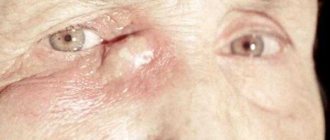
One of the common complications of prostatitis is epididymitis. This is an inflammation localized in the epididymis, often accompanied by pain in the perineum or groin and fever. Epididymitis requires complex treatment, for which a man should consult a doctor.
We will tell you what symptoms the disease manifests, how it is diagnosed and what treatment methods are used.
Reasons for the development of epididymitis
The disease can be caused by infections or non-infectious causes. The following factors increase the risk of developing pathology:
- Presence of urological diseases.
- Promiscuous sex life.
- Horseback riding.
- Hypothermia.
- Physical overexertion.
- Interrupted sexual intercourse.
- Masturbation.
Infection can enter the appendage in the following ways:
- With blood flow.
- With lymph flow.
- Along the lumen of the seminal ducts.
- From the testicle, by contact.
Reference! In some cases, epididymitis develops after sterilization (removal or ligation of the vas deferens). Sperm continue to be synthesized in the testicles. They accumulate in the appendages and, as a result, an inflammatory process develops.
Causes of the disease
of pathogenic microorganisms into the genitals . They can be transported into the epididymis through the genitourinary system or through the blood supply. The causative agents of the disease are the following pathogenic bacteria:
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- stagnation of lymph in the blood vessels of the pelvis;
- mechanical damage or injury to the external genitalia;
- infectious infections;
- surgery or catheter installation;
- non-bacterial origin, formed due to prolonged abstinence from urination.
Factors that stimulate the development of epididymitis in men are the following:
- urine entering the vas deferens;
- hypothermia of the body;
- long-term course of infectious diseases - influenza, rubella, tonsillitis of various etiologies, pneumonia;
- transportation through the urethra to the appendages of infection or pathogenic bacteria, such as staphylococcus, Escherichia coli, pseudomonas , Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis;
- frequent occurrence of erection without proper sexual intercourse;
- obstructed flow of urine through the ducts, caused by prostate adenoma.
The development of epididymitis is caused by a decrease in the activity of the body’s immune system after severe illness. Therefore, it is important to continue to treat any ailments that arise and monitor the occurrence of symptoms, preventing them from growing.
Epididymitis in men: symptoms
Symptoms of acute epididymitis include:
- Severe pain in the scrotum area, on one or both sides, can radiate to the abdomen, groin, perineum, and lower back.
- Swelling of the scrotum, redness of the skin.
- Increase in body temperature to 38–39 °C.
- Hardening and enlargement of the epididymis (and the part of the scrotum in which it is located).
- Feverish state: weakness, significant decrease in performance, headaches, nausea.
- Painful urination.
- Blood in the urine.
Reference! Pain in the scrotum intensifies when palpating the organ or moving. They can also be localized in the side or abdomen (on the side on which the pathological process developed).
Subacute epididymitis is characterized by approximately the same symptoms as acute, but there are differences. Symptoms are less severe (moderate pain, slight swelling, the scrotum enlarges and becomes less noticeable, etc.). The body temperature is subfebrile, that is, it rises to 37.1–38 °C and remains at this level for a long time.
With chronic epididymitis, body temperature does not rise. The pain is minor. The appendage (and more often both appendages) becomes denser and moderately enlarged.
Symptomatic manifestations
Painful sensations in the groin or scrotal area, in the lateral areas just above the inguinal fold, occur suddenly and reach maximum values within 24 hours. These manifestations characterize the occurrence of a primary focus of infection located in the vas deferens. After time, pathogenic microorganisms descend down the paths, passing directly into the appendages themselves.
At the same time, other symptomatic phenomena are possible:
- swelling and pain in the scrotum area - in most cases, the appendage almost doubles in size in a couple of hours;
- radiating pain in the lower back, groin area, iliac region;
- pain when urinating with blood in the urine;
- purulent or mucopurulent discharge from the urethra - the symptom predominates in young men;
- hyperemia of the skin of the scrotum and local increase in temperature in this area;
- low-grade fever, turning into febrile conditions;
- feelings of general weakness and nausea developing against it;
- a feeling of increased pressure or fullness in the testicle area;
- significant enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes;
- pain during sexual intercourse and subsequent ejaculation;
- pain when walking, defecation and urination;
- increased urge to empty the bladder;
- premature ejaculation with blood in the semen;
- frequent urination.
Any manifestations require consultation with a specialist and treatment appropriate to the symptoms. Refusal of medical care is fraught with the development of complications, including the removal of one of the testicles.
Main indicators of chronic and acute epididymitis
| Development option | Acute phase | Chronic phase |
| Flow time | Up to 1.5 months | More than six months |
| Pain syndrome | Acute pain syndrome that occurs at rest, with difficulty in any movement and directed to the groin, peritoneum, lumbar region | Mild pain that occurs periodically, intensifying with physical activity and sudden movements. Recoil to the groin, back, and peritoneum areas is weakly expressed. |
| Condition of the appendage | Increase in size, tense, dense in consistency, painful | Slight enlargement, tension and soreness |
| Symptoms of intoxication manifestations | Weakness, chills, fever (up to 40 degrees), general malaise | There are no general symptoms of intoxication, occasionally the temperature may rise to 38 degrees |
| Features of the course | The danger of orchitis (inflammation of the body of the testicle), abscess of the epididymis and the appearance of pus-like fistulas in the scrotum | There is a high probability of developing sterility; both testicles are involved in the process |
Based on the listed signs, the degree of development of the disease can be easily determined. Mild symptoms indicate that the disease has become chronic, which complicates its possible cure.
Possible complications of the acute phase of epididymitis
Develops when contacting a medical facility is late or against the background of a late diagnosis of the disease (preliminary incorrect diagnosis):
- testicular abscess - a purulent inflammatory process in the tissues of the testicle, occurring on a limited surface, accompanied by fever, weakness, a state of general malaise, headaches and feverish conditions);
- the formation of tissue adhesions between the scrotum and testicle;
- necrosis – appearing against the background of disruption of normal blood circulation of testicular tissue;
- the appearance of fistulas on the skin of the scrotum;
- development of epididymitis on both testicles (bilateral).
During the transition of the acute phase of the disease to the chronic version, the following changes are observed due to the direct effect of infection on sperm:
- infertility is a common result of bilateral epididymitis, which consists of functional death of the epididymis and testicle, occurring in 60% of patients;
- violation of the secretion of the sex glands;
- disruption of the functionality of the autoimmune system - the resulting antibodies attack the body’s own cellular structures.
Symptomatic manifestations play a leading role in determining the disease. All subsequent measures diagnose the degree of tissue damage and the level of weakening of the body.
Tuberculous epididymitis in men
In some cases, tuberculosis affects not only the lung area, but the entire body. The symptoms of this subtype in the acute phase are indistinguishable from simple epididymitis, with a rapid transition to the chronic phase. If one or both testicles are affected, there is a risk of abscess formation and subsequent fistula.
Specific cheesy masses emanating from the wound are a direct sign of the tuberculous variant of epididymitis. The subtype of the disease is not a direct threat to life, but leads to infertility. Conservative treatment is not effective; surgical intervention is always used.
Complications of epididymitis
If left untreated, acute epididymitis can lead to the following consequences:
- Abscess (purulent inflammation of tissues with their subsequent melting and the formation of a purulent cavity).
- Orchitis (inflammatory process extends to the testicle).
- The progression of the disease into a chronic form.
- Transition of the inflammatory process to the duct of the other testicle.
- Blood poisoning.
- Fournier's gangrene (necrosis of scrotal tissue).
- Phimosis (inability to expose the head of the penis due to narrowing of the foreskin).
- Pyocele (suppuration of the serous sac consisting of the tunica vaginalis of the testicle).
Important! The chronic form of the disease is a common cause of infertility.
Chronic form
Chronic epididymitis develops in a man if adequate treatment of the acute form of the disease is not carried out in a timely manner. In total, this process takes more than 6 months. A person may not even suspect the development of this complex pathology. If in acute epididymitis the symptoms appear immediately and reach their peak activity within a day, then in this case there are practically no symptoms. A man feels some discomfort in the testicular area only during an exacerbation of the disease. Externally, the scrotum does not change either shape or color.
With chronic epididymitis, the epididymis becomes several times larger (but not always), becomes denser and painful on palpation. The spermatic cord thickens, and the vas deferens becomes wider in diameter.
Epididymitis and infertility
The epididymis is a paired organ of the male reproductive system located in the scrotum. It consists of 3 conventional parts: head, body and tail. The tail of the epididymis passes into the vas deferens.
Sperm accumulate in the epididymis for maturation. Moving along the duct, they are finally formed and gain mobility. An optimal environment for sperm maturation (temperature, pressure, etc.) is maintained inside the appendages. Inflammation interferes with this process, which negatively affects sperm quality.
With long-term chronic epididymitis, connective tissue grows in the appendage, which often leads to obstruction of the duct. With a bilateral process, obstructive infertility occurs (the movement of sperm along the seminal ducts is blocked).
Reference! If the obstruction is observed in only one duct, the man does not become infertile, but the sperm count is significantly reduced.
As a result of treatment, the ability to fertilize returns. If the patency of the ducts is restored by less than 30%, sperm are taken during a puncture biopsy and used for IVF.
Etiology
The main cause of epididymitis is a bacterial infection. Microbes penetrate the appendages from the external environment ascending through the urethra. Infection of the epididymis also occurs through blood or lymph from distant or nearby sites. The causative agents of the pathology are:
- Coccus microflora – staphylococci, streptococci, pneumococci, enterococci,
- Sexually transmitted microorganisms - chlamydia, gonococci, mycoplasma, ureaplasma,
- Common coliform bacteria that live in the intestines are Escherichia coli, Proteus, Klebsiella, Citrobacter, Enterobacter,
- Mushrooms of the genus Candida,
- Spirochete pallidum (the causative agent of syphilis),
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
In children, epididymitis can be caused by viruses - the causative agents of mumps, influenza, and herpes. Another reason for the development of pathology in boys is trauma to the genital organs.
Epididymitis often occurs against the background of existing dysfunction of the male reproductive system - inflammation of the prostate gland, urethra, seminal vesicles.
Chemical epididymitis is classified into a separate group. This is a rare pathology caused by the reflux of urine from a full bladder during sexual intercourse. In more rare cases, the cause of the disease is long-term use of certain medications.
Epididymitis often complicates the course of certain infectious diseases: respiratory infections, typhoid, pneumonia.
Factors contributing to the development of pathology:
- Decreased immunity
- Chronic fatigue
- Hypo- and vitamin deficiency,
- Endocrinopathy - diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, obesity,
- Oncological diseases,
- Inflammatory diseases of the liver and other internal organs,
- Previous surgeries: adenomectomy,
- BPH,
- Urethral stricture,
- Hypothermia or overheating,
- Urethral catheterization.
Diagnosis of epididymitis
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out as follows:
- Conversation with the patient, collection of anamnesis.
- Inspection.
- Ultrasound of the scrotum to determine the exact location and extent of the pathological process.
- General blood and urine tests.
Additional research may also be required:
- Color Doppler mapping (CDC) is an assessment of the nature of blood flow using ultrasound radiation, carried out to exclude testicular torsion.
- Scraping from the urethra - in the presence of urethritis and suspected sexually transmitted infections.
- Urine culture - to determine the causative agent of infection.
- Seminal fluid examination.
Acute epididymitis
The occurrence of an acute form is characterized by the appearance of vivid painful symptoms. Most often, patients aged 15 to 35 years are infected. Elderly men are rarely diagnosed with this condition.
Testicular epidymitis of abacterial nature
The following symptoms of illness are identified:
- The initial sign that forces you to seek qualified help is pain in the groin area.
- The pain may radiate to the groin or sacrum of the spine.
- Frequent urination appears.
- The size of the testicle doubles in 3-4 hours.
- Nausea and body chills occur.
- In severe situations, when urinating, you may notice streaks or blood clots in the urine.
Attention! Acute epididymitis occurs within 2-5 days. Severe pain does not last long and does not always prompt a man to see a doctor.
As a result of the ongoing process, adhesions are formed in the appendages, interfering with the normal passage of sperm through the tubes, which leads to the development of infertility.
Acute left-sided epididymitis
In most cases, men experience left-sided epididymitis, affecting the epididymis on the left side. This is due to the anatomical structure of the body of male representatives - in men, the left egg is located slightly lower than the right one.
The course of the clinical picture of the disease has vague signs, and therefore identifying it in the early stages is problematic . Symptoms often correspond to various diseases of the genitourinary system (with orchitis, as well as with torsion or traumatic damage to the egg).
Important! Self-treatment when acute epididymitis has begun is strictly prohibited; incorrectly selected medications have a negative impact on the patient’s well-being. To avoid starting the process, you should immediately seek help from a qualified specialist.
Bilateral epididymitis
In the absence of therapeutic treatment, the acute form of unilateral epididymitis transforms into bilateral epididymitis.
There is a proliferation of connective tissue in the genital appendages. In this case, a narrowing of the lumen is observed, as a result of which the normal passage of sperm through the tubules is disrupted.
Due to the spread of the disease, the doctor may make a diagnosis in which the disease spreads to both cavities of the epididymis.
Treatment is carried out in a hospital setting with antibiotics and other medications aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease.
Epididymitis of bacterial nature
Epididymitis of a bacterial nature in the testicles of a man is provoked due to a previous infectious disease. The cause of the development of malaise is severe infections that last in the body for a long period. Infection can be caused by sore throat, rubella, influenza, pneumonia , and sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Bacteria remaining in the body after illness enter the genitals in a hematogenous manner - moving with the bloodstream, as well as using the ascending path of movement through the urethra.
Infection of testicular epididymitis of a bacterial nature through the genitourinary organs can be provoked in the following ways:
- unprotected sexual intercourse;
- installing a catheter in the bladder and keeping it in one place for a long time;
- anal sex.
Treatment of epididymitis
The main goal of treating any form of epididymitis is to eliminate the inflammatory process and prevent complications. Medications prescribed:
- Antibiotics.
- Painkillers.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Immunomodulators.
- Vitamins.
- Absorbable.
- Novocaine blockades.
Treatment is usually carried out on an outpatient basis. Hospitalization is carried out if there is a risk of complications and a severe course of the disease. The patient is advised to rest in bed. The mobility of the scrotum should be limited using a rolled up towel or a special suspension (bandage). Your doctor may also recommend the use of cooling compresses. During the treatment period, the patient must adhere to a diet: exclude fried and spicy foods from the diet. After the swelling of the scrotum has subsided, physical activity should be resumed slowly and carefully.
After eliminating the acute symptoms of the disease, physiotherapeutic procedures are often prescribed:
- UHF;
- Microwave therapy.
Physiotherapy allows you to speed up the process of inflammation subsiding, eliminate congestion by normalizing blood microcirculation and avoid the formation of fibrous tissue.
Surgical treatment of epididymitis is rarely performed; it is usually performed in the presence of an abscess, phimosis, or pyocele. In particularly severe cases, the affected appendage is removed, in others it is treated with drainage. The operation is also performed to widen the ducts when they are blocked.
Diagnostics
If any of the above symptoms appear, it is recommended to immediately visit a qualified urologist to conduct an examination and clarify the diagnosis. Sometimes the patient will need hospitalization. Not only the effectiveness of the treatment, but also the ability to reduce the risk of complications depends on how early a man sees a doctor.
The most effective methods for diagnosing chronic and acute epididymitis:
- a patient interview, during which the doctor will examine the man’s main complaints;
- inspection. At this stage, the doctor detects external changes in the shape and color of the scrotum, palpates the localization of inflammation, and palpates the inguinal lymph nodes;
- UAC;
- OAM;
- A swab from the urethra;
- BAK-urine culture;
- PCR and ELISA - make it possible to identify STIs;
- Ultrasound Dopplerography of the genitourinary organs;
- Ultrasound of the scrotum;
- CT scan;
- magnetic resonance imaging.
Diagnosis of epididymitis
It is imperative that the patient’s sexual partner be examined, even if he does not have any symptoms.
Prevention of epididymitis
Prevention of the disease involves timely treatment of urological pathologies. The patient should also be attentive to his body after suffering from infectious diseases (sore throat, pneumonia, influenza, etc.). If you have any alarming symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Hypothermia is the most common cause of inflammatory processes. Therefore it is necessary to avoid it. Care should be taken to ensure safe sexual intercourse to avoid contracting sexually transmitted infections.
If you have signs of the disease, make an appointment at the Otradnoe Polyclinic at a time convenient for you, get diagnosed and receive the necessary treatment!
Prevention measures
Preventive measures are aimed at strengthening the immune system and preventing factors that contribute to the development of the inflammatory process in the appendages. To this end, all men are recommended to:
- do not change sexual partners, avoid casual relationships;
- do not abuse alcohol, do not take drugs;
- treat pathologies in the genitourinary system promptly and completely;
- do not take antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription;
- protect yourself from hypothermia.
Viral infections should be treated with bed rest, in which case the risk of complications is reduced. It is also important to protect the penis and scrotal organs from injury, especially when engaging in active sports.
Cephalosporins in conservative therapy
Epididymitis in men can be provoked by concomitant diseases - urethritis, prostatitis, tuberculosis, mumps. The inflammatory process can develop against the background of a purulent infection in the body. Treatment of epididymitis is aimed at eliminating infectious agents, blocking pain symptoms and reducing tissue swelling. To choose effective therapy, the form of the disease is determined - chronic or acute epididymitis. A common method of conservative therapy using antibacterial drugs of the cephalosporin series. They are prescribed to patients with prostatitis and pyelonephritis complicated by epididymitis.
Ceftriaxone
Administered intravenously or intramuscularly against inflammation using freshly prepared solutions. The components inhibit the synthesis of cell membranes of epididymitis pathogens. Ceftriaxone is well tolerated with minimal side effects. The course of therapy depends on the indications.
Ceftriaxone
Cefotaxime
The antibiotic inhibits the synthesis of microbial cells. The medicine is administered intravenously or intramuscularly every 8-12 hours, one gram for mild cases of the disease. If acute epididymitis is painful and severe, the doctor may increase the dosage.
Cefpir
A fourth generation drug with pronounced antibacterial properties. Prescribed intravenously or intramuscularly to suppress the growth and reproduction of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, strains that are resistant to other antibiotics. Cephalosporins show high effectiveness in the treatment of epididymitis caused by various pathogens of the inflammatory process. To treat chronic inflammation of the epididymis, it is important to use conservative antibacterial therapy, and acute epididymitis is additionally treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. How long treatment lasts depends on the stage and cause of the inflammatory process.
It is possible to restore erectile function! Proven FOLK CARE ... Reviews My story spotenciey.ru
Treatment of PROSTATITIS using a new method To restore the functions of the prostate, you need every day... Website Interview with a doctor bezprostatita.ru
The problem of the small size of the dignity has been solved. The mechanism of erection has been revealed... Official website Recovery bigbigrazmer.ru
Causes
Orchiepididymitis most often develops as a consequence of orchitis and epididymitis. In most clinical situations, acute orchiepididymitis develops on the left, in more rare cases - on the right. This occurs due to the anatomical features of the structure of the genitourinary system in men.
The causes of the disease are quite varied, but most often epididymitis orchiepididymitis develops due to:
- physical injury to the testicles or scrotum;
- reduced immunity;
- hypothermia;
- past infectious and non-infectious diseases (trichomoniasis, mumps, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, chlamydia, etc.). This is the most common cause of epididymitis orchiitis;
- circulatory disorders in the groin area;
- history of chronic diseases of the genitourinary system – balanoposthitis, cystitis, urethritis;
- orchiepididymitis can develop as a complication from tonsillitis, pneumonia, syphilis, tuberculosis, cryptococcosis;
- incorrectly performed catheterization of the bladder in urological pathologies.
All these reasons and unfavorable factors pose a serious threat to a man’s health. Therefore, it is important to promptly treat diseases and prevent them.
Treatment
Treatment of epididymitis involves treating the underlying infection and reducing symptoms. In case of chronic recurrent course of the disease, bed rest is indicated during exacerbations. Treatment is usually successful, but long-term. Sometimes it may take several weeks for the soreness or discomfort to completely disappear. Most cases of epididymitis are completely cured within 3 months.
According to research results, the most common medical treatments for chronic epididymitis are antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Drug therapy
Pharmacological treatment consists of drugs from the following groups:
- Antibiotics (Doxycycline, Ciprofloxacin and others depending on the pathogen). Taking medications from this group is indicated for 4–6 weeks for chronic epididymitis. When treating epididymitis caused by chlamydia and gonococcus, it is also necessary to simultaneously treat the sexual partner for these infections.
- Analgesics. They have an analgesic effect. The group includes drugs available over the counter (Ibuprofen) as well as prescription drugs (Codeine or Morphine).
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (Piroxicam, Ketorolac). Reduce swelling and other inflammatory phenomena.
Photo gallery: medications for the treatment of epididymitis
Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum antibiotic prescribed immediately after diagnosis.
Ibuprofen has analgesic and antipyretic effects
Piroxicam is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that helps overcome the symptoms of epididymitis.
Surgery
In some cases, invasive treatment may be required.
One of the serious complications of epididymitis is an intrascrotal abscess (an accumulation of pus), which must be opened and drained surgically. The patient is urgently hospitalized in the urology department for surgery. The intervention is performed under local anesthesia through open access:
- Opening all the cavities of the abscess with a longitudinal incision, the surgeon empties them and washes them with an antiseptic.
- The wound is packed to separate the abscess from the surrounding tissues. Since the body perceives the tampon as a foreign body, it begins to produce fibrin on the surfaces of the tissues that come into contact with it. Then the formation of young connective tissue occurs.
- The tampon is removed after 7–8 days, when the body begins to reject it on its own.
- The wound is stitched up.
- After surgery, antibiotic therapy is administered.
- Regular dressings are performed until the wound heals.
A scrotal abscess that is operated on in a timely manner usually ends favorably
In the long term, complications may arise in the form of:
- dysfunction of the testicle and its epididymis;
- loss of patency of the vas deferens;
- insufficiency of male sex hormones;
- infertility.
In case of necrosis of epididymal tissue, an epididymectomy (removal of the epididymis) is performed, and if the destructive process has affected the testicle itself, then a decision is made to perform orchiectomy (amputation) of one testicle, especially if the second remains healthy.
A dangerous rare complication of an abscess is rapid necrosis of the scrotal tissue - Fournier's gangrene. The negative scenario in the form of death in the case of gangrene reaches 80%.
Surgery may also be required to correct any physical defects (such as urinary tract obstruction) that may be causing epididymitis.
Recommendations from experts
During the treatment of chronic epididymitis, doctors recommend:
- decreased level of physical activity of the patient;
- Limiting heavy lifting;
- lifting and supporting the scrotum using a suspensor (special medical bandage);
Suspension - a special support bandage for the scrotal organs
- cold compresses of ice on the scrotum (for exacerbations);
- warm sitz baths, heating pad, warm compresses (during the period when inflammation subsides).
In cases of STIs, the patient and his sexual partner should abstain from sexual intercourse for a week after finishing the course of antibiotics and confirming recovery.
Treatment of pediatric epididymitis
Treatment for pediatric epididymitis will depend on the underlying cause of the disease. In most cases, the condition can resolve on its own with rest and painkillers such as Ibuprofen. If a bacterial infection similar to that coming from a UTI is confirmed, antibiotics are prescribed. Children are also advised to drink more water and avoid the urge to urinate for a long time.
Folk remedies
There are many plants that are useful in the treatment of epididymitis, they have a natural antibacterial effect and are also a natural pain reliever:
- Horsetail tea. This herb has numerous antibacterial properties that prevent further spread of the disease. Herbal tea must be taken once a day to get a noticeable effect. To brew a medicinal drink, take 2 teaspoons of herbs per 250 ml of boiling water.
- Cranberry juice. The combination of acids (malic, citric, benzoic) in this berry can kill bacteria that cause infection. Preparation and use:
- mash 0.5 kg of berries, pour the resulting juice into a separate bowl, after straining it;
- pour 1.5–2 liters of boiling water over the cake;
- bring to a boil, stir and leave to brew for 30 minutes;
- strain, add drained cranberry juice;
- drink 2-3 glasses a day, maybe with the addition of honey.
- Raw garlic. For a natural antibiotic effect, you can use a few cloves of raw garlic to season your dinners. It is advisable to crush them before use, since this releases allicin, an organic compound that has a bactericidal effect.
- Oregano (oregano). This natural medicine is rich in essential oil with a high content of carvacrol. Such oils are superior in their bactericidal properties to many existing antibiotics. To obtain the desired effect, it is enough to add oregano daily as a seasoning to various meat and mushroom dishes, sauces, and gravies.
Photo gallery: components of folk remedies for epididymitis
Horsetail tea for epididymitis is drunk once a day
The combination of natural acids in cranberry juice has an antimicrobial effect
Oregano (oregano) essential oil contains the substance carvacrol, which slows down the growth of certain bacteria.
Garlic has natural antimicrobial properties
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy methods are used as auxiliary methods outside the period of exacerbations. These include:
- UHF therapy - treatment with a high-frequency electromagnetic field (oscillation frequency 40.68 MHz or 27.12 MHz);
- diathermy - deep heating of tissues with high-frequency currents (electrotherapy method);
- mud therapy.
Dietary nutrition for chronic epididymitis
A beneficial diet for treating epididymitis includes consuming foods that can reduce inflammation. Foods that may be helpful in reducing inflammation include:
- spinach;
- blueberries;
- strawberries
Since patients with chronic epididymitis usually suffer from urinary problems, they need to eat foods such as celery and parsley that relieve these symptoms. Typically, epididymitis is caused by a bacterial infection. To treat the cause, patients should eat more fresh vegetables and fruits rich in vitamin C. This is beneficial for boosting immunity. Foods rich in vitamin C include:
- kiwi;
- orange;
- lemon;
- grapefruit;
- bell pepper;
- tomatoes.
Foods high in vitamin C increase the body's anti-inflammatory function
Orchitis and epididymitis: treatment
Orchitis, epididymitis: treatment or both diseases in one called orchiepididymitis - how to treat it? Orchitis and epididymitis, the treatment of which in one pathology is often carried out exclusively in a hospital setting, can sometimes also be carried out at home, but strict medical supervision is necessary.
If left untreated, this disease can pose a great danger to the male body. This is due to the fact that with it the temperature rises to forty degrees, the patient shudders. The same can be said about orchitis and epididymitis separately. Constant pain distracts the patient and torments him. In this case, you need to urgently call a doctor.
Orchiepididymitis: treatment - which antibiotic is better to take?
Treatment of orchiepididymitis with antibiotics is the most commonly used therapeutic method. So, epididymitis orchioepididymitis: antibiotic treatment - which is better to choose?
It is advisable not to prescribe such treatment yourself. This may lead to aggravation of the situation in the future. Before prescribing an antibiotic to a patient, the doctor checks his sensitivity to them and makes a definite conclusion about what will act on the disease better and more effectively. We list the main antibiotics that are used in the treatment of epididymitis orchioepididymitis.
- Ceftriaxone. This is the third generation of cephalosporins. Before prescribing such a drug, the doctor assesses whether its properties are capable of harming the patient. Among them are low effectiveness against gram-positive flora, excellent effectiveness against resistant microorganisms, effective effect on gram-negative microflora;
- Vibramycin or Doxycycline. This antibiotic is usually prescribed in conjunction with cephalosporins if epididymitis orchiepididymitis occurs along with a sexually transmitted disease;
- Ofloxacin. This antibiotic has the ability to penetrate the prostate and have an effect on chlamydia trachomatis. The spectrum of action is wide. Often prescribed to men whose age exceeds thirty-five years;
- Azithromycin or Zithromax. Such an antibiotic will be effective against uncomplicated orchiepididymitis, especially if there is a suspicion of chlamydial or gonorrheal etiology. It synthesizes dehydrofolic acid, which inhibits bacterial growth. Often also prescribed to men after thirty-five years of age;
- Ciprofloxacin. This antibiotic is highly effective against gram-negative bacteria. After the symptoms of the disease disappear, you must continue to take the drug for two days. If you choose to treat orchiepididymitis at the chronic stage with this drug, it is prescribed for a long period, up to twenty-eight days.
If children are treated with antibiotics, so-called protected penicillins are prescribed, for example, Amoxiclav and Augmentin.
Chronic orchiepididymitis: treatment with antibiotics - in this case, the antibiotic most suitable for the patient will also be selected based on testing his sensitivity to them.
Treatment of orchiepididymitis in men at home
It is hardly possible to get a good treatment at home. It must be remembered that throughout the entire therapy, doctors can change the type of antibiotic from one to another.
However, it should be mentioned that treatment of epididymitis orchioepididymitis can be carried out not only through the use of antibiotics.
Orchiepididymitis in men: treatment - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are also often used in its course. These are Ofen, Ketanol and Diclofenac. They relieve swelling and inflammation and promote regeneration at the cellular level. The patient may also be prescribed medications that relieve pain, but this is only relevant for the first days of the disease, when the pain syndrome is pronounced.
As for the treatment of the chronic form of orchiepididymitis, it can be noted that it will take place much more slowly. Initially, medical practice usually involves prescribing a wide range of drugs, after which doctors often add new drugs, otherwise the effectiveness of treatment will be low. In addition, the course of treatment itself can last quite a long time, since the condition of the disease is close to advanced. If an abscess has started, surgery will be performed to open the chronic focus of suppuration.
Treatment of orchitis and epididymitis: diet and local treatment
In order to recover, the patient must eat well. It is necessary to limit sour, salty, spicy and smoked foods. It is important that the diet is as balanced as possible.
You should try to drink as much liquid as possible. To generally strengthen the condition of the body, it is recommended to take vitamins. This can be either pharmacy complexes or the consumption of fresh berries, fruits and vegetables.
In order to reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process in the prostate gland, you can take Vitaprost suppositories in a course of ten to twenty days.
Local treatment is carried out using alcohol compresses, half diluted with water. It is also useful to make compresses with Vishnevsky ointment.
Epididymitis and orchitis: treatment through surgery
Since epididymitis orchioepididymitis is often successfully treated with antibiotics, surgical intervention is, in principle, rarely performed. The operation, if used, consists of opening and draining the scrotum. If areas of abscess or necrosis are found, surgery will need to be performed to remove the testicle as it will no longer be considered viable. After this, it is necessary to send the tissue for histological examination to exclude the possibility of a malignant neoplasm. This risk may exist if the disease has been going on for a long time.
Is there anything else that can be noted about the treatment of epididymitis orchitis in men through the use of antibiotics?
Consequences of chronic epididymitis
The consequences of chronic epididymitis are varied. Epididymitis is not such a dangerous disease, but it can cause serious problems with the male reproductive system and lead to purulent inflammation.
Chronic epididymitis: the consequences are associated with untimely treatment of the inflammatory process. If you do not pay attention to the manifestations of minimal symptoms in time, then after three or four days they will no longer exist, but after a short time the disease will worsen. When the process has worsened, there are minor manifestations: swelling, pain, irritation, discomfort. But after some time, the symptoms will pass without a trace, outwardly the man will get better and nothing will bother him, but in fact this is far from the case. The process will get worse. The absence of swelling and changes in color can only signal that the process has begun to fester. The patient will feel worse, the condition will worsen. Which will lead to intoxication of the whole body. If the process is started, orchitis may begin or inflammation may spread not only to the epididymis of the second testicle, but also to the testicle itself, resulting in fistulas, abscesses, necrosis and other unpleasant situations. If the process begins to spread through the lymph nodes, then you can get blood poisoning, which can soon develop into cancer. Any abscessive process has a detrimental effect on metabolic processes in the body.
Chronic epididymitis and infertility are very close. As mentioned earlier, the epididymis takes an important part in the maturation and preservation of sperm, and if the trophism of the epididymis is disrupted, the production of sperm will change. Complete and partial obliteration of the appendage occurs (patency changes due to the adhesive process). Chronic epididymitis is most often bilateral and therefore obliteration of the vas deferens leads to obstructive infertility. For a long time, in the absence of treatment, the process will contribute to the growth of connective tissue and incomplete blockage, and over time, complete obstruction of the epididymis for sperm, which leads to their death. Chronic epididymitis and urethritis occur more often in men, because the infection is constantly present in the patient’s body. Urethritis is an inflammation of the walls of the urethra due to infection, which provokes epididymitis. When it comes to sex and chronic epididymitis, there are no contraindications.
Sex does not cause discomfort and the process itself will not be difficult, but do not forget that the infection in the body can be transmitted to your partner.
Treatment of orchiepididymitis
For orchiepididymitis, treatment is carried out using both conservative and surgical methods. The method of treatment is largely determined by the specific signs of the disease in men - if the symptoms indicate acute inflammation, antibiotic therapy is prescribed, and in case of a purulent form, urgent surgery is indicated.
The male disease is treated by a urologist or andrologist - it is this specialist who diagnoses orchiepididymitis and prescribes therapy aimed at eliminating symptoms and the inflammatory reaction.
Conservative treatment
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy helps treat chronic epididymitis orchiitis. Preliminary tests are taken to detect infection. If pathogenic microorganisms are found in a smear, the patient must be prescribed antibiotics. What antibiotics to take here also depends on what exactly caused epididymitis orchiitis
Left- or right-sided chronic epididymitis orchioepididymitis is treated with compresses, heating, laser therapy, and magnetic therapy. All these methods allow you to restore blood flow, eliminate congestion in the scrotum, and prevent the formation of scars. If scars are found in the appendage, absorbable drugs in ointments are additionally prescribed, enhancing their effect with physiotherapy.
Surgery
In case of purulent inflammation and the development of an abscess, urgent surgery is necessary, otherwise epididymitis orchitis will lead to irreversible consequences. For this purpose, an incision is made in the skin of the scrotum, followed by drainage of the abscess.
The operation cannot be postponed, since in the most severe cases the testicle will have to be removed due to complications.
Which doctors should you contact if you have epididymitis?
- Urologist
Diagnosis of epididymitis and its features are determined by the type and form of the disease. Typically, it includes familiarization with the patient’s complaints and collection of medical history, physical examination using palpation, laboratory studies of biological material removed from the urethra, prostate gland, and ultrasound of the scrotal organs. Laboratory diagnostics consists of general and bacterial urine tests, and culture of urine culture on nutrient media. Such tests make it possible to identify a true urinary tract infection and correctly select the optimal combination of medications.
If there is an acute manifestation of it, then the diagnosis itself is not complicated, since the symptoms are very specific and absolutely obvious:
- palpation indicates an enlarged appendage of the testis, it is sharply tense and compacted;
- the patient experiences pain in the inflamed area both during palpation and outside of it;
- the surface of the testis is usually smooth, it is easily differentiated from the appendage, however, if inflammation has not affected it.
The development of deferentitis and funiculitis is indicated by intense pain in the groin, and orchitis or epididymitis is accompanied by the development of reactive dropsy.
It is important to differentiate chronic nonspecific epididymitis from a number of diseases, such as tuberculous epididymitis, which may be indicated by tuberosity of the epididymis, clearness of the vas deferens and the occurrence of purulent fistulas of the scrotum. In this case, the patient is examined to detect another tuberculosis focus in the body.
It is, among other things, appropriate to differentiate chronic nonspecific epididymitis from neoplasms of the appendage and its syphilitic lesions. Neoplasms of the testicular appendage are very rare and are characterized by the absence of pain and inflammatory reaction. The diagnosis is confirmed or refuted only during surgery or after an urgent biopsy. Serological tests play an important role in the diagnosis of syphilis of the epididymis.
The clinical course of gonorrheal epididymitis is most often erased and does not differ from the manifestations of nonspecific epididymitis. It develops after urethritis, and for a correct diagnosis it is necessary to look for gonococci in a smear from the urethra.
Rationale for surgery
In cases where acute epididymitis is severe (high temperature, intoxication, severe pain), the patient is urgently hospitalized. After examination and diagnosis, the attending physician decides to prescribe conservative treatment or surgical intervention. Symptoms that serve as indications for surgery: abscess or microabscess, suppuration of the epididymis, acute traumatic and tuberculous epididymitis, lack of effect from conservative treatment, chronic epididymitis with constant relapses, formation of an epididymal cyst or compaction in the epididymis, testicular torsion or appendage of the epididymis, complex and severe acute epididymitis.
Surgery
Surgery is a last resort in the treatment of epididymitis, but sometimes only this method is effective. Depending on the diagnosis and clinical picture, a rational method of surgical intervention is chosen. Possible options:
- Resection is the removal of part of the appendage with the elimination of a limited purulent area without damaging other structures and organs. Low efficiency, high risk of relapse, frequent complications.
- Incisions – detection and elimination of microabscesses by applying incisions several millimeters deep to the appendage. Effective for diagnostic purposes.
- Puncture is a puncture of the scrotal cavity with a needle under local anesthesia to reduce pressure inside the male organs and stop inflammation. Ineffective in treating extensive infection.
- Epididymectomy - removal of the epididymis with the vas deferens to radically prevent possible serious complications. Full reproductive function is impaired.
- Orchiectomy is the removal of the entire testicle and epididymis due to the need to save the patient’s life. When performing a bilateral operation, a man is deprived of reproductive function.
To avoid drastic measures, it is necessary to contact a specialist in a timely manner, pay attention to prevention and prevent the development of the disease. Ignoring treatment can lead to serious consequences - infertility, abscess, sepsis, orchiepididymitis, necrosis, adhesions, scars, fistulas, cyst growth. Whatever the form of the disease, treatment must be comprehensive. Maintaining intimate hygiene, controlling sexual intercourse, avoiding scrotal injuries and a healthy lifestyle helps prevent inflammation.
Chronic epididymitis on the right, what is it?
What is chronic epididymitis on the right in men? This is a unilateral lesion of the scrotum. It is characterized by an asymmetrical lesion. Chronic left-sided epididymitis will manifest itself in the fact that the appendage will first swell and increase in size, and then the symptoms fade away, which indicates soreness of the scrotum, the appendage is painful on palpation, hyperemia of the entire scrotum appears, the folds straighten out and the scrotum becomes smooth. And the testicle itself becomes denser, becomes larger, it is impossible to touch it due to severe pain. Swelling forms very quickly in soft tissues, within a few hours or in one day, and pain increases due to this. The pain will occur against the background of exhaustion of the body, loss of strength, chills, lethargy, weakness, and disruption of the daily diet. The patient will have no desire to eat or drink, and all this will be accompanied by nausea and unpleasant sensations throughout the body, physical inactivity, and even aching joints. Dyspeptic disorders are also not uncommon due to decreased immunity and diarrhea. At the same time, urination becomes frequent and quite painful. Patients experience severe burning of the genitals. The epididymis is well innervated and supplied with blood, so any damage to it is manifested by certain symptoms. With a chronic process, a man’s sex life and erection will suffer, and he will not immediately suspect the process.
Preventive measures
To eliminate the risk of developing this disease, you should follow a few simple recommendations. Since STIs are a common cause of orchiepididymitis, men are recommended to constantly use condoms. If you have previously suffered an injury to the groin area, you should not hesitate and visit a doctor for diagnosis.
The scrotum must be protected not only from injury, but also from hypothermia. Men are recommended to wear underwear made from natural fabric.
It is also important to promptly treat existing diseases of the genitourinary system in order to prevent the development of complications.
Diagnosis of orchiepididymitis
To avoid an incorrect diagnosis, the patient is offered to undergo a full range of examinations. This is necessary in order to identify the root cause of the disease and find out the nature of its occurrence.
A doctor's examination alone is not enough.
Diagnosis of this disease is carried out only by a urologist, who must manage the patient’s illness. Of the standard tests, the patient must pass:
- Analysis of urine
- Blood analysis
- Bakposev
Also, the doctor must urgently take a smear from the urethra to identify the cause of the disease (infection, bacteria, virus). Ultrasound is prescribed in case of swelling of the scrotum. Thanks to this study, the doctor will be able to see if there is pus in the testicle or appendages. A puncture is taken if there is an abscess (to investigate the cause of suppuration).
The presented studies help to build a clear picture of what is happening in order to prescribe competent treatment.
Causes of chronic epididymitis
The causes of chronic epididymitis are very extensive, they include everything that concerns the body as a whole. This is a way of life, and the flora in which a person is located, this is the nutrition that he absorbs, and the daily diet, and of course, what a person encounters in his daily life. A person must learn the rules of hygiene from an early age; the ability to provide one’s body with cleanliness and care are important factors of existence. Chronic epididymitis is caused by all possible previous infectious processes; this reason comes first when affecting the appendages in a man.
This can be caused by diseases that are sexually transmitted. Men who are active in their sex life often suffer because sex is not protected, the partner is not constant and the choice of form of sex is often unconventional and not protected. Microbes can also enter the bloodstream and spread throughout all organs and tissues and affect problem areas of the systems, which will soon provoke disease. Another reason is the reflux of urine during sexual play when the bladder is aroused or full. Long-term use of medications can also cause side effects. Stagnant processes, such as hemorrhoids or constipation, will also soon lead to chronic diseases of the scrotum.
Classification
In medicine, epididymitis orchioepididymitis is classified according to its course:
- acute course;
- chronic course;
- abscessive form.
There is also another classification of the disease, depending on the class of pathogen that caused the inflammation:
- specific orchiepididymitis. The disease develops against the background of tuberculosis, brucellosis, syphilis, etc.;
- nonspecific orchiepididymitis. In most clinical cases, its development is provoked by STIs (sexually transmitted infections). The causative agents can be nonspecific infections and viruses.
Possible complications
Epididymitis leads to damage to the male gonads and the formation of purulent foci within them. Delayed treatment is accompanied by the following complications:
- scrotal abscess;
- bilateral testicular damage;
- atrophy of the gonads;
- infertility;
- Fournier's gangrene;
- fistula (fistula) in the scrotum;
- scarring of the spermatic cord;
- testicular infarction.
If an infection from the reproductive organs enters the systemic bloodstream, sepsis is possible - blood poisoning.
Complications are easy to prevent with adequate and timely treatment. Before taking medications, a man must undergo a comprehensive examination.
Treatment of other diseases starting with the letter - e
| Treatment of eczema |
| Treatment of pleural empyema |
| Treatment of emphysema |
| Treatment of endocarditis |
| Treatment of endocrine ophthalmopathy |
| Treatment of endometriosis |
| Treatment of endometritis |
| Treatment of enteritis |
| Treatment of enuresis |
| Treatment of epilepsy |
| Treatment of erectile dysfunction |
| Treatment of erythremia |
| Treatment of cervical erosion |
| Treatment of pulmonary echinococcosis |
| Treatment of liver echinococcosis |
| Treatment of echinococcosis of the spleen |
| Treatment of escherichiosis |
The information is for educational purposes only. Do not self-medicate; For all questions regarding the definition of the disease and methods of its treatment, consult your doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis is simple, it begins with a confidential conversation in the urologist’s office. Examination and palpation give the doctor the opportunity to make the correct diagnosis. But the disease is similar to other ailments. And in order to exclude an incorrect diagnosis, a laboratory examination is prescribed that will help identify the pathogen.
In medical practice, there are cases when such symptoms are diagnosed as acute stage pyelonephritis. This is easily explained by the fact that pain in both diseases radiates to the lumbar region in men. The patient is usually admitted to inpatient treatment, after which the following is carried out:
- blood test (general);
- blood test for biochemistry;
- semen analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
- urethral culture;
- nuclear scan.
Most laboratory examination methods are well known to men, but not everyone knows what urethral culture and nuclear scanning are. The culture test is partly carried out on urine.
But in addition, men insert a small tampon into the urethra. It is not painful and not deep: the insertion depth is no more than one centimeter. After this, the swab with biological material is sent for laboratory examination.
Urethral culture data should be obtained no more than one day later. This is the only way to most accurately analyze and identify the pathogen. Equally important is nuclear scanning, which allows you to exclude or identify diseases with similar symptoms.
It can be:
- testicular torsion;
- presence of neoplasms;
- hydrocele;
- hernia;
- abscess;
- gangrene.
Moreover, most of these diseases can develop against the background of untreated epididymitis. Therefore, such a disease is extremely dangerous due to its complications.
In parallel with laboratory diagnosis, an instrumental examination of the disease is prescribed:
- Ultrasound. Helps determine possible inflammation and its stage. But in most cases, it is difficult to determine the stage of the disease with such an examination. Therefore, another instrumental examination is prescribed.
- MRI. Usually this method is carried out for a fee, which not all patients can afford. But this is the most accurate method that allows you to determine the severity and stage of the disease of the testicles and appendages.
During a diagnostic examination, doctors recommend checking your sexual partner for the presence of pathogens. This is important even if the sexual partner does not have severe symptoms.
Types and types
Epididymitis orchioepididymitis is classified by form (acute and chronic). By type it can be one-sided (left-sided, right-sided) or two-sided. There are many types, mainly in medicine they distinguish purulent and stagnant.
Acute and chronic
Acute is characterized by piercing pain in the testicle. The main part of the scrotum increases (2-4 times), becoming smooth and glossy due to smoothing of the skin. Even a slight touch causes discomfort in the inflamed area. The temperature rises, general weakness is observed. Sometimes vomiting occurs.
Chronic is considered a complication. The temperature decreases, the pain becomes tolerable (during remission), but when palpating the inflamed area, a thickening will be felt. The main feature is relapses over a long period of time (from six months), 1-2 times every 3 months. Difficult to treat, provokes infertility.
Left-handed and right-handed
In medicine, left-sided and right-sided orchiepididymitis are classified. It all depends on which side of the scrotum the inflammatory process occurs on. The first is most common, which is due to the structure of the male genitourinary system, where the appendage on the left is more elongated. Accordingly, it is the left side that is most often affected (in 70% of cases). The right-sided variant is recorded less frequently, in 25% of cases. Bilateral orchiepididymitis is possible (mainly, it develops from the left side or right side, when treatment is delayed).
Purulent
Purulent orchiepididymitis is an abscess lesion of the scrotum. It is also called the third form of the disease. Without timely measures, the general condition worsens, the testicle (or both) atrophies, and a man’s ability to have children is reduced to a minimum. If you do not consult a doctor after this, infection of other organs and systems of the body is possible with all the ensuing consequences. Self-medication is unacceptable.
Stagnant
Congestive orchiepididymitis appears due to severe circulatory disorders in the pelvic organs. It may be a consequence of a sedentary lifestyle, inactivity, chronic constipation or hemorrhoids, or the practice of PPA.
If doctors cannot determine the cause, a diagnosis of “nonspecific epididymitis orchioepididymitis” is made.
Treatment methods
Most often, conservative therapy is used to treat epididymitis: antibacterial drugs, analgesics, antispasmodics, vitamins and immunomodulators are prescribed. At an advanced stage of the disease, hospitalization and surgical intervention are required.
Conservative therapy
Appointment with a urologist: preparation for examination, diagnosis and treatment measures
Treatment at home requires bed rest. A suspension is prescribed to pull the scrotum up. This significantly reduces pain. The dosage is determined strictly by a specialist, taking into account the form of the disease. It is of primary importance to eliminate infectious agents, block pain symptoms, and reduce tissue swelling. Antibacterial therapy is also prescribed. The simultaneous use of two antibiotics is often prescribed, since the pathology arose due to mixed microflora.
Treatment of men under 40 years of age is carried out with the following drugs:
- cephalosporins intramuscularly in combination with tablets, the course of treatment is 10 days;
- modern macrolides, for example, Sumamed for 3-5 days.
Treatment of epididymitis in men over 40 years of age is carried out using:
- Levofloxacin or Ciprofloxacin for oral administration;
- combinations of a sulfonamide agent and trimethoprim for oral administration.
Regardless of the complexity of the disease, the course of treatment with antibiotics is strictly prescribed by a doctor. Depending on local conditions, the doctor may change the antibiotics and duration of therapy. Incorrect therapy at an early stage can cause complications that will be difficult to eliminate without surgery.
If the cause of epididymitis is not infectious, then anti-inflammatory medications are prescribed. In the chronic form of the disease, physiotherapy is prescribed. If sexual transmission of bacteria has been confirmed, you should tell your sexual partner about the disease so that he also undergoes a course of therapy even in the absence of symptoms. Otherwise, after recovery, you will get sick again.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine can be used together with antibiotics, but only after consulting a doctor. This type of therapy involves the use of various infusions and decoctions based on beneficial plants:
- Mix equal parts juniper cones, shepherd's purse and bearberry leaves, dandelion and steelgrass roots, anise and dill seeds. Place three tablespoons of the resulting mixture in a half-liter container, pour boiling water over the mixture and leave to steep for half an hour. Strain the resulting infusion and drink it in two doses throughout the day.
- Mix birch leaves, juniper cones, celandine leaves, steelweed roots, and cinquefoil grass in equal proportions. Pour four tablespoons of the mixture into a liter container and pour boiling water over it. Leave the liquid to cool and then strain. Drink the mixture in one day, dividing it into three doses.
- Mix corn silk, birch buds, dry bean pods and violet flowers. Pour one tablespoon of the mixture into half a liter of boiling water. Take two spoons three times a day.
- Mix lingonberry leaves, horsetail grass, tansy flowers. Pour boiling water over 4 tablespoons of the mixture. Drink in one day in two doses.
To each of the listed medicinal mixtures you can add peppermint, yarrow, calamus root, licorice, wormwood herb, strawberry leaves, currants, St. John's wort, nettle, rose hips, linden blossom. It is recommended to take any of the herbal infusions for no more than a month. For a chronic disease, if surgery is not required, treatment should be repeated 3-4 times a year.
Diet for epididymitis
In order for the male reproductive system to begin fully functioning again, it is necessary to consume foods containing vitamins A, B, C, E, phosphorus, magnesium, zinc, iron and beta-carotene. The following products are recommended:
- nuts: peanuts, hazel, pistachios, walnuts, almonds;
- fruits: pomegranates, lemons, oranges, figs;
- onions: onions, green, leeks;
- seafood: shrimp, shellfish, flounder, mussels, crustaceans;
- spices: mint, anise, St. John's wort, cumin, parsley, tarragon, celery, purslane, thyme;
- pumpkin seeds, turnip seeds and sesame seeds;
- rye bread or with bran;
- fermented milk products: kefir, yogurt, cheese, cottage cheese;
- game and cattle meat;
- honey and its by-products.
Important: it is recommended to completely exclude canned food, fatty meat and lard, hot spices, fried and smoked foods, and alcohol from the patient’s diet.