This article is addressed to those who are concerned about lower back pain, fatigue, and sleep disorders. Often such problems are a consequence of poor posture. Many people perceive curvature of the spine only as an aesthetic defect, and yet such a pathology, left without treatment, can lead to disruption of the functioning of internal organs, limited mobility and chronic lower back pain.
From this article you will learn the reasons why lumbar lordosis occurs, what consequences it leads to, and most importantly, how to properly and safely deal with the problem, maintain back health and motor activity for many years.
Causes
Physiological lordosis develops during the first year of a child’s life. Thanks to the curves of the spine in the neck and lower back, a person can assume a vertical position.
With hyperlordosis (pathological curvature), an abnormal bend can form not only in the cervical and lumbar, but even in the thoracic region.
The disease can be congenital or acquired. Causes of lordosis:
- excessive loads;
- vertebral displacement, bruises, dislocations and other spinal injuries;
- overweight;
- tumors, inflammatory processes in the spinal column;
- congenital anomalies, for example, pathologies of the hip joints, hip dislocation;
- kyphosis, flat feet;
- osteochondrosis and osteoporosis;
- consequences of surgery;
- lack of nutrients;
- rickets, bone diseases;
- infectious diseases of the spine, for example, tuberculosis;
- intervertebral hernias.
Pregnancy can also cause curvature of the spine, but after childbirth the spinal column takes on a normal shape.
In children, predisposing factors to the onset of the disease are birth trauma, cerebral palsy, hip dysplasia, rickets or a sharp growth spurt. The most common cause is congenital pathology.
Straightening physiological lordosis often occurs in schoolchildren. The appearance of this pathology is provoked by a sedentary lifestyle and sitting in an incorrect position. The reason may be genetic predisposition.
Risk factors, causes
The main risk factors for the development of this pathology include:
- heredity;
- injuries received during childbirth;
physical inactivity;
- weakness of muscles and ligaments;
- pathological or congenital dislocation of the hip;
- immobility of the hip joint;
- osteochondrosis;
- intervertebral hernia and other chronic pathologies of the spine;
- spinal injury;
- malignant neoplasms in the spine or nearby organs;
- tuberculosis;
- pregnancy.
The risk of hyperlordosis increases significantly if a person is overweight, has bad habits, including smoking and drinking alcohol, or endocrine pathologies.
The reasons for the development of lordosis in the lumbar region may be:
- excessive load on the spine;
- pathologies of the musculoskeletal system;
- cerebral palsy;
- tuberculosis;
- brucellosis;
- rheumatism;
- lupus erythematosus;
- diabetes;
- vertebral fractures.
Video: “What does straightening lordosis mean?”
Classification
To get rid of lordosis, it is necessary to determine its type and degree of curvature.
Classification:
- Depending on the location and - lordosis of the cervical and lumbar spine.
- From the etiology of origin - secondary and primary. The latter appears as a result of pathological changes directly in the spine. Secondary is caused by external factors and defects of the musculoskeletal system.
- Taking into account the shape of the bend - physiological and pathological (hyperlordosis and hypolordosis).
- From the possibility of returning to the normal position - unfixed (it is possible to straighten the back), partially fixed and fixed (it is impossible to return to the normal position).
Treatment of lumbar lordosis
How to treat lordosis and is treatment possible at home? Only a doctor can answer these questions after making a diagnosis. And first of all, he prescribes the following set of conservative measures.
Exercises and gymnastics
Regular, daily performance of special exercises with a gentle load on the cervical and lumbar spine, working out the necessary areas strengthens the back muscles and helps normalize the blood supply to the spine. With this disease, this is a necessary part of treatment, which also contributes to the overall health of the body.
Gymnastics - the answer to the question “How to correct lumbar lordosis in children.” The fact is that exercises are especially effective in childhood.
Massage
Massage is indicated in most cases, unless there are contraindications. For example, in case of oncology, or detection of hemangiomas in the vertebral body measuring more than one centimeter, massage is contraindicated. There are other restrictions. Therefore, this procedure should be done only as prescribed by a doctor.
Massage procedures have an excellent effect in normalizing blood circulation, improving lymph drainage, restoring the outflow of venous blood, and helping to relax muscle spasms.
It is important to carry it out in systematic courses.
Drug therapy
Drugs are prescribed by the attending physician, depending on the stage of the disease, concomitant diagnoses and the presence of contraindications.
It can be:
- Medicines to relieve inflammation and pain (Movalis, Ibuprofen, Celecoxib). For severe pain, intramuscular injections are prescribed. You can use the gels “Fastum-Gel”, “Voltaren”, “Nice Gel”, “Diclofenac”.
- Vitamins, especially group B.
- Drugs that relieve muscle spasms (“Mydocalm”).
- In special cases, hormonal therapy is prescribed (Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone).
- Sometimes external compresses with medicinal drugs, for example, Dimexide, are prescribed.
Correct sleeping place
You need to pay special attention to organizing your sleeping area. Taking into account your weight, you need to choose a high-quality orthopedic mattress with independent spring blocks.
If severe pain is present, you can purchase a latex mattress that retains its shape. This will relieve muscle tension during sleep.
Manual therapy
If the vertebrae are stable, without deformation, and tumor formations are excluded, manual therapy sessions are prescribed.
During such procedures, a soft cushion or pillow should be placed under the patient's abdomen to elevate the deflection area of the spine.
The techniques are aimed at stretching the spinal column and increasing flexibility.
Not used during exacerbation of the disease.
Wearing a bandage
The bandage helps relieve stress from the lower back. A corset for lumbar lordosis is especially effective for weakened back muscles, in pregnant women (from 16 weeks) and in overweight patients.
The product must be correctly selected, only in this case will the therapeutic effect be achieved.
Surgical treatment
If conservative methods do not produce results, the patient’s condition worsens, and surgery is resorted to.
The procedure is very serious and is performed under general anesthesia.
It is carried out using two methods:
- The vertebrae in the area of lordosis are fastened with metal rods or plates
- Modern endoscopic techniques make it possible to remove affected discs. Instead, implants are installed to preserve the mobility of the spine. At the same time, the pathological curve in the lumbar region is corrected.
The recovery period is quite long. In some cases, up to one and a half years.
Symptoms
Signs depend on the type of disease. Common symptoms include changes in posture, pain in the neck or lower back, fatigue, and bulging of the abdomen.
Symptoms intensify after physical activity and being in an uncomfortable position.
Straightened lordosis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- protrusion of the head and shoulders forward, dizziness, decreased concentration, memory impairment (with curvature in the cervical spine);
- change in gait, feeling of numbness in the lumbar region.
It is imperative to get rid of the disease, since straightening the lordosis in the cervical region leads to impaired blood circulation in the brain; in the later stages, mobility may be limited.
With hyperlordosis, a person's appearance changes. The buttocks and stomach protrude forward, but the pelvis is tilted back, the legs move apart to the sides. It is very difficult to bend forward, as well as to sleep on your stomach. Such a dream causes severe painful sensations. The back muscles are constantly under tension.
Concept of Lordosis
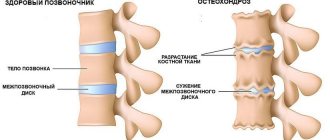
Lordosis (from the Greek lordos - curved) is one of the types of curvature of the spine, characterized by its bending forward . When the bulge is directed backwards, they speak of kyphosis, and to the side, they speak of scoliosis. A newborn's spine is almost straight. Changes in the lower back and the formation of the muscle corset are in full swing when the child learns to sit, stand and walk.
We can talk about the final formation of lumbar lordosis by the age of 18, when bone growth ends. By the same age, cervical lordosis and kyphosis - sacral and thoracic - are formed. At this stage, cervical lordosis is preserved, like kyphosis, throughout life.
If scoliosis is always a pathology, then lordosis and kyphosis can be physiological norms. The amount of deflection is important here. Doctors talk about flattened and hyperlordosis. Smoothed lumbar lordosis, what is it? If the lordosis curve is less than normal, it is called flattened; if it is more than normal, it is lumbar hyperlordosis. And these are conditions that require correct, timely diagnosis and treatment.
Physiological lordosis
With physiological, normal lordosis, the angle is 150-170°. In this case, when the body moves, the loads on the vertebrae are distributed evenly.
People often ask, “Lumbar lordosis is preserved, what does this mean?” Doctors believe that if the angle is within these limits (150-170), then this is the norm.
Pathological lordosis
If the doctor has doubts, an MRI, CT or X-ray is prescribed. If the angle deviates from the physiological norm, a diagnosis of Pathological lordosis is made. If lumbar lordosis is increased, this means that the structure of the spinal column is disturbed.
In this case, it is possible that the vertebrae may be displaced during sudden movements, pain may occur due to pinched nerves, or a disruption of the blood supply to the brain. Posture disorders are often noted. This pathology occurs in people of all ages, even children.
Physiological lordosis is smoothed if its angle is less than 150°.
What do the diagnoses mean?
After an X-ray examination, the attending physician can make the following diagnoses:
- physiological;
- hyperlordosis, that is, excessive bending;
- hypolordosis or flattened lordosis.
Lordosis is smoothed
Smoothing of lordosis – reduction of the physiological curvature of the lower back or neck. The angle is more than 169-172°.
The smoothing looks like a straight back, that is, there is no natural curve in the back of the head or lower back. At the same time, posture changes.
Straightened, as well as smoothed lordosis, requires medical attention at an early stage. It progresses at a rapid pace; within a year after diagnosis, you can notice a sharp deterioration in the patient’s well-being.
Lordosis preserved
If the diagnosis “lordosis of the spine is preserved” is made, then the curvature corresponds to the norm, that is, the angle is within the range of 150-170°. However, even with this, there is a possibility of developing spinal column disease. When exposed to unfavorable factors, pathological curvature of the spine may appear.
Lordosis increased
In other words, we are talking about hyperlordosis, that is, the bending angle is too pronounced, it is less than 145°.
Lordosis is aggravated by poor posture, pregnancy, congenital pathologies of the limb structure, and previous polio.
Prevention
Experts make the following recommendations for the prevention of lumbar lordosis:
- It is important to use a hard orthopedic mattress for sleeping.
- It is necessary to lead an active lifestyle (play sports, do exercises daily), while excluding excessive physical activity. One of the most beneficial and safest sports for the spine is swimming.
- It is worth paying attention to posture, especially when it comes to sedentary work. Periodic warm-up helps improve blood circulation and relieve tension from the vertebrae.
Simply put, the basis of health and a measure of prevention of any disease is the “correct” lifestyle. Sound sleep, proper rest, a varied and “healthy” diet and moderate physical activity allow you to avoid many diseases.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of lordosis consists of a visual examination of the patient and radiography. To identify the disease yourself, you need to stand with your back to the wall. In this case, you need to touch the wall with the back of your head, shoulder blades, buttocks and heels.
There should be a little free space in the lower back area so that the hand fits tightly. If the arm does not pass at all or moves too freely between the back and the wall, then this indicates lordosis.
A more accurate diagnosis can be obtained using x-rays of the spine in frontal and lateral projections.
Physical exercises for pathological lordosis
There are simple physical exercises that help correct poor posture and pathological lordosis. They can be successfully performed at home. So, lie down on the floor, with your legs and arms placed on a chair so that a right angle is formed between the hips and knee joints. With your left hand, try to reach the space between your lower back and the floor. When performing these exercises, you need to try to pull in your stomach as much as possible and try to move your pelvis anteriorly. Repeat 4-6 times.
Here are a number of very effective exercises used to eliminate pathological lordosis:
- The initial position of the patient is lying on his back. Raise your legs up, throwing them behind your head, and then returning to the starting position. Repeat 4-6 times.
- Starting position lying on your back. Perform abdominal pumping exercises - rising from the floor, without using your hands. Repeat 4-6 times.
- The starting position of a person is lying on his back. Slowly raise your legs at a 90-degree angle and also slowly return to the starting position. Repeat 4-6 times.
- Starting position standing. Perform vigorous bends while reaching your shins with your hands. Repeat 6-8 times.
- Stand against the wall. Relax and try to press your back and lower back completely against the wall. Repeat 10 times.
- Bend to the sides while keeping your arms on your sides. Repeat 6-8 times.
- Stand up straight. Rotate your entire body to the right and left without lifting your heels from the floor. Repeat 6-8 times.
You need to understand that treatment of pathological lordosis is, first of all, aimed at eliminating the cause that provoked the development of the disease.
Treatment
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to establish the cause of the disease. Otherwise, the therapy will be ineffective.
If lordosis appears due to excess weight, you need to lose those extra pounds.
Treatment of lordosis is complex, it includes:
- exercise therapy;
- swimming;
- massage;
- physiotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- traction and bandaging.
How to treat a disease with exercise therapy? A set of exercises is selected individually for each patient, aimed at strengthening the back muscles and relieving pain. If you practice daily, you can achieve good results in a short period.
You can't do it by force. Exercise may cause fatigue and minor muscle soreness, but should not cause severe pain.
How to correct your posture? To do this, you need to wear special corsets and bandages. These devices are especially effective for muscle weakness. They prevent the progression of the disease.
How to get rid of primary lordosis? Doctors most often resort to surgery. Secondary lordosis must be compensated if it cannot be corrected.
To eliminate the symptoms that arise during an exacerbation, you will need medications, namely painkillers, diuretics, corticosteroids and muscle relaxants.
Straightening in the early stages is much more effective than getting rid of advanced lordosis.
Diagnosis of lordosis
The main examination method for making a diagnosis is radiography in two projections. It can provide information about the presence of a bend, its location, and in some cases, the probable cause of the development of the bend. Using this procedure, you can identify various deformations of the spinal column: lordosis, kyphosis, scoliosis.
MRI and CT are more informative and expensive. Ultrasound examination can also be used to evaluate the structural and functional features of neighboring organs that are adjacent to the vertebrae.
Complications
Regardless of the type, lordosis of the spine leads to increased stress on the bones and muscles, and the ligaments are stretched. The person feels weak and lethargic.
If lordosis is not corrected at the initial stage, the following complications develop:
- mobility of the vertebrae, spontaneous dislocations;
- disc loss;
- intervertebral hernia, psoitis;
- deforming arthrosis.
Restricted mobility leads to loss of ability to work.
With hypolordosis, spondylosis, spondyloarthrosis can develop, the spinal cord can be compressed, and the functioning of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity, heart and lungs can be disrupted.
Possible consequences
If left untreated, the curvature begins to progress and discomfort increases as the hyaline cartilage is already destroyed. Restricted mobility of the spinal column and joints leads to disability over time.
If the chest is deformed, then disturbances in the functioning of many organs will occur. When lordosis is advanced, the diaphragm begins to work incorrectly, and this reduces the capacity of the lungs. As a result, intra-abdominal pressure changes. Over time, this will lead to a malfunction of the stomach, liver and other organs.
What kind of curvature could it be?
According to ICD 10 (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision), kyphosis and lordosis are coded M40.0. There are several degrees of development of the disease. The degree of kyphosis is expressed in degrees. In this regard, there are three degrees of increased kyphosis (also called pathological kyphosis). The bending angle, which characterizes kyphosis of the 1st degree, is increased by no more than 35 degrees. A curvature of 31 degrees is a sign that the patient has grade 2 kyphosis. Kyphosis of the 3rd degree is characterized by a curvature angle of more than 60 degrees. The classification, which includes four degrees of the disease “pathological kyphosis,” is also often used by doctors. 4 degrees of disease are most often used by international medical schools. The magnitude of the curvature can be characterized by the thoracic kyphosis index on a three-point scale.
Smoothed or straightened
There are 2 main types of lordosis – hypo- and hyperlordosis. Hypolordosis is relatively rare and is characterized by a curvature angle of more than 171°. That is, it is an almost unfolded angle, the sides of which lie on the same straight line. This means that the spine will be smoothed and almost straight.
The second type is hyperlordosis. The angle of curvature is up to 150°, but rarely less than 140°. With hyperlordosis, the lumbar or cervical deflection is increased, the contact between the vertebrae in the area of curvature is disrupted and becomes uneven. Adjacent vertebrae are in closer contact with each other in the back, and fan-shaped in front.
With smoothed lordosis, the back becomes flat, exaggerated lordosis makes the figure wavy
When they say that lordosis is preserved, they mean a normal, physiological bend with an angle of curvature in the range of 150-170°. The apex of the angle of this bend is located at the level of 3-4 lumbar vertebrae.
Features of cervical lordosis
So, the pathology is an arc, convex forward (from the back - deflection). It is characterized by pain that occurs in the neck, head, shoulder girdle, and numbness in the forearms and hands. In addition, posture is disturbed.
Important! According to the frequency of diagnosis, cervical lordosis is evenly distributed between male and female patients. It occurs in the age range of 16-35 years. And if lordosis is detected in a child under 16 years of age, then this is a congenital pathology and not an acquired disease.
Women who spend all day in high heels are more likely to suffer from hyperlordosis
There are several reasons for the pathological phenomenon. Moreover, congenital can arise from only two of them. Either these are problems with intrauterine development, or a spinal injury that occurred during childbirth. As for the acquired form, below are all the reasons for its appearance.
Table. Why does acquired lordosis form?
| Cause | Description |
| Injuries | Any injury to the cervical spine, be it a fracture or an ordinary bruise, can lead to curvature later. |
| Chronic diseases | Neck lordosis can result from one or more chronic diseases of the cervical spinal region. |
| Ankylosing spondylitis | Ankylosis (fusion) of the vertebral joints in this disease makes them less mobile and increases the amplitude of bending. |
| Arthritis | Lordosis can occur due to rheumatoid cervical arthritis. |
| Osteochondrosis | With this disease, when it is localized in the cervical area, there is also an increase in the amplitude of the curvature. |
| Tumor | Any tumor-like formation that is malignant and formed in the cervical area or nearby can cause deformities that will result in lordosis. |
| Hernia | If intervertebral discs located in the cervical area are susceptible to herniation, this may result in cervical lordosis. |
| Radiculitis | With radiculitis of the cervical area, the amplitude of the deflection of the vertebrae changes. |
| Inflammation | If inflammatory diseases of this vertebral zone occur in an acute form, they can cause deformities. |
| Muscle spasm | It's called contracture, and it can happen for a variety of reasons. If the spasmodic state is prolonged, displacement of the vertebrae may occur. |
| Spondylitis | It begins as a result of bacterial infection and causes pathological changes in the vertebrae. |
Cervical lordosis can develop due to rheumatoid arthritis
In addition to the reasons that cause pathological curvature, there are a number of factors that can promote, provoke and aggravate it.
Predisposing factors.
- Obesity.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Exchange disorders.
- Smoking.
- The child's spine grows too quickly.
- Alcoholism.
Obesity together with poor diet contributes to the development of lordosis
Curvature of the spine - what to do?
If self-diagnosis reveals a problem, you should immediately seek medical help. In the initial stages, the deformity can be corrected. Not knowing how to treat spinal curvature can only make your situation worse. Due to lost time, the deformation intensifies, and the disease moves to a new stage of development. In addition, only the doctor knows what not to do if a curvature of a weakened spine is diagnosed.
For scoliosis (regardless of the degree of development of the deformity), the following prohibitions exist:
- You cannot maintain the same body position for more than half an hour. In addition, every hour you need to do a 5-minute warm-up to relax your back muscles.
- Exercises on horizontal bars are prohibited.
- You cannot carry weights in one hand. It is advisable to carry the load in a backpack.
- Heavy physical work that places heavy strain on the back is prohibited. Such activity can lead to the formation of intervertebral hernias. As a result, surgery will be required.
Curvature of the spine - which doctor should I contact?
The patient should refer his complaints to a therapist. This specialist will carefully assess the clinical situation and prescribe a diagnostic test. Then he will decide which doctor to refer the person to. If C-shaped scoliosis or other deformity of the spinal column is previously diagnosed, you may need to consult the following specialists:
- neurologist;
- orthopedist;
- vertebrologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- oncologist;
- surgeon
Curvature of the spine - treatment
To eliminate the initial stage of deformation, an integrated approach is required. This treatment includes:
- drug therapy;
- massage;
- physiotherapy;
- therapeutic exercises.
The following medications are most often prescribed:
- chondroprotectors (Glucosamine, Chondroitin);
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ketorol, Melbek, Nimesulide, Nalgesin, Dicloberl);
- muscle relaxants (Mydocalm, Tolperisone);
- vitamin-mineral complexes (Complivit, Supradin, Centrum, Pikovit).
Physiotherapy includes the following procedures:
- acupuncture;
- electrophoresis with anabolic steroids;
- magnetic effect on the affected area;
- hirudotherapy;
- underwater spinal traction;
- swimming.
Therapeutic exercises for curvature of the spine are also effective. At the first stage of therapy, they should be performed under the supervision of an instructor. He knows how to correct the curvature of the spine without causing harm. This specialist, taking into account the permissible load, will individually select a set of exercises for the patient. After some time, you can switch to home procedures: perform therapeutic exercises yourself.
With this pathology, massage is also highly effective. It should be performed by an experienced specialist. A competent massage helps to relax tense muscles and activate tight ones. This procedure improves blood circulation and metabolism, and also calms the nervous system. The treatment course consists of 15-20 sessions. After this, they take a 2-month break and repeat the procedures again.
If conservative therapy does not give the desired result or the disease is too advanced, surgical intervention is required. During surgery, metal plates are attached to the spine. They help eliminate existing violations. After 2-3 years, a repeat operation is performed, during which the metal structures are removed.
Symptoms: how to determine lordosis
Physiological lordosis is a natural bend that ensures normal functioning of the musculoskeletal system. Pathological lordosis is dangerous to health and its treatment is mandatory!
The development of pathological lordosis in schoolchildren occurs due to failure to maintain normal posture while reading, doing homework and schoolwork. In adults, pathological lordosis develops when spending a long time at the computer or watching TV.
The development of primary cervical lordosis occurs as a result of complications - inflammation, tumors.
Secondary cervical lordosis is formed against the background of birth injuries.
Read more about the types and causes of lordosis in this article.
Symptoms of hyperlordosis:
- A low-set head that protrudes sharply forward.
- Visually incorrect posture is a clear bend in the neck.
- Pain in the affected area of the neck.
- The appearance of pain when turning the head.
- Limitation of head movement to the left and right due to unpleasant discomfort.
With straightened lordosis, restrictions in movements are revealed.
There is a disturbance in blood flow, which disrupts the nutrition of the brain. This syndrome is dangerous due to fainting and ischemic stroke. Symptoms of straightening cervical lordosis:
- Pain in the neck is severe.
- Frequent fatigue and depressed mood.
- Constant headaches, frequent dizziness.
- Signs of skin numbness.
- Feeling of darkening in the eyes.
- Decreased appetite.
- Trophic disorders.
At an advanced stage of lordosis, disturbances in the cardiovascular system, breathing, and disturbances in heart rhythm are noted.
Symptoms of lumbar hyperlordosis:
- Lumbar pain. Aching, sharp.
- Incorrect posture in the form of a curved lower back.
- A protruded belly and excess weight aggravate the curvature.
- Deviation of the entire body and pelvis backwards.
- Knees spread apart.
- Fatigue when walking and standing for long periods of time.
With smoothed lordosis, compression syndromes are observed. Soreness appears in various places around the spine, heart of the stomach, etc.
Symptoms of straightened lordosis in the lower back:
- Pain and limitation of movement in the lumbar region.
- Tiredness when walking and standing.
- Feeling of numbness in the back and legs.
- Change in gait.
- Feeling of flat back when palpating.
If treatment is not prescribed on time, the disease is aggravated by disorders of the internal organs - gastrointestinal upset, heart pain, metabolic disorders.
Symptoms of hypo- and hyperlordosis of the lower back
The specific symptoms of pathological lordosis may vary, since it all depends on the characteristics of the body, general health and concomitant diseases. It is necessary to take into account how far the vertebra has shifted, how damaged the nerve endings are and whether the functioning of the internal organs is disrupted. Also, the disease may manifest itself differently if there is any change in other departments. However, some signs of pathological lordosis are the same for all patients:
- Backache.
- Discomfort in the lower extremities.
- Poor posture.
- Sleep problems.
- Malfunctions in the functioning of internal organs.
The initial symptoms of pathological lordosis do not cause serious concern. The only manifestation of the disease is mild fatigue and discomfort when standing for long periods of time. After a short rest, the unpleasant sensations go away, and pathological changes continue to develop. Over time, the discomfort increases, but goes away after bending forward or sleeping on a hard surface.
Symptoms of the disease may differ depending on the form of pathological lordosis.
With hyperdordosis, changes such as:
- Shifting the buttocks back.
- Severe protrusion of the abdomen.
- Back muscle tension.
- Inability to sleep on stomach.
- Difficulty bending forward.
- The appearance of a large distance between the lower back and the floor.
When the lordosis of the lumbar spine is increased, when trying to lie on the stomach, the spine is aligned - and pain occurs. Also, discomfort increases when bending forward, which involves the hip joints.
Hypolordosis manifests itself differently:
- Back pain.
- Flattening of the spine.
- Rapid fatigue in sitting and standing positions.
- Change in gait.
- Feeling of numbness in the affected area.
If a person decides to arch their back back with lumbar lordosis, they will feel increased pain. Also painful is the attempt to increase the angle of lordosis to normal levels through arching and fixing. In order for lordoscoliosis to be successfully defeated, correct diagnosis and competent medical care are required.
Lordosis during pregnancy
During the period of bearing a child, deformation of the musculoskeletal system can be a secondary disease as a result of injuries, inflammatory diseases, and physical activity. There is also lordosis in pregnant women, which is not dangerous and is reversible. The appearance of such a bend in the spinal column is due to the fact that as the fetus grows, the stress on the back increases. To withstand this load, the spine is deformable. Pregnant women experience a typical appearance when walking: the body is slightly tilted forward, the legs are separated at the knees, and the gait is unnatural. A woman may be concerned about low blood pressure, weakness, and fatigue.
After the birth of the baby, the tension on the musculoskeletal frame is relieved. In order for the spinal column to return to its physiological position, during pregnancy you need to perform special exercises and wear a corset for lordosis in order to prevent irreversible changes in the internal organs.
If the woman in labor listens to all the advice of the attending physician, after the birth of the child, the deformity will disappear.
Prevention and consequences of lordosis
Complications of the disease include the following conditions:
- degenerative processes in the intervertebral discs, resulting in the development of osteochondrosis;
- disruption of the pelvic organs: frequent constipation, urination disorders, sexual activity disorders in men, dysmenorrhea in the female population;
- intervertebral hernia;
- deformation of the diaphragmatic muscle, resulting in breathing disturbances and changes in the functional parameters of the lungs.
A number of recommendations have been formulated that are aimed at preventing deformities of the musculoskeletal system, they are as follows:
- maintaining the correct posture while walking and sitting;
- choosing a suitable quality mattress for sleeping;
balanced diet with a full range of vitamins, minerals, trace elements and other essential nutrients;
Forecast
The prognosis for lordosis in adults varies, but is generally favorable. As a rule, pathology develops slowly, which makes it possible to identify it and eliminate it before critical consequences appear. At the same time, patients’ normal lifestyle is not disrupted.
The prognosis worsens under such circumstances as:
- previous diseases or injuries of the affected part of the spine;
- involutive disorders that appear in old age;
- advanced conditions due to late presentation of the patient to the clinic.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
2, total, today
( 61 votes, average: 4.87 out of 5)
Osteomalacia - symptoms and treatment in adults and children
Compression fracture of the spine
Related Posts
Symptoms and treatment of cervical and lumbar lordosis of the spine
Treatment of this disease is a very labor-intensive and lengthy process, especially if the lumbar lordosis is smoothed. You need to understand that in addition to compulsory gymnastics, you will have to undergo several massage courses, physiotherapeutic procedures and other types of treatment.
If lordosis is straightened, what does it mean and how to treat? In order to understand that you can independently diagnose straightened lumbar lordosis, just stand with your back against the wall and press your buttocks and shoulders against it.
If you cannot put your hand between the wall and your back in the lumbar region, then with almost one hundred percent certainty you can talk about straightened lordosis.
The main method of treating the disease, of course, should be therapeutic exercises. Only with its help can you strengthen your back muscles and relieve pain. Exercises for lumbar lordosis should be performed with pleasure and regularly.
It is also necessary to undergo a massage course every few months, which helps restore blood supply. Another popular treatment method is spinal traction.
However, this method is not suitable for everyone and should only be used under the supervision of a specialist. A neurologist can also additionally prescribe drug therapy.
Lie flat on your back. At the same time, spread your arms in different directions. Raise your legs slowly, pulling them as close to your head as possible.
Useful different inclinations that help strengthen your back and make your spine more flexible. The legs can be together, or they can be shoulder-width apart.
Surgical intervention
The progressive development of the disease, acute back pain, complete muscle atrophy, respiratory and circulatory disorders, vertebral fractures, congenital kyphosis - these are indications for surgery that will help correct kyphosis. Spinal surgery is a fairly complex type of surgery. They are performed under anesthesia. Sometimes several operations are required to cure a disease. Two surgical techniques can be used: osteotomy and kyphoplasty. The advantage of kyphoplasty compared to osteotomy is the use of an endoscope and small incisions, which makes this method effective for microtrauma of the spinal column. However, this method also has disadvantages - it is less effective in advanced cases than osteotomy.
To fix the spine, the surgeon installs metal structures made of low-active metals and alloys. The most common of them are titanium and titanium nickelide. They are not rejected by the body and do not enter into chemical reactions with intercellular fluids. Therefore, implants can remain in the body for many years and not bother a person.
Types of spinal curvature
The main danger of this group of diseases is not the physical defect they create, but the fact that these pathologies provoke a malfunction in all systems of the human body. This is due to the fact that when the column is deformed, blood circulation is disrupted and dysfunction of internal organs occurs. When neglected, such pathologies provoke serious limitations in ability to work. There are the following types of spinal curvature: kyphosis, lordosis, scoliosis. Each such pathology has its own developmental characteristics.
Scoliosis of the spine
This pathology is represented by a complex deformation of the column. It is accompanied by curvature in the lateral plane. With such deformation, the vertebrae can twist, which increases the physiological bends of the column. Due to changes in the location of the bones of the chest, the position of nearby organs shifts. The heart and lungs are most affected.
Lateral curvature of the spine is diagnosed in 30% of cases with pathologies of this organ of the musculoskeletal system. According to etiology, scoliosis can be of the following types:
- Congenital
(also called dysplastic) is a disorder that occurs due to malformations of the fetus. - Acquired
- a pathology diagnosed after some illness or injury. - Idiopathic
- a disorder whose cause is not clear.
Depending on the number of arches, the following types of scoliosis are distinguished:
- C-shaped
is the most common pathology. It is characterized by one arc of curvature. - S-shaped scoliosis
is a disorder in which there is deformation of two arches (scoliotic and compensatory). Pathology develops in the overlying part of the spine. For example, if the lumbar region is deformed to the right side, then a left-sided displacement occurs in the thoracic segment. - Z-shaped
- the most severe violation. It is diagnosed very rarely. This deformation is characterized by the formation of three arcs of curvature.
In addition, scoliosis can be of the following types:
- right-handed;
- left-handed.
Depending on the area of location, spinal curvature can affect the following areas:
- Cervicothoracic
- the apex of the scoliotic arch is located near the 4-5 vertebrae of the thoracic segment. Its upper part is on the neck. Subsequently, a compensatory arc is formed. - Thoracic
(this type of scoliosis is also called thoracic) – the apex of the arch is located at the 7-8 vertebrae of the department of the same name. Right-sided deformity is more often diagnosed. This curvature of the spine rapidly progresses and quickly leads to disability. - Thoracic lumboscoliosis
(this scoliosis is also known as thoracolumbar scoliosis) is a deformity whose apex is located in the area of 10-12 thoracic vertebrae. Right-sided pathology develops more intensively. With left-sided curvature, the disease progresses at a slow pace and is accompanied by a less pronounced clinical picture. - Lumbar scoliosis
(also known as lumbar scoliosis) is a common pathology. Left-sided deformity is more often diagnosed. - Lumbosacral
is a rare curvature of the spinal column. The apex of the arch falls on the lower lumbar segment.
Spinal kyphosis
The term used to designate it helps to understand the features of this pathology. Literally, “kyphos” translates as “crooked” or “hunched over.” This pathology occurs at any age, but is more often diagnosed in children and adolescents. The following types of disease are distinguished:
- congenital;
- juvenile (more often affects boys than girls);
- postural (results from poor posture);
- paralytic;
- post-traumatic (progresses at a rapid pace);
- postoperative;
- degenerative;
- rachitic;
- senile
Kyphosis of the thoracic spine and its other segments can be of the following degrees:
- Stage 1 – the angle of deformation is 31°-40°;
- Stage 2 – the arc of curvature varies between 41°-50°;
- Stage 3 – the angle of curvature is 51°-70°;
- Stage 4 – the arc of curvature is greater than 71°.
Kyphosis can affect the following areas:
- cervical;
- chest;
- lumbar.
Spinal lordosis
With such a pathology, the convexity of the deformity is directed forward. Physiological lordosis is needed for:
- head support;
- shock absorption during movement;
- walking with your head straight;
- facilitating bending.
Normally, a healthy person has lordosis of the lumbar and cervical spine. However, such curvature can change pathologically. Taking into account the causes of the problem, the following types of lordosis are distinguished:
- primary – bending occurs due to the growth of the formation;
- secondary – a defect caused by injury to the spinal column.
Based on the time of onset of deformation, the following types of pathology are distinguished:
- congenital;
- acquired.
Depending on the type of deviation, there are two types of defects:
- hyperlordosis (bending more than normal);
- hypolordosis (the angle of inclination is almost flattened).