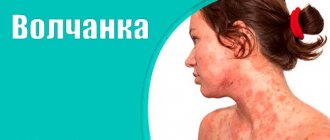
What is hormonal imbalance
Hormonal imbalance is a dysfunction caused by pathology of the endocrine and neuroregulatory systems in both women and men. All processes occurring in the body largely depend on hormonal status.
In women, such a failure causes various diseases of the reproductive system and, in combination with immunity disorders, inflammation and sexually transmitted infections, causes a number of serious problems: menstrual irregularities, uterine fibroids, endometrial hyperplasia, polyps and polycystic ovaries. It is very important to regularly conduct gynecological examinations, because a number of diseases of the female genital area are asymptomatic, without pain, bleeding and other clinical manifestations.
What do you need to know about female hormones? Complex processes in the female body are controlled by estrogen and progesterone. These hormones are responsible for puberty and the onset of menstruation in adolescence, breast and hair growth, and regulation of the reproductive period.
Hormonal levels change after a woman becomes pregnant: a new hormone is released - human chorionic gonadotropin. In a woman preparing to become a mother, the amount of estrogen and progesterone increases, and at about the fourth month the placenta begins to support the pregnancy thanks to its own hormones.
The next hormonal surge occurs after childbirth, and the biological functions of the body return to normal. Now the main task of female hormones is to ensure the production of breast milk to feed the baby.
Thus, before menopause, when the ovaries stop producing eggs and estrogen, hormone levels in the body may change.
But if in past years a hormonal imbalance meant the pathological functioning of the endocrine glands only in women, now this concept has spread to the male part of the population. It was found that their abnormal functioning of the endocrine system also leads to disturbances. Moreover, the fact that the reproductive system in men and women is far from the same does not negate the similarity of symptoms caused by hormonal pathologies.
Content:
Critical periods of the female body
As already noted, hormone imbalance can most often occur during certain periods. To prevent this phenomenon and minimize its manifestation, it is necessary to take a closer look at each period in a woman’s life.
Hormonal imbalance in teenage girls
For the first time, a woman encounters a similar disorder during puberty. Usually this is 11-14 years old. At this time, the girl “turns” into a girl. Her mammary glands begin to form and her first menstruation begins.
During this period, hormonal disruption may occur in girls. This may manifest itself in premature maturation or, conversely, delayed sexual formation.
If puberty is delayed, menstruation may occur at 15-16 years of age. The reason for this may be poor nutrition, stress, and frequent infectious diseases.
The main “side factor” accompanying hormonal imbalance in adolescence is acne. If the girl is generally healthy, then acne can be quickly cured in a beauty salon using drying masks, liquid nitrogen and other procedures.
_
But if irritability, aggressiveness, lack of sleep and menstrual irregularities are added to problem skin, then this is a serious reason to take your child to the doctor.
In a healthy teenager, minor manifestations of hormonal imbalance can be adjusted with a proper daily routine, a balanced diet, good sleep, and taking vitamin complexes.
At this age, parents should be attentive to their daughter. Very often, girls need a warm family environment, close communication with their mother, and understanding. You should be patient and become your child's best friend. A warm attitude towards your daughter will be rewarded many times over. After all, happy is the person who was able to raise good and worthy children!
Hormonal imbalance after childbirth
Pregnancy and childbirth are the most important period in a woman’s life. At this time, she secretes many different hormones. If a girl did not have serious illnesses before pregnancy and led a healthy lifestyle, then after giving birth she recovers very quickly without side effects within 2-3 months.
However, childbirth and pregnancy can often disrupt the functioning of various systems. Childbirth is a great stress for the body and the endocrine system “suffers” the most from this.
Symptoms of hormone imbalance include:
- unstable mental background;
- weight gain;
- pressure surges;
- decreased libido;
- problems with lactation.
If the recovery period drags on for more than six months, you should contact an endocrinologist. The doctor must order tests and then prescribe the appropriate medications.
Gaining weight after pregnancy is normal. With a healthy lifestyle, your weight will return to normal very quickly. You can lose weight during hormonal imbalance with the help of fitness and proper diet. Sports and diet can be started no earlier than 6 months after giving birth. After all, intense exercise and dietary restrictions can have a destructive effect on milk production.
_
You need to lose weight after childbirth only in consultation with a doctor, so as not to harm either yourself or the baby!
Hormonal imbalance after abortion
In the vast majority of cases, after an abortion, a woman experiences a hormonal imbalance. This can be explained this way: for the development of the fetus, various hormones begin to be actively released into the woman’s blood, ensuring the vital functions of both the unborn baby and the mother. But an abrupt cessation of this physiological process causes a disruption in the hormonal system.
https://youtu.be/59aY7RKGo_o
Causes of hormonal imbalance in women and men
There are many factors contributing to hormonal imbalance in both men and women. This is primarily due to the dependence of hormonal status on the neuroendocrine regulation of the central nervous system, which occurs in the brain, and on the proper functioning of the endocrine glands, which are localized in the periphery.
In this regard, the reasons contributing to hormonal disorders can be divided into two large groups:
- Causes caused by disturbances in the functioning of central regulation.
- Causes provoked by pathological processes occurring in the peripheral glands. Malfunctions in their work can be caused by tumors, infections, inflammatory processes, etc.
So, let’s highlight all the possible causes of hormonal imbalance:
- The neuroendocrine regulation system, also called the hypothalamic-pituitary system, may begin to malfunction as a result of damage of organic origin. These include severe brain and skull injuries, encephalitis, and cancerous tumors. In addition, internal and external reasons can cause failures in the functioning of this system. For example, it could be exhaustion of the body, chronic fatigue, like a syndrome, etc.;
- Glands that do not affect the reproductive function, such as the adrenal cortex or the thyroid gland, can have a direct effect on a person’s hormonal levels;
- Due to the fact that hormonal metabolism occurs in the liver, and the removal of metabolites is carried out using the kidneys, disturbances in their functioning can also cause a malfunction;
- The factor of heredity cannot be ruled out. It plays an important role in the development of hormonal imbalance, especially those changes that occur during menopause and after it;
- Congenital pathologies of the systems that are responsible for the production of hormones also represent a separate cause leading to imbalance. Such pathologies usually first manifest themselves as delayed puberty or its absence;
- Most often, hormonal disruptions occur during periods of physiological changes. Among the most significant stages are puberty and similar decline. Women, unlike men, experience several more sexual storms - childbirth and, in some cases, abortion.
How to restore hormonal imbalance in the body
If several signs of a violation have been noticed, then you should contact a specialist as soon as possible. In this case, a therapist and gynecologist can help. For diagnosis and further treatment, it is necessary to donate blood and test for hormones.
Only a doctor should determine the course of treatment. Based on the clinical picture and test results, he will determine which hormone level needs to be brought back to normal.
You need to restore the normal state of the body using two methods at once:
- eliminate the cause that caused it;
- stabilize hormone levels with medications.
In any case, you need to act simultaneously in two directions. It is very important to eliminate the cause, otherwise further treatment will not make sense.
As for the duration of therapy, everything is decided on a case-by-case basis and depends on the causes and level of imbalance. Restoring normal hormonal levels can take from several weeks to several years.
What to do in case of hormonal imbalance?
The answer is clear - do not self-medicate. The therapy is very simple and effective. A woman or girl can continue to lead a normal lifestyle, because usually the same hormonal drugs are used to eliminate the problem.
However, many patients note their side effect – weight gain. An alternative is products based on natural ingredients. They normalize hormonal levels, but can do it more gently.
These include dietary supplements, as well as homeopathic medicines. However, in very severe cases, surgical intervention is resorted to.
Symptoms of hormonal imbalance
Symptoms of hormonal imbalance in young girls 14–16 years old may be the absence of menstruation or its irregularity. At this time, the cycle should already be established, but if this does not happen, there is a possibility of insufficient production or absence of estrogen and progesterone in the body. Alarming symptoms are also excessive body hair and underdevelopment of the mammary glands. Often, girls with insufficient levels of sex hormones in the blood are tall, thin, and have long arms and legs. The menstrual cycle is almost always disrupted if body weight is less than 48 kg.
Hormonal imbalance can cause cystic degeneration of the ovaries and underdevelopment of the uterus. Also, after the start of sexual activity, you should regularly undergo examination by a gynecologist, since some sexually transmitted diseases can cause inflammation of the reproductive organs and hormonal disorders. In pregnant women, symptoms of hormonal imbalance may include premature uterine contractions and pain in the lower abdomen.
An alarming sign is also an increase in premenstrual syndrome: sudden changes in mood, soreness and swelling of the breasts, joint pain, depression and absent-mindedness. During menstruation, uterine bleeding may occur and anemia may develop. You should also pay attention to weight fluctuations, skin changes and visual disturbances.
Hormonal imbalance can cause serious diseases: fibroids, polycystic disease, uterine and ovarian cancer.
Malfunctions of the reproductive system
At a young age, malfunctions in the functioning of the reproductive system manifest themselves in the fact that a teenage girl experiences delayed sexual development with delayed formation of sexual characteristics (secondary). In this case, the ontogenesis of differences that are uncharacteristic of a particular gender often occurs. Women develop secondary male characteristics (masculinization), and men develop female characteristics (feminization process).
In addition, the reproductive system suffers:
- Sexual desire is significantly reduced, up to its complete absence;
- Erectile function in males suffers;
- Women have difficulty achieving orgasm (anorgasmia);
- Infertility develops.
Disorders of the nervous system
With hormonal dysfunction, the process of cerebrovascular disease develops. Symptoms of exhaustion are as follows:
- Hypersomnia;
- Nervousness and short temper, unreasonable irritability;
- Fatigue after short work;
- Emotional instability, tearfulness;
- Emotional disorders that can lead to depressive disorders;
- A decrease in intellectual capabilities that is reversible.
Metabolic pathologies
Metabolic problems that arise from hormonal imbalance are most often expressed in weight gain. A sharp jump in weight makes doctors think about hormonal pathology.
In addition, patients begin to suffer from osteoporosis. Problems with bone tissue arise against the background of calcium metabolism disorders.
However, with correct and timely treatment, all symptoms can be eliminated. However, if you ignore the failure for a long time, it may well lead to more pronounced health problems, which will be provoked by long-term functional disorders in the work of most of the most important organs and systems.
Signs and symptoms of hormonal disorders
It must be taken into account that dysfunctions and many diseases caused by hormone imbalance are very difficult to treat. But if you know why hormonal imbalance occurs, its signs and how you can cope with it, you can significantly ease such an unpleasant process. Symptoms of hormonal disorders can be very diverse.
Unstable and irregular menstruation
Menstruation becomes irregular, takes a very long time, or, on the contrary, passes in a day or two. The nature of the discharge during menstruation also changes noticeably - it can be heavy or very scanty. In some cases, menstruation does not occur at all for several months. This symptom is often present in girls with anorexia nervosa.
Malfunction of the central nervous system
The woman begins to get very nervous for no serious reason, depression and melancholy appear, and her mood changes dramatically. Sometimes there are unjustified attacks of aggression and ladies often react painfully to things that previously did not even deserve their attention. Premenstrual syndrome worsens, becomes severe and the woman is constantly nervous.
Body weight increases sharply
Another sign of hormonal imbalance is unexpected weight gain and body weight cannot be adjusted. Physical activity does not help you lose weight, and different diets do not help. Therefore, a woman gains weight without obvious reasons, since this does not depend on nutrition and such a phenomenon cannot be dealt with.
Decreased or absent sex drive
Ladies become indifferent to sex, libido decreases or is completely absent. Sometimes there is even complete indifference to the partner, and there is no desire to enter into intimate intimacy with him. His previous caresses irritate and do not bring any effect. During sexual intercourse, the secretion of mucous secretion from the vagina is disrupted and sexual intercourse itself is sometimes painful and with painful sensations for the woman.
The condition of nails and hair worsens
Some women notice that their hair has begun to fall out significantly, their curls become dry, brittle and dull. The picture is the same with nails: they break, become grayish or yellowish and look ugly.
Skin rashes in different parts of the body
The main symptom of hormonal imbalance is considered to be changes in the skin on the chest, back and face. Acne appears very often, the rash cannot be treated with anything. Sometimes thick black hairs begin to grow on the body, and this worries the woman very much, as they look ugly.
Sleep disturbance and increased fatigue
There may be prolonged insomnia, the woman cannot fall asleep for a long time, and the sleep itself becomes sensitive and anxious. Increased fatigue was also noted, while there was no strong mental and physical stress.
Reproductive dysfunction
This is the most difficult moment for any woman, because she cannot conceive and carry a baby. When hormones malfunction, there are miscarriages, fetal death in the early stages of pregnancy, and long-term impossibility of fertilization.
Consequences of hormonal imbalance
Complications that can be caused by long-term hormonal imbalance are as follows:
- Inability to conceive a child, including male infertility;
- Inability to have an adequate sex life, complete loss of libido;
- Obesity;
- The formation of malignant tumors, the growth of which depends on the hormonal status;
- Fractures caused by osteoporosis;
- Heart attacks and strokes developing against the background of atherosclerotic lesions;
- The second type of diabetes.
How does hormonal imbalance affect menstruation?
Any changes in hormonal levels affect the frequency and intensity of menstruation.
Abundant
The concept of heavy discharge means blood loss of 150 ml over the entire period of menstruation. This necessitates changing pads almost every hour. Usually the duration of menstruation is increased (from 7 to 12 days), and the cycle is often shortened to 18-21 days. The main cause of hormonal disorders is excess estrogen.
Causes
Excess estrogen is associated with:
- obesity;
- use of hormonal contraceptives, especially for a long time and without medical supervision;
- the use of spermicides (destroy sperm) in suppositories, vaginal gels to protect against unwanted pregnancy;
- contact with insect control agents, detergents, plastic products, including plastic utensils;
- eating meat with hormones used in factories to speed up growth;
- stress, depression;
- frequent intake of alcohol, abuse of coffee, beer;
- lack of vitamin A and its plant analogue carotene, folic acid, selenium, and plant fiber in food;
- low physical activity;
- diseases of the liver, intestines (especially dysbiosis), biliary tract;
- polycystic ovary syndrome, tumors, cysts;
- excess adrenal cortisol;
- lack of thyroid hormones.
Heavy menstruation is often combined with fibroids, endometriosis, and endometrial hyperplasia (overgrowth), as these diseases are called estrogen-dependent.
Treatment
To reduce the intensity of menstrual flow, it is necessary to establish the cause and undergo a course of treatment. Non-specific methods help by eliminating meat, switching to a predominantly plant-based diet, and reducing body weight. If anemia is present due to severe blood loss, iron supplements are prescribed.
Scarce
When blood discharge decreases to 50 ml, menstruation is considered scanty. A woman can get by with one pad per day. In this case, the duration of bleeding usually does not exceed 3 days, and the cycle lasts more than 5 weeks. Extreme manifestations include the appearance of menstruation 2-4 times a year.
Causes
This condition is caused by a lack of estrogen when:
- disorders of puberty;
- ovarian dysfunction (premature exhaustion syndrome);
- increased production of male sex hormones by the ovaries or adrenal glands;
- smoking;
- overly strict diets;
- lack of vitamins E, C and D;
- intensive sports activities;
- injuries and operations on the uterus, ovaries;
- incorrect selection of contraceptives;
- stressful conditions.
Treatment
If the examination reveals no diseases, then to normalize the cycle, vitamins, consumption of fish and meat of moderate fat content, cottage cheese and fermented milk drinks are indicated. It is important to make changes to your lifestyle - avoid physical and emotional stress, and ensure sufficient sleep.
Absence
If a woman does not have a period for six months or more between the ages of 16 and 45, then this condition is called amenorrhea.
Amenorrhea
It can be congenital due to chromosomal abnormalities, but the acquired form is more common due to:
- weight loss after debilitating illnesses, diets, food refusal due to anorexia nervosa, abuse of weight loss drugs;
- sports overload or heavy physical work;
- polycystic ovary syndrome with signs of excess male hormones - excessive hair growth on the body and face, persistent acne, deposition of belly fat, infertility;
- early menopause (up to 40 years), appears after psychological trauma, ovarian dysfunction due to inflammation, concomitant diseases of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland, autoimmune pathology (antibodies are formed to one’s own cells);
- increased production of prolactin, this pituitary hormone causes galactorrhea-amenorrhea syndrome. It is characterized by an increase in menstruation and the discharge of milk-like fluid from the nipples.
For ovarian disease
If the reason for the absence of menstruation is ovarian disease, then the hormonal background is characterized by a decrease in the level of estrogen and progesterone with an increase in the content of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormone. With primary damage to the pituitary gland and/or hypothalamus, the last two indicators are below normal, but prolactin is often elevated.
Treatment for absence of menstruation
Treatment is prescribed in accordance with the identified disease; in case of functional failure (weight loss, stress), a diet with a normal calorie intake and frequent split meals are indicated. Additionally, psychotherapy, physiotherapy, vitamins and natural sedatives are prescribed.
Tea with mint, lemon balm, and essential oils of lavender and sage help well.
Delay
If your period does not come on time for more than 7 days, then this is regarded as a delay.
Main reasons
The delay is caused by:
- the formation of the menstrual cycle, the gradual formation of cyclicity in the secretions of pituitary hormones - follicle-stimulating and luteinizing;
- the onset of pregnancy and an increase in progesterone, suppressing subsequent menstruation;
- feeding the child and the release of prolactin, which inhibits the restoration of the menstrual cycle;
- menopause and a decrease in estrogen, an increase in pituitary hormones.
All other options are signs of diseases or functional disorders. The first group includes:
- inflammation, tumors, polycystic disease, ovarian cyst;
- abortion, accompanied by both hormonal imbalance and a decrease in the endometrial layer;
- sudden weight gain or excessive weight loss after a serious illness.
Stress, overload, and climate change can lead to ovarian dysfunction and delay.
Birth control pills can also cause cycle changes when you stop taking them or use emergency contraceptives containing high doses of hormones. Some women note a disruption in the rhythm of menstruation after the flu, long-term antibiotic therapy, it is also provoked by exacerbations of chronic diseases, diabetes mellitus.
Treatment of delay
Treatment is carried out only after identifying the cause of the delay. It should be taken into account that during sexual activity there is always a possibility of pregnancy. This happens even when using contraceptives, since no method can be 100% effective.
Signs of hormonal imbalance in girls during puberty
Delayed puberty
An indicator of normal puberty in females is its manifestation in the period from 7 to 8 years. This process is completed by the age of 18. During puberty, there is an acceleration in the rate of maturation of the body, an increase in height and weight, and the formation of secondary sexual characteristics. It is at this time that the formation of the female reproductive system occurs, which is responsible for the process of reproduction in the future.
If secondary sexual characteristics are observed in children under 7 years of age, then sexual development is considered premature. In this case, an early start of menstruation occurs (sometimes this can happen even at 4 years), the formation and growth of the mammary glands. Girls begin to quickly increase in height, however, it will ultimately not exceed 152 cm. This is due to premature ossification of the skeletal zones responsible for the girl’s height growth.
There are several types of early onset of puberty:
- Pathological premature maturation, caused by disturbances in central genesis or occurring against the background of existing ovarian tumors that produce hormones. Most often, it is tumors located in the area of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus that become the causes of early puberty;
- Early sexual development is of a constitutional type, its cause is the child’s genetic predisposition to the early onset of puberty. At the same time, there are no pathological disorders in the systems responsible for hormonal levels. Such girls have a normal ability to reproduce and do not require therapy. The first menstruation does not begin until 6 years of age.
The fact that a girl has a delay in the onset of puberty will be indicated by the absence of secondary sexual characteristics before the age of 16. More often, such problems arise as a result of genetic predisposition. Moreover, all systems after the onset of menstruation (at 17 or 18 years old) will work normally, and this developmental feature will not complicate the process of further conception and childbearing.
However, there is also a pathologically caused delay in puberty. It can be a consequence of either Shereshevsky-Turner disease or disturbances in the functioning of the pituitary gland.
Currently, delayed puberty is increasingly occurring due to nutritional depletion. It becomes the result of starvation due to the massive craze for diets and the desire of girls to become painfully thin.
Sexual development with erased virilization
Puberty with erased virilization is a pathological process in which a person exhibits sexual characteristics that are not inherent to his gender. For example, women grow hair in a male pattern or their skeleton becomes distorted. If the basis for such a failure is a violation of metabolic processes, then characteristic signs may appear: acne, excess body weight, stretch marks.
Genetically determined pathologies in the development of the ovaries or adrenal cortex can be the basis for a failure with latent virilization.
The most common hypothalamic syndrome of puberty occurs, the causes of which are not fully understood. However, it is generally accepted that such a response of the body occurs against the background of existing chronic tonsillitis or other infection, or as a result of a skull injury. The influence of emotional stress, previous viral infections, and the fact of chronic overeating cannot be ruled out.
Hypothalamic syndrome, which provokes hormonal dysfunction, manifests itself immediately after the girl’s first period, that is, in the age period from 11 to 13 years. At the same time, the teenager’s appearance exudes health: such girls are usually tall, slightly overweight, and their hips and shoulders are wider than those of their peers. However, behind the apparent external well-being there are many problems hidden, including headaches, instability of blood pressure, excess blood pressure, excessive irritability and fatigue.
Striae are another characteristic sign of hypothalamic syndrome, and these purple stripes that appear on the skin are most often not associated with obesity. Their appearance signals the activation of pathology.
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
If there is a hormonal imbalance, heavy uterine bleeding may occur during the onset of the next cycle. In this case, disturbances are observed in the related work of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland and ovaries.
Juvenile uterine bleeding is a fairly common problem and accounts for up to 20% of all adolescent gynecological pathologies.
As for the etiology of dysfunctional bleeding, it can be vitamin deficiency, acute respiratory viral infections, or mental and physical stress. Moreover, the pathology can develop in a teenager who does not have health problems, but is studying in an overly intensive program.
Symptomatically, this pathology is accompanied by the development of bleeding after a prolonged absence of regular menstruation. Moreover, the delay can vary from two weeks to several months. Menstruation preceding juvenile bleeding usually does not have any deviations from the norm for 2 years. The bleeding itself can be either heavy or scanty, but long-lasting (up to 15 days). They are often the cause of anemia.
If pathological menstruation becomes too intense, this may cause the development of DIC syndrome. In this case, urgent medical attention is needed, since increased blood loss threatens the life of the teenager.
What it is
The entire process of human life is directly related to physiological changes characteristic of the hormonal background, which is responsible for the development and decline of the body. Functions regulated by the central nervous system, metabolic processes, as well as the functioning of organs that ensure the necessary healthy state depend on it.
Most often, hormonal imbalance in women, after all the studies, manifests itself in menstrual irregularities, which should serve as an alarming signal about trouble in the endocrine system. Although there are other, quite diverse symptoms, and treatment for this reason is prescribed only according to individual indications.
Signs of hormonal imbalance in women of reproductive age
Amenorrhea
Amenorrhea is characterized by the absence of menstruation in women who have not entered menopause, are not pregnant or are not breastfeeding.
There are amenorrhea that occurs:
- Due to ovarian pathology;
- Due to a failure of central nervous regulation;
- Due to dysfunction of the adrenal cortex.
If amenorrhea occurs as a result of ovarian pathology, then most likely the cause is polycystic disease. It becomes the result of stress, difficult childbirth, early start of sexual activity, etc. At the same time, the woman will suffer from more or less pronounced obesity, as well as from male-type hair growth (hair grows on the chin and lip, on the inner thighs). Stretch marks appear on the skin, nails become brittle, and hair falls out. If you ignore this condition, it threatens the further development of diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis, since these diseases are the result of a malfunction in the metabolic processes of lipids and carbohydrates.
When amenorrhea of central origin is observed, the patient suffers from anemia, bradycardia and hypotension. Such hormonal imbalances can be caused by prolonged illness or starvation, a hereditary factor that damages the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, injuries and cancer.
Hormonal imbalance caused by Itsenko-Cushing syndrome occurs severely, with damage to internal organs. Amenorrhea in this case is one of the symptoms of the disease. The signs of this pathology are quite specific: specific obesity is observed, in which fat accumulates in the neck, face and upper body, the limbs gradually atrophy, stretch marks appear along the body, and hair grows in a male pattern. In parallel, the woman suffers from osteoporosis, hypertension and impaired glucose sensitivity.
If a woman has signs of this syndrome, then it makes sense to suspect adrenal pathology. The cause may be hormone-producing tumors, or neoplasms localized in the pituitary gland and synthesizing steroids that are normally produced by the adrenal glands.
A common phenomenon leading to hormonal imbalance is pseudo-Cushing's syndrome. It provokes disturbances in the functioning of the neuroendocrine system, and functional hypercortisolism can be caused by alcoholism, mental illnesses and obesity.
Intermenstrual uterine bleeding
It is hormonal dysfunction that most often causes uterine bleeding. Menstruation occurs at irregular intervals, the risk of cancer increases, a woman’s reproductive ability decreases, and problems arise with bearing a child.
There are two types of functional uterine bleeding. The first type is ovulatory, in which case blood loss occurs some time after the cycle is delayed. The delay itself can last more than 2 months. The blood loss is not too abundant, however, it is quite long in time. There is a periodic increase in blood loss followed by a decline.
The second type - anovulatory - is characterized by a progressive lengthening of the cycle. The duration of such menstruation can exceed a month.
Premenstrual syndrome
Premenstrual syndrome is characterized by a cyclical symptom complex in women, which is caused by disruption of the hypothalamus in relation to the regulation of hormonal production. This pathology can occur at any age, but most often affects women over 30 years of age. As for the causes of the occurring disorders, scientists suggest that a hereditary factor plays a role. In addition, severe stress, abortion and infectious diseases can provoke hormonal dysfunction. The influence of a sedentary lifestyle, dietary errors, central nervous system pathologies, as well as gynecological pathologies cannot be ruled out.
The syndrome starts a few days before the start of the next menstruation, on the first day of the cycle it gains maximum strength, after which it disappears on its own. With severe pathology, the duration of symptoms can increase significantly.
The nature of the course of premenstrual syndrome may be as follows:
- According to the type of metabolic disorders with swelling of the limbs and face;
- Migraine type with severe headaches, nausea and vomiting;
- According to the type of neurosis with excessive irritability, depressive states, increased fatigue and sleep disturbances;
- A type of dystonia with a slow pulse, decreased blood pressure and flatulence;
- Like a sympathoadrenal crisis with pressure surges, unfounded fears, an increase in the number of heart contractions, ending with copious urine output. Such crises are a consequence of disruption of not only the hypothalamus, but also the adrenal glands.
The common symptoms for most women are pain in the mammary glands and increased olfactory function. Sometimes there is an increase in body temperature, heart pain, and allergic manifestations. The younger the woman, the more prone she is to depression during premenstrual syndrome, and the older she is, the higher the tendency to irritability during these days.
Causes of hormonal disorders in women
Most often, hormonal disruptions in the female body occur during menopause, or arise due to the peculiarities of the endocrine glands and the characteristics of the menstrual cycle. At the same time, very often clinicians have to deal with other causes of hormonal disorders.
- Heredity. Congenital defects of the hormonal system are a rather complex condition that is difficult to correct. As a rule, the main cause for concern in this case is primary amenorrhea (the complete absence of menstruation in girls after 16 years of age).
- Diseases of the adrenal glands, pancreas and thyroid glands;
- Previous infectious diseases (acute respiratory infections, sore throats, STDs, etc.), which caused a decrease in immunity;
- Cystic neoplasms, uterine fibroids, polycystic ovaries, endometrial hyperplasia, endometriosis, bronchial asthma, frequent migraines, mastopathy;
- Induced abortions and other surgical operations in the abdominal cavity and internal genital organs;
- Nervous breakdowns, chronic stress, fatigue and other negative factors;
- Puberty (puberty), pregnancy, childbirth, menopause;
- Poor nutrition (refusing food or overeating);
- Use of hormonal contraceptives;
- Use of hormonal drugs.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions;
- Lack of sleep;
- Early or very late onset of regular sexual activity;
- Presence of parasites;
- Smoking and alcohol abuse;
- Autoimmune processes.
Hormonal imbalance in women after abortion
In terms of frequency of occurrence, hormonal dysfunction is the most common complication of abortion. This procedure is accompanied not only by a complex restructuring of the body, but also by severe nervous shock. If this is a woman’s first pregnancy, the risk of complications increases significantly. Moreover, the method of interruption does not have a significant effect on this. However, it is best to perform the procedure at the earliest stages, this somewhat reduces the risks of possible complications.
If a medical abortion is chosen as a method of terminating a pregnancy, the woman must be prescribed hormonal therapy to help normalize the cycle. When no complications develop, it returns to normal after a month.
The onset of hormonal dysfunction after an abortion may be indicated by:
- Increase in body weight;
- Striae;
- Nervous symptoms;
- Blood pressure surges, pulse instability, increased sweating.
Treatment
The course of treatment includes:
- taking vitamins, hormonal drugs;
- psychotherapy;
- surgical intervention.
Treatment depends on the identified pathologies. For serious disorders associated with benign and malignant neoplasms in the glands that regulate hormonal levels, surgery, laparoscopy or curettage, as well as appropriate therapy, including radiation and chemotherapy, are necessary.
In other cases, hormonal-correcting drugs are prescribed. Treatment can be aimed at eliminating symptoms, as, for example, during menopause (with menopause, drugs are prescribed that reduce the intensity of the symptoms of menopausal syndrome).
If a hormonal imbalance occurs due to natural circumstances, such as childbirth, medical attention is not required, as it returns to normal on its own. After an abortion, medications are taken that normalize hormonal levels.
During the period of treatment you must refrain from:
- sexual intercourse;
- physical activity;
- bad habits.
Hormonal imbalance in women after childbirth
The body of any woman who has given birth undergoes complex hormonal transformations, so menstruation may begin with a certain delay, even if the child is not breastfed.
Hormones influence weight gain during breastfeeding, however, their action is a physiologically determined need that ensures milk production. In this regard, women who are breastfeeding need to move as much as possible and not consume foods that are high in calories. Most often, proper nutrition and physical activity allow you to eliminate excess body weight after lactation stops.
If the weight does not go away, despite following all the doctor’s instructions, then this most often indicates hormonal dysfunction.
You should consult a doctor if:
- Weight increases unmotivated;
- A process of virilization is observed;
- The menstrual cycle is not restored, discharge between periods is disturbing;
- Neurological disorders appear.
Stress, infections, exacerbation of existing chronic diseases, as well as gynecological pathologies can increase the risk of developing hormonal dysfunction after childbirth. Overwork, which most young mothers experience, has a negative impact on the hormonal system.
Hormones that influence the state of the female reproductive system
Female sex hormones necessary for the normal functioning of the reproductive system include:
- Prolactin, which is responsible for the growth and development of the mammary glands and stimulates milk production during breastfeeding, and also participates in water-salt metabolism;
- FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone), responsible for stimulating the growth of follicles in the ovaries;
- LH (luteotropic hormone), which stimulates the secretion of progesterone, the synthesis of estrogen and the formation of the corpus luteum;
- Estrogens, responsible for secondary sexual characteristics and the regularity of the menstrual cycle;
- Progesterone is a hormone that promotes the normal development of pregnancy and suppresses uterine contractions;
- Androgens. These are male sex hormones, which are produced in the female body in small quantities, and, in the case of the development of hormonally active tumors, cause the development of secondary male sexual characteristics.
Hormonal imbalance in women during menopause
When a woman reaches 45 years of age, her sexual functions begin to gradually decline. This process is called menopause. The period is characterized by an irregular menstrual cycle followed by the complete disappearance of menstruation. However, this process should not be perceived as a pathology, because it is a physiological norm. Recently, there has been an increase in the incidence of menopausal syndrome among women, which is provoked by hormonal dysfunction.
Signs of the development of a pathological menopause are divided into three groups:
- Developing early - about three years before the complete stop of menstruation;
- Delayed in time - begin to bother a woman three or two years after the complete cessation of menstruation;
- Late – develops 5 years after the cessation of menstruation.
Hot flashes are the most pronounced symptom of early menopausal pathology caused by hormonal dysfunction. During such attacks, the woman experiences sensations of heat, mainly in the facial area. Other symptoms include depressive disorders, vegetative-vascular dystonia, migraine-type headaches, etc. (Causes and symptoms of hot flashes and how to deal with them?)
If we consider the symptoms of delayed menopause, then these are mainly damage to the skin in the genital area and dystrophy of the appendages. Urinary incontinence develops, pain occurs during intimacy, and the likelihood of developing cystitis and vulvovaginitis increases. These phenomena are associated with a decrease in the level of estrogen in the blood. Brittle nails, hair loss and dry skin are characteristic signs of estrogen deficiency.
Delayed symptoms of menopause are gross metabolic disorders. Women suffer from osteoporosis, atherosclerosis and diabetes.
Why changes occur in the hormonal sphere during menopause is a question that is still open. However, there are suggestions that the provoking factors are poor nutrition, stress and bad habits.
The development of pathological menopause threatens women:
- With pathologies of the nervous system;
- With disorders of neuroendocrine regulation;
- With gynecological infections;
- Those who have gone through miscarriages, abortions, or have had a complicated birth.
Folk remedies for restoring hormonal imbalance
To normalize hormonal levels, homeopathic remedies are prescribed, which are considered safer, although you should also be careful when taking them and take them only as prescribed by a doctor.
- Cyclodinone. The drug is made from twig fruits, which reduce prolactin. Increased concentrations of the hormone can affect follicle maturation, ovulation, the balance of estrodiol and progesterone, which generally causes menstrual irregularities. The drug prevents the development of pathological processes in the mammary glands, in particular the expansion of the milk ducts. As a result of taking it, the second part of the menstrual cycle returns to normal, which is characterized by the formation of the endometrium in the uterus, which is responsible for the possibility of pregnancy. Indications: PMS, mastodynia. The drug is taken 1 time per day. in the morning, for 3 months. Contraindications: hypersensitivity.
- Mastodinon. Indications for use: mastopathy, PMS, all kinds of menstrual irregularities, including those leading to infertility. The product contains a complex of plant extracts. Dosage: 1 tablet. 2 rubles/day for 3 months or more. Contraindications: lactase intolerance, galactase intolerance, pregnancy, lactation, breast cancer.
- Klimadinon. Contains black cohosh extract. Indications: signs of VSD and others during menopause. The drug relieves the symptoms of hormonal disorders, restoring the menstrual cycle, reducing the intensity of menopausal symptoms, PMS. Dosage: 1 tablet. 2 rubles/day
Folk remedies will help stabilize female hormonal levels. However, plants can also have harmful properties. They contain hormone-like substances of plant origin, which can be harmful to the body in increased dosages.
- To stabilize the cycle, it is recommended to take infusions and decoctions based on calendula, nettle, and meadow clover.
- For menopause, folk remedies based on mint, lemon balm, St. John's wort, sage (contains phytoestrogens, so products based on it help prevent estrogen deficiency), lily of the valley, and black crow will help.
- Oregano activates the production of female sex hormones.
- Fenugreek is taken after childbirth, for painful discharge.
- Black cumin oil is used for infertility.
- Flax oil normalizes estrogen levels.
- Potentilla cinquefoil will help normalize progesterone levels.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Ureaplasma symptoms in men and women.
How to use some of the above plants and oils should be considered in more detail. To normalize hormonal levels, black cumin oil is used. Dosage: 1 tsp, separately from meals. The oil will be more effective if taken before meals, and it will be better digested after meals.
The product is combined with hormonal therapy, but the oil cannot be taken simultaneously with hormone-containing tablets. There should be a break of at least 3 hours between medications.
Flax oil contains a significant amount of phytoestrogens, including lignin. It can be taken to reduce the symptoms of menopause. Dosage: 2 tbsp. You can use it to dress salads. The effect will be noticeable in 1-2 weeks.
Sage activates the process of endometrial formation, promotes the maturation of follicles, which increases the likelihood of conception. Doctors recommend taking water decoctions and infusions of sage orally, while simultaneously conducting therapy with Duphaston and Utrozhestan at the beginning of the cycle.
One of the infusion recipes: 1 tsp. leaves are brewed with slightly cooled water after boiling (1 tbsp), infused, then filtered. Dosage: 1⁄4 tbsp. 3 rubles/day It is not recommended to take the infusion in the evening.
It is important to know that the plant is contraindicated:
- for fibroids, endometriosis;
- hypersensitivity;
- problems with the thyroid gland;
- increased estrogen levels;
- during lactation and in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Throughout the entire cycle, you can take wormwood, sage and boron uterus - each plant on certain days:
- wormwood – from 1-5 days;
- sage – from 6-15 days;
- boron uterus - from 16-25 days.
Wormwood increases monthly bleeding. Recipe: 2 tbsp. herbs for 1 tbsp. hot boiled water. Then the container is placed in a steam bath for 15 minutes. Take 2 tbsp. 30 minutes before meals, 3 times a day. Sage is taken strictly before ovulation. 1 tsp Brew 1 tbsp in a thermos. water, leave for 15-20 minutes. The strained solution is taken 20-30 minutes before meals.
Borovoy uterus take 1 tsp. for 1 tbsp. Brew and insist. Drink 0.5 tbsp. 2 rubles/day Infusions are taken for 3 months. It is recommended to combine herbal medicine with taking vitamins.
Fenugreek seeds increase estrogen and prolactin levels in the body. It can be taken in the form of powder, decoctions or infusions. Tea is prepared from the powder by brewing it. The infusion is prepared in a thermos for 2 minutes. For 1 tbsp. seeds take 1 tbsp. water.
Take the product 2 times a day. The course of treatment begins a week before the onset of menstruation and ends with the onset of menstruation. 1 tbsp. sacred vitex brew 2 tbsp. boiling water in a thermos and leave for 6-8 hours in the thermos. The infusion stimulates ovulation and helps stabilize the cycle.
Causes of hormonal imbalance in men
To ensure the normal development of secondary sexual characteristics in adolescence, hormones produced by the testicles - androgens - are responsible for muscle strength, impressive growth and aggressiveness of adult men. However, in order for a man’s body to function smoothly, he also needs female hormones – estrogens. Therefore, against the background of complete health of a man, his blood will have the same estrogen content as a woman in the menopausal period.
They are the ones responsible for a man’s sexual desire, which will suffer if there is a shortage or excess of them. Estrogens enable the successful maturation of sperm, are responsible for mental abilities, and regulate metabolic processes, in particular lipid and calcium metabolism in bone tissue.
Estrogens in men are the result of the work of the liver and adipose tissue, which convert testosterone. A negligible amount of it is formed in the gonads.
The activity of the male gonads is also regulated by the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, which work in the system, as well as the work of the testicles. Therefore, the main cause of male hormonal dysfunction is considered to be hypogonadism - secondary and primary.
Secondary hypogonadism is a pathology of central origin, which, as in women, becomes the result of brain tumors (pituitary and hypothalamic areas), neuroinfection, congenital malformation or trauma.
Sometimes hormonal imbalance occurs as a result of chronic poisoning due to alcoholism, drug use, or harmful professional activities. Such intoxication entails increased formation of estrogen from testosterone.
Endocrine pathology is a rare cause of hormonal dysfunction in the male body. Hormone-dependent tumors, liver and kidney pathologies also rarely provoke such disorders.
Causes
A disruption in the hypothalamus-pituitary-ovarian system provokes hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body. Heavy or scanty menstruation occurs, endometrial hyperplasia, fibroids and cysts appear, spontaneous abortion and much more.
In addition, hormonal imbalance can occur under the influence of impaired functioning of other endocrine glands. These include various diseases of the thyroid and pancreas (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, etc.).
However, changes in hormone levels are not always pathological. For example, during adolescence and menopause, the level of hormones gradually changes in the fair sex.
In the first case, this situation is provoked by physiological maturation. Girls develop breasts, secondary sexual characteristics (hair growth, etc.), and the menstrual cycle is established. The hormonal balance is gradually normalized. But we must remember that hormonal imbalance in girls is also possible.
During menopause, the opposite picture is observed. Hormone levels begin to decline and reproductive function fades. But hormonal imbalance in women after 40 years is also not uncommon, so examinations should be carried out regularly.
It is worth touching on the situation with pregnancy. Everyone knows that pregnancy is not a pathology, but the hormonal background is significantly different from that of non-pregnant women.
Causes of hormonal imbalance in women:
- Pathological processes of the endocrine glands.
- Brain diseases, injuries and tumors.
- Diseases and pathological processes of the pancreas, kidneys and liver.
- Hereditary factor, genetic predisposition.
- Frequent stress, depression.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Poor nutrition.
- Obesity.
- Excessive weight loss (dieting, anorexia).
- Frequent acute respiratory infections, flu and colds.
- Chronic systemic diseases.
- Abortions, spontaneous miscarriages, complicated pregnancy and/or childbirth.
- Surgical intervention, complications in the postoperative period.
- Long-term use of oral contraceptives, hormonal drugs.
- Incorrectly selected drugs containing hormones, for example, Postinor.
- Bad habits (alcoholism, drug addiction, smoking, etc.).
There are many factors causing failure. However, psychosomatic reasons are considered the decisive factors that trigger the entire process. Psychosomatics is a fairly new branch of medicine that determines the influence of psychological factors on the occurrence and development of diseases in the body.
It often happens that despite a lot of medical treatment and medications used, recovery never occurs. This happens because the subconscious “holds on” to the disease. And if you determine the underlying cause of this phenomenon, then recovery will not be long in coming.
Psychosomatic reasons include the following situations:
- Stressful situations. In the modern pace of life, it is not possible to maintain peace of mind all the time. Overstrain at work, traffic jams, and the desire to complete all household chores and responsibilities have a negative impact on the nervous system.
- Dissatisfaction in sexual relations. This may include the inability to relax during sex and the lack of orgasm. In addition to the accumulation of stress levels and the formation of mental beacons, such situations provoke blood stagnation in the pelvic organs, which further enhances hormonal disorders.
- Accumulation of grievances towards your man, taking on “male” functions, such as providing for the family, doing housework that requires “male hands”, etc.
- Cultivating fears about one’s possible inadequacy: I will be a bad mother/wife; I will repeat all the mistakes of my mother and so on.
- Career growth at the expense of family life and ignoring one’s own interests and desires.
The emergence of such psychological problems provokes the creation of mental beacons that trigger destructive processes in the body. A woman subconsciously, unconsciously, abandons her role, and therefore her reproductive organs. Malfunctions in the functioning of the ovaries appear, which provoke further disorders.
Symptoms of hormonal imbalance in men
Puberty
Puberty in young men can begin either late or early. If we are talking about premature puberty, then it is caused by brain tumors localized in the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. In addition, the cause may be genetic predisposition. In this case, secondary sexual characteristics can appear in a boy as early as 7 years old. The child begins to grow rapidly, but this process stops during adolescence, since the skeletal growth zones ossify prematurely.
If a boy has obesity and other symptoms of metabolic disorders, then most often this hormonal imbalance is provoked by the pathological functioning of the adrenal cortex. An additional provoking factor is the child’s consumption of hormone-containing foods. For example, meat and milk with steroids.
There may be several reasons leading to a delay in the onset of puberty in boys:
- Poisoning, infections, injuries - any damage to the central nervous system;
- Diseases of the thyroid gland, obesity - pathologies of an endocrine nature;
- Chronic diseases that cause exhaustion of the body.
In the treatment of delayed puberty, hypogonadism and hereditary predisposition should be taken into account as possible influencing factors.
Hormonal imbalance during reproductive age
Manifestations of sexual dysfunction during the reproductive period most often occur against the background of increased estrogen formation:
- Excess body weight;
- Pathologies of the nervous system;
- Growth of the mammary glands;
- Violations of sexual desire and reproductive potential.
The reasons for the failure can be very diverse: pathologies of internal organs and systems, poisoning, bad habits, nervous tension, poor nutrition, etc. Symptoms in each specific case will be supplemented with corresponding etiological signs.
Menopause in men
A natural physiological stage is the decline of sexual function in men in adulthood. However, it also happens that this process is accompanied by pathological disorders.
First of all, menopause in men will be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Increased irritability;
- Fatigue;
- Depressive moods;
- Loss of self-esteem;
- Panic attacks;
- Decline in cognitive abilities, decrease in creative capabilities;
- Feeling of inadequacy and uselessness.
In addition to disorders in the nervous system, men suffer from impotence, which is paralleled by problems with urination.
The mammary glands may begin to enlarge, body weight increases, and fat begins to accumulate in places uncharacteristic for men - on the sides, on the hips. Hair on the face and chest stops growing.
The cardiovascular system suffers, atherosclerotic vascular lesions and hypertension begin to develop.
The skin gradually atrophies, the condition of nails and hair worsens. Like women, men may experience hot flashes and increased activity of the sweat glands.
The provoking factors of pathological male menopause are as follows:
- Pathologies of the central nervous system caused by injuries, infections, poisoning;
- Diseases of the endocrine gland;
- Bad habits, poor nutrition, low physical activity;
- Liver diseases;
- Prolonged stress;
- Somatic diseases;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Previous hormonal dysfunctions.
Why do hormonal imbalances occur in women?
If a woman has a hormonal imbalance, the reasons for this phenomenon are very different, but the most important factor is considered to be low progesterone levels. The thing is that the female half of humanity produces hormones such as progesterone and estrogen. Progesterone is considered a female hormone and, although the body produces these two hormones in the same quantities, it often happens that the level of estrogen is higher than the level of progesterone. And then the hormones go astray.
This is influenced by the following reasons:
There is no ovulation in the female body. The ovaries cannot produce progesterone, and its levels drop. On the contrary, there is more estrogen, because the ovaries have not been able to produce eggs that can be fertilized monthly. All this adversely affects hormonal balance; poor diet and strict diets. The female body simply needs enough fiber, but not all products contain it; if a woman is on a strict diet, this leads to the appearance of symptoms of hormonal imbalance; genetic predisposition. If there is a congenital defect of the body’s hormonal system, then against the background of such factors it is very difficult to cure hormonal imbalances, because this will require a thorough examination and complex treatment; overweight and obesity. Overweight ladies have a lot of excess subcutaneous tissue, and this directly leads to hormonal decline; infectious diseases. These include constant acute respiratory infections and sore throats in childhood and more serious diseases - chlamydia, syphilis, gonorrhea and many others that are sexually transmitted; strong physical activity. If they are also combined with strict diets and malnutrition, then this leads to an increase in the intervals between menstruation and hormonal imbalance; disruption of the endocrine system. These are diseases of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands and pancreas, which most directly affect hormonal imbalance in women; nervous breakdowns. Suffered stress or constant nervous tension also lead to this condition; operations in the abdominal cavity or surgical treatment on the genitals. Artificial childbirth is especially dangerous; during the operation there is a very strong disruption of hormones and this can even lead to such a terrible diagnosis as infertility; a specific time period in a woman's life. The causes of hormonal imbalance can be such familiar periods in the life of any woman as sexual development, childbirth and pregnancy, as well as menopause. In certain cases, these conditions require adjustment or even serious treatment; women's diseases. These include uterine fibroids, polycystic ovary syndrome, breast cyst and many others. Atherosclerosis, migraine and bronchial asthma can also affect hormone imbalance. Signs and symptoms of hormonal disorders
It must be taken into account that dysfunctions and many diseases caused by hormone imbalance are very difficult to treat. But if you know why hormonal imbalance occurs, its signs and how you can cope with it, you can significantly ease such an unpleasant process. Symptoms of hormonal disorders can be very diverse.
Unstable and irregular menstruation
Menstruation becomes irregular, takes a very long time, or, on the contrary, passes in a day or two. The nature of the discharge during menstruation also changes noticeably - it can be heavy or very scanty. In some cases, menstruation does not occur at all for several months. This symptom is often present in girls with anorexia nervosa.
Malfunction of the central nervous system
The woman begins to get very nervous for no serious reason, depression and melancholy appear, and her mood changes dramatically. Sometimes there are unjustified attacks of aggression and ladies often react painfully to things that previously did not even deserve their attention. Premenstrual syndrome worsens, becomes severe and the woman is constantly nervous.
Body weight increases sharply
Another sign of hormonal imbalance is unexpected weight gain and body weight cannot be adjusted. Physical activity does not help you lose weight, and different diets do not help. Therefore, a woman gains weight without obvious reasons, since this does not depend on nutrition and such a phenomenon cannot be dealt with.
Decreased or absent sex drive
Ladies become indifferent to sex, libido decreases or is completely absent. Sometimes there is even complete indifference to the partner, and there is no desire to enter into intimate intimacy with him. His previous caresses irritate and do not bring any effect. During sexual intercourse, the secretion of mucous secretion from the vagina is disrupted and sexual intercourse itself is sometimes painful and with painful sensations for the woman.
The condition of nails and hair worsens
Some women notice that their hair has begun to fall out significantly, their curls become dry, brittle and dull. The picture is the same with nails: they break, become grayish or yellowish and look ugly.
Skin rashes in different parts of the body
The main symptom of hormonal imbalance is considered to be changes in the skin on the chest, back and face. Acne appears very often, the rash cannot be treated with anything. Sometimes thick black hairs begin to grow on the body, and this worries the woman very much, as they look ugly.
Sleep disturbance and increased fatigue
There may be prolonged insomnia, the woman cannot fall asleep for a long time, and the sleep itself becomes sensitive and anxious. Increased fatigue was also noted, while there was no strong mental and physical stress.
Reproductive dysfunction
This is the most difficult moment for any woman, because she cannot conceive and carry a baby. When hormones malfunction, there are miscarriages, fetal death in the early stages of pregnancy, and long-term impossibility of fertilization.
During what period can hormonal imbalance occur?
Symptoms of hormonal imbalance appear at different periods of life, both in women and men. Despite the differences in the structural features of the reproductive system, hormone failure causes almost similar symptoms in both sexes.
Disorders during puberty
In adolescence, a girl experiences changes in her hormones for the first time, as her body transforms from a child’s body to a woman’s. The mammary glands begin to enlarge, the first menstruation comes, and the like. And at this time the hormonal system first fails, this can lead to delayed puberty or premature maturation. It is worth noting that puberty may be absent.
If a girl’s body lacks sex hormones, sexual development is delayed, and menstruation may begin at 16 years of age or even later. This happens due to severe stress, various diseases or poor nutrition. Acne is the first sign of a disorder, followed by headache, lack of sleep, irritability, irregular menstruation and much more. If you notice that your daughter has become irritable, consult a doctor. In many cases, you will need to establish the correct daily routine for the girl and everything will go away on its own. But in severe cases, they may prescribe hormonal medications, which are taken strictly according to the instructions. If puberty occurs earlier than normal and the girl is completely healthy, she does not need treatment. Boys can also experience hormonal disruption; early puberty is associated with neoplasms of the hypothalamus - pituitary system. If pathologies of the adrenal cortex are present, then hormone failure is expressed in obesity and other signs of impaired metabolism. Delayed sexual development in boys is indicated by the fact that normal maturation is delayed by more than two years compared to normal periods.
Hormonal problems after abortion
If a woman has a hormonal imbalance after an abortion, the symptoms of this pathology are not difficult to distinguish.
These include:
weight gain; stretch marks appear on the skin; blood pressure and pulse are unstable, sweating is present; the woman becomes irritable, restless, complains of depression and headaches. The earlier the abortion was performed, the less risk for the woman, but the normal functioning of hormones is disrupted already during the surgical intervention itself. A month after the operation, the menstrual cycle should resume, but if this does not happen, go to the doctor immediately. It may also be that you will need to prescribe hormonal medications.
Diagnosis of hormonal imbalance
A comprehensive survey should include:
- Tests to determine hormone levels, general and biochemical blood tests;
- Examination of internal organs, which allows you to assess their possible damage caused by hormonal dysfunction;
- Exclusion of pathologies of organic origin, for example, tumors, cirrhosis of the liver, etc.;
- Conducting differential diagnostics to identify hypogonadism, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, etc.
Diagnosis and treatment of hormonal disorders in women
Due to the fact that any hormonal imbalance can lead to quite serious consequences, this condition requires mandatory correction. However, first you need to find out the reason that provoked the hormonal shift. To do this, you need to consult an endocrinologist and also take a blood test to check your hormonal status. It should be noted that this type of research is carried out before and after menstruation (and, if necessary, during menstruation). Further, if, after laboratory diagnostics, an imbalance in the level of a particular hormone is detected, additional studies (ultrasound, hysteroscopy or laparoscopy, fundus examination, CT scan of the brain) are required to determine the cause of the imbalance.
Treatment of hormonal disorders in women involves the prescription of hormonal drugs that normalize the level of biologically active substances in the body (sometimes patients need to take them constantly). At the same time, when prescribing treatment, great importance is given to normalizing diet and rest.
The dosage of the hormonal drug is calculated taking into account weight, age and the level of the hormone in the blood, and the general condition of the patient and some minor factors are also taken into account.
Treatment of hormonal imbalance and delayed menstruation
If you are experiencing symptoms of hormonal imbalance, it is best to inform your gynecologist-endocrinologist, who will recommend appropriate medications based on individual indicators.
For women with an increase in the male hormone androgen and constant cycle disruptions, the doctor may prescribe oral contraceptives aimed at increasing estrogen. These drugs include:
- Androcur.
- Chloe.
- Diana is 35.
- Femoden.
- Jazz.
- Janine.
- Yarina.
The treatment regimen depends on the initial data. For successful therapy, long-term treatment is used.
Tablets can be used to regulate prolactin and progesterone:
- Duphaston.
- Norkolut.
- Utrozhestan.
Often, two-phase therapy is used, which includes different drugs. Therefore, before starting treatment, you should be tested for hormone levels in the blood. It is recommended to take it on a certain day of the cycle.
- The level of prolactin, FSH and LH is usually indicative on days 3-5 of the cycle.
- Testosterone and cortisol - day 8-10 of the cycle.
- Estradiol and progesterone - 21-22 days of the cycle.
Therapy may also be selected to reduce weight. When we eat food, leptin levels increase. Then the appetite subsides and we feel full. Deterioration of leptin can lead to the development of obesity.
Weight gain that is not associated with dietary errors can also be caused by hypothyroidism. This is a condition in which the thyroid gland produces too little thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These hormones have a strong effect on metabolism and are necessary for burning fat. Accordingly, deficiency is detected with weight gain.
On the other hand, significant weight loss for unexplained reasons may be the result of hyperthyroidism. Patients are constantly hungry, even at night, but still lose weight within a few months.
It is important to comprehensively study all the symptoms of hormonal imbalance in women, signs, and delayed periods. Only in this case can the disorder be stopped and the condition of the internal organs returned to normal.