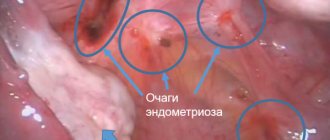
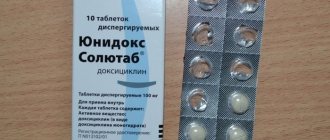
Many diseases occur in the body asymptomatically. They are dangerous because they are detected at the stage of complications, a sharp deterioration in health. To avoid consequences, a person is recommended to undergo regular examinations. Analysis for hidden infections in women helps to identify herpes, papillomavirus, cytomegalovirus, HIV, mycoplasma, and hepatitis.
Gonococci
Gonococci cause a disease called gonorrhea. Gonorrhea is transmitted sexually. Severe inflammation, redness, and swelling appear in the external and internal genital organs. A person experiences itching, accompanied by yellow discharge. The process of urination becomes difficult and pain occurs. Gradually, hematuria begins, at first hidden, then it becomes obvious, that is, the urine turns red.
What other pathologies should you be aware of?
There are many microorganisms located on the genitals of women. Some of them are opportunistic, others are pathogenic. Mandatory therapy is carried out only for the second type, so that complications do not form.
To identify pathogenic microorganisms, a smear is taken from the vagina. It is inoculated on a nutrient medium or microscoped. In other cases, blood will need to be drawn to determine the genetic material of the viruses. With the help of research, pathologies are identified that you need to be aware of.
- Actinomycosis. The disease belongs to the group of mycoses. A granuloma of external and internal organs is formed. The incubation period after infection is several weeks, so it is impossible to immediately detect the disease. It occurs in acute and chronic forms. Pathogenic microorganisms multiply in the granuloma; when the fluid comes out, a fistula is formed. The patient's body temperature rises and malaise appears.
- Trichomoniasis. This is a disease of the genitourinary system due to the pathogen Trichomonas. Foamy yellow or green discharge and a fishy odor appear. A woman experiences itching, burning, pain, which intensifies with urination and sexual intercourse. The external genitalia are hyperemic. Foci of bleeding appear.
- Hepatitis. The causative agent is a different type of hepatitis virus. The disease is transmitted through household contact, sexual contact, and blood transfusions. The disease does not manifest itself for a long time. Therefore, liver hepatocytes begin to become inflamed and die. The parenchyma is replaced by connective tissue, and the function of the organ is impaired. Gradually, the patient develops jaundice, dark urine, and pain under the right hypochondrium. Therefore, doctors recommend preventative blood donations to detect the virus.
- HIV. This is a virus transmitted sexually, through dirty syringes and other medical instruments, through the transfusion of contaminated blood. The disease has no cure, only the elimination of symptoms and correction of immune function are possible. Gradually, the patient develops AIDS, which leads to death.
- Syphilis. Infection occurs through household contact, sexual contact, and through dirty medical instruments. Syphilis is diagnosed using the Wasserman test.
Doctors warn that prolonged presence of viruses, bacteria and other STIs in a latent form gradually causes a deterioration in health. But if the pathogen is detected in late stages, the disease can be eliminated. For example, with hepatitis or HIV infection. Therefore, it is recommended to undergo preventive blood tests for HIV and hepatitis.
Diagnostics, what tests are performed for hidden infections in women
It is impossible to take one test to identify all hidden infectious agents. To determine them, several different tests are performed that allow timely identification of the disease.
- Microscopy . A smear is taken from women's external and internal genital organs. Biological material is examined under a microscope. In this way, mushrooms and spores are identified and their varieties are determined. The presence of bacteria is also determined, but it is not possible to classify them in this way for every species. Therefore, in some cases additional research will be required.
- Bacterial culture . The smear is inoculated onto a nutrient medium. The types of bacteria and the antibiotic to which they are sensitive are determined. This is a specific test that allows you to identify the exact causative agent of the disease.
- Linked immunosorbent assay . This is a test that detects antibodies that are released in response to the introduction of a pathogen. The method determines herpes and other viruses.
- Polymerase chain reaction . This is a blood test for hidden infections (using the PCR method), which reveals the exact genetic material of the pathogenic microorganism. That is, it is not one’s own cells that are detected, but a certain infection. It is determined even in the presence of a small amount of biomaterial.
If a woman has never been examined, it is recommended to undergo tests to detect hidden infections when prescribed by a gynecologist. This is especially important for patients who are preparing for pregnancy.
Features of laboratory diagnosis of certain sexually transmitted infections
Typically, diagnostics are carried out after making an appointment with the presentation of a passport.
However, many institutions allow anonymous testing for STDs.
Anonymity does not provide any particular advantages, since the doctor is obliged to maintain medical confidentiality.
Therefore, information does not go beyond the boundaries of the medical institution in any situation.
Anonymously, more often they do only a smear for STDs in women and men.
In other cases, more detailed information about the person will be required.
In addition to the classic examination of genital tract discharge, there are other examination methods.
These include:
- throat swab for STDs;
- scraping from the urethra for STDs;
- semen testing for STDs;
- comprehensive urine test for STDs;
- blood test for STDs;
- culture for STDs;
- PCR analysis for STDs.
For diagnosis, tests that diagnose several infections at once provide significant assistance.
The material can be not only vaginal or urethral discharge, but also blood.
A comprehensive PCR analysis for STDs is carried out using any material.
In this case, it is not antibodies to microorganisms that are detected, but their DNA or RNA.
This significantly specifies the diagnosis, allowing one to learn about the presence of the disease in a short time after infection.
To monitor treatment, provocation was previously recommended when taking an STD test.
It was believed that for this it was enough to drink a glass of kefir or 50 grams of any alcohol the evening before the study.
There were also methods of mechanical, thermal or biological (gonovaccine) stimulation.
It was assumed that such a provocation increases the activity of microorganisms, even when their numbers are small, helping to more accurately monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
This procedure has not been used since the last century.
Human papillomavirus infection is a pathology in which the skin and mucous membranes are affected as a result of the activity of human papillomaviruses (HPV).
There are over a hundred types of virus that can cause a wide variety of diseases (vulgar warts, plantar warts, anogenital warts, etc.).
The most serious problem caused by HPV is cervical cancer (93% of episodes of this disease are associated with the activity of the virus).
The group of high oncogenic risk HPV includes several types of virus - 16, 18, 31, etc.
The diagnostic algorithm for HPV-related diseases is clearly defined.
Condylomas and warts are easily identified during examination, sometimes requiring additional instrumental examination.
As for the diagnosis of neoplastic (precancerous) changes and cervical cancer, the fundamental measure here is the Pap test.
Based on its results, changes in cells are judged and additional studies are prescribed:
- colposcopy with acetic acid test, test with Lugol's solution;
- histological study.
When small lesions are detected by Pap test, various tactical diagnostic options are possible.
In one of them, PCR diagnostics for HPV is immediately carried out and membership in the group is determined by oncogenicity.
An alternative test is the hybrid capture method (Digene test).
Unlike PCR, it allows you to detect only clinically significant levels of the virus (from approximately 5000 copies of DNA).
Timely testing for hidden infections and adequate treatment of such conditions allows you to avoid or significantly reduce the risk of very serious health consequences.
To get tested for hidden infections, contact the author of this article, a venereologist in Moscow with many years of experience.
Different STDs are diagnosed differently.
Let's look at the main ones.
Let's discuss what tests are done for sexually transmitted infections, depending on the suspected pathogen.
Syphilis
It can be diagnosed by both direct and indirect methods.
Direct ones are preferable.
But they are used exclusively for initial confirmation of the diagnosis.
Moreover, it is not possible to obtain clinical material containing Treponema pallidum at all stages.
The most sensitive direct diagnosis may be:
- in the primary stage, when the material can be obtained from chancre;
- lymph node punctate is used less frequently;
- in the secondary stage, when there are rashes on the body (secondary syphilide).
Various methods are used to identify the pallidum spirochete.
The main ones:
- dark field microscopy;
- PCR.
A more sensitive method is PCR.
But if there are no obvious foci of syphilitic infection, the disease is diagnosed by serological methods.
As we have already said, the method for determining antibodies is less reliable.
After all, it is not the pathogen itself that is detected, but only signs of its presence in the body.
Therefore, to establish a diagnosis, you need at least two positive results from different laboratory tests.
For this purpose research is used:
- non-treponemal – aimed at identifying antibodies to antigens formed as a result of the breakdown of one’s own tissues under the influence of an infectious process;
- Treponemal - antibodies to the bacterium that causes syphilis are detected in the blood.
Nontreponemal tests are used as screening.
Treponemas are confirmatory.
At the same time, to confirm cure, antibodies to the pale spirochete are not determined.
This study is not informative, since after eradication of bacteria, antibodies remain in the blood for years, and sometimes for a lifetime.
But the titer of immunoglobulins to autoantigens gradually decreases.
Therefore, the effectiveness of treatment is monitored using non-treponemal serological tests.
Gonorrhea
The simplest and most inexpensive method is microscopic.
True, he does not always have sufficient sensitivity.
You can detect gonococcus with 100% probability if:
- a man suffers from gonorrhea;
- the urethra is inflamed;
- There is copious purulent discharge.
In other cases, problems arise with diagnostics using the microscopic method.
Both the sensitivity of the test and the specificity are reduced.
In women, symptoms are usually mild, and there are few gonococci in the smear.
Therefore they may not be detected.
When collecting smears from other parts of the body, in addition to the urethra, the material often contains bacteria that are similar to gonococci, but are not the causative agents of gonorrhea.
These are primarily non-pathogenic Neisseria.
When swabs are taken from the throat, meningococci may be detected in them.
To increase the specificity of the test, the diagnosis of gonorrhea is made microscopically only if all three signs of the presence of gonococcus coincide:
- bean-shaped bacteria arranged in pairs;
- some bacterial cells are located intracellularly;
- Gram stained negatively.
If at least one sign does not match, a diagnosis is not made.
Additional examination is also recommended in situations where the smear for microscopy was not taken from the urethra.
PCR is the main method for detecting gonorrhea.
Allows you to quickly and accurately establish a diagnosis even with an asymptomatic form of the disease.
Culture is a rarely used method for diagnosing gonorrhea.
It is used in the following cases:
- examination of menopausal women or minors;
- medico-legal cases;
- the need to assess the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics.
Culture diagnostics are more specific than PCR.
It never gives false positive results.
Therefore, during a forensic medical examination, it is the culture that is done.
In other cases, PCR is preferred because it is simpler, faster and cheaper.
In addition, the technique has greater sensitivity compared to culture (it detects gonococci even in their minimal quantity).
Trichomoniasis
The diagnostic principles are approximately the same as for gonorrhea.
Microscopy reveals only clinically expressed forms.
Important conditions for making a microscopic diagnosis:
- the patient is a woman;
- a smear is taken from the vagina;
- the presence of severe symptoms (heavy discharge);
- examination of a native (unstained) smear as soon as possible after collecting the biomaterial.
Trichomoniasis is mainly a disease of women.
Men get sick 2 times less often, are prone to self-healing and in most cases do not suffer from severe symptoms.
There is not much discharge from the urethra.
Therefore, it is theoretically possible to detect Trichomonas there, but in practice it is rarely possible.
In women, the symptoms are more pronounced.
There are much more Trichomonas in the vagina than in any other organs.
They can only be detected in a native smear.
Because Trichomonas must remain mobile.
If there is no movement, a diagnosis cannot be made.
In a native smear, the doctor detects large cells with flagella under microscopy.
They make jerking movements and “push” neighboring cells.
PCR is the main method for diagnosing trichomoniasis.
It allows you to detect Trichomonas DNA in a smear from the urethra, vagina, cervix, urine or ejaculate.
Including in the chronic form with no symptoms.
Culture is used in the same cases as for gonorrhea.
These include the need to assess antibiotic sensitivity and medico-legal cases, as well as the examination of minors or menopausal women.
Chlamydia
There are many methods for diagnosing chlamydia.
Theoretically it can be used:
- microscopy with Romanovsky-Giemsa staining;
- mutual fund;
- ELISA;
- PCR;
- sowing.
In practice, PCR is overwhelmingly used for the primary diagnosis of chlamydial infection.
Because other methods are either not sensitive enough or have low specificity.
Chlamydia is an intracellular parasite.
It is unstable in the external environment and grows poorly in cell cultures.
To obtain reliable cultural results, you must:
- the presence of severe symptoms;
- perfect compliance with the rules of preparation for testing for sexually transmitted infections;
- compliance with the rules for taking biomaterial, its storage and transportation.
Often chlamydia dies and does not grow in cell culture.
Therefore, the sensitivity of culture testing is only 40-50%.
Due to the high risk of a false negative culture result, PCR is preferred in the primary diagnosis of chlamydia.
Mycoplasmosis and ureaplasmosis
Mycoplasmas and ureaplasmas are very small.
The microscopic method is not used to diagnose these infections.
They do PCR or culture.
Moreover, cultural testing is not possible for all types of these bacteria.
How to properly prepare for testing for hidden infections
To undergo examinations, it is important to prepare for them. If a vaginal smear is taken, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- 1 week before the test, do not take new medications, especially vaginal suppositories;
- You cannot drink alcohol or use chemicals;
- 1 day before, the doctor prohibits sexual intercourse that violates the test results;
- Before examining the smear, you need to wash the external genitalia with bactericidal soap.
If a patient undergoes blood sampling, no specific preparation is required, since the virus or infection is located in it, regardless of lifestyle. But many doctors recommend not drinking alcohol, not eating fatty, spicy, fried foods 1 day before the test.
The time for drawing blood or smear is not important. If the infection is present in the body, the woman’s biorhythms do not affect it.
Linked immunosorbent assay
In an abbreviated version, this method is called ELISA. The examination includes smears from the urethra or cervical canal, as well as blood serum. What should you know? The most common and effective blood test for infections. It must be given to a patient who is suspected of having diseases such as hepatitis, STIs, mycoplasmosis, HIV, papillomavirus, influenza and others.
The appointment must be made by a doctor, after which you should prepare for the study. It is based on the detection of antibodies to pathogens. When faced with an infection, the human immune system begins to work, producing a protein characteristic of a specific type of disease. The ELISA method provides 90% accuracy for identifying those infections to which antibodies are formed.
For the study to be reliable, blood sampling from a vein must occur in the morning on an empty stomach. This is done in the treatment room in compliance with all standards. Sometimes the study can be carried out during the day, but the person must not eat for at least 6 hours.
How soon will the results and their interpretation be ready?
If the studies are not urgent, patients receive the results 2-5 days after removal of the biomaterial. The exception is bacteriological culture. The growth of pathogenic microorganisms takes a long time, so the time period increases to 7-10 days.
A note indicating the presence or absence of infection is placed on the study form. If bacteria or fungi are detected in a smear for hidden infections, the doctor additionally notes whether there are many or few of them present in the field of view.
Leukocytes and ESR
The presence of a bacterial infection in the body can be determined using a simple general blood test. When deciphering, you need to pay attention to the number of leukocytes. It is leukocytes that neutralize pathogenic bacteria, so an increase in their number indicates the presence of infection in the body. In addition, an increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate or ESR indicates the presence of infection. If such abnormalities are detected in a general blood test, the doctor may recommend that you undergo a PCR or ELISA test again to clarify.
Preventive measures
Hidden infections lead to complications, so doctors have included the following basic prevention methods:
- maintain daily hygiene of the external genitalia;
- use contraceptives to eliminate the possibility of contracting an infection; they are also used to prevent unwanted pregnancy;
- before conception, studies are carried out in order to eliminate the development of the disease in a timely manner;
- visit a gynecologist every 6-12 months and undergo laboratory tests;
- it is necessary to carry out treatment in time before complications occur;
- refrain from casual sexual intercourse;
- do not use medications without a doctor’s prescription (improper use of antibiotics can lead to superinfection and candidiasis).
For prevention purposes, you need to take tests to identify all pathogens that can harm your health. A blood test for latent infections is a mandatory laboratory diagnostic method that allows timely identification of pathogenic microorganisms. It is not recommended to do them yourself. To determine the method and procedure for diagnosing the condition of the uterus and vagina, consult a gynecologist. Timely identification of the pathogen will eliminate the presence of cancer, infertility, and other systemic diseases.
Herpes virus
This is a rather unpleasant pathology from which it is impossible to completely recover. It is provoked by various types of viruses found in the body of all people, even completely healthy ones. In the case of certain factors, for example, a sharp decrease in immunity, the pathology begins to develop rapidly.
Symptoms of latent infections in women and men are quite similar.
The following signs indicate herpes:
- pain, itching in the genital area;
- rashes on the skin and mucous membranes (we are talking about a blistering rash);
- presence of mucous discharge;
- body temperature may increase;
- After the bubbles burst, scabs form, causing severe pain.
The disease can lead to quite unpleasant complications:
- meningitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- keratitis;
- encephalitis;
- damage to the central nervous system.
This infection leads to the appearance of various formations on the skin and mucous membranes: warts, condylomas. The pathology is characterized by a long course without pronounced symptoms. Exacerbation of the disease occurs against the background of decreased immunity.
Most often, HPV is detected during examinations during pregnancy or during studies to detect cancer.
A woman may suspect the development of the disease based on the following signs:
- genital warts, warts appear on the lips, in the mouth, on the genitals;
- cervical erosion is diagnosed.
If not treated promptly, HPV can lead to various types of malignancies.
Blood tests for STIs
Blood tests for STIs
- examination using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Blood is donated on an empty stomach, taken from a vein.
The method is not applicable to all infections and may not always give an unambiguous result.
Only in the absence of all types of antibodies in the blood can we speak of a negative test.
All other options require further examination using the PCR method.
Intrauterine infections
Intrauterine infection (IU) is an infection that can develop in the fetus in the womb. Its source is the maternal organism. In this case, the baby is born sick or infected. In addition, infection is possible during childbirth, when the child passes through the woman’s birth canal.
A blood test for intrauterine infections includes tests to identify the following infectious diseases:
- complex of TORCH infections – toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus infection, herpes virus; these infections cause very severe intrauterine pathologies of the fetus, and most often their presence in a woman is an indication for termination of pregnancy;
- sexually transmitted infections – ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis;
- HIV infection, hepatitis B and C viruses, syphilis.
Screening for intrauterine infections is mandatory for all pregnant women.
Women's tests for infections: where to get them
A woman can get tested for infections either in a municipal hospital or in a paid center.
The main thing when choosing a medical institution is experienced and qualified doctors.
In a regular clinic, you can get smears for infections for free.
In this case, you will have to wait your turn.
The readiness of test results can take up to 1 - 2 weeks.
Commercial centers win in terms of the quality of gynecological services.
Appointments by phone are available, test results will be ready the same day or the next.
The research can be conducted anonymously.
Paid clinics are equipped with anonymous rooms, and complete confidentiality of the results is guaranteed.
Bacterioscopy
For bacteriological examination, a vaginal smear is taken to identify pathogenic microflora (bacteria, fungi) and diagnose bacterial vaginosis (changes in vaginal microflora), vaginitis, candidiasis (thrush), and STDs.
The smear reveals the causative agent of the disease, its type and quantity, as well as the concentration of leukocytes. Bacterioscopy does not always determine the nature of the pathogenic agent; in this case, other types of diagnostics are prescribed. Bacterioscopy is indicated not only for diseases, but also during pregnancy or its planning, after antibacterial or antitumor therapy.
Several days before the examination, you should not use vaginal tampons, suppositories and other transvaginal drugs, douche, or have sexual intercourse. On the day of sampling, antibacterial and antiseptic gels for intimate hygiene should not be used. You need to wash only with clean water without soap.
The procedure for collecting material is simple and does not cause discomfort: using a special small brush, cells are scraped off from the mucous membrane of the vagina and/or canals (cervical or urethral), the instrument is placed in a sterile tube, and sent to the laboratory.
It takes 3-4 days to get results. But you can submit the material to a laboratory where rapid tests are carried out, then the result is possible on the day of the test.
Women's tests for infections: when to take them
When the first signs of an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system appear, you should not delay your visit to the doctor.
It is also necessary to take tests for infections for the purpose of prevention.
Some STDs have a long incubation period and are asymptomatic.
In this case, you may not suspect an infection for a long time.
If you have only one sexual partner, it is recommended to visit a gynecologist at least once a year.
Warning symptoms when you should get checked:
- 1.Discharge
- 2. Pain in the lower abdomen
- 3.Discomfort when urinating
- 4. Inability to get pregnant or miscarriage
Women's tests for infections: preparation
In order for the test results to be as reliable as possible, preparation is needed.
Following simple rules will allow you to get reliable results.
If a woman has to undergo a smear test for infections, she must:
- Avoid taking antibiotics
- Do not enter into sensual relationships a couple of days before the analysis
- Do not use antifungal or antibacterial agents
- Wash yourself the day before collecting biomaterial with warm water.
During menstruation, a smear for infection is not taken.
When you have taken antibiotics, consult your doctor.
It is recommended to take tests no earlier than after 2 weeks.
Blood is taken for venous examination.
To identify the inflammatory process in the body, urine must be collected in the morning.
To do this, use a sterile container.
Women's tests for infections for the purpose of prevention
Preventive examinations and tests are carried out at least once a year.
More frequent screening is recommended for women at risk.
You need to follow simple rules to avoid infection:
- Have a permanent sexual partner
- Avoid accidental communication without barrier protection
- Don't forget about personal hygiene rules
- Support the immune system
It is worth getting tested for infections periodically.
This is recommended for both healthy women and those who have previously had sexually transmitted diseases.