A widely used instrumental diagnostic method in gynecology, colposcopy, is aimed primarily at identifying oncological processes at the initial stage of their development. For a more detailed study of the female genital organs, an extended colposcopy is performed using special chemical reagents. During this procedure, the doctor evaluates the condition of the mucous membrane and the color reaction of the epithelial cells to the reagent. Analysis of the changes that occur allows us to diagnose the pathology as accurately as possible.
The essence of the procedure
Using a colposcope, the doctor examines the cervix, vaginal walls, and cervical canal (the area where the cervix and uterus connect). A colposcope is a small medical device equipped with a lighting system and optics with multiple magnification. Gynecological speculums are used as auxiliary instruments.
A modified, more modern version of the procedure, video colposcopy, is performed using a digital colposcope and computer technology to process the resulting video image. In the extended version, after a general examination, the mucous surface of the cervix and vaginal walls is treated with a chemical reagent. Today the following substances are used as test reagents:
- Three percent solution of ethanoic acid (aka acetic acid). The reaction of the mucous membrane to acid is a narrowing of blood vessels in healthy tissues, and a significant lightening of the color of the epithelium. This does not happen in the affected areas because the vessels are not sensitive to acid. In cases where the use of acetic acid is contraindicated, lactic acid can be used as a reagent.
- Three percent Lugol's solution with glycerin (Schiller's test). Under the influence of iodine-containing lugol, healthy epithelial cells undergo pigmentation. Areas with pathology do not change color. This allows you to assess the scale and boundaries of changes. In addition, cells must be collected from unstained fragments. Subsequent cytological studies of the biomaterial will help determine the nature of the changes (malignant or benign).
- Adrenaline (epinephrine). Used to assess the vascular system of organs.
The latter test is rarely practiced. In most cases, diagnosis is based on the results of a sequential vinegar test and Schiller test.
How is the examination carried out?
Diagnosis is carried out on a gynecological chair and resembles a regular examination. A speculum is inserted into the genital tract, allowing a good examination of the mucous membrane.
Why is the genital tract illuminated with a colposcope beam and examined using optics. To identify dilated vessels in the cervix, green or blue lenses are used, making vascular changes visible.
For other examinations, halogen, xenon or tungsten light sources are used, providing bright white light that does not distort the resulting picture. The intensity of illumination and the size of the light beam can be adjusted.
Previously, during a colposcopy, a specialist had to sketch the detected changes. This created problems when referring patients to other doctors. Now a picture of the mucous membrane is taken, which shows all the pathological changes. The results of video colposcopy can be recorded on media in the form of a video image.
Purpose of the study
The colposcopy procedure is carried out for preventive purposes, or as prescribed by a doctor. The basis for examination, most often, is erosive changes in the mucous membrane identified during a standard gynecological examination (suspected erosion of the cervix). Also, the study shows:
- for symptomatic complaints that a woman presents at a doctor’s appointment (pain not associated with menstruation, unhealthy vaginal discharge, the presence of blood in the discharge after intimate contact);
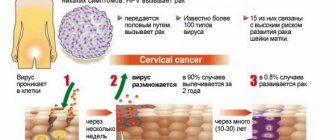
- with a positive HPV test (human papillomavirus);
- as a control procedure during the treatment of a previously diagnosed disease;
- in case of deviations from the normative indicators of the results of previous cytology, in particular, a positive Pap test (Papanicolaou smear) to establish a precancerous and cancerous condition of the cervix.
Detection of pathological changes at an early stage will avoid further complications
Colposcopy with biopsy is performed specifically to identify malignant changes.
When can a colposcopy be prescribed?
Colposcopic examination is carried out both for preventive purposes and to identify pathological processes affecting the woman’s reproductive system. The procedure is mandatory if the following diagnoses are suspected:
- erosion, dysplasia, ectopia;
- oncological pathologies;
- polyps;
- hyperplasia;
- erythroplakia.
The study allows you to confirm or refute the suspected diagnosis. In some cases, the results of colposcopy require the appointment of additional diagnostic techniques to confirm the suspected diagnosis.
Often the necessary way to confirm the presence of a pathological process is to obtain and subsequently study a biopsy - a piece of tissue that is taken by a gynecologist during colposcopy from a suspicious lesion.
Gynecological diseases that are detected during colposcopic examination
Contraindications to the procedure
There are no absolute contraindications to examination with a colposcope. The exception is an allergic reaction to iodine and iodine-containing drugs. In this case, an incomplete colposcopy (without the Schiller test) can be performed.
Relative (relative or temporary) contraindications include the postpartum period (the time interval must be at least 2 months, subject to uncomplicated delivery), the period after artificial termination of pregnancy, including medical abortion (at least 30 days), and the days of menstruation itself. Gynecologists recommend undergoing diagnostics 5–7 days after the end of the critical days.
Do you need preparation for colposcopy?
No preliminary preparation for colposcopy in gynecology is required. However, some recommendations still need to be taken into account.
- Before the procedure, it is necessary to avoid sexual intercourse for at least 24 hours.
- If menstruation has begun, colposcopy is postponed, and you should not use tampons at this moment.
- Before the examination, do not douche, avoid the use of vaginal suppositories, sprays, and tablets.
- Carrying out hygiene procedures should be carried out only with water, and do not even think about using detergents.
When preparing for the procedure, do not use soap.
To ensure that the information received is more reliable, colposcopy is performed 9-20 days after menstruation.
Important! If it is necessary to conduct an examination before the required date, you should not delay, but the doctor must be notified about this.
If the patient has irregularities in the menstrual cycle, the doctor must be notified.
Read also: about menstrual cycle irregularities.
Progress of the procedure
The examination is carried out in a regular gynecological chair. Speculums are inserted into the vagina and remain there until the end of the procedure. During the examination, the woman's genitals are repeatedly irrigated with saline to prevent the mucous membrane from drying out. Next, the doctor performs an initial examination (conventional colposcopy). The structure, color, and vascular pattern are studied.
How to prepare for colposcopy?
After assessing the external condition of the organs, the mucous membrane is treated with a swab dipped in a water-acetic solution. An assessment of the vascular reaction to acid can be obtained 2–3 minutes after treatment of the visible part of the vagina, its walls and the cervix.
Vasospasm means a positive test result. If the vessels of certain fragments of the examined surface remain unchanged, we can say that cancerous (atypical) cells are present there. In this case, the test will be negative.
The vinegar test is replaced by the Lugol-glycerin test. The treatment solution consists of distilled water, iodine, potassium iodine, in a ratio of 100:1:2. In the absence of pathological changes, the entire area of the epithelium should turn brown. Uneven pigmentation indicates the presence of atypia. At the same time, the areas affected by cancer have clear boundaries. The next stage is the collection of biomaterial for laboratory analysis (biopsy).
The size of the uterine tissue fragment for cytology is about 2 mm
The time range of extended colposcopy usually does not exceed a quarter of an hour. The time is determined individually, depending on the scale of changes in the organs.
What is extended cervical colposcopy
What are the features of extended colposcopy of the cervix, what is it, and how are its results interpreted? After a visual examination, the doctor uses a tampon to apply a small three percent solution of acetic acid to the cervix. Under its influence, the blood vessels in the mucous membrane narrow, and this makes any pathological changes more clearly defined and noticeable.
In addition to acetic acid, iodine or special reagents that can glow under ultraviolet radiation can be used for additional examination. If there are affected areas on the cervix, then when iodine is applied they will not turn dark, which will allow the doctor to accurately identify their location and extent. When using other reagents, the affected tissues may turn a certain color under the light of an ultraviolet lamp.
Post-procedural period
If the examination did not include a biopsy, the patient may be bothered for some time by a discharge of an uncharacteristic color, as a reaction to an iodine-containing reagent. If biological material was collected, the discharge may be bloody. This is due to mechanical damage to epithelial tissue. Such effects are usually short-lived and disappear spontaneously.
Basic recommendations that should be followed for 3–5 days after colposcopy: refrain from visiting the bathhouse, solarium, sauna, refuse sexual intercourse, and suspend sports training. Women are not recommended to use sanitary tampons. For the speedy healing of the wound, pads are the best option. If bleeding continues for several days, sharp pain appears, or hyperthermia (fever), you should seek medical help.
After diagnosis
A woman should know not only how to prepare for colposcopy, but also what to do after it.
If tissue for biopsy was not taken during the study, then sexual activity can be restored on the day of the procedure. Sometimes slight bleeding may occur after diagnosis. Usually it lasts no more than three days. In this case, the woman should refrain from sexual intercourse, douching, and taking medications until the bleeding stops.
Many people ask what to do if after the examination the bleeding does not stop for more than three days. In this case, you need to see a doctor immediately.
Possible test results
A simple colposcopy determines:
- the condition of the epithelium (normally it should be pink with a smooth surface);
- the presence of erosive changes in the vaginal walls and cervix;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal (endocervicitis);
- inflammation of the epithelium of the vaginal part of the cervix (exocervicitis);
- the presence of viral and genital warts (papillomas and condylomas).
Diagnosed leukoplakia of the cervix (photo)
Extended colposcopy diagnoses both the listed abnormalities and more serious diseases:
- changes in tissue structure that precede cancer pathologies (dysplasia);
- the presence of part of the epithelium of the cervical canal on the surface of the cervix (pseudo-erosion or ectopia);
- the presence of growths (polyps);
- cancer of the cervix and vaginal walls;
- proliferation of epithelial cells (endometriosis);
- death (atrophy) of individual tissue fragments;
- keratinized fragments of the mucous membrane (leukoplakia).
The gynecologist reports conclusions on the diagnostic results immediately after the procedure. A full analysis of the obtained indicators may take several days. The colposcopic method is safe and informative. This is a real chance to detect malignant changes at the initial stage, preventing their further development. Women aged 35+ are recommended to undergo this examination annually.
Colposcopy results
After the procedure is completed, the specialist draws up a written protocol - a form that contains information about the characteristics of the condition of the cervix and the presence or absence of signs indicating the possible development of pathologies. Interpretation of the results of colposcopy may contain descriptions of such anomalies as the formation of pathological vessels, the presence of whitened areas after treatment with acetic acid, the presence of areas not stained with iodine.
Colposcopy is a safe examination, does not cause side effects or complications such as pain or bleeding, and does not require recovery time. In rare cases, after the procedure, mild pain in the lower abdomen or slight discharge containing iodine may be observed, which disappears after 2-3 days.
Manipulation technique
Many patients are very afraid of this procedure. We will try to describe the biopsy technique in detail in order to dispel many fears.
- A cervical biopsy is performed on any day of the menstrual cycle, with the exception of menstruation itself.
- The patient comes to the cervical pathology office at the appointed time and sits on the gynecological chair in a standard position.
- The doctor places speculums and performs a colposcopy with all the standard tests to identify areas for biopsy.
- The walls of the vagina and cervix are treated with antiseptic solutions and a biopsy is performed in one way or another.
- Many patients are very concerned about the issue of pain relief during the procedure. I would immediately like to emphasize that the cervix, as an organ, is completely devoid of pain receptors - that is, it does not hurt. Therefore, doctors use a maximum of Lidocaine spray or, in the case of excision, intracervical injections of Lidocaine or Novocaine.
- After taking a biopsy, the doctor monitors the condition of the biopsy wound and, if necessary, coagulates the bed or places sutures. In practice, such a need arises quite rarely, especially when using loop biopsy.
- A loose tampon with one or another antiseptic is placed in the patient’s vagina, which will remain there for 3-4 hours.
- For the next three to five days, the patient is advised to abstain from sexual activity, baths, swimming pools and saunas. During this period of time, the patient may be bothered by scanty bleeding.
- In the case of excisional biopsy, the period of discharge and, accordingly, the specified restrictions is much longer - up to 4-5 weeks. Healing of the surface occurs under the supervision of medical personnel; the patient is prescribed suppositories for speedy healing of the wound surface, as well as treatment of the scab after coagulation, which is carried out by a doctor or midwife 2-3 times a week.
• How is colposcopy done?
As a rule, the entire procedure takes 10-20 minutes. At the same time, the woman lies in a gynecological chair, in fact, as during the most ordinary gynecological examination. How is colposcopy done? The gynecologist inserts a vaginal speculum into the vagina. The metal frame of a mirror can cause a few unpleasant sensations, simply because it can be cold, but under normal conditions it should not be painful or particularly uncomfortable. Then the doctor places the colposcope in close proximity to the gynecological chair, at a distance of several centimeters. The device will allow the doctor to examine the cervix, vagina, and vulva in an enlarged form, down to the cellular level.
To identify pathological changes in tissues, the doctor can apply Lugol's (an aqueous solution of iodine), as well as a vinegar solution, to the cervix. A slight but quickly passing burning sensation is caused by contact with vinegar. Lugol's solution does not cause any sensations at all. But healthy, normal tissue cells upon contact with it change color, becoming dark brown, but pathologically altered cells remain unchanged. Thus, they are easier to detect, and the research result is more reliable. If abnormal areas are detected, the doctor can immediately perform a biopsy, taking a small sample of tissue for analysis - one way or another, but if there is pathology, it will have to be done anyway, so it’s better right away.
A cervical biopsy is a painless procedure due to the absence of nerve endings, but it can sometimes provoke mild spasmodic or pressing pain in the lower abdomen. As for a biopsy of the lower part of the vagina and vulva, it can be painful, so local anesthesia is used before starting, applying the agent to the area of tissue being examined. In some cases, a special hemostatic agent is used to reduce bleeding after the tissue sample is collected. By the way, the method of such sampling can be scraping, separation with a scalpel, or maybe excision of tissue with a wire radio wave loop. You can expect to receive the results of a cervical biopsy after 10-14 days. As for the reliability of the analysis, it is very high, namely 98.6%. 4-6 weeks after the biopsy, you should go to an appointment with the antenatal clinic.
Top
What is colposcopy?
A colposcope consists of a miniature microscope, an illuminator and a light system for non-contact examination. It has a binocular head and a specially selected tripod so that you can install and then use the device for the most convenient position. The binocular system of such a colposcope allows you to examine tissues with high magnification, in the smallest detail. The illuminator works in such a way that the doctor can examine even the most difficult to reach tissues.
A simple colposcopy of the uterine cervix allows you to examine only its tissue after preliminary cleansing. Extended colposcopy is done after treating the tissue with 3% acetic acid. This makes it possible to examine the tissue in more detail. This is explained by the fact that after treatment of the cervical tissue, it swells a little, and some contraction of the blood vessels occurs in it.
To detect interstitial glycogen, tissue structures are treated with Lugol's solution. Thus, in the case of painful tissue changes, the specialist will see white areas against the normal dark brown color. During the examination, a biopsy can be done, that is, a piece of tissue can be taken for further medical research.
Interpretation of test results
Deciphering the results of a cervical examination is especially important after a biopsy.
In normal condition, the cervical mucosa is shiny, smooth, pale pink in color, with an evenly distributed vascular pattern. Lugol's solution or iodine normally changes the color of the cervix to dark brown.
In the presence of abnormal modifications of the mucous membrane of the cervix and vagina, only a doctor can accurately interpret colposcopy!
At the conclusion of the survey, the following indicators may be found:
- Flat and columnar epithelium - healthy cells inside the cervix, are present in the analysis normally.
- Ectopia is the spread of cylindrical cells beyond the boundaries of the cervix. This condition usually does not require special treatment.
- The transformation zone is the place where squamous epithelium transitions to cylindrical. This area requires particularly close study, since it is often the focus of the degeneration of benign cells into malignant ones. In ST, infection occurs with the human papillomavirus.
- Metaplasia – metaplastic cells of a healthy transformation zone. When mature, they have a normal vascular pattern, glands and islets. The presence of immature metaplastic epithelium indicates pathological processes in tissues.
- Iodine-negative areas also indicate a possible disease. If healthy cells are successfully stained with iodine or Lugol, then areas with abnormalities remain light. This is observed in atrophies, leukoplakia, inflammatory processes, and dysplasia.
- of acetowhite epithelium also indicates dysplasia and HPV infection . It consists of areas of the mucous membrane that have turned white when treated with acetic acid.
- Leukoplakia is a condition of hardening of the stratified epithelium that is unusual for a healthy cervix. It occurs with deep tissue damage and looks like a white spot.
- of mosaics and punctuation in the results of colposcopy indicates vascular disorders. They are sometimes present in a mild form in normal analysis. In rough form, they speak of a high degree of dysplasia and a possible malignant neoplasm.
- Atypical vessels in a cancerous tumor differ from healthy ones in that they do not respond to testing with acetic acid.
- Condylomas appear under the influence of infection of the mucous membrane with the human papillomavirus and are benign growths of a whitish hue.
Abnormalities such as polyps, stenosis, endometriosis, ulcerations, and necrotic areas may be present in the examination results. To clarify the meaning of the indicators, you should consult a doctor.
What is a transformation zone and its types
In the results of colposcopy, the gynecologist’s special attention is drawn to the transformation zone (abbreviated as ZT). It comes in three types and contains two types of cells: cylindrical and flat. Based on the state of the boundaries of the junction of two types of cells, the doctor can judge the state of the metaplastic epithelium of the cervix:
- During colposcopy, the type 1 transformation zone is visible on the outer surface of the cervix. Its inner border is represented by glandular (cylindrical) cells, and its outer border by multilayered squamous epithelium. CT type 1 is known as the congenital transformation zone and is found in young girls and young women.
- During colposcopy, the transformation zone of type 2 is found closer to the pharynx of the cervical canal. The border of the glandular cells is partially hidden in the cervical canal, so the doctor may need cervical dilators for a thorough examination. Type 2 OST is often mentioned in colposcopy descriptions in sexually mature women who have given birth.
- Type 3 transformation zone during colposcopy is often mentioned in the transcript of the study in women during menopause. The border of squamous and glandular epithelium in type 3 CT is shifted deep into the cervical canal and is not visualized without cervical dilators.
In addition, the ST can be described in the transcript as completed or incomplete. In the first case, the doctor observes the complete replacement of the immature surface epithelium with multilayered squamous cells. When the process of formation of multilayered squamous epithelium is not completed, accumulations of germ cells and squamous metaplasias are observed at the border of two cells. In childhood and adolescence, during pregnancy and when taking oral contraceptives, the transcript indicates that a low-atypical zone is present.
Good to know! In young women, type 3 ST is indicated in the colposcopy transcript as an atypical transformation zone, even if there are no other signs of pathological processes.
Negative changes and the presence of pathologies in the interpretation of colposcopy are indicated by:
- abnormal (atypical) vessels in the transformation zone;
- keratinized, that is, completely covered with multilayered epithelium, glands;
- iodine-negative zone;
- punctuation and mosaic;
- the presence of acetowhite epithelium at the junction of two types of tissues.
To make a correct diagnosis, such colposcopy results are not enough. To clarify, the doctor prescribes a Pap test, biopsy and histology.
Reviews
Tatyana: I undergo examination by a gynecologist every year. The last time the doctor did not like the results that the smear showed, and she suggested a colposcopy. The procedure was completely natural and did not cause me any discomfort. But some problems were detected in time, and I was prescribed appropriate treatment.
Irina: Not long ago I had a colposcopy. It didn't hurt. It feels like a regular gynecological examination, only a little longer. Our doctor is very attentive and prescribed me an examination herself. The preliminary diagnosis was not confirmed, but I sleep peacefully.
Vera: When they ordered a colposcopy, I chickened out! I thought they would torture me there. Nothing of the kind, a routine examination by a gynecologist. The only unpleasant moment was the treatment with vinegar and iodine, but this can be tolerated. You should take care of your health.
• Colposcopy during pregnancy
Colposcopy for pregnant women is an absolutely safe procedure; however, in any case, the doctor must be notified of pregnancy before performing the procedure. But if treatment is necessary, appropriate measures are postponed until the birth of the child (except in cases where neoplasms seriously threaten women’s health and require immediate medical intervention). Colposcopy during pregnancy does not threaten the health of the child; it does not affect childbirth or the ability to conceive a child in the future. There are no reasons that could classify the procedure as dangerous during pregnancy. In fact, even a biopsy is safe for a pregnant woman, which is often resorted to during or after colposcopy if there are suspected abnormalities in the tissues and mucous membranes (although a biopsy in such cases can cause quite severe vaginal bleeding).
Treatment after colposcopy is usually delayed until after delivery due to the risk of bleeding, especially if the pregnancy is more than ten weeks. Colposcopy during pregnancy is done to eliminate the risk of developing cervical oncology (cancer). Pregnancy can modify the cervical mucosa (cervical dysplasia is more pronounced; an increase in the amount of mucus in the cervical canal can complicate the examination), therefore the colposcopy procedure should be performed exclusively by a qualified gynecologist. In most cases, a biopsy, which usually follows a colposcopy, is not recommended during pregnancy.
The reason for this is increased vascularization of the uterine cervix and an increased risk of heavy bleeding during pregnancy. But if colposcopy reveals the presence of potentially dangerous neoplasms or third-degree cervical dysplasia, then a biopsy should be performed, regardless of the risks to pregnancy. Taking tissue samples for analysis from the cervical canal is contraindicated due to the possibility of fetal damage.
Top
How to prepare to reduce pain?
There are no special preparatory measures for the examination of the cervix and vaginal walls. The woman is recommended to refrain from intimate relations two days before the procedure and not to use sprays for genital hygiene. This is necessary so that the real picture of the health of the mucous membranes is not distorted.
Gynecologists advise undergoing a colposcopic examination within a week after the end of menstruation. Before the procedure, it is necessary to inform the gynecologist about the presence of an allergic reaction to acetic acid and iodine, since one of the examination options is carried out with the participation of these ingredients.
Examination using a conventional colcoscope is a mandatory stage of medical examination of the female population.
Contraindications
Despite the simplicity of the study, there are a number of contraindications to colposcopy:
- first 8 weeks after birth,
- 3-4 weeks after the abortion,
- recent treatment of the cervix using cryodestruction or surgical treatment.
When performing a special, extended colposcopy, a contraindication is an allergy to iodine or acetic acid.
Temporary contraindications for colposcopy may include:
- bleeding from the uterus or cervix, including menstruation,
- pronounced inflammatory process,
- severe state of ectocervix atrophy.
Further actions of the doctor and patient
If dangerous changes occur in the tissue of the cervix, it will be necessary to carry out appropriate treatment. In addition, to clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may recommend other diagnostic measures:
- repeat biopsy;
- smears and subsequent cytological analysis;
- examination for papillomavirus;
- biochemical blood test;
- bimanual rectal examination of the pelvic organs;
- laboratory tests of blood (general analysis), urine;
- palpation, listening to the abdominal organs.
Such examinations are indicated primarily to exclude malignant neoplasms. So, if the doctor suggests undergoing colposcopy of the cervix, there is no need to postpone this examination. It is highly informative and completely safe for health. And if such an examination reveals pathologies of the female reproductive system, treatment must be started immediately. And, of course, we warn all women against the dangers of self-medication for diseases of the genital organs, as this can have disastrous consequences.
What does it show
Colposcopy shows the presence of pathological abnormalities in the cervical mucosa. The obtained data is highly accurate. Using a similar procedure, you can diagnose endometriosis, ectopia, erythroplakia, dysplasia and leukoplakia, and study erosion (character, stage) and other lesions in detail.
Through colposcopy, a specialist is able to see oncological abnormalities in the first stages, which greatly increases the patient’s chances of a favorable outcome.
From this video you will learn some useful information about colposcopy:
Colposcopy is an important and necessary study in modern gynecology, allowing a quick and convenient way to determine the presence of pathologies in the cervical area. Such a diagnostic event is highly informative and has a low chance of injury. Thanks to a simple procedure, it is possible to recognize the pathology in a timely manner and begin treatment, which is very important for a favorable outcome.