bone mineral density.
Many women complain of pain in the long bones during therapy. Prescribing calcium supplements does not always compensate for mineral deficiency.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists
The mechanism of action is based on blocking the release of luteinizing hormone and inhibiting follicle maturation. This is used in IVF protocols. Studies note that using the medicine for 28 days leads to a decrease in the volume of the uterus, but does not affect the size of the nodes. Drugs of this group are not used for the treatment of fibroids, but they are not contraindicated in women with signs of the disease who resort to assisted reproductive technologies.
Aromatase inhibitors
Medicines in this group lead to inhibition of estrogen synthesis, but they are not used for the treatment of fibroids. The action develops gradually. In peripheral tissues, the activity of the aromatase enzyme decreases, and the synthesis of estrone and then estradiol from androgens is suppressed along the chain.
In a Cochrane study, when treating postmenopausal women with breast cancer and uterine fibroids, a side effect of the drug was identified - a reduction in the size of fibroids by 50%.
But the severity of adverse reactions due to a lack of estrogens does not allow their targeted use for drug therapy of fibroids.
Drugs that affect progesterone receptors
In 90% of myomatous tumor cells, the number of progesterone receptors is increased. Interaction with progesterone leads to the production of growth factors and an acceleration of the increase in the size of the pathological lesion. At the same time, factors that trigger cell apoptosis are suppressed. Therefore, cells in fibroids actively divide, but do not die.
The development of drug therapy methods has led to the creation of the following groups of drugs that modulate progesterone receptors:
- progesterone agonists (progesterone and its analogues);
- progesterone antagonists (Mifepristone, or Ginestril);
- selective modulators (Esmiya).
Progesterone is rarely used for conservative drug therapy of fibroids. This is due to its ability to stimulate tumor growth. Some doctors allow its use in the initial stages of the disease, when the size of the nodes is small. At this stage, the number of receptors in pathological foci has not yet increased to a critical level. For large tumors, progesterone is not prescribed. Other drugs give a good effect, but may be accompanied by side effects.
Mifepristone
The mechanism of action is based on blocking progesterone and glucocorticoid receptors in the uterus. Ginestril is used to treat uterine fibroids up to 12 weeks of pregnancy. The use of the drug inhibits the growth of the node and causes its regression. The course of therapy is 3 months. After cessation of therapy, pathological lesions also resume their growth, but this does not occur as actively as after treatment with Zoladex and its analogues.
Mifepristone drugs
Ginestril has a large number of contraindications. It is not prescribed to women during pregnancy. Blocking progesterone receptors will lead to miscarriage. This effect applies to medical abortion up to 9 weeks. Other contraindications are:
- long-term treatment with glucocorticoids;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- acute and chronic renal failure;
- porphyria;
- treatment with anticoagulants and bleeding disorders;
- submucosal growth of nodes;
- ovarian tumors;
- endometrial hyperplasia;
- individual intolerance.
Adverse reactions are rare if the dosage is followed. Their frequency has not been established. The instructions for Ginestril indicate that the following may develop:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- allergic reactions;
- headache;
- menstrual irregularities;
- endometrial hyperplasia.
After discontinuation of the drug, side effects disappear on their own and do not require special treatment.
Uterine artery embolization
The most modern method of treating fibroids without surgery is uterine artery embolization. The procedure is performed not by a gynecologist, but by a vascular surgeon. There is no abdominal incision made, and the entire operation lasts about 15 minutes.
Embolization is a concept that means closing the lumen of a vessel and stopping blood flow in it. This term originally referred to pathological conditions. You can often hear about a detached blood clot that has blocked the lumen of a vessel in the brain, heart or lungs. Medicine has learned to use this to its advantage.
Uterine artery embolization is one of the newest methods for treating fibroids.
The procedure was originally used to stop massive bleeding. Uterine artery embolization began to be used in 1994, but not as an independent treatment, but as a preparation for surgery to remove the uterus. This made it possible to reduce the amount of blood loss.
It is also useful to read: Uterine fibroids and endometriosis
French physician Jacques Henri Ravina proposed using this method to treat women with fibroids. The success of the first embolizations led to the widespread introduction of this procedure into medical practice.
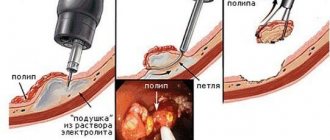
The mechanism of action of the technique is extremely simple. If you block a certain branch of the artery that feeds the fibroid, the tumor will not be able to exist. Therefore, the node gradually “dries out” and regresses. In the case of a submucosal location of the formation, due to malnutrition, it separates from the muscles of the uterus. But the node does not remain in the cavity - its birth occurs with characteristic symptoms.
Preparation for the procedure and methodology for performing UAE
To perform uterine artery embolization, hospitalization is not required, as with classical surgery. It is enough for a woman to undergo a minimal examination, as before any other invasive procedure.
On the day of embolization, the woman must come to the clinic where she will undergo treatment. After the registration procedure, she is sent to the operating room. Anesthesia is not required for UAE; such an intervention is painless and only requires local anesthesia of the skin.
Stages of the operation:
- The procedure is carried out through the femoral artery as the widest and most accessible. The doctor makes a small incision and finds the vessel. A special thin catheter is inserted into it, which is advanced to the uterine artery on one side and then on the other;
During the UAE procedure, an incision is made in the patient's groin area and a catheter is inserted into the femoral artery.
- Emboli are introduced through the catheter - special small polymer balls that do not react with the body. Their size is only 500-700 microns, and they look more like bubbles;
- Emboli rush with the blood flow through the uterine arteries into the blood supply area of the fibroids and clog the vessels. The nodes stop feeding, and gradually the tissues in them begin to die;
- Emboli also enter other arteries of the uterus, which supply blood to healthy tissues. But they don’t stay there for long and quickly leave. Therefore, the remaining tissues of the uterus are not affected;
- The catheter is removed. The puncture site is sealed with a plaster, under which there is a special can of air. It is necessary to stop bleeding from the artery. The can should remain in place for 6 hours. At this time, you cannot move your leg or bend it.
After the procedure, the woman is transferred to a ward, where she must stay for a day for observation and medical care. The peculiarity of the destruction of myomatous nodes is associated with ischemic processes in them, and this is accompanied by intense pain. Therefore, on the first day after surgery, it is necessary to provide the patient with adequate pain relief.
After the UAE procedure, the patient must stay in a medical facility for 24 hours under the supervision of a doctor.
Uterine artery embolization in Moscow is carried out by large medical centers and small private clinics. In some clinics, pain relief begins at the stage of preparation for UAE, in order to saturate the body with drugs, and pain is not a problem. In other cases, anesthesia is performed after UAE. Severe pain is observed for 2-10 hours after the procedure, and then gradually subsides. Those women whose discomfort persists longer can take analgesics at home for a while.
Consequences of the procedure
EMA triggers the irreversible process of node death in the uterus. After the procedure, post-embolization syndrome develops. It is accompanied by the following manifestations:
- Pain in the lower abdomen - pulling, cramping;
- Bloody discharge from the genital tract;
- Increased body temperature;
- General weakness and fatigue.
If the node was located under the mucous membrane, then after UAE it may be born in a few days or months. Gradually, the formation “melts”, and unpleasant bloody discharge appears from the vagina. The temperature may rise. If during menstruation, going to the toilet, or unrelated to them, the pain increases sharply, this indicates expulsion of the node.
If the node is located deep in the muscles (interstitial), then it may not completely disappear, especially if it is large. In this case, a process of “drying out” of muscle tissue and preservation of connective tissue is observed. Therefore, as a result, up to 50% of the former volume of education remains. But the activation of the growth of the pathological focus will no longer occur.
Anatomical and morphological changes in the myomatous node after the UAE procedure.
The body recovers completely after removal of fibroids only after a year. All this time, the woman may not feel the changes happening to her. Moreover, if, for example, the tumor grew towards the bladder and already led to dysfunction of urination, then a return to the usual routine of going to the toilet gradually becomes noticeable.
Indications and contraindications for UAE
The UAE technique is universal and can be used for fibroids of almost any size. But in this situation, the question of the feasibility of performing the procedure is resolved. If the formation is up to 1-2 cm in size, practically does not grow and does not affect the general condition of the woman, then there is no need for intervention.
With fibroids of gigantic size, when almost the entire body of the uterus is altered tissue, performing UAE is also not advisable. After the procedure, the organ will not return to its original size. In this case, only surgery is necessary.
If the myomatous node is large, then surgical intervention is necessary. The EMA procedure will not help in this case.
Absolute contraindications for UAE are cancerous and precancerous diseases. No allergic reactions to emboli were recorded. The only exception is iodine, which is used as an antiseptic. In case of an allergic reaction, the drug is replaced with another antiseptic solution.
Relative contraindications are inflammatory processes in the pelvis and foci of infection in the body. Therefore, such women are initially treated for inflammation, and only then - UAE.
Complications after UAE are very rare. There is a certain risk of damage to the ovarian artery, which can also be blocked by an embolus. But such complications are rare and are associated with the anatomical features of the blood supply in a particular woman.
The main goal of organ-preserving operations is to allow a woman to become a mother. After the EMA, this is quite possible. However, before planning a pregnancy, doctors recommend waiting at least a year after the procedure. If there were submucosal nodes, then you need to wait for their birth and then wait another 2-3 cycles before conception. But it is known that even in cases where women did not wait until the full term recommended by the doctor had expired, their pregnancy proceeded without complications. Therefore, anyone who wants to get an ultrasound photo of the unborn child, and not symptoms of fibroid progression, should take a closer look at modern methods of treatment without surgery.