Red blood cells are the cells that contain the largest amount of the red pigment hemoglobin. The main function of red blood cells is to carry oxygen from the lungs throughout the human body, delivering it to all tissues and organs. That is why red blood cells take a direct part in the breathing process. In the blood, the norm of these cells is from 3.7 to 4 per 1 liter.
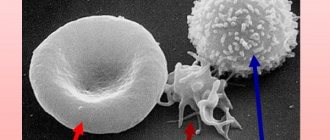
Red blood cells are disc-shaped. These cells are slightly thicker at the edges than in the center, and when cut they look like a biconcave lens. This structure helps them to be saturated with oxygen and carbon dioxide as much as possible, passing through the bloodstream of the body. Under the influence of a special kidney hormone, erythropoietin, red blood cells are formed in the red bone marrow.
Mature red blood cells moving in the blood do not contain a nucleus and cannot combine nucleic acids and hemoglobin. Red blood cells have a low metabolic rate and therefore have a lifespan of approximately 120 days from the time they enter the bloodstream. At the end of the term, “old” red blood cells are destroyed in the liver and spleen.
Red blood cells are normal for women, men and children
For the normal functioning of internal organs and systems, blood cells must be present in sufficient quantities in the human body. The leading role in this matter is played by red blood cells (the norm is from 3.7 to 4 per 1 liter). These cells are responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs and removing carbon dioxide from the body.
What is the norm of red blood cells in the blood for a person? It depends on gender
and age group.
- The norm for women is 3.7–4.7x1012/l.
- For men, the norm varies from 4.0 to 5.3x1012/l.
The norm of red blood cells in a child’s blood is from 2.7 to 4.9x1012/l (from 2 months of age), from 4.0 to 5.2x1012/l (from 6 to 12 years of age). Any deviations from the norm are associated with the presence of pathological processes in the body. Daily fluctuations of these cells in the blood should not exceed 0.5x1012/l.
Deviations from the norm
Average Er volumes may deviate from the norm; there are conditions in which the indicator of this test is:
- reduced – the average size of Er is less than 80 fl, Er is called microcytes;
- normal - the range of red blood cell sizes is 80 - 100, cells of this volume are called normocytes;
- increased - the average size exceeds 100 fL, and such Er macrocytes are called.
MCV reduction
When a large number of small red blood cells appear in the blood, this erythrocyte index will be reduced. Developing at low Wed volume. erythr. anemia is classified as microcytic.
A decrease in the average size of red blood cells is observed in anemia:
- iron deficiency;
- sideroblastic – immature Er with iron granules are found in the bone marrow (sideroblasts);
- associated with disorders of erythropoiesis - the process of Er formation; a hereditary form in men associated with impaired synthesis of porphyrins, a component of hemoglobin;
- acquired forms, provoked by a lack of vitamin B6, lead poisoning, impaired formation of porphyrins;
Hereditary and acquired anemia, associated with a decrease in the synthesis of porphyrins, is caused by the disruption of the production of hemoglobin molecules. Iron entering the body is not incorporated into the hemoglobin molecule, but is deposited in various organs.
The process of accumulation of unbound iron occurs predominantly:
- in the liver – a process starts that leads to cirrhosis of the liver;
- ovaries – sexual function is impaired;
- pancreas – diabetes mellitus is provoked;
- adrenal glands - hormone production is disrupted.
Anemia associated with blocking the synthesis of porphyrins is detected in young people. The disease is often unexpressed. This means that the symptoms of the disease are mild, and although a person’s average red blood cell volume is low, his iron content is high, and hemoglobin gradually drops, and can reach 50–60 g/l in an adult male.
This index is reduced in children with thalassemia, a hereditary disease that affects the genes encoding the synthesis of hemoglobin chains. If only one gene is affected, this means that the average volume of red blood cells will be slightly reduced, and the child may even be asymptomatic.
But if all 4 genes responsible for the synthesis of alpha-hemoglobin chains are affected, the fetus develops intrauterine hydrops and the child dies immediately after birth or in utero.
Increase in average volume indicators
If the average volume of erythrocytes is increased, this means that a lot of Er of large sizes have appeared, exceeding the norm. The appearance of macrocytes and an increase in the average volume of Er are observed in diseases:
- anemia; hemolytic;
- aplastic;
- folate deficiency;
- B12-deficient;
The average volume of erythrocytes and RWD in an adult with myelodysplastic syndrome are increased, which means that the number of macrocytes in the blood is increased and anisocytosis is observed - a phenomenon of high variability in cell sizes. With an increased average volume of Er in an adult and normal hemoglobin, it can be assumed that the person suffers from alcoholism.
The MCV of red blood cells may be slightly increased if a person smokes, and in women, an increase in the average volume is provoked by taking hormonal contraceptives.
What does a fluctuation in red blood cell counts mean?
A physiological upward deviation in the number of red blood cells can occur due to the following factors:
- intense muscle work;
- emotional arousal;
- loss of fluid due to increased sweating.
A decrease in the number of “oxygen” cells in the blood is facilitated by drinking and eating heavily. Deviations from the norm that arise as a result of the above reasons are usually short-term and are associated with nothing more than the distribution of red blood cells, thinning or thickening of the blood.
Average hemoglobin concentration in erythrocyte
This parameter is designated as MCHC and expresses how full the red blood cells are with hemoglobin. MCHC characterizes the density of filling a red blood cell cell with hemoglobin.
Calculated as follows:
MCHC = Amount of hemoglobin * 100/Hematocrit. Hematocrit is the ratio of plasma volume to red blood cell volume. It is usually directly proportional to the total volume of red blood cells and is measured in g/dL, just like the amount of hemoglobin in general.
The MCHC norm varies depending on gender and age, but in general it can be said that for men it is 324-366 g/l, and for women 323-356 g/l. In childhood, the minimum limit for the average concentration of hemoglobin in an erythrocyte is reduced. So, for example, for a child up to 1 month old, MCHC = 280-260 g/l. All normal indicators should be checked with a doctor, especially for children, when literally every month the body works in a new way.
If the mean concentration of HB in MCHC red blood cells is increased, there is a possibility of an imbalance in the blood and the presence of hyperchromic anemia.
In general, even if the average hemoglobin concentration in a red blood cell is increased, it cannot exceed 380 g/l. This phenomenon can be explained from a chemical point of view: hemoglobin does not dissolve in water infinitely, but upon reaching a certain density threshold it begins to crystallize, which can lead to hemolysis of red blood cells.
So an overestimated analysis result may be an experimental error or an inaccurate calculation.
If the average concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells is reduced, the reasons should be sought in hypochromic anemia. But this is not the only disease that can affect blood tests. In addition, the average hemoglobin content in a red blood cell is reduced if the patient has the following abnormalities:
- Anemia caused by lack of iron;
- Disorders of blood balance and metabolism;
- Deviations in hemoglobin synthesis;
- Macrocytic, sideroblastic anemia;
- Hemoglobinopathy.
As you can see, the average concentration of hb in the erythrocyte is reduced in various forms of anemia and disorders of the blood composition.
What diseases contribute to changes in red blood cell counts?
The level of red blood cells in the blood plays an important role in the diagnosis of many diseases. The norm or deviations from it indicate the absence or presence of a particular disease. When the number of blood cells increases, we are talking about the presence of diseases associated with the blood system or oxygen starvation.
A decrease in red blood cell counts is the main laboratory sign of anemia. Typically, such changes are associated with large blood losses or anemia. In the presence of chronic blood loss, deviations from the norm may be insignificant or completely absent.
Indications for use
MCV in the analysis is determined to clarify the composition of the blood under the following conditions:
- metabolic disorders (changes in ion balance in cells);
- hemolytic abnormalities (anemia);
- hemoglobinopathies (the synthesis or breakdown of hemoglobin molecules is impaired);
- myeloblastic syndrome (develops when the synthesis of red blood cells is impaired or when cells of different sizes are produced);
- causeless decrease in immunity;
- hormonal imbalance;
- metabolic disorders.
In addition to diagnosing diseases, indications for an MCV blood test include:
- routine medical examination;
- liver pathologies;
- preparation for surgery;
- undergoing chemotherapy;
- presence of blood disease in close relatives;
- leukemia.
Under the influence of toxic substances (chemotherapy), during illness, the amount of MCV in the analysis will decrease or increase. Based on changes in laboratory data, the doctor determines the nature and severity of the pathological process.
We recommend: What does ASLO show in a blood test?
What causes the increase in blood cell levels?
If the red blood cells in the blood are higher than normal, this may indicate the presence of the following reasons that caused pathological processes in the body:
- vitamin deficiency due to improper liver function;
- neoplasm that stimulates the production of red blood cells;
- temporary or chronic oxygen deficiency;
- dehydration during physical activity or during the hot season;
- treatment with corticosteroids or steroids;
- acquired or congenital heart defects;
- undergoing a course of radiation therapy;
- drinking contaminated or chlorinated water;
- lack of enzymes necessary to digest food;
- smoking, which increases the level of carboxyhemoglobin in the body.
Only an experienced hematologist can find out the reason for the increase in the number of blood cells in the body. Therefore, you should not deal with such changes in the blood on your own: this can lead to the development of irreversible processes. Self-medication, and especially traditional medicine, are not appropriate in this case.
What to do if you get promoted
If red blood cells are elevated, you should immediately contact the clinic for medical help. The main condition for effective treatment is timely detection of the cause of erythrocytosis.
In case of severe erythrocytosis, drugs are prescribed that help thin the blood and normalize blood clotting. In some cases, chemotherapy is used. In pre-stroke or pre-heart attack conditions, an emergency bloodletting procedure is prescribed to reduce blood pressure and the likelihood of blood clots.
After carrying out health measures, a person who had elevated red blood cells must be given glucose and plasma (supplemented with the introduction of an isotonic solution of sodium chloride). In hereditary erythrocytosis, oxygen inhalation is indicated to maintain the normal transport function of red elements.
A diet with a high content of red blood cells is aimed at preventing blood thickening and maintaining its dilution. If there are a lot of red blood cells, fatty foods are prohibited: this measure reduces the amount of cholesterol and prevents the formation of blood clots. Foods containing large amounts of iron are temporarily excluded: buckwheat, some fruits and berries. Vitamin complexes that increase the amount of iron and hemoglobin are prohibited.
Important information: What is the osmotic resistance of red blood cells
To normalize elevated levels of blood elements, it is recommended to follow medical recommendations:
- Drink enough clean water throughout the day. Carbonated water remains banned because it can increase the number of red blood cells.
- Eat fresh fruits and berries (according to the season).
- Normalize your sleep schedule, take walks in the fresh air.
- Regulate physical activity.
- Avoid stressful situations and emotional stress.
During the gestational period, the following recommendations should be followed:
- normalize your rest regime: walk more, monitor the intensity of physical activity;
- avoid stress;
- exclude fatty and fried foods (because of this, red blood cells increase);
- monitor the amount of spices in the diet;
- exclude tobacco and alcohol.
Traditional methods of treatment also help to normalize the excess number of red blood cells. For example, dill seeds help normalize blood pressure and reduce the number of blood cells. To prepare the medicine, 100 g of seeds are ground into powder and consumed 1 tsp. 2 times a day, dissolving in the mouth and drinking a small amount of water. The duration of treatment is from 7 days to 2 months.
It is useful to take a decoction of wormwood, fireweed, and mint leaves. It is recommended to take all components in equal proportions. To prepare the decoction, you need to pour 1 tsp. chopped herbs 2 liters of boiling water. Leave for 40 minutes. Then drain the liquid, strain and take ½ glass before meals 3 times a day. The duration of treatment is up to 2.5 months.
Erythropenia
The leading position among the cells of the bloodstream in terms of number is occupied by red blood cells. The normal number of these cells decreases in the presence of the following factors:
- anemia of various origins;
- acute leakage of connecting fluid;
- constant blood loss (uterine, intestinal or hemorrhoidal bleeding);
- endocrine system disorders;
- infectious diseases.
There is a relative and absolute reduction in the number of red blood cells in the blood. With a relative (false) decrease, a large amount of fluid enters the bloodstream. The blood thins, but despite this, the level of red cells remains unchanged.
Absolute erythropenia refers to insufficient production of red blood cells. This type of disease is also characterized by accelerated death of blood cells due to blood loss. A decrease in the number of red blood cells in the blood is considered a criterion for anemia, but this circumstance does not indicate the essence of its development.
The essence of the study
Perhaps we should recall long-known facts:
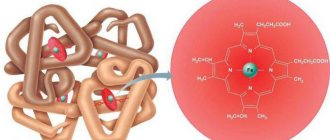
- red blood cells contain hemoglobin (hb);
- red blood cells carry oxygen;
- the amount of hb determines how firmly the cell will hold the oxygen molecule, transporting it to the tissues;
- The hemoglobin content in a cell affects its size.
Determining MCV in an analysis is one of the ways to diagnose the performance of an erythrocyte.
The average volume of an erythrocyte gives a reliable picture of the functionality of the cell and often serves as the main parameter in the differential diagnosis of anemia. Errors in the study are possible only in the case of an abnormal structure of erythrocyte cells (sickle-shaped anemia), in this case, in addition to MCV, the value of MCH and MSHC is additionally taken into account in the blood test.
Diagnosis and treatment of erythropenia
To find out the reason for the decrease in the level of red blood cells in the bloodstream, it is not enough to conduct only a general analysis. In this case, there is a need to prescribe auxiliary examinations. If we take into account the indications obtained in practice, the trigger for the development of anemia is in most cases iron deficiency.
It is not difficult to determine a decrease in the norm of blood cells; it is enough to monitor your well-being and if you experience general weakness, frequent infectious diseases and low-grade fever, consult a doctor for help. Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis of erythropenia after studying the results of a complete blood test. If the rate of red blood cells (leukocytes) in the blood remains low after 3 blood samples are taken in a row, then the patient needs immediate medical attention.
Treatment of this disease includes identifying the causes of the development of the pathological process and its elimination. It is not advisable to treat low blood cell levels by increasing them. If erythropenia has developed as a result of the use of medications, then their use should be stopped, replacing them with safer analogues.
As additional research procedures are prescribed
the following:
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland and abdominal area;
- bone marrow puncture;
- general urine analysis.
To restore normal levels of red blood cells in the blood, it is important to take medications that contain substances that help increase hemoglobin.
Why are red blood cells elevated?
An increased level of red blood cells can be triggered by a number of pathological processes and diseases:
- A malfunction of the respiratory system when the body at the cellular level does not receive enough oxygen. Most often, the cause is pneumonia, asthma, pneumonia and other degenerative processes.
- Heart disease. This has a bad effect on blood flow and accordingly affects the supply of oxygen to all tissues, and the level of red blood cell production increases.
- Neoplasms that affect the kidneys, liver, adrenal glands - it is a failure in their work that will inhibit the breakdown of red blood cells.
- Pulmonary hypertension is a rare disease, and the nature of its origin has not been established for certain. The disease is marked by a high increase in the level of pulmonary vascular resistance, which leads to increased pressure in the arteries of the lungs.
- Acute, infectious nature of the origin of the disease, such as whooping cough or diphtheria.
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease, in which there is an excess production of corticosteroids, which provokes an excess of red blood cells.
- What does an increase in red blood cells in the blood mean? The course of polycythemia vera is one of the types of blood cancer that does not pose a threat of death to the patient.
Erythrocytosis (polycythemia)
Erythrocytosis (polycythemia) is an increase in the number of red blood cells in the bloodstream, which is accompanied by an increase in hemoglobin levels. Primary, secondary acquired and hereditary types of the disease can be distinguished. The reasons for the development of erythrocytosis are as follows:
- arterial hypoxemia;
- chronic pulmonary diseases;
- congenital heart defects;
- pulmonary vascular pathology;
- violation of hemoglobin transport functions.
The clinical picture of this disease is a variety of symptoms, which are determined by the essence of the leading pathological process. When performing hemograms, an increase in blood cell counts is detected. The norm of platelets and leukocytes remains unchanged. The development of pancytosis should be highlighted as complications, which significantly complicates the process of diagnosing the disease.
Reasons for the downgrade
There are many reasons why the average volume of red blood cells is reduced:
- dehydration (with diarrhea, vomiting, large burns);
- hypertensive dehydration (infusion of large amounts of saline solutions);
- anemia due to hb deficiency (hypochromic, microcytic);
- hemoglobinopathy;
- some congenital blood diseases (thalassemia);
- poisoning with metal salts (mercury, lead);
- pathology of hematopoiesis (MCV is lowered due to irregular shape or smaller size of red blood cells).
A decrease in the volume of red cells is always a sign of disease. If a person feels well, but the average volume of red blood cells is reduced, this indicates a hidden course of the pathological process.
Treatment of erythrocytosis (polycythemia)
The principles of treatment of polycythemia are based on eliminating the causes of the disease. In the presence of hypoxic forms of the disease, oxygen therapy is mandatory. Vascular shunts are eliminated through surgical treatment. Smokers are strongly advised to quit this bad habit. People suffering from excess weight are prescribed a fasting diet.
In some cases, the cause of erythrocytosis cannot be eliminated completely or partially. In such a case, the degree of threat associated with the disease and the likelihood of developing undesirable consequences are assessed. Most often, a procedure is prescribed to reduce hematocrit (tissue hypoxia). Bloodletting is carried out with caution in case of heart defects and obstructive pulmonary diseases. Small bloodlettings are allowed once every 7 days, 200 ml. The hematocrit level should not decrease by more than 50%.
Prescribing cytostatic drugs when the number of red blood cells increases is not allowed. The prognosis for the effectiveness of the treatment directly depends on the progression of the underlying pathological process. The danger of erythrocytosis is the development of thrombotic complications.
The average volume of red blood cells is reduced - what does it mean if MCV is lowered in the blood test
Content
- 1. What does “average volume” mean?
- 2. Types of anemia
The average volume of red blood cells is reduced, what does this mean? What might this statement mean? An analysis of the problem with all the details is what those who are concerned about this issue need. Various diseases, including blood diseases, can cause changes of varying severity in the structure of some organs and tissues of the body. One of these tissues is blood, or more precisely, red blood cells - small red cells primarily responsible for transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide within the body. Like any organ, red blood cells have their own pathologies that can cause changes in the structure of blood cells. A very common phenomenon is that the average volume of a red blood cell decreases. There is an explanation for this.
What does "average volume" mean?
To understand what the phrase “reduced average red blood cell volume” means, you first need to know what the expression “average volume” means. An erythrocyte is nothing more than a blood cell consisting of a large number of hemoglobin proteins bound together. Thanks to this ligament, red blood cells manage to retain molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
The average volume of an erythrocyte expresses the hemoglobin content in one bundle of these proteins. To obtain a number expressing the average volume of red blood cells, or ESR, the hematocrit percentage is multiplied by 10 and divided by the total number of red blood cells in the patient's blood. The resulting value in medicine is designated as mcv and expresses the average volume of red blood cells. The norm is considered to be between 80 and 110, although in some children, especially infants, it can be 70.3265
If the value of the average volume does not fit into this framework, we can talk about the presence of some disease in the body. The diagnosis depends on whether mcv is low or high. In the first case, this is usually anemia, in the second - macrocytosis.
A routine blood test is not enough to determine ESR. For this purpose, detailed analysis is used. And if the average volume of red blood cells is reduced, several more studies are carried out aimed at identifying abnormalities and all kinds of anemia.
A blood test performed microscopically can often visually determine the presence of a red blood cell defect.
Types of anemia
Practice shows that low red blood cell volume is a consequence of various types of anemia. Anemia is a disease of red blood cells, in which the latter change their structure and, consequently, their physical properties.
There are three types of such deviations:
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- thalassemia;
- sideroblastic anemia.
All these deviations pose an equal threat to the normal functioning of the human body. Their only difference from each other is that each implies a lack of any one substance, due to which the composition and structure of red blood cells is disrupted. This, in turn, leads to a decrease in mcv.
Iron deficiency anemia by its name makes it clear that in this case we are talking about the incorrect construction of the hemoglobin protein caused by a lack of iron in the body. In this case, the protein helix is not fully aligned.
The production of hemoglobin with a disrupted structure and structure makes red blood cells unable to normally bind oxygen and carbon dioxide for further transportation.
This causes oxygen deprivation and causes the body to increase production of red blood molecules containing hemoglobin. The insufficient effect of unhealthy red blood cells is compensated for by their quantity. The cells become smaller in size, which is why the average value of the geometric dimensions of each cell decreases, which is clearly visible in a blood test.
Thalassemia is a gene level disease.
As a result of the activity of a genetic malfunction, the following picture is observed:
- Healthy red blood cells are damaged, and the affected pinpoint areas provoke dysfunction of the entire cell.
- The formation of complete hemoglobin chains becomes impossible. As a result, blood cells lose their main abilities and cannot remain in the blood circulation for a long time. Sometimes this puts the human body into a state of shock.
- As in the first case, the rate of production of abnormal red blood cells increases, and the protein molecules themselves are unable to maintain their vital functions for a long time.
The number of patients with thalassemia is quite impressive, which allows us to include this pathology in the list of the main reasons for the average size of red blood cells to become below normal.
Sideroblastic anemia
This type of anemia occurs due to a lack of vitamin B6. The lack of the required element, again, makes it impossible to form complete protein chains. Failures in the course of synthetic processes also provoke a lack of protoporphyrins and coproporphyrins in the components of hemoglobin. All this worsens the binding properties of the protein - it cannot transport oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Erythroblasts are formed in the cell, and iron accumulates in the cytoplasm, due to which erythroblasts with cytoplasmic inclusions are visually detected in a blood test under a microscope. Due to the mutations that occur, normal red blood cells turn into unhealthy ones, practically unable to function properly. The results of calculating the average volume of red blood cells are reduced, and the blood cells themselves die quickly.
Unlike iron deficiency anemia and thalassemia, sideroblastic anemia progresses rapidly and also quickly worsens the patient's condition. In this situation, surgical medical intervention is required, otherwise even death is possible.
The average volume of red blood cells in the blood is reduced - what does this mean? This means that a blood test should show an abnormality, usually manifested as one of three types of anemia. If everything happens according to this scenario, you will need to take appropriate measures as soon as possible, in particular, you need to consult a hematologist. He will tell you what to do for a specific type of anemia.
Rate this article:
We recommend reading:
boleznikrovi.com
ESR – erythrocyte sedimentation rate
The rate of erythrocyte sedimentation in the blood is a fairly well-known indicator when conducting laboratory tests. If the indicators increase, this means that functional processes in the body are disrupted. Most often, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases when bacteria, fungi or viruses enter the blood. This is due to changes in protein ratios due to an increase in the level of protective antibodies.
In the presence of mild inflammatory processes, the indicators increase to 15 or 20 mm/h, in severe inflammation - from 60 to 80 mm/h. If during the treatment period the indicators decrease, then the treatment has been chosen correctly. Please note that ESR levels may be elevated during pregnancy and menstruation.
Average volume of red blood cells: decreased, increased - what does this mean?
A clinical blood test is the simplest and at the same time indispensable in primary diagnosis, and the average volume of red blood cells is one of its indicators.
What diagnostic conclusions can be drawn from data on the average volume of red blood cells in an adult or a child?
General information about red blood cells
The ancient Greek word for red blood cells literally means “red cells.” In the Russian language, a synonym for erythrocytes has taken root - “red blood cells”.
Together with leukocytes and platelets, red blood cells in the blood plasma make up its formed elements.
In a sense, red blood cells are the main elements of blood:
- inside these cells there is no nucleus or other structural components; they are entirely filled with hemoglobin, which colors them red, associated in the minds of every person with blood;
- Red blood cells are the most numerous blood cells, moreover, the most numerous cells in the human body - making up a quarter of all cells in the body.
The number of red blood cells is associated with the function they perform and which is rightfully considered the main one in the body - they allow cells to breathe.
The peculiarity of hemoglobin, which fills red blood cells, is its ability to easily bind to oxygen and carbon dioxide atoms and just as easily get rid of them.
The larger the total surface area of all red blood cells in the body, the larger volumes of gases they can carry.
Red blood cells contribute to this due to their tiny size - the smaller each cell, the greater the total surface area of all cells combined.
Red blood cells are like trailers that are loaded with oxygen in the lungs and carry it to the farthest corners of the body - their shape and size allow them to easily move even in the smallest capillaries, several times narrower than themselves.
Having unloaded oxygen, red blood cells take carbon dioxide from the cells and “carry” it back to the lungs. Red blood cells move through the capillaries quite slowly (2 cm per minute), which gives them time to unload and load.
Red blood cells are born in the bone marrow of the spine, skull, ribs, and in a child, also in the long bones of the limbs.
The hormone erythropoietin produced by the kidneys informs the bone marrow about the number of new red blood cells needed. About 2.4 million new red blood cells are produced every second.
Video:
Cell primordia first have nuclei and structural components and are colored blue. Gradually, the nuclei become smaller, then are forced out of the cell membranes, the concentration of hemoglobin increases, and the cells acquire their usual color.
Teenage red blood cells, reticulocytes, first enter the bloodstream, which take up to three days to finally mature and turn into normocytes. Red blood cells live for 3-4 months, then die and are absorbed by orderly phagocytes.
Study of red blood cells
A clinical or complete blood count (CBC) is the simplest and most widely used test that is performed during almost any routine medical examination.
This study is not a routine task at all, but a source of information about problems in various organs and systems of the body.
The results of a blood test alone cannot be the basis for a diagnosis, because when asked for each indicator, what does it mean? – there are several answers.
But the data obtained allows us to make assumptions about where the problem lies and plan further diagnostic actions.
A complete blood count provides the following information about red blood cells:
- The number of red blood cells is calculated in units per liter of blood. The resulting number contains 12 zeros;
- the average amount of hemoglobin in one cell shows their ability to provide gas exchange at the cellular level;
- hematocrit (Ht) is an indicator of blood thickness, which demonstrates the ratio between its liquid part (plasma) and formed elements;
- the number of reticulocytes is calculated in ppm (number per thousand normocytes). Normally, for every thousand mature cells there are 5–12 reticulocytes;
- ESR is the rate at which red blood cells settle in the blood volume within an hour.
Each indicator can indirectly indicate certain pathologies in the body, and their combination will narrow the range of these pathologies.
Take, for example, the sedimentation rate of red blood cells, which sink to the bottom of a test tube under the influence of gravity at a certain speed.
However, during a number of inflammatory processes, substances accumulate in the blood that act on red blood cells like glue, holding them together. The mass of such accumulations increases, therefore, they settle faster.
Normal and pathological blood tests
The results presented on the form can only be interpreted competently by a doctor, but it is difficult for patients to resist solving the mysterious numbers in which the norm or disease is encrypted.
In order not to panic in vain, it is important to understand what the norm of any diagnostic test is and where it comes from.
First, the analysis is carried out for thousands of people, then the extreme indicators are cut off, and the average is taken as the norm.
This is a fairly arbitrary value, so one increased or low indicator cannot be the basis for making a diagnosis, but only a reason to study it in more detail.
Children and their illnesses are of particular concern. Seeing that certain indicators are elevated or do not reach the norm, parents run to the Internet, where terrible diagnoses are the first to catch their eye.
Whatever the tests show, for a competent doctor the primary reference point is the clinical picture, mainly the well-being and development of the child.
Video:
The opposite situation is also possible, especially with such an indicator as the amount of hemoglobin, which in the minds of the average person is associated with good health.
However, hemoglobin above normal in combination with increased hematocrit and the number of red blood cells may indicate dehydration, in which the amount of blood plasma decreases and, accordingly, its density and concentration increase.
The first thing to do, having received similar results of the OAC (with other indicators within the normal range), is to increase the amount of fluid drunk per day to the age norm.
Average volume indicator: calculation, meaning
To calculate the mean cell volume (MCV), it is necessary to operate with the number of red blood cells and hematocrit. The amount of hematocrit (mm³) must be divided by the number of red blood cells.
If the average volume of erythrocytes is reduced, then we are talking about microcytosis (abnormally small cells), but if the average volume of erythrocytes is increased, then macrocytosis is stated - pathologically large blood cells.
However, changes in the shape of red blood cells can result in one patient having both micro- and macrocytosis, which together will give a normal average volume of red blood cells in the blood.
Since this indicator is necessary to calculate the volume of one red blood cell, in order to eliminate error, the volume is calculated after examining the blood smear under a microscope, which provides information about the number of red blood cells of a changed shape.
The MCV indicator is necessary for the differential diagnosis of anemia:
- microcytic anemia – thalassemia, iron deficiency anemia;
- macrocytic - aplastic anemia, characterized by a lack of folic acid and vitamin B12;
- normocytic anemia.
In addition to various types of anemia, secondary oncological conditions (metastases), liver disease, decreased thyroid function (hypothyroidism), smoking and alcoholism can cause an increase in the volume of red blood cells.
Among the reasons for a decrease in the average volume of red blood cells (in addition to anemia), one can name various hemoglobin pathologies, and in rare cases, increased function of the thyroid gland - hyperthyroidism.
The volume of red blood cells is measured in femtoliters (fl, fL), one unit equals 1 µm³ - cubic micrometer.
Video:
The average volume of red blood cells changes frequently throughout life, in the first months of life this happens every few weeks.
Until the age of 12, the norms do not depend on gender (the indicators are the same for boys and girls); after 12 years, the average volume of red blood cells in boys and men is higher than in girls and women. After 45 years, the average red blood cell volumes are compared.
moydiagnos.ru
Functions of red blood cells
Red blood cells fulfill their main purpose in the body - they are carriers of respiratory gases - oxygen and carbon dioxide.
This process is carried out in a certain order:
- Nucleated discs, as part of the blood moving through the vessels, enter the lungs.
- In the lungs, the hemoglobin of red blood cells, in particular its iron atoms, absorbs oxygen, turning into oxyhemoglobin.
- Oxygenated blood, under the influence of the heart and arteries, penetrates through capillaries into all organs.
- Oxygen carried by iron is detached from oxyhemoglobin and enters cells experiencing oxygen starvation.
- Empty hemoglobin (deoxyhemoglobin) is filled with carbon dioxide and converted into carbohemoglobin.
- Hemoglobin combined with carbon dioxide carries CO2 to the lungs. In the vessels of the lungs, carbon dioxide is broken off and then removed to the outside.
In addition to gas exchange, formed elements also perform other functions:
- Absorb and transport antibodies, amino acids, enzymes,
- Human red blood cells
- Transport harmful substances (toxins), some medicines,
- A number of erythrocyte factors take part in stimulating and preventing blood clotting (hemocoagulation),
- They are primarily responsible for blood viscosity - it increases when the number of red blood cells increases and decreases when it decreases,
- Participate in maintaining the acid-base balance through the hemoglobin buffer system.
When is MCV analysis necessary?
The doctor refers to determining the average volume of red blood cells for the following purposes:
- To give a more in-depth assessment of developing anemia;
- Identify metabolic disorders;
- Determine the degree of water-electrolyte imbalance in the patient;
- To adjust the treatment of severe pathologies.
This analysis is only an auxiliary method that sheds light on the nature of disorders in the body.
The reliability of this method in identifying various types of anemia or water-electrolyte balance disorders is beyond doubt.
Thus, hypertensive hyperhydration in most cases is accompanied by macrocytosis, and in hypotensive patients indicators of microcytosis are recorded.
The MCV indicator, along with other 20 indicators, is included in the general analysis, for which capillary blood is taken from a finger. To prevent measurement errors, it is recommended not to eat before analysis.
What does anisocytosis mean?
If red blood cells of different sizes are found in the blood - both micro- and macrocytes, then to characterize them, the distribution by volume of red blood cells is determined, which is denoted by the abbreviation RDW.
It is measured using a hemolytic analyzer that differentiates medium cells and determines the heterogeneity of red blood cells, that is, the deviation from the standard volume, and is expressed as a percentage.
The RDW norm is 11.5-14%. To correctly differentiate between anemia and other pathologies, RDW measurement is always carried out in conjunction with MCV measurement.
These measurements revealed the following patterns:
- A reduced MCV with a normal RDW indicates blood transfusion, thalassemia, or a removed spleen.
- With increased MCV and normal RDW, liver pathologies are observed.
- If MCV is decreased and RDW is increased, iron deficiency, beta thalassemia, or erythrocyte sludge syndrome is suspected.
- If both indicators are elevated, then vitamin B12 deficiency, the effects of chemotherapy or cold agglutination are suspected.
It is characteristic that in all the presented disorders of blood structures, one of the most significant reasons is a deficiency of vitamin B12 in the body, and this is not accidental.
This vitamin is the most important factor in hematopoiesis, since only in its presence bone marrow stem cells can differentiate towards oxygen carriers, that is, red blood cells.
And even if all the other necessary elements of red blood cell synthesis are present, if there is a lack of B12, the hematopoietic chain will break.
This essential vitamin for the blood comes to us both from the outside, with food, and is synthesized in large quantities in the large intestine through the activity of beneficial microflora (bifidobacteria and lactobacilli).
Therefore, in order to prevent disorders of hematopoietic function, preventing a reduced amount of this element in food, monitoring intestinal health and a balanced diet is a primary task.
The MCV indicator alone should not be trusted without supporting it with indicators of other erythrocyte indices. For example, the average red blood cell volume will not be accurate if abnormally shaped cells are found in the blood.
Only an integrated approach to assessing blood parameters will allow a doctor to promptly and competently identify an incipient pathology and determine the diagnosis as accurately as possible.
Deviations of red blood cells from normal values
The concentration of red cells in the blood can be determined by doing a complete blood count. Now analyzes are processed using modern equipment, so you will receive an error-free result immediately.
You can see the condition and saturation of red blood cells in the general analysis form. With the help of such an analysis, it will be easier for the doctor to assess your body and hurry up with subsequent treatment, if necessary.
Red blood cells sometimes change their size and shape, leading to:
- Microcytosis - the blood contains a large number of red blood cells smaller than average in size (4.9 - 6.4 microns). Such a number of small bodies indicates possible: malignant tumors, thalassemia, hemolytic anemia.
- Macrocytosis – cells are larger than normal. This may occur for the following reasons:
- During pregnancy, the size of red blood cells may increase.Anemia in pregnant women,
- Pathologies of the liver and lungs,
- Decreased thyroid function
- Features of physiology in infants.
- Megacytosis - the size of red blood cells significantly exceeds their standard sizes (more than 12 microns). As they enlarge, they become oval. Such changes may result from:
- Worms,
- Folate deficiency anemia,
- Dyserythropoiesis.
Place of formation of red blood cells
In the human embryo, the first place of blood formation is the yolk sac. Later, the liver becomes the most important organ in which red blood cells are formed. As the fetus develops, bone marrow develops, which is the only source of red blood cells in adult life.
Erythropoiesis is the process by which new blood cells are produced and takes about seven days. In a healthy adult, red blood cells are produced continuously in the red bone marrow of large bones at a rate of about 2 million cells per second. The main sites for the formation of red blood cells are the bone marrow spaces of the vertebrae, ribs, sternum and pelvis.
Erythropoiesis can be stimulated by the hormone erythropoietin, which is synthesized by the kidneys in response to hypoxia (systemic oxygen deficiency). During the final stages of development, immature red blood cells absorb iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid—nutrients that are essential for proper hemoglobin (iron) synthesis and normal red blood cell development (B12 and folic acid). Immediately before and after leaving the bone marrow, the developing cells are known as reticulocytes. These are immature red blood cells that have lost their nuclei after initial differentiation. After 24 hours in the bloodstream, the reticulocytes mature into functional blood cells.
Preparation and performance of red blood cell level analysis
Preparing the patient for blood collection for clinical analysis:
- 4 hours before taking blood, do not drink anything except water;
- no physical activity during this time interval;
- avoid stress;
- temporarily stop taking medications.
This is done so that the clinical blood test shows a more accurate level of red blood cells. The procedure for drawing blood will be performed by a nurse. Typically, venous (from a vein) or capillary blood (from a finger) is taken for analysis. The last option fades into the background, because venous blood is the most informative.
Before blood sampling, a venous tourniquet is applied above the injection site. The nurse treats the intended area with medical alcohol twice from the center to the periphery. 2 ml of venous blood is taken, after which the patient is released with the cotton wool clamped. The nurse fills a special tube with the collected blood and sends it to the laboratory.
For what blood diseases can the analysis be within normal limits?
Often, with severe anemia associated with a deficiency of hemoglobin formation, the volume of erythrocytes may remain within normal limits.
This is observed in the following situations:
- In hemolytic anemia, when red blood cells are both destroyed and at the same time intensively synthesized;
- With significant blood loss;
- For hemoglobinopathies (improper formation of hemoglobin protein structures);
- In case of hormonal disorders (lack of function of the adrenal glands, pituitary gland);
- During a tumor process;
- For chronic foci of infections.
Ontogenesis of red blood cells
An erythrocyte, the structure of which has a number of characteristic features, remains viable for 120 days. Subsequently, they are destroyed in the liver and spleen. The main hematopoietic organ in humans is the red bone marrow. It continuously produces new red blood cells from stem cells. Initially they contain a nucleus, which as it matures is destroyed and replaced by hemoglobin.
Normal limits by age category
The indicator is called normal if the average volume of red blood cells is in the range of no less than 80 and no more than 100 femtoliters. In newborns, the normal range is somewhat wider - from 70 to 110. With age, a person tends to increase the indicator, from the minimum of the norm to the maximum, which is a physiological norm and does not require medical intervention.
MCV values are independent of gender.
There are several erythrocyte characteristics:
- Red blood cells
If normal, the state of blood red blood cells will be called normocyte. - If the MCV value is less than 80, then this state of the erythrocyte will be designated as a microcyte,
- If it is more than 100 feet, then there is an increased level - macrocytoma.
- In some cases, anisocytes are recorded in the blood - red blood cells are different in both shape and size.
The blood condition will be called normocytosis, microcytosis, macrocytosis or anisocytosis in such conditions.
Macrocytosis, microcytosis and anisocytosis are accompanied by a certain pathology of the circulatory system, or a tendency to it. For example, detection of a large number of microcytes indicates a lack of hemoglobin in the blood. Macrocytosis may indicate liver problems or hormonal imbalances.
| Age | Acceptable values, or norm, fl |
| 1 – 3 days | 75 – 121 |
| 7 days | 86 – 126 |
| 14 – 30 days | 88 – 124 |
| 2 months | 77 – 115 |
| 3 – 6 months | 77 – 108 |
| 16 years | 73 – 85 |
| 7 – 10 years | 75 – 87 |
| 10 – 15 years | 76 – 95 |
| 16 – 20 years | 78 – 98 |
| 21 – 40 years | 80 – 98 |
| 41 – 65 years old | 80 – 100 |
| over 65 years old | 78 – 103 |
Reduced red blood cell counts in adults. Erythropenia
An important function of red blood cells is oxygen transport
The norm of indicators differs by age and gender.
Men (*10 12/l):
- up to 25 years - 4.0 - 5.0;
- from 25 to 55 years - 4.3 - 5.4;
- after 55 years - 3.9 - 4.3.
Women (*10 12/l):
- from 18 to 45 years old - 3.5 - 4.7;
- after 45 years - 3.5 - 5.2.
In women, deviations towards a decrease or increase are associated with the menstrual cycle. Separately, reference values are calculated for pregnant women. In this case, the norm of indicators will depend on the trimester of pregnancy.
Indicators below standard values are a sign of erythropenia. Erythropenia is characterized by a lack of oxygen in the blood and, accordingly, anemia. This condition is not a disease, but only reflects its consequences. A slight decrease is not considered a pathology, but significantly reduced levels require additional examination and treatment.
The mean red blood cell volume or MCV in a blood test is low in a child
Content
- 1. Norm
- 2. Demotion and Promotion
- 3. Treatment
Why does it happen that the average volume of red blood cells is reduced in a child? During a blood test such as a general blood test, various components of the blood are checked, among which the average volume of red blood cells plays an important role. It characterizes the state of red blood cells in the serum and is designated MCV. The results of this study are used to establish and clarify the cause of hemoglobin deficiency.
Norm
For babies whose age does not exceed one year, the norm should not exceed 126 fl. Thus, the lower threshold of this indicator gradually increases in proportion to age. It does not vary depending on gender, and over the age of eighteen the normal MCV is from 80 to 100 fl.
For different age characteristics, there are established MCV standards:
- from birth to three days – 95 – 121 fl.;
- from two weeks to a month – 88 – 124 fl.;
- from three months to six months – 77 – 108 fl.;
- from one to five years - 73 - 85 fl.;
- from five to ten – 75 – 87 fl.;
- from ten to sixteen years – 76 – 95 fl.
But there are cases when there is severe anemia, but the average volume of red blood cells shows the norm:
- Chronic infections.
- Blood loss.
- Destruction of the hemoglobin protein structure.
- In the presence of hemolytic anemia, when there is destruction of red blood cells, but at the same time erythropoiesis increases.
- Presence of tumors.
This analysis is prescribed mainly for two purposes: identifying abnormalities in water and electrolyte balance and diagnosing anemia. To determine this indicator, blood from a finger is used, which must be taken on an empty stomach in the morning.
Relegation and Promotion
If the average volume of red blood cells decreases, then no pathological process occurs in the baby’s body; this condition is called erythropenia.
In order for the reasons for the occurrence of a low indicator to be more reliably identified, it is worth paying attention to the color of red blood cells - if the color turns out to be lighter than normal, this means that there is not enough iron in the blood.
When test results show a low red blood cell count, it means:
- Mature cells are destroyed.
- Lack of hemoglobin in them.
The reasons for this condition are:
- hypertensive dehydration;
- dehydration;
- hereditary blood diseases;
- intoxication;
- dysfunction of porphin synthesis;
- iron deficiency anemia.
If a child does not have adequate nutrition and rarely goes out into the fresh air, then he may well develop anemia, which occurs due to reduced hemoglobin.
When, upon receiving the test results, the MCV value is above 100 fL, this happens for the following reasons:
- lack of hormones produced by the thyroid gland;
- pathological processes in the kidneys;
During a condition when the body lacks vitamin B12 and folic acid, the level of red blood cells decreases, but their volume increases significantly.
In newborns and pregnant women, elevated MCV levels are often observed, but this situation is normal and goes away on its own without drug intervention.
An interesting fact is that in adults who consume alcohol and tobacco products, the level of this indicator also increases. But after eliminating the bad habit, the average volume of red blood cells returns to normal.
Treatment
When the average volume of red blood cells is reduced in a child, first of all, you should contact a specialist who will identify the cause of the disease.
As for newborn premature babies, the attending physician often prescribes a transfusion of blood components.
The situation is similar for children who:
- Sick with cancer.
- Have hematological disorders.
- Correction of blood element deficiency.
However, not all situations require surgical intervention, because along with its undeniable advantages, it also has its significant disadvantages. The whole procedure is carried out similarly with adult patients, but with children the situation is somewhat different. If for an adult before a transfusion it is necessary that the hemoglobin level remain at least 80, then for children there is no such requirement. This is due to the fact that children’s hemoglobin level is physiologically different from that of an adult.
When it comes to the postoperative period, transfusion of blood components is not always necessary, since the baby’s body can independently produce red blood cells with the help of iron therapy.
A specialist who makes a decision on prescribing a red blood cell transfusion should be based not only on the level of hemoglobin in the blood, but also take into account the following factors:
- The baby has diseases related to the central nervous system and vascular nature.
- Symptoms.
- The patient’s body’s ability to heal independently.
- The reasons that led to the development of anemia.
- Possibility of using another treatment.
When the condition of the newborn remains stable, but the hemoglobin is slightly below normal and there is no anemia, then the decision about transfusion should not be made, since this is a physiological norm.
Rate this article:
We recommend reading:
boleznikrovi.com
Reasons for the increase
An excessive increase in red blood cells in the blood is called erythrocytosis. This disease indicates serious physiological abnormalities in the body and can be the cause of a number of dangerous diseases.
Depending on the causes, erythrocytosis is distinguished:
- pathological;
- physiological.
The first is due to a number of reasons:
- Low amount of oxygen in the body. Lung diseases lead to a decrease in active oxygen. In this regard, more red cells are produced in order to maximally provide all organs and systems with the necessary amount of O2.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the bone marrow, due to which a large amount of them is produced. This disease is called erythremia.
- Kidney diseases.
- Smoking can cause an increase in the number of red blood cells in the blood. The smoker's body experiences oxygen starvation, which causes an increase in the content of red blood cells in the blood.
A condition called relative erythrocytosis is often observed. In this case, the number of red blood cells remains the same, but the volume of plasma decreases, the blood becomes less fluid, and the content of red blood cells per unit volume of blood increases. The cause of relative erythrocytosis may be dehydration caused by increased body temperature, diarrhea, and vomiting. The same condition appears in case of prolonged use of diuretics or blood loss. In this condition, it is assumed to drink large amounts of clean water, which will restore water balance and normalize blood cells. In a hospital setting, IVs with saline are used to replenish plasma volume.
Sometimes a number of diseases lead to erythrocytosis:
- hereditary familial erythrocytosis;
- renal failure;
- diseases of the endocrine system: thyroid gland, adrenal dysfunction;
- heart pathologies;
- oxygen starvation;
- lung diseases: bronchitis, asthma, inflammation;
- increased blood viscosity;
- vascular pathologies;
- Pickwick's syndrome;
- whooping cough and diphtheria;
- laryngitis.
Important! People who live high in the mountains, are hostage to a polluted atmosphere (air, water), and work on airplanes are susceptible to increased levels of red blood cells.
Red blood cell growth in children
In a child, the volume of red blood cells can be caused by a number of reasons, both independent and dependent on the mother during intrauterine development. The second phenomenon is considered a congenital pathology. If during pregnancy the mother experienced oxygen starvation, smoked, or drank alcohol, then the child may experience erythrocytosis. It is believed that even passive smoking can cause an excess of red cells in the baby's blood.
Living in the mountains or places close to them can increase the number of red blood cells; this is due to low atmospheric pressure in high mountain areas, which means a reduced supply of oxygen to the body. Constant physical activity and sports in adolescents often affect their health. During exercise, the body needs oxygen. Therefore, the number of red cells increases.
How is diagnosis carried out?
The number of red blood cells in the blood is determined during a clinical analysis. To do this, material is collected for analysis by puncturing the skin of a finger. The procedure is invasive. It is performed in a manipulation room.
After taking blood for analysis, it is added to a special solution. This is where red blood cells are counted. The action is performed under a microscope using a Goryaev camera or using a special hematology analyzer.
Taking any test requires preparation. It is performed in the morning strictly on an empty stomach. Instead of breakfast, a woman can drink unsweetened tea or still mineral water. The night before, it is recommended to avoid fatty and fried foods, as well as drinking alcohol. Dinner should be as light as possible. On the day of the test, you should stop smoking and also try to minimize emotional and physical stress. The use of medications is not recommended. They can distort the final results. If stopping medications is not possible, you must inform your doctor.
Red blood cells in urine - can this situation arise?
Yes, the doctors’ answer is definitely positive. Of course, in rare cases this may occur due to the fact that the person was carrying a heavy load or was in an upright position for a long time. But often an increased concentration of red blood cells in the urine indicates the presence of problems and requires consultation with a competent specialist. Remember some of its norms in this substance:
- the normal value should be 0-2 pcs. in sight;
- when a urine test is carried out using the Nechiporenko method, there can be more than a thousand red blood cells in the laboratory technician’s field of view;