Everyone should know the reasons why the tail of the pancreas is enlarged. You should also know what the pancreas serves. It has two main functions: the production of necessary hormones - glucagon, lipocaine and insulin, which control carbohydrate metabolism in the body, and the production of enzymes that facilitate the digestion of food. The work of the pancreas is determined by its size and structure. Pancreatic disease is characterized by very rapid tissue changes, up to necrosis. Any injury to this organ is extremely dangerous. If there are any changes, this indicates pathology. In the initial stage, many diseases pass without obvious symptoms. This makes it difficult for a specialist to make a correct diagnosis and prescribe subsequent treatment. Therefore, for pain in the pancreas, the first step is to prescribe an ultrasound examination.
Enlarged pancreas: causes, symptoms and treatment
The pancreas is one of the vital organs in the human body.
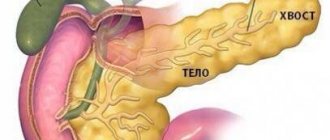
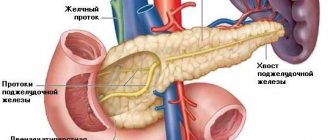
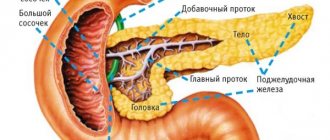
It is elongated and located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. The head, tail and body of the organ, which inside is a duct, are distinguished. Iron is necessary for the production of digestive enzymes (enzymes), which then enter the gastrointestinal tract. This organ is also an endocrine gland and performs an endocrine function. The insulin and enzymes it produces are involved in the breakdown of food.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vRu40lzXJYc
If the tail of the pancreas, its body and head are enlarged, this most often indicates non-compliance with nutritional rules and the occurrence of inflammation. Normally, the head of the organ should be 18-26 mm, the tail - 16-20 mm (this depends on the age of the person). Due to inflammatory processes, iron increases, which can lead to a dangerous disease - pancreatitis. With this disease, the outflow of digestive juice and enzymes produced by the pancreas into the small intestine is disrupted.
The pancreas is a large organ that has the amazing ability to combine two important functions - digestive and hormonal. Violations of the gland will lead to serious consequences for the entire body. Diseases of the organ can be judged by the results of ultrasound, especially an enlarged pancreas.
An enlarged pancreas can indicate very dangerous changes in the body, but diagnosing this pathology right away is almost impossible. The pancreas is hidden deep in the abdominal cavity; upon palpation it is impossible to detect an enlargement, and symptoms sometimes do not appear until the last minute. Why does the gland enlarge, what diagnostic methods will help recognize the problem and how to choose the right treatment?
https://youtu.be/XK2VxRAUilA
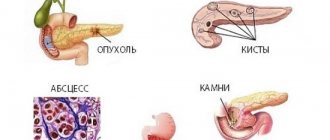
Complications after pathologies
Tail disease is dangerous because of its complications, which are caused by the underlying pathology. When the tissue is affected and there is pain in the tail area, this leads to the formation of diabetic disease, chronic pancreatitis, and pancreatic necrosis. If oncological formations are observed, then there is a rapid spread of metastases to neighboring organs, which have an unfavorable outcome.
The following complications develop:
- tissue changes, up to necrosis;
- cysts, fistulas;
- purulent processes in the abdominal cavity due to formed fistulas;
- change in gastric motility.
Signs of inflammation of the pancreas
During inflammation, the pancreas does not always enlarge evenly. The most common pathology of the tail is expansion (compaction), leading to obstruction of the splenic vein and portal subrenal hypertension. Consolidation may be caused by:
- A stone closing the duct;
- Cystic adenoma;
- Suppuration of the head of the organ;
- Pseudocyst;
- Duodenitis of the duodenum;
- Tumor of the small intestinal papilla;
- Scar of the small intestinal papilla;
- Oncology.
According to statistics, in only 1 out of 4 cases of inflammation of an organ, the focus is located in the tail. However, this fact does not allow us to neglect the inflammatory process in the tail and changes in size, because the neoplasm can be malignant. Difficult diagnosis rarely allows one to suspect the disease at an early stage, therefore, as a rule, it becomes known when the tumor reaches a suggestible size. In order to get to the tail of the gland, you have to penetrate through the spleen or left kidney.
Symptoms of inflammation of the tail of the pancreas are as follows:
- Dull or aching pain.
- Pain sensations radiate to the epigastric region, heart and chest.
- Leaning forward or sitting can help ease the pain a little.
- Decreased appetite;
- Stool disorders;
- Vomiting;
- Increased body temperature;
First of all, the doctor prescribes urine and blood tests. Spicy, smoked, fried, and pickled foods are excluded from the diet. Alcohol, coffee and cigarettes are prohibited.
If there is a tumor, then the therapeutic effect as such is unacceptable. Therefore, believing advertisements about miracle pills, herbs and infusions, and even more so taking them, will only aggravate an already disastrous situation.
The only chance to get rid of the tumor is surgery. This manipulation is quite complex, so you need to trust a qualified doctor and an innovative center with high-quality equipment. There are frequent complications that may appear on the first day after the intervention. The patient must be under reliable control so that, if necessary, the required assistance can be provided on site.
During the operation, the affected tail of the pancreas is removed and the blood vessels are stopped. If adjacent organs are also injured, the doctor decides to excise them partially or completely. Everything that was removed during the process is sent for additional histological examination. Further recovery therapy depends on its results.
There are 2 types of organ enlargement:
- Total - characterized by changes in all parts of the organ.
- Local - involves an increase in one part, while other parts remain unchanged. For example, the tail of the pancreas may be enlarged, but the head and body are not affected by these phenomena.
Why does the gland change shape? The organ is able to change its configuration due to the fact that:
- inflammatory processes occur with the appearance of edema;
- there is a need to compensate for the insufficiency of its work.
In adults, the reasons leading to an enlarged pancreas may be:
- excess calcium in the blood;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- abdominal damage due to trauma or cuts;
- blockage of the duct with a gallstone;
- virus infection;
- cystic fibrosis;
- the presence of diseases provoked by the immune system;
- circulatory disorders;
- side effect from taking medications.
This process can be provoked by: a cyst, a tumor, or complicated pancreatitis. Most often, with pancreatitis, part of the organ may become enlarged, but changes in the entire pancreas are also common.
It is impossible to immediately determine that the organ has changed in size, since it is located inside the abdominal cavity. It will be possible to detect an enlargement of the head of the pancreas only by performing ultrasound diagnostics or magnetic resonance imaging.
The development of symptoms of the disease manifests itself depending on the individual characteristics of the body. It is possible that the pancreas will not make itself known for years, although inflammatory processes are already underway. And the pain can be of different strength in different people. The following factors indicate a problem in the organ:
- significant increase in temperature;
- diarrhea, nausea and vomiting;
- lack of appetite, presence of bitterness in the mouth;
- pain of varying intensity in the abdomen (in the upper part), radiating to the lumbar spine or arm.
Why is this pathology dangerous? If the head of the pancreas is enlarged, it can cause obstruction of the duodenum, as it puts pressure on it. The disease can lead to impaired liver function, as indicated by the appearance of vomiting, diarrhea, bitterness and belching. A sign of pathology may also be an expansion of the Wirsung duct (the main one in the gland). The causes of the condition are the same as for other organ lesions.
An enlarged pancreas in an adult and a child requires urgent action - you need to consult a specialist. Before a medical examination, you should refrain from drinking alcohol, do not heat your stomach, and stop eating spicy, fried, smoked and fatty foods.
Enlargement of the tail of the pancreas (or head) can also be diagnosed in a child. Symptoms of damage:
- Painful sensations in the upper abdomen.
- Fever (during the acute period).
Increased pain in the abdominal area is observed in the chronic form of the disease.
The disease also affects infants. Causes of the condition:
- low body resistance to microbes;
- weak immunity;
- insufficient and unbalanced nutrition;
- lack of physical activity;
- non-compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards of maintenance.
All this negatively affects not only the health, but also the overall development of the baby.
Sometimes ultrasound shows diffuse (or uniform) changes in the organ. This pathology of the gland has the following causes:
- food poisoning;
- getting injured;
- excessive physical activity;
- excessive pill intake;
- hereditary diseases;
- eating fatty and fried foods;
- non-compliance with diet.
Such changes are a cause for concern for parents, because inflammation of the pancreas can lead to liver disease, which, together with the organ in question, is important for human life.
To determine the presence of an illness, you need to tell your doctor about the signs of illness. But in order for a specialist to be able to prescribe procedures and the necessary medications, it will be necessary to perform an ultrasound diagnosis of the organ and undergo an examination.
In some cases, emergency surgery may be required. Indications for it are acute inflammatory process, purulent inflammation of organ tissue.
For chronic pancreatitis, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment in a hospital and be constantly under the supervision of a doctor.
If tests show that the pancreas is enlarged, then treatment will include the following:
- diet;
- decreased activity of the digestive system;
- applying a cold compress;
- taking digestive enzyme medications.
If pain in the pancreas area does not give you peace, then you need to immediately take a number of measures. First aid: daily fasting, applying ice to the stomach (under the ribs on the left side). In case of acute pain, you can take No-shpa or Papaverine, then you should call an ambulance. Other medications should not be taken. Only a doctor should prescribe medications to treat the organ.
To resist the disease, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system. It is necessary to increase resistance to viruses and bacteria that can disrupt pancreatic function. It is especially important to monitor children’s nutrition during the following periods of life:
- infancy, when complementary feeding begins;
- when transferring the baby to artificial feeding;
- during tooth growth;
- before starting school and upon entering preschool;
- during the teenage period of a child's growing up.
The most effective way of prevention is to normalize your diet and lead a healthy lifestyle. You will need to give up tobacco, since smoking introduces tars and harmful substances into the body that contribute to the exacerbation of the disease. Avoiding alcohol, the destructive effects of which are known, will help relieve the burden on the pancreas.
If treatment is not started in time, the gland will continue to enlarge, abscesses may appear, and tissue necrosis may begin. In especially severe cases, the disease can become life-threatening, turning into oncology.
An enlarged pancreas is the result of a serious pathology. In this case, you cannot decide for yourself what and how to treat. The organ must be treated by a specialist, taking into account all the individual characteristics of the patient and based on test data and examination results. Then the question will not arise about what to do if the pancreas is enlarged.
Enlargement of the pancreas in a child and an adult occurs individually. In some cases, the pathology may not show any symptoms for quite a long time. In such situations, the disorder is diagnosed completely by accident during instrumental examinations to identify a completely different disease or for preventive purposes.
Most often, this organ enlarges due to an inflammatory process occurring in it, which is why the disease has pronounced symptoms. The very first clinical manifestation is pain, which can be acute or aching. The location of the pain is the upper abdomen. Often the pain radiates to the lower back or left arm.
If the head of the pancreas is enlarged, then the main symptoms, in addition to pain, are considered to be stool upset, which is expressed in the form of diarrhea. The severity of such manifestations is determined by the proximity of the affected organ to the duodenum.
The pancreas and liver are two interconnected organs, which is why when one becomes ill, the other suffers. With this disorder, signs of liver damage can be considered:
- attacks of nausea, which almost always end in vomiting;
- bitter belching;
- the appearance of a bitter taste in the mouth;
- profuse diarrhea;
- decreased appetite;
- change in the shade of the skin and mucous membranes. Often the jaundice is mild in nature.
- constant nausea, but vomiting is rare;
- increased sweating;
- pale skin;
- heaviness and discomfort in the stomach;
- feeling of pain behind the ribs;
- weakness and increased fatigue;
- intense headache and dizziness;
- significant increase in temperature;
- complete lack of appetite.
- a detailed survey of the patient or his parents - to obtain information regarding the first time and severity of symptoms;
- familiarization with the patient’s medical history and life history to identify the possible cause of pancreatic enlargement;
- a thorough physical examination - involves palpation of the entire surface of the abdomen, examination of the condition of the skin and sclera, and measurement of temperature.
- in cases of acute inflammation or the formation of an abscess, urgent hospitalization of the patient is necessary. The surgeon will decide on conservative or surgical treatment;
- if a pseudocyst and stones are detected, surgery is indicated;
- during the oncological process, chemotherapy, radiation treatment or surgical excision of the tumor is carried out;
- if the cause is chronic pancreatitis, then an individual treatment strategy will be drawn up by a gastroenterologist.
- lead a healthy and active lifestyle;
- follow dietary recommendations;
- take medications only as prescribed by a clinician;
- promptly treat those diseases that can lead to enlargement of the pancreas.
Description of the pancreas
In normal condition, the pancreas has the following dimensions depending on the age of the person: the head is centimeters, the tail is centimeters. The organ is located in the upper abdomen, behind the stomach near the gallbladder.
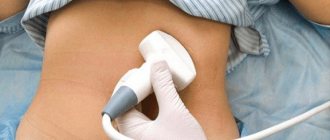
Since the pancreas is located behind other organs, it is impossible to detect changes in its structure and quickly determine that it is enlarged by palpation. In such cases, an ultrasound or MRI of the organ is mandatory.
With these types of diagnostics, a specialist is able to determine the size of the pancreas, the presence of neoplasms, for example, cysts, and the presence of foci of inflammation, which can affect both the grip and be located in the head.
To make a diagnosis, you also need to visit a gastroenterologist, who, based on the images and results of other tests, determines the type of disease.
The most likely cause of pain in the pancreas is the development of pancreatitis. In patients with pancreatitis, ultrasound shows a change in the size of the organ; the tail and head of the pancreas may be enlarged.
Moreover, a general enlargement of the gland is not as dangerous to human life as its local enlargement, that is, if the tail or head is enlarged.
Pancreatitis is difficult to detect during an exacerbation of the disease. In case of severe pain, the size of the pancreas is normal and it is not enlarged. Before diagnosing the organ, you must wait at least 6-7 hours after the attack, and only then determine the condition of the tail, and the organ itself, whether it is enlarged or not.
When diagnosing, the doctor must not miss even a slight change if the pancreas is enlarged. This may indicate both pancreatitis and the development of oncology.
With the development of cancer, a local increase in the tail or head of the organ is observed. Pancreatitis is characterized by an enlargement of the entire organ, as well as a violation of its homogeneity and boundaries.
Treatment of benign tumors of the pancreas
Treatment is only surgical. For hormone-producing tumors, they are enucleated (husked). Resection of the head of the gland or tail is advisable if there is a tumor in the corresponding part of the organ. In case of localization of large neoplasia in the area of the head of the gland and a violation of the outflow of bile, pancreaticoduodenectomy is performed (the formation is removed along with part of the gland and the duodenum). A fairly effective method of treating hemangioma is selective arterial embolization. The technique involves blocking the blood supply to the tumor formation.
In some cases, when it is impossible to carry out radical surgical treatment for multiple hormone-producing neoplasms, symptomatic therapy is necessary. For insulinoma and glucagonoma, the main goal is to normalize blood sugar levels. With the development of episodes of hyper- and hypoglycemia, appropriate correction is carried out with insulin or glucose solutions. Diet therapy is required. When treating gastrinoma, drugs that suppress gastric hypersecretion are used: ranitidine, famotidine, omeprazole and others. In severe cases, excision of the gastrinoma with gastrectomy is performed (to prevent relapses due to incomplete removal of the tumor).
Symptoms of an enlarged pancreas
- severe crying;
- unnatural posture of the child - children tuck their legs towards their stomach;
- heat;
- profuse vomiting.
In cases where one or more of the above signs appear in an adult or child, you should seek qualified help as soon as possible, because there is a possibility of damage not only to the pancreas, but also to internal organs such as the spleen and liver.
An enlarged pancreas can cause pain of varying intensity. Most often, the pain affects the upper abdomen, periodically radiating to the arm or lower back. Very often there is a significant increase in temperature.
Symptoms of an enlarged pancreas in the event of an inflammatory process appear quite quickly. If the disorder is caused by the formation of neoplasms of various types, signs of the pathological process may not appear for a long time.
The most common symptoms of this disease are:
- painful sensations of varying degrees of intensity;
- constant nausea, vomiting;
- loss of appetite;
- loose stools with various types of impurities;
- a feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- increase in body temperature.
It is imperative to treat an enlarged pancreas, since it can put pressure on nearby vessels and other internal organs. Often the head of the organ puts pressure on the duodenum, which leads to obstruction.
The causes of this disorder can be very serious, even cancer, so in this case it is impossible to do without medical help.
An acute attack of inflammation of the gland is very characteristic: severe cutting pain in the middle of the abdomen, which spreads along the costal arch to the left, to the spine (“shingles”), nausea with repeated vomiting, a rise in temperature to febrile levels (above 38).
There is steatorrhea (fatty stool) with a foul odor. Patients cannot sit still, rush around, and try to find a comfortable position.
Painful shock may develop with a sharp drop in blood pressure, loss of consciousness and cardiac arrest. The patient's face becomes ashen-gray, cold sticky sweat appears, and in some cases intestinal paresis occurs.
Usually the problem manifests itself through pain of varying strength and localization. It can be painful and aching or burning, reminiscent of a slight burning sensation. The source of discomfort is usually in the upper abdomen, and can radiate to the lower back or left arm. The temperature often rises to high values.
If, in parallel with the disease of the pancreas, the liver also suffers, the person is tormented by symptoms such as nausea, regular vomiting, bitter belching, stool disorders (diarrhea without impurities in the stool). When the head is enlarged, due to its proximity to the duodenum, constipation may begin and even intestinal obstruction may develop.
The main signs of an enlarged pancreas, which will help the doctor make an initial diagnosis and refer the patient for tests and procedures, are pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, fever and diarrhea.
If the gland enlarges against the background of inflammation, symptoms appear immediately. Cysts and tumors do not make themselves known for a very long time. You can find out the correct diagnosis by comparing certain symptoms, such as:
- burning or nagging pain in the upper lobe of the peritoneum, radiating to the lower back;
- lack of appetite;
- nausea and vomiting, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- diarrhea;
- heat.
Possible consequences of an enlarged gland are compression of the surrounding organs and vessels.
Due to the small size of the tail and body of the pancreas, their enlargement extremely rarely leads to compression of neighboring organs. The head, on the other hand, is larger in size; as soon as it enlarges, it compresses the duodenum, which, in some circumstances, provokes intestinal obstruction.
- abdominal pain, often of a girdling nature, can radiate to the supraclavicular region, shoulder and scapula, both on the right and on the left;
- nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief;
- bloating, belching;
- yellowness of the skin and icterus sclera;
- loose stool.
All these signs appear more often during inflammatory processes of this organ, since the disease occurs acutely. As for formations, pancreatic cysts, they may not manifest themselves for a long time. If such symptoms occur, you should immediately seek help from a doctor.
The doctor will prescribe the necessary examination:
- Blood test (leukocytosis, increased amylases and lipase, increased activity of alkaline phosphatase, ALT and AST).
- Determination of amylase in urine is a convenient and informative screening test.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, computed tomography, plain radiography.
- Invasive methods (FGDS, laparoscopy, biopsy, cholangiography).
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs helps to establish the diagnosis. Computed tomography is prescribed to see how widespread the process is, for differential diagnosis, and when visualization of the organ is not possible with ultrasound due to gases in the intestines. What to do if, during an examination, all signs indicate a disease of the pancreas with its enlargement.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of this pathology is based on the characteristic clinical picture of certain types of neoplasms, as well as the results of instrumental and histological research methods. A consultation with a gastroenterologist allows you to guess the type of tumor, find out how long ago the symptoms appeared and whether they are progressing. The patient's life history may include inflammatory diseases of the pancreas and alcohol abuse.
When examining the patient, the doctor can determine the yellowness of the skin and sclera, indicating mechanical compression of the pancreatic or common bile duct by the tumor. When assessing a general blood test, changes are detected extremely rarely. A biochemical blood test in the case of insulinoma and glucagonoma confirms changes in blood sugar levels. It is necessary to determine tumor markers: carcinoembryonic antigen, CA 19-9, which are not elevated in the case of a benign nature of the disease.
The most informative diagnostic methods are instrumental studies. An ultrasound of the abdominal organs is performed to visualize the formation, determine its size, and the condition of the regional lymph nodes. However, for hormone-producing tumors of small size, this method is ineffective. CT and MRI of the pancreas are highly informative, making it possible to detect small tumors and study their prevalence in detail.
To determine neoplasia with multiple foci (this is typical for insulomas, gastrinomas), scintigraphy is performed - radiopharmaceuticals are introduced into the body, which are actively accumulated by tumor cells, and their radiation is recorded on the image. If a hemangioma is suspected, angiography is performed to assess the blood flow in the formation and its relationship with the systemic blood flow. To study the histological structure of the neoplasm and differentiate it from malignant tumors, a puncture biopsy of the pancreas is performed, followed by a morphological examination of the biopsy samples.
Diet for enlarged pancreas
What should you do and how to eat with such a diet? The basic principles of the diet for treating the pancreas are:
- Small meals are the most important thing. You need to eat 5-6 times a day (3 full meals, 2-3 healthy snacks).
- The percentage of proteins and carbohydrates in the menu should be standard, the amount of fat should be sharply limited. The priority is fiber and pectin.
- Cold and hot foods should not be eaten so as not to cause symptoms of pancreatic irritation. All food is only warm.
- Solid foods should also be limited. It is better to cook dishes in pureed form (porridge, pureed soups, pureed meat, etc.).
- Try to eat vegetables and fruits fresh, no sautéing or frying.
Only natural sweets
With this diet, the basis of the menu is soup with low-fat broth. Lean pork, chicken, and lean fish are allowed. Low-fat dairy products, about 200 grams per day. You can have porridge, dried bread, flour products - inconvenient. For dessert - only natural sweets. This is jam, marshmallows, marshmallows, honey, marmalade.
All fried, smoked and spicy foods, fatty meats and fish, and canned food are prohibited. Legumes and mushrooms are not recommended. Sorrel, onions, radishes and garlic will have to be crossed out from the menu. Factory-made sweets, baked goods, soda and alcohol are also prohibited.
Enlarged pancreas is a serious problem, but timely treatment will help cure the underlying cause and relieve unpleasant symptoms. Therefore, it is very important to listen to your own body and, at the slightest sign of problems in the pancreas, consult a doctor.
physiotherapy for pancreatitis
It is important to immediately go to the doctor at the initial signs of pancreatic dysfunction. This will allow timely detection of the disease and prevent further development of pathology, avoid serious complications, and improve the prognosis.
The pancreas will not function properly without the right food. If the digestive system suffers, then diet No. 5 is most suitable, limiting the consumption of foods high in fat. Dietary nutrition will help restore organ cells.
Forbidden food:
- alcohol;
- foods high in fat (lard, butter, sour cream);
- rich broth and soups;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- smoked meats, fried foods;
- spices;
- sweet treats.
Will be useful:
- stewed vegetables (stew);
- porridge with water;
- stale bread;
- cottage cheese and kefir without fat;
- boiled or baked meat and low-fat fish.
You can improve the condition of your organs and get rid of pain only with proper nutrition. Sometimes a well-chosen diet helps reduce swelling, relieve inflammation, and subsequently avoid surgery. Previously, a person could not live after removal of the gland. In the modern world, people are able to do without an organ; in this case, replacement therapy in the form of enzyme preparations, lipotropic drugs and insulin is mandatory. But it is still better to keep the organ in a healthy state.
Enlarged pancreas is a serious problem, but timely treatment will help cure the underlying cause and relieve unpleasant symptoms. Therefore, it is very important to listen to your own body and, at the slightest sign of problems in the pancreas, consult a doctor.
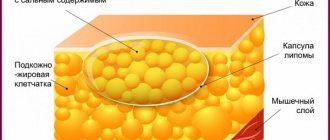
The pancreas is located deep in the abdominal cavity. It belongs to the parenchymal organs: unlike hollow organs, the gland consists of a cellular mass covered with a capsule of connective tissue, the processes of which penetrate deep into the mass of cells.
These anatomical features of the gland do not allow the doctor to use palpation or auscultation techniques for examination and diagnosis. There are no external signs that the pancreas is enlarged: it cannot be felt in any way, changes can only be seen with the help of MRI or ultrasound.
An enlarged pancreas in both adults and children may indicate a number of diseases or simply be a congenital feature of the organ. Such anomalies usually do not cause any discomfort to the patient and do not pose any danger.
Ultrasound diagnostics evaluates the morphological state of the organ: tissue density, size, shape and presence/absence of neoplasms. If the parenchyma has a homogeneous structure, and the size of the organ is within normal limits, there are no pathologies. Changes in size, a uniform decrease or increase in echogenicity indicate problems with the organ.
Traditional recipes will help
Sometimes these time-tested remedies can offer significant health benefits, allowing you to abandon expensive traditional drug treatment. Healing decoctions, infusions, and juices are prepared from herbs, root vegetables, and cereals. Potato juice is an effective remedy for pancreatic diseases. They drink it 2 hours before meals, 100 g each. Take it for 2 weeks, then take a break for 2-3 months, then continue treatment again.
This decoction has also proven itself to be effective: take burdock root, crush it, then add water (0.5 l). The product is infused for 5 hours. After this, it is boiled over fire for 30 minutes. Then you need to strain the broth and drink 1 glass after meals.
Etiology
The pancreas consists of parts such as the head, body and tail. The entire organ or one of its parts can become enlarged. In each case, the sources of the pathological process will be different.
The pancreas becomes completely enlarged in adults and children in the vast majority of cases due to an acute inflammatory process in this organ. However, this condition can also be caused by:
- the formation of stones that lead to blockage of the duct;
- cystic fibrosis is a hereditary disease, the causes of which remain unknown;
- alcohol abuse;
- a wide range of traumas and wounds of the abdominal cavity;
- the course of an infectious disease, for example, influenza or hepatitis, intestinal infections, mumps or sepsis;
- uncontrolled use of certain groups of medications, in particular hormonal substances;
- excessive physical activity;
- increased calcium levels in the blood;
- anomalies of the development of the pancreas, in particular, a ring or horseshoe shape, as well as the presence of bends and constrictions;
- bile duct dyskinesia;
- the presence of autoimmune processes in a person, in which the body produces antibodies against its own healthy cells and tissues;
- inflammation of the duodenum, spreading to the major papilla, into which the pancreatic duct opens;
- severe food poisoning;
- ulcerative lesions of the duodenum or stomach;
- disturbance of local blood supply - often formed against the background of vascular atherosclerosis, compression by a neoplasm or accidental dressing during medical intervention.
However, not in all cases the course of pancreatitis leads to changes in the volume of the entire organ. It is not uncommon for a situation in which the pathological process is active in the head, body or tail of the pancreas. But during diagnostic measures, other diseases can be identified that lead to deviations from the norm in the size of one or another structural part of the pancreas.
Thus, the enlargement of the tail of the pancreas is due to:
- the formation of pseudocysts, which are a consequence of pancreatitis;
- the formation of abscesses filled with purulent fluid;
- benign tumor developing from glandular tissue;
- an oncological process in which neoplasms are large and compress the tail of this organ;
- a stone, the localization of which is the Wirsung duct, located in the area of the body of the gland.
Enlargement of the head of the pancreas occurs due to:
- the presence of a pseudocyst or abscess in this structural zone;
- metastasis of a cancer tumor from nearby internal organs or its own malignancy;
- presence of cystic adenoma;
- duodenitis, leading to inflammation of the minor papilla of the duodenum, into which an additional duct opens, located in the head of the pancreas;
- scarring or the appearance of a tumor in the minor papilla of the duodenum;
- the appearance of stones.
All of the above etiological factors lead to the fact that during instrumental diagnostics a condition will be identified in which the pancreas is enlarged in a child or an adult.
The main risk groups are:
- people who have been drinking alcohol or smoking cigarettes for many years;
- babies during teething;
- adolescents of adolescence;
- infants who are transferred from breastfeeding to artificial nutrition;
- persons whose menu is dominated by fatty, salty and spicy foods. It is for this reason that diet is an important part of therapy.
How to treat?
How can such a pathology be treated if the child is one month old? The pancreas is enlarged - you should immediately contact your pediatrician. After all, only an experienced doctor will be able to determine the true cause of the development of such a pathological process, as well as identify its threat to a small organism.
It should be especially noted that each individual case of pancreas enlargement in children requires its own individual treatment. According to experts, such therapy can be conservative and surgical.
If we talk about the general principles of treatment, they boil down to the following scheme:
- Reducing swelling of the pancreas by applying cold compresses to the affected area.
- Mandatory adherence to a strict diet, which includes the complete exclusion of spicy, fatty, and fried foods. Also, many experts strongly recommend abstaining from eating for at least a few days. In some cases, doctors even inject nutrients into the patient's body (so-called parenteral nutrition).