Prostatitis can affect potency or cause infertility. The success of treatment largely depends on how quickly treatment was started, so the man must independently pay attention to the first signs. Let's look at how prostatitis manifests itself in acute and chronic forms, and also provide information about clinical manifestations and symptoms.
What is prostatitis
About 40% of men in the entire world population know what prostatitis is. This is a prostate disease caused by an attack by inflammatory agents. As a result of their exposure, unfavorable microflora develops, which, if left untreated, causes complications.
Prostatitis in men usually begins acutely, with typical clinical manifestations. But the danger of the disease lies in the fact that it can also occur covertly, gradually turning into a chronic stage.
The most susceptible to inflammation of the prostate gland are men aged 30-50 years, leading an inactive lifestyle and having bad habits. But recently the disease has begun to “get younger” and occur even in young guys aged 20-25 years.
Pathology treatment methods
In modern medicine, there are many methods for solving problems related to men's health. Help is provided in inpatient and outpatient settings. The method of treatment is chosen taking into account the clinical picture, the period of limitation of the pathology, and the general condition of the body. Before prescribing therapy, the patient must be examined to determine the cause of prostatitis.
Drug treatment
Therapy is selected individually. For informational purposes, we will consider an approximate treatment regimen for prostatitis in men.
- In case of bacterial etiology of the disease, antibiotics must be prescribed. The most commonly used drugs are Amoxicillin, Summamed, Cifran, Gentamicin, Tavanic and other medications based on penicillin and ciprofloxocin.
- Alpha adrenergic blockers help with the chronic course of the disease (Finasteride, Omnic, Tamsulosin, Alfuzosin). The drugs have an analgesic and anti-edematous effect.
- It is advisable to take non-steroidal medications if the patient is diagnosed with an acute form of the disease (Nimesil, Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Paracetamol). For prostatitis, drugs in the form of suppositories have an effective effect on the body.
Important! Finding an effective medicine for inflammation of the prostate gland on your own is very difficult. Errors lead to worsening of the pathology, transformation of the acute form into the chronic stage.
Surgical methods
Recently, many other innovative ways to get rid of the problem have appeared. Therefore, surgical intervention is used extremely rarely.
Transurethral resection is performed in a closed manner to remove part or all of the prostate gland. Relief occurs after the pressure on the urinary canal is relieved and pain disappears.
Adenectomy is performed using the open method. During the operation, the gland is removed using surgical instruments. After the procedure, the patient expects a long recovery.
Non-surgical methods
Innovative methods of combating prostatitis have been recognized as quite effective. All manipulations can be classified as gentle methods of therapy, i.e. less painful.
- With transurethal microwave treatment, prostate tissue is reduced by high temperature.
- Inflamed tissue is amputated using cryodestruction. The method is based on the effect of liquid nitrogen on the prostate.
- One of the most effective methods of therapy is the use of ultrasound. Its waves affect the inflamed prostate. The technique is absolutely painless.
- Laser treatment gives good results at any stage of the disease. Under the influence of the beam, coagulation occurs, evaporation of fluid from the prostate tissue. Along the way, the procedure has a positive effect on local immunity and regeneration processes.
- The balloon urethral dilation method involves widening the urethra. During the procedure, a catheter is inserted into it. On the outside of the device there is a balloon that supplies air to dilate the urethra.
- The use of laser and magnet in combination improves blood circulation, reducing congestion. In the area of influence, cell regeneration is accelerated, and pain can be eliminated. The effectiveness of medications is further enhanced.
- Stenting involves widening the walls of the urethra. The procedure involves the introduction of a special cylindrical frame into the canal. It is made of polymer materials.
Most often, prostatitis at 30 years of age is easier to cure than at 50. The younger the body, the more active its immune system is. But even in old age, the main thing is to choose the right therapy, reconsider your lifestyle, and strictly adhere to all the recommendations of your doctor.
Having learned about all the causes that provoke inflammation, it becomes clear that pathology can occur at any age. Absolutely all representatives of the strong half of humanity need to monitor their health and know what causes prostatitis.
Signs of prostatitis
Symptoms of prostatitis in men rarely appear at the initial stage. Primary signs are weak and often go unnoticed. This causes the disease to become purulent or chronic.
Knowing the first signs of prostatitis in men, you can prevent complications such as impotence and cancer. What symptoms should you pay attention to:
- frequent, painful urination;
- deterioration of potency, early ejaculation, lack of ejaculation, decreased libido;
- pain during defecation;
- pain in the abdomen, sacrum and groin area;
- weakness, drowsiness, general malaise;
- increased sweating;
- increased body temperature, signs of intoxication: headache, fever, etc.
The main symptom of prostatitis in men is pain. It can be pronounced or weak, extending to the lumbar and groin area. Often the patient cannot determine the source of pain, since it radiates to other organs.
Dysuric disorders occur in acute and chronic forms of male prostatitis.
They manifest themselves as frequent urination with a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. The urge bothers you even at night, forcing you to wake up several times. In this case, a small amount of urine comes out in the toilet, and the process itself is accompanied by painful sensations. This symptom of prostatitis is very similar to the symptoms of bladder stones.
It is necessary to consult a doctor in time to make an accurate diagnosis and prevent complications. Sexual function disorders tend to increase. One of the main signs of prostatitis in men is decreased erection. As the disease progresses, the quality of sexual life deteriorates, and sex ceases to be enjoyable. There is a deterioration in reproductive function. Inflammatory prostate disease in men can cause infertility.
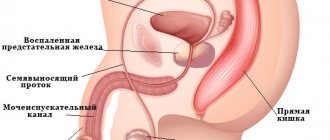
Inflammation of the prostate: symptoms caused by prostatitis and other diseases
The symptoms of various diseases periodically coincide. How to distinguish the symptoms of prostatitis from the symptoms of other diseases of the male genitourinary system? The most reliable and correct way is to go to the clinic to see a specialist who will examine you, take all the necessary tests and conduct a detailed examination. Bladder cancer, prostate adenoma, cystitis, urethritis, inflammation of the prostate - their symptoms largely repeat each other.
Cystitis, urethritis and prostatitis have equally frequent and painful urination with a burning sensation, especially at the end of the process, and difficulty emptying the bladder. In all cases with these diseases, the urine may be cloudy and contain blood. Weakness, nausea, and fever are often felt.
Adenoma (benign tumor) of the prostate gland and prostatitis together have the following signs of the disease: the prostate is enlarged in size, pressing on the urethra, it prevents the complete and easy emptying of the bladder, the patient experiences a false urge to urinate. The stream of urine is thin, intermittent, does not have the proper pressure, there are frequent cases of stagnation in the bladder, disturbances in night sleep due to frequent visits to the toilet.
Bladder cancer and prostate inflammation: the symptoms of these two diseases are also largely similar. Painful urination, pain in the lower abdomen, blood in the urine, a feeling of fullness in the bladder after visiting the toilet and chronic fatigue.
How, then, can one distinguish the symptoms of prostatitis from the symptoms of other diseases, since they are so similar in their manifestations?
The fact is that during the examination, the doctor identifies and examines the entire picture of the disease as a whole, supplementing it with tests, non-invasive diagnostic data and the presence of other symptoms characteristic only of specific diseases. And only after being completely confident in the correctness of the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes antibiotics, procedures and other therapeutic measures.
Causes and provoking factors
The reasons for the development of prostatitis are different and relate, first of all, to non-compliance with the rules of contraception and a healthy lifestyle. Although the disease often occurs against the background of infectious processes in the genitourinary system.
Causes of prostatitis include:
- sexually transmitted sexually transmitted diseases;
- hypothermia;
- inactive lifestyle (sedentary work);
- stagnation of blood in the prostate gland and surrounding tissues;
- chronic constipation;
- decreased immunity;
- protection through interrupted sexual intercourse;
- perineal injuries;
- wearing tight underwear;
- alcohol abuse, smoking.
Diseases causing prostatitis syndrome:
- urethritis;
- haemorrhoids;
- foci of bacterial infection;
- diseases of the rectum;
- chlamydia, gonorrhea and other STDs.
Prostatitis is often a consequence of an unhealthy lifestyle. Provoking factors include:
- unbalanced diet, predominance in the diet of foods that increase the load on the body (fried, fatty foods, fast foods, etc.);
- frequent stress and solving it through alcohol and drugs;
- smoking. Reduces the body's protective functions;
- lack of sleep;
- low physical activity and, conversely, overtraining.
To prevent inflammation of the prostate gland, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle, promptly treat existing pathologies and use barrier contraception.
It’s not for nothing that the prostate is called a man’s second heart. With diseases of this organ, the quality of life deteriorates, the nervous system suffers, and the psychological state is disturbed.
.
Causes
In pursuit of a successful career and material well-being, men forget about their health. The occurrence of prostatitis is due to many reasons, but the main one is neglect of the body.
The inflammatory process occurs due to poor circulation. Sedentary work, as well as obesity, can provoke pathology. Prostatitis occurs from mechanical injuries to the genital organs. Damage to soft tissues disrupts blood circulation in them, as a result of which the prostate increases in size and becomes inflamed. Damage can be caused not only by a strong blow to the groin, but also by vibrations, shaking, and stress on the perineal muscles.
The choice of sexual partners should be taken with particular seriousness. Casual relationships end in infection with infectious and sexually transmitted diseases, which in turn can provoke prostatitis. The bacterial flora affects not only the external genital organs, it enters the urethra, prostate gland and even the kidneys.
Prostatitis appears most often against the background of such diseases as:
- gonorrhea;
- urethritis;
- chlamydia;
- ureaplasmosis;
- tocoplasmosis;
- gardnelosis, etc.
To cure prostatitis, you first need to eliminate the sexually transmitted infection. Both sexual partners must undergo treatment, otherwise re-infection is possible.
The cause of prostatitis is sometimes hidden in hypothermia and sexual abstinence. Lack of sexual contact and hypothermia cause congestion in the pelvic organs. Blood flows poorly into the prostate and an inflammatory process occurs. A similar situation occurs in the presence of varicose veins of the perineum and atherosclerosis. Due to vasoconstriction, blood circulates poorly in the body, and the gonad experiences hypoxia.
The appearance of prostatitis may be due to the presence of chronic diseases:
- diabetes;
- multiple sclerosis;
- endocrine diseases;
- hormonal imbalance;
- pathologies of blood vessels and heart;
- osteochondrosis.
Each disease has its own impact on a man’s sexual health. Spinal injuries, multiple sclerosis and cardiovascular diseases are accompanied by circulatory disorders. With endocrine pathologies, there is a lack of testosterone, which reduces the functionality of the prostate gland, inhibits erection and reduces sperm production.
Important!
If prostatitis is not treated, a man will face complications. Bacterial flora, which is activated during inflammation, negatively affects the functioning of the liver and kidneys.
The presence of inflammation in the urethra or rectum can also cause prostate infection. Bacteria, along with contaminated urine, rise through the urethral canal and partially enter the gland.
Types and forms of prostatitis
Manifestations of prostatitis depend on the type and form of the disease. This parameter also helps determine the treatment method.
Acute form
This is the very beginning of prostatitis, which has pronounced clinical symptoms. The development is caused by microorganisms that can live in the body permanently and not cause harm. But with a decrease in immunity, they become more active and begin to actively multiply, affecting the genitourinary system.
The acute form is characterized by rapid development. First, the body temperature rises, then pain and discomfort join this symptom.
Chronic form
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis in men are mild or may be absent. The main symptom is difficulty urinating, accompanied by pain in the groin area.
But the absence of manifestations does not mean that the pathology can go away on its own and is not dangerous to health. It is the chronic form that causes prostate adenoma and other pathologies of the genitourinary system.
The peculiarity of this form is that with a decrease in immunity, the disease returns to the acute stage. And each relapse becomes more pronounced and painful.
Chronic prostatitis is divided into the following types:
- Bacterial. The cause is bacteria, which are activated when immunity decreases. This type also includes inflammation of the prostate gland caused by sexually transmitted diseases. The first sign of bacterial prostatitis is pain and burning during sexual intercourse and urination.
- Calculous. The cause is the accumulation of stones. This type is rare and occurs predominantly in older men. A typical sensation with calculous prostatitis is pain in the sacrum and groin area when walking.
- Stagnant. This is a non-infectious form of the inflammatory process caused by stagnation of blood in the pelvis. Provoking factors are a sedentary, sedentary lifestyle. Also, insufficient number of sexual contacts or complete absence of sex. It manifests itself with symptoms such as pain when urinating and in the groin area.
- Infectious. This type is similar in characteristics to the bacterial species. The infectious form is caused by fungi and single-celled microorganisms that penetrate from other organs of the genitourinary system. The provoking factor is a decrease in immunity.
- Purulent. A severe form of the disease that is infectious in nature. Signs of purulent prostatitis in men include an increase in body temperature to 39 degrees or more, symptoms of general intoxication and purulent discharge from the urethra.
Based on the first signs of prostatitis, it is almost impossible to determine the form and type of the disease. Diagnosis and thorough examination of the condition of the prostate gland is necessary.
Office workers are 80% more susceptible to prostatitis than men working in other fields
.
How to suspect the onset of the disease
If a man has not had prostatitis before, he may be at risk of acute inflammation of the prostate gland. Its development begins with an increase in general body temperature. It can rise to 40 degrees. This symptom is accompanied by severe chills. At the same time, difficulties in the process of urination begin to appear. It becomes painful and uncomfortable. After visiting the toilet, a man does not feel significant relief.
At this stage of the development of an exacerbation, swelling of the prostate occurs, which provokes urine retention in the body. A man who develops the initial stage of acute prostatitis will complain of constant pain in the perineum, anus and groin.
Pain
With pathology, the lower back hurts a lot
Men who have experienced an inflammatory disease know that pain is the first symptom characteristic of prostatitis. They can accompany infectious and non-infectious pathologies. The first variant of the disease is more common among representatives of the stronger sex who have sexually transmitted infections.
Due to the disease, the man suffers from severe pain and cramping in the urethra. The appearance of a burning sensation in the same organ cannot be ruled out. These symptoms are especially pronounced at the time of urination.
Patients begin to experience pain in the perineum and testicles. The pain syndrome can spread to the joints. In this case, the pain is nagging and dull. The pain increases significantly when a doctor performs a rectal examination of the prostate.
The non-infectious form of prostatitis most often occurs in older people. It is caused by leading a sedentary lifestyle, which leads to stagnant processes in the body. Due to illness, men may complain of pain in the lower back and perineum. They radiate into the scrotum and pelvis. The pain syndrome with this disease suddenly appears and goes away as well.
Discharge
The initial signs of acute prostatitis are not limited to pain. As with the chronic course of the disease, men experience abnormal discharge, indicating inflammation.
Unnatural discharge from the genitals indicates that pathogenic bacteria are present in the body, namely cocci, proteus and E. coli. These are the most common pathogens that can cause prostatitis.
There are several types of discharge, the presence of which in a person can suspect the development of prostatitis:
- Spermatorrhoea. This is the name for the release of droplets of sperm, which cannot be controlled. This phenomenon has nothing to do with a man’s arousal or orgasm. Such discharge usually occurs during exercise, urination and defecation. They are considered quite scarce and flow out very slowly.
- Prostate discharge. They can be observed even in a man who is in good health. Therefore, they are considered to be the norm. This liquid contains mucus cells that have died. The amount of discharge increases significantly if the prostate gland becomes inflamed.
- Purulent masses. They appear by the time the disease becomes advanced. Pus may contain blood impurities. Because of this, it turns brown. The mass itself is colored green or yellow.
Purulent discharge is considered the most dangerous, as it indicates a strong progression of the inflammatory process, which reaches its final point. Pus appears after pathogenic microflora appears in the lower part of the urethra. Because of this, stagnation of secretory fluid occurs and clogging of the excretory ducts.
Danger of prostatitis
In the absence of timely, adequate treatment for prostate inflammation in men, there is a risk of complications. These include:
- Urethritis. This is an inflammation of the genitourinary canal that occurs due to the spread of infection from the prostate gland to nearby organs. But urethritis itself is not dangerous, but the kidney failure that appears against its background poses a serious threat to health and life.
- Vesiculitis. This is an inflammation of the seminal vesicles, leading to erectile dysfunction and infertility.
- Abscess. This is a possible complication of the purulent form of prostatitis, in which pus accumulates in the prostate gland. Abscess with improper treatment and its absence leads to death.
- Adenoma. Inflammation of the prostate gland leads to its dysfunction and benign formations. The tissue growth is prostate adenoma.
- Cancer. Adenoma and chronic prostatitis are the main causes of cancer. And due to weak clinical signs, it is very difficult to differentiate it from other pathologies of the genitourinary system.
- Infertility. The prostate gland is involved in the synthesis of spermatozoa necessary for successful fertilization of the egg. When this organ becomes inflamed, the natural process of procreation is disrupted.
When inflammation of the prostate in men causes unpleasant symptoms, this leads to psychological discomfort. The patient's quality of sexual life deteriorates and signs of inferiority appear. Against this background, there is discord in the family, isolation, and depression. Therefore, prostatitis and neurological diseases are closely related.
Treatment of prostate inflammation
If the disease is chronic and not complicated by purulent processes, the patient can be treated at home, under the outpatient supervision of a urologist, otherwise hospitalization will be required. Therapy has three goals: stopping the inflammatory process, destroying the infectious agent and eliminating symptoms.
For this they may recommend:
- a course of medications;
- special food;
- physiotherapy.
Prostate massage plays a secondary role in inflammation of the prostate gland and is not always effective, therefore it is prescribed according to individual indicators. It is impossible to cure the disease using mechanical action alone, and with an illiterate approach, the condition can be aggravated. Rectal massage is contraindicated for calculous prostatitis, adenoma, prostate cancer, as well as for some pathologies in the rectal area. You cannot do it yourself.
Drug treatment
It is impossible to cure a bacterial form of prostate inflammation without antibiotics. There are different types of these drugs, the selection of the right drug is carried out taking into account the type of microorganism (determined by bacterial culture), the man’s health status, his age and other factors.
The modern approach to therapy involves the prescription of broad-spectrum antibiotics. These include:
- Sumamed;
- Doxycycline;
- Amoxiclav;
- Tavanik;
- Cefspan.
The treatment regimen and dosage are individual.
To eliminate inflammation, various anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Prostatilen has proven itself well - suppositories or injection solution. The main substance of the drug is animal prostate extract. After the course of treatment, there is a decrease in swelling of the gland and a decrease in the area of inflammation. At the same time, the functioning of the immune system is regulated.
Prostatilen is not prescribed in the presence of cardiovascular diseases and increased blood clotting. The dosage and dosage form are selected by the doctor; rectal suppositories are most often prescribed.
As necessary, painkillers and antipyretics are prescribed, vitamin-mineral complexes and dietary supplements are selected.
Diet
The patient's diet is calculated in accordance with the daily nutrient requirements and taking into account the man's body mass index. At the same time, the doctor tries to select products that will help restore prostate tissue and excludes anything that will increase the load on it.
If you have prostate inflammation, you should not eat:
- fatty meats and fish;
- spices and herbs;
- alcohol, strong coffee;
- marinades, canned food, pickles;
- all fast food, semi-finished products.
If signs of intoxication are detected, meat is completely excluded from the diet, and the man is switched to a plant-based diet. In case of acute inflammatory process, a dairy-vegetable diet, including fermented milk products, is suitable. However, it is necessary to take into account the state of the gastrointestinal tract - if there is increased gas formation and a tendency to diarrhea, this diet is not suitable.
Meals for prostatitis should be fractional; the intestines should not be overloaded. The diet should contain a sufficient amount of fiber, and salt should be limited. It is better to cook dishes steamed or in the oven.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
When used correctly, physiotherapy enhances the effect of medications, helps cope with prostate inflammation, and relieves pain. In case of acute prostatitis, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are first prescribed; in the case of a chronic form, a course without prior preparation is acceptable.
To combat the disease you can use:
- cold medicinal enemas;
- electrical stimulation;
- electrophoresis.
Various exercises related to exercise therapy and aimed at strengthening the pelvic floor muscles and improving blood microcirculation are also recommended. They help get rid of stagnant processes, which is important for treatment.
Physiotherapy should be prescribed by a doctor. It is impossible to determine on your own what effects it is permissible to expose the prostate gland to, and an error in this matter can lead to serious complications.
Traditional methods
Various infusions and decoctions are not suitable for monotherapy, but will be indispensable as aids. Plants contain various substances, including vitamins important for the prostate, selenium and magnesium, so recovery will be faster. More often, this approach is justified in case of chronic inflammation; in acute form, the principles of treatment are fundamentally different.
The most accessible recipes are:
- Pour 3 g of powdered orchis roots into 500 ml of water and boil for 10 minutes. Drink 50 ml in the morning, lunch and evening.
- Pour 40 g of marshmallow root into a glass and fill with water to the brim, keep in a water bath for 20 minutes, drink a third of a glass three times a day.
- Pour 20 g of celery root with a glass of boiling water, simmer in a water bath for 15 minutes, strain and drink 100 ml in the morning and evening.
Pumpkin seeds are good for prostate inflammation. They can be eaten raw, fried or mixed with honey. It is also good to make powder from this raw material and add it to salads.
Treatment of prostatitis
Treatment of prostatitis begins with diagnosis. To do this, a digital and ultrasound examination of the prostate gland is performed, a general and biochemical blood test, and a general urinalysis are prescribed. The doctor draws up a clinical picture of the disease and studies how prostatitis manifests itself in a man. Based on the research conducted, therapy is prescribed.
Complex treatment is required, including:
- taking antibacterial medications;
- prostate massage;
- physiotherapy;
- correction of the immune system;
- diet;
- folk remedies.
In some cases, surgical treatment is indicated. Reasons for surgery are:
- the inflammatory process affected several organs in the pelvis;
- complications of prostatitis in the form of benign or malignant neoplasms;
- conservative treatment is ineffective;
- prostate abscess;
- urinary retention or difficulty urinating;
- stones in the bladder or kidneys.
The operation is not performed on men over 70 years of age and with diabetes mellitus, except for suspected cancer.
.
Diagnosis of the disease
It is impossible to accurately diagnose based on symptoms alone. To understand how prostate inflammation can be treated, the doctor must know what microorganism it is caused by, what form it has, and also have an idea of concomitant diseases. Laboratory diagnostics are widely used for these purposes:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- bacteriological and general urine analysis;
- prostate secretion analysis;
- PCR diagnostics to identify the type of infection;
- spermogram if there are problems with conception.
Of the instrumental methods, ultrasound is used, both abdominal and transrectal. On the resulting images, the doctor can see changes in the structure of tissues; if inflammation is present, determine its area, determine the size of the prostate gland, which increases with prostatitis.
If in doubt, the patient may be referred for an MRI or CT scan. These are examination methods that allow you to create a three-dimensional model of the organ being examined on a monitor screen and therefore give clearer results. As a rule, this step is resorted to if there is a suspicion of prostate cancer. In this case, a biopsy may be taken.
For chronic prostatitis, the doctor may conduct a rectal examination of the gland through the wall of the rectum. This technique allows you to determine the soreness, size and consistency of the prostate, as well as collect its juice for further laboratory testing. In case of acute prostatitis, as well as in the presence of hemorrhoids, a rectal examination is not performed.
History plays an important role in diagnosing the disease, so you need to answer the doctor’s questions as truthfully as possible. A specialist can clarify some features of intimate life, try to find out about chronic diseases and operations, and record complaints. All this is necessary for a more complete clinical picture.
Prevention
A urologist talks about how to treat prostatitis. He also gives recommendations on lifestyle modifications to prevent inflammation and prevent relapse. These include:
- Use of barrier contraception when changing partners.
- Quitting alcohol and smoking.
- Moderate physical activity.
- Proper, balanced nutrition, including foods rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Measured sex life.
Preventing a disease is much easier than treating it and the consequences of the inflammatory process. And every man definitely needs to know what the symptoms of acute and chronic prostatitis look like. If you notice the first signs, you should immediately consult a doctor and not self-medicate.
Chronic prostatitis
Chronic prostatitis develops as an independent disease or as a complication of an acute form of inflammation . During remission, symptoms are mild or completely absent; during exacerbation, they become more pronounced. The clinical picture resembles acute prostatitis.
The first symptoms of a chronic form of inflammation:
- Frequent urge to urinate;
- Dull pain in the lower abdomen;
- Discomfort in the prostate area (the area from the testicles to the anus) when sitting for a long time. Subsequently, it becomes impossible to sit for more than an hour due to the burning sensation;
- Intermittent, painful urination;
- Dull pain in the rectum during bowel movements;
- Deterioration of erection, possible discomfort in the groin during ejaculation.
The above symptoms in the chronic form of prostatitis do not appear all at once.
Initially, this may be a blurred orgasm, premature ejaculation, then the man has to strain when urinating, and pain gradually develops. Have you ever experienced any of the symptoms listed above?
On ultrasound with chronic inflammation, a decrease in the density of prostate tissue and increased echogenicity (the degree of wave reflection by the tissue) are observed . In some places it decreases in the presence of cysts or increases in places where calcifications (stones) are located, foci of sclerosis (consolidations of connective tissue formed as a result of recovery processes after acute inflammation). In the later stages, there are more and more foci of connective tissue and fibrosis. The size of the prostate gland decreases. During visual diagnosis, it is already difficult to distinguish it from the surrounding tissue.
Most common symptoms
Common symptoms of the disease include various signs that most often bother a man:
Problematic urination (pain, frequent urge, incontinence). Urinary problems are one of the first signs of pathology and can manifest themselves in different ways. In addition to unpleasant or painful sensations, there is a burning sensation and sluggish flow of urine. The patient is left with the feeling of incomplete emptying, and effort must be made to complete emptying;
Pain in the pelvic area;
Sexual disorders (impotence, pain during erection, decreased libido, blood in semen, discharge). In the acute form of the disease, the problems are temporary, in chronic pathologies they become permanent;
Problems with the reproductive system often cause nervous disorders in the form of stress, apathy, depression, aggression, frequent mood swings, and sleep disturbances;
General symptoms – chills, malaise, fever, weakness, headache;
Disruption of normal functioning occurs when the urethra narrows and urine stagnates. The patient experiences constant discomfort, the rhythm of life is disrupted, and it becomes impossible to fully rest and work.
Prostate cancer
The prostate in men becomes inflamed as often as the ovaries in women. Of all types of cancer, the most common among the stronger sex is prostate cancer. The tumor is observed in 10% of patients, and trends in its growth are also noted.
It is difficult to pinpoint the exact causes of tumor formation. Men who are predisposed to cancer are most often affected (there have been cases of the disease in their family). Long-term inflammatory processes that are left unattended can also precede the appearance of a tumor.
The risk group includes people who smoke and abuse alcohol; men over fifty years of age; and those who engage in backbreaking labor or work with harmful toxins.
The whole danger of prostate cancer is that the disease does not manifest itself in any way. Patients complain already at the stage of metastasis, when treatment becomes ineffective. The only thing left is supportive therapy.
Therefore, doctors advise periodically taking a PSA blood test. This is the only way to promptly diagnose precancerous changes in prostate tissue.
Complications
When the first signs of prostate inflammation appear, you should consult a specialist and carry out the necessary treatment. Often men may ignore periodic symptoms and hope that the disease will go away. However, the pathology progresses and requires urgent treatment. Any form of the disease can provoke disease in other organs: kidneys, bladder and genitourinary system. If left untreated, the disease can cause various complications:
Vesiculitis - inflammation of the seminal vesicles manifests itself with acute symptoms: pain in the groin and pelvis, pain during erection and ejaculation, frequent urination. Symptoms can easily be confused with prostatitis, which will lead to even more complex and lengthy treatment;
Sclerosis of the gland is accompanied by pelvic pain syndrome, renal failure, disruption of the bladder and urine output, acute urinary retention;
Prostate abscess is manifested by acute throbbing pain in the area of the prostate, rectum and perineum. Accompanied by disturbances in urination, defecation, fever, and chills. If left untreated, purulent contents can break into the abdominal cavity, perineum, scrotum, urethra;
Cystitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder, which occurs from infection of the organ or stagnation of urine. Manifested by frequent, painful urination, pain and discomfort in the organ area;
Pyelonephritis is an infectious inflammation of the kidneys, which is characterized by pain, difficulty urinating, a sharp increase in body temperature and a disturbance in the general condition of the patient;
Sexual dysfunction - manifests itself in impaired potency, the impossibility of normal sexual intercourse and the occurrence of unpleasant sensations;
Infertility is the result of lack of treatment for the inflammatory process and sexual dysfunction;
Cancer is a malignant degeneration of gland cells.
Complications
If the symptoms of prostate inflammation are ignored or the treatment course is incorrectly prescribed, there is a possibility of developing complications of both acute and chronic inflammation.
The acute form of prostatitis is characterized by the following consequences:
- abscess formation;
- bacteremia;
- spontaneous rupture of the abscess. Such a complication will be indicated by such signs as an increase in temperature to 40 degrees, the release of cloudy urine with a sharp and unpleasant odor - when purulent fluid penetrates the urethra, impurities of pus and mucus in the stool - when an abscess is opened in the rectum.
The following complications are most typical for the chronic inflammatory process:
- pyelonephritis;
- cystitis;
- spread of the inflammatory process - the epididymis or seminal vesicles are often affected;
- male infertility.
Causes of acute form
When an infection enters the body through the external genitalia, the result of bacterial activity is inflammation of the prostate tissue. The acute process is clinically pronounced, therefore problems with diagnosing prostatitis in men rarely arise. To avoid unpleasant sensations that can affect potency, it is useful to know the main reasons that cause acute prostatitis in men, including the following:
- infectious pathogens (streptococci, staphylococci, trichomonas, chlamydia, E. coli);
- promiscuity in sexual relations;
- use of a urethral catheter;
- instrumental intervention when examining the area of the urethra;
- hypothermia;
- congestion, circulatory disorders.
Causes of bacterial prostatitis
Many men are interested in what causes bacterial prostatitis. Its name already indicates the main cause of the pathology. This disorder can be provoked by pathogenic microflora, which enters the genitourinary system in different ways and reaches the prostate. There are a number of other factors that cause inflammation. They increase the likelihood of illness. The doctor must determine and become familiar with the cause of the pathology in order to select the most optimal course of treatment for the patient.
Bacterial prostatitis can be provoked by both pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microorganisms
Bacterial prostatitis occurs due to damage to the genitourinary system by the following pathogens:
- Chlamydia;
- Streptococci;
- Gonococci;
- Escherichia coli;
- Trichomonas;
- Treponema pallidum.
When asking a doctor about what causes prostatitis in a man, the patient will receive the most accurate answer from him. He will tell you that this form of the disease is most often transmitted sexually, since its causative agent may be microorganisms that provoke the development of sexually transmitted pathologies.
Bacterial prostatitis is caused by the following causes and factors:
- Infectious diseases of the genitourinary system, which occur in acute or chronic form;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Having promiscuous sex life;
- Long-term abstinence from sex;
- Unprotected intimate relationships;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Hypothermia;
- Weak immunity;
- Excess weight;
- Having bad habits.
It is very easy to get prostatitis from hypothermia in the cold season. Cold weather is dangerous not only for men, but also for women. In their case, severe hypothermia of the body is fraught with the development of cystitis.
Many factors that negatively affect the body, such as hypothermia, can provoke an exacerbation of prostatitis
Chronic bacterial prostatitis, which can occur due to lack of timely treatment, in most cases occurs in a latent form. The man does not even notice that unhealthy changes are occurring in his body. The disease reminds itself only in moments of exacerbation. If the patient is influenced by unfavorable factors, the chronic form of prostatitis quickly gives way to acute. After this, painful symptoms arise that force the man to go to the urologist.
Exacerbation of chronic prostatitis can happen due to any reason. To avoid this, a man does not need to overcool, succumb to stress and strong emotions, and also allow himself to become infected with viral diseases.
Relapse of prostatitis is sometimes caused by surgery on the genitourinary system.
Congestion and sexual activity
Despite the fact that non-infectious inflammation of the prostate gland is considered a disease of older men, this form of pathology is also quite common in young patients. The main reason for stagnant processes in this case is the man’s sexual behavior.
The disease may be caused by the lack of regular ejaculation and regular interruption of sexual intercourse. Long periods of abstinence have a negative impact on health. The lack of regular ejaculation leads to stagnation of seminal fluid, which provokes a disruption in the production of prostate secretions.
Sexual activity
Regular interruption of sexual intercourse leads to the fact that the seminal tract is not completely emptied. At the same time, secretion production does not decrease. Over time, this develops into inflammation of the organ. The accumulation of secretions causes insufficient emptying of the prostate lobes. Incomplete emptying increases blood flow to the gland, which increases the risk of inflammation.
Causes of prostate inflammation
After the reader has learned what an inflamed prostate is, it is important to understand the reasons for the development of the pathology. In general, doctors are inclined to believe that one of the possible reasons for the formation of nodules in the prostate gland is a man’s low sexual activity. But at the same time, sexually active patients are diagnosed with inflammation of the gland in the same way as less active ones.
Basically, experts are inclined not to the direct causes of the formation of pathology, but rather to the factors that provoke its development. These include:
- Changes in hormonal levels with age;
- Frequent stressful situations and psycho-emotional stress;
- Sexually transmitted diseases transmitted at a young age;
- Atherosclerosis;
- Lifestyle (low mobility, tendency to alcoholism and smoking, eating fatty foods);
- Ecology (as a possible risk factor).
Important: the urinary canal blocked by the inflamed prostate gland interferes with the normal outflow of urine in the patient. As a result, over time, inflammation of the bladder first develops. Later the process spreads to the kidneys. In the worst cases, prostate adenoma can lead to kidney stones, hyperhidrosis and kidney failure.
Prognosis and prevention
You can get rid of prostatitis once and for all, but only with a timely diagnosis. Treatment should only be carried out by a qualified specialist. Self-medication or the use of traditional methods is prohibited. The treatment regimen is selected by the urologist individually for each patient. Complex therapy includes not only taking medications, but also changing habits and lifestyle.
Any disease is easier to prevent than to cure. Knowing how prostatitis manifests itself and what causes the disease, you need to follow simple rules to prevent the disease:
Proper nutrition
- Physical activity will prevent the development of stagnation and poor circulation. Regular exercise is recommended for men. The most useful types of physical activity, from the point of view of male physiology, are running, walking with long strides, volleyball and football.
- A balanced diet will normalize hormonal levels, prevent excess weight gain and provide the body with necessary vitamins and microelements. The diet is not strict and consists of limiting the consumption of salty, fried and spicy foods.
- Since infectious forms of inflammation of the prostate can be provoked by sexually transmitted diseases, it is necessary to always use contraception.
- Regular sex life is an important preventive measure that will help avoid the occurrence of stagnant processes. To support normal prostate function, a middle-aged man should have at least 2 sexual intercourse per week.
Interestingly, a large number of sexual acts per day can negatively affect health. With frequent ejaculation, the prostate gland may not completely empty, and the production of secretions increases, which can cause inflammation.
Men over 50 years of age are recommended to undergo an annual examination by a urologist. This will allow timely detection of the onset of the pathological process and cure the disease at the initial stage.
Prostate massage
In addition to medications and alternative medicine recipes, experts strongly recommend that the patient undergo a course of prostate massage. The procedure helps normalize blood circulation in the organ area, prevents blood stagnation, relieves spasm of nearby muscles and speeds up the healing process.
The massage is performed by a specialist on an outpatient basis. The procedure resembles a digital examination of the gland through the rectum, but during the manipulation the doctor not only palpates the organ, but also massages it with careful movements for several minutes. The course consists of 10−15 sessions. After this, the patient’s condition improves significantly, and the risk of relapse decreases.
Treatment of inflammation of the prostate gland should be comprehensive. Missing any element may affect the final therapeutic outcome.
Diagnosis of pathology
After we have looked at the signs and symptoms of prostate inflammation, it’s time to understand how diagnosis is made for such a disease. In general, the following methods are used to make a diagnosis:
- Patient's blood test. Performed on patients over 50 years of age. This diagnosis makes it possible to detect prostate cancer by the level of prostate-specific antigen in a man’s blood (PSA);
- Ultrasound of the genitourinary system and prostate gland. Makes it possible to assess the general condition of the urinary canals, bladder, kidney condition, as well as evaluate the parameters of the prostate gland in the stage of inflammation;
Important: if necessary, a man can be prescribed ultrasound diagnostics using a rectal sensor.
- General urine analysis. Provides information about the presence of chronic inflammatory processes of the urinary system in the patient’s body;
- Special survey. In this case, the questionnaire, developed in accordance with international standards, has only 7 questions, by answering which, the patient outlines the general picture of his condition and lifestyle. Based on the answers, the attending physician can determine the stage of the pathology.
The questionnaire also contains a special urination diary, which must be filled out by the patient.
Features of the non-bacterial form
Non-infectious inflammation does not pose a threat to the partner, as it is not sexually transmitted. Usually the cause of the disorder is autoimmune processes, congestion in the pelvis, trauma, and severe long-term stress.
The distinctive features of non-infectious prostatitis are:
- slight increase in body temperature;
- absence of itching and burning in the urethra;
- absence of pus in the discharge from the urethra;
- pain in the lower abdomen, mainly pulling;
- metabolic disorders - externally manifested by changes in skin color and the appearance of an “orange peel”.
Types of disease
Prostatitis is classified by reason of development. There are infectious and non-infectious inflammations of the prostate gland.
Infectious inflammations include prostatitis caused by fungi, viruses or bacteria.
Pathogenic microorganisms
Non-infectious prostatitis develops against the background of systemic disturbances in the functioning of the entire body. This disease may be caused by natural aging of the body, which is accompanied by an increase in the size of the prostate gland.
Classification
Inflammation of the prostate in men can occur in several forms:
- acute – characterized by a sudden and unexpected onset of symptoms. This course also has several varieties and is divided into catarrhal, follicular and parenchymal prostatitis;
- chronic – characterized by a lower intensity of characteristic clinical manifestations, as well as alternating periods of exacerbation and remission.
In addition, there are several ways through which pathogenic bacteria infect an organ such as the prostate gland:
- ascending - the infectious process spreads to the prostate through the urethra, which can be facilitated by unprotected sex or poor genital hygiene;
- descending - pathological microorganisms penetrate from other organs of the genitourinary system;
- lymphogenous - the most unusual route of penetration of bacteria, in which they are transported using lymph flow from other inflamed internal organs.
Late symptoms
Late manifestations of the disease occur when it persists for a long time. This is observed in chronic types of inflammation. Chronic prostatitis is characterized by alternating periods of exacerbation and remission. It is dangerous for its sluggish manifestations, in which a man may not pay the necessary attention to the disease. Late symptoms include:
Pain in the bladder, genitals, perineum, scrotum, inguinal, suprapubic and lumbosacral areas;
Painful sensations during erection and ejaculation, which disappear on their own within an hour;
Feeling of squeezing and pain in the perineum;
Nagging pain in the groin area;
Burning, cutting during urination;
Frequent and painful urge to go to the toilet;
Excretion of urine in small portions;
Stagnation of urine, which causes pain and can provoke inflammation of the bladder;
Sexual dysfunction: sexual dysfunction, decreased desire, pain during intimacy, erection problems, short duration of sexual intercourse.
How does prostatitis manifest in men?
Doctors divide the disease into different forms according to the patient’s symptoms and clinical picture. It can be acute, chronic, bacterial, calculous, stagnant, infectious, purulent, and depending on this, prostatitis manifests itself in the form of various symptoms. It can be diagnosed by sudden attacks of severe pain in the scrotum, difficulty urinating, and weak potency. In the presence of the disease, the properties of sperm and the quality of ejaculation deteriorate. If any of the listed symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor.
Prevention of prostate diseases
The best prevention of not only prostate diseases, but also any other diseases is a healthy lifestyle.
The following have a beneficial effect:
- Proper and balanced nutrition.
- Physical exercises, sports - running, swimming, walking.
- Drugs and procedures that strengthen the immune system.
- Regular sex life.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- The body must not be overcooled.
“Prostate in men, symptoms, treatment” is a topic that is relevant for most representatives of the stronger sex. It is possible that if preventive measures are taken against this disease, the number of patients will decrease significantly.
Causes of viral prostatitis
The viral form of the disease is caused by:
- cytomegaloviruses;
- simplex viruses;
- influenza type A and B;
- human papillomavirus (HPV).
Cytomegaloviruses that provoke the development of prostatitis include herpesviruses, which can remain in the human body for a long time without any characteristic symptoms. A typical example of a simplex virus that causes the development of prostatitis is the herpes simplex virus. Simplex viruses manifest themselves as genital inflammation, including damage to the urethra. Infection can also be caused by the Epstein-Bar virus.
Interesting fact: what causes prostatitis depends on viral diseases suffered by a man in childhood, since the herpes and measles viruses remain in the body forever. Under the influence of a number of factors (decreased immunity, systemic diseases), activation of the “sleeping” virus and infection of the urethra is possible. Through the bloodstream, the infection enters the prostate, causing an acute inflammatory process.