Medical editor: Trofimova D., pediatrician. July, 2019.
ICD-10 code: L20-L30.
In infants, diathesis usually manifests itself as symptoms on the skin - on the cheeks and scalp. In children 3-6 years old, lymph nodes may become enlarged. From 7 to 12 years, joint pain and gastrointestinal disorders are possible. The disease occurs due to the structural features of the immune system and gastrointestinal tract. The development of diathesis is due to the presence of a hereditary predisposition in combination with errors in diet. Treatment includes antihistamines, local therapy and a hypoallergenic diet.
Diathesis is not a specific disease, it is a whole complex of symptoms and changes associated with constitutional anomalies - a genetically determined feature of the body. These characteristics are expressed in a tendency to certain diseases. At its core, diathesis is a “pre-disease”, which is characterized by a predisposition to negative reactions to irritants (food components, household chemicals, etc.) and the ability to transform into a disease under the influence of such negative reactions.
There are 3 forms of diathesis:
- Up to 3 years: exudative-catarrhal: manifests itself on the skin and mucous membranes;
- 3-6 years: lymphatic-hypoplastic: lymph nodes enlarge;
- 7-12 years: neuro-arthritic: gastrointestinal disorders, enuresis, joint pain.
Diathesis in a child: causes and treatment
Diathesis is a certain condition of the child’s body, which is transmitted hereditarily and is characterized by a tendency to develop certain diseases, the basis of which are allergic reactions.
Diathesis in a child is a general concept and many young parents do not attach much importance to it or even mistake it for a completely different disease. In reality, one should understand the allergic reaction of a child’s body, which is the first sign that determines a tendency to more serious diseases, such as dermatitis, neurodermatitis and eczema.
Most young families with children aged 3 months to 3 years face this problem. Symptoms can appear over a long period and disappear as soon as possible, even without special treatment. But you should not hope for such a rosy outcome, and at the first signs you should consult a doctor, because we are talking about the health of the smallest and most defenseless member of the family.
Neuro-arthritic diathesis
Neuro-arthritic (uric acid) diathesis is characterized by increased nervous excitability in the child and disturbances in the metabolism of uric acid salts. It usually manifests itself at primary school age, and goes away by puberty. Among other diathesis, this variant of constitutional anomaly more often ends in the formation of various persistent diseases and metabolic disorders in children.
Factors contributing to the manifestation
Hereditary metabolic disorders, poor nutrition and illnesses of the mother during pregnancy, and pathologies during childbirth are responsible for the formation of neuro-arthritic diathesis in a child. Manifestations and exacerbations of uric acid diathesis are facilitated by an excess of highly extractive foods, salt, fats in the diet, a lack of easily digestible carbohydrates against the background of a long break between meals, stress (including strong positive emotions), mental and physical stress, acute infection, and surgery.
Main symptoms
- Increased nervous excitability - noted already from infancy in the form of shudders, loud choking crying due to minor external stimuli (sudden sound, bright light, injection, etc.). Children are often seen by a neurologist for perinatal damage to the central nervous system. In the future, nervous excitability manifests itself as night terrors, enuresis, nervous tics, mood swings, and an obsessive dry cough without signs of ARVI. Vomiting often occurs when the child is overexcited.
- With increased excitability, children with neuro-arthritic diathesis are very capable, easy to learn, and inquisitive. They say about such kids that they are smart beyond their age.
- Unfounded (after a thorough examination of the child, no diseases or organic disorders are found) the child’s complaints of pain in the abdomen, muscles, legs, joints, and head. Poor appetite, including anorexia, is more common in early childhood, but some children may be overweight from birth. There are causeless rises in temperature.
- Tendency to acetonemic crises: after exposure to provoking factors (eating disorders, stress, infections), excessive repeated vomiting, the smell of rotten apples from the mouth, and lethargy occur. Ketone bodies are detected in urine.
- Laboratory urine tests periodically reveal salts (dysmetabolic nephropathy), microhematuria (single red blood cells), and acetone.
Outcomes
Without appropriate correction of nutrition, daily routine, and treatment of complications, neuro-arthritic diathesis can lead to the formation of neuroses, neurasthenia, various metabolic diseases and disorders already in adolescence and adulthood: gout, urolithiasis, metabolic arthritis, interstitial nephritis, diabetes mellitus II- type, obesity, atherosclerosis, etc.
Nutrition
- It is necessary to monitor the regularity of your child's meals. Be sure to find out how your child eats at school and whether he eats there at all. Long periods of fasting should not be allowed. At the evening meal, give hearty foods (porridge, potatoes); a few minutes before bedtime, sweet yogurt and cottage cheese are recommended.
- Force feeding is prohibited. If a child refuses some food, you should not persuade or intimidate him. Don’t insist, limit yourself to a small snack, and after a couple of hours, offer your child to eat again.
- The child’s menu should contain “light” carbohydrates daily in the form of fruits and juices.
- The diet is dairy-vegetable, with some restriction of meat and fish (especially fried and smoked).
- Avoid fatty foods, smoked meats, pickles, marinades, canned food and foods high in purine bases, organic acids and salts (rich broths, meat of young animals, offal, jellied meat, sorrel, rhubarb, spinach, parsley, green peas, cocoa and chocolate, strong tea and coffee).
- Extended drinking regime - dried fruit compotes, rosehip decoctions, cranberry and lingonberry fruit drinks, alkaline mineral waters without gas.
Mode
When planning your daily routine, you should adhere to general rules and recommendations. Children with neuro-arthritic diathesis must be protected from overwork. Rest during the day is mandatory (if the child refuses to sleep, invite him to just lie down or read a book). Control your bedtime and evening activities – exclude active or mentally demanding games, TV, and computer.
Despite the child’s abilities, he should not be overloaded: classes should be selected taking into account his age, and there is no need to pile up several different types of educational programs in one day. Alternate mental exercises with physical exercises - children with neuro-arthritic diathesis are recommended for sports such as swimming, skiing, yoga, cycling and other relatively calm sports. Daily walks in the fresh air are necessary. You can additionally use various techniques to achieve relaxation - warm baths, breathing exercises, light massage.
We must not forget about correcting the child’s psycho-emotional status, which requires the help of a psychologist. Individual, group and family counseling and auto-training are shown. Try to achieve the most comfortable psychological conditions in your family and school. Drug therapy in the form of even mild sedatives is rarely used and only as prescribed by a neurologist or psychologist.
Treatment
During an acetonemic crisis, a child needs a drink containing easily digestible carbohydrates: sweet tea, compote or pharmaceutical glucose solution.
Treatment requires complications of neuro-arthritic diathesis, among which acetonemic crises come to the fore. In case of the first signs of acetonuria (characteristic sweetish breath, lethargy, nausea, vomiting), it is necessary to immediately begin measures to remove toxic ketone bodies and provide the child’s body with glucose:
- provide a source of easily digestible carbohydrates - sweet tea, compote, glucose solution;
- carry out oral rehydration by giving the child small portions (3–5 ml) of water-salt solutions (Regidron, Glucosolan), compote, mineral water;
- adhere to a strict diet until the crisis is completely relieved and for another 1–2 days, followed by gradual expansion;
- Give a short course of enterosorbents (Polysorb, Enterosgel, Smecta, Filtrum).
Causes and symptoms of diathesis in children
The causes of diathesis can be very diverse. A predisposition to allergic reactions can develop both in the mother’s womb and during the first months of the baby’s life. The cause may be a violation of the diet of a pregnant woman or nursing mother, consumption of foods such as honey, eggs, berries, oranges and other citrus fruits, canned and pickled foods or caviar. Also, the causes in children can be hereditary.
A polluted environment, dust, pets, as well as taking medications that are not recommended during pregnancy or lactation can cause the baby to develop the disease.
Based on the above, we can summarize that the root cause of diathesis in children is nutritional disorders. Let's not neglect bacterial or viral infections, which in turn can also cause this unpleasant disease.
We bring to your attention a brief description of the ways in which allergens enter the child’s body:
- Through food. The most common reason that must be taken into account when introducing new components into a child’s diet.
- Contact path. An allergic reaction can occur as a result of contact of children's skin with synthetic materials, wool, washing powder and other substances.
- Air. This refers to dust, perfumes and deodorants used by parents, and pet fur.
The use of perfume by relatives and the consumption of allergenic foods by a nursing mother are possible reasons for the development of diathesis in a child
Symptoms of diathesis in children are as follows:
- Redness of baby's skin
- The appearance of itchy gray or brown scales
- A crust forms on the head
- Skin elasticity decreases
- Decreased muscle tone
- Gastrointestinal disorders manifest themselves in the form of diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain
- Pallor
- Conjunctivitis
- Possible complications such as bronchitis or laryngitis
- Urine changes its composition
- Girls may experience cystitis or vulvovaginitis
a) crusts on the head; b) redness of the skin
The above symptoms depress the child’s immune system, resulting in an increased risk of complications.
Prevention
Often, a tendency to diathesis arises as a result of the abuse of certain foods during pregnancy. The baby, while still inside the mother, develops a predisposition to an acute reaction to certain foods or drinks. Therefore, it is necessary to think about the prevention of diathesis even before the child is born.
Follow these preventive measures:
- Use foods from the group of strong allergens with caution or completely avoid them during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- To wash children's clothes, use only baby powder.
- Take care of your toddler's skin. If any changes occur, promptly treat your baby's skin with hygiene products.
- Temper your child.
- Do not delay contacting a doctor if primary symptoms of illness appear.
- If complementary foods are introduced to your child, make sure that age standards are observed and that the correct sequence of products is introduced.
- In the first six months, the baby must bathe exclusively in boiled water.
- Air and sunbathing techniques are important.
You should not be calm about the appearance of diathesis in a toddler. Mom must promptly identify the cause and respond to it in a timely manner. Don’t think that diathesis will go away on its own. We must not forget that a neglected condition can cause serious complications. It’s even better to prevent the occurrence of diathesis by following simple preventive measures.
How to treat diathesis in a child
You can eliminate the consequences of the disease in your baby first of all by removing from the diet the foods that, in your opinion, became the causes of the allergic reaction. The treatment is simultaneously accompanied by procedures for caring for damaged skin.
Since the types of this disease are different, only a doctor can prescribe the treatment necessary for each individual case:
- Treatment of weeping diathesis with special drying agents.
- Peeling is softened with hypoallergenic ointments.
- Drugs are prescribed that reduce itching, which also normalize the microflora, plus vitamins.
- In case of a complication that is accompanied by a bacterial infection, a special antibacterial ointment or antibiotic is prescribed.
- Use of antiseptic solutions.
a) skin restoration cream “La-Cri”; b) cream for the treatment of skin diseases "Bepanten"
The answer to the question “how to cure diathesis in a child” can only be given by a certified specialist, but no one forbids resorting to folk recipes; the main thing is to approach the question wisely and monitor the course of the disease together with a doctor. Baths with the addition of herbal decoctions of chamomile, string, oak bark, and calendula have proven effective.
Exudative-catarrhal diathesis
This is the most common constitutional anomaly: more than 80% of infants have some manifestations of exudative-catarrhal diathesis. It can begin in a child from the first days of life.
Factors contributing to the manifestation
The main reason for the manifestation of exudative-catarrhal diathesis is improper nutrition (violation of the timing of the introduction of complementary foods, feeding the child with food inappropriate for his age, switching to artificial feeding, feeding with cow's milk, etc.). The abuse of highly allergenic foods (citrus fruits, chocolate, strawberries, nuts) by a woman during pregnancy and breastfeeding is important.
Other allergens can also provoke symptoms of exudative-catarrhal diathesis - household (washing powder, diaper fragrances), medicinal (including components of baby care products), insect (house dust mites), animal hair and dander, etc.
Main symptoms
- Tendency to allergic reactions. Most often, allergens enter the child’s body with food - a typical picture of allergic (atopic) dermatitis develops: the baby’s cheeks turn red, itchy rashes appear on the cheeks and buttocks. The rash varies in size, from small to large-spotted, may coalesce, and ranges from pink to bright red. In addition to the rash, the formation of “milky crusts” on the cheeks (a kind of compaction and shine of the skin over the area of redness, followed by the formation of crusts and scales), and the scalp (in the form of dense, fatty yellow scales stuck to the head at the roots of the hair) is characteristic. If treatment is not started in time, the rash begins to become wet, cracks and erosions appear on the surface of the skin, and a secondary infection may develop. As the child grows, the appearance of the rash changes: after six months the rash becomes drier and is localized mainly on the extremities. By the age of 2, the skin becomes dry, thickening, constant scratching in the area of the popliteal and elbow folds, skin of the wrists and ankle joints, and small itchy nodules are observed.
- With the slightest errors in care (overheating due to warm clothes, untimely change of a wet diaper or diaper), prickly heat occurs, and then diaper rash in large folds of skin (cervical, axillary, buttock, thigh).
- Frequent lesions of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity (stomatitis, gingivitis, changes in the relief of the tongue - “geographic tongue”), eyes (conjunctivitis).
- Tendency to colds (rhinitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, bronchitis, including obstructive).
- The child is often overweight, has loose or tender white skin.
Outcomes
In most children, exudative-catarrhal diathesis begins to gradually subside after 2 years and completely disappears by 3-4 years. In the future, children do not suffer from symptoms of food or any other allergies; they can safely consume strawberries, citrus fruits, cow’s milk and other products.
But in some cases, diathesis develops into diseases of an allergic nature: atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, allergic bronchitis, bronchial asthma, etc. To prevent this from happening, a child with the first signs of exudative-catarrhal diathesis must be provided with proper nutrition, care and timely treatment of emerging symptoms.
Nutrition
Long-term breastfeeding is the most important measure for the prevention of exudative-catarrhal diathesis.
The diet for children with exudative-catarrhal diathesis must comply with all the principles of a hypoallergenic diet:
- Maintaining breastfeeding for as long as possible (with mandatory adherence to a hypoallergenic diet by the nursing mother). When artificial feeding, the mixture should be selected together with a pediatrician. You should not change a suitable mixture to another, even if for some characteristics (composition, additional additives, price, manufacturer) it seems better to you.
- The introduction of complementary foods should not begin before 6 months. Hypoallergenic dishes of vegetable or cereal complementary foods (zucchini puree, rice porridge) are introduced first. Be sure to monitor your baby and make entries in a food diary, noting allergic reactions to foods in order to subsequently eliminate them from the diet. Whole milk, strawberries, honey, and nuts should not appear on a child’s menu earlier than 2 years, and even then, provided the child’s skin is in normal condition. Chicken eggs (not earlier than 8 months, after meat), fruit and vegetable juices (after a year) are introduced extremely carefully. Preference should be given to food that you prepare yourself: exclusively “canned” food, despite all the advertising assurances about the absence of preservatives and other harmful substances, in practice is often accompanied by allergies.
- Don't hesitate to ask! Local pediatricians do not always give complete information about the baby’s diet, relying on your knowledge or simply due to lack of time. Check, consult with your doctor, find out details about nutrition. Do not introduce new products based on the principle that “what if everything will be fine.”
- Don’t worry that you are depriving your child of vitamins and all kinds of goodies. Firstly, this is not forever: with the right approach, in a couple of years the baby will be allowed strawberries, milk, as well as other tasty and healthy foods. And secondly, a properly formulated hypoallergenic diet has almost no effect on the vitamin and mineral value of the diet.
Baby care
As a rule, the tendency to allergies is not limited to skin manifestations, and over time the child's sensitivity to other potential allergens increases. To reduce the risk of sensitization of the child’s body, follow a number of basic measures:
- Wash your baby's clothes and diapers, as well as your own home clothes, with special baby powder or baby soap, and then iron them (high temperature destroys allergens).
- Use clothes only made from natural fabrics.
- Do not give your baby soft toys, and check hard toys made of plastic and rubber for a quality certificate.
- Do not have pets, and if you already have one, avoid contact between the animal and the child. The animal should not enter the room where the baby sleeps.
- Minimize the number of “dust collectors” (upholstered furniture, carpets, books and clothes in uncovered closets, etc.) in the baby’s room.
- Try to do wet cleaning at least in the baby's room every day.
- If your child is sick, do not give him medications without a doctor's prescription - many medications contain allergenic flavors and dyes.
- To care for your child's skin and hair, use special medicinal children's cosmetics. It is not necessary to purchase expensive brands, but it should be medicinal cosmetics (Emolium, Lipikar lines, creams such as Bepanten, Skin-cap, Topicrem). Special products carefully moisturize the skin without causing irritation or allergic reactions.
Treatment
Manifestations of exudative-catarrhal diathesis in the form of milky crusts or rashes require treatment. But never use topical medications (medicinal creams, gels, emulsions, etc.) without a doctor’s prescription - you can only harm the child!
Therapeutic baths
Daily hygienic baths perfectly cleanse the skin of babies. To carry out the bath, dechlorinated water (standing in an open container for at least an hour) is used. Baths with the addition of:
- potato starch (1/2 cup per bath);
- infusion of string, chamomile, sage, oak bark (1-2 tablespoons of dry raw materials are poured with a glass of boiling water, simmered in a water bath for 20 minutes and added to bathing water);
- wheat bran (1/2 cup is brewed with a glass of boiling water, and then diluted in a bath);
- rolled oats (1/2 cup is boiled in 500 ml of water for 20–30 minutes and the resulting solution is poured into the bath);
- bay leaf (1 pack weighing 10–15 g is boiled in 0.5 liters of water for 5–10 minutes and the decoction is added to the bath).
For local drug treatment of allergic dermatitis, hormonal and non-hormonal creams and ointments are used. Hormonal creams (Advantan, Elokom) are good because they quickly give effect. But their use in young children is limited by the high risk of side effects. Of the non-hormonal ones, Elidel and Fenistil have proven themselves well, but they also should not be used without a medical prescription. If an infection occurs, an antibacterial cream or a combination of an antibiotic and a hormone (Oxycort, Polcortolone) may be required. Creams should not be rubbed onto severely inflamed, eroded surfaces; only the careful application of light gels, emulsions and medications in the form of aerosols is allowed.
In case of severe swelling and weeping on the child’s skin, it is advisable to perform wet lotions: a sterile gauze bandage rolled up in 6–8 layers is moistened in a cooled solution (an aqueous solution of furatsilin, a decoction of birch buds, tea, chamomile, oak bark) and applied to the affected area for 10– 15 minutes, then repeat the procedure with a new bandage - 2-3 more times. Such lotions are done 3-5 times a day.
If there are crusts on the skin and scalp, they should be soaked before applying the medicine by applying a lotion with warm boiled water or giving the child a hygienic bath. Under no circumstances should the crust be removed from the head with a fingernail or a hard comb - this will injure the skin and promote infection. To comb out scales that have softened after swimming, use a special comb-brush with soft bristles, which should be doused with boiling water before each use.
Diathesis on a child’s bottom - photo
An allergy to the butt in a child manifests itself in the form of dense red spots with clear boundaries. Scales may form as a result of skin peeling. Papules, blisters, or small red dots may also appear. The danger is that by scratching the skin, the baby can get an infection that will be much more difficult to cure. If after hygiene procedures the color of the spots lightens and the rash goes away, then there is diaper rash and it is important not to confuse it with diathesis, since the latter is formed as a result of an autoimmune inflammatory process and cannot be cured by simple methods.
The above photo will clearly help you determine that it is diathesis on the child’s bottom.
Typical symptoms
Unlike children, in whom diathesis appears most often on the face, in adults the rashes are localized on the arms, back, legs and neck. In addition to this symptom, there are others:
- increased skin sensitivity, dryness and flaking;
- swelling that does not go away for a long time;
- covering the rashes with crusts;
- pain in the areas of the rash, accompanied by itching of the skin;
- redness and tearing of the eyes, irritation of the mucous membranes;
- sleep problems.
Symptoms develop quickly - within 10-15 minutes after eating food, contact with household chemicals or other allergen.
If diathesis appears for the first time, a person does not focus on it. The unpleasant condition passes quickly. But with each subsequent time, the symptoms become more and more protracted, and treatment becomes more complicated if it is not started in a timely manner.
Treatment of diathesis on the cheeks of a child
The modern pharmacological industry offers many effective drugs for treatment, but you should not ignore traditional methods. Treatment of diathesis on the cheeks of a child first begins with a consultation with an allergist, who will give competent recommendations regarding the exclusion of certain foods from the diet.
It is necessary to treat diathesis on the cheeks of a child (photos attached) comprehensively, following the recommendations below:
- anti-itch medications
- only a doctor can prescribe antihistamines
- sedatives
- ultraviolet treatment
- Taking vitamins will improve immunity
The skin of the baby’s cheeks must be systematically lubricated with a special cream, which is applied in a thin layer.
Adult diet for diathesis
When diathesis manifests itself, following a diet for at least 6 months with keeping a food diary is effective. During the diet of an adult, provoking antigens that affect the appearance of allergies should be excluded:
- bakery products;
- citrus fruit;
- fruits, vegetables, red and orange berries;
- products containing GMOs;
- spicy, salty, processed, fried foods.
The diet must include:
- dairy-free cereals;
- lean meat;
- green vegetables and fruits;
- sour milk.
Treatment of diathesis in infants
How to treat diathesis in an infant? The answer, as a rule, involves the use of antihistamines, which effectively alleviate the course of the disease, relieve swelling and itching.
The specific treatment of infants differs in the use of medications that cleanse the child’s body of harmful toxins and allergens. If the baby is fed breast milk, then first of all the young mother is obliged to adjust her diet. It is also a fairly common practice for a doctor to prescribe vitamins that help maintain the balance of minerals in a child’s body.
You may be interested in: First aid kit for a newborn - list of essentials
How to treat diathesis in an infant?
We bring to the attention of our readers the most popular folk remedies for treating infants among parents:
- Treatment with eggshells. Grind the shells, dried for several days, into powder and give the child 1 teaspoon twice a day, dilute with water, lemon juice or other liquids. A large amount of calcium alleviates acute manifestations of the disease.
- Bath in a decoction of string and chamomile. Effectively relieves itching and inflammatory processes on the skin.
- Fir oil ointment. Mix 1 part of the oil with 3 parts of baby cream and treat the baby's skin morning and evening.
- Tinctures from dandelion or burdock roots.
a) crushed eggshells; b) fir oil
Traditional methods of treatment are more gentle on the child’s body, but if their use does not bring visible results within a period determined by the doctor, then it is worth resorting to drug treatment described in the previous chapters of our article.
What does diathesis look like?
After your baby turns 3 months old, redness may appear on the cheeks or body. They are covered with a thin film - a milky crust, which causes itching and irritation. The manifestation of the first signs is incurable diaper rash, prickly heat, greasy crusts on the eyebrows and hair of a yellow and gray hue. Lymph can be released through the crusts, then they are called a wet rash. Its danger lies in poor protection against infections.
Diathesis looks like a rash and appears all over the body: cheeks, ears, nasolabial triangle, chin, arms, abdomen, buttocks, legs. With dry diathesis, swelling and peeling occur. The child's face becomes puffy and excess weight increases. He lags behind his peers in physical and mental development. In advanced cases, the tonsils, larynx and nose with the organs of vision become inflamed. Characterized by painful defecation - emptying the rectum.
- Creams and ointments for diathesis for adults and children up to one year and older - hormonal and non-hormonal preparations
- What is scrofula in children and adults - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention
- Causes of red cheeks in adults and children - how to get rid of them with medicines and folk remedies
Hemorrhagic diathesis in children
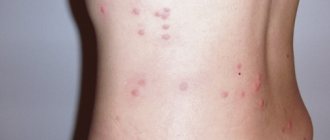
The hemorrhagic type of the disease is characterized by an increased tendency of the body to bleed. Hemorrhagic diathesis in children is accompanied by the spontaneous appearance of bruises on the child’s body, even as a result of a light touch. The number and their size often do not correspond at all to the actual damage.
The key symptom is the formation of various rashes, bleeding or extensive hematomas on the body. When the disease is severe, the rashes can turn into ulcers. The patient may also experience severe discomfort in the abdominal area, nausea, and vomiting of blood.
Treatment methods directly depend on the type and manner of bleeding. Thus, corticosteroid medications, ascorbic acid, vitamin PP, and rutin can be prescribed. With frequent and heavy bleeding, surgical intervention and removal of the spleen is possible.
Diagnostics
Due to the fact that diathesis is not an independent nosological entity, patients are often treated by the following specialists:
- rheumatologist;
- dermatologist;
- nephrologist;
- homeopathist;
- otorhinolaryngologist;
- neurologist and others.
Laboratory methods for diagnosing pathology:
- clinical analysis of urine;
- clinical blood test;
- blood biochemistry;
- immunological research;
- taking excrement for analysis for dysbacteriosis.
Instrumental diagnostics:
- Ultrasound. It is imperative to use this method to check the adrenal glands, lymph nodes, liver, thymus and spleen;
- X-ray.
Lymphatic hypoplastic diathesis
This diagnosis is made very rarely and most parents have probably never heard of it. We will try to explain clearly what lymphatic hypoplastic diathesis in children is. From the name of the disease we can conclude that the baby’s lymphatic system takes part in its development. This type of diathesis is characterized by increased growth of cells in the lymphatic system; in addition, disturbances in the endocrine system also occur, which makes this type of disease more than serious.
It is important for children to provide adequate nutrition and limit the consumption of foods containing dyes and preservatives. New foods should be introduced with caution and parents should pay special attention to the introduction of cow's milk.
Compliance with the daily routine is of great importance and the hardening process, gymnastics and massage procedures have shown themselves to be effective.
You may be interested in: How to properly massage a newborn
Varieties
There are several types of diathesis in children depending on the etiology:
- Respiratory - allergens that cause a response in the form of diathesis enter the body by inhalation.
- Food - is a consequence of the consumption by a nursing mother or the baby of a product that provoked an allergic reaction.
When my son was 4 years old, at his grandmother’s for Christmas, he ate a tangerine, which caused the appearance of diathesis on his cheek, and only on the left one.
My niece had severe diathesis until she was one year old. Doctors could not identify the cause for a long time and prescribed different drugs. The pediatrician prescribed something different, the dermatologist prescribed something else, and the allergist prescribed something else. I had to eliminate foods, change powders, hygiene products, and frequently carry out wet cleaning. Turned out to be an allergy to eggs.
- Contact - most often occurs as a result of washing with inappropriate powder, using hygiene products not intended for children, or wearing poor-quality clothing.
- Autoimmune – revealed as a tendency to systemic pathologies.
- Infectious-viral - the source of diathesis was the penetration of viruses or bacteria into the baby’s body.
- Exudative-catarrhal – a tendency to false allergic reactions, a violation of water-salt metabolism.
- Lymphatic-hypoplastic – characterized by hyperplasia of the lymph nodes and thymus gland, decreased immunity, and dysfunction of the endocrine system.
- Neuro-arthritic – characterized by increased excitability, changes in uric acid metabolism, and increased ammonia levels in the toddler’s body.
Classification and types
It is customary to distinguish two types of diathesis in infants, which differ from each other in external manifestations:
- Dry diathesis
Accompanied by red spots that last 3 to 5 days. But unlike the wet type, the inflamed areas are not covered with weeping blisters. The skin peels, itches and cracks. The stomach, butt, and thighs become like sandpaper, the skin lacks moisture.
Most often, cracks appear on the fingers, neck, knees, elbows, and less often behind the ear. Without proper care, these areas bleed and become gateways for infection.
Diathesis gives the baby discomfort, pain and burning. This causes constant crying and hysterics.
- Wet diathesis
The first sign of this type of dermatitis is crimson cheeks with blisters and swellings. First, red areas appear on the face, neck, chest, then they become covered with watery blisters. They are very itchy and wet. The child combs them and eats them. The infection spreads further. The process is repeated again.
The skin of a baby with this type of diathesis becomes thinner and becomes sensitive. He feels discomfort, cannot sleep peacefully, play, or stay awake.
Any type of atopic dermatitis requires care, especially in the acute period. Parents should remember that a newborn baby receives most of its oxygen through the skin.
Treatment
The principles of treatment and prescription are carried out by the attending physician. For therapy, medications, diet and traditional medicine recipes are used. Starting from the age of one month, babies can be treated with the antihistamine Fenistil orally or externally.
The usual regimen includes complex treatment:
- Oral antihistamines (Fenistil, Zyrtec, etc.).
- Probiotics (Bifidumbacterin, etc.).
- If a child is excitable due to diathesis, use fennel tea.
- External ointments and gels.
- To cleanse the body, Polysorb.
When the baby is breastfed, the mother must adhere to a diet excluding allergenic foods (honey, citrus fruits, etc.), coarse fiber and fatty foods. During complementary feeding, all new foods should be introduced one at a time at intervals. Baby care products are selected even more carefully.
Important! Self-medication can be harmful. All measures must be agreed with a doctor.
Why is it dangerous?
Many parents are interested in how long diathesis lasts in infants and why it is dangerous. The insidiousness of the symptom cannot be underestimated, because in the absence of proper treatment it has long-term consequences:
- violent allergic reaction to external and internal irritants in the future;
- the addition of bacterial infections and the development of pyoderma due to scratching of the skin due to constant itching;
- development of bronchial asthma and chronic diseases of the respiratory system;
- malfunctions of the immune system;
- obesity caused by metabolic disorders, gout, diabetes mellitus are the consequences of a neuro-arthritic form of diathesis.
The danger of the exudative-allergic type of disease is the severe vulnerability of the skin and mucous membranes - they are more often damaged and infected.
Drug treatment
Complex drug therapy includes several drugs that help reduce symptoms. Their action is aimed at solving the following problems:
- remove inflammation on the skin;
- cleanse the body of allergens;
- regulate the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- regenerate epidermal cells.
Medicines are used for local and internal effects on the child’s body. The first include ointments, creams, and the second - drops, powders, tablets. Let's look at each group separately.
For external use
The most commonly used are hormonal drugs. These are corticosteroids. They are adapted to children's age and are considered safe, but they should be used only as prescribed by a doctor. Quickly relieve inflammation, redness, itching.
The most popular drugs are the following:
- «Elokom»
Refers to vasoconstrictor drugs. Restores the integrity of the epidermis. Well absorbed. It can be used even at an advanced stage. You need to use it once a day.
- «Advantan»
Effectively eliminates cracks and peeling, and is often used to treat dry diathesis. Recommended for babies from 3 months.
- «Celestoderm»
Effective for the treatment of allergic dermatitis. Prescribed for babies from 6 months. Can be used 3 times a day, but no more than 10 days.
- «Sinaflan»
Eliminates inflammation, eczema. Sinoflanic acid in children can be addictive if used frequently. Use it for no more than a month.
Hormonal ointments should be discontinued when the crimson areas on the body and weeping eczema, which cause discomfort to the child, disappear. For infants, you can use a mixture of ointment and baby cream in a 1:1 ratio. Be sure to apply it to a small area of your child's skin before using it for the first time to check for allergies to any of the ingredients.
Non-hormonal ointments include “ Zinocap ”, “ Tsindol ”, “ Fukortsin ”, “ Pimafukort ”. They have antifungal properties and heal wounds. They can be smeared for a long time without harm to the baby’s health. " Panthenol " is used as a moisturizer, against cracks in the groin, on the skin.
Oral drugs
These include adsorbents and antihistamines. They cleanse the body of accumulated allergens and toxins, and help reduce the manifestations of a negative allergic reaction. Taking them will make the baby’s illness easier.
Antihistamines
These are “ Fenistil ”, “ Zodak ”, “ Erius ”. Apply once a day. The dosage is calculated according to the weight and age of the baby. Dilute the drops with water. The treatment course can last 30 days. When taking, strictly follow the instructions and doctor's recommendations.
Adsorbents
The following drugs are used effectively:
- «Polysorb»
This is a powder that is diluted in a large amount of water. It should be drunk 30 minutes before meals.
- «Enterosgel»
For infants, it is better to dilute the gel with water or mother’s milk. The dosage is calculated according to the age and weight of the baby.
- «Smecta»
It does not so much neutralize allergens as it helps the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Apply 1 - 3 times a day. Infants can be diluted with water and given in a bottle.
- «Sorbex baby»
Improves intestinal microflora, removes allergens. Approved for use in newborns. Absolutely safe for infants, since the active ingredient is activated carbon. The prepared suspension is given to the child a little at a time, the rest can be stored in the refrigerator for no more than a day.
Important ! Parents of infants and older children should remember some of the subtleties of treating diathesis:
- The use of corticosteroids and antihistamines should not be combined over time. Apply the cream in the morning and give the drops at night.
- Do not combine Zodak, Fenistil and other drops with adsorbents. "Polysorb", "Smecta" and "Sorbex" neutralize their effect. Give drops an hour before taking adsorbents or 2-3 hours later.
- "Polysorb" and "Smecta" can cause constipation in babies. It is necessary to monitor bowel movements and increase the amount of fluid consumed during the treatment period.
- Pay attention to the spring and autumn periods. If the child’s signs of diathesis intensify at this time, start prophylaxis with antihistamines and adsorbents in advance.
Watch the video in which the famous pediatrician Evgeny Komarovsky talks in detail about the symptoms and treatment of diathesis.
Causes of diathesis
Stress, nervous overload - these are the main causes of diathesis in an adult. Overexertion and fatigue lead to rashes and itchy skin. Other common factors in the occurrence of pathology are:
- food allergy to haptens in sweets, fluoride in toothpastes;
- a cold allergic reaction occurs;
- cholinergic allergy – sweating due to stress, being in a hot room, swimming, physical activity;
- genetic predisposition;
- the effects of malnutrition;
- chronic diseases.
In pregnant women
Doctors are faced with the fact that diathesis manifests itself in pregnant women. Its main types, according to the approved classification, are uric acid, allergic and hemorrhagic. The causes include blood clotting pathologies, allergies, and metabolic disorders of oxalic acid salts and calcium phosphates. Diathesis during pregnancy is treated by maintaining proper nutrition, water-salt balance, and eliminating contact with the allergen. It is important to get rid of the disease before the baby is born, otherwise it will be passed on to him.
Features of the disease
There is an opinion among people that diathesis is a purely childhood pathology that occurs only among infants. But this is not true at all. In fact, diathesis often occurs in adults, and is practically no different from a childhood disease. Usually, adults do not even realize that this particular pathology is bothering them.
In fact, diathesis is a generalized name for a whole group of diseases that are characterized by a person’s predisposition to infectious, allergic and inflammatory diseases. In other words, in this condition the body reacts inadequately to stimuli. It can be provoked by infectious diseases, unhealthy diet and improper daily routine.
Diathesis is considered by many to be a skin disease due to the fact that it manifests itself primarily on the integument. Symptoms can affect literally any part of the body: face, legs, back and chest. But most often diathesis occurs on the hands. In the photo you can see how it looks in adults and children.
The pathology itself is of allergic origin, and despite its widespread occurrence among infants, it can occur in older children and adults. If you do not treat this disease, then at an older age it can lead to the development of neurodermatitis - a more serious defect that is difficult to treat.
In childhood, the key factor for the occurrence of diathesis is considered to be insufficient development of the body. Over the years, the reasons for the appearance of such allergies can be stress, weakened immunity, emotional stress and drug therapy using potent drugs.
Causes
Diathesis does not occur in an infant without a reason, but it is difficult to identify a single factor that caused the appearance of pronounced symptoms. Often, babies have a hereditary predisposition when one of their parents or direct relatives suffers from allergic reactions. The problem is clearly manifested by a combination of several factors, external and internal. Causes of diathesis in infants and newborns:
- abuse by the expectant mother during pregnancy of products containing preservatives, dyes, and chemical additives;
- a pregnant woman's passion for chocolate, honey, oranges, strawberries, eggs;
- infections suffered by a woman during pregnancy, severe toxicosis, taking antibiotics;
- early termination of breastfeeding or lack thereof;
- improper introduction of complementary foods, transfer of infants to formulas containing large amounts of cow protein;
- reaction to low-quality diapers, hygiene and care products, synthetic underwear;
- living in unfavorable environmental conditions.
Diathesis occurs in different forms, and the development paths are as follows: contact, food, or inhalation of irritants from the outside. Only a specialist can determine the true cause of the disease and prescribe adequate treatment.
Important tips for caring for your baby
An atypical disease requires special attention. The rules of care are quite simple and will not cause any trouble for caring mothers.
- Keep your skin clean. Wipe your hands with wet wipes, wash your butt after using the toilet, change your diaper more often. Apply zinc ointment to the rash to dry it out.
- Buy white underwear for your baby.
- Use baby powders, rinse thoroughly, iron things.
- For bathing, choose special products designed for dry skin. Avoid regular soap.
- Wash your baby for no more than 10 minutes in warm water. After the bath, do not dry your baby immediately; let the water soak into the skin.
- For dry diathesis, carefully lubricate the baby’s skin with non-hormonal emollients and balms. They retain moisture in the skin. An excellent remedy is “Bipanthenol” (“Bepanten”), it moisturizes the epidermis, relieves dryness and cracks, and regenerates cells. Dr. Komarovsky talks about this in detail in his books and broadcasts.
- Monitor the air temperature in the apartment. Don't overheat your baby. When a baby sweats, he loses the necessary moisture.
- Carry out daily cleaning of the house, remove carpets, animals, and soft toys from the apartment for a while. They are sources of dust, wool, dirt.