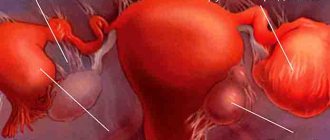
Reasons for the formation of adhesions in the fallopian tubes
Before considering the causes of adhesions in the fallopian tubes, you should familiarize yourself with the mechanism of development of the adhesions process. The fallopian tubes are externally covered with visceral peritoneum, and the abdominal cavity itself is lined internally with parietal tissue. These layers have a smooth surface and secrete a certain amount of fluid, which allows the organs to move freely relative to each other.
If reasons arise that lead to the formation of adhesions, then the fallopian tubes and other organs involved in the pathological process become swollen. A sticky fibrin coating appears on their surface. It is he who contributes to the fact that organs located next to each other are connected to each other. When the inflammatory process has a long course or becomes chronic, adhesive cords form in place of the glued surfaces. In this way, the body responds to inflammation and prevents its further spread. However, the formation of adhesions cannot be considered a normal physiological phenomenon, since it is both pathological and protective in nature.
When the infection penetrates the fallopian tubes, exudate begins to accumulate in them. With adequate therapy, it resolves and does not lead to the formation of adhesions. However, situations are not uncommon when this exudate becomes purulent and spreads throughout the pipe. It is capable of pouring into the peritoneal cavity with fibrin loss. This provokes blockage of the abdominal opening of the fallopian tube by adhesions.
Further progression of the pathological process leads to the fusion of the opposite surfaces of the pipe with each other through partitions. Often, adhesions glue the fallopian tubes to the uterus, oviduct, ovary, intestines, and omentum.
So, doctors consider the inflammatory process to be the main reason for the formation of adhesions in the fallopian tubes, although other factors also influence the growth of strands, including:
- Endometriosis.
This pathological process is characterized by the growth of the endometrium in atypical places, including in the fallopian tubes. (Read more: What is endometriosis? Causes and symptoms of endometriosis).
- Mechanical effects on the fallopian tubes, namely surgical interventions.
In this regard, surgical abortion, ovarian resection, myomectomy, hysteroscopy, intrauterine contraception, IVF attempts, etc. are dangerous. Statistics show that 50% of women who have undergone gynecological operations develop adhesions. Factors such as heavy blood loss, the addition of a purulent infection, and a prolonged course of the operation increase the risk of their formation.
- Undergoing laparoscopy of the genital organs.
No matter how carefully the procedure is performed, it is almost impossible to avoid trauma to the serous membrane of the peritoneum. Therefore, even this operation can trigger the formation of adhesions, which can ultimately block the lumen of the fallopian tubes.
- Difficult childbirth can result in the formation of adhesions
. In this case, the connecting cords grow in the uterine cavity, reach the fallopian tubes and block the entrance to them. A cesarean section, as well as multiple ruptures during the delivery process, are the main factors that lead to the proliferation of connective tissue cords.
- Injuries to the pelvic area accompanied by rupture of an ovarian cyst are dangerous.
In this case, external adhesions are able to attach to the wall of the fallopian tube and block its lumen.
- Infections play a role in the pathogenesis of adhesions formation
sexually transmitted diseases: syphilis, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, etc. No less dangerous is genital tuberculosis, which leads to deformation of the tissue structure and the formation of obstruction of the fallopian tubes due to adhesions and scars.
- Inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system
non-infectious nature, for example, salpingitis is another cause of tubal obstruction.
- Reasons that less often lead to the formation of adhesions
– these are hormonal imbalances and irradiation of the genital organs for the treatment of cancer.
The number of inflammatory processes experienced directly affects the risk of developing adhesions in the fallopian tubes.
The statistics are as follows:
- Single inflammation of the fallopian tubes – the risk of formation of adhesions is 12%.
- Having had inflammation twice – the risk increases to 35%.
- Three episodes of inflammation of the appendages - the risk of formation of adhesions in the fallopian tubes is 75%.
How to treat?
Before starting treatment, the doctor conducts a thorough diagnosis. During this process, it is necessary to make sure that the patient has only this diagnosis. After a comprehensive examination, the doctor becomes aware of the reason for the formation of adhesions. Treatment of the adhesive process is aimed at completely eliminating the pathology. There are several methods:
- conservative treatment;
- surgery;
- treatment using traditional methods.
Conservative treatment. Based on medications and physiotherapy. Drug therapy includes the use of vitamins, painkillers, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and absorbable drugs.
Physiotherapy. Capable of softening structures, as a result of which their thickness noticeably decreases. This eliminates pain, the pathological process stops progressing, and bowel function improves. One of the effective physiotherapeutic methods is ozokerite and paraffin applications. They are placed on the stomach. The duration of the procedure is no longer than 15 minutes.
The adhesive process can be effectively treated without surgery in cases where several months have passed since the onset of the pathological phenomenon. If the illness lasts for a long time, the woman is forced to decide on surgery.
Surgical intervention. Doctors recommend the operation for women under 35 years of age. In this case, it is taken into account that ovulation is regular, and obstruction does not always occur. Surgical treatment does not guarantee 100% recovery. If pregnancy occurs after treatment, even in the absence of symptoms, the woman must be regularly monitored by a doctor from the first days.
In addition to traditional surgery, laparoscopy is practiced in modern gynecology. It is a surgical procedure performed through small punctures. The surgeon makes 3 punctures in the wall of the abdominal cavity. An optical device and special instruments are introduced through them. The optical device is equipped with a small camera. With its help, the doctor performs an operation to remove adhesions without dissecting the abdominal cavity.
This figure schematically shows the principle of laparoscopic surgery.
Alternative treatment can only eliminate symptoms and improve the condition at the initial stage of the disease. For adhesions, medicinal plants such as sage, milk thistle, cinquefoil, juniper, and Chernobyl have proven themselves well. Herbal infusions should be taken orally. Douching with propolis is widely used. It has antibacterial and antiseptic effects.
Symptoms of adhesions in the fallopian tubes
The presence of connecting cords in the fallopian tubes may not give themselves away. The fact is that this pathological process does not affect the woman’s well-being. It is possible to suspect adhesive disease of the fallopian tubes only when pregnancy does not occur for a long time (a whole year) in the absence of contraception. Although, with partial patency of the fallopian tubes, conception can still occur.
If the patient suffers from acute or chronic inflammation of the appendages, then the clinical signs of the existing disease come to the fore. They can be diverse and depend on the specific pathology. However, the inflammatory process against the background of formed adhesions will always be reflected by painful sensations in the lower abdomen. The pain can be either moderate or quite severe. They tend to intensify during intimacy and physical activity.
A change in the nature of vaginal discharge is possible. They may contain pus and mucus. The volume of discharge, even without pathological impurities, increases.
Other signs indirectly indicating the adhesive process:
- Periodically occurring pain in the lower abdomen;
- Exacerbation of discomfort due to mechanical irritation of the uterus during regular menstruation;
- Increased volume of vaginal discharge;
- Hypomenstrual syndrome with scanty discharge, which is observed for a long time;
- The menstrual cycle may become unstable, periods will be absent for a long time;
- All symptoms occur against the background of normal body temperature.
An ectopic pregnancy can also be an indirect sign of adhesive disease of the fallopian tubes. Therefore, after the first such incident, it is imperative to check the remaining pipe for patency.
What are the symptoms?
The main symptom of adhesions in the tubes is infertility. In most cases, this symptom does not cause painful complaints. Menstruation is normal, there is no pain in the lower abdomen.
However, adhesions can still be suspected. A woman will be able to notice the adhesive process only when there are symptoms of inflammation. In this case, pain of a different nature appears in the lower abdomen. Some patients experience an increase in body temperature. Depending on the individual characteristics of the body and the course of the disease, the adhesive process causes other symptoms.
There is no exact information regarding the connection between adhesions and pain. In most cases, pain occurs as a consequence of surgical interventions or an inflammatory process. The frequency of pain in women with adhesions is similar to those without them. The intensity of pain depends on the stage of inflammation and the size of the scar.
Complications of the adhesive process of the fallopian tubes
Reproductive dysfunction is the main complication of the presence of adhesions in the fallopian tubes. A woman may become infertile or unable to bear a child. The basal layer of the endometrium becomes damaged, which will prevent fertilization of the egg or cause difficulties with implantation of the embryo.
A third of patients, even with successful conception and gestation, face certain problems during the delivery process. These difficulties are associated with the development of bleeding in the postpartum period.
Failures after IVF can also be caused by the presence of adhesions in the tubes and uterus.
Another complication of adhesions in the fallopian tubes is the occurrence of chronic pelvic pain, which worsens a woman’s quality of life and contributes to the development of neuroses.
Diagnosis of adhesions in the fallopian tubes
To evaluate the patency of the fallopian tubes, a woman must undergo a hysterosalpingography procedure. This study boils down to the fact that a contrast agent is supplied into the uterine cavity through the cervical canal. It, having passed through the fallopian tubes, should end up in the abdominal cavity. During the procedure, a series of pictures are taken that show the condition of the fallopian tubes. The procedure can be carried out using both X-ray equipment and an ultrasound machine. In the second case, a sterile saline solution is used as a fluid filling the uterus and appendages, rather than a contrast agent. It is worth considering that these manipulations only make it possible to clarify the fact of the presence of an obstacle, but do not make it possible to assess its nature.
Therefore, a number of additional studies may be required, including:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
- Bacteriological examination of vaginal discharge, PCR and smear ELISA. These methods make it possible to detect infectious agents that can provoke adhesions.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy with the introduction of a contrast agent. This study allows you to evaluate the shape and size of pipes, identify the presence of defects and eliminate them.
- Blood test for hormones.
If necessary, a woman can be referred for consultation to an endocrinologist, oncologist, or reproductive specialist.
Treatment of fallopian tube adhesions
Fallopian tube adhesions cannot be cured with medication correction. It can only be carried out with the aim of eliminating pathological processes that provoked the formation of connective tissue cords.
When a patient is diagnosed with an inflammatory disease, she is advised to take antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, depending on the type of infectious agent. In case of hormonal imbalances and endometriosis, hormonal medications are prescribed. Vitamin complexes are used to strengthen the immune system.
Physiotherapeutic techniques help soften adhesive cords and make it easier to carry out surgery to remove them. For this purpose, mud treatment, gynecological massage, and enzyme therapy methods are used. A procedure such as electrophoresis helps increase blood circulation in the pelvis. During treatment, vitamin B, lidase and zinc are used.
Hirudotherapy, that is, treatment with leeches, can also be recommended for adhesions. In combination with other medical measures, this procedure gives a good effect and helps to resolve many small adhesions. The saliva of leeches contains special substances that make the cords mobile and elastic, and destroy existing scars.
Laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes is an effective method for removing adhesions. During the procedure, the doctor can see and cut all the formed cords. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia in a hospital setting.
As for the effectiveness of the technique, it depends on the extent of the adhesions in the fallopian tubes. In case of complete obstruction, even surgery cannot achieve a positive effect, since it will not be possible to restore normal mobility of the ciliated epithelium of the tubes.
Another surgical method for treating fallopian tube adhesions is to blow them with a saline solution with the addition of medicinal substances or carbon dioxide. The procedure is called perturbation (blowing with gas) or hydrotubation (blowing with liquid). However, this method is associated with a number of complications and does not achieve an effect in the presence of large adhesions in the fallopian tubes.
It is worth considering that even surgical removal of adhesions in the fallopian tubes does not guarantee that the tubes will be passable in the future. Therefore, doctors recommend that many patients not waste time on operations and immediately resort to the in vitro fertilization procedure. It should be taken by women aged 40 years and older, as well as by patients who have not become pregnant 1-1.5 years after laparoscopy.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the adhesive process begins with an examination in a gynecological chair. If signs of obstruction of the fallopian tubes and adhesions are detected, the doctor will prescribe a series of instrumental studies.
First, a transvaginal ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs is performed. Women are worried about whether fallopian tube adhesions are visible on ultrasound. It all depends on the size of the adhesive formations. During examination, adhesions are visualized as inhomogeneous echo signals of varying intensity, located in the form of cords.
The main diagnostic methods are still considered:
- sonosalpingoscopy;
- hysterosalpingography (X-ray exposure);
- laparoscopy.
The latter method is highly informative, accurate, and makes it possible to immediately carry out surgical intervention to remove adhesions.