Uterine artery embolization technique
Embolization of the uterine arteries is used to preserve the uterine organ and to ensure the normal functioning of the reproductive system in the future. The technique is also used before surgery to prevent severe bleeding.
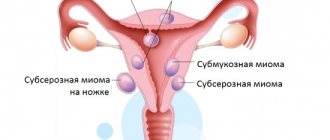
This method is used in the following cases:
- growing uterine fibroids with normal functioning of the reproductive system or the development of pathology against the background of female infertility;
- constant bleeding from the uterus, which can threaten a woman’s health.
The embolization procedure was approved in 1998 and has been successfully performed by doctors since then. In order to carry out the manipulation, there must be clear indications and the approval of the attending physician. The technique is considered one of the newest and most effective ways to prevent the negative consequences of removing a benign tumor.
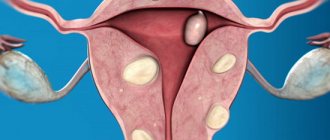
The essence of the technique is that the blood supply to the fibroids is completely stopped. As a result, the nodes significantly decrease in size or dissolve. A woman’s reproductive function is not impaired, and after some time the menstrual cycle is restored, which means she is ready to conceive children.
Embolization of the uterine arteries is recognized as an innovative technique that, without additional complications, gives positive results and allows a woman to restore the normal functioning of the reproductive system and maintain women's health. To prescribe a procedure, a preliminary consultation with the attending physician is necessary after an accurate diagnosis has been established.
https://youtu.be/X1-CS02AI10
Preparation for embolization
After consultation with a gynecologist and an endovascular surgeon, the patient is prescribed a list of laboratory and instrumental tests that she can perform in a clinic. General preoperative examination includes:
- UAC;
- OAM;
- TANK;
- coagulogram, blood group and Rh factor;
- tests for syphilis, HIV, viral hepatitis;
- fluorography;
- examination by a therapist with an ECG;
- bacteriological examination of vaginal discharge;
- cytological analysis of smears from the vaginal part and endocervix of the cervix;
- colposcopy;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs with color Doppler mapping.
Before embolization of the uterine arteries for fibroids, an RDV with hysteroscopy or aspiration biopsy of the endometrium with histological evaluation of the biopsy is required. According to indications, magnetic resonance imaging is performed.
The patient needs to shave the area of the right thigh and groin in advance. Embolization is performed on the day of hospitalization, so you need to enter the department on an empty stomach. Before the intervention, an elastic bandage is applied to the lower limbs, and medical compression stockings can be used. Direct preparation for surgery consists of prescribing sedatives, anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs, preventive antibiotic therapy, emptying the bladder and catheterizing it with a Foley catheter.
Carrying out the procedure
The embolization procedure requires preliminary preparation and some manipulations in the form of an ultrasound examination and a smear to determine inflammatory processes in the vagina. These measures are needed to eliminate contraindications to the process.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia and a special catheter is inserted through the inguinal fold. Using an X-ray machine, the doctor controls the movement of the tube and directs it to the location of the vessels that supply the fibroid with nutrition.
To accurately control the location of fibroids and the necessary vessels, a special substance is injected, which is clearly visible on x-rays. After correct implementation of all stages of the procedure, the specialist controls the flow of substances into the artery from polyurethane or polyvinyl. These compounds help limit the flow of blood into the tumor and ensure its gradual death.
Manipulation is carried out in two femoral arteries to obtain an accurate and positive result. After embolization, a bandage is applied to the incision site for 12 hours, and the procedure is considered complete. During the first 2-3 hours, the patient is under observation, and then can be sent to recover at home.
Preparatory procedures before surgery
Obtaining a positive result during embolization largely depends on the preparatory stage. In order to carry out the operation without additional complications, you need to undergo a number of certain studies:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- ultrasonography;
- examination of microflora in a smear;
- CT scan.
After all the tests and accurate diagnosis are completed, a date for the operation is set. Before the procedure, it is recommended not to eat anything and prepare the groin area (hair removal). In case of severe stress or overexertion, your doctor may prescribe mild sedatives. The process is preferably carried out under local anesthesia.
Advantages of the chosen technique
Many women are afraid of the possible consequences after embolization, so in this case it is important to familiarize yourself with the obvious advantages of the procedure:
- high efficiency of the technique 90–95%;
- no scars or incisions after surgery;
- recurrence of the tumor is almost impossible after using the technique;
- the use of local anesthesia does not require additional recovery time;
- when performing embolization, the stay in the hospital will be only 2–4 days;
- the operation has no serious contraindications and can be carried out if surgical intervention is prohibited;
- After the procedure, the woman remains able to bear children.
The benefits of fibroid embolization described above indicate that the procedure is highly effective and safe for most women. To exclude possible contraindications and complications, you must adhere to the recommendations prescribed by your doctor.
Methodology
The UAE procedure is performed by an angiosurgeon in a cath lab equipped with a digital angiography machine, under local anesthesia. The arterial access to the uterine vessels is most often the right common femoral artery, which is punctured and catheterized using the Seldinger technique.
In the right groin area, the pulsation of the femoral artery is determined by palpation, the skin and underlying tissues are infiltrated with an anesthetic solution. The puncture needle is inserted into the lumen of the artery at an angle of 45 degrees. An introducer is installed along the guide system, through which a specially modeled catheter is inserted into the aorta.
For embolization of the uterine arteries for fibroids, a thin radiopaque catheter with a soft atraumatic tip is used.
First, selective catheterization and embolization of the contralateral (left) uterine artery is performed. The catheter is lowered through a guidewire under fluoroscopic control into the left internal iliac artery. To assess the anatomy of the internal iliac artery and the nature of the blood supply to the uterus, the angiosurgeon performs selective angiography by injecting an iodinated contrast agent and taking a series of images.
Using a controlled hydrophilic guide, the catheter is placed at the mouth of the uterine artery, the guide is removed, and superselective arteriography of the left uterine artery basin is performed. The obtained angiograms evaluate the diameter of the uterine artery, the nature of anastomoses (communications) with the ovarian arterial system, as well as the architectonics of the vessels in the nodes to exclude atypia. The surgeon receives an angiographic image of the vascular network of uterine fibroids, which has the appearance of a rounded perifibroid plexus surrounding the myomatous node.
The end of the catheter is advanced as far as possible in the distal direction, moving away from the origin of the cervicovaginal branch. Next, proceed directly to the embolization stage.
A syringe with microspheres for embolotherapy is attached to the catheter, and the embolisate is injected in a fractional motion until arterial blood flow in the myomatous nodes completely stops. Moving with the blood flow, embolic particles block the lumen of pathological vessels.
The effectiveness of endovascular intervention is assessed using control arteriography, which determines the break in the contrast of the uterine artery trunk. The manipulation is carried out similarly on the ipsilateral (right) side. Upon completion of the operation, the catheter and introducer system are removed, and hemostasis of the puncture site is performed by finger pressure and applying a pressure bandage. The duration of embolization of the uterine arteries for fibroids is 20-40 minutes.
Efficiency of the technique
The effectiveness of embolization is based on the large number of successfully performed operations. Most women, after the process, successfully became pregnant and gave birth to absolutely healthy children. The technique is innovative and has proven its effectiveness in practice.
One of the main advantages of the technique is also its safety compared to surgery. The integrity of the uterus is not compromised, and the menstrual cycle is completely restored. Therefore, this method is popular among doctors and is effective in most cases.
Advantages and disadvantages
Each treatment method has advantages and disadvantages. At the same time, the advantages of embolization compared to traditional node removal are obvious:
- Removal or damage to the uterus is excluded, which makes it possible to fully preserve the woman’s reproductive function (this also makes it possible to use UAE to stop intense uterine bleeding in minors). Many patients gave birth to healthy babies after completing treatment.
- Low risk of relapses and negative consequences, including in the treatment of multinodular fibroids.
- Hospitalization takes 2–3 days, while the procedure itself is performed within half an hour and under local anesthesia.
- Relatively short rehabilitation period.
- Rapid improvement in the patient's well-being.
- Possibility of using embolization when surgery is excluded.
Of course, this method also has disadvantages (however, they are less significant):
- The equipment for performing UAE is quite expensive, and there are currently few specialists capable of performing this procedure. Because of this, embolization has a fairly high cost.
- The use of radiography, due to which the patient’s body receives a certain dose of radiation. True, it is small (approximately equal to that obtained with fluorography).
- The impossibility of taking tissue for biopsy to diagnose oncology. However, an experienced doctor will be able to determine whether it is cancer or not based on the vascular picture obtained during an antigraphic study.
Indications and contraindications
Embolization is a safe method, but doctors still prescribe surgery only if there are clear indications:
- unsuccessful treatment with hormones;
- preservation of the reproductive organ on the part of the woman;
- the presence of contraindications to the administration of anesthesia or surgery;
- large tumor size;
- rapid increase in formations with constant monitoring by doctors;
- persistent postpartum bleeding;
- preparatory treatment before removal of the uterus;
- the presence of infertility with the development of fibroids;
- vascular diseases in the uterus.
It is also important to take into account contraindications to embolization:
- individual intolerance to substances that are injected into the uterine artery;
- oncological tumors;
- autoimmune diseases;
- liver and kidney dysfunction;
- the presence of infectious diseases in the pelvic organs;
- the onset of the period after menopause.
Purpose and essence of the procedure
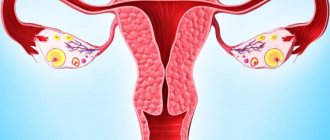
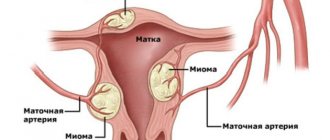
The method is based on the peculiarities of the structure and functioning of the uterus. The main source of its blood supply is the uterine arteries. Moreover, the network of blood vessels is so extensive that even if these arteries are blocked, the uterus will receive a full blood supply.
But the myomatous nodes that arise with fibroids are supplied only through the main arteries, because their own end vessels. Accordingly, the use of UAE is reduced to blocking these arteries. Neoplasms are deprived of vital sources of supply and die.
Thus, the patient’s complete recovery occurs - the tumor gradually decreases and dies. The operation itself boils down to blocking the uterine arteries - embolism.
The use of embolization is indicated not only for fibroids, but also for intense uterine bleeding, when the use of other methods threatens the patient’s life. In this case, the bleeding vessel is blocked. Subsequently, a blood clot forms in the blocked area.
Find out what embolization is, how it works, and where the best course of treatment is.
Negative consequences after surgery
Complications after embolization are quite rare. The most common symptoms observed in the patient are pain in the lower abdomen, a slight increase in temperature or nausea. The symptoms pass quickly enough and after 48 hours the woman is ready for discharge.
If after the procedure your health worsens, then in this case it is necessary to monitor the specialist who performed the operation and bed rest. It is best to stay in the hospital for the first day and return home after stabilizing your general condition.
Possible problems
Although in general the UAE procedure is safe with minimal risks of complications (about 20 times less than after surgery), some unpleasant moments can still arise. The most common complaint is the occurrence of a hematoma on the thigh. This formation does not require treatment and can go away on its own. Let's take a closer look at the effect of embolization on the functioning of the female body.
Menstrual cycle
For most patients, after UAE, their periods come as expected. Bleeding may be scanty if the operation itself was performed shortly before menstruation. In the early stages of using the embolization method, after the intervention, delays could occur for a period of one month to six months. However, at the present stage, this problem has been solved by changing the composition of the administered drug and the size of the emboli.
In isolated cases (1–3%), women over 45 years of age who are on the verge of menopause may experience menopause. However, most often, periods gradually become normal. If, after normalization, they intensify again, then this is most likely due to the “birth” of a nodular clot, that is, its removal from the body naturally. This usually occurs with subcumus nodes, which are small in size (3–5 cm). Sometimes, in very rare cases, when their size is quite large, the help of a gynecologist may be required. After the node exits, everything goes back to normal.
Possibility of having a child
After the UAE procedure, the vast majority of women retain the ability to conceive, bear and give birth to a healthy baby. Moreover, often this procedure is an opportunity to save the uterus for those planning a pregnancy.
Previously, when the technology for using emboli was still imperfect, they were too small in size and could clog the auxiliary blood vessels of the uterus. Nowadays, this drawback has been eliminated; the size of the blocking particles allows only large arteries to be blocked.
Is a relapse possible?
According to statistics, the likelihood of fibroid recurrence after uterine artery embolization is very low (1%). In cases where a relapse does occur, it is characterized not by the growth and development of nodes that were exposed, but by the appearance of new formations.
The reason for this is the complex anatomy of the blood vessels in some patients, which prevents the main arteries from completely blocking. At the same time, the supply of tumor-like neoplasms does not completely stop, as a result of which myomatous nodes are formed again.
Postoperative recovery
The recovery period after embolization is on average 2 weeks. The woman is advised to remain in bed and monitor her general condition. For minor pain, you should take anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by your doctor. To quickly resolve fibroids, experts advise following some rules:
- increasing fluid intake during the first 10 days after the procedure;
- avoiding taking blood thinning medications (aspirin);
- prohibition on taking a hot bath, going to a sauna or steam bath;
- maintaining physical and sexual rest for 14 days;
- After embolization, the use of hygienic tampons is prohibited for the first 3 months after surgery.
Compliance with the above recommendations will allow you to prevent tumor growth as quickly as possible and cause a sharp decrease in its size. For the dynamics of the disease, periodic monitoring using ultrasound is necessary.
Stages
Treatment of fibroids using embolization consists of the following steps:
- Examination.
- Preparation for EMA.
- Direct execution of the procedure.
- Rehabilitation period.
Let's take a closer look at each of them.
Examination and preparation
At the preparatory stage, patients undergo a series of tests. This is done to clarify diagnostic information and influences the choice of treatment methods. Here is their list:
- blood test for group and Rh factor + general analysis;
- platelet test;
- general urine analysis;
- blood sampling for sugar;
- kaogulogram - shows blood clotting;
- analysis of liver proteins, fats and electrolytes;
- renal complex analysis;
- tests for infectious diseases (syphilis, HIV, hepatitis);
- electrocardiogram;
- fluorography;
- vaginal smear;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- cytogram of the cervix.
As you can see, the list contains mainly general tests that allow us to assess the patient’s health status and readiness for uterine vessel embolization before surgery. Before the intervention, the patient is consulted by an endovascular surgeon and a gynecologist. They also prescribe hospitalization.
On the specified day, the patient is placed in the clinic ward. In the morning you must refrain from eating, you can only drink. Usually surgery is performed on the same day.
The puncture through which the drug is administered is usually made at the top of the right thigh, so you need to shave this area, as well as the groin, in advance. Before the procedure, compression stockings are put on the legs and elastic bandages are applied, which must then be used over the next 5-7 days.
Often, in order to overcome natural anxiety and relieve psychological stress, the patient is given a sedative injection before UAE. After this, she is transferred directly to surgery.
Carrying out the procedure
Embolization of the uterine vessels is carried out under the influence of a local anesthetic with the addition of sedatives, which deprives the skin on the thigh of pain sensitivity. The thigh and abdomen are treated with an antiseptic, after which the body is covered with sterile sheets.
Next, a puncture is made in the thigh, through which a microcatheter is inserted. Using X-ray endovascular examination (observing the blood vessels), the surgeon will precisely insert it into the desired uterine vessels. Then emboli with saline and an X-ray contrast agent pass through the catheter (for good visibility of the results of the intervention). When these particles reach the terminal branches of the arteries, which are small in size, they block the vascular lumens.
To block the uterine arteries, emboli made of polymers, consisting of 95% water, are used. They reduce the risk of restoring blood supply to myomatous nodes and inflammation in blocked vessels. In this case, the doctor first blocks the left uterine artery, and then the right one.
The solution is injected until blood flow completely stops. After this, the blood supply to the myomatous tumors gradually stops. The process of their sclerosis begins, that is, drying out and replacement with connective tissue. Nodes with a diameter of less than 3–4 cm are dissolved and removed from the body.
https://youtu.be/cgKRXCpwVbo
The duration of the operation is from 10 to 30 minutes, and if preliminary preparation is included at this time, the amount of time increases to one and a half hours. After its completion, the patient is re-administered painkillers. This eliminates postoperative pain.
Rehabilitation
Approximately 30–40% of women after surgery are susceptible to post-embolic syndrome, which is characterized by:
- Weakness and discomfort.
- Aching pain in the lower abdomen.
- Increasing temperature.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Increased number of leukocytes.
The duration of this syndrome is usually 1–2 days and during this time the patient must be in the hospital under the supervision of a doctor. Symptoms are most pronounced in the first 6–8 hours after surgery, and subsequently they weaken. The patient can be discharged home on the second or third day, when the pain decreases and vomiting disappears. After this, she can take her medications on her own.
Very rarely, individual symptoms may appear with a gradual decrease over 10–14 days.
Recovery after embolization is aimed primarily at relieving post-embolic syndrome and depends on its intensity. To do this, medications are used to relieve pain, reduce body temperature and stop vomiting.
It is also necessary to remove the radiopaque solution from the body and reduce intoxication of the body, for which infusion therapy with large (from 3 l) quantities of electrolyte solution is used. After discharge, the patient must limit physical activity for 10–14 days:
- Avoid heavy lifting.
- Refrain from sexual intercourse.
- Do not take hot baths and avoid visiting saunas.
Sexual activity can be resumed after the first postoperative menstruation. Within 7 days to a month after the operation, it is necessary to visit the surgeon and conduct control ultrasound examinations in a month, six months, and a year.
EMA results
The results of embolization are the achievement of certain goals that doctors set when prescribing the procedure. Depending on the degree of localization and severity of the tumor, the following tasks are distinguished:
- a significant reduction in nodes with multiple fibroids, since this pathology is not always accurately determined by ultrasound. Therefore, embolization makes it possible to minimize their number and reduce the size of benign formations;
- preventing the growth of nodes and the appearance of new tumors. The procedure leads to the bleeding of the fibroid, which gradually causes its complete death, and it cannot further grow favorably;
- elimination of pain, as they appear as a result of compression of the nerve fibers of organs. With the reduction of fibroids, there is a significant improvement in the woman’s general condition and possible pregnancy;
- cessation of bleeding after embolization. During the menstrual cycle, if a woman has fibroids, the uterine arteries are damaged and significant blood loss is observed. The operation allows you to reduce the size of the nodes and their pressure on the vessels, which stops the emerging pathology.
Predictions after the procedure
The first improvements in patients become noticeable 2-3 weeks after the operation. They are characterized by normalization of symptoms, such as menstrual bleeding (decreasing its volume and duration) and pain. The feeling of tightness gradually goes away; this is a longer process, taking a couple of months.
Myomatous nodes decrease most rapidly in size during the first 6–8 months after the intervention. After a year, their size is usually 25–28% of the original, nodular formations become 4 times smaller. In this case, small fibroids disappear within a month.
As already mentioned, the risk of relapse is extremely low and 99% of women do not need additional treatment after UAE. The occlusion of the main arteries affects both subcumus (internal) and subserous (external, often located on the uterine pedicle) nodes. In the case where the tumors are multiple, the effectiveness of treatment is assessed based on the reduction in the volume of the uterus. Over the course of a year, it becomes 2 times smaller.
Note that the connective tissue that replaces the nodes does not grow, but decreases. In this case, scars are formed that do not cause discomfort.
Who performs the embolization procedure and where?
The procedure for uterine artery embolization is an innovative technique and its implementation requires expensive equipment and a specially equipped clinic for such operations. Therefore, it will not be possible to perform the manipulation in a regular hospital.
The technique has not been extensively developed in Russia, so there are few specialists in endovascular surgery in the country. Before carrying out the procedure, a consultation with the treating gynecologist and referral to a special center for restoring reproductive health in women is necessary. At the same time, the pricing policy of the issue is quite high and requires material costs.
Cost of the procedure
The cost of embolization is quite high and is justified by the high cost of equipment, as well as the lack of an adequate number of qualified specialists. The average price of the service in Russia is 80,000–100,000 thousand rubles. Before performing the operation, you need to understand that the technique will be truly effective and will help stop the development of the tumor.
If we talk about prices in Moscow, they range from 100,000–150,000 thousand rubles. This cost is determined by the choice of specialist and equipment to carry out the procedure. In this case, the operation will help stop the growth of fibroids, but does not guarantee its complete disappearance.
When is it better not to perform embolization?
Despite the advantages and high efficiency of the UAE method, it also has contraindications:
— the patient’s pregnancy;
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs;
- allergy to the components of the drug used;
- presence of malignant tumors;
- renal failure;
- rapid growth of fibroids.
Before the procedure, it is necessary to conduct an examination for the presence of contraindications. The final decision on the possibility of embolization is made by the doctor based on the data obtained.
Clinics with experience in performing UAE
Not every medical institution can afford to carry out this procedure due to the lack of necessary equipment and specialists. Among the capital's clinics, the following received the largest number of positive reviews:
- Medical Center for Endosurgery and Lithotripsy.
- Military hospital named after P.V. Mandryk.
- City Clinical Hospital named after Pirogov.
- Family Planning Center.
- City Clinical Hospital No. 31.
Among regional medical institutions the following are recognized as the best:
- Clinic of reproductive medicine (Chelyabinsk).
- Volgograd Cardiology Center.
- City Clinical Hospital No. 6 (Ufa).
- City Hospital No. 41 (Ekaterinburg).
In Ukraine, the greatest number of positive reviews were received by doctors from the A.A. Institute of Surgery and Transplantology. Shalimova.
Of course, the list of clinics is not complete, because uterine artery embolization is becoming increasingly widespread, which means that the number of medical institutions that perform it is growing.