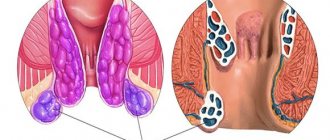
I was found to have a cervical polyp. the uterine canal He did not manifest himself in any way. I never noticed any pain or bleeding. The doctor says that most likely it appeared as a result of my hormonal changes.
Girls, who has encountered this? How were you treated? Were there any relapses?
I found an article on this topic on the net. Maybe it will be useful to someone.
POLYP, a small mass of tissue protruding above the surface of the mucous membrane into the lumen of a hollow organ - stomach, large intestine, rectum, bladder, uterus, larynx. There are inflammatory polyps (appearing at the site of inflammation), hyperplastic (the result of excessive growth of normal tissue) and neoplastic (proliferation of atypical cells). Polyps of inflammatory and hyperplastic nature are benign and usually do not turn into malignant ones. Neoplastic can be both benign and malignant. Polyps come in different shapes and are differently connected to the wall of a hollow organ; A distinction is made between a “pedunculated” polyp (attached to the wall of the organ with a clearly visible thin stalk) and a “sessile” polyp – having a wide base. Based on their microscopic structure, they are classified as tubular (the cells form structures similar to tubes), villous - with many thin thread-like “villi” on the surface of the polyp, and tubular-villous - a combination of the first two types.
Most benign polyps are small formations, less than 1 cm in diameter, which do not manifest themselves in any way. Larger polyps sometimes bleed and produce mucus. If a person has one polyp, then it is likely that their number will increase.
Malignant polyps consist partly or entirely of cancer cells that can metastasize (spread) to other organs. The likelihood of metastasis is increased if the polyp has a villous structure, there is no stalk, and its diameter is more than 1 cm. It is believed that most malignant tumors of the large intestine and rectum originate from polyps. See also CANCER.
When a polyp is detected, it is important to establish its microscopic structure. This usually involves taking a tissue sample (biopsy) or removing the entire polyp. Most benign and many malignant polyps of the colon and rectum can be removed using a colonoscope, a long, flexible optical instrument designed to view the intestines and equipped with an additional tool to remove the polyp. If the polyps are so large that they cannot be removed with a colonoscope, or are located in a place inaccessible to the colonoscope, then they are removed surgically.
Source: https://forum.forumok.ru/index.php?showtopic=34703
Polyps of the cervix and uterine body
Messages:
4363
Where:
Kyiv
Floor:
Female
Endometrial and cervical polyps
Polyps of the cervix and uterine body are pathological proliferation of the glandular epithelium of the endometrium or endocervix against the background of a chronic inflammatory process.
Hormonal disorders play a role in the genesis of polyps, especially uterine ones. Recognition is sometimes possible by examining the cervix using mirrors. A soft, pinkish mass is visible hanging from the cervical canal into the vagina. The diagnosis is clarified using colposcopy. A common symptom of polyps of the body and cervix is uterine bleeding such as menorrhagia.
An accurate diagnosis is made by direct examination of the uterine cavity (hysteroscopy), as well as by x-ray examination of the uterus (metrography).
Polyps of the uterine body can be diagnosed by ultrasound. Curettage of the uterus followed by histological examination of the removed material is the most commonly used diagnostic (and treatment) method. Adenomatous polyps should be considered a precancerous condition.
Treatment. Cervical polyps are removed by unscrewing them (polypectomy). For recurrent polyps, curettage of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal is necessary, which is best done 4-5 days after polypotomy, since due to infection of the polyps, direct curettage can lead to the spread of infection to the uterus (endometritis). Uterine polyps are removed by curettage. Depending on the detected ovarian dysfunction, appropriate hormonal treatment must be carried out. The prognosis for life is favorable. A woman is incapacitated only during bleeding, diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
Prevention. Treatment of inflammatory changes and correction of hormonal disorders must be timely and adequate.
The doctor’s opinion that you need to get pregnant with polyps in the uterus and everything will go away is clearly unprofessional. After all, if the polyp is large, it can interfere with or even threaten the intrauterine development of the child or disrupt the normal course of labor.
Consult doctor Marchak at the Women's Health Center for Petro Zaporozhets, my mother consulted and many of my friends were treated by this doctor - they are very satisfied, he is a good specialist and does not charge extra money.
_________________
Beauty will save the world, but who will save beauty?
We all walk under God and only resuscitators argue with his decisions.
Source: https://forum.natali.ua/viewtopic.php?t=19757
https://youtu.be/VTx0DaS-dNU
Hog queen
One of the effective medicinal plants, often used for various gynecological pathologies, is the boron uterus or one-sided ortilia.
A similar representative of the flora belongs to female mother plants. Borovaya uterus is known for its incredible benefits:
- Diuretic effect;
- Effective anticoagulant (blood thinner);
- Anti-inflammatory qualities;
- Antitumor activity;
- Hormonal corrector (normalizes progesterone and estrogen);
- Immuno-strengthening properties;
- Lowers cholesterol.
Borovaya uterus is used to prepare various medicines. For tincture, the plant (5 large spoons) is mixed with vodka (0.5 l) and kept for 3 weeks. The bottle of medicine is shaken 2-3 times every day. Take in a dosage of 15 drops before meals (about an hour).
Uterine polyp: causes and consequences
What is a uterine polyp
As you know, the uterine cavity is lined with endometrium (mucous membrane). The upper layer of the endometrium is functional and is shed during each menstruation, and grows back at the end of the menstrual cycle. Under the functional layer is the basal layer, which gives rise to the growth of the functional layer.
The nature of all uterine polyps is benign. Endometrial polyps are found in women of reproductive and menopausal age (35-50 years). But in medicine, cases of uterine polyps occurring in young women (20-25 years old) have been described.
The structure of the polyp consists of a stalk, which is attached to the basal layer, and a body, consisting of epithelial cells. Uterine polyps can be either single or multiple. In the latter case, they speak of endometrial polyposis.
A classification of endometrial polyps has been developed depending on their histological structure. The following types of polyps are distinguished:
- Adenomatous uterine polyp is the largest type of polyp. Their diameter usually reaches four centimeters, but there are also huge polyps 10-15 cm in diameter. It is adenomatous polyps that most often transform into malignant neoplasms, and when they are detected, patients are prescribed a thorough examination;
- A glandular polyp in the uterus, as the name suggests, is formed from endometrial tissue and glands. These are the smallest polyps - their diameter usually does not exceed one and a half centimeters, and the safest - they very rarely become malignant. However, even with polyps of this type, the possibility of developing endometrial cancer cannot be excluded;
- Fibrous polyp in the uterus. Polyps of this type are very dense and quite large, consisting of fibrous tissue. Due to their high density, they are clearly visible during ultrasound examination, and the doctor can detect them quite quickly;
- Glandular fibrous polyp in the uterus. This is a mixed type polyp; its size can reach three centimeters in diameter.
- trauma to the uterine cavity (after abortion, diagnostic curettage and long-term wearing of an intrauterine device. Intrauterine device: a proven means of contraception - more than five years);
- abortions, spontaneous miscarriages, remnants of placenta after childbirth, bleeding during childbirth and other complications;
- various endocrine pathologies (diabetes mellitus, obesity Obesity: a disease of well-being? . thyroid disease);
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the genital organs (inflammation of the uterus and appendages, sexually transmitted infections);
- weakening of the body's defenses.
It is typical that glandular polyps occur in young women, while fibrous and adenomatous polyps more often develop in older women (mainly in menopause).
Causes of endometrial polyps
The cause of uterine polyps has not yet been precisely established. The main factor contributing to the appearance of endometrial polyps is considered to be hormonal disorders (progesterone deficiency and excess estrogen).
In addition, predisposing factors include:
How do uterine polyps appear?
As a rule, endometrial polyps, especially those that are small in size, are invisible, that is, there are no signs of the disease. Such polyps are an incidental finding on ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
If the uterine polyp is large or there are a large number of polyps, then characteristic symptoms appear.
First of all, there is a disturbance in the menstrual cycle in the form of intermenstrual bleeding. Many women complain of pain in the lower abdomen, which intensifies during sexual intercourse. Cramping pain indicates the birth of a polyp (exit of the polyp into the cervical canal). In addition, pathological leucorrhoea appears, which is very pronounced and watery. The appearance of leucorrhoea is characteristic of large uterine polyps. Some patients note the appearance of contact bleeding after sexual intercourse. In young women, the presence of a polyp is complicated by infertility.
What does a uterine polyp look like?
On ultrasound, polyps appear as a tumor on the wall of the uterus (or fallopian tube), usually having the same light gray color as the uterine wall itself. They are clearly visible if an ultrasound is performed after filling the uterine cavity with liquid. Then the fluid in the uterus will appear completely black in the image, and the contours of the polyp will be clearly outlined against its background. Unfortunately, ultrasound alone cannot determine the nature of the tumor; this requires other procedures, such as a biopsy.
Uterine polyp and pregnancy
Small-sized polyps do not interfere with conception and implantation of the egg, and also do not affect the course of pregnancy.
Source: https://www.beautynet.ru/gynecology/712.html
Removal of a polyp in the uterus
Content:
Uterine polyps are local growths of the uterine mucosa ranging in size from a few millimeters to 3-4 cm, shaped like a mushroom or wart. They are initially benign in nature, but can occasionally develop into cancer. More often, polyps become the causes of uterine bleeding, painful menstruation and infertility.
Polyps can form both in the cervix and inside its cavity. Such neoplasms can appear at any age, the incidence rate is 6-20%. Polyps are detected using instrumental studies, and treated only surgically.
Decoctions for use
In the arsenal of folk medicine there are many recipes for preparing decoctions that are effective in the treatment of uterine and cervical polyposis:
- Pine decoction. Pine or Christmas tree needles need to be chopped and poured with boiling water (take 1 liter of water per soup spoon of raw materials). Then you need to slowly boil the mixture for half an hour, and then, pour it into a thermos, leave for another 3 hours. Drink half a glass of the decoction before meals. The duration of such therapy is about 3-4 weeks;
- Red brush. Pour 20 grams. dried grass with a glass of boiling water, then wrap it and leave it for about another hour. The decoction is drunk after filtering in a large spoon before meals;
- Herbal and berry infusion. Nettle (2 tsp), rose hips (3 tsp) and black currant berries (1 large spoon) - grind everything and mix thoroughly. Then pour a dessert spoon of the mixture into half a liter of boiling water, mix everything and cover with a lid. Let the mixture stand for about an hour. The drink should be divided into 4 parts and consumed throughout the day. For a more pleasant taste, you can sweeten the broth with honey.
- Alcohol tincture of golden mustache. For 3 stacks. vodka take 50 g of golden mustache. The mixture must be infused in a dark place for about 10 days, shaking systematically. The resulting tincture is used according to a special scheme:
- Day 1 of the course - mix 10 drops of tincture with 3 tablespoons of water, drink on an empty stomach in the morning and at night;
- Day 2 of the course – 11 drops of tincture and 3 tablespoons of water, taken half an hour before meals. 2 doses per day;
- Day 3 of the course – dilute 12 drops of tincture with 3 tablespoons of water, drink the same as on the second day.
The structure of polyps
This new formation consists of three main parts:
- endometrial glandular cells;
- the stroma (framework) on which these cells are located;
- a blood vessel that runs through the center of the polyp and feeds it.
Depending on the types of cells that make them up, polyps are:
- glandular, consisting of many cells of the tissue from which the glands of our body are built; develop more often in young women;
- glandular-fibrous: the basis of formation is tissue similar to scar; glandular cells are “strung” on it;
- fibrous: they consist of fibrous (connective) tissue and may include single glands. Such formations most often develop in older women.
Separately, placental polyps are isolated - fragments of the placenta that remain in the uterus after childbirth, abortion, miscarriage, or frozen pregnancy. Such formations are very dangerous in terms of degeneration into cancer; they can also provoke prolonged and heavy bleeding.
Ulcers may form on polyps; these formations can become infected, grow into underlying structures (cervix, vagina) and die. The most dangerous in terms of cancerous degeneration are glandular polyps.
Herbal decoction for douching
Douching is quite effective for polyposis, as it kills harmful microflora, improves blood circulation and provides a healing effect.
There are many different collections and infusions, solutions of which are used for douching:
- Take celandine (3 parts), agrimony, calendula flowers and St. John's wort (2 parts each), badyagu (1 part). All components are mixed, then a large spoon of the mixture is poured with boiling water and kept in a container, sealed with a lid, for about 6 hours. The resulting solution is douched twice a day;
- Shiitake mushroom. To make a syringe solution, take 30 g of mushroom crushed to a powdery state and pour half a liter of boiling water. Keep this infusion for a couple of weeks, and then douche with it twice a day for 10 days. The main thing is to use only high-quality raw materials, so it is better to purchase it at pharmacies;
- A mixture of herbs. Mix one part each of chamomile and oak bark, five parts knotweed and 3 parts nettle leaves. Take 2 large spoons of this mixture, pour boiling water (1 liter) and keep on the stove for another 7 minutes until ready. Douching is carried out 2-3 times a day. This product has a high absorbable effect;
- This syringe solution has also proven itself to be effective in the treatment of polyposis. Take 3 parts of viburnum bark, 2 parts each of angelica root, cinquefoil herb and boron uterus, 1 part each of nettle, cinnamon and cumin. The finished mixture (2 large spoons) is poured with half a liter of boiling water, kept in a bathhouse for about half an hour, then filtered. Douche twice a day. The product can be used to impregnate vaginal tampons and for internal use.
Reasons for appearance
The main “culprit” of polyps is an imbalance of female sex hormones, in which estrogens become the predominant hormones, which normally stimulate an increase in the number of cells of the uterine mucosa in the first half of the cycle. This condition occurs if the normal interaction between the endocrine and nervous systems is disrupted: under the influence of head injuries, hunger, stress, or viral infection.
Uterine polyps are most often found in conjunction with the following diseases:
Other reasons for the development of uterine polyps are:
Systemic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and thyroid diseases increase the risk of polyp formation.
Prevention
Preventive measures play an important role not only after therapy, but also to prevent the appearance of formations. The recommendations are as follows:
- timely treat infectious diseases, including those of the genitourinary system;
- avoid casual relationships, always use contraception;
- correct disrupted hormonal levels, as they can cause benign and malignant tumors of the reproductive system;
- treat inflammatory processes, avoid hypothermia;
- visit a gynecologist once every six months for a routine examination, even if nothing bothers you;
- lead a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits.
It must be remembered that women during menopause and with a hereditary predisposition are at risk, so they must strictly adhere to all preventive recommendations.
https://youtu.be/N9NMLdx9jBo
Girls! Help, tell me... what to do. Two endometrial cysts, each about 5 cm, were discovered. A little later, an ultrasound scan also found a polyp. After hysteroscopy, they diagnosed it as an adenomatous polyp of the endometrium without atypia. I have not given birth for 36 years. I want to give birth, but they pose the question bluntly , because this is a precancerous condition. Either remove everything at once (including the uterus), or try to remove the cysts on the spot, see what their nature is and try to save the organs so that after hormones, try to get pregnant, and then remove everything. I want to ask - are there really no other options other than removal? So what should I do? Maybe you shouldn't think about pregnancy? What if it triggers the development of cancer? Or is it worth the risk? In general, what do you think about surgery at Central Clinical Hospital No. 2 named after. N.A. Semashko JSC Russian Railways. I'm just going crazy about what to do. Because I still want to have time to give birth and at the same time I’m afraid of how the hormones will act and in general. What if I suddenly became pregnant with these cysts. suddenly they would dissolve
Symptoms of a polyp in the uterus
Polyps in the uterus do not show up for a long time. Their growth in the uterine cavity is evidenced by:
In some cases, the above symptoms are either not pronounced or do not cause concern in the woman. They are not very worried (or they attribute it to other diseases that can also be diagnosed) by weakness, fatigue, unusual tastes that develop as a result of large blood losses. She may consult a gynecologist because she has been unable to get pregnant for a long time.
Sometimes a polyp is discovered in the initial stages of pregnancy - during a routine examination or due to bleeding.
The growth of the polyp increases (and, accordingly, the symptoms increase) when taking oral contraceptives and those drugs that contain estrogen.
How is the diagnosis made?
Based on complaints, a gynecologist may suspect the presence of a polyp in the uterus, but he will be able to see it during examination only if the formation is located in the cervix (read more about the polyp in the cervix in our other publication: healthy-lady.ru/polip-shejki-matki) . This will require additional research:
These methods can make a diagnosis, but you can be sure that it is a polyp and not a cancerous tumor only if you remove it and send the material for histological examination.
Treatment
Single polyps that have a typical structure (not similar to those that can degenerate into cancer) in extremely rare cases can resolve on their own. The main treatment for polyps is surgery.
Surgical intervention can have different volumes:
Before surgery, a woman should be examined: take blood tests for coagulation and biochemical indicators, examine a vaginal smear for STDs.
After surgery, up to 10 days after surgery, slight vaginal bleeding (like menstruation or “spotting”) and cramping pain in the lower abdomen will be normal. During the first 10 days it is prohibited:
On days 3-4, a transvaginal ultrasound is performed to exclude postoperative complications.
If the biopsy reveals a glandular or glandular-fibrous structure of the polyps, hormonal therapy is prescribed after surgery to prevent recurrence of the pathology: combined or progestin contraceptives, installation of Mirena.
Treatment without surgery
If polyps have formed against the background of frequent inflammatory diseases of the endometrium of the uterus, then under ultrasound control and after a biopsy, the results of which did not reveal cancerous degeneration, conservative treatment can be prescribed. It includes the purpose:
Traditional methods
Treatment with folk remedies is not only ineffective for uterine polyposis, but also dangerous: in such ways, the manifestations of the disease can be masked, while the neoplasms acquire signs of malignancy. In addition, such a widely recommended recipe as douching with celandine is simply dangerous: the juice of this plant can cause burns, and when absorbed into the blood, it can cause severe intoxication and liver failure.
Source: https://healthy-lady.ru/polipy-v-matke