What is mastopathy of the mammary glands
Benign breast pathologies with hyperplasia, associated with changes in hormonal levels, are combined into a group of diseases under the general name “mastopathy”. And WHO defines mastopathy as a fibrocystic pathology, which is characterized by proliferative processes and a violation of the ratio of connective tissue and epithelial components. Fibrocystic mastopathy (FCM) can develop into breast cancer.
General concept
Fibrocystic mastopathy (FCM) is an abnormality of the mammary gland, which is benign in nature. It is a hormonal disorder, as a result of which tissue changes are observed - proliferative and regressive.
Proliferation is the growth of organic tissues due to cell division. Regression is a decrease in the size of tissue areas.
These changes entail an incorrect ratio of the epithelial and connective tissue components.
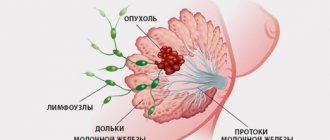
Epithelial tissue (glandular) is the protective outer layer of the skin. Connective tissue (fibrous) – nutritious: fat, cartilage, blood.
Diffuse FCM
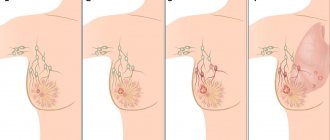
The onset of the disease is excessive growth of connective tissue with the appearance of symptoms such as cysts - small nodules similar to millet grains, and cords - oblong elastic formations. The main manifestation of this type of FMC is mastalgia - painful sensations in the chest that occur during the premenstrual period and disappear at the beginning of the cycle. Then the cyst periodically forms in the form of dense balls in the upper part of the mammary gland.
On a note! Such manifestations cannot be ignored and not contacted specialists for a long time. After all, mastopathy at an early stage is often cured with conservative methods.
Nodal FCM
The further course of the disease leads to the formation of large-sized nodes: from a pea to a walnut. At the same time, the pain in the chest intensifies, sometimes there is a return to the shoulder or armpit. Even a light touch can be very painful. There are also cases of fluid discharge from the nipples.
On a note! The FCM stage, when the pain becomes constant and the mammary glands do not return to normal with the onset of menstruation, is very dangerous. She requires an immediate visit to the doctors.
https://youtu.be/y_hHkA1qLXk
Types of fibrocystic mastopathy
This pathology is classified as follows:
— Diffuse mastopathy of the mammary gland.
There are four options here:
• Fibrocystic mastopathy of the mammary glands, in which the glandular component predominates.
• Mastopathy with a predominant cystic component.
• Mastopathy, in which the fibrous component is predominant.
• Mixed option.
— Nodular fibrocystic mastopathy of the mammary gland.
In cases where the glandular component predominates, differentiated hyperplasia of the gland lobules is noted. The formations transition smoothly into adjacent tissues. This variant of pathology is more common in young patients. X-ray of the gland (mammography) gives the following picture: regular-shaped shadows with invisible boundaries. The shadows coincide with areas of hypertrophy of the lobules and lobes. In some patients, the shadows completely cover the gland.
Diffuse form of mastopathy with a predominance of the glandular component (adenosis)
When the cystic component predominates, numerous cystic structures are observed in the mammary gland. They are elastic, with a clear separation from nearby tissues. Such areas are formed from atrophied lobules and dilated ducts, in which there are fibrotic processes. In the epithelial tissue of these cystic structures, proliferative processes are possible, which lead to the formation of papillary formations. This variant of mastopathy is characteristic of the perimenopausal period (especially postmenopause). X-ray examination gives a picture of a pattern of large spots, with many clearings and a clear outline. Cysts vary in consistency and shade. In some cases, calcification is possible.
Photo of a mammogram with the formation of microcalcifications of various shapes.
Mastopathy with a dominance of the fibrous element usually occurs in premenopausal patients. The connective tissue undergoes fibrous changes, proliferation of intraductal tissues occurs, the lumen of the ducts narrows, and even complete obliteration of the ducts is possible. X-ray examination reveals homogeneous dense areas, which are characterized by pronounced heaviness.
Sclerosing adenosis.
With a mixed form of the disease, the following pathological changes occur: sclerotic processes in the connective tissue, lobular hyperplasia, alveolar atrophy. In this case, the ducts expand and turn into cysts.
Cyst
In the nodular form of the disease, nodes appear in the mammary gland (they can be multiple or single). Their morphological characteristics are similar to the corresponding diffuse forms of the disease.
Mastopathy is also classified according to the presence or absence of atypia and proliferation. Proliferation is excessive cell division; atypia is said to occur when cells appear that differ from normal ones. Such cells are not yet malignant, but their structure is no longer the same as that of their predecessors.
In addition, the modern classification defines a special variant of breast disease - mastodynia or mastalgia. In women with this problem, the mammary glands swell cyclically. This phenomenon is based on venous stagnation, as well as swelling of the stroma.
A benign neoplasm, which is formed from the epithelial tissue of the lobules, is limited and has a capsule, is called “fibroadenoma”. On palpation, a mobile area is noted, having smooth contours and a round shape. Fibroadenoma forms during puberty due to the fact that hormone levels increase and tissues grow rapidly.
The x-ray shows a round or oval formation with clear outlines. Patients with mastopathy have an increased risk of developing malignant processes. Depending on the form of the disease, this risk increases 4-37 times. The greatest danger in this regard is represented by cystic structures, calcification, proliferation of epithelial tissue of the ducts and cyst walls.
fibroadenoma
Signs
Fibrous mastopathy
It is characterized by soreness, a feeling of fullness in the chest and special sensitivity to touch. The resulting neoplasms can reach a size of 7 centimeters.
Discharge from the nipples (sacral or greenish-brown) intensifies as the disease progresses, although at first this symptom is not pronounced.
Cystic
With cystic mastopathy, the pain is more pronounced, there is swelling of the gland tissue and a burning sensation in the area of cyst formation. As the pathology progresses, the pain becomes constant.
Discharge from the nipples appears mainly with multiple cysts or a single, but very large formation. Sometimes the milk ducts become blocked.
Both with fibroma and with cystic mastopathy, with unilateral lesions, pronounced asymmetry of the mammary glands is often noted.
An infection may also occur. In this case, there is an increase in body temperature, hyperemia of the skin of the mammary gland, and the appearance of purulent discharge from the nipple.
Diffuse
With diffuse mastopathy, the breasts become larger and heavier, and a feeling of fullness and distension appears. The pain intensifies when touched.
The compactions in the breast tissue are uniform or resemble fine-grained formations concentrated in one focus.
Diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy
The most dangerous phenomenon. It is classified as a precancerous condition. The non-proliferative form of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy is characterized by compactions that exist for many years and gradually change in size.
At the same time, the ducts expand and connective tissue grows. With proliferative mastopathy, the epithelium of the ducts and glandular lobules undergo proliferation, and with fibroepithelial proliferation, papillomas (cystodenopapillomas) are formed in the milk ducts. It is in the latter case that malignancy of the process most often occurs.
Classification of mastopathy
Classification of breast density by mammography (Wolfe JN, 1987; Byrne S, Schairer S., 1995)
N1 - parenchyma consists of adipose tissue, there are single fibrous connective tissue strands;
P1 - ductal structures are determined, occupying no more than 25% of the volume of the mammary gland;
P2 - ductal structures are visible, occupying more than 25% of the volume of the mammary gland;
DY - opaque, very dense parenchyma is visible - connective tissue hyperplasia.
Types of fibrous cysts
Cysts are benign neoplasms filled with fluid and having an elastic and clear structure. Externally, they are limited by a capsule, which consists of connective tissue. In the early stages, the disease is almost impossible to detect, since women will not be able to feel the lump by palpation at home.
Mastopathy (fibrous cystic) is a pathology that should be clearly separated from a benign neoplasm called “fibroadenoma”. As the disease progresses, many patients experience deformation of the mammary glands, they increase in size, and their structure becomes heterogeneous.
There are several types of fibrocystic mastopathy:
- Nodal. A large number of nodes are formed, which may be harbingers of the degeneration of neoplasms. When diagnosing this form of the disease, emergency intervention by specialists is necessary.
- Diffuse. Tissue growth is observed, compactions appear, and the mammary glands acquire a granular structure.
Pathogenesis of mastopathy
Hyperestrogenemia (absolute or relative) and progesterone deficiency play a special role in the development of the disease.
The most important estrogen for the female breast is estradiol. The connective tissue of the mammary gland contains more of this substance than the blood. This hormone promotes the processes of differentiation and development of the breast ducts, activates the mitotic activity of epithelial tissue, promotes the formation of the acinus, increases vascularization, and is necessary for the hydration of connective tissue.
Another hormone, progesterone, counteracts these changes. It prevents proliferation, promotes normal differentiation of the epithelium, slows down mitotic activity in the epithelium, prevents increased capillary permeability, and relieves stromal edema. If the progesterone effect is weak, proliferative processes begin in the connective tissues and epithelium of the mammary gland.
Breast fat contains many estrogen receptors. But the number of progesterone receptors is not so large. Adipocytes are a depot of androgens, progesterone and estrogens. Under the influence of aromatase, estrone and estradiol are formed from androgens. Such processes become more intense over time, which increases the likelihood of malignant changes.
Prolactin is of great importance in the development of mammary tissue hyperplasia. Under its influence, the number of estradiol receptors increases. When prolactin levels increase when breast pathology is combined with uterine diseases, progesterone production decreases. And this leads to worsening pathological changes. Under the influence of prolactin, the thyroid gland is inhibited. Thyroid hormones modulate the action of estrogens at the cellular level and disrupt the histo- and organogenesis of hormone-dependent formations. They also contribute to the development of endometrial hyperplasia.
Elevated cortisol levels also play a significant role. An excess of this substance provokes hyperplastic processes in the breast in two ways: through corticosteroid receptors directly and through an increase in the number of prolactin receptors.
An increase in the level of prostaglandins in the female body affects the lumen of blood vessels and the permeability of their walls, changes the water-salt balance and hemodynamics. As a result, tissue hypoxia develops. In the blood of patients with mastopathy, Pg E2 is several times higher than normal. One of the reasons that provokes the development of mastopathy is excess body weight, primarily if it is combined with high blood pressure and diabetes. Pathologies of the hepatobiliary complex lead to the development of hyperestrogenism due to the fact that the processes of estrogen utilization in the liver slow down. In addition, the connection between mastopathy and intestinal dysfunction, constipation, changes in intestinal flora, and lack of fiber in a woman’s diet was confirmed. There is a hypothesis that in such cases, estrogens that have already been excreted in the bile are reabsorbed in the intestine.
Causes of mastopathy
The main causes of hormonal disorders include:
— Genetically determined features.
— A large number of pregnancies and births, abortions, early and late births, multiple fetuses, prolonged lactation, late menarche, late menopause, problems with the menstrual cycle.
— Gynecological problems, primarily of an inflammatory nature.
— Presence of atypical cells.
— Hormone therapy.
— Oral contraceptives.
— Pathologies of an endocrine nature (diabetes mellitus, dysfunction of the thyroid gland).
— Liver problems, biliary tract pathologies.
- Chronic colitis.
— Psycho-emotional stress: dissatisfaction with life, problems in the sexual sphere, frequent conflicts in the family and at work, stress, nervous strain, etc.
- Bad habits.
- Excessive indulgence in tea, coffee, chocolate and other products that contain methylxanthines.
Pregnancy and illness
With diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy of the mammary glands, pregnancy and a successful birth are possible. If conception occurs, it is important to inform your doctor. Mammography, examination of the milk ducts by injecting dyes, and other complex procedures are not recommended for pregnant women. It is recommended to be careful when treating with herbs.
Typically, expectant mothers are prescribed light maintenance therapy with hormonal correction. The doctor can prescribe safe herbal medicines that have a calming, decongestant and analgesic effect.
Breastfeeding is also allowed with diffuse FCM. Often it helps to correct the patient’s condition. Cysts may decrease in size or disappear altogether. The only thing is that it is important not to feed the baby for too long (no more than 12 months). Otherwise, the risk of tumors increases.
Symptoms of breast mastopathy
Breast mastopathy makes itself felt by pain that occurs in the middle of the cycle. At the same time, the glands become denser, and discharge from the nipples is possible. The pain can be of different types: radiating to the neck or back, sharp, shooting, stabbing. It occurs due to the fact that the nerve endings are compressed by swollen tissue, cystic structures, and are involved in sclerotic areas.
By palpation, you can detect lobular seals that have an uneven surface. Tissue pain and heaviness are also noted.
When menstruation ends, the pain becomes insignificant (in the case of a diffuse form), the breasts are evenly compacted, and are characterized by heaviness. In the nodular form, lesions (single or multiple) are noted. They are mobile, not connected to the skin, cannot be detected by palpation in a supine position, and are slightly painful. There may be some enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes; upon palpation they show sensitivity. Patients with mastopathy may experience galactorrhea, usually grade 1. In such cases, upon palpation, a grayish liquid appears from the nipples.
Phases of mastopathy
There are three clinical phases of mastopathy:
Phase 1.
Begins at a young age (20-30 years). A week before the start of menstruation, the glands become rough and painful. They are compacted and sensitive to palpation. The cycle is usually regular, but may be too short (20 days).
Phase 2.
Typical for ages 30 to 40 years. In the second phase of mastopathy, pain is felt almost constantly, appearing two to three weeks before the onset of menstruation. Seals with cystic inclusions appear.
Phase 3.
Develops in women over 40 years of age. The pain in such cases is intermittent and becomes less pronounced. Multiple cystic structures are formed in the breast, filled with a greenish secretion, which comes out when pressed on the nipple.
Who is at risk?
Mastopathy (fibrocystic) most often develops in women of the following categories:
- nulliparous;
- artificially terminated pregnancy;
- those who have had spontaneous abortions;
- having bad heredity;
- older age group (over 40);
- patients who have begun menopause;
- having various diseases of the genitourinary system, etc.
Diagnosis of mastopathy
Diagnosis of mastopathy involves the following methods:
— Study of anamnesis data.
Here, special attention is paid to the presence of increased risk factors.
- Medical examination.
The mammary glands are examined in good lighting. The patient should stand with her head leaning forward and her arms down. She is also examined in the supine position, placing a cushion under the shoulder blades, and then in the side-lying position. In this way, even minor manifestations of mastopathy can be detected.
- Palpation.
This study is carried out with the patient standing, lying on her back and on her side. First, superficial palpation is performed with the fingertips. They study the area of the areola, then move on to the peripheral areas. The study is given in this order: upper-outer quadrant, upper-inner, lower-inner and, finally, lower-outer. Then deep palpation is performed in the same sequence. After this, they proceed to palpation of the axillary lymph nodes, supraclavicular and subclavian areas.
Clinical signs of a malignant process are: palpable tumor, nipple retraction and asymmetry, nipple erosion, pain, enlarged lymph nodes, swelling of the arm, swelling of the skin of the breast (the so-called lemon peel), pain in the armpit.
You should regularly perform breast self-examination to ensure that you do not notice any changes in your breasts.
— Mammography (x-ray of the mammary glands).
X-rays are taken in two projections. If necessary, perform a targeted examination with magnification. Thanks to such diagnostics, it is possible to obtain an accurate picture of changes in the breast tissue, determine the presence of microcalcifications, assess the condition of the axillary lymph nodes, and notice tumor formations that are not detected by palpation (primarily, this applies to small tumor nodes located deep in the breast tissue). The sensitivity of mammography may vary depending on the situation (size of the tumor, its location, age of the patient). One of the most important diagnostic and prognostic criteria is mammographic density. With increased mammographic density, the risk of developing a malignant process increases three times.
- Ultrasound of the breast.
This test is performed using a linear probe (7.5 MHz). In addition to the standard echography study, the parenchyma is measured in all sectors of the gland along conditional lines that converge in the nipple area. The echo density of tissues is also assessed. The layer of glandular tissue becomes thinner over time, and the echo density indicator after 54 years increases to its maximum value. This phenomenon is considered completely normal (age-related involution). Fatty transformation of the gland tissue occurs, its quantity decreases, diffuse fibrosis begins, which, in fact, increases echo density. FCM has the following indicators for ultrasound examination: with the glandular variant – hyperplasia of the glandular tissue 15-33 mm, echo density 28-30, reverse involution is not noted; in the cystic form - the thickness of the glandular tissue is 10 mm, the echo density is 37 - 55, multiple small cystic formations are noted; with fibrosis, the glandular tissue thickens to 16 mm, echo density increases significantly - 41-43. In patients with a mixed form of mastopathy, the layer of glandular tissue thickens to 22 mm, the echo density is 35-37, cysts are detected, ductectasia is noted, and involution is not observed. In the case of connective tissue hyperplasia, the echo density is increased, and stranded structures with an irregular shape are noted. Cysts are round echo-negative areas, their boundaries are clear.
— Biopsy with cytological examination.
This method allows you to clarify the nature of the tumor in the breast.
— Sectoral resection with histological examination.
This radical method is resorted to when there are special indications.
— Thermography.
The method is based on recording infrared rays using a thermograph. A malignant tumor can be detected due to the fact that the skin temperature above it is slightly increased compared to the temperature above benign formations. This helps to differentiate mastopathy from breast cancer.
Treatment of mastopathy
How is breast mastopathy treated using conservative methods?
Treatment with medications is prescribed after examination by an oncologist in order to eliminate the need for surgical treatment in the presence of a nodular form of mastopathy, the presence of calcifications in the gland, and the presence of roliferative changes in the mammary epithelium during a biopsy. You can find out how to treat breast mastopathy from the table.
Table of drugs and treatment regimens for mastopathy
| Drugs | Treatment regimen for mastopathy | Explanation |
| Group of gestagens | The course of treatment is 6-9 months. | Used to treat women of reproductive age. Drugs from the gestagen group regulate the conversion of active estradiol into the less active estrone, inhibit proliferative processes by influencing growth factors, and reduce cyclic edema of the connective tissue stroma of the mammary gland by reducing capillary permeability. |
| Norethisterone (norkolut, primolutnor) | 5-10 mg daily for 10 days | Taken from the 16th day of the menstrual cycle to the 25th day. |
| Orgametril (linestrenol) | 5 mg daily for 10 days | Taken from the 16th day of the menstrual cycle to the 25th day. |
| Pregnin | 0.02 g (2 tablets) sublingually 3 times a day for 10 days | Taken from the 16th day of the menstrual cycle to the 25th day. |
| Progesterone | 1 treatment regimen: intramuscularly 10 mg (1% solution - 1 ml); 2nd treatment regimen: intramuscularly 25 mg (2.5% solution - 1 ml) on days 21, 23, 24, 26 of the cycle, every other day; | 10 injections from the 16th day of the menstrual cycle to the 25th day. Injections on the 21st, 23rd, 24th, 26th day of the cycle |
| 17-OPK | intramuscularly 125 mg (12.5% solution - 1 ml) | 10 injections from the 16th day of the menstrual cycle to the 25th day. |
| Utrozhestan | 100 mg 2-3 times a day daily for 10-14 days | Taken starting from the 16th day of the menstrual cycle. |
| Duphaston (dydrogesterone) | 20 mg each | An analogue of natural progesterone that does not have androgenic, thermogenic or corticoid activity. Used from 11 to 25 days of the menstrual cycle. |
| Medroxoprogesterone acetate | 5-10 mg daily for 10 days | Taken from the 16th day of the menstrual cycle to the 25th day. |
| Progestogel 1% | 1 dose 1 time per day | Gel with micronized progesterone is applied from the 16th day of the menstrual cycle to the 25th day. |
| Antiestrogens group | Course from 3 to 6 months. | The mechanism of action is based on competitive binding to estradiol receptors in breast tissue. |
| Tamoxifen (Nolvadex) | 10-20 mg daily for 5-6 months | Has a teratogenic effect. |
| Fareston (toremifene) | 10-20 mg daily for 3-6 months. | Due to estrogen stimulation, the risk of endometrial changes, such as hyperplasia, polyposis and cancer, increases. |
| GtRH agonists group | They cause a decrease in the frequency of pulsating GnRH emissions in the hypothalamus, have a direct effect on steroidogenesis in the ovaries, binding a number of enzymes involved in the synthesis of steroid hormones, and inhibit the synthesis of LH and FSH in the pituitary gland. Used after 45 years for combined endometrial hyperplasia, adenomyosis, and uterine fibroids. | |
| Goserelin (zoladex) | subcutaneously in the abdomen 3.6 mg once a month, course 2-4 months | Available in the form of a depot preparation. |
| Triptorelin (decapeptyl, diferelin) | >subcutaneously 525 mcg daily for 1 week, then 105 mcg daily as maintenance therapy | |
| Decapeptyl-depot | subcutaneously or intramuscularly, 1 injection (3.75 mg) daily, course 28 days | Composition of the substance: triptorelin and polymer depositing filler. |
| Buserelin | subcutaneously 500 mcg 3 times a day, after 8 hours for 1 week, from the 8th day of treatment they switch to intranasal administration of buserelin 1.2 g (in 4 doses) | |
| Nafarelin (sinarel) | 200 mg 2 times a day | endonasal spray |
| Leucoprolide (Lupron) | intramuscularly 3.75 mg once a month | |
| Dopamine receptor agonists | Drugs in this group have a dopaminergic effect aimed at reducing prolactin levels and regulating local hormonogenesis in breast tissue. | |
| Bromocriptine (parlodel) | 2-2.5 mg for 4-6 menstrual cycles | Taken from the 16th day of the menstrual cycle to the 25th day. |
| Dostinex | 1 tablet 2 times a week, course 3-6 months | |
| Androgens | Used to treat women over 45 years of age. | |
| Methyltestosterone | 5-10 mg 1-2 tablets, course 8 months | Taken from the 16th day of the menstrual cycle to the 25th day. |
| Sustanon-250 (omnadren-250) | intramuscularly 1 ml once a month, course 4-6 months | |
| Iodine preparations | The course is 6-12 months with a break during menstruation. | They help reduce the proliferative activity of tissues, have a positive effect on cysts and activate the function of the thyroid gland. |
| Potassium iodide | 10 ml 0.25% solution 4 times a day | |
| 5% iodine tincture | 5 drops in milk 3 times a day | |
| Klamin | 50 mcg (1 tablet) 3 times a day | A plant adaptogen produced from the lipid complex of brown seaweed. |
| Iodomarin | 200 mg 1 time per day | |
| Enzyme preparations | They have anti-edematous, anti-inflammatory, secondary analgesic, absorbable and immunomodulatory effects, increase the production of a-interferon by leukocytes. | |
| Wobenzym | 5 tablets 3 times a day, course 16-30 days | |
| Serta (serratiopeptidase) | 5-10 mg, 3 times a day after meals, swallow, course of treatment from 2 to 4 weeks |
Surgery for mastopathy
The following types of mastopathy are treated with the help of surgery:
- fibroadenomas;
- intraductal papillomas;
- breast cysts.
Surgical treatment is prescribed after consultation with an oncologist.
Treatment of pathology
Regardless of the form, degree and other points indicated when making a diagnosis, treatment of cystic fibrous mastopathy cannot be done without changing the diet. Even if the doctor prescribes a particularly effective drug that promises to instantly cope with the problem, eliminating the primary cause will be incomplete if a diet is not followed, the purpose of which is to reduce the production of female sex hormones.
- Eliminate tea, caffeine and cocoa from the diet, while any of their derivatives (for example, chocolate) are also unacceptable. Theobromine is also unacceptable.
- The proportion of fat is reduced in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations, but the general parameter is considered to be 50-70 g per day for an adult. Therefore, foods with saturated fats (mayonnaise, butter, etc.) are excluded.
- Refusal from premium wheat flour and products containing it, as well as semolina as its derivative.
- Salty foods and foods, canned, fried, and smoked are unacceptable. Sparkling water and confectionery.
- Cabbage is used with caution as a product that promotes the binding of iodine.
- The basis of the menu should be legumes, sources of iodine and selenium, nuts and seeds rich in fiber, beets, spinach and broccoli, sources of calcium, white and green tea.
- Additionally, it is recommended to take vitamins A and E, since they will be almost not supplied with such a diet, as well as B vitamins.
If we talk about other non-hormonal methods of treating fibrocystic mastopathy, then among them the following deserve attention:
- Immunostimulating drugs
- Anti-inflammatory non-steroids that reduce the rate of tumor growth
- Acupuncture
- Physiotherapy
- Neuroleptics and sedatives
- Physical activity, walks, changing sleep and wakefulness patterns, reducing the amount of stress and other psychological stress.
- Herbal infusions
Drug treatment should be prescribed by a doctor based on a number of nuances in the diagnosis. Thus, nodular type mastopathy most often requires surgical intervention, during which the nodes are dissected.
- Hormonal treatment of cystic fibrous mastopathy can be carried out using natural progesterone or synthetic progestogens, as well as androgens (for people over 45 years old) and agents that inhibit prolactin production. The products can be used both externally and internally.
- Among the medications most often used to treat fibrocystic mastopathy are Mastodinone, which lowers prolactin levels, Cyclodinone, and Indomethacin. The course of treatment is always long.
https://youtu.be/FaJousXSB1E
Mastopathy and mastodynia - treatment features
If mastodynia is present, then treatment of mastopathy should be expanded by using, starting from the 16th to 25th day of the menstrual cycle:
1. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
, such as: indometazh 25 mg 3 times a day; ibuprofen (Brufen) 0.2 g 3 times a day; nimesulide 100 mg 2 times a day, after meals.
2. Diuretics
, such as hydrochlorothiazide (hypothiazide) 0.05 g 2 times a day; furosemide 0.04 g 1 time per day, preferably in the morning.
3. Herbal medicines (infusions and decoctions of herbs).
Herbal medicine in the treatment of mastopathy
Traditional methods of treating mastopathy are used as an addition to the main treatment and only after the permission of the attending physician. Folk remedies for the treatment of mastopathy of the mammary glands are infusions and decoctions of herbs and rhizomes of medicinal plants.
Recipes for mastopathy
1. Aloe or agave juice is mixed with honey in a ratio of 1 to 2, take 1 tsp. 2-3 times a day.
2. 2 tbsp. l. crushed Veronica officinalis herb, pour 1 cup of boiling water, let it brew, take 1 tbsp. l. before eating.
3. Pour 25-50 grams of dry Euphorbia Pallas root into 0.5 liters. vodka, then leave for 3 weeks in a dark place. Take 7-10 drops 3 times a day, course 1-3 months.
4. Take 1 part of crushed kopeck root and 9 parts of vodka, place in a dark place for 2-3 weeks. Take 20-30 drops 3 times a day.
5. Extract from the roots and rhizomes of Rhodiola rosea (a ready-made preparation that can be bought at a pharmacy) is taken 15-30 minutes before meals, 5-25 drops 2-3 times a day, course 10-30 days.
6. 1 tbsp. l. Pour 1 cup of boiling water over calendula officinalis flowers, let it brew, take 1/3 cup 3 times a day.
7. 1 tbsp. l. Pour 1 cup of boiling water over chamomile flowers and let steep. Take 1/3 cup 3 times a day.
8. Pour 15 grams of motherwort flowers into 200 ml of boiling water and let cool. Take 1 hour before meals, 1/3 cup 3 times a day.
9. 10 g of herb tripartite, pour 200 ml of water, leave. Take 1/3 cup 3 times a day.
10. 1 part of the rhizome of Eleutherococcus senticosus and 1 part of 40% alcohol (a ready-made preparation is sold at the pharmacy). Take 20 drops 30 minutes before meals.
Treatment
The doctor decides what method will be used to treat diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy, taking into account the form, stage and characteristics of the course of the disease. Only an integrated approach is effective, including the elimination of provoking and concomitant diseases, medicinal effects on pathological processes, adherence to diet and contraindications. It is extremely important to make sure that the tumors are not malignant.
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating hormonal imbalances and restoring the full functioning of all organs. For this purpose, physiotherapy (laser treatment and electrophoresis) and various medications are used:
- iodine preparations;
- sedatives - to stabilize the psycho-emotional background;
- analgesics – to eliminate pain;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – relieve swelling and inflammation;
- diuretics - to maintain kidney and liver function.
The complex effects of these medications are systemic in nature, so only a doctor should prescribe them.
Vitamin therapy provides good results. To strengthen the vascular wall and reduce swelling, taking vitamins A, C and P is recommended. B vitamins stimulate metabolism. Vitamin E is a natural antioxidant and affects hormonal and fat metabolism.
Hormonal therapy is selected according to the woman’s age. Patients in the reproductive period are prescribed oral hormonal contraceptives. Progestogens that are taken in the second phase of the menstrual cycle (Duphaston, Utrozhestan) are also effective. In perimenopausal age, antiestrogens (Tamoxifen) and androgens (Testobromlecid, Methyltestosterone) are recommended. In case of pronounced cyclicality of the pathology, drugs that block the production of prolactin and homeopathic remedies are used.
Diet plays an important role in the treatment of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy. You should reduce your salt intake, give up fatty foods, chocolate and fast food. It is recommended to replace strong coffee and black tea with herbal or green tea. The diet should be dominated by foods rich in fiber - cereals, fresh vegetables and fruits. It is advisable to eat fish and lean meats twice a week. By adhering to these rules, you can not only speed up recovery, but also reduce the risk of developing the disease.
Surgical treatment is performed in very rare cases. The form of surgical intervention is selected based on the indications: if breast cancer is suspected, rapid tumor growth (within 3 months), complications (suppuration), recurrence of cysts after a recent puncture. The nodes are removed through sectoral resection. During surgery, the tumor is excised along with a healthy part of the breast. It lasts only 30–40 minutes. After a few hours, the patient can leave the clinic.
If a cyst is detected, it is punctured, removing the cystic fluid. Sclerosing agents are injected into the resulting cavity. They promote fusion of the walls of the cystic membrane. It is also possible to remove the cyst with suturing of the mammary gland. During the operation, an urgent histological examination of the excised material is performed. If the results confirm cancer, the scope of surgery is expanded to include removal of the entire mammary gland.
During the treatment of diffuse FCM, it is prohibited to drink alcohol and smoke. Strong thermal effects can activate the pathological process, so you should limit visits to solariums and baths, sunbathe moderately and in a swimsuit. The bra should not put pressure on the breasts.