Benefits of MRI
The magnetic resonance imaging method is valued for its high quality images and information content. Main advantages of diagnostics:
- During the procedure, patients feel comfortable, as the diagnosis is painless;
- Magnetic fields are safe for the human body, unlike x-rays, which involve radiation exposure. For this reason, examination of the cervix using MRI can be performed several times over a short period of time;
- Diagnostic results can be found out literally an hour after the diagnostic procedure;
- If necessary, photographs can be issued not only in printed form, but also in digital form.
More information about the diagnosis of cervical cancer
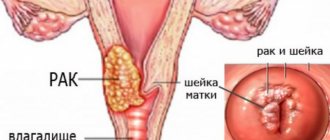
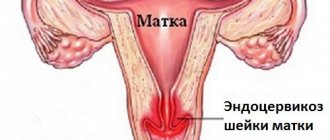
Magnetic resonance imaging is often used to diagnose malignant neoplasms of the female reproductive system. Cervical cancer is a malignant tumor consisting of the mucous membrane - the endocervix. Such a neoplasm was previously diagnosed only in elderly women or menopausal patients. Currently, the problem is more acute because the lesion is detected in young girls.
Clinical symptoms of cervical cancer do not always appear. As a rule, at the first stage they are absent, therefore it is quite difficult to identify a neoplasm with the naked eye. Other methods do not allow one to accurately determine the stage of the tumor before surgery, which is why this diagnostic procedure is recommended for all women with suspected cancer. Currently, MRI for pelvic cancer is the only method that allows determining the stage of a tumor before intervention. With the help of such a tool, a specialist can see how deeply the neoplasm has grown into the wall of the uterus and measure its size, assess the condition of the surrounding organs.
Attention! Modern tomographs make it possible to obtain layer-by-layer images (photos) of the pelvic organs with visualization of all anatomical details.
The value of such an examination method cannot be underestimated. The correctly determined stage of cancer influences the treatment method. The gynecological oncologist must know the size of the tumor, its position and relationship to the surrounding tissues. If the stage of the oncological process is established incorrectly, there is a high risk of relapse.
The technique has other advantages in comparison with other diagnostic methods:
- safety;
- absence of x-ray radiation;
- quick results;
- high value of diagnostic information.
If you suspect cervical cancer, you should not waste precious time on various diagnostic procedures. Despite the high cost of MRI, it is better to pay once, because this technique allows you to detect a tumor at an early stage.
How to prepare for the procedure
An important point is that the study is not carried out during menstrual bleeding. The best period for diagnosis is determined by the first half of the cycle, namely from 6 to 12 days. For certain indications, MRI may be prescribed for the second phase of the cycle.
Attention! When registering for an examination, a woman must have her personal calendar with her.
The quality of the image of the organs of the reproductive system can be reduced by the bladder, small intestine, and loops filled with gas. To minimize the effect of intestinal contents on the quality of images, it is necessary to:
- stop eating foods that cause active gas formation the day before diagnosis (this includes cabbage and other vegetables, carbonated drinks, legumes and sweets)
- before the examination, take Espumisan or activated charcoal (as prescribed by your doctor);
- empty your bowels in the morning on the day of the examination, or better yet, do a cleansing enema;
- plan a meal no later than 4 hours before the diagnosis;
- half an hour before the examination, take an antispasmodic tablet;
- The bladder should be moderately full during the examination, so you should empty it 1.5-2 hours before the procedure, and then not drink unless necessary.
Compliance with such rules will allow you to obtain informative diagnostic results.
Conducting a survey
The diagnostic process is considered painless. It causes discomfort because the patient must lie still during the scan. If the study is carried out with contrast, the substance is introduced into the body using a catheter. The product is supplied to the tissue throughout the examination.
The patient is placed on the tomograph table, lies on his back and is secured with straps. After this, the table slides into the tunnel. Communication with the doctor is carried out using the built-in microphone. The procedure is monitored via video link. After turning off the tomograph, a full tissue scan begins. The duration of the procedure without contrast is about 30 minutes. Using a contrast agent for about 1 hour.
Indications for MRI of the cervix
For gynecological problems, doctors usually prescribe an ultrasound examination. This technique allows you to recognize most common problems, and ultrasound equipment is available in almost every medical institution. But ultrasound diagnostics is not always informative.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the cervix is prescribed if other diagnostic methods are not indicative. The study is prescribed in the following cases:
- Pain during sexual intercourse;
- Bleeding outside the menstrual period;
- Menstrual irregularities;
- Pain in the lower abdomen that occurs for no apparent reason;
- Suspicion of cancer;
- Inability to conceive a child naturally;
- Uncharacteristic vaginal discharge;
- Suspicion of ectopic pregnancy;
- Miscarriage.
If there is a hereditary predisposition to the development of malignant neoplasms, experts recommend MRI of the cervix at least twice a year. This will significantly reduce the risk.
MRI for ovarian cysts
Tomographic examination allows you to obtain an image of the pelvic organs in different projections. It is this quality of modern MRI diagnostics that is indispensable in the following cases:
- on an ultrasound, the doctor doubts the location of the tumor in the abdomen;
- to identify the risk of malignant transformation;
- if a cyst is suspected of spreading into neighboring organs;
- to assess the structure of the tumor (cystic, solid);
- if there is a possibility of an inflammatory process in the area of the uterine appendages;
- against the background of concomitant diseases - fibroids and endometriosis.
Ovarian cyst on ultrasound
The main task of MRI diagnostics is to detect the exact location of the ovarian cyst and assess the risk of oncological pathology. If there is any suspicion, there is no time to waste: on our website you can sign up for an MRI examination by choosing a suitable clinic. It is better to identify a dangerous problem in the uterine appendages in time than to miss the chance for recovery.
Possible contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging of the cervix is not performed on women in the following cases:
- There are metal structures installed in the body that cannot be removed independently. These include prostheses, implants, knitting needles, pins, pacemakers, etc.
- First trimester of pregnancy. At this time, the formation of organs and the formation of the fetal nervous system occurs, so doctors do not recommend conducting such studies.
- The patient's weight exceeds 130 kg. With greater weight, diagnosis is difficult due to the limited volume of the tomograph capsule.
- Deviations in the functioning of the nervous system, due to which a woman is unable to remain motionless for a long time.
- Fear of confined spaces. With claustrophobia, research is difficult, because being inside the tomograph can cause panic in the patient.
- Relative contraindications include menstruation; in the presence of menstrual flow, MRI of the cervix is postponed until the end of periodic bleeding.
The contrast agent is contraindicated in women who are breastfeeding or pregnant. Be sure to consult your doctor and rule out an allergic reaction to the injected drugs. In addition, the contrast agent should not be used in case of chronic renal failure (the contrast is excreted primarily by the kidneys, significantly increasing the load on them).
Ovarian cyst during pregnancy
Under favorable circumstances, pregnancy can occur against the background of a cystic tumor in the ovary. Some retention formations (follicular, luteal) disappear spontaneously during pregnancy, some do not increase in size and do not bother the pregnant woman. In cases where surgery is unavoidable, the doctor will prescribe removal of the cystic tumor in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, when the risk of miscarriage is minimal. In emergency situations (rupture or torsion, high risk of malignancy), surgery is performed at any stage of pregnancy. When carrying a fetus, you should be wary of the following complications associated with the presence of a tumor in the appendages:
- frozen pregnancy;
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- constant pelvic pain;
- violation of excretory functions (problems with urination and defecation);
- premature birth;
- venous disorders (hemorrhoids, perineal varicose veins, varicose veins of the legs).
The discovery of an ovarian cyst during a random or routine examination is a reason for a full examination. The best diagnostic option is a combination of ultrasound, MRI and laparoscopy. Most types of ovarian tumors must be removed surgically. Women planning a pregnancy need to remove the cyst before the desired conception occurs in order to safely carry and give birth to a healthy baby.
Preparatory measures
There is no need to prepare for magnetic resonance imaging if we are talking about the classical diagnostic method (without contrast). If contrast enhancement is necessary, you must come to the MRI on an empty stomach. Let's consider general recommendations that you should familiarize yourself with before diagnosis:
- Don't take any jewelry with you, leave it at home. You need to remove all metal items, earrings, piercings, bracelets, etc.
- Have clothes ready to change into during the examination. Any loose clothing without metal inserts will do.
- Before the procedure, you should empty your bowels; if you have problems with stool, you can use an enema.
- A couple of days before the test, avoid foods that cause gas.
- Be sure to empty your bladder to avoid discomfort during the procedure.
- If you are very concerned about the diagnosis, consult your doctor. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe sedatives.
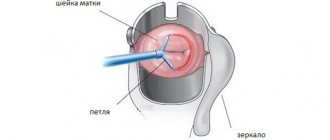
How is an MRI of the cervix performed?
There should be nothing metallic on the clothing you will be wearing for the examination. You can take a change of clothes with you and change. You also need to take off your shoes, empty all metal objects from your pockets, turn off your mobile phone and lie down on the extendable table.
If necessary, the doctor will inject a contrast agent through a vein, after a couple of minutes the drug will be distributed throughout the circulatory system and the table will move inside the magnetic resonance imaging scanner. Magnetic resonance imaging of the cervix takes no more than half an hour. During this time, the specialist receives the required number of images.
The presence of lighting, ventilation and an alarm button makes the diagnostic process completely comfortable. If a woman feels unwell, she has the opportunity to stop the examination process at any time. You can also contact the doctor via speakerphone if necessary.
Variants of ovarian cysts
Ovarian cysts should first of all be distinguished by oncological characteristics:
- benign (70-80% of all cases);
- border;
- malignant.
The following options for localization are possible:
- right ovarian cyst;
- left ovarian cyst;
- bilateral cystic tumors;
- cystic cavity not associated with the ovary.
Depending on the structure there are:
- ovarian retention cysts;
- epithelial tumors;
- endometrioid cyst;
- hormonally active tumors.
Ovarian cyst
The most common type of cystic formations are retention tumors that arise against the background of natural changes in the ovaries. Every month, ovulation occurs in the female body - the process of follicle formation and maturation of the future egg. This event can become the basis for the appearance of a cyst on the ovary. In addition, inflammation and endometriosis can provoke the appearance of a benign neoplasm in the ovary. Retention tumors include:
- follicular cyst;
- luteal (corpus luteum cyst);
- parovarian (cyst not associated with ovarian tissue);
- endometrioid cyst;
- inflammatory formation.
Any neoplasm in the area of the uterine appendages can create many problems for a woman’s health. This is especially important in case of infertility or recurrent miscarriage. The detection of an ovarian cyst is the reason for examination using high-tech tomographic and endoscopic equipment, which will be the main factor in preventing dangerous complications and sad consequences.
Interpretation of results
At the end of the diagnosis, the specialist needs to decipher the results of the study. When interpreting the results, the doctor takes into account the features of the structures of the cervix. During the examination, the following pathological changes can be identified:
- Malignant neoplasms (cervical cancer);
- Benign neoplasms;
- Inflammatory diseases;
- Adhesive processes;
- Anomalies in the structure of the cervix;
- Cervical erosion;
- Endometrial proliferation;
- Cervical dysplasia.
To avoid serious illnesses, do not forget about preventive examinations with a gynecologist. You need to go through them at least once every six months, even if nothing bothers you. Be healthy!
What pathology can be determined?
MRI shows the following diseases and pathologies:
- An increase in the size of these organs;
- Benign or malignant neoplasms, metastases;
- Inflammatory processes occurring in connection with infections or other diseases;
- Growth of the inner layer of the uterine wall;
- Weakness of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the pelvis.
Since MRI can be used to see anatomical changes up to 1 cm in size, this makes it possible to detect many more nosological forms that are less common in gynecological practice than the diseases listed above.