Features of the menstrual cycle
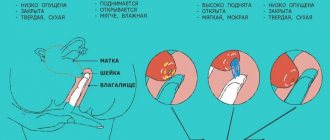
Enlargement of the reproductive organ in the middle of the cycle may be a sign of ovulation. This is the process of the release of a mature egg from the follicle. During this phase, the endometrium begins to form, necessary for the attachment of the fertilized egg. The epithelial layer is completely formed in two weeks, the organ becomes larger. Therefore, the uterus is enlarged before menstruation. After menstruation, the uterus is enlarged for several more days. The organ has already been freed of blood and endometrium, but it still needs time to recover.
Symptoms
Before a woman begins to find out the causes of uterine enlargement other than pregnancy, she will need to pay attention to certain symptoms that accompany this condition. Unfortunately, in most cases, the pathology develops without any characteristic signs.
Even if there are minor symptoms, women often associate them with other circumstances. And only during a gynecological examination will the doctor tell the patient that the reproductive organ does not correspond to normal sizes, exceeding them. To do this, the girl will have to undergo ultrasound screening, which will also confirm or exclude pregnancy.
This need is due to the fact that some symptoms of an enlarged uterus are very similar to early signs of pregnancy. To confirm or rule out this fact, you can initially do a regular test, as well as a blood test to determine the level of hCG. After this, the doctor will be able to tell why the uterus is enlarged but there is no pregnancy.
The reasons for the increase in the size of the uterus are determined during the examination. Source: babyplan.ru
Some of the most common anxiety symptoms include the following:
- Prolonged mild pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar back;
- Frequent urge to go to the toilet or urinary incontinence;
- Increased volume and increased level of pain during menstrual bleeding;
- The occurrence of bleeding in the middle of the cycle;
- Development of anemia;
- Flatulence or bloating;
- Increase in body weight, which occurs against the background of changes in the balance of hormones.
If a woman is attentive to the health of her reproductive system, then these signs will not go unnoticed. The most correct decision in this situation would be to immediately contact a gynecologist, as well as undergo a thorough examination of the whole body.
Myoma
Benign neoplasm in the muscles of the reproductive organ. It is a tangle of intertwined muscle fibers. The reasons for the appearance of the tumor are not fully understood. Most versions agree that it’s all about hormonal imbalances. The main sign of pathology is more abundant and painful menstruation. As the nodes grow, the patient's condition worsens. The pain is cramping in nature and can be constant. There is a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen. When the stem of the growth is twisted, severe pain occurs. The small size of the tumor and the absence of clinical manifestations are an indication for observation. When tumors grow, medications are prescribed to reduce bleeding and suppress hormone production. The radical solution to the problem is surgery. Its type is selected based on the size and location of the tumor.
How is diagnosis and treatment carried out if the uterus is enlarged?
If a woman has symptoms characteristic of diseases of the uterus, an examination is carried out to determine whether it is enlarged or not.
In this case, methods such as ultrasound and x-ray are used. If an abnormality is detected, a biopsy and histological examination of endometrial samples or tissue from tumors are performed. The presence of inflammatory processes and infections is determined using blood tests and mucous membranes of the reproductive organs. If necessary, a blood test for hormones is prescribed.
Ovarian cyst
It is a capsule formed from an unruptured follicle filled with fluid. It is assumed that it appears due to hormonal imbalances. Small tumors are often discovered by chance at an appointment with a gynecologist. They do not cause discomfort and can resolve on their own. However, even small growths can cause the uterus to become enlarged. Large cysts cause pain in the lower abdomen, spreading to the groin, perineum, and rectum. Intermenstrual bleeding occurs. The process of urination is disrupted. In rare cases, the capsule ruptures or twists, causing severe pain, nausea and vomiting, and fever. This condition is urgent and requires surgical intervention. In less serious cases, conservative treatment is carried out, consisting of taking painkillers and hormonal drugs, and physiotherapy.
Symptoms
First of all, you should consider the characteristic signs of conditions that may be accompanied by an increase in the size of the uterus. This is manifested by various symptoms, which means that the clinical picture will suggest the possible origin of this phenomenon.
If we talk about normal ratios in the body, then the uterus should not be larger than a woman’s fist: the length is up to 8 cm, and the width is about 5–6 cm. If there has been a history of childbirth, then the size may differ slightly in the direction of increase. But in pathological conditions it can reach several weeks of pregnancy, up to the second trimester.
Condition after menstruation
The menstrual cycle is accompanied by hormonal changes in the body. Estrogens and progesterone play the main role in this. The release of blood is accompanied by rejection of the surface layer of the uterine mucosa.
After the end of menstruation, gradual growth of the endometrium and its loosening are observed. Therefore, there may be some enlargement of the uterus, but the cervix contracts. If after menstruation the size of the organ exceeds the permissible limits, then you need to look for other reasons for this condition.
Premenopausal period
As women age, their reproductive function declines. The expansion of the uterine cavity during this period is mediated by a decrease in estrogen levels. Menstruation becomes irregular and the cycle may shorten. The woman notes other signs:
- Feeling of heat in the body.
- Increased sweating.
- Emotional lability.
- Increases in blood pressure.
- Headache.
If other genital symptoms appear, it is necessary to exclude gynecological pathology.
Fibroids
Quite often, women of reproductive age have benign formations in the uterus - fibroids. These tumors can have different localizations: submucosal (internal), intramural (in the thickness of the organ) or subserous (external). Symptoms depend on their location, the stage of development of the pathology, and may include:
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Increase in organ size.
- Irregular periods.
- Uterine bleeding.
When the tumor reaches a significant size, neighboring organs can be compressed, which provokes bloating, constipation, and frequent urination. On palpation, the uterus is hard to the touch.
Endometriosis
This disease occurs when cells of the functional layer of the mucous membrane begin to develop outside the uterine cavity. A special case of pathology is adenomyosis, a condition in which the endometrium grows into all layers of the organ. Often the disease affects the cervix and peritoneum. This is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Lower abdominal pain.
- Menstrual irregularities.
- Brown discharge.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Infertility.
It must be remembered that endometriosis can be accompanied by cell degeneration, leading to cancer.
Cancer of the uterus or cervix
The cause of an increase in the size of the organ may be a malignant process - cancer. Cervical lesions are the most common cancer in women. The disease is completely asymptomatic for a long time. But as it progresses, the following signs appear:
- Scanty bleeding.
- Unpleasant sensations during sexual intercourse.
- Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen.
During a gynecological examination, changes in the mucous membrane of the cervix and contact bleeding are noticeable. The examination is also painful.
Uterine cancer is more common in women over 50 years of age. In addition to an increase in the size of the organ, the disease is accompanied by intermenstrual bleeding and heavy periods. Pain syndrome may appear when the pathology is widespread.
Every woman should always have a clear oncological alert. Her health and future life may depend on this.
Inflammatory diseases
Among the inflammatory pathologies of the female genital area, endometritis is most often accompanied by an increase in the size of the uterus. Often the infection spreads from the vagina or develops during the post-abortion or postpartum period. The following symptoms are observed:
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Cloudy bloody discharge, often purulent in nature.
- Soreness of the uterus on palpation.
- Rise in body temperature.
- General weakness, malaise.
The acute stage of the pathological process sometimes becomes chronic, which can cause infertility.
Endometriosis
Pathological growth of the inner epithelial layer of the uterus. The mechanism of pathology is not fully understood. Neither version has enough evidence. The most likely opinions are about genetic predisposition and hormonal imbalances. The disease causes irregular menstrual cycles. Menstruation becomes more abundant and is painful. Bleeding can also be spontaneous. Possible disturbances in stool and urination. Patients are prescribed hormonal medications and painkillers. In difficult cases, surgery is performed to remove the affected areas or the entire organ.
Consequences of pathological enlargement of the uterus
A significant and persistent increase in the size of the organ occurs when diseases of an inflammatory or tumor nature occur. If pathologies are not detected in time and treatment is not carried out, then the diseases progress. The consequences of this are usually disruption of the menstrual cycle, hormonal imbalance and often infertility.
Serious complications can occur during pregnancy. Enlargement of the uterus, caused by pathological processes in its cavity, provokes the onset of an ectopic pregnancy or its termination at an early stage. Stretching of the walls and changes in the condition of the organ’s neck are often the cause of infection entering its cavity and the development of the inflammatory process.
Endometritis
Inflammation of the endometrium. Usually occurs after childbirth or gynecological surgery. It can also be a complication of other genitourinary tract infections. Characterized by fever and chills. The uterus increases in size and puts pressure on nearby organs. Therefore, problems with defecation and urination occur. Unpleasant sensations appear in the lower abdomen. Purulent discharge comes out of the genital tract. The disease is treated with antibiotics and drugs that improve blood clotting. Physiotherapeutic procedures are useful. In some cases, it is necessary to open the purulent lesion and drainage of its contents. Damaged tissues are washed with antiseptic solutions.
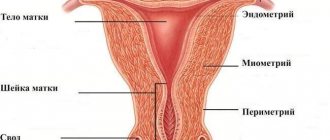
Dimensions - normal and pathological
The main purpose of the uterus is to create conditions for the full growth and development of the fetus. It consists of a body and a cervix, inside which the cervical canal passes. There are three layers in the structure of the reproductive organ:
Endometrium.
Internal mucous membrane undergoing monthly cyclic changes.
Myometrium.
Middle muscle layer.
Perimetry.
Outer serous membrane.
Basic parameters of the uterus of a nulliparous woman:
- Length – 4.5 cm;
- Width – 4.6 cm;
- Anteroposterior size – 3.4 cm.
If a woman has a history of pregnancy and childbirth, it is considered normal when her uterus has increased by 0.5-1 cm in all respects.
During menopause, it decreases in size by an average of 35%, that is, the above parameters decrease by 1-2 cm. The decrease in size occurs slowly, over 20-25 years after the last menstruation.
Organ weight:
- For a nulliparous woman – 45-60 g;
- For a woman who has given birth – 80-100 g;
- In perimenopause – 40-45 g, in old age – 20-30 g.
Any deviations from the norm force the doctor to look for the causes of uterine enlargement, because ignoring this symptom can cost a woman her life or complete loss of fertility.
Molar pregnancy
It's also called chorionadenoma. It occurs because after fertilization of the egg, the embryo cannot develop. Instead of a normal fetus, a chaotic accumulation of tissue is formed. This condition occurs mainly in girls under 20 years of age and old-time women. For about a month and a half, pregnancy proceeds normally. Bleeding occurs from 6 to 12 weeks. They can be quite abundant and long lasting. A feeling of heaviness and fullness appears in the stomach. The uterus grows faster than during normal pregnancy. Women complain of nausea, vomiting and abdominal cramps. Patients undergo a mini-abortion by curettage or suction of pathological tissue.
How to identify the symptoms of a “pregnant uterus”
The uterus during early pregnancy requires close attention from a specialist and examination. There are several ways to do this. It makes sense to be examined after a 2-week absence of critical days. All procedures will be quite informative and will allow not only to diagnose an “interesting situation”, but also to identify many problems with it, if any.
One of the reliable means of establishing pregnancy and the proper quality of its course at this level of development is intravaginal ultrasound. A special device is inserted into the genital tract, which will detect and demonstrate what the uterus has become during a normally developing pregnancy in the early stages, especially if pathology is present. At this moment there is already a chance to also feel the fetal heartbeat.
No less important and used by all specialists is a method such as a gynecological examination and two-handed examination of the organ. Palpation in the early stages of pregnancy can reveal all the changes that have occurred in the organ:
- The doctor inserts one hand into the genital tract, and the other examines the woman’s abdomen. Due to the softening of the tissues in the isthmus area, the fingers, meeting, feel each other.
- During a bimanual examination, the tissue consistency does not remain constant. Directly upon contact with the doctor’s hands, the uterus slightly tenses and its size decreases. After eliminating the irritation, the tissues become soft again.
- During a normal pregnancy in the early stages, the uterus has a dome-shaped protrusion on the left and right, which is easy to feel right now. Localization depends on the site of attachment within the embryo. As the fertilized egg develops, the bulge disappears.
- Manual examination allows you to detect mobility of the neck of the organ, which is not typical for it in other conditions.
- The weakening of the elasticity and density of the isthmus tissue makes it necessary to tilt the uterus forward. The specialist can feel a thickened line on the front surface of the organ in the middle.
Palpation at the initial stage in the absence of incomprehensible or negative manifestations does not need to be carried out frequently. The study gives the doctor enough information, and unnecessary examinations can lead to activation of the smooth muscles of the uterus, increase its movements and create a threat of interruption.
During pregnancy, the uterus in the early stages needs to be treated with care, but also to control the processes occurring in it. It is important to visit regularly, monitor your well-being, and follow all recommendations. Any deviations must be reported immediately! After all, this can save the unborn baby. And to determine them, it is worth imagining what the uterus is like after conception in a normal position.
Since the uterus is located in the abdominal cavity, a woman may often not be aware that this organ is altered. It is known that expansion of the uterine cavity occurs during pregnancy. However, its size can also increase for other reasons, which are not always safe for women’s health.
Let's consider the main causes of uterine enlargement, the symptoms of this disease, as well as methods of its treatment and prevention.
Oncology
Tumors can develop in the endometrium or muscle layer of the uterus. Cancer usually affects women during menopause. Risk factors include poor heredity, weak immunity, smoking, and taking hormonal medications. Infectious diseases, excess weight, and late menopause can also provoke pathology. In the initial stages of the disease there are no symptoms. Then intermenstrual bleeding appears, intensifying during sexual intercourse. Sex becomes painful. Pain also occurs in the abdomen and lower back. The unpleasant sensations are nagging and paroxysmal in nature. Weight loss is noted. Treatment depends on the patient’s condition and the severity of the pathology.
The uterus does not remain unchanged throughout life. It becomes larger or smaller at different phases of the menstrual cycle. Natural physiological processes can also influence its size. But in some cases we are talking about pathologies. The doctor who detects abnormalities will prescribe the necessary examinations and provide appropriate treatment. It is important to remember that the older a woman is, the more often she needs to visit a gynecologist and have an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Causes
It’s worth saying right away that the reasons for an enlarged uterus in women, other than pregnancy, can be associated either with a serious disease or be a significant deviation that arose under the influence of negative factors, and act as a temporary feature of the body.
Changes in the size of the reproductive organ, which should not cause concern, are associated with the onset of pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause. But there are also more frightening conditions that can not only cause severe complications, but also provoke infertility.
Myoma
In situations where the uterus is larger than normal size, but at this time the woman does not have regular bleeding, the test shows a negative result, and menopause has not yet occurred, it will be necessary to find out the reasons, among which doctors often consider fibroids, oncology, endometriosis, and hypertrophy cervix.
With fibroids, the uterus enlarges without pregnancy. Source: fb.ru
When specialists begin to find out why the uterus may be enlarged other than pregnancy, they first conduct studies that can confirm or refute the presence of fibroids. With this benign tumor, the reproductive organ increases in size against the background of the fact that active division of cells in the muscle layer occurs.
With this pathology, the size of the tumor is indicated in weeks, the same as during pregnancy. If the tumor was detected at an early stage, then hormonal therapy is carried out; in advanced situations, the problem is solved through surgery.
Oncology
The most dangerous cause of uterine enlargement in the absence of pregnancy is the development of an oncological process. In most cases, the formation of malignant cells occurs in the mucous membrane of the organ. Often the age of patients is 35 years or older. However, women with high body weight are also at risk.
Oncological diseases can progress asymptomatically over many years. This is why women may not know that they have a malignant tumor. Only an experienced specialist can detect cancer, and the sooner the correct diagnosis is made and the correct therapy is carried out, the better the prognosis for recovery.
Endometriosis
The presented disease is quite common and is characterized by the proliferation of endometrial cells beyond the reproductive organ, which leads to an increase in the size of the uterus. In most cases, the pathology affects the front and back, so it takes on the shape of a ball.
Endometriosis causes an enlarged uterus. Source: sovets.net
In certain situations, pathological cells can grow deep into the tissues of the uterus. As a result, the entire organ is damaged, and a specific pathological focus is absent. In this condition, the patient is diagnosed with diffuse endometriosis, the treatment of which is quite complex.
Just as with many gynecological diseases, endometriosis may not manifest itself for a long period of time, especially in the first and second stages. The only thing a woman can notice is a violation of the stability of the menstrual cycle. Therefore, if there is a delay and the test is negative, you need to contact a gynecologist.
Hypertrophy
An important feature of this pathology is that with the progression of the hypertrophic state, only the cervix increases, which is due to thickening of the walls of the reproductive organ. Often, hypertrophy develops against the background of a complex inflammatory process in which the cervical canal was damaged.
This disease must be diagnosed promptly. It will be possible to get rid of it only when the underlying pathology that provoked the inflammation is initially eliminated. Often, patients are prescribed drug therapy, which necessarily includes antibiotics.
It is easy to understand why gynecologists recommend that women do not neglect preventive examinations, even if nothing worries them. The main part of the reasons under the influence of which the uterus enlarges is easily treatable, especially if the diseases are identified at the initial stage.