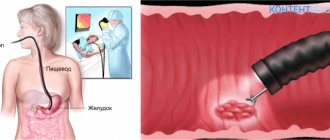
One of the modern diagnostic and therapeutic procedures in gynecology is hysteroscopy. This operation allows you to examine the uterus, identify and, if necessary, promptly remove pathology, and in many cases determine the causes of infertility. The doctor decides whether to perform hysteroscopy, based on the indications and contraindications for this procedure, but the last word, of course, remains with the patient.
Briefly about hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a therapeutic and diagnostic manipulation that allows you to visually evaluate the uterus from the inside, identify pathological formations or anomalies in its structure and, if necessary, remove them promptly, that is, without penetrating the abdominal cavity. This method is endoscopic and is performed using a special optical device - a hysteroscope - by a trained specialist.
Translated from Greek, hysteroscopy means “to examine the uterus.” Manipulation can be diagnostic or therapeutic. Diagnostic hysteroscopy is performed not only to examine the internal uterine surface, but also to collect material (endometrium) for histological examination (biopsy). During therapeutic hysteroscopy, surgical interventions are performed, for example, removal of tumors or foreign bodies.
Hysteroscopy: consequences and their cause
In most cases, negative reactions develop after surgical hysteroscopy, and serious and life-threatening complications are diagnosed extremely rarely. All arising consequences of hysteroscopy can be divided into the following groups:
- Surgical;
- Anesthetic (such consequences of hysteroscopy are often associated with an allergic reaction to the anesthetic, so it is important to undergo a full examination before the procedure);
- Complications associated with expansion of the uterine cavity;
- Consequences caused by prolonged positioning of the patient.
You can undergo a full examination and get all the information about hysteroscopy and possible risks from the specialists of the IVF Center clinic in Kursk.
Preparation for the procedure
Since hysteroscopy is an invasive procedure and is akin to surgery, before undergoing it the patient is prescribed an examination (excluding emergency cases):
- blood and urine tests (general tests);
- smears from the vagina and cervix to determine the microflora;
- blood for syphilis and hepatitis;
- blood for HIV infection;
- blood biochemistry (especially blood glucose in overweight patients);
- blood group and Rh factor.
The following instrumental methods are prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the pelvis;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity (if indicated);
- fluorography;
- blood clotting test;
- ECG (if indicated).
If the patient has chronic extragenital diseases, a consultation with a doctor of the appropriate profile with corrective therapy is indicated. If colpitis is detected, vaginal sanitation is prescribed (up to 1–2 degrees of cleanliness).
The examination is carried out on an outpatient basis. After admission to the hospital, the patient is given a cleansing enema (bowel preparation) before the procedure, and immediately before hysteroscopy it is necessary to empty the bladder. Eating on the day of the procedure is prohibited due to intravenous anesthesia during hysteroscopy. Hysteroscopy is planned for days 5–7 of the cycle, that is, in the first (proliferative) phase, when the new functional layer of the endometrium has just begun to grow and the inner surface of the uterus is accessible for inspection.
It is also necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse 3 days before the procedure, and stop douching a week before. The use of spermicides and vaginal suppositories 7 days before hysteroscopy is also not recommended.
Planning a pregnancy
How long after hysteroscopy can you plan a pregnancy? If the procedure was carried out for diagnostic purposes, then it is highly likely that you can become pregnant as early as next month. However, if even minor surgical procedures have been performed, the body requires much more time to recover.
When planning a pregnancy, you should consider the following facts:
- regularity of the menstrual cycle;
- absence of inflammatory diseases;
- absence of recurrent development of pathological formations removed during surgery.
If the results are positive, pregnancy may occur within 3 months. However, the optimal period for completely restoring the reproductive functions of the body after hysteroscopy is considered to be 6 months.
The need for hysteroscopy before IVF is controversial. Due to the fact that the IVF procedure is quite complex in terms of collecting material and preparing the patient, the risk of miscarriage due to possible injuries from the previous diagnostic procedure is quite high. However, given the fact that women who have unsuccessfully tried to get pregnant for quite a long time resort to IVF, undergoing hysteroscopy will identify and eliminate any structural deformations of the uterus (adhesions, septa) that prevent the implantation of the fertilized egg into the endometrium and its subsequent development.
According to statistics, a much larger percentage of women who have not undergone hysteroscopy (12%) have experienced unsuccessful IVF, while women who underwent surgical treatment of intrauterine pathologies using hysteroscopy and underwent IVF have only 5% of failures.
In all cases, after a certain period of time, it is necessary to do an ultrasound and undergo a full examination to minimize the risk of premature termination of pregnancy.
It is impossible to guarantee a positive outcome of the IVF procedure with 100% certainty, but if after hysteroscopy a woman’s chances of giving birth to her own child increase significantly, this chance has a right to exist.
Hystroscopy today is the most informative method for identifying intrauterine pathologies, the average cost of which ranges from 3,000 to 60,000 rubles, depending on the equipment used, the purpose of the procedure and the prestige of the clinic. Following the recommendations after hysteroscopy will help to avoid the development of complications, minimize the consequences and restore health in a short time.
Uterine curettage and hysteroscopy
Curettage of the uterus is the most common minor operation in gynecology. Among themselves, women often call this operation “cleansing.” But, unfortunately, doctors do not tell all patients about the essence of this operation in an accessible form, but curettage is often a very important step in the treatment of the patient.
Even more interesting:
What are sores on the back of the throat?
Egg for herpes
Why is uterine curettage performed?
Typically, curettage of the uterus has two purposes - diagnostic (obtaining material - scraping the mucous membrane - for histological examination) and therapeutic (stopping bleeding or removing pathologically altered mucous membrane of the uterus).
Indications for uterine curettage in gynecology:
- Suspicion of endometrial hyperplasia or polyp detected by ultrasound. Endometrial hyperplasia is an excessive growth of the uterine mucosa, when it becomes thicker than it should be normally during a given phase of the menstrual cycle. An endometrial polyp is a pathological tumor-like formation “on a stalk”, growing from the mucous membrane of the uterus.
- Acyclic bleeding and uterine bleeding
- Any bleeding in postmenopausal women
- Suspicion of chronic endometritis (chronic inflammation of the uterine mucosa) as one of the causes of female infertility
- Non-developing (frozen) pregnancy
Are there any contraindications to uterine curettage?
Curettage of the uterus is not routinely performed in case of inflammation in the vagina and cervix (presence of purulent discharge from the genital tract and inflammatory changes in the vaginal smear), as well as the general serious condition of the patient due to advanced age and concomitant diseases of the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, blood, when the risk of pain relief and the intervention itself is quite high.
How is uterine curettage performed?
Uterine curettage is a minor gynecological operation, which in the vast majority of cases is performed under general anesthesia. Intravenous anesthesia is usually used. After a special drug is injected into a vein, the patient falls asleep and wakes up in her room when the operation is completed. If there are contraindications to intravenous anesthesia or allergies to certain drugs, curettage may be performed under local anesthesia. In this case, an anesthetic drug (novocaine or lidocaine) is injected into the cervix and vaginal vaults. When local anesthesia is used, the patient remains conscious throughout the operation.
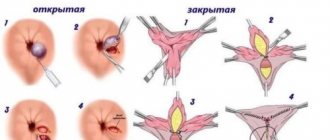
Types of hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy, depending on the purpose, can be:
- diagnostic – when it is necessary to identify the causes of “problems” in the female line (to diagnose endometrial polyposis, submucosal myomatous node or other pathology);
- therapeutic - after examining the inner surface of the uterus, surgical intervention is performed (excision of polyps, resection of a myomatous node, dissection of adhesions or septum in the uterus);
- control - carried out after a certain time (usually six months) after intrauterine interventions using hysteroscopy.
For a successful operation, it is necessary to straighten the uterine walls, stretch and expand the uterus. For this purpose, media are introduced into the uterine cavity. Depending on the medium used, hysteroscopy is divided into:
- liquid (saline solution or 5% glucose is injected);
- gas (carbon dioxide is introduced).
Office hysteroscopy
Office endometrial hysteroscopy is one of the options for diagnostic hysteroscopy and is performed on an outpatient basis. This name for the procedure comes from Europe, where hysteroscopy for diagnostic purposes can be performed not only by a gynecologist, but by a general practitioner, and it is performed on an outpatient basis, in medical offices (by Western definition - in offices).
Office hysteroscopy is called simple hysteroscopy, mini-hysteroscopy, diagnostic video hysteroscopy. The latter term implies showing the patient a picture of the inner surface of the uterus during the manipulation. Advantages of minihysteroscopy:
- low traumatic procedure (a hysteroscope with the smallest diameter is used, without expanding the cervical canal);
- there is no need for general anesthesia, which reduces the cost of hysteroscopy and the risk of anesthetic complications;
- Possibility of outpatient implementation, does not require hospitalization and does not affect the ability to work;
- short period of the procedure (no more than half an hour);
- good tolerance to manipulation;
- It is possible to perform an endometrial biopsy.
Operation methods
The surgical intervention is carried out in the operating room, the patient first undergoes tests and prepares for the procedure. The operation is performed by a qualified gynecologist in the presence of an anesthesiologist, assistant and nursing staff.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Beer and tomato juice for hangovers
The patient is given an anesthetic intravenously or mask anesthesia is used. In exceptional cases, paracervical anesthesia may be used - anesthesia of the tissues of the cervical area. After anesthesia, the doctor expands the cervical canal, inserts a hysteroscope and fills the cavity with gas or solution for better visualization.
The techniques for performing gas and liquid hysteroscopy differ. Let's look at them separately.
With gas
A portion of carbon dioxide is injected into the uterine cavity, expanding the space. The doctor monitors gas pressure and the filling level of the uterus. If the gas is supplied without violating the rules, the patient does not experience complications. If gas supply rules are violated, heart failure and even death can occur.
The gas technique is not used if there are traces of bloody discharge in the cavity - this interferes with clear visualization. Also, gas is not used during surgical interventions.
Using solutions
Hysteroscopy using solutions to enlarge the uterine cavity is the most popular procedure. Saline solution, glucose, glycine or simply distilled water are used as the basis for solutions. Can there be complications after the administration of liquid solutions?
Complications are possible with any examination technique. In this case, there is a risk of postoperative infectious tissue damage. However, hysteroscopy of the uterus using solutions is considered the most gentle compared to gas.
The advantage of therapeutic hysteroresectoscopy is the ability to preserve the integrity of the uterine body while eliminating neoplasms from it. A simple operation on the uterus does not require preliminary preparation and can be performed in a gynecologist’s office. We are talking about polyps and small processes, the elimination of which is not difficult.
During a simple operation, fragments of the fertilized egg or an ingrown intrauterine device can be removed. Foreign bodies and a thin intrauterine septum are also removed in the office.
Carrying out complex operations involves a large amount of work; they are carried out using special equipment and in appropriate conditions. Sometimes preparation for a complex operation requires a course of hormone therapy. It is also practiced to combine hysteroscopy with laparoscopy.
In medical practice, the following types of hysteroscopic operations are performed:
- mechanical surgery;
- electrosurgery;
- laser surgery;
- cryodestruction;
- use of radio waves;
- vacuum aspiration.
Mechanical surgery involves removing processes on the mucous membrane using conventional instruments - scissors, tweezers. Electrical surgery uses high-frequency electric current. Using this method, cutting and coagulation can be carried out.
Filling the tissues with high-frequency current breaks the cell membranes, resulting in the destruction of pathological tissue. The coagulation method involves drying the pathological tissue by touching electrodes. Sometimes both methods are used simultaneously. In preparation for electrosurgery, a liquid that does not conduct current through itself is injected into the cavity - glucose, glycine.
Laser surgery is performed using non-contact and contact methods. This is the most gentle method, since it results in rapid healing of wounded tissues. Laser correction is carried out on the 5-7th day of menstruation. When resection of a polyp, a non-contact method of tissue evaporation is chosen. This allows you to prevent blood loss and reduce complications. The laser is not used for malignant tumors.
Cryodestruction of pathological tissues is exposure to low temperature. Compared to electric shock, cryodestruction does not destroy the surrounding tissue of a polyp or other neoplasm. However, compared to laser surgery, tissue restoration takes a rather long period - 3 months.
Surgery using radio waves removes tumors and does not leave tissue scars. The absence of postoperative adhesions is especially important for women who have not yet given birth, so this method is primarily indicated for them. Unfortunately, radiosurgery is performed only in large regional centers.
Vacuum aspiration is used to remove polyps - it is literally sucked from the body of the uterus. However, vacuum is used only to remove small tumors with a thin stalk.
Indications
The decision on the need for hysteroscopy is made by the doctor based on the following indications:
- various disruptions in the menstrual cycle in girls, women of childbearing and premenopausal age;
- bleeding and spotting in postmenopause;
- suspicion and for confirmation: submucosal myomatous node;
- adenomyosis;
- endometrial cancer;
- malformations of the uterus;
- intrauterine synechiae;
- perforation of the uterus;
- remnants of the fertilized egg and membranes;
- cervical cancer;
- polyposis and endometrial hyperplasia;
- foreign body in the uterine cavity;
As it becomes clear, hysteroscopy is the most effective and efficient method for diagnosing and treating gynecological pathology, so it is not advisable to refuse the procedure.
Hysteroscopy: indications, progress of the operation, recovery - MEDSI
Table of contents
- Hysteroscopy: indications
- Preparation for the procedure
- Stages of the procedure
- Postoperative period, recovery
- Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
Hysteroscopy
is a method of examining the uterus using a hysteroscope (a type of endoscopic equipment), which allows for diagnostics and therapeutic manipulations (according to indications).
This manipulation comes in several types:
- Diagnostic (to detect pathology)
- Therapeutic (to eliminate the disorder)
- Test (to check the result)
There are two types of hysteroscope: rigid and flexible. It is equipped with a light source, optics, a hysteropump and a video system consisting of a video camera, video monitor and cable. All this allows for accurate diagnosis and, if necessary, surgical intervention.
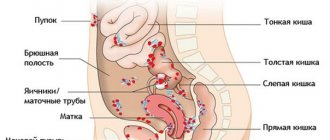
Hysteroscopy: indications
This procedure allows not only to examine the inside of the uterus, but also to perform minimally invasive surgery. Therefore, the doctor prescribes hysteroscopy in cases such as:
- The presence of anomalies or malformations of the uterus and fallopian tubes (septa, fusions, etc.)
- The development of malignant or benign neoplasms (tumors) is expected
- The appearance of changes in the condition or structure of the endometrium (polyps, hyperplasia, endometriosis)
- The patient has myomatous submucosal nodes
- Possible perforation of the uterus
- Disorders of the monthly cycle, development of postmenopausal bleeding
- Diagnosed with infertility
- To monitor the condition, as well as eliminate various violations that appeared after:
- Performing a medical abortion
- Termination of non-developing pregnancy, miscarriage
- Carrying out a caesarean section
- The appearance of postpartum inflammation
- Unsuccessful attempts at IVF (in vitro fertilization)
- Performing hormonal therapy or surgery
- Installation of intrauterine device
Hysteroscopy allows surgical manipulations to be performed accurately and with minimal disruption of the internal walls of the uterus, which ensures rapid healing. This feature of the procedure is especially important for women who are planning to become pregnant.
Preparation for the procedure
Before prescribing a hysteroscopy, it is necessary to undergo several types of examinations:
- Blood tests:
- General
- Research for diseases:
- Syphilis
- Hepatitis
- HIV
- Biochemical
- Coagulation study
- Determination of blood type, Rh factor (if they have not been clarified earlier)
You should also be examined by a therapist. Additional examination of other organs may be required if there is a suspicion of their pathology in order to avoid risks during the operation.
It is necessary to warn your doctor about taking medications. Before undergoing hysteroscopy, you must stop using blood thinning medications.
Like any other surgical procedure, hysteroscopy has contraindications:
- Excessive bleeding
- Cervical cancer
- Presence of an ectopic pregnancy
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system, kidneys or liver
- Cervical stenosis
- Inflammation of the genital organs
- Acute forms of infectious diseases
Stages of the procedure
When performing hysteroscopy, the following procedure is typical:
- Treatment of cervical tissue in the intimate area with antiseptic agents
- Fixation of the organ neck with mirrors
- A probe is inserted to measure the size of the uterus
- Expansion procedures are carried out using liquid or gas
- After these manipulations, a hysteroscope is inserted into the cavity of this organ, which is moved clockwise
- Inspection of tissues, their structure and shape is carried out
- If necessary, therapeutic or minimally invasive surgical procedures are performed
Depending on the type of intervention that needs to be performed, the hysteroscope can be equipped with:
- Biopsy forceps (taking a tissue sample for further examination)
- Scissors
- Electrodes (providing tissue coagulation)
- Laser (to remove tumors and pathologies or cut the septum, etc.)
The procedure allows for the minimally traumatic elimination of uterine tumors such as:
- Polyps
- Partitions
- Remains of the fruit or its membranes
- Fusion
- Myoma
- Excessive growth of the endometrium
This procedure removes foreign bodies from the uterus, including contraceptives. This manipulation also allows for sterilization.
Hysteroscopy for nulliparous women in some cases helps in the fight against infertility.
For some pathologies, the doctor may prescribe a repeat procedure.
Postoperative period, recovery
Rehabilitation options depend on the type of hysteroscopy that was used. During the diagnostic procedure, there is no need for recovery, so the very next day the patient can carry out her usual activities.
When performing a surgical intervention, it is necessary to undergo antibiotic and antifungal therapy.
In the postoperative period, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Refrain from sexual contact (up to several weeks - it depends on the complexity of the operation)
- Don't use tampons
- Refrain from going to the bathhouse, swimming pool or sauna
- Don't douche
For the first time after hysteroscopy, physical activity should be minimal.
During the recovery period, in 1% of cases, complications such as:
- Trauma to adjacent organs
- Getting infected
- Severe bleeding (usually the bleeding is insignificant and disappears in the first days after the intervention)
If any complications or discomfort occur, you should consult your doctor.
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
- MEDSI uses the latest equipment equipped with bipolar electrodes, which allows for extremely low trauma
- Hospitalization in a modern comfortable hospital and the procedure is possible on the day of treatment
- Reception is conducted by experienced, highly qualified specialists who have diplomas and certificates in the field of gynecology and are constantly improving their professional level
You can make an appointment for a consultation at a time convenient for you by calling 8 (495) 7-800-500.
Contraindications
Like any other intrauterine procedure, hysteroscopy is not performed in the following situations:
- acute infectious diseases (colds, sore throat, thrombophlebitis or pyelonephritis and others);
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- acute inflammation of the genital organs (colpitis, endometritis, adnexitis);
- intrauterine pregnancy (desired);
- ectopic pregnancy or suspicion of it;
- advanced cervical cancer;
- extragenital diseases in the stage of decompensation (cardiovascular pathology, liver, kidney diseases);
- profuse bleeding from the uterus;
- atresia of the cervical canal.
Recovery period
The recovery period after the manipulation is conventionally divided into 2 stages. The first stage consists of the primary restoration and normalization of the structure and functioning of damaged uterine tissue (mucous membrane and muscle layer). At the first stage, microdamages and surgical incisions are completely healed, and the cervical canal is restored and regenerated. This stage lasts about 2–3 weeks and ends with complete regeneration of surgical damage and the formation of scar-free tissue.
The second stage of recovery is aimed at the formation of new, newly formed tissue, that is, a new endometrium after hysteroscopy. The new uterine mucosa must have a normal structure and all its inherent functional properties (proliferation and rejection of the endometrium according to the phases of the menstrual cycle). The second stage of recovery requires more time and lasts up to 6 months.
Discharge after the procedure
Blood and moderate spotting will occur in the first 2 to 3 days after the procedure. This is explained by traumatic damage to the uterine mucosa by instruments. Subsequently, the discharge becomes bloody or yellow, which can last up to two weeks. The duration of ichor discharge is due to the expansion of the uterine cavity with liquid during hysteroscopy; the liquid penetrates into the vessels, damaging their walls, which leads to the release of “ichor”. But if heavy bleeding or blood clots appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Menstruation after hysteroscopy
When does your period come after hysteroscopy? It all depends on the purpose of the procedure. In the case of diagnostic, especially office hysteroscopy, menstruation occurs according to the usual cycle schedule, but slight delays are possible (2 - 3 days). This is explained by the fact that during the diagnostic procedure the endometrium is practically not injured, so a long time for its recovery is not required. But in the case of therapeutic hysteroscopy, especially after completion of the procedure by curettage of the uterine cavity, a longer delay in menstruation is possible. In this situation, the first day of the menstrual cycle should be considered the day of the operation and expect menstruation in about a month. It is important to monitor the nature of the first menstruation after the procedure. If there is a change in color or consistency, or an increase in the amount of bleeding, you should consult a gynecologist.
Pain after the procedure
Pain after hysteroscopy is considered absolutely normal if it is minor or moderate, localized in the lower abdomen or lower back/sacrum and lasts a couple of days. Painful sensations are explained, firstly, by the stretching of the uterine cavity during the procedure with gas or liquid, and secondly, by traumatization of the tissues of the cervix and uterus with instruments. Women with a low pain threshold complain of severe pain; in such cases, the doctor may recommend taking NSAIDs with a good analgesic effect (ketorol, indomethacin, Nise). But if the stomach hurts unbearably, the nature of the pain is cramping, dagger-like or shooting, the temperature rises significantly and the symptoms of intoxication increase, the pain radiates to the perineum or leg, then you must immediately seek medical help to eliminate possible complications.
General recommendations
In the early recovery period, it is necessary to strictly follow all the recommendations of the gynecologist:
- abstain from sexual activity for about 3–4 weeks (ideally, before your first period);
- It is prohibited to take a bath, visit a bathhouse and sauna, or swim in a pool or open water for at least 3 weeks;
- maintain personal hygiene (shower daily, wash twice a day using detergents with a pH-neutral reaction (intimate gels, baby soap);
- as a rule, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory treatment after hysteroscopy (prophylactically) with antibiotics (ciprofloxacin) and metronidazole for a course of 5–7 days;
- daily monitoring of body temperature (in the morning and before bedtime);
- stop taking aspirin as a pain reliever (the drug thins the blood, which will increase spotting and can cause bleeding);
- postpone intense physical activity, heavy physical labor and lifting weights of more than 3 kg for 1 - 1.5 months (health-improving sports exercises are allowed after 2 - 3 weeks);
- refusal of tampons during the period of bleeding, it is better to use pads;
- a ban on intravaginal administration of tablets, suppositories, gels and creams, as well as douching;
- after hysteroscopy, you should not use spermicides for a month;
- adhere to a balanced diet so as not to provoke constipation (refusal of spicy, salty, pickled foods, fried and fatty foods).
- Empty your bladder in a timely manner.
What changes indicate complications?
Modern medicine knows the following complications of hysteroscopy:
- Intense uterine bleeding after hysteroscopy of the uterus.
- Development of air embolism.
- Infection of the organ cavity during surgery.
- Infertility.
- Pathological processes developing in the endometrium.
One of the most dangerous complications after diagnostic and surgical intervention is perforation of the uterine walls. This problem arises due to the incompetence of the surgeon who performs the manipulations. Also, if a hysteroscope is used ineptly, a specialist can damage the intestinal walls, after which their contents will begin to penetrate into the periuterine space.
When the operation is performed correctly, complications rarely occur, however, sometimes they do occur. This list includes:
- Uterine bleeding. Occurs infrequently, in a particular risk group are patients with bleeding disorders. Heavy discharge after endometrial curettage should occur within several days after the manipulation, while much later bleeding that occurs poses a great threat to the health and life of the patient.
- Hematometra is an accumulation of blood clots in the reproductive organ. The pathology develops against the background of excessive compression of the cervix, which appears after the operation. Hematometra causes progression of the infectious process. For preventive purposes, gynecologists prescribe injections of antispasmodics.
- Endometritis is an infectious process caused by pathogenic microflora entering the uterus. To avoid complications, gynecologists prescribe antibiotic injections.
- Infertility - given modern methods of performing surgery, there is only a small probability that such a complication will occur.
After mechanical damage to the endometrium, inflammatory or infectious processes can occur in the uterine cavity, which naturally affects the nature of the discharge. They can be:
- Excessively thin, slimy and copious.
- Yellow or pink.
- With an unpleasant odor.
After cleaning, wounds appear on the mucous membranes of the uterus, which release liquid exudate interspersed with blood (ichor). If blood discharge is observed in very large quantities, this indicates poor wound healing.
In this case, special attention should be paid to the color of the secretion released from the vagina. If a woman experiences yellow discharge after cleansing, she should immediately inform the doctor about this, since their appearance indicates the development of a bacterial infection, which can endanger the patient’s life.
It should be noted that yellow discharge that occurs due to the addition of a bacterial infection always eliminates the unpleasant aroma. The appearance of such an odor occurs as a result of the active activity of pathogenic microorganisms that produce volatile compounds that mix with uterine secretions and give them such an unpleasant aroma.
Considering that after abrasion the likelihood of complications always remains high, a woman needs not only to know how long the discharge normally lasts after cleaning, but also what symptoms may appear if complications develop.
Types of discharge after taking Duphaston and what they mean
So, a woman needs to immediately visit a doctor if, after an abortive cleansing of the uterus:
- There is a high temperature (over 38 degrees).
- There is severe pain in the lower abdomen.
- The nature of the discharge changes (consistency, aroma, shade).
- Severe weakness is noted, frequent dizziness occurs, nausea is felt, etc.
It should be noted that after a woman has been cleaned, her temperature may rise slightly. After all, curettage is a type of surgical intervention, and after it, an increase in temperature to 37–37.2 degrees is considered quite normal. Moreover, it can be observed for 2–3 days. At this time, the woman’s condition itself can hardly be called normal. She may be bothered by abdominal cramps and slight weakness.
This condition can persist throughout the entire period while the daub continues. And as soon as it ends, the woman will feel a significant improvement. But if this does not happen, it is necessary to immediately inform the doctor, even if no pathological changes are observed in the discharge itself.
It must be said that no less dangerous is the condition when after curettage there is no discharge or a transparent mucous vaginal secretion is observed. This is also not the norm, and therefore the woman urgently needs to undergo a re-examination.
Any surgical operation, including curettage, is dangerous due to possible complications. Any deviation from the clinical picture of banal menstruation can serve as a symptom of pathology. If after gynecological cleansing you notice one of the manifestations of an impending disease, then consult a doctor, because any ailment affecting the organs of the female reproductive system can be fraught with infertility.
Common complications of the uterine cavity curettage procedure include:
- hematometer after cleaning;
- uterine bleeding;
- endometritis.
Continuous discharge after curettage may soon acquire the character of extensive uterine bleeding. This pathology is caused by a violation of the body's hemostasis system due to the deficiency of one or more blood clotting factors.
The condition in question is characterized by copious and prolonged discharge. If you do not stop the bleeding, then after 2 weeks the hypoxia will become acute. Cells and tissues in conditions of oxygen deficiency will begin to undergo necrosis. The most sensitive brain cells will suffer first. Therefore, in order to prevent this from happening, monitoring of one’s own condition should be organized after the operation.
In this particular case, the everyday diagnostic criterion for the development of uterine bleeding is the number of hygiene products (pads and tampons) used per day - more than ten.
Hematometra is a retention of blood in the uterine cavity, which is formed as a result of spasm of its cervix. The complication develops rapidly immediately after the procedure. A large blood clot forms in the organ cavity, which is a favorable environment for the proliferation of microorganisms. To solve the problem, it is necessary to open the cervical canal.
Endometritis
Endometritis is an inflammation of the uterine mucosa. This pathological process is caused by the penetration of infection into the uterine cavity from the natural microflora of the genital tract or as a result of exogenous infection.
Pregnancy after hysteroscopy
Most women who undergo a hysteroscopy procedure are concerned about when pregnancy will occur after it. If the procedure was performed for diagnostic purposes, and no surgical interventions were performed in the uterine cavity, for example, excision of a polyp, then conception is possible already in the next cycle. This is due to the rapid restoration of the uterine mucosa and hormonal levels. But doctors warn the patient that there is no need to rush, and when you can get pregnant depends on many other factors:
- the nature of the menstrual cycle (regular or not);
- the presence of other gynecological diseases (inflammation of the appendages, background processes of the cervix, external endometriosis and others);
- the presence of extragenital pathology (it is necessary to correct the condition and undergo treatment);
- preparation for pregnancy (healthy lifestyle, taking folic acid, moderate physical activity for at least 3 months);
- examination for sexually transmitted infections and treatment of both partners if they are detected (chlamydia, cytomegalovirus, human papillomavirus and others).
Under favorable conditions, it is allowed to plan a pregnancy no earlier than 3 months after the procedure.
IVF after hysteroscopy
When a patient is preparing for IVF, she must undergo a fairly complex examination, the protocol of which includes hysteroscopy. But not all IVF clinics require this procedure. IVF after hysteroscopy may fail (miscarriage) in the case of undetected and untreated intrauterine pathology, which is why most reproductologists consider the procedure mandatory. What a doctor can identify and remove (if necessary) during hysteroscopy before IVF:
- excise polyps;
- remove hyperplastic endometrium;
- cut intrauterine adhesions;
- excise the intrauterine septum;
- remove foci of endometriosis;
- correct the shape of the uterus in case of its abnormal development;
- remove the submucosal myomatous node;
- check the patency of the pipes (inserting a catheter into the pipes).
After surgical hysteroscopy, planning a pregnancy is allowed no earlier than six months later. In case of successful fertilization and implantation of the egg, the woman is registered at the dispensary from the moment pregnancy is established and is carefully monitored. The course of pregnancy depends not only on the intrauterine surgery performed, but also on other factors:
- hormonal levels before pregnancy;
- age;
- number of births and abortions;
- cervical condition (UC);
- extragenital pathology.
What is hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is used for various purposes: diagnostics, to monitor the condition of the organ after surgery, to monitor the effectiveness of treatment, to perform simple surgical operations.
Hysteroscopy is performed using a hysteroscope, a device that is an ultra-thin optical instrument. The hysteroscope is equipped with a camera that transmits images of the examined area of the cavity to the screen. The procedure is carried out with tenfold magnification, which allows you to clearly see areas of pathology.
- Diagnostic hysteroscopy
– with the help of diagnostic hysteroscopy, the following intrauterine diseases are identified: endometrial hyperplasia, uterine fibroids, synechiae of the uterine cavity, polyps, malignant neoplasms and other diseases. - Surgical hysteroscopy
is an invasive procedure that is performed to treat pathologies of the uterine cavity: polyps, fibroids, eliminates adhesions, remnants of the fertilized egg after an abortion or childbirth, and other pathologies. - Control hysteroscopy
– performed after treatment of diseases and pathologies of the uterine cavity. This procedure will help to detect the leg of the polyp remaining in the cavity after removal of the polyp, the remains of the fertilized egg after an abortion, and other pathologies.
Indications for hysteroscopy, diagnosis of diseases:
- adenomyosis, endometriosis;
- infertility;
- unsuccessful in vitro fertilization;
- abnormal development of the uterus;
- endometrial polyps;
- submucosal uterine fibroids;
- menstrual irregularities;
- cervical cancer, uterine cancer;
- assessment of the consistency of the scar after cesarean section, myomectomy, uterine perforation - preparation for pregnancy;
- removal of an intrauterine device that has grown into the uterine tissue;
- monitoring the condition of the uterine cavity after abortion, drug therapy;
- removal of adhesions in the uterine cavity.
Hysteroscopy is most often performed under general anesthesia, which allows immediate diagnosis and surgical treatment of the disease. Before hysteroscopy, a complete examination of the patient is prescribed according to the preparation plan for surgery. After hysteroscopy, you do not need to be in a hospital; the procedure is performed on an outpatient basis.
Hysteroscopy can eliminate the following symptoms:
- spotting, which often appears during menopause,
- difficulty conceiving,
- pain during sexual intercourse,
- miscarriage,
- premenstrual syndrome,
- dysmenorrhea,
- prolonged, spotting discharge,
- amenorrhea,
- premature menopause.
When the hysteroscopy procedure cannot be performed:
- progressive pregnancy
- late stages of cervical cancer,
- cervical stenosis,
- inflammatory process of the genitals,
- the patient is sick with ARVI, acute respiratory infections or other infectious diseases,
- severe form of the disease (heart attack, stroke, renal failure, cardiovascular failure), serious condition of the patient (decompensation of diabetes mellitus and others).
There are certain rules for performing hysteroscopy:
- Hysteroscopy is prescribed in relation to the days of the cycle and the nature of the pathology (the first phase of the cycle - endometrial polyps, endometriosis, submucous fibroids; the second phase of the cycle - endometrial hyperplasia, infertility of unknown origin, intrauterine synechiae).
- It is mandatory to perform a control hysteroscopy after surgical hysteroscopy.
- In case of separation of synechiae inside the uterus, the procedure is controlled using laparoscopy.
Cost of hysteroscopy
The cost of hysteroscopy depends on the purpose for which it is performed. Diagnostic or office hysteroscopy, respectively, is cheaper since it does not include surgery. Prices for surgical hysteroscopy vary according to the level of complexity of the operation, the qualifications and experience of the doctor and the quality of the equipment. Increases the cost of the procedure and the need (in some cases) for hospital stay. But, of course, the price of the service depends on the region and the level of the clinic.
For example, in Moscow, diagnostic hysteroscopy will cost 15,000 - 35,000 rubles, and the price for an operating room reaches 60,000 - 65,000 rubles. In the provinces, the price of office hysteroscopy ranges from 2,500 to 9,000 rubles, and the procedure with surgical treatment of intrauterine pathology costs from 3,500 to 25,000 rubles. The average price for a hospital stay is 1,500 – 4,000 rubles.
Bottom line
Hysteroscopy of the uterus is considered a type of endoscopy - examination of internal cavity structures. Hysteroscopy is carried out in two directions - as a diagnosis and as a therapeutic minimally invasive procedure for removing various types of tumors.
If previously the diagnosis of submucous fibroids required the complete removal of the uterus from the body, now there is a chance to preserve the reproductive organ and subsequent pregnancy with such a terrible diagnosis. With the help of hysteroscopy, it has become easier to recognize the nature of neoplasms and distinguish a malignant tumor from a benign one.
Pain after diagnostic hysteroscopy is a consequence of forced dilation of the cervical canal (cervix); it goes away without therapeutic treatment. We should not forget that the intensity of the pain syndrome largely depends on the patient’s individual perception of medical manipulations, and not on the nature of the intervention in the body.
Possible complications
Hysteroscopy, like any invasive procedure, is fraught with complications.
Early complications
Among the early postoperative complications, the following should be noted:
- inflammation of the uterus and peritoneum of the small pelvis (endometritis, pelvioperitonitis) – accounts for 90% of all complications;
- intravascular hemolysis caused by the duration of the operation and the use of distilled water or electrolyte-free media or increased intrauterine pressure;
- bleeding – no more than 5% of all complications (observed after resection of fibroids, resection or ablation of the endometrium).
Late complications
Late complications include:
- formation of pyometra in postmenopausal patients (in case of rough manipulation);
- formation of hydrosalpinxes, especially with chronic adnexitis;
- deformation of the uterine cavity (after resection of the endometrium or removal of large myomatous nodes);
- exacerbation of chronic inflammatory processes;
- incomplete removal of intrauterine formations.