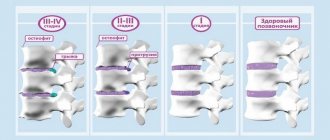
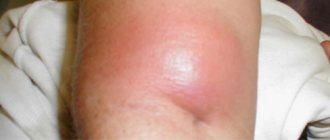
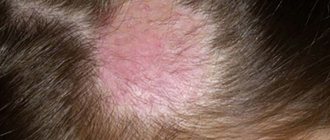
In the jaw lymph nodes, the lymph circulating in the cells and capillaries of the oral cavity and head area is processed. Submandibular lymphadenitis is a polyetiological disease: its development can be caused by both chronic diseases and infections in the acute stage. The disease requires mandatory treatment from a specialist; it is impossible to cure lymphadenitis on your own .
What is lymphadenitis?
What is lymphadenitis? It is called the inflammatory process that occurs in the lymph nodes. Rarely does this disease occur on its own. Usually it is a consequence of the occurrence of other infectious and inflammatory diseases. It often accompanies diseases of the respiratory tract, heart, nose, throat, and ear. The disease causes enlargement of the lymph nodes and their pain. In 80%, the submandibular lymph nodes are affected. But there are other areas that can also be inflamed.
Lymphadenitis is the body’s reaction to a foreign organism that has penetrated into it. When a certain part or organ becomes ill due to infection by a bacterium or virus, then the infection through the lymph or blood can penetrate the lymph nodes. Leukocytes located in these areas are activated and cause an inflammatory process that should destroy pathogenic agents.
Enlargement of the lymph nodes occurs due to the fact that with massive penetration of infection into the lymph nodes, additional leukocytes begin to flow into these areas, which further provoke the process of inflammation. The lymph nodes grow and become enlarged, as well as their pain.
Thus, lymphadenitis is a beneficial inflammatory process, which means that the body is fighting infection.
go to top
Symptoms of cervical lymphadenitis
Clinical manifestations of cervical lymphadenitis depend on the stage of the pathological process.
Serous inflammation can be recognized by the following signs:
- Pain in the neck and under the lower jaw. The symptom increases as the disease progresses. It may intensify when moving the lower jaw.
- Enlargement of the lymph nodes in size - upon examination and palpation, they are determined in the form of round or oval formations the size of a bean to a nut.
- Redness and swelling of the skin in the area of inflammation.
- Local and general increase in temperature.
When turning into a purulent form, the severity of symptoms increases:
- The affected lymph nodes become dense and fuse into a single formation.
- The skin over the abscess tightens, becomes purple-bluish and hot to the touch.
- The pain bothers the patient even without touching the affected area.
- Movement of the lower jaw is difficult.
- The temperature rises to 40 degrees.
- Signs of general intoxication of the body are added - weakness, drowsiness, headache, pain in joints and muscles.
Manifestations of chronic inflammation are less striking. The lymph nodes are slightly enlarged in size, dense, but quite mobile. There is slight pain and swelling of the adjacent tissues due to stagnation of lymph in the affected area.
Reactive lymphadenitis is characterized by a lightning-fast increase in clinical symptoms.
Classification
- By the routes of infection penetration into the lymph nodes:
- Hematogenous - through the blood;
- Contact – from nearby organs and tissues;
- Mechanical (exogenous) – from the environment during injury.
- According to the causes of occurrence, the following types are distinguished:
- Specific;
- Non-specific.
- By form:
- Acute - manifests itself with vivid symptoms and turns into a purulent form if not treated.
- In the purulent form, the lymph nodes melt and the disease affects neighboring tissues.
- Chronic - provoked by some specific microorganisms, as well as as a result of a long course of the inflammatory process, the acute form has not been treated.
- Reactive – characterized by lightning-fast enlargement of lymph nodes.
- According to the nature of inflammation:
- Catarrhal (simple) - a violation of the permeability of lymphatic capillaries and the release of blood from the vascular bed, permeating the tissues. Redness occurs. Moderate migration of leukocytes occurs.
- Hyperplastic is an inflammatory process in later stages, when a massive influx and proliferation of leukocytes occurs.
- Purulent - is the last stage of bacterial lymphadenitis, when suppuration and destruction of the lymph nodes are observed. Abscesses or adenophlegmons form.
- Serous (non-purulent) – slight deterioration in health.
- Fibrinous - abundant exudation and loss of fibrin.
- Hemorrhagic - soaking in blood from plague or anthrax
- Necrotic - rapid and extensive tissue necrosis.
- According to pathogens, it is divided into types:
- Bacterial;
- Fungal;
- Viral.
- By location:
- Submandibular;
- Cervical;
- Axillary;
- Parotid;
- Mesenteric (mesadenitis);
- Inguinal.
- By prevalence:
- Single;
- Regional;
- Total.
go to top
Diagnosis of lymphadenitis
To make an appropriate diagnosis, the doctor is guided by the clinical picture, taking into account the anamnestic information. Superficial lymphadenitis ( inguinal , cervical lymphadenitis ) is easily determined by the doctor. It is more difficult to diagnose lymphadenitis, a complication of which is periadenitis , and the inflammatory process involves the adipose tissue between the muscles, the cellular spaces of the mediastinum and the retroperitoneal space.
To establish a differential diagnosis, it is important to know where the primary purulent-inflammatory focus is located. It is important to differentiate chronic nonspecific lymphadenitis from enlarged lymph nodes in other infectious and other diseases. In the process of recognizing chronic lymphadenitis, the doctor evaluates a whole range of symptoms of the disease. If the diagnosis is difficult, then a biopsy of the lymph node should be performed or removed for subsequent histological examination. Such a study of the material means a lot in the process of differential diagnosis of chronic lymphadenitis and detection of metastases of malignant tumors .
The diagnosis of “ specific lymphadenitis ” is established based on the results of a comprehensive examination of the patient. This takes into account the patient’s contact with tuberculosis , his reaction to Tuberculin , the presence or absence of tuberculous lesions in the lungs and other organs.
You can also establish the correct diagnosis using puncture of the affected lymph node. Using an x-ray, you can determine the formation of calcifications , which are visible on an x-ray as dense shadows on the cervical soft tissues, under the jaw, in the armpits and groin area. It is important to differentiate tuberculous lymphadenitis from nonspecific purulent lymphadenitis, metastases of malignant tumors, and lymphagranulomatosis .
If inguinal lymphadenitis is suspected, a thorough examination of the rectal area and genital organs should be performed to determine the condition of the pelvic and hip bones. It is important to establish the correct diagnosis, because in some cases inguinal lymphadenitis is defined as a strangulated hernia .
Causes
The causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes are conventionally divided into specific and nonspecific. Nonspecific lymphadenitis is provoked by microorganisms of different infectiousness and structure:
- Bacteria and their toxins. Various bacterial microorganisms (staphylococci, E. coli, etc.) can live in the human body. Their waste products that they secrete are toxic. Thus, damage to an organ or department is carried out not only by bacteria, but also by their waste products, which can remain after a massive fight against the main pathogens.
- Viruses. These microorganisms are like living beings that have their own DNA or RNA. When they enter a living organism, they force cells to change their genetic code and form new viral cells.
- Mushrooms. These microorganisms do not change the human code, but simply parasitize it. They multiply, penetrate other organs, suppress the immune system, in other words, they live at the expense of the human body.
Specific lymphadenitis develops when the lymph nodes are damaged by specific microorganisms:
- Microbacterium tuberculosis;
- Treponema pallidum;
- Brucella;
- Plague stick;
- Tularemia bacteria;
- Actinomycete.
These microorganisms cause their own unique set of symptoms that are unique to them.
Each section of the lymph nodes is provoked depending on what disease the person is suffering from. Thus, the causes of inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes are:
- Skin infections: boil, impetigo, trauma, herpes, carbuncle, herpes zoster, hidradenitis, erysipelas.
- Oral infections: gingivitis, glossitis, caries, infectious stomatitis.
- Salivary gland infections: bacterial and viral infections.
The causes of cervical lymphadenitis are:
- Otitis.
- Fungal diseases of the scalp.
- Pharyngitis.
- Sinusitis.
- Rhinitis.
- Infectious thyroiditis.
- Rubella.
- Infectious mononucleosis.
- Adenoviral infection.
- Flu.
- Festering wounds on the head and neck.
The causes of the axillary appearance are:
- Purulent diseases of the skin of the upper jaw.
- Felon.
- Suppuration of wounds in the area of the arms and torso.
- Fungal infections of the skin.
- Mastitis.
- Osteomyelitis of the hand bones.
Factors that provoke inguinal lymphadenitis are:
- The above inflammatory diseases.
- Gonorrhea.
- Colpitis.
- Balanoposthitis.
- Vulvitis.
go to top
What is submandibular lymphadenitis, stages of development
Submandibular lymphadenitis is called inflammation of the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes , which can be acute or chronic. Often the disease is secondary, that is, it does not occur independently, but as a symptom of a primary infection.
Acute stage
In the acute form of the disease, one lymph node or several may become inflamed. Depending on what kind of exudate is contained in the inflamed node - pus or serous fluid - lymphadenitis is divided into purulent and non-purulent. The acute form of the disease is treated by removing pus from the lymph node and eliminating the root cause of inflammation.
If there is pus inside the lymph node, there is a danger of it breaking through and infecting surrounding tissues.
Chronic stage
The transition of the disease to the chronic phase is a consequence of the lack of adequate treatment. The node no longer increases in size and hardens. The pain syndrome intensifies, and severe intoxication of the body occurs. The skin around the node becomes purple.
Compared to the acute phase of the disease, with chronic lymphadenitis there is a clearly noticeable increase in the area of inflamed tissue around the lymph node . The danger of this form of pathology is that it may require removal of the lymph node.
Symptoms and signs of lymphadenitis of the lymph nodes
Let's consider the symptoms of lymphadenitis of the lymph nodes according to their location. The submandibular form is characterized by the following features:
- Enlarged lymph nodes. They become round or oval.
- Pain that gradually increases as the illness progresses. Accompanied by jaw movement.
- Change in skin color in the area of the lymph nodes: it becomes red and swollen. Local body temperature may be observed.
- In the purulent form, suppuration occurs, fusion of the lymph nodes, and their compaction. The skin becomes red, swollen, and tight. There is pain even at rest. Jaw movements are limited.
- Temperature rises to 40ºС.
- Pain in the head.
- Weakness.
- Muscle pain.
- Drowsiness.
go to top
Types and degrees of development
There are several forms and degrees of severity of submandibular lymphadenitis.
By localization:
- Left-sided, if the nodes on the left side of the neck are affected;
- Right-sided, if on the right;
- Double sided if on both sides.
Along the flow it is divided into:
- Acute, characterized by a rapid course, up to two weeks. Symptoms occur in one or several nodes simultaneously. The cervical lymph nodes are enlarged, painful to the touch, the skin around them turns red;
- Subacute lymphadenitis is diagnosed very rarely; it lasts 2-4 weeks. It differs only in the less pronounced coloration of the skin;
- Chronic. Lasts much longer, more than a month. Lymph nodes become hard and painless. The inflammatory process occurs in waves, with periods of exacerbation followed by periods of remission. May indicate systemic infection or cancer.
READ What is a radicular cyst and how to treat it?
According to the nature of the changes in the lymph nodes, they are divided into:
- Purulent lymphadenitis, when neglected, threatens the breakthrough of pus into the surrounding tissues;
- Serous, without corrosive discharge;
- Necrotic, rarely diagnosed, the lymph node partially or completely dies;
- Hyperplastic. When this happens, lymph node tissue grows.
According to the microorganisms that caused it:
- Nonspecific, with staphyllo and streptococcal lesions;
- Specific, caused by Koch's bacillus (tuberculosis), treponema pallidum (syphilis) and others.
In the international classification of diseases, submandibular lymphadenitis is assigned the number L-04.0. For lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph nodes without specifying the cause), the ICD 10th edition code is R59.9.
With the cervical form, symptoms appear:
- Enlarged oval or round lymph nodes.
- Pain occurs when turning the head, talking, eating and swallowing, as in asthma.
- The skin becomes red, swollen, and edematous, which appears not only in the area of the lymph nodes, but also beyond them.
- In the purulent form, the skin becomes red, pus breaks out, the temperature reaches 40ºC, sleep is disturbed, weakness and pain in the head occur.
- Limited neck movement. Any turns or movements cause severe pain.
- Compression of the cervical organs - vessels, trachea, vocal cords, esophagus - which causes the corresponding symptoms: change in voice, as with laryngitis, difficulty breathing, as with tracheitis, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), as with esophagitis.
go to top
Causes of the disease
Lymph nodes are designed to filter lymph and serve as a kind of barrier between it and the circulatory system.
When harmful microorganisms find themselves in the intercellular space, they do not enter the cardiovascular system, but remain in the lymph nodes.
If the immune system fails to suppress them, the affected node itself becomes inflamed.
This is followed by filling the node with exudate, tissue infiltration, growth and proliferation of cells, due to which it swells sharply.
Thus, lymphadenitis of the submandibular node occurs with streptococcal or staphylococcal damage to nearby organs:
- Teeth (caries, stomatitis);
- Gum (gingivitis, periodontitis), in infants - during teething;
- Nasopharynx (sinuses, larynx, tonsils);
- Middle and inner ear;
- Jaw bones;
- Infected skin injury.
In some cases, the cause of submandibular lymphadenitis is a global infection that has spread throughout the body:
- Tuberculosis;
- Syphilis;
- AIDS;
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
With the axillary form, the following symptoms are observed:
- Enlarged lymph nodes and even blood vessels.
- Pain that radiates to the shoulder and side of the chest. The patient takes a forced position, lying on his side, moving his arm to the side, due to which the pressure in the area of the lymph nodes is reduced, which reduces pain.
- Usually the skin does not change color. But with a purulent form, it can become purplish-red in color and take on a swollen, tense appearance.
- Hand movements on the side of the affected area are limited.
- Swelling of the hands appears in the affected areas.
- The sensitivity of the affected area of the hand is impaired. Possible tingling, numbness, crawling, etc.
go to top
Classification of lymphadenitis
Lymphadenitis is a disease that can occur in different ways. The manifestations of the disease are influenced primarily by what caused its appearance, how long the inflammatory process lasts, whether or not there is a primary infectious focus, and what is the location of the affected lymph node. All these parameters are taken as the basis for the clinical classification of lymphadenitis, the symptoms and treatment of which directly depend on whether this disease in a particular patient belongs to a certain group. There are several varieties of this disease.
By origin
Primary lymphadenitis
Primary lymphadenitis accounts for about 5% of all cases of this disease, because there is no initial source of infection. Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate immediately into the lymph node when the skin or mucous membrane above its surface is damaged. However, in most healthy people, with adequate wound treatment, such a complication still does not occur. And, nevertheless, if this does happen, then the lymph node is already a source of infection and the patient must definitely see a surgeon. In some cases, it may be necessary to open it, drain it, and prescribe antibiotics for lymphadenitis to prevent bacteria from spreading through the lymph and blood to other lymph nodes throughout the body.
Secondary lymphadenitis
In 95% of cases, lymphadenitis is a complication caused by the development of the inflammatory process in the primary focus. It can be anywhere, most often these are the ENT organs, oral cavity, skin, genitals, mammary gland, etc. The human immune system is designed in such a way that after foreign pathogenic bacteria enter the body, it begins to produce protective blood cells and antibodies against infection. In this case, living, destroyed or severely weakened microbes are delivered through lymph or blood flow to the lymph nodes that are closest to the primary focus. They, in turn, increase in size, become painful, dense, the skin over them turns red and becomes warm to the touch. This is precisely the mechanism of occurrence of secondary lymphadenitis in adults and children.
The main link in the treatment of this disease is the fight against microorganisms in the primary focus: treatment of sore throat, tooth extraction in severe periodontitis, competent treatment of gonorrhea, syphilis, etc.
According to the course of the inflammatory process
Acute lymphadenitis
In most cases, patients develop acute lymphadenitis, which is characterized by a fairly rapid course and violent clinical manifestations. Moreover, in its course it goes through three phases, but this does not happen to everyone, which depends on the activity of the patient’s immune system and the timeliness of medical care.
Acute lymphadenitis can be catarrhal, hyperplastic and purulent. At the first stage of the inflammatory process, the lymph node increases in size, becomes dense, painful when touched, and the skin over it becomes red and hot. In this case, a person suffers from symptoms of general intoxication: fever, headache, weakness, aches in muscles and joints.
The hyperplastic phase is intermediate between catarrhal and purulent; during it, a gradual melting of the lymph node occurs. During the purulent phase, the lymph node is an infiltrate filled with pus. At the same time, it can break through to the surface of the skin through its thin areas. In all patients, a high fever is noted; the patient spares the affected area, since the slightest touch to it causes severe pain.
If the patient is not provided with competent medical care in a timely manner, then acute lymphadenitis can cause a total spread of infection throughout the body (sepsis) and threaten life. Often, with a purulent form, the capsule ruptures and its contents spill into the surrounding tissues with the formation of phlegmon and paralymphadenitis. In this case, the tactics are determined by the surgeon; in most cases, he will choose a radical method, that is, opening the affected lymph node and prescribing antibiotics.
Acute lymphadenitis is a serious disease in which it is worth giving preference to traditional methods of therapy from a qualified specialist rather than resorting to self-medication and alternative methods.
Chronic lymphadenitis
Not all people have a bright and violent course of this disease. In some patients, doctors identify the protracted nature of the inflammatory process, in which they diagnose chronic lymphadenitis. Its peculiarity is a long-term latent type of course; it stops at the catarrhal phase for several weeks or even months, that is, it does not undergo purulent melting for a long time.
Clinical manifestations are not so pronounced: the patient is concerned about a slight enlargement of the lymph node (one or more), moderate pain when touched and moved, the color of the skin and its temperature may change slightly, and in some cases remain the same. The patient complains of low-grade fever, chills, sweating, fatigue, and weakness. All symptoms of chronic lymphadenitis are combined with those that cause an inflammatory process in the primary focus. For example, with gonorrhea - purulent discharge from the urethra, increased urination, with chronic periodontitis - pain when pressing on the tooth, which intensifies when chewing, etc. Sometimes the patient cannot clearly formulate the symptoms of his condition, he simply complains that he does not feel well .
Sometimes it is chronic lymphadenitis that allows the doctor to suspect a long-term inflammatory process in the human body. Therefore, any enlargement of the lymph nodes, especially if there are no obvious reasons for this (a cold), requires a thorough examination by a specialist. Chronic lymphadenitis must be differentiated from other ailments in which the lymph nodes are enlarged for a long time - lymphogranulomatosis, leukemia, metastases of a malignant tumor.
By the nature of inflammation
Serous lymphadenitis
Serous lymphadenitis is, as a rule, the primary phase of the inflammatory process in this disease. In the acute form, it can last from several hours to several days, after which the lymph node undergoes purulent melting. With a chronic course, it can last for several weeks or even months. In this case, the lymph node increases in size and becomes painful when touched or moved, but the patient may not have a high fever (but this depends on the primary disease). At this stage, timely identification of the disease that caused the appearance of lymphadenitis and adequate treatment are very important. Most often, doctors resort to conservative methods of therapy.
Purulent lymphadenitis
Purulent lymphadenitis is characterized by the fact that the lymph node undergoes purulent melting. Sometimes the capsule ruptures and the exudate spills into the surrounding tissues, spreading throughout the body with the flow of blood and lymph. This condition is life-threatening and does not go away on its own without the help of specialists.
Purulent lymphadenitis, the symptoms of which are very bright and pronounced, cannot but attract the attention of the patient. The area where the lymph node is located is swollen, painful, impossible to touch, the patient spares it and therefore makes a minimal range of movements. The skin over it is red, hot to the touch, sometimes the abscess is visible through thin areas of the skin. In some cases, it ruptures and exudate pours onto its surface; it can be white or greenish in color with a characteristic sweetish odor. The patient usually has a very high temperature and symptoms of intoxication (ache, weakness, headache, chills).
By process localization
Cervical lymphadenitis
Cervical lymphadenitis develops quite often, because the main reason for its appearance is the primary pathology of the ENT organs or the oral cavity. Another disease in which the lymph nodes of the neck can become significantly enlarged is infectious mononucleosis, which is extremely difficult to diagnose. More rare, but very serious diseases in which cervical lymphadenitis can develop are tuberculosis, syphilis, gonorrhea, and HIV infection.
With this disease, you can visually see enlarged anterior or posterior cervical lymph nodes. As a rule, the pathological process involves several of them at once. The neck increases in size; with infectious mononucleosis, it can become wider than the head and resemble a bovine neck. When cervical lymphadenitis appears, especially if the patient cannot indicate the presence of a disease in the ENT organs or oral cavity (tonsillitis, sinusitis, stomatitis, periodontitis, etc.), he must be sent for consultation to a general practitioner. After a conversation and an initial examination, he will send him for a series of clarifying tests and examinations. It is very important to identify what disease led to the appearance of cervical lymphadenitis.
Submandibular lymphadenitis
Submandibular lymphadenitis is the most common localization of this disease. It is especially common in children, since infections of the upper respiratory tract or oral cavity are not uncommon for them. The main cause of submandibular lymphadenitis is tonsillitis, stomatitis, periodontitis, nasopharyngitis, gingivitis. It can also be caused by specific pathogens of syphilis, gonorrhea, tuberculosis, mononucleosis, etc. In a child, this sometimes causes childhood diseases such as mumps, diphtheria, whooping cough, scarlet fever, etc. Sometimes short-term submandibular lymphadenitis appears during teething.
Patients complain of pain under the lower jaw, which can be either unilateral or bilateral. Enlarged lymph nodes interfere with normal movement in the temporomandibular joint and make it painful for people to chew food. Because of this, small children may refuse breastfeeding altogether for several days; they cannot suckle at the breast, as this requires active work of the muscles and joints of the jaw apparatus.
After adequate treatment of the primary disease (if necessary, taking antibiotics), the lymph nodes may remain enlarged and somewhat painful for another 1-2 weeks. However, if it has been treated completely and the inflammation in the lymph node has not become purulent, they gradually decrease without special treatment. But in the second case, when submandibular lymphadenitis has acquired a purulent character, the help of a surgeon is needed, because more radical treatment is necessary - its opening and drainage.
Axillary lymphadenitis
Axillary lymphadenitis is much less common than the first two forms. And unlike them, it most often acquires a purulent character, which requires the mandatory participation of a surgeon. The most common causes of axillary lymphadenitis are infected wounds on the arm, chest, back, boils and carbuncles, which often develop directly in the armpit area. They are possible due to injury to the hair follicles due to careless shaving and depilation. The second common cause for the appearance of axillary lymphadenitis is purulent mastitis or inflammation of the mammary gland. In addition, it can be caused by sexually transmitted infections, tuberculosis, etc.
The patient complains of the appearance of a painful lump in the armpit, which interferes with the normal movement of the arm (especially when trying to lift it up), and makes it impossible to sleep on the side. Quite quickly, the inflammation becomes purulent, and the skin above it turns red, becomes hot, and sometimes exudate breaks out through thinned areas of the skin in the armpit. Axillary lymphadenitis very often requires active action by a surgeon: opening, drainage and prescribing systemic antibiotics. Under no circumstances should the patient try to open the abscess on his own, make compresses, and especially apply a heating pad to it.
Inguinal lymphadenitis
Inguinal lymphadenitis, in most cases, is the result of a current sexually transmitted infection. Very often it is the first symptom of diseases such as gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia, etc. Sometimes patients do not notice the symptoms of these ailments and go to the doctor with a complaint about the appearance of an enlarged lump in the groin. It can be painful, but in some cases it is not (as, for example, with syphilis). Inguinal lymphadenitis can be both unilateral and bilateral - with genital infections this option is most often found.
The second possible reason for this localization of the pathological process is inflammation of the skin, muscles, and bones of the lower extremities. Most often these are boils, carbuncles, infected wounds, thrombophlebitis, osteomyelitis, trophic ulcers, erysipelas. And the rarest cause of inguinal lymphadenitis is such specific diseases as plague, tularemia, anthrax, etc.
The nature of the inflammatory process can be either serous or purulent. Therefore, doctors do not always resort to opening the affected lymph node. When inguinal lymphadenitis appears, it is very important to promptly identify the cause and begin treatment of the primary source of infection.
More rare localizations of lymphadenitis
Much less common in practical medicine is mesenteric lymphadenitis, which develops as a result of the appearance of a focus of infection in the abdominal cavity. It can be both acute and chronic and is very difficult to diagnose in a timely manner.
Symptoms of the groin form are:
- Enlarged lymph nodes up to several centimeters.
- Pain that gets worse when walking, causing the patient to move less.
- Pain in the affected area, as well as in the lower abdomen and thigh.
- Swelling and tension of the skin appears.
- The skin may be normal or pinkish in color if purulent lymphadenitis has not developed.
- Swelling of the legs on the side of the affected area.
- The general condition is satisfactory until a purulent form develops, in which the temperature rises, weakness, headaches, rapid heartbeat, pain in the abdominal and leg muscles occur.
Symptoms of acute lymphadenitis develop very clearly. The chronic form is sluggish. The lymph nodes become enlarged, but practically do not hurt, swell, and only slightly change the color of the skin.
go to top
Prevention of submandibular lymphadenitis
Prevention of submandibular lymphadenitis involves taking measures to prevent the development of diseases that can cause an inflammatory process in the lymph nodes:
- During periods of acute respiratory infections epidemic, you should avoid crowded places and take all measures to prevent respiratory diseases.
- It is necessary to undergo a timely examination by a dentist and carry out all necessary treatment measures.
- It is necessary to properly and completely treat diseases of the nasopharynx, to prevent acute forms of ENT pathologies from becoming chronic.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of inflammation of the lymph nodes begins with the collection of symptoms that are troubling, as well as a general examination (palpation, auscultation, identifying all signs of lymphadenitis). Additional studies help determine the cause of the disease, as well as determine the severity:
- Blood analysis.
- Radiography.
- Ultrasound of the affected area.
- Lymph node biopsy.
- Consultations with doctors who treat the disease that caused lymphadenitis: otorhinolaryngologist, urologist, therapist, dermatologist, phthisiatrician, surgeon.
- Diagnosis of the underlying disease.
go to top
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
At first, lymphadenitis does not manifest itself in any way, but very quickly such characteristic symptoms appear as:
- Swelling of the affected nodes, sometimes up to seven centimeters in diameter, while the jaw looks extremely unnatural;
- Pain when pressed, difficulty swallowing;
- Redness of the skin at the site of the node.
The following symptoms of submandibular lymphadenitis appear with the development of the acute form:
- Body temperature rises, up to forty degrees;
- General weakness of the body;
- The mucous membrane of the mouth becomes inflamed;
- Attacks of pain radiating to the ear.
In a chronic course, these symptoms do not appear.
Making a diagnosis begins with an analysis of the medical history and examination of external signs of the disease. For acute superficial lesions, this is usually sufficient.
If the symptoms are nonspecific and the cause of the disease is unclear, a number of diagnostic procedures are also prescribed:
- General blood analysis. An elevated white blood cell count is expected;
- Ultrasound examination of lymph nodes;
- X-ray examination of the chest;
- Mantoux and Pirquet tests for tuberculosis;
- Puncture and biopsy of the affected lymph node and examination of the material taken.
Differential diagnosis is needed to exclude options such as:
- Metastases from malignant neoplasms;
- Tumors of the salivary glands;
- Osteomyelitis, leukemia, sarcoidosis;
- Granulating periodontitis;
- Cysts;
- AIDS.
Only after eliminating all possible unnecessary options can you begin treatment.
Treatment
Treatment of lymphadenitis of the lymph nodes takes place in 4 directions:
- Medicines;
- Physiotherapy;
- Traditional methods;
- Surgical intervention.
The main thing is to treat the underlying disease, against which inflammation of the lymph nodes has developed. Medicines that are used in the treatment of lymphadenitis are:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Ketorolac, Nimesulide;
- Antihistamines: Cetirizine;
- Antibiotics: Amoxiclav, Ceftriaxone, Clindamycin, Benzyllenicillin;
- Antiviral drugs: Acyclovir, Rimantadine;
- Anti-tuberculosis drugs: Ethambutol, Rifampicin, Capreomycin;
- Antifungals: Fluconazole, Amphotericin B.
go to top
Types of lymphadenitis, photo
lymphadenitis under the ear, photo
Depending on the location of the occurrence of inflammatory processes, lymphadenitis can be cervical, submandibular, or inguinal.
Cervical lymphadenitis is associated with various inflammatory and tumor processes. Lymph from all parts of the body passes through the neck area completely or partially.
Acute streptococcal pharyngitis, paratonsillitis, tonsillitis, diseases of the teeth and oral cavity, respiratory viral infections may be accompanied by acute or chronic lymphadenitis.
In diagnosis, the location of the inflamed lymph nodes is important. Nodes located at the back of the neck may change in size with rubella and toxoplasmosis, and enlargement of the parotid nodes is observed with infections of the conjunctival membrane.
photo of lymphadenitis in a child
Submandibular lymphadenitis is more common and is observed in most cases in childhood and adolescence. The development of lymphadenitis is complicated by inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsils.
Submandibular lymph nodes enlarge during dental inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis. Such lymphadenitis resolves with the cure of the underlying disease.
Inguinal lymphadenitis - most often its cause is inflammatory diseases of the external and internal genital organs, which are of an infectious nature. Purulent processes in the lower part of the torso and extremities can cause enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes.
Such processes include purulent wounds, boils, felons, and trophic ulcers.
What is treated in physical therapy?
- Ultrahigh frequency therapy;
- Laser therapy;
- Galvanization;
- Electrophoresis with iodine preparations.
Traditional methods that can be used at home and complement (but not replace) drug and physiotherapeutic treatment are not excluded:
- Warming up with dry heat. Heat salt or sand in a frying pan, put it in a cloth bag and apply it to the affected area. If after the procedures the temperature rises and the condition worsens, you should stop the procedures and seek medical help.
- Herbal decoctions and infusions:
- Pour boiling water over 10 g of crushed dandelion roots, leave for 4 hours and consume a tablespoon at a time.
- Add honey (200 g) to aloe juice (100 g) and leave for an hour. Take a teaspoon.
- Echinate tinctures, either purchased at a pharmacy or prepared yourself: pour 100 g of crushed roots of the raw material with 60% alcohol (500 ml) and leave for 2 weeks. Strain. Use both internally and externally.
- The diet consists of consuming vitamins and foods rich in fiber and proteins.
Surgical intervention is resorted to only in the purulent form of lymphadenitis, when abscesses and adenophlegmons form. The purulent focus is opened, the contents and destroyed tissue are removed. Everything is washed with antiseptics and drained so that liquid and pus can subsequently come out through the tube.
go to top
Treatment of lymphadenitis with folk remedies
Medicinal herbs can be an effective aid in the treatment of lymphadenitis at an early stage. Ointments and compresses help relieve inflammation, reduce itching and pain. To alleviate the condition, speed up recovery and strengthen the immune system, it is recommended to use medicinal infusions and decoctions . The juice of will help get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of this disease . Traditional medicine can be combined with traditional therapy prescribed by your doctor.
Dandelion juice
To obtain healing juice, you need to grind fresh dandelion grass and squeeze the liquid out of it. Next, soak a cotton pad or gauze with the resulting liquid and apply it to the inflamed area for 2 hours. A similar procedure is carried out 2 times a day, for 3 days. If the inflammation does not decrease and the symptoms of the disease do not go away, then you should immediately seek medical help.
Knotweed infusion
A medicinal infusion for lymphadenitis is prepared from 3 teaspoons of crushed dry herbs. They need to be poured with 100 ml of boiling water and mixed. The solution is kept in a water bath for 10 minutes, after which it settles for another hour in a warm place. You need to consume 3 tablespoons 3 times a day before meals.
Horsetail for lymphadenitis
For lymphadenitis, the medicinal properties of horsetail can be used to relieve the inflammatory process. For treatment, 2 tablespoons of crushed and pre-dried herbs of this plant are poured with 1 glass of boiled water. The solution is kept over low heat, stirring, for about half an hour. Drink a third of a glass 4 times a day.
Medicinal herbal collection
To make a healing drink that will help reduce inflammation and speed up recovery, you need to mix the following herbs. Add 1 tablespoon of finely chopped nettle leaves, yarrow herb, oregano and hop cones, as well as 3 tablespoons of horsetail. All ingredients are thoroughly mixed. For 1 tablespoon of this raw material you need to pour 300 ml of water. The mixture is placed in a water bath and simmered for a quarter of an hour. Then the broth should stand in a warm place for about 10 minutes. The strained drink is taken 100 ml 3 times a day before meals.
Mistletoe tincture
Alcohol tincture of mistletoe can be used to rub inflamed lymph nodes. To enhance the therapeutic effect, it is recommended to take it orally, 40-50 drops 3 times a day, with a small amount of water. To do this, mistletoe leaves are collected, dried and crushed, after which they are poured with alcohol in a ratio of 1:5. Leave the tightly closed jar with the solution in a dark, cool place for 2 weeks, shaking the container periodically. The finished tincture is filtered. This remedy helps get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of this disease. It is forbidden to use it to treat children or pregnant women.
Avran medicinal for lymphadenitis
To prepare a tincture for the treatment of lymphadenitis, you need 50 g of crushed leaves or roots of Avran officinalis, pour 300 ml of vodka. The mixture should be placed in a dark place for 2 weeks. Shake the ingredients periodically for better saturation. Then the finished product is filtered and used to rub painful lymph nodes. Can be used as a compress by soaking gauze in a heated solution and applying it to the inflamed area.
Aloe juice
To prepare this medicine, you need to cut off the bottom leaf of aloe. Then it should be crushed to a pasty state and applied to the inflamed lymph node for 20 minutes. For mild itching, it is enough to apply a sheet cut in half to the problem area for a few minutes.
Golden currant for inflammation of the lymph nodes
To get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of a disease such as lymphadenitis, use an external remedy based on golden currant buds. To do this, you need to pour 1 teaspoon of raw material with 1 glass of boiling water and leave for 15 minutes in a warm place. Moisten gauze in the resulting solution and apply to problem areas. It should not be consumed internally, as the buds of this plant are poisonous.
Infusion of Adonis spring
To relieve inflammation due to lymphadenitis and to speed up treatment, you need to collect spring Adonis flowers. Then 1 tablespoon of such raw material should be brewed in 200 ml of boiling water, set aside until completely cooled and then strain. Take the finished product orally, 1 tablespoon 3 times a day.
Cocklebur juice
Juice from the cocklebur herb has an effective analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. To prepare a medicine for lymphadenitis, freshly harvested herbs are scalded with boiling water, finely chopped and the juice is squeezed out of the finished mass. After this, mix the solution with vodka in equal proportions and leave to infuse in a closed container for 1 week. It is recommended to shake the tincture periodically. After settling, the liquid is filtered and used as an external means for rubbing inflamed lymph nodes. In case of severe pain or itching, you can take this solution orally, but not more than 15 ml per day
Life forecast
How long do people live with lymphadenitis? The disease is not considered fatal. Attention should be focused on eliminating the cause of the disease, while simultaneously treating lymphadenitis. The life prognosis is favorable with timely treatment. Sometimes the disease goes away on its own, especially if the source of infection (that is, the underlying disease) is eliminated. However, you should not rely on this, so as not to develop a chronic form. Complications are possible if treatment measures are not taken:
- Thrombophlebitis,
- Fistula;
- Cancer;
- Tissue phlegmon;
- Sepsis.
Lymphadenitis in children
Acute lymphadenitis in children occurs rapidly, with a pronounced general reaction and local symptoms. General disorders that are symptoms of intoxication often come to the fore:
- chills,
- increase in body temperature,
- malaise,
- loss of appetite,
- headache.
The younger the child, the more pronounced the clinical symptoms, which is why parents most often turn to a pediatrician. Chronic lymphadenitis in children is a companion to a long-term chronic infection - odontogenic (chronic periodontitis) or non-odontogenic (chronic tonsillitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, otitis media, etc.). According to the clinical course, chronic hyperplastic lymphadenitis is distinguished and chronic in the acute stage.
Symptoms of lymphadenitis
The disease is most pronounced in young children. After the third day, inflammation begins to develop rapidly, and symptoms of general intoxication appear - fever, headache, weakness, nausea. In addition to systemic manifestations, local changes are observed - the lymph nodes and the surrounding area swell, and shooting pain is bothersome. At this stage, a purulent process often begins to form, which only worsens the patient’s condition. The release of purulent contents beyond the lymph node provokes the development of adenophlegmon, sepsis, thrombosis and other dangerous conditions.
Chronic lymphadenitis occurs against the background of chronic infection or as a result of untreated acute lymphadenitis. The symptoms are not so pronounced, but the size of the nodes exceeds normal ones. In this case, no pain is observed, suppuration occurs rarely, mobility is only partially limited, and the general condition of the child is not impaired. This course is dangerous because over time the lymph nodes are destroyed, replaced by connective tissue and become unable to perform their functions.
Prevention
As a rule, in order to prevent lymphadenitis of the submandibular region on the right or left, it is necessary to treat diseases of the oral cavity in time. Preventive measures are:
- regular visits to the dentist;
- maintaining oral hygiene;
- elimination of foci of infection in the oropharynx;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- rejection of bad habits;
- maintaining normal immunity.
Symptoms and treatment of lymphadenitis
Previous post
Causes and treatment of inflammation of the parotid lymph nodes
Next entry
Discussion: 2 comments
- Irina:
03/27/2019 at 12:06I had the same problem: the lymph node on one side of my neck hurt and became enlarged. Terrible thoughts came into my head. It turned out that it was all due to the difficult eruption of the wisdom tooth, it crashed into the bone tissue
Answer
- Olga:
04/20/2019 at 15:12
After suffering from acute respiratory viral infection, the submandibular lymph nodes were enlarged for a long time. I was prescribed a course of Lymphomyosot and UHF therapy.
Answer
Why does lymphadenitis occur?
Like any inflammation, lymphadenitis occurs due to the activity of bacteria: streptococci and staphylococci. The causes of submandibular lymphadenitis are diseases of the oral cavity and infection that enter directly into the lymph nodes as a result of diseases such as:
- caries, pulpitis, periodontitis;
- gum disease;
- chronic diseases (for example, tonsillitis);
- syphilis bacteria;
- tuberculosis bacillus;
- external infections that enter the body as a result of injury.
Treatment (conservative and surgical)
The fight is aimed at eliminating the cause that provoked it. The following drugs are used to treat submandibular lymphadenitis:
- Burov's liquid, which has astringent, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. Cold lotions are made on its basis. Also used for rinsing. The product is first diluted with water.
- Saline solution. Used for rinsing the mouth for chronic tonsillitis of bacterial origin. Other solutions can be used (as recommended by a doctor).
- Antibacterial drugs are prescribed by a specialist. As a rule, broad-spectrum drugs are used, i.e., aimed at several possible pathogens.
Anti-inflammatory ointments are prescribed as adjuncts. Your doctor may recommend the use of traditional medicine. All therapeutic activities are carried out in a complex. The use of drugs aimed at strengthening the immune system is encouraged.
Burov's fluid
To speed up recovery, it is recommended:
- give up fatty, salty and smoked foods;
- do not use semi-finished products for food;
- consume more dairy products;
- give preference to lean meat;
- do not drink alcoholic beverages.
Antibiotics for submandibular lymphadenitis in adults
The course of antibiotic treatment is determined by the doctor. When administered by injection, therapy lasts at least a week. Medicines in tablet form may be prescribed for a longer period. A lymph node puncture is first performed, the results of which reveal the sensitivity of microbes to drugs.
Submandibular lymphadenitis in children and adults, the treatment of which is complex, usually requires the use of penicillin medications. A specific medicine is prescribed by a doctor, focusing on the characteristics of the disease and the patient’s health condition.
In most cases, non-advanced lymphadenitis of the jaw can be dealt with with the help of rinses (if it is caused by a sore throat) and antibiotics. In case of a purulent lesion, surgical intervention is performed, during which an incision is made, and the exudate is removed from the lymph node through a drainage tube.
If several immune components are affected at once, an operation aimed at eliminating the entire pathological process is indicated. The doctor makes an incision in the lower jaw, and then places a drainage tube there, through which purulent fluid gradually drains out. At the end of the procedure, the wound is closed with clamps.
Pathogens
The development of the disease is provoked by microorganisms that penetrate into the nodes from foci of inflammation with the flow of lymph and blood. Dangerous pathogens of the disease are Koch's bacillus and treponema (the causative agent of syphilis).
The causative agent of tuberculosis
If a tuberculosis bacillus is detected, the patient is immediately admitted to the hospital. Such medical examination is an effective way to prevent the spread of the disease.
The treatment is complex and consists of the following stages:
- determination of the pathogen by laboratory examination;
- clinical examination;
- treatment of tuberculosis;
- treatment of secondary disease;
- rehabilitation.
When lymphadenitis is in an advanced, severe form, its treatment is carried out in conjunction with tuberculosis.
The causative agent of syphilis
Lymphadenitis is a secondary disease when infected with syphilis, but often it is the first signal of treponema infection.
If a patient presents with inflammation of the lymph nodes, he is first examined for the presence of the causative agent of syphilis. There are 2 types of therapy: inpatient or outpatient. The choice of type depends on the degree of development of syphilis.
How is the diagnosis made?
Usually, the doctor only needs to carefully examine and palpate the patient to suspect the presence of an inflammatory process in the submandibular lymph nodes. But to begin treatment, it is necessary to determine the cause that caused such a symptom. For this purpose, laboratory and instrumental techniques are used.
While working at a research center, I often had to deal with the fact that many stool and urine tests were brought in food jars. This made diagnostic processes very difficult, and some samples had to be taken repeatedly. That is why doctors strongly advise purchasing special containers from pharmacies.
Studies required to make a diagnosis:
- General blood analysis. During inflammatory processes, an increase in white blood cells - leukocytes, as well as ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) is often observed. This indicates the presence of a foreign agent in the body.
- Analysis of stool for worm eggs. Often the cause of the development of submandibular lymphadenitis is the presence of parasitic worms that release their waste products into the human body. Their eggs can be detected by microscopic examination of stool.
- Puncture of the lymph node is carried out to determine the nature of its contents. It can be purulent, mucous or bloody, which also indicates the cause of the development of the disease.
What general treatment is prescribed?
Only a doctor can correctly diagnose and determine the stage of development of the disease, on which the treatment process depends. But general measures to promote recovery include:
- At home, it is recommended to use anti-inflammatory ointments , which are applied as a bandage. The most commonly used are heparin ointment, troxevasin, boric vaseline and Vishnevsky ointment.
- In addition, it is necessary to provide the body with vitamin C , which is needed in large quantities for inflammation. It is possible to take special multivitamins or increase the diet of foods high in this vitamin: kiwi, oranges, sauerkraut, spinach and celery, green onions and parsley, black currants, and so on.
- The patient should drink plenty of fluids (especially water) in order to quickly remove the infection from the body.
- to stay warm more and try to avoid any hypothermia.
- Physiotherapy is very effective for the treatment of submandibular lymphadenitis. This can be quartz irradiation, UHF therapy and other thermal procedures.
- If lymphadenitis is caused by inflammation in the oral cavity, it is necessary to brush your teeth and tongue more thoroughly to prevent the development of a microbial environment.
In cases where the disease is advanced, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics. In case of ineffective therapy, when the lymph nodes continue to enlarge and serious suppuration appears, surgical intervention is performed.
Features of the course and treatment of submandibular lymphadenitis in children
As you know, the body of a small person has many differences from an adult. Children under one year of age practically do not eat solid food, so it is impossible to suspect submandibular lymphadenitis if chewing is impaired. Also, the immune system of babies is much less developed and has a harder time withstanding any external influences. The formation of an inflammatory process in the submandibular nodes in a child in 90% of cases begins with a sharp increase in temperature to 39–40 degrees. Children become capricious and lethargic and refuse to eat. When trying to feel the area of damage, an acute negative reaction occurs in the form of crying.
In severe cases of the disease, febrile convulsions occur in children under three years of age. These are sharp and strong contractions of the muscles of the whole body, during which the child bends in an arc and stops breathing. Often this symptom is a harbinger of brain damage. Children with this pathology require immediate hospitalization in the intensive care unit.
When treating submandibular lymphadenitis in children, systemic therapy is used predominantly. Local medications are ineffective in 80% of cases. The groups of medications in children are practically no different from the treatment of lymphadenitis in adults: only some active ingredients and their dosages have been changed.
- Antibacterial agents kill pathogenic microbes and reduce the risk of complications. The following drugs are used in pediatric practice: Flemoxin Solutab, Sumamed, Asketil, Ceftriaxone. For children, all drugs are administered intramuscularly, while tablets and capsules are provided for older patients.
- Glucocorticosteroid drugs reduce the severity of inflammation and reduce the load on the kidneys. Most often, doctors use Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Prednisone, Triamcinolone. Their administration is carried out intravenously or intramuscularly.
- Preparations for restoring fluid volume in the body. This group includes solutions of glucose, Lugol-Ringer, Disol, Trisol, Acesol, Regidron, sodium chloride, Hemodez. They enter the baby’s body through an IV or a tube.
Photo gallery: medications used to treat illness in children
Flemoxin Solutab is a gentle antibiotic that helps get rid of bacteria
Regidron allows you to remove toxins from the body
Dexamethasone is a systemic anti-inflammatory drug
Video: Dr. Komarovsky talks about lymph node damage in children
Complications
If treatment is not started promptly, this can lead to the development of more serious diseases.
The most common complication of regional lymphadenitis is suppuration of the lymph nodes, which can lead to:
- abscesses,
- tissue necrosis,
- sepsis,
- the appearance of fistulas,
- thrombophlebitis,
- phlegmon,
- destruction of vascular walls and bleeding.
That is why it is necessary to treat the disease.
Are antibiotics needed?
For lymphadenitis, antibiotic drugs are used in case of microbial infection. Without their use, it is not possible to completely cure inflammation in the lymph nodes. Only a doctor can select a medicine. Basically, he does this taking into account the primary disease, or evaluates the results of culture of the internal contents of the affected lymph node.
In this case, the doctor pierces the affected organ with a thin needle and pulls out a little of the material being examined. This manipulation makes it possible to identify which microorganisms cause the pathology and accurately select the medication. If bacteriological analysis is not carried out, then drugs with a wide range of effects are prescribed.
The effectiveness of treatment is considered after 3-4 days. If there is no improvement, the drug must be changed. When performing a treatment course, you should strictly adhere to the dose and duration of administration prescribed by your doctor. This process may take from 1 to 3 weeks.
Antibiotic therapy is not used for lymphadenitis that appears for the following reasons:
- infection of viral etiology (herpes, rubella);
- systemic diseases (lupus erythematosus);
- metabolic destabilization.
Early therapy brings good results. A gentle method, suitable for children and the elderly, involves a stepwise approach. In the initial stages, the medication is administered intravenously, and when the condition improves, the same drug is taken in tablet form.
Taking antibiotics for lymphadenitis can cause side effects such as intestinal dysfunction and fungal diseases. In this case, the therapeutic course includes bacterial agents and digestive supplements.
Basically, for inflammatory processes of the lymphatic system, antibiotics from the group are prescribed:
- penicillins (Ampicillin, Amoxicillin);
- macrolides (Clarithromycin, Sumamed);
- cephalosporins (Ceftriaxone, Cefazolin);
- tetracyclines.
When submandibular lymphadenitis is in an advanced stage, it cannot be cured without the use of antibiotics. But it is worth understanding that they are prescribed not to get rid of inflammation in the lymph nodes itself, but to eliminate precisely the cause. Therefore, it is fundamentally important to consult a doctor who will accurately diagnose.
When self-medicating, you can miss the choice of medications: after all, antibiotics are ineffective in the fight against viral, fungal and parasitic diseases. What can we say about the fact that sore throat and gum disease are treated very differently, but can equally be the cause of lymphadenitis.
Most often, specialists prescribe the following antibiotics as additional therapy:
- Amoxiclav;
- Ampicillin;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Amoxicillin;
- Flemoxin;
- Ceftazidime.
Therefore, only a doctor can decide on a course of antibiotics, but you can contribute to the healing process with the help of traditional medicine.
Primary sources of development
The most common cause of lymphadenitis in the body is the entry of pathogenic microflora into the lymph, which is most often represented by staphylococci and streptococci.
In turn, the foci of bacteria are teeth and gums affected by oral diseases. Periodontitis, gingivitis and caries are diseases whose environment is an excellent way of transporting pathogenic microflora to the lymph nodes through the lymph. Against this background, inflammation occurs.
The next primary source of lymphadenitis is chronic infectious processes in the nasopharynx and tonsils. Such diseases include tonsillitis and sinusitis. This is why it is so important to identify the cause of lymphadenitis. To effectively treat a secondary disease, the source of infection must be eliminated.
It is also possible that bacteria enter the lymph nodes directly, for example, when they are injured. Infection can occur when the skin is damaged.
It is worth noting that pathogenic microflora cannot always be represented by streptococci and staphylococci. There are other types of bacteria, by which the classification of the disease is determined.
Find out more about how to treat a fistula on the gum, about traditional and folk methods. In this material you will find the answer to the question of how to get rid of caries at home in one day.
Follow the link if you are interested in methods of treating mucositis of the oral mucosa.
What types of disease are there?
Classification of submandibular lymphadenitis depending on the nature of the lesion:
- purulent - greenish or yellowish contents come out;
- serous - the discharge is colorless and cloudy;
- fibrinous - typically the presence of bloody streaks.
Types of disease by localization:
- unilateral - only the right or left submandibular region is involved;
- bilateral - the pathological process is located on both sides.
Forms of the inflammatory process by type of pathogen:
- nonspecific - caused by staphylococcus, streptococcus, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus, pneumococcus;
- specific ones arise against the background of an infection provoked by the development of parasitic worms, chlamydia, mycoplasmas and ureaplasmas, diphtheria bacillus, tuberculous mycobacterium (Koch bacillus).
Types of disease according to the nature of the course:
- acute (all symptoms quickly increase and develop);
- chronic (exists for three or more months).
What is regional lymphadenitis?
Enlarged lymph nodes occur due to a bite, scratch, or the entry of animal saliva into the human bloodstream
Regional lymphadenitis is a pathology accompanied by inflammation and an increase in the size of regional lymph nodes that collect lymph from various parts of the body. It can affect the following lymph nodes:
- lower extremities: inguinal and popliteal,
- pelvic: rectal, uterine, vaginal,
- abdomen: pancreas, gastric, lower diaphragmatic, hepatic, mesenteric,
- chest: upper diaphragmatic, thoracic, intercostal, pulmonary, esophageal, tracheal,
- upper extremities: axillary, ulnar, deep, superficial,
- neck and head.
Causes
In the vast majority of cases, regional lymphadenitis is a consequence of primary septic inflammation. Pathogenic microorganisms and the toxins they produce enter the lymph nodes along with blood or lymph, or through injured skin and mucous membranes. In this case, the disease can be provoked by:
- streptococci,
- staphylococci,
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa,
- Koch's wand,
- coli,
- pneumococci,
- HIV,
- fungal and parasitic infections,
- viral mononucleosis.
In addition to infections, the following can lead to the development of lymphadenitis:
- lymphoma,
- metastases in the lymph nodes,
- foreign bodies.
Symptoms
Symptoms of regional lymphadenitis may include:
- swelling and redness of the skin, which are a consequence of the immune system fighting pathogenic microflora,
- deterioration of appetite, loss of strength and headaches accompanying intoxication of the body with waste products of fungi, viruses or bacteria,
- suppuration of the lymph nodes, their melting,
- tachycardia, which is a consequence of involvement of the cardiovascular system in the pathological process,
- gas crepitus, accompanied by a slight crunching sound when pressing on the lymph node,
- limited movement
Reviews
Lymphadenitis is dangerous due to its consequences if its treatment is neglected at the initial stage. The acute form will turn into chronic, non-purulent - into purulent, and then - surgical removal.
When pus breaks out, infection of all neighboring tissues, blood and the development of sepsis occur. The picture is terrifying, so it is important to see a doctor for help.
If you have encountered this disease or would like to express your opinion about it and treatment methods, please leave comments on this article.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.