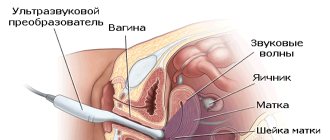
Ultrasound diagnostics opens up enormous opportunities for identifying diseases of the pelvic organs even at the initial stages of their formation. So, to accurately assess the condition of the uterus and ovaries, transabdominal ultrasound is widely used.
It is performed through a peritoneal examination: the device’s sensor moves over the surface of the abdomen. This allows you to visualize internal organs and obtain accurate information about the features of their functioning. The essence of the method is that supplied ultrasonic waves with a frequency of 2.5-3.5 MHz are reflected from the organ, transforming into electrical impulses. This phenomenon is called the piezoelectric effect. This is how the photo appears on the screen. Modern software allows you to make accurate measurements of organs in the “picture”.
Advantages of transabdominal ultrasound
Transabdominal ultrasound is often the primary diagnostic method along with laboratory tests. With its help, you can study the functions of the abdominal organs, pelvis, and retroperitoneal space. Its advantages include:
- non-invasiveness and minimal intervention - the diagnostic method does not require violating the integrity of tissues or introducing a sensor;
- no restrictions;
- safety for the fetus at any stage when studying pregnant patients;
- the ability to assess the work and condition of several organs at once;
- accuracy and information content - both large and small tumors will be noticeable as a result of the study;
- painless, can be used in children of any age;
- efficiency - the procedure takes no more than 15-20 minutes, the patient receives the results immediately;
- minimum list of contraindications.
The disadvantages of the procedure include a decrease in its information content in patients with a large layer of subcutaneous fat, as well as those who suffer from adhesive disease in the gastrointestinal tract or pelvic organs. A drawback is also the lower accuracy of the results if the doctor’s simple recommendations are not followed.
results
As mentioned above, transabdominal examination of the genitourinary system is completely painless. No additional anesthesia will be needed. If the patient is very sensitive, she may experience slight discomfort when the sensor comes into contact with the skin.
In the ultrasound room, the woman needs to undress, exposing her stomach, and then sit comfortably on a special couch. The area treated by the sensor is pre-lubricated with gel, which will ensure reliable contact of the device with the patient’s skin.
The sonologist gently presses the sensor and gently moves it across the abdomen. The structure of organs and tissues is reflected on the monitor. The image is as accurate and dynamic as possible.
If any dangerous pathologies are detected during a transabdominal ultrasound, the doctor prescribes additional diagnostics and laboratory tests for the patient. Using ultrasound, the following types of gynecological diseases can be identified:
- Congenital anomalies of the genital organs;
- Tumors in the uterus and ovaries;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the reproductive system;
- Polycystic disease;
- Inflammation;
- Endometriosis.
The diagnostic results are assessed by a medical specialist directly during the procedure. The doctor carefully examines the position of the uterus, the size and shape of the ovaries, and the degree of patency of the fallopian tubes. It is important to correctly determine the thickness of the internal mucous layer of the patient’s reproductive organ. The presence of fluid in the pelvic organs may indicate the development of inflammatory pathologies. Neoplasms and adhesions are often the main cause of female infertility.
Research results
Transabdominal ultrasound can be prescribed both if certain diseases are suspected and if certain symptoms are present: abdominal pain, impaired outflow of urine, cramps, menstrual irregularities in women, pain in the scrotum in men, etc. In general, this type of study makes it possible to study condition and functions of organs: their size and position, patency of the fallopian tubes, structural features and thickness of the endometrium. It is also possible to see fluid in the pelvis and suspect an adhesive process.
Using an examination, you can confirm or refute the following diagnoses:
- tumors and pathological changes in organ structure;
- polyps, cysts, fibroids;
- endometriosis;
- inflammatory diseases;
- pregnancy (accuracy up to a week), etc.
This diagnostic method is included in the standard list of examinations during pregnancy. Ultrasound allows you to verify the normal course of pregnancy, fetal development, exclude pathology and gross defects, and predict the date of birth by determining the exact date.
Visualization of the embryo is possible at 6-7 weeks, from 12-13 weeks - you can examine the baby’s internal organs and limbs. It is during this period that the first ultrasound (screening) is mandatory. The second is done at 18-21 weeks, the third at 30-34. The latest study makes it possible to determine the presentation of the fetus, predict the date of birth and weight of the child, and exclude entanglement of the umbilical cord. In some cases, more examinations are required, and there is no need to be afraid of this: ultrasound is harmless to the baby and the health of the expectant mother.
When is a transabdominal examination prescribed?
This procedure should only be prescribed by the attending physician: gynecologist, proctologist, urologist. Under no circumstances should you self-diagnose. Indications for such an examination may include a variety of diseases of organs located in the abdominal cavity. For women, these are the appendages and uterus, and for men, these are the prostate gland.
When is this research method prescribed for women?
This study is prescribed for women:
- To determine the parameters of the uterus and appendages. Helps determine the presence of any pathologies in the reproductive system.
- If there are all the signs of an ectopic pregnancy.
If there is suspicion of adhesions and tumor.- To verify the presence of pregnancy in the early stages.
- To monitor fetal development throughout pregnancy.
- Determine if the pregnancy is developing or if it has frozen.
- Confirms the presence of serious diseases in the fetus in the last stages of pregnancy.
- Helps determine the size and location of a cyst or fibroid.
- To diagnose a malignant tumor.
- Helps detect endometriosis, polyps and other pathological diseases of the appendages.
- Helps in identifying endometrial cancer.
- In case of failure of the ovaries.
- For polycystic and multifollicular ovaries.
- For problems with conception.
When is this research method prescribed for men?
This study is prescribed for men:
- For pain in the groin.
- For discomfort in the perineum and scrotum.
- With painful and frequent urination.
With difficulty passing urine.
- If you have the urge to go to the toilet, but cannot void.
- If there is a constant feeling of a full bubble.
- For suspicious and unnatural discharge from the urethra.
- If you have problems conceiving.
- For chronic diseases of the reproductive system.
- If you have problems with potency.
- If the man is already over forty years old.
- For sexually transmitted infectious diseases.
- When blood clots appear in the urine.
How to prepare
Preparation for a transabdominal ultrasound includes maintaining a special drinking regime. 1-2 hours before the test you need to drink 1-1.5 liters of clean water. This is necessary to fill the bladder, which provides good visualization of the pelvic organs.
It is better to prepare for the examination several days in advance, eliminating foods that cause gas formation: fresh vegetables, fruits, baked goods, milk.
It is worth noting that when planning a study, it is important for women to pay attention to the menstrual cycle. The best period is 5-7 days - at this time reliable information will be received. If it is important to determine functional characteristics, several examinations can be carried out per month. This will allow you to track the dynamics of processes.
Transabdominal ultrasound can also be performed during menstruation.
Preparation for transabdominal examination
As mentioned earlier, in order to obtain correct results for this study it is necessary
prepare correctly and thoroughly. This method is considered classic. Preparation consists of:
- For two to three days, it is necessary to exclude from the patient’s diet foods that can cause gas formation. Check with your doctor for a list of these products. If there are accumulations of gases in the intestines, then interference will occur that interferes with the visualization of the organ.
- On the day of the examination, it is not recommended to go to the toilet four hours before the procedure. A full bladder helps to better view the organ being examined. If you cannot withstand that much time, then you need to drink at least a liter of still water in an hour. This research method is not recommended after gastroscopy or colonoscopy. If these studies are scheduled for the same day, then ultrasound is performed first.
A disposable diaper and napkins must be brought to the procedure.
The transabdominal examination method helps diagnose diseases in the early stages. At the first alarming symptoms, you should contact a specialist doctor to receive a referral for this examination.
Who needs an ultrasound
Preventive annual examinations are necessary for patients with chronic diseases of the pelvic organs. An ultrasound should be performed urgently if unpleasant symptoms appear: pain in the lower abdomen, uncharacteristic discharge, suspicion of a foreign body of the uterus (parts of the intrauterine device), etc. In addition, this type of diagnosis makes it possible to clarify the causes of infertility or recurrent miscarriage.
Ultrasound is required in preparation for surgical interventions and after them, in order to dynamically assess the condition of organs and earlier identify possible complications. In some cases, the study is performed after the installation of intrauterine contraceptives to determine their position. It is required after childbirth and termination of pregnancy.
Types of ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women
- Transabdominal. The main method for examining the pelvic organs in children, adolescents and women who are not sexually active. A special gel is applied to the lower abdomen. Organs are examined through the anterior abdominal wall.
- Transvaginal. The main method of research in women who are sexually active. A small amount of gel is applied to the sensor itself, on which the condom is placed, and a small amount of gel is always applied to the outside of the condom. The sensor is inserted into the vagina.
- Transperinal. This research method is used both in patients who are sexually active and those who are not. A small amount of gel is applied to the sensor, which is applied directly to the vaginal opening, without penetration.
How is transabdominal ultrasound performed?
This type of examination is carried out only after the patient has consulted a doctor. Mandatory training is required. For the results to be correct, you must adhere to the rules of the study.
Rules for examination:
- You need to lie down. If necessary, the doctor can tilt or raise the couch.
- The specialist applies a gel designed specifically for the procedure to the patient’s skin. This gel helps the sensor slide smoothly and prevent air from getting under it (if air gets under the sensor, signal transmission may interfere).
- After applying the gel, the ultrasound technician examines the patient, pressing the sensor tightly onto the body surface at different points. At the same time, he is obliged to move the sensor around the area from one point to another.
- After the entire examination, the doctor must decipher the ultrasound and give the finished results to the patient.
Only a specialist is required to make a decoding and conclusion. Correct interpretation of research data will help the doctor prescribe effective and correct treatment.
Genitals
The diagnostic capabilities of transabdominal ultrasound in the study of the genital organs in men and women are extremely high. However, the diagnosis often requires clarification using other methods. Perhaps this situation is associated with a wide variety of pathologies and the associated need to differentiate diagnoses. The study of the prostate gland in men comes down to assessing its size, condition of the capsule, symmetry, severity of the periprostatic venous plexus and parenchymal structure.
To obtain information about the size of the gland, each lobe is measured in two directions, and then the volume is calculated. Symmetry is judged by its location relative to the urethra, which should visually divide the prostate into two equal parts. An increase in one of the lobes most often indicates a malignant neoplasm. With benign hyperplasia, the gland increases in volume symmetrically.
Changes in the echostructure of the parenchyma indicate a fairly wide range of diseases, from inflammatory to oncological, so this sign is assessed comprehensively. When diagnosing the organs of the female reproductive system, transabdominal ultrasound allows you to visualize:
- external contours of the uterus and cervix;
- vagina;
- uterine cavity;
- ovaries (only in half of the cases);
- thickness of the endometrial mucosal layer;
- folliculogenesis.
Ultrasound can also be used to detect all types of fibroids larger than 1 cm (intramural, subserous, submucosal) and endometrial cysts. When diagnosing pathologies of the female reproductive system, the best results can be achieved using transvaginal ultrasound. The widespread use of ultrasound diagnostics is due, first of all, to its accessibility and safety. However, one cannot deny the high information content of the method, which makes it possible to identify pathological conditions of some organs with 80% accuracy.
The disadvantages of the transabdominal method, such as difficulties in visualizing various anatomical structures (ovaries, fallopian tubes, bile ducts, ureters), recognizing only large tumors, false positive results, are successfully compensated by the use of transurethral, transvaginal and other ultrasound methods. However, all of the listed methods have some limitation in the viewing range, and in addition, they are invasive, which means that transabdominal ultrasound will retain its position as a first-line diagnostic method.
Ultrasound of the mammary glands
Until the age of 40, women are recommended to undergo annual preventive ultrasound examination of the mammary glands. Ultrasound helps identify a number of serious diseases:
- mastitis,
- mastopathy,
- cysts,
- fibroadenomas,
- cancerous tumor.
It is recommended to undergo this examination if:
- injuries,
- inflammatory diseases of the breast,
- as well as when bulk or diffuse formations are detected during examination.
The study is highly informative when identifying the initial manifestations of pathological processes in the mammary glands, studying the vascular pattern and architectonics of the mammary glands, assessing the condition of silicone and gel implants, as well as when examining lactating and pregnant women.
Sign up for a study
When is ultrasound indicated?
Although the method is informative, this does not mean that on your first visit to the clinic the doctor will send you for this procedure. Indications for this type of ultrasound are abdominal pain and impaired urine flow. Moreover, pregnant women also need to undergo this study. It can be prescribed not only by a gynecologist or urologist, but also by a therapist.
The indication for ultrasound is pain in the groin area.
But not only the above violations can serve as a reason to sign up for transabdominal ultrasonography. Doctors recommend this examination for men if they complain of:
- pain in the groin, scrotum, as well as discomfort during urination;
- various discharge from the urethra and urination disorders.
If such symptoms are detected, the doctor will write out a referral for an ultrasound of the prostate gland, which will be performed transabdominally. During the examination, it will be possible to assess the condition of the organ as accurately as possible. Moreover, the doctor will eliminate the possibility of developing tumors and pathologies.
If there are indications, the doctor writes a referral for an ultrasound scan.
Transabdominal ultrasound in women is also very informative. And therefore it can be prescribed even to girls who are not pregnant.
The decision to conduct an ultrasound is made directly by the gynecologist. It is carried out to exclude the presence of tumors, cysts, and polyps.
Urinary tract organs
Assessment of the condition of the urinary tract organs includes examination of the following organs:
- kidneys;
- adrenal glands;
- ureters;
- bladder.
Ultrasound of the kidneys performs a comprehensive assessment of the size of each organ individually and in comparative relation to each other, the state of the pyelocaliceal system (PCS), the presence or absence of hyperechoic structures in the PSC and the condition of the renal parenchyma.
Table: Main ultrasound signs of kidney pathology
| № | Name of pathology | Ultrasound signs |
| 1 | Aplasia | Absence of echostructures of one kidney and increase in size of the other |
| 2 | Kidney duplication | Doubling of the echo signal from the CLS or significant dilation of the pelvis |
| 3 | Polycystic | Detection of a large number of echo-negative foci of various sizes in the renal parenchyma |
| 4 | Trauma, hematomas | General changes in the structure of the kidney associated with a violation of its integrity: changes in structure or density |
| 5 | Urolithiasis | Detection of fragments with increased echogenicity in the CLS |
| 6 | Hydronephrosis | Increasing the volume of the CLS and dilating the ureters |
| 7 | Pyelonephritis | Increased CL, thinning of the parenchyma with normal ureter sizes |
| 8 | Tuberculoma, carbuncle | Changes in the external contour of the kidney due to the formation of large foci with a heterogeneous echostructure |
The adrenal glands are not always detected during transabdominal ultrasound. Normally, they are defined as triangular-shaped structures. An increase in the size of the adrenal glands to 2 cm or more indicates tumor-like changes. Ultrasound examination of the bladder includes assessment of the following indicators:
- form;
- uniformity of the wall structure;
- symmetry;
- amount of residual urine after urination;
- the presence of a communicating cavity (diverticulum);
- the presence of stones and intracavitary cysts.
General concepts
Ultrasound diagnostics is based on the ability of human body tissues to reflect sound waves with varying degrees of intensity. Since the speed of passage of an ultrasound wave depends on the density of a specific biological tissue, the main amount of information is obtained when the echo signal passes through sections of tissue environments.
Table: Velocity of echo signal propagation in various biological media
| Biological tissues | Unit change | Speed indicator |
| Soft tissues (including the brain) | m/s | 1530 |
| Fat | ** | 1450 |
| Liver | ** | 1550 |
| Kidneys | ** | 1560 |
| Muscle | ** | 1585 |
| Skull bones | ** | 4080 |
| Concretions (gallbladder stones) | ** | 5000 |
| Water | ** | 1500 |
| Air | ** | 340 |
Thus, the higher the tissue density, the higher the ultrasound speed, and, accordingly, the stronger the reflected sound signal. The acoustic resistance of each specific area is reflected on the monitor in the form of different shades of gray. The higher the density of the area under study, the lighter its image on the monitor.
When areas with high acoustic density that are not typical for the area under study are detected, the term “zone of increased echogenicity” is used. For example, stones are displayed on the monitor in white, and objects filled with fluid (cysts) are shown in black. The average penetration depth of the ultrasound beam during transabdominal ultrasound, depending on the frequency used, is 8–20 cm, which makes the study difficult in obese patients.
Pros and cons of this type of research
Like everything in this world, transabdominal ultrasound has its advantages and disadvantages. Now let's look at them in more detail.
Pros:
- Due to the fact that not only the organ being examined, but also neighboring ones are examined, the doctor can make a more accurate diagnosis and select the correct treatment;
- When examining a woman, this ultrasound method helps to examine wide and voluminous tumors of the appendages and uterus;
- The method is painless, does not require supernatural preparation and is not harmful to the body;
- In virgins, it is only possible to assess the general condition of the appendages and uterus using this method;
- For men, the simplest and most informative method for examining the prostate gland.
Minuses:
- The image is less clear, and the detail of the organs is not as detailed due to the fact that part of the ultrasound waves is absorbed by the tissues of the abdominal cavity;
- The frequency of the sensor waves affects the accuracy and clarity of the results. In this case, the transvaginal sensor is stronger than the transabdominal one;
- The observed image of the appendages and uterus will be distorted if the woman is obese or the abdominal wall is thickened;
- They do not have a very good effect on displaying the results of adhesions in the abdominal cavity, which could have formed after a cesarean section, removal of appendicitis or a cyst.