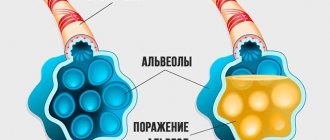
It was first described by the German therapist Quincke in the 19th century. The basis for its development is an immediate allergic reaction with the release of biologically active substances: histamine, heparin, serotonin, etc. Under their influence, the permeability of the smallest vessels increases and therefore edema develops.
People of all age groups can get sick, but angioedema most often occurs in young women. In childhood and old age they get sick much less often.
Causes
Quincke's edema can be allergic and pseudo-allergic.
Allergic Quincke's edema appears upon contact with an allergen. For an allergic reaction to develop, the body must already be sensitized - there has already been an encounter with the allergen, and the body has developed antibodies. When this allergen re-enters the site of contact, inflammation is caused: small vessels dilate, their permeability increases, and as a result, tissue swelling occurs.
Allergens can be:
- Pollen.
- Various insect bites.
- Wool and animal waste products.
- Cosmetics.
- Food products (citrus fruits, chocolate, eggs, fish products, various berries).
- Medications. The most common reaction is to antibiotics, painkillers, and vaccines. The reaction can range up to anaphylactic shock, especially if the drug is administered by injection. Vitamins and oral contraceptives rarely cause anaphylactic shock.
Pseudoallergic edema is a hereditary disease; patients have a pathology of the complement system. This system is responsible for triggering an allergic reaction. Normally, the reaction starts only when an allergen enters the body. And with pathology of the complement system, activation of inflammation also occurs from thermal or chemical exposure, in response to stress.
Classification
According to clinical manifestations
| — with an acute course (up to 1.5 months) | - with a chronic course (from 1.5-3 months or longer). |
In relation to urticaria
| - isolated | - combined with urticaria |
According to the mechanism of edema development:
| - caused by dysregulation of the complement system: | - caused by dysregulation of the complement system: |
| - a consequence of allergies | - a consequence of pseudoallergy, |
| hereditary (there is an absolute or relative deficiency of the C1 inhibitor, as well as its normal concentration); | acquired (with inhibitor deficiency), - angioedema that develops with the use of ACE inhibitors; |
| - against the background of autoimmune diseases | - against the background of infectious diseases. |
| Idiopathic angioedema is also distinguished when it is not possible to identify the specific cause of angioedema. | |
Symptoms of Quincke's edema
Quincke's edema is manifested by the occurrence of certain symptoms, this is the appearance of edema in places with developed subcutaneous tissue - on the lips, eyelids, cheeks, oral mucosa, and genitals. The color of the skin does not change. There is no itching. In typical cases, it disappears without a trace after a few hours (up to 2-3 days). The swelling may spread to the lining of the larynx, which can cause difficulty breathing.
In this case, there is a hoarseness of the voice, a barking cough, difficulty breathing (first exhale, then inhale), noisy breathing, the face is hyperemic, then suddenly turns pale. Hypercapnic coma occurs and then death may occur. Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and increased peristalsis are also noted.
Angioedema differs from ordinary urticaria only in the depth of skin damage. It should be noted that manifestations of urticaria and angioedema may occur simultaneously or alternate.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Quincke's edema depend on where the process is localized.
Thus, the following manifestations are distinguished:
- Swelling of the larynx. When the respiratory system is affected, the swelling is almost always in the larynx. Patients experience hoarseness of voice, difficulty breathing, which turns into suffocation, and cyanosis of the face. This is all accompanied by excitement, which is caused by lack of air and fear of death.
- Swelling of the face. Swelling of the subcutaneous fat layer in the eyelids, cheeks or lips is often observed. The most severe process is considered to be one that affects the eyelids, as this makes the patient’s vision difficult. This form of edema can lead to injury.
- Acute urinary retention. It develops when the pathological process is localized in the urinary system. The main reason for this manifestation is considered to be wearing synthetic underwear or a reaction to the components of intimate hygiene products. This form of pathology requires immediate medical attention. This is due to the fact that swelling of the urethral mucosa prevents the outflow of urine, which continues to be excreted by the kidneys. A prolonged absence of urination is fraught with hydronephrosis (accumulation of urine in the kidneys) and subsequently, kidney rupture.
- Peritonitis. In rare cases, swelling of the abdominal organs occurs, which manifests itself in the idea of peritonitis. This pathology does not require surgical intervention, unlike inflammation of the peritoneum of another etiology, but is difficult to diagnose. Often this condition is not correctly diagnosed and is detected during surgery.
- Brain swelling. This form is considered the most dangerous, as it is accompanied by convulsive syndrome and can be fatal. Patients with cerebral edema experience disturbances of consciousness, convulsions, and develop signs of inflammation of the meninges.
Most clinical cases require hospitalization. Varieties of Quincke's edema are based on the localization of the process. Depending on the severity of the condition, assistance may be provided in the allergy department or intensive care unit. Most often, patients with Quincke's edema are treated in intensive care.
Complications
With Quincke's edema affecting any organ, especially if it is accompanied by intense manifestations of urticaria, anaphylactic shock can develop at lightning speed. This is an extremely life-threatening allergic reaction that spreads throughout the body. Manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- generalized (widespread) itching;
- swelling of the tissues of the pharynx, tongue, larynx;
- nausea, vomiting, cramping abdominal pain, diarrhea;
- convulsions, respiratory arrest, coma;
- the appearance of urticaria (swelling and itchy red-pink spots, blisters);
- lacrimation, sneezing, bronchospasm with excessive mucus production, blocking the flow of oxygen;
- increased heart rate, drop in blood pressure, cardiac arrhythmia, increase in acute cardiovascular failure.
Incorrect treatment of hereditary angioedema also leads to fatal consequences for the patient.
Review of the main groups used for treatment
When angioedema, called Quincke's syndrome, occurs, medications and drugs are prescribed in stages:
- First, the reason that caused the pathology is determined. Basically, the reason lies in an allergy to an irritant from the environment.
- Next, a medicine is prescribed that relieves swelling and bulge in the problem area.
- The main help for edema is to reduce the histamine released into the patient’s blood.
The main groups of medications prescribed for allergic rhinitis or other symptoms of an allergic reaction:
- drugs with antihistamines, when taken, reduce the body’s sensitivity to irritants - Suprastin, Diphenhydramine, Diazolin;
- hormonal medications suppress the reactions of the immune system, sometimes administered intramuscularly - Prednisolone and Dexazone.
As an additional remedy, the attending physician prescribes Ascorutin to reduce the permeability of blood vessels. You should not self-medicate, especially for people with diseases of the stomach and other digestive organs, as unauthorized prescription of medications will worsen the condition.
First aid
Quincke's edema develops very unpredictably and poses a threat to the patient's life. Therefore, the first thing to do is to call an ambulance, even if the condition is currently satisfactory and stable. And under no circumstances should you give in to panic. All actions must be quick and clear.
Before the emergency ambulance team arrives, you must:
- Make the patient sit in a comfortable position and calm him down
- Give an antihistamine (fenkarol, diazolin, diphenhydramine). Injectable forms of antihistamines are more effective, since it is possible that swelling of the gastrointestinal tract develops and the absorption of substances is impaired. In any case, you need to take 1 - 2 tablets of the drug if it is not possible to get an injection. The medicine will weaken the reaction and alleviate the condition until the ambulance arrives.
- Limit contact with the allergen. When bitten by an insect (wasp, bee), the sting must be removed. If you cannot do this yourself, you need to wait for specialists to arrive.
- Enterosgel or regular activated carbon can be used as sorbents.
- Be sure to drink plenty of alkaline water (per 1000 ml of water, 1 g of soda, either Narzan or Borjomi). Drinking plenty of fluids helps remove the allergen from the body.
- Provide good access to fresh air, remove objects that make breathing difficult.
- To reduce swelling and itching, you can apply a cold compress, a heating pad with cold water, or ice to the swollen area.
In case of severe swelling, it is better not to take any measures on your own, so as not to provoke a worsening of the patient’s condition, and wait for an ambulance. The main thing is to do no harm.
Treatment of angioedema
Since swelling occurs suddenly and develops very quickly, it is extremely important to provide the patient with emergency medical care. Quite often there is no time to wait for an ambulance to arrive, so you need to know what actions to take in case of angioedema before specialists arrive.
Emergency care for angioedema includes the following measures:
- elimination of the allergen;
- relieving emotional stress - the patient should be reassured, it is necessary that he stops being afraid of suddenly appearing unpleasant symptoms, this will help carry out further activities more effectively;
- ensuring access to fresh air - the windows in the room need to be opened, the patient needs to take off his tie, unbutton his shirt collar;
- to relieve the symptoms of Quincke's edema, you need to apply a cold compress to the lesion;
- You need to put vasoconstrictor drops into your nose.
Further treatment should be carried out by doctors. First of all, the patient is given antihistamines.
If the development of Quincke's edema occurs quickly and the patient begins to have asthma attacks, then the administration of glucocorticoids is indicated. After acute symptoms have resolved, the patient is hospitalized for further therapy.
If laryngeal edema is present, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit. In addition, a strict diet is indicated, the essence of which is to exclude the most allergenic foods from the patient’s diet.
Diagnostics
First of all, the doctor conducts an examination to familiarize himself with the existing symptoms. In addition, the reaction of edema to the administration of adrenaline must be taken into account.
The next stage is to establish the cause of the pathology. As a rule, it is enough to ask the patient about what allergic diseases are present in his or his immediate family history, what his body’s reaction is to eating various foods, taking (administering) medications, and contact with animals. Sometimes specific blood tests and allergy tests are required to detect the cause.
Emergency assistance in case of swelling
Upon arrival of medical workers, the moment of emergency care begins.
Emergency care is provided by ambulance workers
The algorithm of their actions includes several points.
- Assessing the state of blood pressure and the occurrence of asphyxia. In case of critical condition, 0.1-0.5 ml of adrenaline solution (0.1%) is injected under the skin.
- Hormonal drugs Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Hydrocortisone are administered intravenously.
- To combat the allergen, injections of Suprastin 2%, Diprazine 2.5%, Diphenhydramine 1% are performed.
- It is necessary to remove water and salt from the kidneys with the help of the diuretics Lasix (intravenous administration of 40-80 mg in a bolus in saline solution), Mannitol 200 ml.
- 30,000 units of Contrical are injected intravenously into 200 ml of saline solution.
- Elimination of intoxication is carried out using hemosorption and energy sorption.
- If asphyxia occurs during emergency care, doctors perform a tracheostomy.
After providing first aid to the patient, hospitalization is indicated. Such patients are assigned to the allergy department, intensive care unit or intensive care unit, depending on the person’s condition.
How to treat?
For allergic angioedema, which is part of an anaphylactic reaction, the drugs of choice for treating patients are adrenaline, glucocorticoid hormones, and antihistamines. In addition, detoxification therapy is carried out by intravenous administration of special solutions (reoplyuglyukin, ringer lactate, saline solution, etc.).
In the case of a food allergen, enterosorbents (activated carbon, enterosgel, white coal, etc.) are used. Symptomatic therapy is also carried out depending on the symptoms that have arisen, namely, in case of difficulty breathing, drugs that relieve bronchospasm and dilate the airways (euphilin, salbutamol, etc.) are used.
It makes sense to provide data on the latest trends in the field of antiallergic drugs, treatment of which is carried out in the acute period of Quincke's edema and between episodes of repeated angioedema.
- First generation antihistamines: chloropyramine (suprastin), promethazine (pipolfen, diprazine), fenkarol (hifenadine), pheniramine (avil), dimethindene (fenistil), tavegil (clemastine), mebhydrolin (omeril, diazolin) act quickly (within 15-20 minutes). They are effective in relieving Quincke's edema, but cause drowsiness and prolong reaction time (contraindicated for drivers). Act on H-1 histamine receptors
- The second generation blocks histamine receptors and stabilizes mast cells, from which histamine enters the bloodstream. Ketotifen (zaditen) effectively relieves spasm of the respiratory tract. Indicated when angioedema is combined with bronchial asthma or broncho-obstructive diseases.
- Third-generation antihistamines do not depress the central nervous system, block histamine receptors and stabilize the mast cell wall: Loratadine (Clarisens, Claritin), Astemizole (Astelong, Hasmanal, Istalong), Semprex (acrivastine), Terfenadine (teridine, Trexil), Allergodil (acelastine), Zyrtec, Cetrin (cetirizine), Telfast (fexofenadine).
For non-allergic Quincke's edema (hereditary, acquired Quincke's edema), accompanied by a decrease in the concentration of C1 inhibitor in the blood, the treatment tactics are somewhat different. In this case, adrenaline, hormones, and antihistamines are not the first choice drugs, since their effectiveness in these types of Quincke's edema is not so high.
The first choice drugs are those that increase the missing enzyme (C1 inhibitor) in the blood. These include:
- Purified C1 inhibitor concentrate;
- Fresh frozen plasma;
- Male sex hormone preparations: danazol, stanazolol;
- Antifibrinolytic drugs: aminocaproic acid, tranexamic acid.
In case of severe swelling of the larynx and complete closure of the airway, an incision is made in the cricothyroid ligament and a special tube is installed for an alternative route of breathing (tracheostomy). In severe cases, they are transferred to an artificial respiration apparatus.
Prognosis and prevention
When symptoms are identified and diagnosis is made, therapeutic therapy begins. To consolidate the result, prevention is carried out. The basic rule is to exclude the allergen from food, medicines and the environment.
In a person’s life, Quincke’s edema does not pose a big threat if you promptly seek help from a specialist.
Galina Polovnikova / author of the article
I write articles in various areas that, to one degree or another, affect such a disease as edema.
Diet
Diet adherence is mandatory. In this case, it is necessary to completely exclude not only products that cause a direct allergic reaction, but also a cross one. The menu of an allergic patient should not contain products with synthetic additives, artificial colors, or histamines. At the same time, the diet should not be depleted by replacing allergenic foods with hypoallergenic ones that are similar in calorie content.
Products that can cause an allergic reaction:
- fish and seafood, chicken, eggs, dairy products, cocoa, peanut butter and nuts themselves;
- strawberries, tomatoes, spinach, grapes;
- spices of different types, chocolate.
Very carefully, people prone to allergic reactions to foods should eat sauerkraut, cheese, rhubarb, legumes, fried and stewed meat and fish dishes, as well as broths. Drinking wine, even in small doses, is completely contraindicated.
Artificial food additives can also cause an allergic reaction: preservatives, dyes, flavors and taste stabilizers.
Definition
Quincke's edema is a rapidly increasing swelling of the skin and mucous membranes, affecting the layer of subcutaneous tissue. In medical terminology, the disease can be called differently:
- angioedema;
- giant urticaria;
- trophoneurotic edema.
Pathology was first discovered in 1882 by Heinrich Quincke, who worked in the field of medicine and surgery. The disease affects people susceptible to allergies, most often the fairer sex, children, and adolescents.
Quincke's edema is localized in the upper part of the body, sometimes affecting the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, less often - the genitourinary organs, gastrointestinal tract, and meninges. The pathology has 2 forms: hereditary and acquired - and requires emergency medical care.
Prevention
Following certain rules will help prevent the development of soft tissue swelling:
- eat right;
- If you are prone to allergies, follow a gentle diet;
- take vitamin complexes to strengthen the immune system;
- avoid contact with foods and medications that cause allergies;
- If you have allergic reactions to certain types of medications, be sure to notify your doctor;
- When taking a new type of antibiotic, keep antihistamines on hand.
Causes
Doctors identify 2 main reasons for the formation of swelling:
- allergy;
- hereditary disorders in the complement system (a complex of serum proteins in the blood), under the influence of which the walls of blood vessels become more permeable.
Allergy
The pattern of swelling formation corresponds to the development of an acute allergic reaction. After becoming familiar with the foreign “agent,” the cells of the human immune system (mast and basophils) are prepared and immunoglobulins E (antibodies) are released. So, when faced with an allergen, the body prepares to repel the attack.
Skin rashes vary in origin. In this article you will find information about what disease is characterized by watery blisters.
Upon repeated contact, immune system cells release mediators - compounds that bind the allergen and prevent it from spreading further throughout the body.
Under the influence of mediators, the capillaries sharply narrow and a spasm occurs. Part of the blood plasma passes into the space between tissue cells. The liquid penetrates most easily into those places on the body where a lot of loose subcutaneous tissue is concentrated (the area of the face, limbs, genitals).
In just 5 minutes, swelling forms. The most common triggering allergens are:
- food (chocolate, eggs, seafood, citrus fruits, red fruits and vegetables);
- medications (antibiotics, oral contraceptives, vitamins, painkillers, vaccines);
- flower pollen;
- insect bites;
- cosmetical tools;
- animal hair;
- infectious agents (bacteria, viruses and others);
- chemical industry products (phenol, turpentine, household chemicals and others).
Hereditary factor
As a result of gene changes, a child is born with congenital disorders in the complement system, in which C1 inhibitor deficiency is detected. The lack of this compound in the body leads to the fact that the allergen provokes swelling at the first encounter with a foreign “agent”.
Thus, the important stage at which immunoglobulins are released is missed. The cells of the immune system are immediately destroyed and release mediators, bypassing the preparation process.
From this material you will learn why hemangioma appears in newborns and how to cure this disease.
Such hereditary disorders are considered by medicine as an immunodeficiency disease (as opposed to ordinary allergies). The impetus for the development of swelling can be not only potential allergens, but also injuries, stress, as well as diseases present in the body:
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- helminths;
- disruptions in the immune system.
An employee of the European clinic “Siena-Med” will tell you in detail about the causes of edema and its symptoms. After watching the video, you will understand how you can prevent the development of an acute allergic reaction.
Allergic reaction limited swelling
Limited edema (Quincke's edema) is an immediate allergic reaction, leading to the release of biologically active substances (histamine, serotonin, etc.) from basophils and mast cells of the skin and mucous membranes, followed by a vegetative reaction, effusion of serous fluid into the subcutaneous tissue, manifested in limited areas of the skin or mucous membranes. Clinically manifested by swelling of the larynx and pronounced suffocation.
The disease is named after the German physician Heinrich Quincke (1842–1922), who first described this pathology.
The disease Quincke's edema develops in young people, less often in infants and the elderly. It is characterized by the sudden appearance of limited swelling of the skin and subcutaneous tissue in the form of one or several dense, painless swellings with a diameter of 2-10 cm; Sometimes swelling affects the entire face, head, scrotum, entire limbs, or even the entire body. Less commonly, swelling appears on the mucous membranes of the mouth, larynx, esophagus, stomach, intestines, gall bladder, accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, colic and cerebral symptoms. Edema can also develop in the cavity of the joints, tendon sheaths, and in the periosteum. Quincke believes that in some cases of serous meningitis there is limited swelling of the brain. Swelling also appears on the face, mucous membranes of the mouth, and soft palate.
Swelling appears quickly and lasts up to several hours, rarely several days. It is often combined with migraine, hysteria, oculomotor nerve palsy, and bronchial asthma.
How to get rid of Quincke's edema using folk remedies?
Quincke's edema usually requires emergency treatment. If this condition is associated with heredity, then treatment should be continuous. Planned therapy will help prevent swelling of the eyelid, as well as reduce the occurrence of allergic reactions. Many people use folk remedies in treatment. Such therapy should not replace traditional medicine. You can use folk recipes to eliminate eyelid swelling only after consulting a specialist.
A popular way to relieve swelling from the eyelid is to apply salt compresses. The chemical properties of salt help it remove excess water from the body. When swelling occurs, this product is one of the most accessible means that eliminates excess fluid accumulation in the eyelid area. To prepare the compress you will need 1 teaspoon of salt and 1 liter of water. You need to apply a compress to your eyelid 2 times a day.
To prevent the formation of edema on the eyelid, you can take a bath with kelp. This is a seaweed that relieves swelling well, normalizes blood circulation and removes allergens from the body. You need to fill 100 grams of kelp thallus with warm water in advance and leave for half an hour. After this, you should pour the swollen algae into the bath. To quickly remove swelling from the eyelid, you can use kelp to wash your face.
Providing assistance to pregnant women
Drug therapy, both during pregnancy and lactation, has a negative impact on the development of the baby. But the presence of danger arising from untimely treatment of an acute allergic reaction is an indication for the treatment of angioedema even in pregnant girls and nursing mothers.
To minimize the harm of medications, a pregnant girl should visit a gynecologist before starting drug treatment. First of all, the doctor will study the individual history of the expectant mother, perform an examination and, based on the examination results, select the optimal drug.
Treatment of Quincke's edema in pregnant girls is based on taking antihistamines - Zyrtec or Claritin. Since allergies increase vascular permeability, to normalize their condition, a woman is given an intravenous solution of calcium gluconate.
Recommendations on how to treat angioedema at home
For many patients, the relevant question is how to treat angioedema at home, because a long hospital stay is not possible for everyone for a number of reasons. Such treatment is, in principle, possible, but only after undergoing special therapy and consulting a doctor. It is also important that the drugs for treatment and dosage are selected by a specialist, taking into account the characteristics of the body and the severity of the disease. The main factor for successful recovery is the complete elimination of the allergen from life.
It happens that Quincke's edema begins after taking medications: acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, naproxen, indomethacin, piroxicam, ketoprofen, etc.), treatment comes down primarily to the exclusion of these drugs. Some allergists suggest excluding foods containing salicylates: cherries, raspberries, strawberries, strawberries, grapes, apples, peaches, apricots, tomatoes, carrots, cucumbers, potatoes. However, this position is not shared by all allergists and nutritionists, since the content of salicylates in these products is very low.
More important is that in patients with pseudoallergic angioedema, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs often have cross-reactions with food processing additives added to products during their production. These include: yellow dye tartrazine (E 102), added to confectionery, soft drinks, ice cream, medicinal tablet shells, etc.; benzoic acid and its salts (E 210, 212), used as a preservative in the production of fish caviar, fish preserves, jam, some fruit and berry juices, marmalade; antioxidants (E 320, 321), used to slow down the oxidation and, consequently, rancidity of fats (rendered animal fats, salted bacon, fats in some food concentrates). Therefore, persons suffering from pseudo-allergic Quincke's edema should pay attention to the text of the labels and avoid products with these food additives. Nutritional supplements act as a causative factor in only 0.6–0.8% of patients with chronic urticaria, i.e. their importance in the development of this disease should not be overestimated.
The patient needs to consult a doctor about what medications are prescribed for Quincke's edema to relieve itching, swelling, redness, and also obstruct the exit of bioactive substances from the body. Typically these are first-generation drugs desloratadine, loratadine, cetirizine, fexofenadine, acrivastine, famotidine, ranitidine or cimetidine.
As a rule, the prognosis is favorable. With rational therapy, ability to work is quickly restored. After relief of acute manifestations, patients are referred to an allergist for a full allergological examination and further observation.
Types of angioedema
The following types of angioedema (AO) are distinguished:
- Hereditary AO (associated with a genetically determined deficiency or functional deficiency of the C1 esterase inhibitor).
- Acquired JSC:
- combined with allergic diseases (urticaria, bronchial asthma, etc.);
- with taking medications (ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers);
- with autoimmune diseases (autoantibodies to C1 inhibitor);
- with lymphoma, leukemia, myeloma;
- idiopathic edema (cause unknown).
Mandatory pharmacy kit for allergy sufferers
The following antihistamines must be present in an allergy sufferer's first aid kit:
- Suprastin
- Tavegil
- Diazolin
- Ketotifen
- Diphenhydramine
The above medications belong to the first generation drugs, due to which they quickly provide a positive effect.
But, despite their high effectiveness, these antihistamines are addictive when used regularly.
If first-generation drugs do not eliminate allergic symptoms, it is recommended to replace them with second-generation antihistamines:
- Fenistil
- Claritin
- Clarotadine
- Telfast
- Zyrtec
The advantage of these medications is that they do not provoke a disorder of the nervous system.
Symptomatic treatment of edema
In many cases, patients with acute angioedema are prescribed symptomatic medications. Thus, administration of saline solutions to the patient is indicated. They are needed to prevent a drop in blood pressure and increase the amount of circulating blood. For this use:
- saline solution;
- hydroxyethyl starch solution;
- Poliglyukin.
Usually, after infusions of the above drugs, it is possible to increase the rate of circulating blood in the body and prevent a sharp drop in blood pressure, leading to the development of a state of shock. After it is possible to normalize the amount of blood circulating in the body, the following means are used:
- Norepinephrine (it must be used together with a certain amount of 5% glucose solution intravenously);
- Dopamine (it should also be used in conjunction with glucose).
The doctor prescribes the dosage of each of these drugs based on the specific individual case. This kind of symptomatic therapy is carried out until the patient’s systolic pressure reaches 90 mmHg. Art.
Atropine subcutaneously is used for bradycardia, that is, a decrease in the number of heart contractions. If necessary, frequent administrations of such a substance with an interval of 10 minutes are indicated. For bronchospasm, bronchodilator and anti-inflammatory drugs are used (the use of a nebulizer is indicated).
Oxygen therapy is indicated for apnea, cyanosis and dry wheezing. In rare cases, the administration of Ephedrine or Adrenaline may be required.
[ads-pc-1][ads-mob-1]
Principles of antishock therapy
Quincke's edema is dangerous, first of all, due to the development of a threatening state of shock. And in order to prevent it or relieve its symptoms, the necessary medications, for example Epinephrine, are urgently administered. The injection is given once, but if necessary, it is repeated. Moreover, the break between injections is at least 20 minutes. Intravenous administration of this drug is allowed when the patient's condition is unstable and there is a high probability of death.
During the administration of Epinephrine, careful and continuous monitoring of blood pressure, respiratory and heart rate is carried out. Systolic pressure should be kept at 100 mmHg. Art.
If the shock is severe, with severe damage to the throat, larynx and respiratory dysfunction, then the person is hospitalized in the intensive care unit. The development of abdominal syndrome in the acute stage of edema is a direct indication for immediate hospitalization in the surgical department of the hospital. If the shock is of moderate severity, then the person is hospitalized in a therapeutic or allergy department if there is no threat to life.
Use of diuretic drugs
It is advisable to administer diuretics for lesions of the bladder. Lasix is most often used for this purpose. This is a diuretic drug that has a diuretic effect by blocking the reabsorption of sodium ions. It removes not only ions of this element, but also potassium and magnesium.
If you administer it intravenously, you can quickly achieve the necessary diuretic effect. Its dosage in the case of treatment of Quincke's edema should be a stream. In some cases, the issue of increasing the dosage is decided.
Lasix can also be administered to relieve acute pulmonary edema. The method of administering the medicine is intravenous, infusion. If the effect of such treatment is insufficient, then after 20 minutes the injection can be repeated.
If such a medicine is administered in large doses, then a sharp decrease in the volume of circulating blood is possible. The patient's water-salt balance is disturbed and blood thickening develops. That is why the doctor must pay special attention to platelet counts in the blood and take the necessary measures to prevent the development of side effects in the case of therapy.
Why is Adrenaline administered to the patient?
Adrenaline is usually administered at the first symptoms of swelling. It is the main medicine used to treat all life-threatening conditions. It is usually injected intramuscularly into the upper third of the thigh: in this area it is quickly absorbed into the blood, which makes it possible to quickly achieve the desired effect.
The drug quickly reduces the production of histamine and bradykinin. Increases blood pressure, which helps eliminate the state of shock. If swelling of the larynx develops, then it is possible to administer such a drug into the larynx or under the tongue. If possible and the need arises, intravenous administration of Adrenaline is used.
The dose of the medicine is usually standard and is used by all doctors in typical cases. Today, special devices have been developed for the precise introduction of Adrenaline into the body. They are very easy to use, and patients in serious condition caused by angioedema can use them independently.
Folk recipes
Folk remedies for the treatment of Quincke's edema cannot replace traditional medical care when the patient's life is at risk. Use them when the danger of the acute stage has passed. With the help of traditional medicine recipes, you can reduce swelling and carry out maintenance treatment, achieving long-term remission.
Since folk remedies themselves can be strong allergens (honey, herbal remedies), before using them, make sure that you do not have a negative reaction to them. Apply a drop of the selected product to the elbow and wait 1-2 hours. If you are not bothered by negative symptoms, you can use it.
Salt water compress
Ingredients:
- Cool water – 1 liter.
- Table salt – 1 tsp.
How to prepare: Add salt to water and mix well. Pour water into a plastic bag.
How to use: Apply a bag of water to the sore area until the swelling goes away.
Result: The swelling gradually subsides, the patient’s condition returns to normal.
Nettle root
Ingredients:
- Nettle root – 2 tbsp. L.
- Boiling water – 1 l.
How to prepare: Pour boiling water over nettle root and leave for 2 hours. Strain.
How to use: Take the prepared product, 3 tbsp. l. 3 times a day for a month.
Result: With the help of nettle root infusion, it is possible to achieve stable remission of chronic edema.
Milk with soda
Ingredients:
- Milk – 1 tbsp.
- Baking soda - on the tip of a knife.
How to prepare: Heat the milk. Add soda to it and stir well.
How to use: Drink milk and soda 3-4 times a day until the swelling goes away.
Result: The swelling gradually subsides. The speed of the onset of results depends on the degree of swelling.