Leukoplakia of the cervix is a complex and at the same time complex gynecological disease.
It affects, as the name suggests, the mucous membrane of the cervix. A descending course of the disease is possible, in which the tissue of the vagina and birth canal, as well as the external genitalia, are involved in the process. The ICD code is N88.1. The essence of the process is the thickening of epithelial tissues, their compaction and keratinization. Translated, leukoplakia means “white plaque,” which well characterizes the pathogenic process.
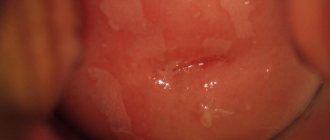
Indeed, areas of leukoplakia look like white thickenings on the walls of the mucous membranes.
Features of symptoms and treatment of leukoplakia
Leukoplakia can form on the mucous membrane of the mouth, lips, on the surface of the clitoris in women, the vulva, in the vagina and on the cervix. As a rule, this disease occurs in people of reproductive age. Leukoplakia of the cervix is manifested by keratinization of epithelial tissue, which is not a normal physiological condition. The disease may not manifest itself clinically and is diagnosed only during a colposcopic examination by a gynecologist. Treatment of cervical leukoplakia consists of carefully following all doctor’s recommendations and is carried out comprehensively. The gynecologist prescribes drug therapy, physiotherapy, special diet and exercise.
Leukoplakia of the cervix, or hyperkeratosis, refers to pathological processes leading to the development of cancer. Therefore, the disease must be treated.
Attention!
Our clinic offers promotions for comprehensive diagnostics of cervical diseases. Diagnostics includes tests and consultation with a specialist. Details can be found in the promotion section or from a consultant, tel. 7 (812) 337-20-07 (free call).
Clinical signs and diagnosis
Most often, the disease occurs secretly, without any complaints. Only some patients are bothered by excessive leucorrhoea, as well as bloody discharge from the vagina during sexual intercourse. There is no pain with leukoplakia.
Due to the asymptomatic course, a complete examination of the woman is of particular importance, especially if she belongs to a risk group.
When questioned, the nature of the menstrual cycle, previous diseases, including pseudo-erosion, are clarified. It turns out how the treatment of pseudo-erosion was carried out.
Diagnosis of cervical leukoplakia is based on the two most informative methods:
- extended colposcopy;
- morphological method.
The lesion looks like an easily removable white film or plaques in the form of lumps, compacted, with clearly visible boundaries. These symptoms of cervical leukoplakia depend on the thickness of the stratum corneum. Beneath it are shiny pink lesions that correspond to the actual size of the damage. Leukoplakia lesions can be very small, or they can occupy a large area, even extending to the vaginal walls.
During colposcopy, leukoplakia appears as an area not stained with iodine, covered with small red dots. These points are outgrowths of connective tissue underlying the epithelium, through which capillaries pass. The pathological focus itself does not have any vessels. Red capillary filaments create a specific mosaic pattern. The Schiller test for leukoplakia is negative.
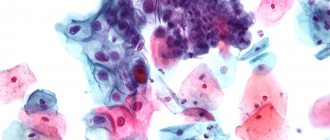
To diagnose a malignant tumor of the cervix with leukoplakia, an imprint smear is taken from the surface of the epithelium. However, this method is not always informative, because due to keratinization, the smear does not penetrate the deep layers of the epithelium, where cellular transformation occurs.
Therefore, the main diagnostic method is biopsy. For a qualitative study, it is necessary to perform a knife biopsy (using a scalpel) from the altered area of the cervix. Therefore, this procedure is carried out under colposcopy control.
Pathology can occur not only in the cervix, but also in the cervical canal. Therefore, it is necessary to perform curettage of the cervical canal mucosa simultaneously with the biopsy. The resulting material evaluates the thickness of the epithelium, the degree of its keratinization, loss of glycogen, changes in the nuclei and shape of cells and other signs.
One of the most modern diagnostic methods is microcolpohysteroscopy. It allows you to enter the cervical canal without anesthesia or dilation, examine its walls, and take a targeted biopsy.
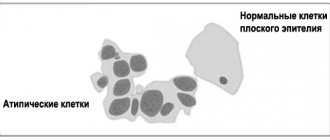
When examining the obtained material under a microscope, the presence of cellular atypia is very important. Leukoplakia of the cervix without atypia is characterized by a normal ratio of cell sizes in the superficial and deep layers, but there are signs of excessive accumulation of keratin in them. This process is called dyskeratosis.
In leukoplakia with atypia, the upper layer is represented by dyskeratosis, and underneath it is hidden a deep layer, in which pathological changes in cells are detected. Many doctors call this condition morphological precancer.
Additionally, to clarify the causes of the disease and its treatment tactics, a bacteriological study is carried out to identify viruses and pathogenic bacteria, and the hormonal levels and condition of the genital organs are also assessed. If necessary, a study of the immune status - an immunogram - is prescribed.
Types and forms of the disease
Leukoplakia happens:
- scaly
- very pronounced and can be diagnosed even during a vaginal examination of the patient on the gynecological chair; - simple
- weakly expressed, unnoticeable during a routine examination on a chair, can only be diagnosed during a detailed colposcopy.
Forms of the disease:
- flat
- sometimes there may be a feeling of tightening of the mucous membrane. If left untreated, the lesion becomes cloudy and upon examination becomes like mother-of-pearl, slightly protruding above the surface of the mucous membrane; - warty
- areas of the affected mucous membrane have sharp outlines and some lumpiness; - erosive
- cracks and bleeding surfaces appear in the affected areas of the mucous membrane against the background of other symptoms.
A correct and final diagnosis can be made only after a thorough histological examination of a sample taken from the altered area of the mucous membrane.
Varieties
The pathology is characterized by the presence of several clinical forms.
Leukoplakia lesions are:
- single;
- multiple.
In gynecology, there are several types of leukoplakia.
- Simple. With this pathology, a characteristic thickening and keratinization of the surface of the epithelium occurs. However, the cells of the deeper layers do not change. Simple leukoplakia is characterized by the appearance of light lesions that do not rise above the healthy tissue. Simple leukoplakia is characterized by an asymptomatic course. Identification of a simple form of the disease occurs by chance during a routine examination or a visit to a gynecologist for another reason.
The initial stage of pathology in a simple form cannot always be diagnosed during a routine gynecological examination.
- Proliferative. With this form, cell proliferation of all layers of the epithelium is observed. The life processes of cells are disrupted, and over time, atypical structures appear. Proliferative leukoplakia is called the precancerous variety or dysplasia (CIN).
- Erosive. This form is characterized by the formation of white spots, cracks and eroded areas.
- Warty. This disease is manifested by formations that can be visualized on the epithelial surface. Warty lesions have a dense structure and are layered on top of each other.
The most favorable form of leukoplakia is its simple version. The simple variety is easier to treat and is less likely to be accompanied by the development of complications. While when a warty type of leukoplakia is detected, a woman is recommended to undergo a biopsy. This is due to the fact that this type of pathology has a significant risk of transformation into a malignant tumor.
What does leukoplakia look like?
Colposcopy
Photo of leukoplakia
Atypical cells
Photo of leukoplakia 2
Causes of pathology
Modern medicine has not yet been able to fully establish the reasons that provoke the development of leukoplakia. There is a theory that the impetus for the spread of the disease is a specific effect on the cervical area. Based on this, causal factors are divided into exogenous and endogenous.
External (exogenous):
- inflammatory process in the uterus and ovaries (endometriosis, cysts);
- cervical injuries after childbirth and abortion;
- diathermocoagulation (cauterization of erosion);
- chemical exposure (the drug "Solkovagin");
- genital infection (papillomavirus, chlamydia, herpes, mycoplasmosis);
- Irregular menstruation (oligomenorrhea) associated with hormonal imbalance.
Internal (endogenous):
- changes in the immune system;
- somatic diseases;
- genetic inheritance;
- weakening of the body's defenses;
- reaction to the intrauterine device.
The mechanism of development of leukoplakia is that due to these reasons, excessive formation of keratin occurs in the epithelium. Changes occur in the structure of cells, the nucleus disintegrates, and glycogen is lost almost completely, and as a result of these pathological changes - an increase in keratinized scales.
Perhaps the development of leukoplakia against the background of cervical ectopia. At the moment when the ectopia heals, its foci are revealed - numerous or single.
Why does cervical leukoplakia develop?
The mechanism of formation of leukoplakia, as well as the reasons for the development of pathology, have not yet been fully studied by scientists. But it is already known that this is a hormone-dependent disease. The prerequisites for the development of pathology are hormonal imbalances and lack of estrogen. Scientists have also proven that the main role in the formation of leukoplakia of the mucous membranes belongs to the human papillomavirus (HPV). Predisposing factors that stimulate the rapid development of the disease are chronic diseases - colpitis, vaginitis and injuries to the external genitalia. Also, the development of cervical leukoplakia is facilitated by disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system, which is responsible for hormonal levels, and a decrease in the immune function of the body. The reasons for the development of cervical leukoplakia can also be attributed to chlamydial infection.
Why does the disease occur?
The causes of cervical pathology are divided into two groups:
- endogenous (internal);
- exogenous (external).
The theory of the hormonal origin of leukoplakia was put forward in the 60s of the twentieth century. According to it, the main cause of hyperplasia (proliferation) of pathological tissues is progesterone deficiency and excess estrogen. This hormonal imbalance occurs due to ovulation disorders in the ovaries. Anovulation develops with any disorders in the hypothalamic-pituitary system, ovaries or uterus.
This condition of the cervix often occurs after an infectious disease of the uterus and appendages, especially against the background of scanty periods (oligomenorrhea).
Of the external factors, particular importance is attached to iatrogenic (medical) physical and chemical influences. Thus, approximately a third of patients with leukoplakia had previously received intensive and often unnecessary treatment for pseudoerosion, and the second third underwent diathermocoagulation (“cauterization”) of the cervix.
So, who is at risk for developing leukoplakia:
- women with irregular menstrual cycles, especially scanty menstruation;
- patients who have suffered from inflammatory processes of the genital tract (salpingitis, endometritis, adnexitis);
- patients who had recurrent pseudo-erosion of the cervix in the past and received intensive treatment for this reason.
The mechanism of disease development is not well understood. Under the influence of the reasons listed above, the processes of accumulation of keratin in the squamous epithelium lining the cervix are activated (normally it does not keratinize). Epithelial cells are slowly rebuilt, their nucleus and other internal elements disintegrate, and the cells lose glycogen. As a result, horny scales are formed.
Leukoplakia can be combined with cervical ectopia. In this case, focal leukoplakia of the cervix occurs during epidermization (healing) of ectopia, when multilayered epithelium begins to grow on the damaged surface. At this time, single or multiple pathological lesions may appear.
Clinical picture of the disease
Leukoplakia itself does not manifest itself clinically. Most often, a woman learns about the pathology by accident, during a routine examination with a gynecologist, or when dealing with another gynecological disease.
Not all women regularly visit a gynecologist for preventive purposes. Most often, the patient comes to an appointment when something is bothering her, then a detailed examination reveals the presence of cervical leukoplakia. But since this is already a precancerous condition, such patients will have to undergo long-term treatment and observation. But with careful attention to health, everything could be different.
Regular visits to a gynecologist are the key to women’s health and the normal functioning of the reproductive system.
Diagnostics
On the road to recovery, first of all, you need to undergo an examination by a gynecologist. This procedure is necessary to assess the condition of the cervix and identify whitish areas characteristic of leukoplakia.
Not all patients are able to visualize white spots on the mucosa. In such cases, the following procedures are used:
- colposcopy;
- microscopic examination of the patient using special solutions;
- histological examination with examination of biopsy material.
Also, for leukoplakia, the Schiller test can be performed. The purpose of the analysis is to stain the walls of the uterus with special substances. If a woman has leukoplakia, the affected mucosa will not stain, which will allow the lesions to be visualized without additional studies.
Smear examination
Taking smears from the vagina is necessary to assess the composition of the microflora. To test a woman for sexually transmitted infections, a PCR test will be required.
Material for subsequent cytological examination is taken with an Eyre spatula or using a cervical brush. These instruments allow you to take a sample from the vaginal part of the cervix, the transition area and the third of the cervical canal.
Despite the fact that the analysis makes it possible to distinguish hyperkeratosis from parakeratosis, such a study for leukoplakia is ineffective. The samples do not allow us to assess the development of the pathological process in the basal layers, so cytological methods will not indicate the form of the disease (with or without atypia).
Colposcopic examination
Colposcopy is used to detail the information obtained during a gynecological examination.
Using a colposcopic examination, it is possible to clarify the size and extent of damage to the cervix and visualize whitish plaques with precise contours. In addition, colposcopy allows you to assess the size of leukoplakia, which can reach large areas.
Diagnosis of leukoplakia
Leukoplakia can be diagnosed based on a detailed examination of the mucous membrane. To do this, the gynecologist prescribes an extended colposcopy, and then examines the material taken for histology and cytology (analysis of cell structure). The detection of atypical (not characteristic of healthy tissue) cells during a cytological study of the material indicates the transformation of leukoplakia into cancer. During extended colposcopy, the mucous membrane of the cervix is stained with Lugol's solution, after which lesions can be seen with the naked eye. Areas with keratinized epithelium are not stained and stand out against the background of healthy areas of the mucous membrane. Cervical leukoplakia is a benign neoplasm that can develop into a malignant lesion with the appearance of atypical cells, in the absence of adequate and timely therapy.
The patient is required to be tested for HPV.
Leukoplakia during pregnancy
If this diagnosis was made before pregnancy, it is recommended to carry out a course of treatment - to relieve symptoms as much as possible (chemical coagulation, cryodestruction, radiosurgical therapy, laser vaporization, and prescribe etiological (in the case of a bacterial or viral infection) and pathogenetic therapy (anti-inflammatory drugs)
During pregnancy, a woman's hormonal status changes several times .
As is known, leukoplakia is a hormone-dependent disease, therefore, during the gestation and postpartum period, the chances of progression of the disease increase.
If signs of the disease are detected during pregnancy, the attending physician assesses the severity:
- In the simple form, treatment is postponed until the postpartum period, since the disease does not pose any danger to the health of the mother and child;
- If a scaly or erosive form is diagnosed, the doctor performs a hormone screening and a biopsy of the lesion. Treatment may consist of hormone suppressive therapy, and in the case of a malignant tumor, the issue of the woman’s ability to give birth to a child is decided.
Treatment of leukoplakia
Treatment of cervical leukoplakia is carried out using different methods, which ones are decided by the gynecologist surgeon. The doctor has at his disposal: cryodestruction, diathermocoagulation (cauterization), electrosurgery and laser.
Cost of oncologist services at the University Clinic
| Service | price, rub. |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with an oncologist, candidate of sciences, associate professor, chief physician, Savinov P.A., primary | 2500 |
| Repeated appointment with oncologist, candidate of sciences, associate professor, chief physician, Savinov P.A. | 2000 |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with an oncologist, candidate of sciences, associate professor, chief physician, Savinov P.A., primary with extended video colposcopy | 4500 |
| Follow-up appointment based on treatment results (examination, colposcopy, recommendations) | 3500 |
| Video colposcopy, extended, digital | 2500 |
| Biopsy of the cervix (1 fragment, without the cost of histological material) | 2500 |
| Vulvar biopsy (1 fragment, excluding the cost of histological material) | 3200 |
Leukoplakia of the vulva
Leukoplakia of the vulva is a disease that mainly affects women during menopause. This is due to sudden and serious hormonal changes in the body. Essentially, this is a dystrophic disease, which is accompanied by hyperplasia (increase in the number of cells) of stratified squamous epithelium. A symptom of vulvar leukoplakia can be itching, which intensifies with movement, urination, at night or during sexual intercourse.
The manifestation of symptoms is not necessary; often a woman learns about her condition only at an appointment with a doctor. Treatment is also carried out by excision of pathological areas using a radioknife, laser or liquid nitrogen.
Diathermocoagulation and cryodestruction
Previously, the main methods of treating leukoplakia were diathermocoagulation and cryodestruction. But now these techniques are used less and less. Cauterization of affected areas of the mucous membrane is highly effective, but often leads to complications:
- bleeding during the procedure;
- bleeding of the mucous membrane during the period of rejection of frozen epithelium;
- stenosis of the cervical canal;
- coagulated cervical syndrome (scarring, impaired blood supply);
- development of endometriosis.
Leukoplakia and pregnancy
Leukoplakia is often detected in young women. At the same time, they may be interested in whether the disease interferes with bearing a child? Is it possible to get pregnant with leukoplakia?
With focal changes, the process of conception is not disrupted. An obstacle to fertilization can be ovulation disorders that cause leukoplakia, as well as the consequences of inflammatory diseases.
In some cases, pregnancy may be difficult if the cervix is severely deformed, for example, as a result of repeated diathermocoagulation procedures performed in the past for recurrent pseudoerosion.
When planning a pregnancy, you should undergo a full gynecological examination and remove leukoplakia. During pregnancy, regular examination using mirrors is necessary. If the condition of the cervix is satisfactory, childbirth through natural means is possible.
Laser treatment
Leukoplakia is most effectively treated with laser coagulation.
Laser treatment is carried out in the first half of the menstrual cycle, always in a clinic or hospital setting. The procedure is painless, so anesthesia is not required. Healing of the mucous membrane depends on the degree and size of the leukoplakia lesion.
Benefits of laser treatment:
- safety;
- does not cause bleeding during the procedure;
- does not damage the surrounding healthy mucosal tissue, since the doctor can regulate the depth of exposure;
- does not provoke the formation of a scab.
Diagnostic methods
At an early stage of the disease, diagnosis of simple leukoplakia is difficult due to the lack of clinical signs. As the pathological process progresses, a visual examination is often sufficient to make a diagnosis.
Diagnosis of pathology includes various methods.
- Gynecological examination. When examined with a vaginal speculum, white spots are visualized, oval in shape and with clear boundaries. These spots rise slightly above areas of healthy tissue and are covered with keratinized scales.
- Cytological diagnosis. To determine simple leukoplakia and other varieties, a scraping of the cervix is performed. However, this study may give incorrect results due to the processes that occur during keratinization and thickening of the mucosa.
- Biopsy. This is the leading research method, which is performed using targeted knife biopsy followed by histological diagnosis. The method allows you to determine or exclude the presence of tumors and cervical dysplasia.
- Diagnostic curettage of the cervical canal area. The study is performed to exclude a malignant process.
- Colposcopy. As a rule, to determine the type and size of leukoplakia, extended colposcopy using special solutions is recommended.
- Laboratory diagnostics. Such a study includes smears for flora, bacterial culture and PCR diagnostics. In some cases, hormonal and immunological tests are necessary.
Various diagnostic methods make it possible to differentiate simple leukoplakia from other types of pathology, as well as pseudo-erosion and oncological process.
Some patients are recommended to be examined by a gynecological oncologist and consult a gynecologist-endocrinologist.
Comprehensive treatment - the ideal approach to leukoplakia
Any method of influencing a pathologically changed area of the mucous membrane will not bring the expected effect if the treatment is not comprehensive. Complex treatment of cervical leukoplakia combines the use of hormonal, antibacterial drugs, cytostatics, immunomodulators, vitamin therapy and laser or surgical treatment. As a rule, at the initial stage of the disease, the patient is prescribed physiotherapeutic treatment, taking multivitamins and following a special diet. A woman is advised to carefully monitor the hygiene of her genital organs, regularly attend appointments with a gynecologist and avoid emotional stress. With severe deformation of the mucous membrane of the cervix, the question arises of amputating the cervix or performing a special operation that involves removing part of the cervix.
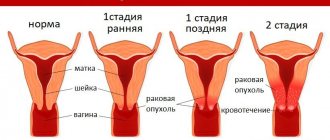
Leukoplakia must be treated, since ignoring the pathology leads to transformation into cervical cancer.
Treatment
The question of how to treat cervical leukoplakia most effectively has not yet been resolved. Quite a few methods of influencing the pathological focus have been proposed, in particular:
- diathermocoagulation;
- exposure to liquid nitrogen;
- laser treatment of cervical leukoplakia using high-intensity radiation;
- radio wave surgery;
- general drug treatment;
- use of drugs locally.
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to make sure that the patient does not have inflammatory diseases of the vulva and vagina caused by viruses, chlamydia, trichomonas, and fungi. According to indications, treatment is carried out with appropriate antimicrobial drugs.
Treatment of cervical leukoplakia with folk remedies is not recommended. Substances such as sea buckthorn oil, rosehip oil, aloe-based products and other popular recipes can increase the proliferation of pathological cells and cause the appearance of atypical cells. We advise women not to risk their health, but to be treated according to modern ideas.
Herbal treatment for leukoplakia is permissible only in order to improve hormonal balance and general condition and includes red brush, hogweed, and white cinquefoil. Courses of adaptogens – lemongrass, eleutherococcus, and Rhodiola rosea – can be beneficial.
Cauterization with the drug "Solkovagin"
Chemical cauterization of cervical leukoplakia with the drug “Solkovagin” is still used. This drug causes coagulation (cauterization) of the epithelium. The medicine penetrates to a depth of 2 mm, which contributes to the destruction of the lesion. Treatment with Solkovagin is painless. In young nulliparous patients with simple leukoplakia, the effectiveness of such therapy exceeds 70%.
Solkovagin has contraindications, in particular, suspicion of cellular dysplasia or malignant neoplasm. Therefore, it should not be used for leukoplakia with atypia.
Diathermocoagulation
Currently, diathermocoagulation is also used - cauterization using high temperature. However, this method has undesirable effects:
- development of endometriosis at the site of exposure;
- bleeding due to rejection of the crust formed during coagulation;
- exacerbation of concomitant adnexitis;
- menstrual irregularities;
- pain;
- long healing;
- often - relapse of cervical leukoplakia.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy is a modern treatment method. Through low temperature it causes necrosis (death) of pathological cells. The procedure is carried out once and lasts, depending on the size of the lesion, from 2 to 5 minutes. The manipulation is painless and is performed on an outpatient basis. Efficiency reaches 96%, but relapses are possible.
To speed up healing and prevent infection after diathermocoagulation or cryotherapy, suppositories are prescribed. Vaginal suppositories are used to restore damaged mucous membranes - with methyluracil or Depantol.
Laser exposure
Laser removal of cervical leukoplakia is the most modern treatment method. A high-intensity carbon dioxide laser is used. The procedure is non-contact and painless. This eliminates the possibility of the patient becoming infected with any infectious diseases or bleeding. The laser evaporates damaged tissue, forming a thin film that protects the wound from blood and infection.
The most modern method of treating cervical leukoplakia is laser exposure
Laser coagulation is performed on an outpatient basis, in the first week of the cycle. Immediately before exposure, the cervix is stained with Lugol's solution to determine the boundaries of leukoplakia. If not only the cervix, but also the walls of the vagina are affected, at the first stage laser coagulation of lesions on the cervix is performed, and a month later - on the walls of the vagina. Complete healing occurs approximately 1.5 months after the procedure.
Radio wave therapy
For leukoplakia, treatment with surgitron is possible. This is a device for radio wave therapy, which allows you to painlessly and quickly remove the pathological focus.
Surgical method
If leukoplakia occurs due to a change in the shape of the cervix (for example, after childbirth), surgical treatment is used. The affected tissue is removed using conization (knife or laser), as well as amputation (wedge or cone). Plastic surgery can be performed to restore the normal shape of the cervix and cervical canal.
Of all treatment methods, laser therapy is preferable.
Can cervical leukoplakia go away on its own?
Unfortunately, the answer to this question is negative. Without treatment, simple leukoplakia can exist for quite a long time, but when atypia appears, the progression of the disease accelerates and can transform into a malignant tumor.
After treatment, you need to balance your diet, try to consume more protein and vitamins. After consulting a doctor, you can take dietary supplements to improve immunity and women's health. They can be taken individually or in programs that include several natural components.
Disease prevention
To avoid the development of leukoplakia, women need to follow simple rules:
- Regularly observe in gynecology.
If there are no alarming symptoms, visit a gynecologist at least twice a year. If any, you need to be examined immediately; - Avoid stress and avoid overcooling
. Both of these factors lead to a decrease in the immune defense of the female body and make it vulnerable to the development of pathological conditions; - Lead a reasonable lifestyle.
Sexual life should be regular, with one sexual partner. Avoid indiscriminate sexual intercourse; use a condom if you do not have a regular partner. During unprotected sex, infection with the human papillomavirus can occur, which subsequently triggers the development of leukoplakia.
To protect yourself from such an unpleasant pathology as leukoplakia, it is necessary to promptly treat gynecological diseases.
UP
Sign up
Ask a Question
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Share link:
Prevention of leukoplakia
To prevent leukoplakia it is recommended:
- maintaining intimate hygiene;
- systematic use of herbal infusions for toileting the genital organs;
- using a condom as protection against unwanted pregnancy;
- consuming enough vitamins with food.
Following these recommendations will help maintain healthy microflora in the cervical area. Contraception will protect against unwanted pregnancy and abortion.
Classification
Depending on the macroscopic picture, the following forms of leukoplakia are distinguished:
- Verrucous or warty (second stage of the disease) - whitish growths are layered on top of each other, which is why the neck looks lumpy, and the foci of leukoplakia themselves rise significantly above the mucosa and are almost impossible not to notice;
- Simple, which is considered the initial stage of the process, while the white plaques are flush with the mucous membrane and do not protrude above its surface; they can easily be missed during examination of the cervix;
- Erosive - whitish plaques have cracks and/or erosive areas.
After a histological examination of a piece of plaque, simple leukoplakia and leukoplakia with atypia (proliferative) are distinguished. Simple leukoplakia (no atypical, that is, cells prone to degeneration, have been identified) is considered a background process of the cervix. Leukoplakia with atypia (there are atypical cells) is considered precancer.
Reviews from women
In my case, the diagnosis was confirmed after a biopsy. Leukoplakia was cauterized using liquid nitrogen. At the moment there are no relapses, we have to be monitored regularly.
Elena
My leukoplakia occurs together with erosion and the papilloma virus. Most likely, the disease was formed due to multiple ruptures during childbirth. They scheduled an operation, but advised me to give birth faster, as there might be difficulties later.
Lyudmila
Since I am nulliparous, the leukoplakia lesions were removed with a laser. The procedure was quick and painless. To prevent the disease from developing into cancer, surgery must be performed.
Olga
My leukoplakia was treated using the traditional method – cauterization. There were no consequences of this treatment. Six months later she became pregnant and successfully carried her son to term.
Catherine
Symptoms of leukoplakia, photos
The symptoms of leukoplakia depend on its type.
Flat leukoplakia (simple) occurs without any symptoms. Discomfort and a burning sensation inside can be caused by warty leukoplakia.
Erosive leukoplakia can leave ichor stains on panty liners, especially after sexual intercourse. If leukoplakia has spread to the vulva area, then there may be itching and, as a result, the appearance of tiny cracks, abrasions, and scratches. These symptoms are quite vague - they also exist in other diseases of the female genital area.
Usually, colposcopy and biopsy are used for differential diagnosis - then with a high probability we can talk about leukoplakia. Most doctors are inclined not to consider leukoplakia a malignant disease, but such a statement can only be given after examining a biopsy specimen. In the presence of atypical basal cells, such leukoplakia cannot be considered benign and further treatment will be based on this point.
Causes of the disease
Most often, leukoplakia develops against the background of infectious or inflammatory diseases.
Factors preceding the onset of the disease also include hormonal imbalances caused by a lack of estrogen and progesterone. The risk of leukoplakia increases in women who have undergone surgery. Chemical and traumatic disorders of the organ can trigger the process of keratinization of epithelial cells. The most common causes of leukoplakia include:
- damage to the cervix during intimacy;
- infectious diseases (chlamydia, thrush, trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis, gonorrhea and mycoplasmosis);
- various forms of vaginal dysbiosis;
- metabolic disease;
- hormonal abnormalities;
- decreased immunity;
- local damage resulting from surgical procedures;
- cervical ruptures during childbirth.
Under the influence of irritating factors, inflammation of the epithelial layer develops. The next step is to activate the mechanisms that promote keratinization of the squamous epithelium. As a result of various rearrangements, horny scales are formed. They are characterized by a complete absence of glycogen. The structure of pathological cells can be modified over time due to decreased immunity or as a result of hormonal changes. The risk of tissue degeneration increases during menopause and gestation. Gradually, the pathology can move to deeper layers of the epithelium.
Symptoms
In most cases, the disease is asymptomatic and is detected only during preventive examinations. However, some patients note the following signs of pathology: pain during sexual intercourse, copious discharge, which is distinguished by an unpleasant odor. The color of the leucorrhoea may vary.
If the disease has spread beyond the cervix, a woman may experience itching, burning, and spotting after sexual intercourse.
Diagnostics
As part of a gynecological examination, the doctor will be able to visually detect a rough white plaque that has clear, blurred or jagged boundaries. Plaque cannot be removed with a tampon. In addition to the mandatory examination by a specialist, the following studies must be carried out:
- Smear cytology. The scraping is taken from the whitish plaque. However, the method is not reliable - atypical cells may not get into the smear.
- Colposcopy. Determines the border and size of the lesion, possible atypical areas. During the Schiller test (staining with Lugol's solution), the plaque will not turn brown.
- Biopsy and histology. The study is carried out under the control of a colposcope. Allows you to accurately determine the presence or absence of a precancerous process.
- Blood tests and smears for infections.
- Determination of hormonal levels.
How to identify and confirm the disease
Leukoplakia, like many other diseases of the cervix, is asymptomatic. Therefore, they are discovered by chance - during preventive examinations, when registering for pregnancy. Sometimes leukoplakia becomes a “find” even for a doctor when performing an extensive examination of a woman. The following methods help identify the disease.
- General inspection in mirrors. A gynecologist can even see white spots on the mucous membrane with the naked eye.
- Cytology. Taking smears from the cervix (liquid or conventional cytology) using an Ayre spatula or cytobrush can, followed by cytological (cellular) examination, help identify tissue that is abnormal in this area.
- Scraping from the cervical canal. Can be performed in an outpatient or inpatient setting. Often accompanied by separate diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity (EDC). The material is sent for histological examination, where specialists detect signs of leukoplakia.
- Biopsy. The material can be collected with a regular scalpel (knife biopsy), a loop or special pliers. It is performed without anesthesia or under local anesthesia - depending on the method and extent of the lesions. The histologist makes a suitable section and examines the tissue under magnification. This is one of the reliable methods for detecting leukoplakia.
- Colposcopy. Quite informative for identifying leukoplakia. For a more accurate diagnosis, not only a simple colposcopy is performed (without exposing the cervix to dyes), but also an extended one. In the latter case, the surface is treated with an iodine solution (the keratinizing epithelium does not absorb it well). On examination, areas of leukoplakia are clearly light in color compared to adjacent tissues. After identifying atypical areas, it is from here that a targeted biopsy should be performed. This way the probability of missing a pathology is minimal.
Almost all tests can be performed on an outpatient basis, sometimes requiring several appointments.
How to cope with the disease
Treatment of cervical leukoplakia includes conservative and surgical methods. Usually they are combined. Schemes are individual and largely depend on the woman’s age, the severity of the changes, and the presence of concomitant dysplasia.
Drug therapy
The following medications are used.
- Antibiotics. Prescribed for concomitant genital infections, the presence of inflammation, for example, in areas of scratching. If there are no such signs, antibacterial drugs are not used.
- Antiviral. If a concomitant lesion of HPV or HSV (herpes simplex virus) is detected.
- Immunomodulatory. Often included in regimens to increase the body's resistance. These are biological supplements, drugs from the interferon group in the form of suppositories.
- "Solkovagin". This is a solution consisting of a mixture of acids. It is used to treat the cervix in affected areas, after which a local small tissue burn is formed in these areas with subsequent restoration. Typically two to three treatments are required, spaced seven to ten days apart. But treatment with Solkovagin cannot be carried out if dysplasia or inflammation is suspected or present.
Popular folk remedies include baths and douching with solutions of boron uterus, St. John's wort, chamomile, calendula and similar herbs. The methods are easy to perform at home. But such treatment alone is unlikely to help quickly get rid of the disease; it is better to combine it with basic regimens and surgical methods.
Surgery
Surgical removal of cervical leukoplakia is the optimal treatment method in many situations. The choice of method is made by the attending physician and depends on age, number of births in the past, degree of damage and examination results.
- Exposure to electric current. Another name for DEC. The cheapest method, but has a number of disadvantages. For example, after such treatment a rough scar is formed, and healing takes more than a month, and all this time the woman will be bothered by copious unpleasant discharge.
- Exposure to cold. Cryodestruction is ideal for small lesions without signs of atypia based on examination results. The manipulation is painless, after it an almost imperceptible scar is formed, healing is not accompanied by copious discharge.
- Laser exposure. Suitable for leukoplakia, similar in its positive aspects to cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen.
- Conization of the cervix. Can be performed using radio waves or using a surgical scalpel. Preference for this method is given in the presence of atypia in the cells, with a combination of leukoplakia and dysplasia. The method has the great advantage that the removed material is sent for histological examination. After this, we can conclude how radical the treatment was.
- Amputation of the cervix. This operation involves shortening the neck; it is the most extensive of all those presented. With a combination of gynecological problems, the question of removing the entire uterus (extirpation) may arise.
In each case, it is necessary to weigh the pros and cons of treatment. Particular attention should be paid to women planning pregnancy or who have not yet given birth. The surgical technologies used in relation to them should imply the minimum possible removal of tissue, otherwise in the future the consequences of such treatment of cervical leukoplakia may lead to problems with pregnancy.
Rehabilitation after surgery
For a speedy recovery and to avoid consequences after surgery for cervical leukoplakia, you must:
- abstain from sexual activity for 1-2 months;
- stop using vaginal tampons;
- refrain from visiting the bathhouse, sauna, or swimming in open water for 1-2 months.
In addition, for favorable rehabilitation after surgery, hypothermia, overheating, drinking alcoholic beverages, and undergoing physical activity are contraindicated.
Causes
Leukoplakia can be caused by various causes. But before starting its treatment, it is still worth studying the main provoking factors of this pathological process.
The most common causes of leukoplakia include the following:
- Diseases of an infectious nature. Ailments of this type often include nonspecific vaginitis, colpitis, endocervicitis, chlamydia and other infectious pathologies transmitted through sexual contact;
- The presence of hormonal imbalance;
- The presence of primary and secondary immunodeficiency;
- Traumatic injuries to the cervix during childbirth, as well as during various doctor’s manipulations during surgical interventions or diagnostics;
- Incorrect and untimely therapeutic therapy for gynecological diseases, especially with pseudo-erosion;
- The presence of external factors - chemical, physical, as well as previous diathermocoagulation.
It is worth noting! The pathogenesis of the disease is based on a disorder in the “hypothalamus-pituitary-ovary-uterus” system. As a result, the ovulation process is disrupted, an active increase in estrogen levels and a decrease in progesterone levels begin. All this causes the development of hyperplasia - the proliferation of cells in the reproductive system.
Features of the structure of the uterus of a healthy woman
A healthy reproductive organ of a young, nulliparous woman weighs about 50 grams; after childbirth, its size doubles. The length of the organ is no more than 8 cm, and the width is 5 cm. An increase in the size of the organ during pregnancy is associated with changes in the structure of the muscle layer. From the inside, the reproductive organ has dense walls.
The organ is located in the pelvic region, part of it runs parallel to the bones and moves along adjacent structures. Such movements cause temporary bends: when the bladder is emptied, the fundus of the uterus is directed towards the peritoneum, stretching of the urinary tract, on the contrary, leads to a bend of the uterus towards the intestine.
Before ovulation, the cervix is dry and hard; it loosens under the influence of hormones that provoke conception. The internal os of the organ is covered with mucus, which increases the chances of sperm penetration. If there is no conception, menstrual bleeding occurs, which ensures the removal of the endometrium and blood clots. After the end of menstruation, the uterus returns to its normal position, the cervix rises, the pharynx narrows, and the endometrium is restored. By the time of ovulation, a woman’s ability to conceive is restored.
A healthy cervix during a gynecological examination:
- The fabric is pale pink.
- Ulcers and erosions are absent.
- Clean, the presence of a small amount of transparent discharge is allowed.
- The contours are smooth.
- Pathological neoplasms are absent.
- True to size.
Attention! According to the described criteria, the health of the female reproductive organ is assessed. The appearance of deviations from the given norms is dangerous for a woman. To prevent consequences, you need to be examined by a doctor once every six months.
The doctor gives a conclusion that the cervix is bad if any deviations from the norm are detected. The causes of pathologies can be different, so you need to deal with them.
Features of the postoperative period
To speed up the recovery process, a woman should follow the recommendations prescribed by the gynecologist. It is necessary to take prescribed medications and make regular visits to the doctor. Constant monitoring of the condition of the genital organs will allow you to detect problems in time and avoid the development of oncology. It is especially important to monitor your health when preparing for pregnancy and while carrying a child. The regularity of the menstrual cycle speaks about the functioning of the reproductive system. If it is violated, then the woman needs to undergo an ultrasound examination.
Observation
In the postoperative period, the patient must ensure due attention to her condition. Keeping track of symptoms will help prevent various complications. The likelihood of relapse depends not only on the quality of the operation and compliance with hygiene rules, but also on lifestyle. The following signs indicate the development of complications after surgery:
- violation of cycle regularity;
- the appearance of pus in the vaginal secretion;
- bleeding of unknown nature;
- severe abdominal pain.
Antibiotic therapy
Taking antibacterial drugs is necessary to prevent inflammatory processes and infectious diseases. It takes several weeks for damaged tissue to heal. During this period, the cervix is most susceptible to bacteria. , macrolides, aminoglycosides, cephalosporins or fluoroquinolones are most often prescribed .
Monitoring the condition of the surgical field
After removal of pathological foci, a woman needs to be regularly checked by a gynecologist . The planned examination includes taking smears, performing colposcopy, oncocytology and testing to detect HPV. To prevent relapses, it is recommended to vaccinate against the papilloma virus. 2 years after the operation, the woman can switch to standard preventive examinations.
To speed up regenerative processes, sutures and resulting wounds are treated with antiseptic ointments and solutions. Solcoseryl ointment is highly effective. If cryodestruction or laser therapy was performed, then after 4 weeks the cervix is examined again for the presence of pathological foci. Such an examination will prevent relapses of the disease.
Monitoring hormone and metabolite levels
Hormonal disorders in leukoplakia are considered one of the risk factors. Therefore, it is extremely important to restore a woman’s hormonal levels. Regular blood donation will help to identify disorders in time. , Bilem or Aromeston is prescribed . It is equally important to conduct a test that detects glucose levels. It will show the body's reaction to surgical procedures. The condition of the heart, kidneys, gallbladder and liver is also assessed. For this purpose, a biochemical blood test is performed.
Diet
There is no need to follow a special diet during the period of treatment and recovery. But it is advisable to follow basic nutritional recommendations. It is necessary to exclude potential allergens from the diet. It is equally important to regularly drink 2-3 liters of clean water. You should also avoid alcoholic beverages.
Physiotherapy
To speed up regenerative processes, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed. For leukoplakia, magnetic therapy and electrophoresis . The effect of magnetic waves on the body increases its resistance and improves metabolic processes. The procedure is carried out over a course of 7 to 10 days. It fights inflammation, relieves swelling and accelerates the tissue healing process.
Electrophoresis involves exposing pathological areas to electrical impulses. The medicinal solution is applied directly to the skin of the abdomen. Electric current helps it quickly and easily penetrate the body. The duration of the procedure is 10 days.
During pregnancy
If leukoplakia is detected during pregnancy, it usually does not affect the fetus and does not cause fetal pathologies. At the same time, there is some risk for the pregnant woman herself - there is a high probability of aggravation of the pathology, which can result in the occurrence of much more severe diseases and even malignancy of the lesion.
Such complications can be caused by hormonal imbalance, weakened immunity, or childbirth, during which the cervical tissues can be seriously damaged by stretching. If the presence of a pathological process is identified before pregnancy during its planning, then it is necessary to get rid of it before conception. If IVF is considered, then leukoplakia must be eliminated.
If treatment is not undertaken, then complications and consequences can lead to irreversible disorders such as malignancy of the pathological process.
Dysplasia
Cervical dysplasia is a background pathology, which is characterized by changes in the epithelium of a pathological atypical nature. The disease is a precancerous process, but in the initial stages it can be successfully treated. Visually, dysplasia looks like areas of excess tissue growth with partially hyperemic areas and flat white spots that partially cover the cervix.
The disease does not have pronounced symptoms, but bloody discharge and discomfort during sexual intercourse can cause concern. Timely diagnosis is complicated by hidden symptoms. Most often, dysplasia is discovered only during a routine examination.
Less commonly observed:
- symptoms of an acute inflammatory process;
- itching;
- burning;
- mucous or mucopurulent discharge with an unpleasant odor.
Pathology has no age restrictions. Women of reproductive age are at particular risk. The disease can develop even during pregnancy. To eliminate the possibility of white spots turning into cancer, it is necessary to undergo a full course of treatment.
Possible reasons
Dysplasia occurs when the differentiation of epithelial cells is impaired. The epithelium of the cervical uterus consists of five layers, the ancestor of which is the germinal basal layer of undifferentiated cells. HPV with a high risk of carcinogenesis affects this layer. As a result, the entire surface epithelium becomes atypical. Areas of white spots or leukoplakia in the area of dysplastic lesions of the cervix are a warty appearance, which is dangerous due to the increased likelihood of degeneration into cancer.
The provocateurs of such violations are:
- insufficient activity of cellular and humoral immunity;
- presence of bad habits;
- chronic diseases of the genital area;
- hormonal problems;
- STI;
- trauma to the cervix;
- heredity.
In rare cases, the pathology goes away on its own without medical intervention.
Treatment
When choosing appropriate therapy, the degree of the disease, the size of the white spots on the cervix and the general condition of the patient’s body are taken into account. Special attention is paid to individual risks of changes leading to the transition of dysplasia to cancer.
At the initial stages, concomitant or background diseases are treated and the normal vaginal microflora is restored. To restore the normal structure of the epithelial layer, eubiotics, probiotics and vitamins are used.
Before surgical treatment, immunocorrection and antiviral therapy are performed.
Considering the volume of the lesion, destruction is carried out by laser, liquid nitrogen, radio waves, but more often conization is performed.
The main task of any type of treatment is to eliminate the site of pathological changes and remove white spots with altered cells. The cervix should return to physiological normal.