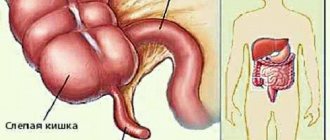
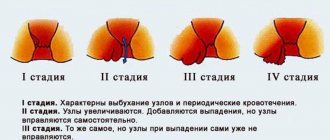
In gastroenterology, the term intestinal dyskinesia defines a symptomatic complex of disorders of the digestive organ that occurs as a result of a violation of its motor and functional activity. Most often, intestinal dysfunction occurs in the colon, representing the so-called irritable bowel syndrome with a predominance of functional constipation. According to statistics from the World Health Organization, colon dyskinesia is diagnosed in every third inhabitant of the planet, with a predominance of frequency in women of childbearing age.
General information
Intestinal dyskinesia is a term that defines a complex of intestinal disorders that arise as a result of disturbances in the motor functions of the intestine. Mostly such disorders occur in the colon.
Intestinal dyskinesia is characterized by the absence of organic changes, but the organ cannot perform its functions normally. According to the World Health Organization, about a third of all people on the planet suffer from this disease. In most cases, the disease is typical for women.
Types of intestinal dyskinesia
In the case of spastic (hypermotor) intestinal dyskinesia, increased intestinal tone and spastic contractions are observed. The consequence of this condition can be constipation, as well as colic in the abdomen. If a patient has atonic (hypomotor) dyskinesia, then there is a sharp weakening of intestinal tone and motility. The consequence of this will be constipation, dull pain, a feeling of fullness, and in some cases, intestinal obstruction occurs. In turn, the consequence of constipation will be the accumulation of feces in the intestines, which leads to dizziness, weakness, nausea, and decreased performance. The contents of the intestines undergo rotting, and this can provoke an allergic reaction. Chronic constipation can cause hemorrhoids and anal fissures.
There are also primary intestinal dyskinesia, in which intestinal motor disorders are an independent disease, as well as secondary dyskinesia, which manifests itself as a symptom in other gastrointestinal diseases. However, it is quite difficult to differentiate these conditions.
Symptoms of intestinal disorder
All symptoms of this disease are divided into those related to the intestines, to other digestive organs and non-gastroenterological. The absence of organic pathology is also important for making a diagnosis. Intestinal symptoms include abdominal pain, flatulence, diarrhea and constipation. Abdominal pain never occurs at night. It can be vague, aching, dull, or dagger-like, constant, twisting. Most often localized in the iliac region, more on the left. Increased pain is associated with eating, easing – with defecation and release of gases. Flatulence usually increases in the evening or after eating.
Diarrhea is typically absent at night and appears in the morning after breakfast. The first portions of stool are usually denser, then several urges to defecate with watery stool occur over a short period of time. A feeling of incomplete bowel movement is characteristic. The total daily volume of feces is very small, no more than two hundred grams. With constipation, the stool is dense, the shape can be like sheep feces, or in the form of a pencil. Often semi-liquid stool is passed behind dense feces. Admixtures of blood and pus are uncharacteristic, but mucus is quite common.
Since the listed intestinal symptoms are not specific and can occur in other diseases, attention should be directed to identifying signs of dysfunction of other digestive organs (esophageal dyskinesia; dyspepsia not associated with gastric ulcer; anorectal dysfunction, etc.), as well as non-gastroenterological complaints (headaches, pain in the spine, feeling of lack of air and incomplete inspiration, internal trembling).
Most often, this disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- Insomnia.
- Obesity.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Mental disorders (development of depression, nervousness, frequent anxiety)
- The appearance of pain in the area of the heart or spine, even when they are completely healthy.
- Mucous discharge during defecation.
- Flatulence.
- Belching.
- Feeling of heaviness in the stomach.
- Feeling of fullness in the abdomen.
- Abnormal stool (diarrhea, diarrhea, constipation).
- Bloating.
- Frequent nausea.
- Cutting pain in the abdomen, which can be of varying intensity. Also, the pain can be cramping and paroxysmal. Sometimes they can get worse after eating or stress.
The patient experiences neurotic and intestinal symptoms. They are multiple in nature, therefore they manifest themselves in several signs:
- increased bloating in the evening;
- violation of the frequency of defecation and the nature of feces: constipation occurs, followed by short-term diarrhea, and if the small intestine is damaged, diarrhea is observed constantly;
- the occurrence of pain: boring, aching, cutting, cramping and dull;
- spread of pain throughout the abdomen: pain intensifies after eating and subsides after the release of gases or bowel movements;
- the appearance of a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the stomach;
- frequent belching and vomiting;
- Mental disorders: nervousness, anxiety.
Frequent constipation leads to the accumulation of feces and poisoning of the body, resulting in the following symptoms:
- fatigue;
- loss of strength and lethargy;
- headache and dizziness;
- loss of appetite;
- decreased performance;
- deterioration of attention.
The spastic form of dyskinesia is characterized by the following symptoms:
- white coating on the tongue;
- convulsions;
- bloating;
- bad breath;
- accelerated bowel movement, accompanied by pain;
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen.
With the development of the atonic form, the following symptoms appear:
- allergic reactions;
- weight gain;
- distension inside the abdomen;
- dull pain of a long nature;
- small volume of feces during bowel movements;
- copious gas emissions with a pungent odor;
- fullness of the stomach and a feeling of heaviness.
- Diarrhea. The stool has a liquid consistency, but not watery. Bowel movements can occur once or several times during the day. The nature of diarrhea also depends on the level of intestinal damage. If the motor activity of the small intestine is impaired, diarrhea occurs half an hour after eating, is not accompanied by pain, but is accompanied by rumbling and a feeling of bloating. Stool can be up to 4 times a day. If the large intestine is affected, diarrhea can occur up to 10 times a day, accompanied by a painful urge to defecate. Feces may contain mucus impurities.
- Impaired absorption of water and electrolytes. The rapid passage of food through the intestines due to increased peristalsis leads to impaired absorption of water and electrolytes, especially bicarbonates, which leads to the development of symptoms of dehydration (thirst, dry skin, dry tongue with a white coating, etc.).
- Pain. They have an aching, bursting character. After the act of defecation, bowel movements may persist. The appearance of pain is associated with increased intestinal motility. The localization of pain depends on the level of the lesion. If the small intestine is affected to a greater extent, the pain is localized in the umbilical region. When the large intestine is affected, pain is localized in the lower and lateral parts of the abdomen.
- Mucoid colic. This is a rare symptom of hypermotor dyskinesia, which is manifested by the release of feces with mucus or only mucus during defecation.
- Constipation. With hypermotor dyskinesia, in some cases constipation rather than diarrhea occurs. In these cases, they are spastic in nature, and the treatment will be the same as for hypomotor constipation.
We recommend reading:
Causes of seething and rumbling along the intestines, methods of elimination
- Constipation. They arise due to a slowdown in the movement of chyme through the digestive tract. Constipation is said to occur when stool retention lasts more than 48 hours or bowel movements occur less than 3 times a week in an adult. After defecation, the feeling of incomplete bowel movement persists.
Atonic constipation occurs when the coordinated activity of all types of bowel movements is disrupted. Feces accumulate in the lumen of the large intestine, stretch its walls and, in severe cases, lead to the development of fecal stones, which create a clinical picture of intestinal obstruction. When bowel movements occur, a large amount of hard stool is released. After the act of defecation, there is an improvement in well-being and subsidence of pain.
Spastic constipation occurs when the circular muscles of the intestine are disrupted. They are excreted in small quantities like “sheep feces” and are accompanied by cramping pain in the abdomen. Constipation may alternate with normal bowel movements.
- Pain. Pain syndrome can have varying degrees of severity and duration. The pain is sharp, cramping in nature with spastic constipation and dull, aching in nature with atonic constipation. They are most often localized in the umbilical region or in the ileal regions, and subside after bowel movement.
- Bloating or flatulence. Stagnation of feces disrupts the digestive processes, leads to rotting and fermentation of food masses, which is accompanied by increased gas formation and the release of toxic products. Flatulence intensifies before defecation and disappears with the passage of feces and gases.
- Intoxication syndrome. Toxic products formed during the rotting of food gruel lead to the development of symptoms of intoxication (decreased appetite, deterioration in general health, loss of body weight, etc.).
General manifestations
- Dyspeptic symptoms: nausea, loss of appetite, feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, belching of air.
- Neurotic disorders. Symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia disrupt a person’s usual way of life, leading to increased irritability and emotional lability. In severe cases, depressive changes develop, sleep is disturbed, and a person’s performance decreases. A person focuses on his problem, trying to find signs of a malignant neoplasm in the symptoms.
- Dysbacteriosis. Existing changes in intestinal function lead to the growth of pathogenic microflora in the intestine and the development of inflammatory changes and the addition of infections.
We recommend reading:
How does defecation occur in humans?
Causes of intestinal dyskinesia
It is generally accepted that primary dyskinesia most often manifests itself due to the influence of psychogenic factors. However, the disease often occurs as a result of excessive consumption of foods that are low in dietary fiber. Many experts tend to consider primary intestinal dyskinesia as a psychosomatic disease that develops as a result of acute and chronic traumatic moments, intrapersonal conflicts, and negative emotions. In addition, acute intestinal infections can serve as etiological factors for intestinal dyskinesia.
Secondary dyskinesia manifests itself as one of the symptoms of diseases of the digestive system. This may be chronic gastritis, liver disease, peptic ulcer, pancreatitis and cholecystitis. Also, such a violation is typical for diseases of the endocrine system. These are various pituitary disorders, diabetes mellitus, myxedema, hyperparathyroidism. Constipation often develops in people who abuse certain medications that have a direct effect on the motility of the large intestine. Such drugs include anesthetics, antibiotics, anticonvulsants, muscle relaxants, anticholinergics, psychotropic drugs, etc.
Causes of the disease
It is important to know: mental disorders can cause many diseases, including stomach ulcers, depression, pancreatitis, disorders of the musculoskeletal system and the nervous system.
Colon dyskinesia is no exception. It usually develops for the following reasons:
- Unstable psycho-emotional state. For example, if a person is often exposed to stress, neuroses, experiences negative emotions or depression, then he is at risk for developing dyskinesia.
- Incorrect (poorly balanced) nutrition. This includes frequent overeating, eating on the run, eating junk food (fatty, smoked, etc.). In addition, a lack of foods that contain fiber (vegetables and fruits) greatly increases the risk of developing this disease.
- Individual intolerance to certain foods, which causes a lack of nutrients in the body.
- Vitamin deficiency.
- Sedentary lifestyle and complete lack of sports.
- Presence of severe chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, physical inactivity, hypertension, etc.)
- Genetic predisposition to dyskinesia.
- The presence of severe infectious diseases of the intestinal system.
- Various endocrine system disorders (obesity, menopause in women).
- Gynecological diseases in women that provoke intestinal dysfunction.
- Frequent use of medications that have a negative effect on the functioning of the colon (taking antibiotics, antipsychotics, anesthetics, etc.).
- Hypovitaminosis (an excess of certain vitamins) can cause dyskinesia in children.
- Disturbances in the hormonal system.
- Increased nervous excitability in children.
- Insufficient production of necessary enzymes in the pancreas leads to dysfunction of the colon.
- Gluten or lactose intolerance.
- The presence of chronic inflammatory diseases of the pelvis.
- Various pathologies and diseases of the musculoskeletal system (osteochondrosis, arthritis, arthrosis).
- Insufficient fluid intake.
- Frequent consumption of salty foods.
In addition, additional reasons due to which a person may develop colon dyskinesia are:
- liver diseases, especially chronic hepatitis;
- stomach ulcer;
- pancreatitis;
- cholecystitis;
- myxedema.
Symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia
In addition, symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia include noticeable bloating, various types of bowel movements, and constant rumbling in the abdomen.
In some cases, rumbling in the stomach and bloating are practically the only signs of the disease. These symptoms appear regardless of what food a person eats. Constipation is most often observed as a bowel disorder, which can sometimes be replaced by short-term diarrhea. In this case, some mucus may be released along with the stool.
However, in the presence of such disorders, in particular frequent diarrhea, a person does not lose weight, and sometimes there is even an increase in body weight. People who suffer from intestinal dyskinesia for a long time often experience some mental disorders: they are overly anxious, nervous, and easily fall into a depressive state. Sometimes patients note pain in the back or heart, but after examination it turns out that all these organs are healthy.
Diagnosis of intestinal dyskinesia
Due to the unclear localization of pain during intestinal dyskinesia, as well as symptoms similar to those of other diseases, it is difficult to diagnose intestinal dyskinesia based on the patient’s complaints, as well as his interview. Consequently, most specialists, faced with such an uncertain clinical picture, make a diagnosis based on the method of exclusion.
Differential diagnosis in this case is carried out in several stages. First of all, the doctor excludes some intestinal pathologies: tumors, polyps, diverticula, and other anomalies. Next, it is important to distinguish between dyskinesia and non-ulcerative colitis. After this, the specialist makes a differential diagnosis of the two types of dyskinesia, determining whether primary or secondary dyskinesia occurs. The causes of the disease are also determined.
To exclude the above diseases, a set of studies is carried out, used to examine patients with colon pathology. This includes scatological examination, irrigoscopy and endoscopy, stool examination for dysbacteriosis and occult blood. It is also important to perform a colon biopsy.
Very often, people suffering from intestinal dyskinesia are diagnosed with dyskinetic syndrome and dysbacteriosis. During endoscopy, organic changes are not detected. A normal histological picture of the intestine is observed.
Symptoms
Intestinal dyskinesia provides the patient with various discomfort sensations, including pain symptoms, which vary in intensity. Acute, dull, aching or cutting pain in the abdomen can bother a person from several minutes to several hours until he receives qualified medical care.
The localization of pain with dyskinesia of the colon affects almost the entire abdominal cavity, and the painful sensations do not subside until gas is released or a complete bowel movement occurs. The pain intensity subsides for a while during sleep and resumes after waking up.
All these factors affecting intestinal motility cause emotional overload and stressful situations in a person. Also, the emerging spastic colitis or irritable bowel syndrome with dyskinesia, leading to stagnation of feces, can provoke an allergic reaction or general intoxication of the body.
General symptomatic characteristic signs, regardless of the degree of neglect and type of intestinal disorder, are as follows:
- constipation;
- nausea and frequent persistent vomiting;
- unmotivated increase in body temperature;
- weight loss or gain, regardless of a person’s appetite;
- increased gas formation and flatulence;
- changes in the general blood test, for example, an increase in ESR, leukocytosis;
- pain in the abdominal cavity without local localization, which goes away after defecation;
- dizziness and general weakness of the body.
The clinical picture is individual for each form of the disease. For example, dyskinesia of the hypotonic type has the following distinctive features:
- dull pain in the abdominal area that is not clearly localized;
- prolonged constipation;
- weight gain;
- feeling of fullness and heaviness in the abdomen;
- excessive discharge of gases;
- feeling of fullness and insufficient bowel movements;
- intoxication of the body;
- attacks of nausea that may result in vomiting;
- development of allergies to fermented milk products and cereals.
The symptoms are characteristic of everyone who is subsequently diagnosed with intestinal dyskinesia of the hypomotor type or hypermotor type. Gender and age category have no restrictions.
Treatment of intestinal dyskinesia
Primary intestinal dyskinesia, which has a psychogenic origin, is successfully treated with the use of psychotropic drugs (in this case, tranquilizers, antipsychotics, antidepressants are used), as well as psychotherapy sessions. Effective will be drugs that have a general strengthening effect on the central nervous system, which, in turn, helps to normalize the functioning of the autonomic nervous system and reduce the level of excitability of the intestinal muscles. In this case, the prescription of medications, as well as the choice of tactics for psychotherapeutic assistance, is carried out by a specialist of the appropriate profile. It is important to note that psychotropic drugs are not recommended for long-term use.
As a rule, the doctor is especially careful when prescribing medications.
In addition, patients are recommended to periodically take oxygen and pine baths. In some cases, the use of heat on the abdomen, ozokerite and paraffin applications on the lower abdomen are effective. Acupuncture sessions are also used in this case.
To calm the nervous system, some folk remedies are also used, in particular medicinal plant therapy. In this case, the herbal infusion described below will be effective.
You should mix the herbs of sage, motherwort, yarrow and St. John's wort flowers, peppermint leaves, and oak bark in equal proportions. Two tablespoons of the collection are poured with boiling water and infused for two hours. The collection should be taken half a glass four times a day after meals. After three days, the dosage is reduced to a third of a glass, and for one week the collection is taken three times a day.
You can also use special compresses on the stomach: for this, half a glass of vinegar is dissolved in three liters of water. The gauze is washed off in the solution, and the compress is placed on the stomach for an hour and a half.
Diet, nutrition for intestinal dyskinesia
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 5-7 days
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of products: 1200-1300 rubles per week
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 1-2 months
- Terms: from 1 month/permanently
- Cost of products: 1600-1700 rubles. in Week
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 20 days
- Terms: from 2 months or more
- Cost of products: 1400-1500 rubles. in Week
If you follow the principles of the diet for intestinal dyskinesia, the disease bothers patients much less.
First of all, all food should be boiled or steamed, and the food should not be chopped. To stimulate intestinal motility, you should include in your diet berries, fruits, and vegetables that have the ability to enhance the evacuation function of the intestines and do not cause fermentation and do not irritate the intestinal mucosa. For different types of dyskinesia, it is necessary to follow a diet that corresponds to the type of intestinal motility. So, if a person suffers from hypomotor dyskinesia of the colon, then foods high in fiber should be included in the daily diet. First of all, these are vegetables - beets, carrots, cabbage, zucchini, tomatoes, herbs. At the same time, vegetables that contain a lot of essential oils are best excluded from the diet. These are onions, radishes, turnips, radishes, mushrooms. It is best to eat bread with bran, made from wholemeal flour; cereal porridge boiled in water is useful. The diet also includes soups, which should be cooked in low-fat and vegetable broths. Lean meat is allowed, fish, eggs can be eaten periodically, but no more than two pieces per day. In addition, you should consume fruit and vegetable juices, dried fruits, bananas and apples every day. The organic acids contained in these products help stimulate intestinal motility. Fermented milk products are no less useful, especially those that contain a live culture of bifidobacteria. In order to stimulate regular bowel movements, you should eat cold foods. You can consume wheat bran in its pure form for some time - it is recommended to eat it regularly for about six weeks. They should be poured with boiling water and can be consumed either on their own or added to a variety of dishes. This helps make bowel movements easier.
People who suffer from hypermotor dyskinesia are advised to regularly consume oils, both a variety of plant and animal oils. You should avoid baked goods, white bread, starchy foods, fatty meats, spicy and canned foods, strong tea and coffee. You also need to be very careful with products that contribute to increased gas formation. In the case of hypermotor dyskinesia of the colon, it is very important to follow a special slag-free diet that contains a lot of vegetable fats. At the same time, foods that contain a lot of fiber should be excluded, as they can cause increased spasticity and pain in the abdomen.
If intestinal motor functions improve, then you can gradually begin to introduce boiled vegetables into the diet, and later move on to the gradual consumption of raw vegetables.
The benefits of dietary fiber in the treatment of peristalsis disorders
To normalize the condition of the digestive canal, you should supplement your diet with dietary fiber. Their quantity is reduced in the diet of modern people. In order to improve the taste of dishes, ballast substances are removed from products during technological processing. As a result, the body does not receive enough valuable substances, and the digestive canal reduces its functions. Hard-to-digest carbohydrates, cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin are important for intestinal bacteria; they determine gastrointestinal motility.
The listed elements are contained in bran
. They should be taken gradually (start with 1 teaspoon, slowly increasing the dosage). It is acceptable to add bran to broth or kefir. As a result of metabolism, short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) are formed - compounds that can retain water inside the intestines. Supplementing the diet in the form of bran will affect his condition - it will prevent the formation of constipation and the increase in intoxication.
The main reason why patients are reluctant to consume dietary fiber is the fear of bloating due to flatulence. Conviction is facilitated by the advice of gradually increasing the portion of bran.
Comments
The article is good, the main thing is to really follow all the recommendations, lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right. I myself now have problems with the gastrointestinal tract, I’m trying to monitor my health and regimen
Please note that with hypomotor and hypermotor dyskinesias, the diets differ, and in some places dramatically
Can not understand anything! For hypomotor dyskinesia, dietary recommendations are given that are completely mutually exclusive - one thing in the first paragraph, the exact opposite in the second. If you are going to give medical advice, at least read what you wrote!
Intestinal dyskinesia is a functional malfunction of the large or small intestine, which manifests itself as a very delicate problem in the form of unexpected constipation and diarrhea. The terminology indicates a violation of intestinal motility and tone.
At the same time, according to analyzes and additional studies, no organic pathology (for example, inflammation) is detected in patients. The connection with the state of neurohormonal regulation of the digestive process is important. According to the International Statistical Classification, intestinal dyskinesia is usually considered a disease and coded K59.8.1.
Prevalence
According to various observations, the disease affects from 20 to 30% of the population. Gastroenterologists believe that the pathology is perhaps more common. Patients are embarrassed to see a doctor; the disease is not always registered due to unauthorized refusal to be examined. The maximum number of cases is detected in the group of people aged 30 to 40 years.
The younger the age, the more female predominant. By the age of 50, the incidence of men and women is no different. The initial signs of the disease are found in children. At 15 years of age, the risk of functional impairment is comparable to that of adults. Dyskinesia of the large intestine is much more common than that of the small intestine.
Why does it happen?
The reasons for the failure of intestinal functions are most often hidden in the disruption of the nervous and hormonal regulation of the tone of the muscle layer. Similar conditions arise when suffering from stress (a tragic event with a loved one, problems in the family and at work, business failures, intense study, an exam session). In women, the emotional background of any event is more vivid, anxiety reaches the level of depression.
Defeat in adolescence is associated with the inability of a growing person to recognize difficulties and withstand stress against the backdrop of vulnerable hormonal changes in the body. Provoking factors are: any physical pain, previous infectious disease, malnutrition (starvation diets in girls), physical overexertion in sports. hall
Intestinal dyskinesia can be combined with similar damage to the biliary tract and mental disorders. Psychiatrists interpret this pathology as an individual characteristic of a person that leads to the transformation of emotional instability (suspiciousness, anxiety) into a disease of internal organs.
The process of peristalsis is influenced by:
- the chemical composition of food entering the intestinal lumen (fiber and vitamins strengthen, high-calorie carbohydrates, fats weaken);
- abdominal muscles - have a massaging effect by changing intra-abdominal pressure during walking and moderate exercise.
Therefore, the quality of nutrition and physical activity of a person play an important role in the development of pathology and treatment of the disease. A careful survey of patients allows us to identify a connection with the factor of heredity, the presence of identical manifestations in relatives. It is typical that by old age the symptoms of dyskinesia disappear or transform into organic intestinal diseases.
Features of the course of dyskinesia in children and pregnant women
Dyskinesia in children is most often observed in the form of alternating severe diarrhea and constipation with painful colic and increased gas formation. In a child, manifestations in the form of lethargy, apathy, disturbances in general condition and mood dominate the specific clinic of dyskinesia. Therefore, it is very important to consult a doctor in a timely manner to exclude developmental anomalies and acute conditions masquerading as a disease. An important aspect of treatment is sleep and rest patterns, nutritional load and complex therapy.
Constipation is a common symptom of dyskinesia in children.
This pathology is often found in expectant mothers, which is due to both physical changes in the body (raising the diaphragm, compression of the vena cava) and hormonal changes (the release of progesterone - weakens intestinal tone).
Most often, the manifestation of dyskinesia in pregnant women is expressed in constipation, a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, and pain. This condition is quite dangerous, since increased intra-abdominal pressure affects the fetus, which can lead to the threat of miscarriage. At the first symptoms, you should immediately contact your doctor.
The essence of the violations
The main changes in dyskinesia are the disruption of the muscle fibers of the intestinal wall in the perception and assimilation of impulses received from the nervous system or hormones. Due to the presence of two muscle layers (inner annular and outer - longitudinal in the small intestine, and in the large intestine three ribbon-like plexuses), the contents are transported gradually from the duodenum to the rectum.
The wave of contractions produces up to 18 pushing movements per minute. At the same time, in a healthy intestine, the processes of assimilation and processing of food, the formation of waste in feces, and the absorption of water occur. The natural activating substance is bile delivered through the common duct.
Untimely intake or lack of bile acids leads to the fact that duodenal dyskinesia is manifested by impaired processing of food masses, reflux of contents in the opposite direction into the stomach. With proper contractile function, the entire volume of bile and pancreatic juice passes into the small intestine.
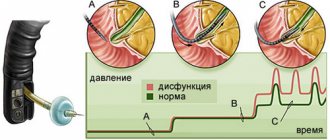
There are 2 types of reactions possible:
- when accumulated, sympathetic nerve impulses increase, tone increases and spasm is caused;
- if there is little acetylcholine, the muscles relax and tone drops.
The activator substance enters through the fibers of the vagus nerve. Therefore, the mechanism of colon dyskinesia is associated with its dysfunction. Sensitivity disorders and subsequent changes in the contractility function of the muscle wall lead to impaired evacuation of contents, accumulation of gases, and instability of bowel movements.
Dyskinesia is classified according to its origin:
Clinical classification in gastroenterology takes into account the relationship with stool frequency and stool consistency. There are 4 types of dyskinesia:
- with the advantage of constipation - of all acts of defecation, more than a quarter is accompanied by dense stool, less than ¼ of the part may be diarrhea;
- with a predominance of diarrhea - more than a quarter of cases are due to diarrhea, less - to constipation;
- mixed type - the above ratio is violated;
- unclassifiable - the signs are not sufficient to establish the form of the disease.
Depending on the type of peristalsis disorder, the following forms are distinguished:
- spastic (hypermotor) - intestinal tone is in an increased state, which causes short-term spasms, constipation or diarrhea, colic-type pain;
- atonic (hypomotor) - a decrease in peristalsis contributes to the accumulation of gases, feces, bursting pain along the intestines, prolonged constipation, reaching acute intestinal obstruction.
The atonic form is characterized by extraintestinal symptoms of large intestinal dyskinesia; they are caused by poisoning of the body with unremoved toxins. It is important for specialist doctors to prescribe optimal treatment, therefore it is important to divide disorders into dyskinesia: with stool disorder, severe pain, with flatulence.
Another classification provides for the principle of origin of dysfunction:
- post-infectious disorders;
- caused by stress;
- having a clear connection with food products (an allergy mechanism cannot be excluded).
Classification
Varieties of malaise, depending on the underlying etiological factor, suggest the existence of the following forms of dyskinesia:
- psychogenic;
- neurogenic;
- toxic;
- medicinal;
- nutritional – caused by errors in nutrition;
- endocrine;
- proctogenic;
- abnormal - associated with congenital malformations;
- hormonal;
- metabolic - provoked by any condition that disrupts metabolism.
Depending on the pathogenesis of development, the following are distinguished:
- primary dyskinesia;
- secondary dyskinesia.
Based on clinical manifestations, colon dyskinesia occurs:
- with a predominance of intestinal disorders;
- with pronounced pain;
- with general neurotic disorders coming to the fore.
Based on movement disorders, it is customary to distinguish the following types of disease:
- Atonic or hypomotor dyskinesia of the colon. Characterized by a sharp weakening of peristalsis and tone of the affected organ. In most situations, there is a relationship between the disease and adherence to strict diets and physical inactivity.
- Spastic or hypermotor dyskinesia. It is characterized by increased hypertonicity and active spastic contractions of the intestines. Often associated with irrational eating habits.
How does the disease manifest itself?
The international criterion for the presence of dyskinesia is the persistence of symptoms for at least three days. It is customary to distinguish manifestations by nature. Intestinal:
- abdominal pain - short-term cramping type or long-term dull, bursting, aching, most often located in the left half of the abdomen, in the iliac zone, intensifies after eating, is relieved by the release of the intestines and the release of gases, does not disturb at night;
- alternating diarrhea and constipation, unstable stools (first dense masses, then semi-liquid), the total volume is small, diarrhea begins after breakfast, there is no stool at night, false urges (tenesmus) are possible, mucus is often secreted;
- bloating from any food, worse in the evening.
Signs expressed by other disorders of the digestive system: at the same time, changes in the functioning of the esophagus (belching, heartburn, difficulty swallowing), nausea, possible changes in the area of the rectum and anus (fissures, hemorrhoids).
How is the diagnosis made?
Despite the presence of symptoms, it is difficult to make a correct diagnosis due to the lack of any specific signs. Colon dyskinesia is a presumptive diagnosis in a patient with the most typical complaints. To identify the final pathology, it is necessary to exclude various diseases of the digestive organs, which are accompanied by similar symptoms, to establish a clear duration of manifestations, probable connections and mechanism of damage, and the effect of the treatment.
A more serious pathology, rather than functional impairment, is indicated by:
- weight loss;
- identification of previous inflammatory or tumor diseases of the intestine;
- blood in stool;
- temperature increase;
- identifying the connection between symptoms in girls and menstruation;
- dependence on medications;
- onset of the disease over the age of 50 years.
It is mandatory to prescribe the most available hardware techniques for intestinal examination:
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy - will exclude pathology of the upper digestive tract;
- X-ray examination of the stomach and intestines with preliminary administration of a barium suspension - a contrast agent, evenly distributed, helps to examine the contours, identify ulcers, polyps, tumor-like diseases, spasmodic areas, dolichosigma, diverticulitis;
- irrigoscopy - carried out by introducing a barium solution in an enema, the lower parts of the large intestine, sigmoid and rectum are clearly contrasted on the x-ray;
- colonoscopy - examination of the large intestine using an endoscopic tube inserted into the rectum under anesthesia, makes it possible to visually examine damage to the intestinal walls (ulcers, diverticulitis, inflammation);
- sigmoidoscopy - examination of the rectum excludes complications of hemorrhoids.
Laboratory techniques are needed to detect intestinal inflammation (a large number of leukocytes, pus in the stool, red blood cells); a stool test for the Gregersen reaction (occult blood) is not positive for dyskinesias.
Scraping for enterobiasis, examination of coprogram - worm eggs indicate the specificity of intestinal damage and the symptom requires targeted treatment. Biochemical blood tests determine the disturbed ratio of protein fractions, enzymes, and hormonally active substances, which indicates a certain disease of the digestive system.
Colon dyskinesia in a child
Intestinal dyskinesia in children is a common condition in which children suffer from sharply alternating constipation and diarrhea.
The disease occurs with a pronounced pain syndrome, which sometimes cannot be relieved even with the use of a large number of antispasmodics.
Most often, dyskinesia in children is neurogenic in nature.
Treatment of the disease in children includes regulation of nutrition. Usually this is enough to help a child suffering from dyskinesia.
If a child has severe diarrhea, it is not possible to manage with diet alone. In this case, therapeutic measures selected by a competent physician are required.
Most often, dyskinesia in children is neurogenic in nature.
In gastroenterology, there are 2 types of digestive pathology under consideration. Dyskinesia of the large intestine of the hyperkinetic type is a separate disease that involves impaired peristalsis of the organ.
The pathology is characterized by the occurrence of increased and frequent spasms. As a result, the food does not have time to be digested. With sudden bursts it moves to the anus. Defecation of undigested foods occurs.
Hypotonic dyskinesia of the colon involves weakened peristalsis and intestinal tone. The consequence of the disorder is a whole complex of symptoms in the form of stagnation.
There is also a combination of two types of pathological motor-evacuation changes.
Only a doctor (gastroenterologist) can prescribe treatment: taking therapeutic measures on your own is contraindicated.
1. Vitamins. They help compensate for the amount of nutrients the body lacks. B vitamins are especially necessary.
2. Antispasmodics - minimize intra-abdominal pain that accompanies all forms of peristaltic failure.
3. Prokinetics - the daily volume of intravenously administered Metoclopromide should not exceed 5-10 mg.
4. Probiotics. Restoring intestinal microflora is a mandatory stage in normalizing motility.
5. Laxatives. Senna preparations are often prescribed. They are taken before bedtime, the dosage is determined by a specialist, taking into account the dosage form. The disadvantage of the drug is that long-term use forms addiction.
Senna promotes the development of intestinal melanosis. Pathology is the formation of dark brown pigmentation on the mucous membrane. The phenomenon develops due to the accumulation of intestinal epithelial cells that have died under the influence of intoxication.
Adsorbents help cope with intestinal intoxication and stop the process of fermentation and rotting.
Additionally, iron supplements (if anemia is detected) and enzymes are prescribed. If a helminthic infestation is detected, anthelmintic drugs must be prescribed.
In addition to a detailed study of symptoms, which, as noted earlier, is necessary, diagnosis involves additional research.
First of all, this is a stool analysis for the presence of blood impurities, scatology, examination using an endoscope, as well as irrigoscopy. Experts call a colon biopsy an equally important study, which must be done in order to determine whether there are hypomotor and other tendencies.
In the presence of secondary dyskinesia, before prescribing treatment, the specialist is obliged to analyze the symptoms of other pathological processes of the digestive system.
This is exactly what needs to be done in order to decide which methods will help restore the body so that increased intestinal motility is normalized.
Treatment, in some cases carried out according to the hypotonic principle, should, first of all, be prescribed taking into account the type of disease, symptoms and causes.
That is why the most effective is complex therapy, which helps not only with dyskinia, but also with other concomitant conditions.
The remaining components can be considered psychotherapy and physical therapy. To restore the body with dyskinesia, agents should be used that normalize stools and regulate intestinal motility.
It is very useful to do enemas, not only massage, but also rinse the colon with special mineral waters. In order for inverse dyskinesia of the hypotonic type to go away as soon as possible, it is strongly recommended to drink waters that have a high degree of mineralization.
In a situation where there is a disease that is of the hypertensive type, on the contrary, it is necessary to use exclusively water with a low mineralization threshold.
Antispasmodics and anticholinergics are used to treat the hypertensive form of the condition. The use of laxative components should be considered a very important stage of therapy.
If the condition was provoked by certain psychogenic factors, you will need to use drugs such as antidepressants, antipsychotics and tranquilizers.
This must be done not only until recovery, but also after its onset. In this case, the treatment will be 100% successful and effective.
Important!
HOW TO SIGNIFICANTLY REDUCE YOUR RISK OF CANCER{q}
Time limit: 0
Navigation (job numbers only)
out of 9 tasks completed
Information
TAKE THE FREE TEST! Thanks to detailed answers to all questions at the end of the test, you can REDUCE the likelihood of disease by several times!
You have already taken the test before. You can't start it again.
The test is loading...
You must log in or register in order to begin the test.
results
Time is over
- 1.Is it possible to prevent cancer{q} The occurrence of a disease such as cancer depends on many factors. No person can ensure complete safety for himself. But everyone can significantly reduce the chances of developing a malignant tumor.
2.How does smoking affect the development of cancer{q} Absolutely, categorically prohibit yourself from smoking. Everyone is already tired of this truth. But quitting smoking reduces the risk of developing all types of cancer. Smoking is associated with 30% of deaths from cancer. In Russia, lung tumors kill more people than tumors of all other organs. Eliminating tobacco from your life is the best prevention. Even if you smoke not a pack a day, but only half a day, the risk of lung cancer is already reduced by 27%, as the American Medical Association found.
3. Does excess weight affect the development of cancer{q} Look at the scales more often! Extra pounds will affect more than just your waist. The American Institute for Cancer Research has found that obesity promotes the development of tumors of the esophagus, kidneys and gallbladder. The fact is that adipose tissue not only serves to preserve energy reserves, it also has a secretory function: fat produces proteins that affect the development of a chronic inflammatory process in the body. And oncological diseases appear against the background of inflammation. In Russia, WHO associates 26% of all cancer cases with obesity.
4.Do exercise help reduce the risk of cancer{q} Spend at least half an hour a week exercising. Sport is on the same level as proper nutrition when it comes to cancer prevention. In the United States, a third of all deaths are attributed to the fact that patients did not follow any diet or pay attention to physical exercise. The American Cancer Society recommends exercising 150 minutes a week at a moderate pace or half as much but at a vigorous pace. However, a study published in the journal Nutrition and Cancer in 2010 shows that even 30 minutes can reduce the risk of breast cancer (which affects one in eight women worldwide) by 35%.
5.How does alcohol affect cancer cells{q} Less alcohol! Alcohol has been blamed for causing tumors of the mouth, larynx, liver, rectum and mammary glands. Ethyl alcohol breaks down in the body to acetaldehyde, which is then converted into acetic acid under the action of enzymes. Acetaldehyde is a strong carcinogen. Alcohol is especially harmful for women, as it stimulates the production of estrogens, hormones that affect the growth of breast tissue. Excess estrogen leads to the formation of breast tumors, which means that every extra sip of alcohol increases the risk of getting sick.
6.Which cabbage helps fight cancer{q} Love broccoli. Vegetables not only contribute to a healthy diet, but they also help fight cancer. This is also why recommendations for healthy eating contain the rule: half of the daily diet should be vegetables and fruits. Particularly beneficial are cruciferous vegetables, which contain glucosinolates - substances that, when processed, acquire anti-cancer properties. These vegetables include cabbage: regular cabbage, Brussels sprouts and broccoli.
7.Which organ cancer is affected by red meat{q} The more vegetables you eat, the less red meat you put on your plate. Research has confirmed that people who eat more than 500g of red meat per week have a higher risk of developing colorectal cancer.
8.Which of the proposed products protect against skin cancer{q} Stock up on sunscreen! Women aged 18–36 are especially susceptible to melanoma, the most dangerous form of skin cancer. In Russia, in just 10 years, the incidence of melanoma has increased by 26%, world statistics show an even greater increase. Both tanning equipment and sun rays are blamed for this. The danger can be minimized with a simple tube of sunscreen. A 2010 study in the Journal of Clinical Oncology confirmed that people who regularly apply a special cream have half the incidence of melanoma than those who neglect such cosmetics. You need to choose a cream with a protection factor of SPF 15, apply it even in winter and even in cloudy weather (the procedure should turn into the same habit as brushing your teeth), and also not expose it to the sun's rays from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m.
9. Do you think stress affects the development of cancer? {q} Stress itself does not cause cancer, but it weakens the entire body and creates conditions for the development of this disease. Research has shown that constant worry alters the activity of immune cells responsible for triggering the fight-and-flight mechanism. As a result, a large amount of cortisol, monocytes and neutrophils, which are responsible for inflammatory processes, constantly circulate in the blood. And as already mentioned, chronic inflammatory processes can lead to the formation of cancer cells.
THANK YOU FOR YOUR TIME! IF THE INFORMATION WAS NECESSARY, YOU CAN LEAVE A FEEDBACK IN THE COMMENTS AT THE END OF THE ARTICLE! WE WILL BE GRATEFUL TO YOU!
- With answer
- With a viewing mark
- Task 1 of 9
- Task 2 of 9
How does smoking affect the development of cancer{q}
- Task 3 of 9
Does excess weight affect the development of cancer{q}
- Task 4 of 9
Does exercise help reduce cancer risk{q}
- Task 5 of 9
How does alcohol affect cancer cells{q}
- Task 6 of 9
Which cabbage helps fight cancer{q}
Is it possible to prevent cancer{q}
READ MORE: Dyskinesia of the large intestine of mixed type
Treatment
Against the background of an anxious and suspicious state, patients with intestinal dyskinesia are always worried about the question of whether their disease is being treated, whether it is developing into a malignant tumor. Most often, therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis; hospitalization may be necessary only if further examination and observation are necessary. The patient needs to get rid of unpleasant symptoms, believe in the safety of his condition and become a socially active person again.
Doctors begin recommendations by choosing a diet depending on the predominant type of dyskinesia. Hypermotility should temporarily exclude fresh vegetables, fruits, and fiber. If you are prone to constipation, on the contrary, they recommend more vegetable dishes, prunes, dried apricots, and boiled beet salads.
To prevent an allergic reaction and intestinal irritation in any form of dyskinesia, it is necessary to switch to a diet of boiled dishes, give up fried and smoked foods, fatty meat and fish, baked goods, lard, pickles, hot seasonings, confectionery, ice cream, coffee, and alcohol. Meals should be provided in small portions, but often. The diet is developed individually in each case.
In the patient's therapy, light sedatives of better herbal origin are needed (tinctures of valerian and motherwort, Novopassit). Antidepressants are rarely used as prescribed by a psychiatrist. If you are prone to constipation, laxatives with osmotic action and stimulating motor function are recommended.
Shown in short courses:
- Regulax;
- Weak;
- Slabicap;
- Phytolax;
- castor oil with kefir;
- Guttalax.
Glycerin rectal suppositories can be used infrequently. For diarrhea, Loperamide, Smecta, and probiotics with bifidobacteria are indicated. Antibacterial agents are prescribed only for secondary intestinal dyskinesia caused by pathogenic infectious agents. The courses and dosage are clearly regulated by the doctor. You cannot arbitrarily reduce or extend the intake of drugs from this group.
To relieve abdominal pain, anticholinesterase drugs are used (by destroying the enzyme cholinesterase, they promote the accumulation of the mediator acetylcholine). Antispasmodics are indicated only in case of cramping pain. In cases of combination with biliary dyskinesia, the doctor prescribes choleretic drugs and herbs that improve the composition of bile.
Significant improvement can be achieved with the help of physiotherapy. The use of the method requires the mandatory exclusion of hidden bleeding and suspicion of a neoplasm. In a sanatorium or in a hydropathic clinic, if you have colon dyskinesia, you can take courses of subaquatic baths twice a year (the intestines are washed and cleansed with water with bioactive substances), oxygen restorative procedures, and Charcot's shower.
In a physiotherapy room it is recommended:
- exposure to electrophoresis on the abdomen and collar area;
- diadynamic currents.
Etiology
Currently, the exact reasons for the formation of the pathological condition are not fully understood.
Specialists in the field of gastroenterology identify a large number of predisposing factors, which are divided into pathological and physiological. Colon dyskinesia often acts as a symptom of such diseases:
- dysbacteriosis;
- bile stagnation;
- allergic reactions;
- diabetes mellitus and other endocrinological pathologies;
- infectious lesion of the gastrointestinal tract;
- problems with the genitourinary system;
- anal fissure;
- diphtheria;
- Hirschsprung's disease;
- liver diseases;
- formation of external or internal hemorrhoids;
- asthenic syndrome;
- ulcerative lesions of the duodenum or stomach;
- megacolon;
- cholera;
- Crohn's disease;
- chronic pancreatitis or cholecystitis;
- parasitic or helminthic infestations;
- damage to the central nervous system;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- hypovitaminosis;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- poisoning from lead, paints and other chemical or toxic compounds;
- hypothyroidism
The second category of provocateurs has nothing to do with the presence of diseases in a person and includes physiological reasons:
- excess body weight;
- poor nutrition - addiction to high-calorie dishes and refined foods, lack of plant fiber in the diet;
- lack of physical activity;
- neuroses, stress and intrapersonal conflicts;
- individual intolerance to any food product;
- uncontrolled use of medications - laxatives or fixatives, psychotropic substances and anticholinergics, antibiotics and anesthetics;
- following an overly strict diet;
- frequent overeating;
- long-term addiction to bad habits;
- lack of sleep and wakefulness.
In infants, the disorder may be caused by errors in breastfeeding, artificial feeding, or early introduction of complementary foods.
The influence of such a source as genetic predisposition should not be excluded.
What can patients expect?
Full recovery can be achieved only in 10% of cases. The remaining patients must constantly support themselves with diet and medications. Gastroenterologists claim that the addition of inflammatory bowel diseases and tumors during therapy is not beyond the possibility for any person of a certain age category.
When the process is advanced, untreated, in patients with mental disorders, people constantly exposed to stress, the prognosis is unfavorable. They are at risk for further development of peptic ulcers and malignant tumors.
Doctors treat intestinal dyskinesia with the greatest caution. The manifestations may hide various rather unpleasant diseases in the preclinical stage. The examination allows them to be identified, which does not please the patient at all. Timely help often consists of reassurance and confidential conversation.