It is quite difficult to rupture or bruise the pancreas on your own, due to the location of the organ. It is located in the retroperitoneal plane and is actually protected. Therefore, in 80-85% of injuries occurs due to a gunshot or cold penetrating wound. Therefore, accurate diagnosis, cause and therapeutic therapy are especially important for this type of damage. It is worth knowing the likelihood of getting a pancreatic injury, symptoms, treatment, as well as possible risks if you do not see a doctor.
Why does gland rupture happen?
Sugar level
Man
Woman
Enter your sugar or select your gender to get recommendations
The morphology of the pathology will also change depending on the nature and strength of the influencing factor. Bruises, hemorrhages, tears of capsular tissue, deep and complete ruptures, extensive crush injuries are accompanied by extensive blood loss in the retroperitoneal region and abdominal cavity.
The destruction of the gland is accompanied by the loss of the integrity of the pancreatic ducts and the entry of enzymes into the tissue, which can cause swelling, fat necrosis, vascular thrombosis and even necrosis of the gland tissue.
The associated inflammatory pathological process causes tissue damage through melting, formation of sequesters and abscesses. The development of these pathologies is caused by the worsening of an ailment such as pancreatitis.
Acute pancreatitis is an acute inflammation of the gland, which is based on the pathological processes of pancreatic necrobiosis and enzymatic autoaggression with the development of necrosis, degeneration of the gland and the addition of a secondary infection.
If this disease is not adequately treated, it can progress and lead to necrotization, which in turn contributes to rupture of the pancreas. A pancreatitis or injury to the organ can result in a pancreatic cyst (an uncharacteristic cavity for the organ, a bubble consisting of a capsule and contents) , abscess (formation in the gland tissue of a cavity filled with pus and necrotic masses), calcifications or plaques on the pancreas.
Due to trauma and damage to nearby organs, which in turn will put pressure on the affected areas of the pancreas, their stretching, or the progression and relapse of the disease can lead to rupture of these formations.
People suffer from pancreatosis for various reasons, but the risk group includes people with the habit of eating spicy and fatty foods in large quantities every day, and washing it all down with alcoholic beverages.
Consequences of injury
The complexity and danger of the consequences depend on the severity of the injury, as well as on the time that has passed since it. The main consequences include:
- Organ rupture (complete or partial).
- Concussion of the gland.
- Through or subcapsular rupture of the parenchyma.
- Vein thrombosis (splenic, mesenteric or portal vein).
- Edema.
- Hemorrhage, organ hematoma. Hemorrhage may occur in the retroperitoneal tissue and adjacent tissues.
- Necrosis of organ tissue.
- Entry of pancreatic juice into the abdominal cavity and tissues.
- Acute inflammatory process.
- The onset of painful shock.
- Peritonitis and pancreatic necrosis.
We also recommend viewing: Treatment of the liver and pancreas with oats
These are the most common consequences of pancreatic rupture. But the most dangerous are necrosis and pancreatitis, since they often lead to death without timely professional medical care.
Types of pancreatic injuries
All pancreatic injuries are divided:
- on open ones - caused by piercing and cutting objects, firearms,
- on closed ones - the result of a bruise of the pancreas or blunt blows to the area of its projection on the stomach and back,
- those obtained during surgical operations on the gland itself or other organs of the abdominal cavity.
Any pancreatic disorders are divided:
- isolated - only the pancreatic parenchyma is damaged,
- for combined - adjacent organs are affected (stomach, liver, intestines, left kidney, spleen).
Damage to the pancreas is more often the result of a closed abdominal injury and is 5:1. There are several types of violations of the integrity of the gland resulting from exposure to the abdominal cavity:
- bruise of the pancreas with preserved integrity of the peritoneum covering the organ from the outside,
- incomplete rupture of pancreatic tissue or one peritoneum,
- complete rupture of the organ parenchyma.
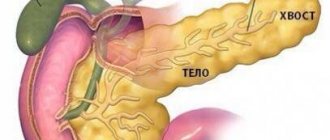
Closed injuries are characterized primarily by damage to the body of the pancreas. This is explained by the fact that the body of the organ is pressed tightly against the spinal column at the time of a bruise or a sharp rise in pressure in the abdominal cavity.
Any pancreatic injury has several degrees of severity. The existing classification distinguishes 5 degrees of damage:
- I - mild contusion of the pancreas or a superficial wound without involving the Wirsung canal, with hemorrhage into the parenchyma of the organ,
- II - severe tear of the parenchyma without compromising the integrity of the main duct,
- III - rupture in the distal part or violation of the integrity of the organ tissue with a change in the patency of the central duct,
- IV - intersection in the proximal part or damage to the main duct,
- V - complete destruction of the structure of tissues and vessels of the head of the pancreas.
If the head of the pancreas ruptures, the symptoms will be similar to intra-abdominal bleeding. This is explained by the localization of the bulk of large vessels in the head. The consequences of injury to the body or tail include acute pancreatitis. In this case, cysts and fistulas form in the parenchyma.
Open pancreatic disorders include:
- stab-cut,
- gunshot wounds.
Different types of disease are divided into separate ailments depending on the nature of the organ damage, depending on the course of the disease, and also depending on the phase of progression of the disease.
The type of disease is determined in the process of diagnosing the pathology.
The classification system, depending on the course, includes the following types of pathology:
- Spicy.
- Acute recurrent.
- Chronic.
- Exacerbation of the chronic form.
Depending on the nature of the lesion, the following forms are distinguished:
- edematous;
- destructive, representing pancreaticonecrosis;
- small-focal;
- medium focal;
- large-focal;
- total-subtotal, which is a simultaneous lesion of all parts of the gland body;
Depending on the progression of the disease, the following phases of the disease are distinguished:
- Enzymatic – up to the first 5 days.
- Reactive, starts from 6 days and continues until 14.
- Sequestration – begins after 15 days.
The last phase of the progression of the disease is the initial phase, which begins six months after the onset of the development of the pathology.
The causes of pancreatic rupture most often include injury from a firearm or bladed weapon, as well as severe beatings, compression of the abdominal cavity, a blow to the abdomen and lower back, or during surgery. Other reasons for the gap are unlikely.
- on open ones - inflicted by piercing and cutting objects, firearms;
- for closed ones - the result of a bruise of the pancreas or blunt blows to the area of its projection on the stomach and back;
- those obtained during surgical operations on the gland itself or other organs of the abdominal cavity.
- for isolated cases - only the pancreatic parenchyma is damaged;
- for combined - adjacent organs are affected (stomach, liver, intestines, left kidney, spleen).
- bruise of the pancreas with preserved integrity of the peritoneum covering the organ from the outside;
- incomplete rupture of pancreatic tissue or one peritoneum;
- complete rupture of the organ parenchyma.
- I - mild contusion of the pancreas or a superficial wound without involving the Wirsung canal, with hemorrhage into the parenchyma of the organ;
- II - severe tear of the parenchyma without compromising the integrity of the main duct;
- III - rupture in the distal part or violation of the integrity of the organ tissue with a change in the patency of the central duct;
- IV - intersection in the proximal part or damage to the main duct;
- V - complete destruction of the structure of tissues and vessels of the head of the pancreas.
- stab-cut;
- gunshot wounds.
Clinical picture and diagnostic methods
The main symptom is persistent pain. The pain radiates under the shoulder blade, on the left side, and also in the back.
Note! When a person lies face up, the pain intensifies.
You can help yourself by turning over onto your left side. A bad sign is the subsidence of pain - this almost always signals the development of peritonitis.
The main symptom is severe abdominal pain
Other symptoms include:
- pale skin;
- hiccups that do not go away within several hours;
- blanching of mucous membranes;
- nausea (combined with heartburn and painful vomiting);
- weak pulse;
- urinary retention;
- bowel dysfunction;
- decreased blood pressure;
- impaired peristalsis;
- drying of the tongue (it becomes covered with a yellowish coating);
- bloating;
- hard, tense belly.
Sometimes the pain becomes piercing, the person suffers greatly.
The symptoms of a pancreatic bruise will be slightly different. The main signs are severe swelling, hemorrhage, and the appearance of a subcapsular hematoma.
If the closed type of injury was very severe, a complete transverse rupture of the pancreas is diagnosed. It is characterized by damage to ducts and large blood vessels. In 12% of cases, crushing of the gland occurs.
If a patient has damage not only to the pancreas, but also to the brain, diagnosis becomes difficult. The reason is the blurred clinical picture.
A typical diagnostic sign is an increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate
If the doctor suspects such damage, he will refer the patient for urine and blood tests. The presence of a gap is indicated by the following indicators:
- decrease in hemoglobin;
- increase in sugar concentration;
- increase in ESR;
- increase in the number of leukocytes.
Sometimes, to clarify the diagnosis, a puncture of the peritoneum is required. An instrumental study is also performed - angiographic and peritoneoscopic scanning of the pancreas.
How to treat a ruptured gland
Treatment is in most cases surgery. Emergency laparotomy is designed to prevent blood loss and the formation of cysts; it is usually combined with manipulations aimed at anti-shock recovery.
If a minor hemorrhage or bruise is diagnosed, they are treated with injections using novocaine. The omental tube is drained or several sutures are placed on the gland capsule.
If deep tears are detected, the edges must be sewn together. It is important that this is a microsurgical procedure that not all doctors are capable of performing. Equipment also matters. Therefore, it would be advisable to look for a hospital with modern equipment.
In cases where there are multiple ruptures or the tail of the organ has been torn off, resection of the pancreas and spleen cannot be avoided. Resection with removal of the damaged fragment of the gland is indicated if there is a rupture of the dietary element and tail.
Tears during surgery
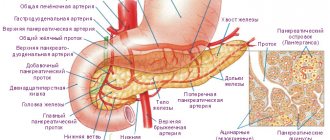
Surgery or any manipulation of the pancreas should be performed with extreme caution. It is abundantly supplied with an extensive network of excretory ducts that open in the lumen of the duodenum, with many plexuses of veins and vessels that flow into the raven vein system. The structure of the organ belongs to the complex alveolar glands.
Complications arising during the operation or inept actions of the surgeon can lead to rupture or tear of the gland. A positive result depends on the qualifications and experience of the doctor.
The following manipulations can cause organ rupture:
- removal of a significant part of the stomach (resection);
- puncture drainage of a pancreatic cyst;
- organ tissue sampling (biopsy);
- elimination of a malignant tumor;
- surgical intervention on nearby organs.
A rupture may occur during surgery. During
the postoperative period, it is necessary to adhere to a special diet, otherwise the gland experiences greater stress, enlarges and becomes inflamed. The diagnosis is complicated by chronic pancreatitis, and there is a risk of organ rupture.
We have selected useful articles on the topic
How to fast properly when you have inflammation of the pancreas
01.05.2019
Consequences of smoking in inflammation of the pancreas
01.05.2019
How to treat pancreatitis and what methods will be the most effective
24.06.2019
Treatment methods for pancreatic injuries
In case of severe damage to the gland, the main role in the first hours is played by the surgical method, which is immediately used for both treatment and diagnosis (diagnostic laparotomy). But the effectiveness of treatment also depends on complete conservative therapy. Since acute pancreatitis always develops, even with minor damage to the pancreas, therapeutic treatment is prescribed in the early stages to interrupt the development of acute traumatic destructive pancreatitis.
Early radical treatment with immediate anti-shock measures for severe pancreatic trauma stops massive blood loss and prevents the development of a traumatic cyst. The scope of the operation depends on the type and degree of damage: an inspection of the abdominal cavity can be performed, removing blood clots and suturing damaged vessels.
In severe cases, resection of the gland and spleen is necessary. If the pancreas is completely ruptured, it is practically impossible to suture the main duct. The tactics of ligation of the duct and bringing the distal stump of the pancreas to the anterior abdominal wall are used. In the future, the second stage of the operation is being carried out - plastic.
Treatment of injury in the pancreas is carried out only surgically using laparotomy. This technique helps prevent large blood losses, as well as possible unpleasant consequences, such as a cyst. Along with this, drug therapy is required to eliminate pain shock.
In case of minor trauma to the organ, they are treated by injecting the injury site with an anesthetic, after which several sutures are placed at the site of organ damage and a drainage tube is installed in the gland capsule. In the case of a large rupture of the gland, a serious operation is required to stitch the edges at the site of the rupture. It is worth noting that such an operation is carried out only with the help of the necessary modern equipment and requires a highly qualified doctor.
Any violation of the usual routine can provoke a disease in a child, including pancreatitis - inflammation of the pancreas.
The pancreas is one of the most important organs that produces enzymes that break down food components. The juice secreted by the gland helps digest food.
Only 5 to 20% of the child population faces this problem.
With closed trauma to the pancreas and open injuries, there is a need for surgery. Even if an exact diagnosis has not been made, a sufficient basis for surgical intervention is the presence of symptoms of an “acute abdomen” in the patient.
If, with a closed or open type of abdominal injury, the rupture of the internal organ is shallow, then the surgeon takes the following measures:
- Removes a hematoma (blood clot) formed at the site of the rupture.
- Places sutures on the burst area of parenchyma.
- Installs drainage into the omental bag.
If, as a result of injury, a rupture of the left part of the gland (body, tail of the organ) occurred and the functions of the excretory ducts were disrupted, then the surgeon will excise the damaged areas so that necrosis does not spread to neighboring tissues. When the head and main outlet of the gland are ruptured, the doctor uses pancreaticoduodenal excision. The method involves partial or complete removal of the organ. The operation is considered very difficult and has a high mortality rate.
After successful surgery for a pancreatic rupture, the patient is prescribed complex conservative therapy to prevent post-traumatic pancreatitis:
- Symptomatic treatment. Involves the use of painkillers, anti-inflammatory, and sedatives.
- Diet therapy. For the first 3 days, the patient is prescribed fasting, drinking and eating are prohibited. The body is supported by intravenous administration of nutrient solutions. On the fourth day, the patient begins to eat independently through the mouth, but with a limited amount of food.
- Droppers. A 10% glucose solution, potassium solution, and human insulin are administered.
- Be sure to give intravenous antibacterial injections.
Once a diagnosis is made, treatment and diet should be the first priority.
The need to change your diet is due to the importance of preventing nutritional deficiencies in the body, normalizing blood sugar levels and facilitating the functioning of the pancreas.
The diet for pancreatitis must be designed in such a way that the patient receives all the necessary nutrients during the day. In this case, an important task is to facilitate digestive function, so it is necessary to select easily digestible foods.
Even with the use of artificial pancreatic enzymes, a significant proportion of food substrates is not digested and is excreted in the stool.
Basic recommendations:
- It is necessary to eat small portions 6-8 times a day. This diet significantly reduces the load on the digestive tract and improves the absorption of nutrients.
- The proportion of fatty foods in the diet should be reduced. It is recommended to pay attention to plant sources of polyunsaturated fatty acids as compensation.
- It is also important to reduce the amount of fiber in your diet. This complex carbohydrate significantly slows down the digestive process and increases the load on the pancreas.
- To prevent deficiency of minerals and vitamins, you can take multivitamin complexes.
- The need to take supplements is due to the inability of the digestive organs to absorb all the necessary nutrients.
A proper diet is an important addition to drug treatment for acute and chronic pancreatitis. It is important to consider what foods the pancreas likes and what foods need to be excluded from the diet.
To prevent possible blood loss and the formation of cystic formations, it is recommended to use laparotomy and combine it with manipulations aimed at anti-shock effects.
Surgery must be carried out before the process of inflammation begins to develop in the pancreas, retroperitoneal region or abdominal wall.
In case of injury to the organ and the presence of small hemorrhages under the capsule, they are limited to injecting with a solution of novocaine and using drainage of the omental bursa or applying sutures with peritonization of the site of damage.
If the left part of the organ is injured with a violation of the integrity of the duct system, resection of its body and tail is performed.
If the head is injured and a rupture of the main duct occurs, pancreatectomy or pancreaticoduodenectomy is performed. A feature of these types of interventions is the high complexity and traumatic nature of the procedure, and postoperative mortality can reach 80%.
To prevent post-traumatic pancreatitis from occurring after surgery, complex conservative treatment is carried out.
Therapeutic measures consist of
- Symptomatic therapy.
- Use of diet therapy. In the first 3 - 4 days, eating and drinking is prohibited. Parenteral nutrition is prescribed. From 4 to 5 days, oral feeding begins. The list of permitted foods is gradually expanding due to the introduction of carbohydrates into the diet, but at the same time the protein content in the diet is limited and fats are excluded from it.
- Suctioning the contents from the stomach cavity with a thin probe.
- Administration of 10% glucose solution, human insulin, potassium solution.
In addition, intravenous administration of antibacterial drugs is used. Medicines can be administered into the abdominal cavity through the use of nipple drainage.
Signs of pancreatic diseases are discussed in the video in this article.
Treatment is complex, using surgical access and conservative therapy methods.
If superficial small tears are suspected, laparoscopic surgery is allowed. In case of large damage or massive bleeding, access is only median. During the operation, it is possible to suturing damaged tissue, excision of part of an organ or hematoma, ligation of blood vessels, sanitation of the abdominal cavity and, if necessary, insertion of rubber drainages.
Thus, traumatic injury to the pancreas is serious and in a large percentage of cases leads to complications and even death.
Treatment of injury in the pancreas is carried out only surgically using laparotomy. This technique helps prevent large blood losses, as well as possible unpleasant consequences, such as a cyst. Along with this, drug therapy is required to eliminate pain shock.
In the case of a large rupture of the gland, a serious operation is required to stitch the edges at the site of the rupture. It is worth noting that such an operation is carried out only with the help of the necessary modern equipment and requires a highly qualified doctor.
Rehabilitation period
After the operation, it is necessary to follow all the doctor’s instructions so that recovery is quick and without complications. In the first 2-3 days, the patient is contraindicated to drink and eat. Next, a special diet is prescribed to remove excess load from the gastrointestinal tract. After 3 days, food is given orally with a gradual increase in carbohydrates. Proteins should be included in the diet in minimal quantities, but fats should be completely excluded. The entire rehabilitation period includes complex measures, which include:
- introduction of protein preparations;
- blood plasma and its substitutes;
- glucose input 10%;
- insulin and potassium;
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics are administered not only intravenously, but also into the peritoneum through an installed drainage.
We also recommend viewing: The functioning of the pancreas, its structure and emerging diseases
Blood transfusion is also considered an important aspect of rehabilitation, especially if there was internal bleeding. In case of tamponade, the tampons must be removed on days 7-10. Next, the patient undergoes frequent regular examinations to exclude the formation of cysts and obstructions of various etiologies.
Although the pancreas is located in such a way that it is protected quite well, it is possible to get seriously injured. Therefore, if you have the slightest injury or feel unwell, you should immediately go to the hospital. Often a few hours play a major role in a person’s health and life.
Development of pathology as a result of injury to the gland
As a result of injury, the organ may suffer a tear or rupture; in such a situation, only a formed cyst, which has been located in the tissues of the organ for a long time, can burst. As a result of injury, enzymes produced by the gland begin to destroy the tissue of the organ. In the event of such an injury, it is very difficult to stitch the tissue tear.
Stitching a damaged gland is an emergency surgical procedure. The location of the gland provides it with relatively reliable protection from external traumatic influences.
Rupture due to injury
The severity and nature of damage to the pancreas depends on the type of injury received. There are open and closed organ injuries. Their differences are presented in the table.
| Open type of injury | Closed type of injury |
Occurs in most cases as a result of a gunshot wound or blows to the abdominal area with sharp piercing or cutting objects. As a result of such injury, complete or partial tissue necrosis occurs due to exposure to pancreatic juice, the composition of which has a sharply alkaline reaction. When the main excretory duct of the gland is damaged, a blood clot forms and the artery becomes blocked. The probability of damaging the pancreas due to a gunshot wound or a stabbing object is no more than 5% of all injuries to this organ. It is protected on all sides by the spine, ribs, back and abdominal muscles; violation of tissue integrity occurs quite rarely. In most cases, neighboring organs are simultaneously affected: the stomach, liver, spleen, kidneys. A person can receive open injuries to the pancreas as a result of:
| Occurs when the pancreas is pressed against the spine, as a result of a blunt blow to the epigastric region and pressure from neighboring organs. Destruction of the pancreas is accompanied by damage to blood vessels and the integrity of the parenchyma, which is accompanied by bleeding and the formation of thrombosis. The following types of gland injuries in closed injuries are distinguished:
The incidence of such injuries and complications is 1-3% of all pancreas injuries. The main causes of closed injuries are car accidents in which damage to the gland is caused by fragments of bones or ribs, severe bruising, prolonged compression and concussion of the internal organs of the abdominal region. |
Possible consequences in the postoperative period
The consequences of removing the pancreas can vary. Any surgical intervention has a high risk of developing inflammatory or infectious processes in the tissues of the body in the postoperative period. And to avoid them, the doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics before and after the operation. If the patient takes them strictly according to the prescribed regimen, the risks of such complications are reduced several times.
After removal of the gland, diabetes mellitus develops, because after the operation there is an acute lack of insulin in the body, which is why the person is forced to constantly take insulin injections. If you skip them or use them incorrectly, this is also fraught with various consequences, among which is hypo- and hyperglycemic coma.
In addition, even the removal of a small part of the pancreas disrupts its exocrine functions responsible for digestion. Therefore, the patient will also have to constantly take enzyme preparations (they are prescribed on an individual basis).